Analysis of competitive failure mechanisms and mechanical properties of self-piercing riveted joints in corrosive environments
-
摘要: 为研究腐蚀环境下自冲铆接头失效模式的转变机理和力学性能特征,采用0.6 mol/L的NaCl溶液对多组自冲铆接头进行周浸腐蚀试验,通过力学测试和扫描电子显微镜对接头的力学性能及失效模式进行分析. 结果表明,异质接头的失效模式随腐蚀周期延长由 Ⅰ 向 Ⅲ 转变,转变速率取决于接头材质,同质接头的失效模式不受腐蚀周期的影响. 短期腐蚀下,搭接区板间腐蚀产物使得同质和异质接头失效载荷均有所上升;异质接头上升幅度较大,腐蚀后期其失效载荷较同质接头损失严重. 异质接头稳定性较差,凸模制备的同质组合接头较平模稳定性好. 异质接头电化学腐蚀剧烈,下板铆接点底部材料的脱落由应力集中所产生的撕裂纹所致.Abstract: In order to study the transition mechanism and mechanical properties of the failure mode of self-piercing riveted joints in corrosive environment, the 0. 6 mol/L NaCl solution was used to carry out the immersion corrosion test on several groups of self-piercing riveted joints. Mechanical properties and failure modes of joints are analyzed by mechanical testing and scanning electron microscopy. The results show that the failure mode of heterogeneous joints changes from Ⅰ to Ⅲ with the prolongation of corrosion cycle, and the transformation rate depends on the joint material, while the failure mode of homogeneous joints is not affected by the corrosion cycle. Under short-term corrosion, the inter-plate corrosion products of self-piercing riveted joints increase the failure load of both homogeneous and heterogeneous joints, the failure load of heterogeneous joints varies widely throughout the corrosion cycle. Heterogeneous joints are less stable, and homogeneous combination joints prepared by convex dies are more stable than flat dies. Heterogeneous joint electrochemical corrosion is intense, self-piercing riveted joints bottom material off by the stress concentration generated by the tear lines.
-
0. 序言
随着能源的枯竭和环境污染的日益加剧,轻量化设计在节能减排中发挥着更加重要的作用[1],铝合金由于密度低、抗拉强度高、耐腐蚀性能好等优点,在满足强度要求的前提下,广泛运用于汽车、航海、航空制造等领域[2]. 但是铝合金的引入也给材料连接技术带来了挑战,钢/铝电阻点焊接头的连接性能较差,甚至难以实现有效连接. 自冲铆(self-piercing riveting, SPR)作为一种机械冷成形技术可以弥补电阻点焊技术的不足,正逐渐成为一种很有发展潜力的新型薄板材料连接技术[3]. 然而自冲铆接头由于常处于腐蚀环境中的工作条件和钢/铝连接带来的电化学腐蚀,会造成接头不同程度的腐蚀破环,从而影响接头的力学性能和可靠性[4].
国内外学者对于铝合金和自冲铆接头的腐蚀行为进行了一系列研究. 马青娜等人[5]研究了7075铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头在3.5%的NaCl溶液中的腐蚀行为和断裂特征,通过扫描电镜分析了接头的腐蚀疲劳断口形貌和显微组织,结果表明,腐蚀疲劳裂纹起源于接头的热影响区,逐渐扩展最终断裂于接头的焊核区. Calabrese等人[6]研究了不同厚度组合下铝合金自冲铆接头在盐溶液中的腐蚀老化行为,结果表明,腐蚀环境对接头的性能和失效机制有显著影响,在非对称接头中,薄铝板的接头在腐蚀环境中耐久性较差,同时提出了一个简化的理论模型来预测腐蚀环境下接头的失效模式. 冯震等人[7]研究了在0.6 mol/L的NaCl溶液下铝合金自冲铆接头的疲劳性能,对不同腐蚀周期的试件进行静力学和疲劳测试,结果表明,腐蚀周期内腐蚀液对接头的失效形式未产生不利影响,短期腐蚀环境会改变接头疲劳断裂的失效特征,同时使接头产生多个疲劳裂纹源. Kang 等人[8]研究了异质金属连接产生的电化学腐蚀现象,通过制备纯粘接接头、自冲铆接头和点焊接头,分别进行盐雾腐蚀老化试验,结果表明,自冲铆接头较其它两种接头静力学受影响程度较小.
国内外对腐蚀环境下自冲铆接头失效模式转变的原因及影响因素分析较少,对腐蚀后自冲铆接头微观层面的失效机理研究较少. 该试验通过制备多组自冲铆接头,采用周浸加速腐蚀试验,结合静力学、失效模式、扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)及竞争失效机制分析,以期从宏观和微观层面研究腐蚀环境自冲铆接头的性能变化和失效机理.
1. 试验方法
1.1 试样制备
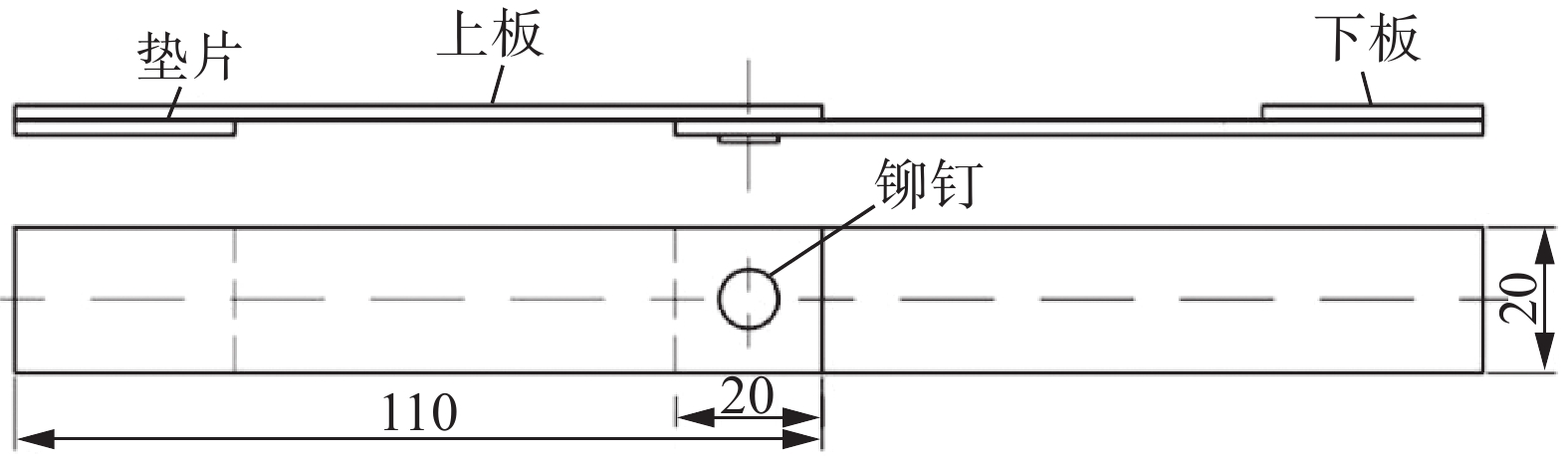
试验板材为热轧双相钢DP590,5052铝合金(AA5052)及7075铝合金(AA7075),DP590试样尺寸为110 mm × 20 mm × 1.5 mm,AA5052和AA7075试样尺寸为110 mm × 20 mm × 2 mm,接头的组合及命名方式列于表1. 铆钉选用德国Bollhoff公司生产的硬度为46 HRC ± 2 HRC的镀锌钢铆钉,下模具分别采用平模和凸模,铆钉及下模具的几何尺寸如图1所示. 试件铆接后用蒸馏水清洗并用无水乙醇脱水处理,最后放入25 ℃的恒温箱,保温24 h.
表 1 接头组合方式及名称Table 1. Combination method and name of the joints试件名称 上板 下板 模具类型 PAA AA5052 AA5052 平模 AA AA5052 AA5052 凸模 DA5 DP590 AA5052 凸模 DA7 DP590 AA7075 凸模 1.2 周浸腐蚀试验
参照国家标准GB/T 19746—2018《金属和合金的腐蚀盐溶液周浸试验》,试验腐蚀介质为0.6 mol/L的NaCl溶液,试验温度为25 ℃ ± 2 ℃,一个试验周期为60 min,其中浸润10 min,干燥50 min,总时长为1 080 h, 每隔360 h后取件,为避免试验误差,每组至少取6个试件.
1.3 静力学试验
采用 MTS Landmark 100 型试验机进行静力学试验测试,拉伸速度为5 mm/min,将试件两端固定垫片,其搭接方式及垫片位置如图2所示.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 试件失效模式
试件在不同腐蚀周期的失效模式如图3所示,将腐蚀后自冲铆接头在剪切作用下的失效模式归为3类:①铆钉管腿从下板拔出,铆接点自锁结构遭到破坏(Ⅰ);②铆接点下板脱落(板材未被撕裂) (Ⅱ);③铆接点下板脱落且搭接区板材被撕裂(Ⅲ). 失效模式 Ⅱ 是由 Ⅰ 向 Ⅲ 转变的过渡模式. PAA和AA组在整个腐蚀周期为失效模式 Ⅰ. 0 h时DA5和DA7组试件为模式 Ⅰ;360 h时DA5组为模式 Ⅱ 或 Ⅲ,DA7组为模式 Ⅰ;720 h和1 080 h时DA5组为模式 Ⅲ,DA7组为模式 Ⅰ 或 Ⅲ.
接头失效模式的转变受接头材质和腐蚀周期的共同影响,图4为腐蚀过程中出现失效模式 Ⅲ 的概率,其概率越高,表明试件失效模式的转变速率越快,试件遭受腐蚀破坏的程度越剧烈. 同质接头(PAA和AA组)失效模式未发生转变;异质接头失效模式的转变速率逐渐增大,且DA5组转变速率较快,在中等腐蚀周期时已转变为失效模式 Ⅲ.
2.2 载荷-位移曲线及竞争失效机制分析
腐蚀效应使得异质接头的失效模式由 Ⅰ 向 Ⅲ 逐渐转变,且不同材质接头失效模式的转变速率不同,结合试件的载荷-位移曲线及竞争失效机制[9]对失效模式的转变进行分析,研究自冲铆接头受腐蚀破坏作用及失效阶段接头的失效过程,以期提高接头的稳定性和承载能力.
图5为试件的载荷-位移曲线,其失效过程分为3个阶段:①弹性阶段. 载荷与位移呈线性关系,接头具有较高刚度,上、下板和铆接点自锁结构未发生塑性变形,此时剪力主要由板材搭接区的摩擦作用和自锁结构传递[10];②塑性变形阶段. 载荷-位移曲线逐渐趋于平缓,接头刚度下降,下板末端发生微小翘曲变形,两板搭接区间隙增大,摩擦阻力降低,载荷逐渐达到最大值;③失效阶段. 载荷-位移曲线经过最高点后缓慢下降,上板铆钉孔壁受铆钉头部挤压而产生轻微塑性变形,铆钉逐渐倾斜,下板翘曲变形程度加大,搭接区间隙进一步增加. 此时剪力主要由上板铆钉孔壁、自锁结构和下板铆接点底部[11]传递,基于竞争失效机制分析,若其中某一传递环节所承受的强度低于与其竞争的其它环节时,该剪力传递的连接关系成为接头的薄弱部分,在失效阶段率先遭到破坏形成失效特征,最终表现为特定的失效模式. 针对失效位移的稳定性同质接头更好,异质接头中DA7组较好,这是因为在中长腐蚀周期下,DA5和部分DA7组试件出现失效模式 Ⅲ,在失效阶段初期上、下板并未完全分离,逐渐形成撕裂纹进而增大了接头的失效位移.
同质接头的失效模式未随腐蚀周期延长发生转变,在失效阶段自锁结构损坏产生失效模式 Ⅰ,基于对竞争失效机制的分析表明,上板铆钉孔壁和下板铆接点底部强度在腐蚀环境下未发生大幅下降,自锁结构在整个腐蚀周期均为剪力传递的薄弱环节,在失效阶段铆钉被逐渐拔出,自锁结构遭到破坏形成失效模式 Ⅰ.
异质接头的失效模式表现为由 Ⅰ 向 Ⅲ 转变,在低腐蚀周期下,DA5组失效模式转变为 Ⅱ 或 Ⅲ,此时下板因电化学腐蚀导致材料强度下降[12],特别是铆接点底部基材较薄,在失效阶段所能承受的剪力较低而产生断裂,造成铆接点底部脱落,试件失效模式由 Ⅰ 转变为 Ⅱ;部分试件下板遭腐蚀较为严重,在铆接点底部脱落时搭接区被铆钉管腿撕裂,该部分试件失效模式由 Ⅰ 转变为 Ⅲ. DA7组下板腐蚀程度较轻,失效模式未发生转变. 在中长腐蚀周期下,DA5组产生失效模式 Ⅲ,此时下板强度进一步降低,质地变得更为松软,在剪力传递过程中所能承受的应力较低,导致铆接点底部脱落,产生失效模式 Ⅱ,而在铆钉拔出过程中,下板搭接区因质地松软而被铆钉剪断,试件的失效模式由 Ⅱ 转变为 Ⅲ. DA7组发生失效模式 Ⅰ 或 Ⅲ,失效模式 Ⅰ 比例较高,表明该部分试件上板铆钉孔壁和下板铆接点底部强度降低,自锁结构在失效阶段为接头连接的薄弱部分;其中少量试样破坏程度更为严重,因腐蚀周期较长,试件失效模式直接由 Ⅰ 转变为 Ⅲ,而未出现过度失效模式.
2.3 接头失效载荷分析
图6为接头的失效载荷测试结果. 同质接头失效载荷随腐蚀周期延长呈现先增大后减小的趋势,腐蚀初期,接头搭接区生成的盐薄夹层和腐蚀产物,增大了上、下板间的摩擦阻力,导致在试件拉伸过程中不仅要克服自锁结构还需克服额外增加的摩擦力,使得接头失效载荷上升;腐蚀后期,由于腐蚀液沿搭接区缝隙逐渐渗入铆接点自锁结构,对自锁结构造成破坏,进而降低了其提供的接头强度,腐蚀液的侵入造成两板间隙进一步增大,降低了搭接区的摩擦阻力,二者共同作用导致试件失效载荷降低.
异质接头失效载荷随腐蚀周期延长呈现先增大后减小的趋势,该变化特征的幅度大于同质接头. 钢/铝异质连接电化学腐蚀剧烈,腐蚀初期腐蚀速率大于同质接头,因此在两板搭接区堆积更多的腐蚀产物,从而增大两板间摩擦力进而提高接头的阻力,促使试件失效载荷上升;腐蚀后期,电化学腐蚀造成接头搭接区下板破坏显著,板材强度下降,内锁结构受损严重,同时搭接区间隙增大导致接头摩擦力降低,共同作用造成接头强度显著下降.
2.4 接头的稳定性分析
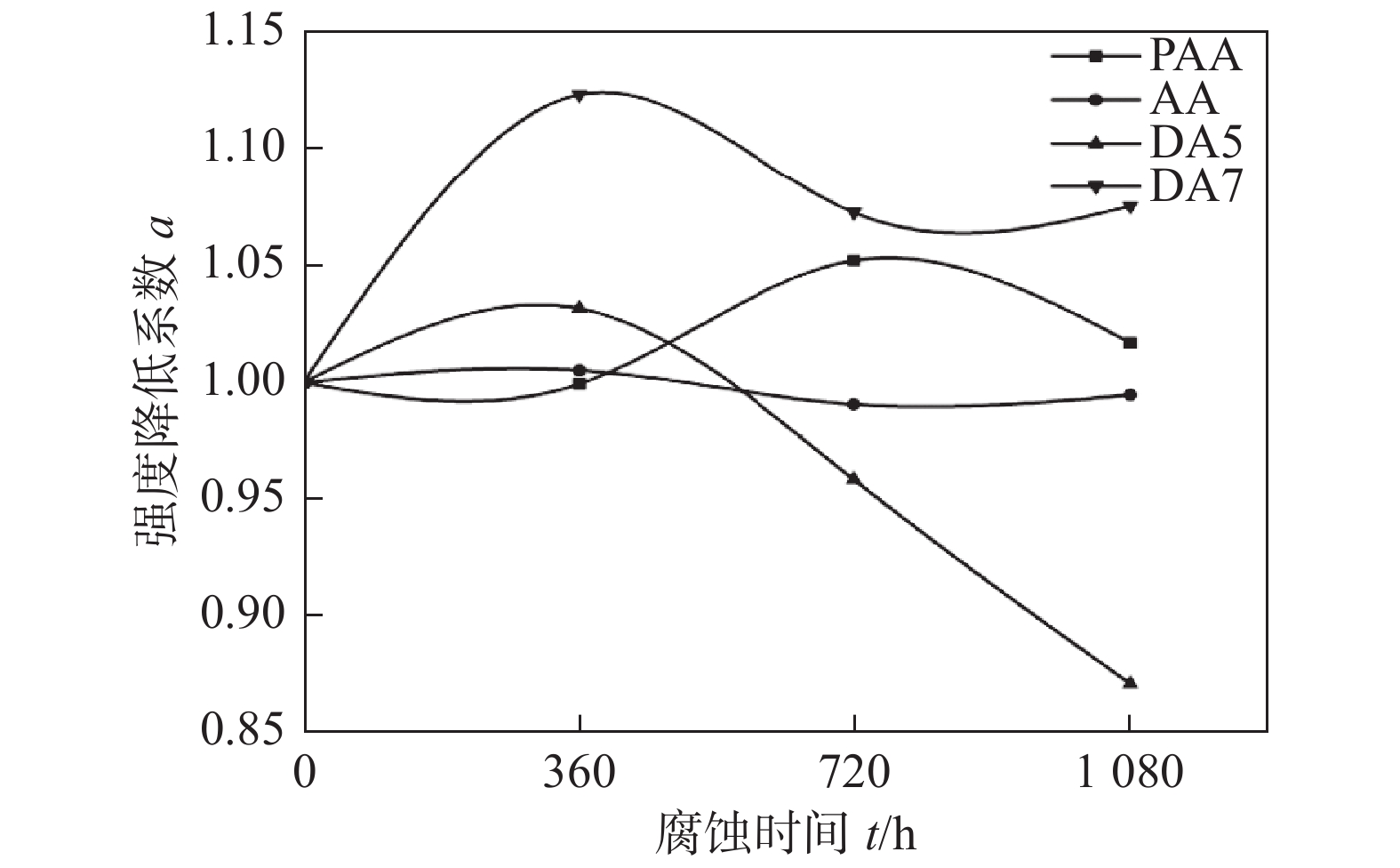
自冲铆接头的稳定性受被连接材料、成形质量及腐蚀周期等多种因素的影响,然而自锁结构复杂的几何形状及三维特征增加了获得各个腐蚀周期下接头理论承载力的计算方法,使得判断腐蚀后自冲铆接头的稳定性变得困难. 基于Fiore等人[13]所做的研究,利用自冲铆接头的强度降低系数的波动反应接头的稳定性,强度降低系数定义为:接头在该腐蚀周期时的强度与其未腐蚀时试件强度之比,其值越接近于1,表明腐蚀后的接头与未腐蚀时性能类似;其波动程度越大,表明接头受腐蚀破坏影响越剧烈. 图7为试件的强度降低系数波动曲线,腐蚀环境下同质接头强度降低系数变化较小,失效模式未发生转变,接头具有较好的耐腐蚀性和稳定性. 异质接头中DA7组稳定性较好,DA5组试件因失效模式的快速转变,接头强度波动程度较大,造成试件稳定性差.
2.5 失效断口分析
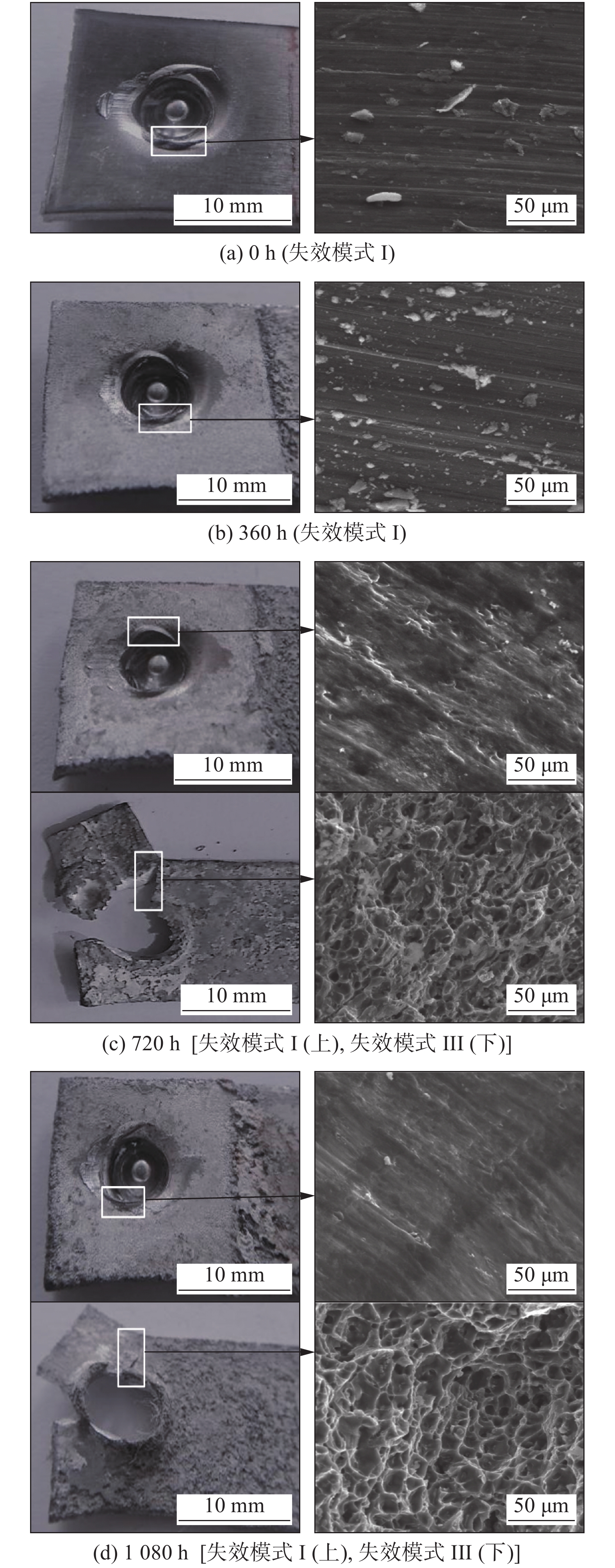
异质接头的失效特征和失效模式的转变较为明显,基于SEM分析腐蚀环境下自冲铆接头的失效机理,DA5和DA7组接头典型失效部位的断口形貌分别如图8和图9所示.
由图8可知,腐蚀周期为0 h时,铆接点颈部组织出现拉长的纤维状,局部呈现出破裂状的横向沟壑,部分沟壑出现泛白迹象且深度较深,表明铆钉在受剪拔出时,铆钉管腿与铆接点颈部区域产生剧烈剐蹭,导致该区域产生破裂状的横向沟壑. 腐蚀周期为360 h时,接头出现两种失效模式,失效模式 Ⅱ 时,铆接点颈部组织呈现和腐蚀周期0 h时类似的剐蹭痕迹,但沟壑的长度和深度较小,表明腐蚀液渗入铆钉管腿和板材的间隙,降低了连接的紧密程度,导致铆钉管腿和板材的摩擦剐蹭作用小于腐蚀周期为0 h时;模式 Ⅲ 时,下板特征部位显现为韧窝状的撕裂纹,表明在铆钉拔出的过程中,下板一端发生翘曲而产生变形,随着变形的累积逐渐发生颈缩现象,从而导致不均匀变形,使得颈缩区域所承受的实际应力大于名义应力,并在该区域产生多向应力状态,随着应力的增加,在应力集中区形成一些微小的撕裂纹,并相互连接形成大量韧窝结构,直至下板被撕裂[14]. 在中长腐蚀周期下,下板强度进一步降低,出现更加密集的韧窝状撕裂纹,在剪切力作用下,产生更多微小裂纹,造成下板一端断裂.
由图9可知,腐蚀周期为0和360 h时,铆接点颈部微观组织结构呈现横向剐蹭条纹,随着腐蚀周期的延长,条纹的深度和数量增加,当腐蚀周期为360 h时,该区域附着大量细小颗粒物,表明腐蚀液随接头缝隙渗入,造成了接头内部的不均匀腐蚀. 当腐蚀周期为720和1 080 h时,出现两种失效模式,失效模式 Ⅰ 时,下板未发生撕裂,呈现出与腐蚀周期为0和360 h时类似的剐蹭条纹,在剐蹭条纹附件出现局部腐蚀凹坑,接头内部受局部腐蚀破坏程度进一步加剧;失效模式 Ⅲ 时,铆接点处颈部呈现大量韧窝状撕裂纹,表明在腐蚀作用下局部不均匀腐蚀产生的凹坑进一步扩大,板材强度下降,凹坑之间相互连接形成空洞,使得该区域产生应力集中,随着载荷的增加产生微小裂纹直至发生断裂,呈现出大量韧窝特征.
3. 结论
(1)腐蚀周期及模具类型对同质接头的失效模式未产生显著影响,异质接头的失效模式随腐蚀周期由失效模式 Ⅰ 逐渐向 Ⅲ 转变,接头稳定性较差的试件具有更高的转变速率.
(2)异质接头失效模式的转变和稳定性降低的主要原因是铝板的腐蚀破坏效应,因此对于暴露于盐性腐蚀工作环境下的异质自冲铆接头,建议适当增加铝板的厚度,提高铝板及铆接点下板底部残余底厚处薄弱材料的防腐性能,以更好地提高接头的稳定性和承载能力.
(3)试件的失效载荷取决于自锁结构和板材搭接区的摩擦阻力,异质接头腐蚀效果明显,失效载荷和失效模式转变较大,接头稳定性差,同质接头具有较好的稳定性.
(4)异质接头铆接点底部材料因电化学腐蚀产生应力集中,该区域的不均匀变形产生撕裂纹,最终造成下板铆接点底部脱落.
-
表 1 接头组合方式及名称
Table 1 Combination method and name of the joints
试件名称 上板 下板 模具类型 PAA AA5052 AA5052 平模 AA AA5052 AA5052 凸模 DA5 DP590 AA5052 凸模 DA7 DP590 AA7075 凸模 -
[1] 李永兵, 马运五, 楼铭, 等. 轻量化薄壁结构点连接技术研究进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(6): 125 − 146. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.06.125 Li Yongbing, Ma Yunwu, Lou Ming, et al. Advances in spot joining technologies of lightweight thin-walled structures[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(6): 125 − 146. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.06.125
[2] 魏文杰, 何晓聪, 张先炼, 等. DP780/AA6061薄板自冲铆接头微动损伤特性[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(6): 169 − 175. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.06.169 Wei Wenjie, He Xiaocong, Zhang Xianlian, et al. Characteristics of fretting damage in hybrid DP780/AA6061 self-piercing riveted joints[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(6): 169 − 175. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.06.169
[3] 曾凯, 何晓聪, 邢保英. 钉脚张开度对自冲铆构件机械内锁刚度的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(6): 143 − 147. Zeng Kai, He Xiaocong, Xing Baoying. Effect of the degree of rivet opening on the rigidity of the interlock in self-piercing riveting joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(6): 143 − 147.
[4] Pan B, Sun H, Shang S L, et al. Corrosion behavior in aluminum/galvanized steel resistance spot welds and self-piercing riveting joints in salt spray environment[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 70: 608 − 620. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.08.052
[5] 马青娜, 邵飞, 白林越, 等. 7075铝合金FSW接头腐蚀疲劳性能及断裂特征[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(6): 72 − 77. Ma Qingna, Shao Fei, Bai Linyue, et al. Study on corrosion fatigue properties and fracture characteristics of 7075 aluminum alloy FSW joint[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(6): 72 − 77.
[6] Calabrese L, Proverbio E, Pollicino E, et al. Effect of galvanic corrosion on durability of aluminum/steel self-piercing rivet joints[J]. Corrosion Engineering Science and Technology, 2015, 50(1): 10 − 17.
[7] 冯震, 邢保英, 何晓聪, 等. 盐性环境下铝合金自冲铆接头的疲劳特性及寿命预测[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(1): 149 − 153. Feng Zhen, Xing Baoying, He Xiaocong, et al. Fatigue characteristics and life prediction of aluminum alloy self-piercing riveted joints in salt environment[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(1): 149 − 153.
[8] Kang M J, Cheolhee K, Kim J K, et al. Corrosion assessment of Al/Fe dissimilar metal joint[J]. Journal of Welding and Joining, 2014, 32(4): 55 − 62. doi: 10.5781/JWJ.2014.32.4.55
[9] Calabrese L, Bonaccorsi L, Proverbio E, et al. Durability on alternate immersion test of self-piercing riveting aluminium joint[J]. Materials and Design, 2013(46): 849 − 856.
[10] Calabrese L, Proverbio G, Bella D, et al. Failure behavior of SPR joints after salt spray test[J]. Engineering Structures, 2015, 82: 33 − 43. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2014.10.020
[11] 谢志强, 张爱林, 闫维明, 等. 薄壁钢板自冲铆接受剪性能及承载力计算方法研究[J]. 工程力学, 2020, 37(6): 234 − 245. Xie Zhiqiang, Zhang Ailin, Yan Weiming, et al. The shear behavior and calculation method of self-piercing riveted connections on thin-walled steel sheets[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2020, 37(6): 234 − 245.
[12] Mo Shuxian, Dong Shaokang, Zhu Hao, et al. Corrosion behavior of aluminum/steel dissimilar metals friction stir welding joint[J]. China Welding, 2021, 30(3): 20 − 30.
[13] Fiore V, Calabrese L, Proverbio E, et al. Salt spray fog ageing of hybrid composite/metal rivet joints for automotive applications[J]. Composites Part B, 2017, 108: 65 − 74.
[14] 钟群鹏, 赵子华. 断口学[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006. Zhong Qunpeng, Zhao Zihua. Fractography [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 张子豪,曾凯,张洪申,邢保英,丁燕芳,田海. 基于球形底模的铝合金自冲铆接工艺多元回归模型. 焊接学报. 2024(07): 59-66 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 邱飒蔚,雷贝,叶拓,张越,蒋家传,王涛. 铝合金自冲铆疲劳性能及寿命预测. 材料导报. 2024(18): 230-236 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨贵秋,邢保英,曾凯,何晓聪,赵腾飞. 腐蚀环境下钢/铝压印-胶接复合接头的静力学性能研究. 工程设计学报. 2024(05): 663-669 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 雷志文,邢保英,何晓聪,曾凯,赵腾飞. 酸性腐蚀环境下钢铝压印接头性能. 塑性工程学报. 2023(07): 167-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: