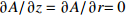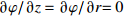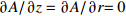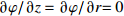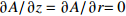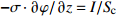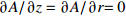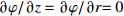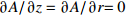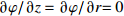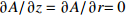Numerical simulation of TIG arc characteristics of hollow tungsten electrode
-
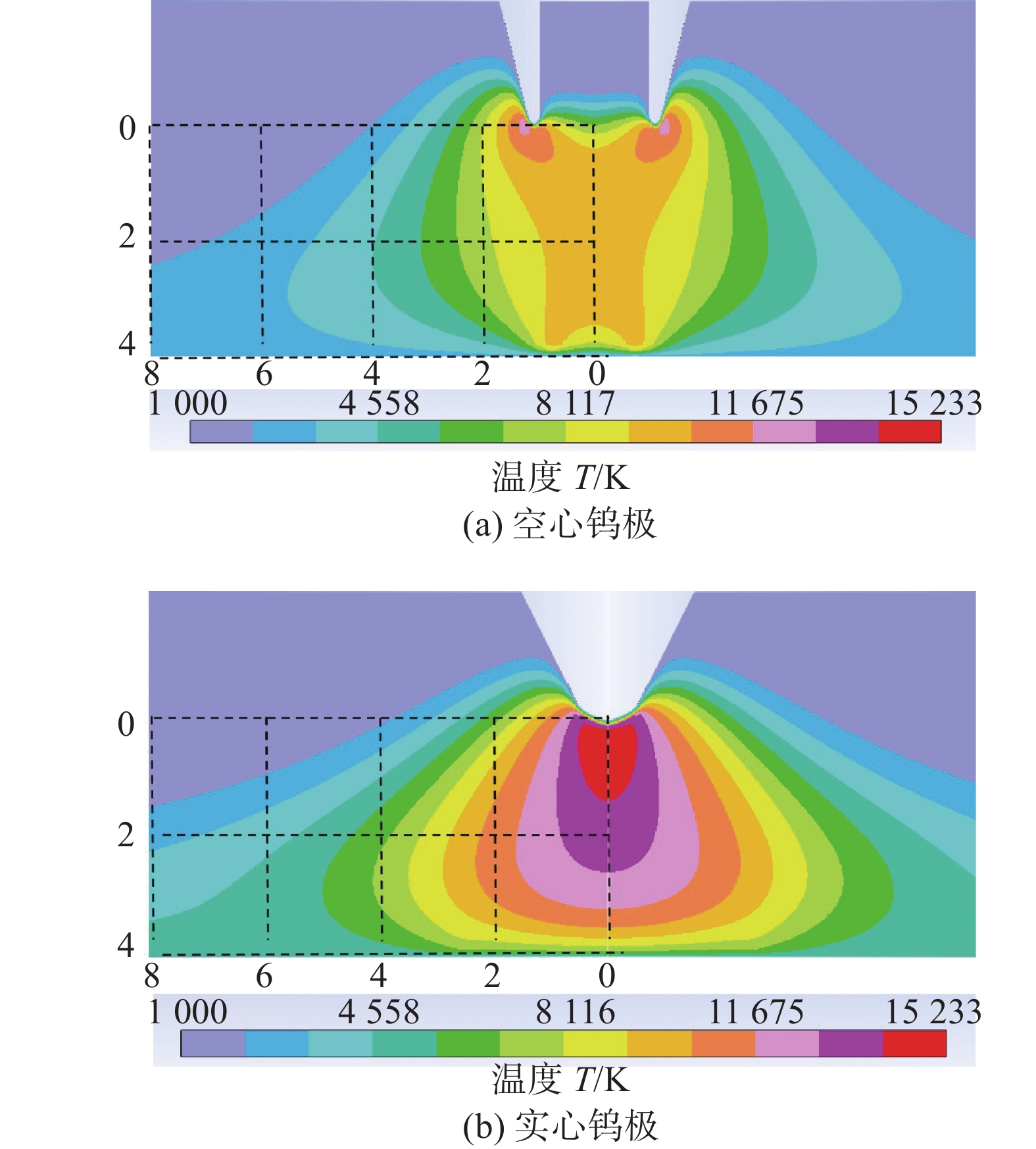
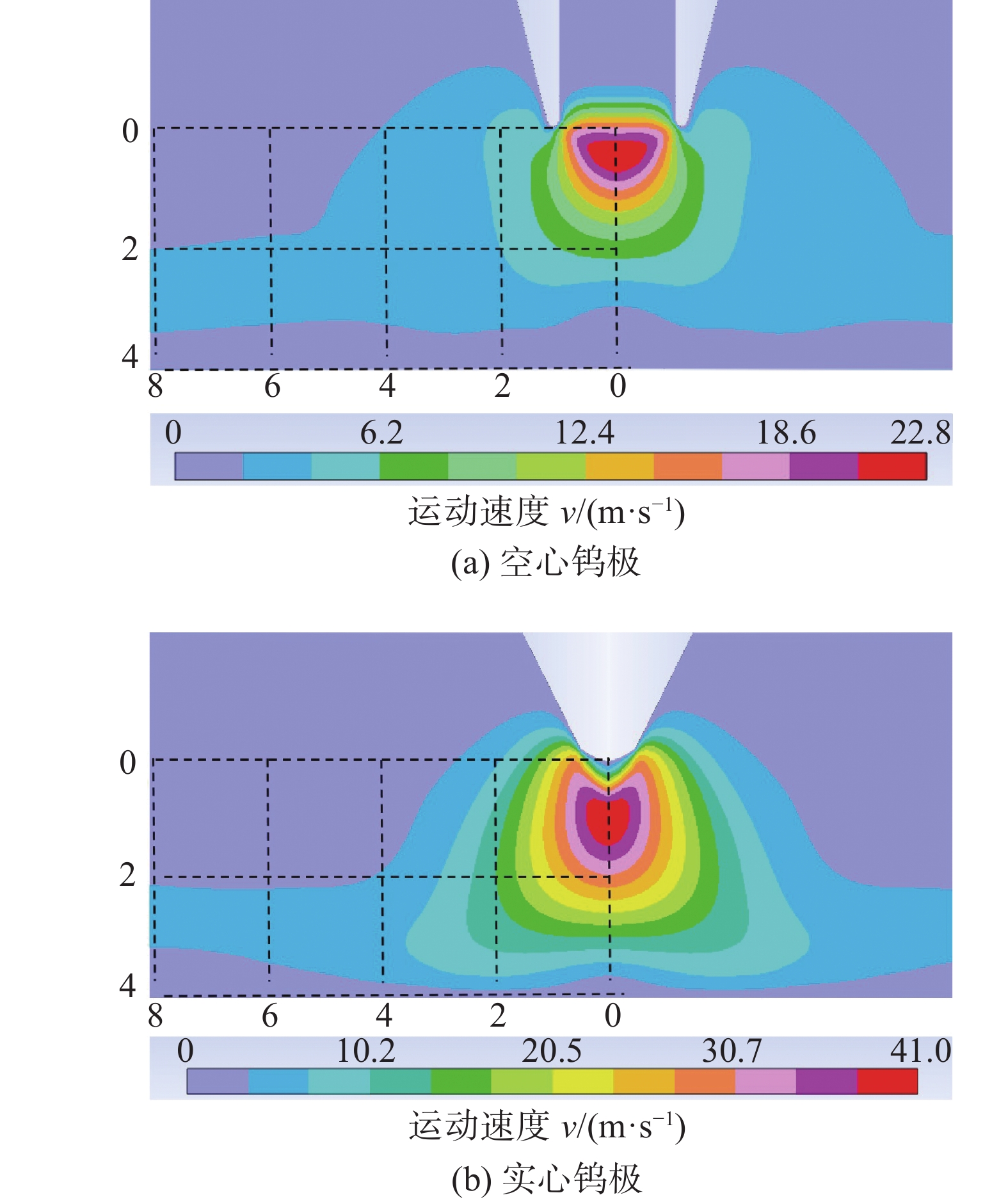
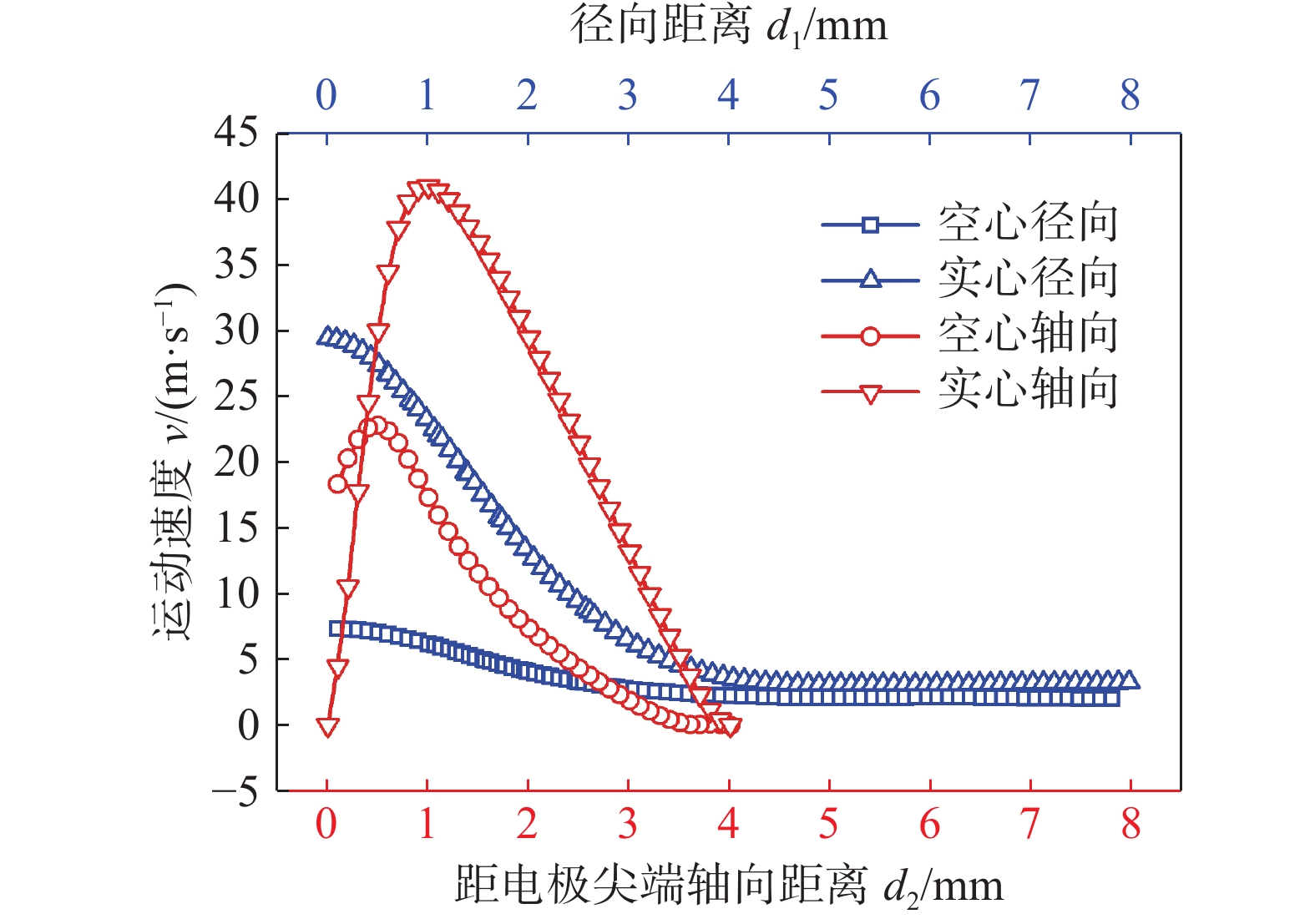
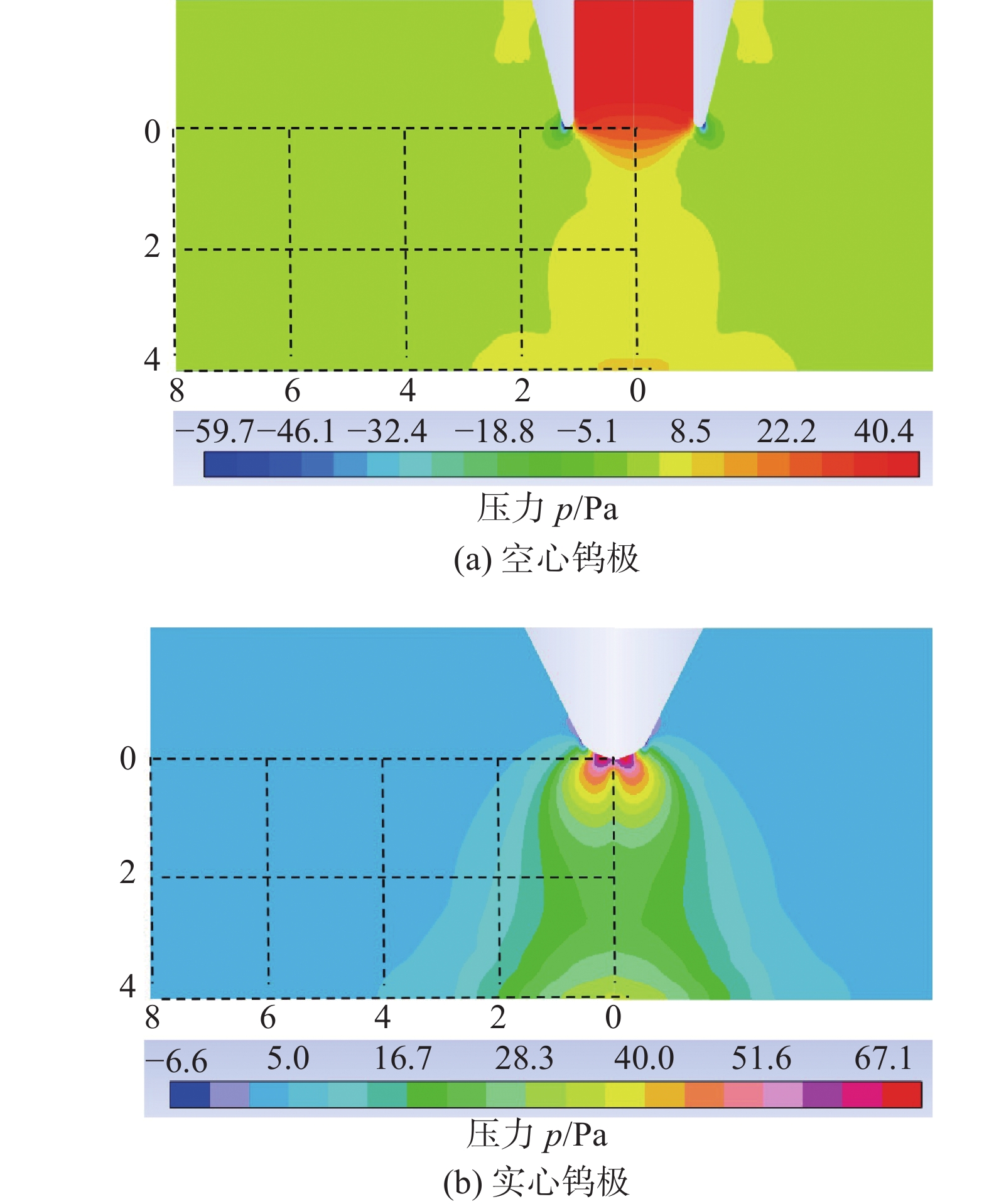
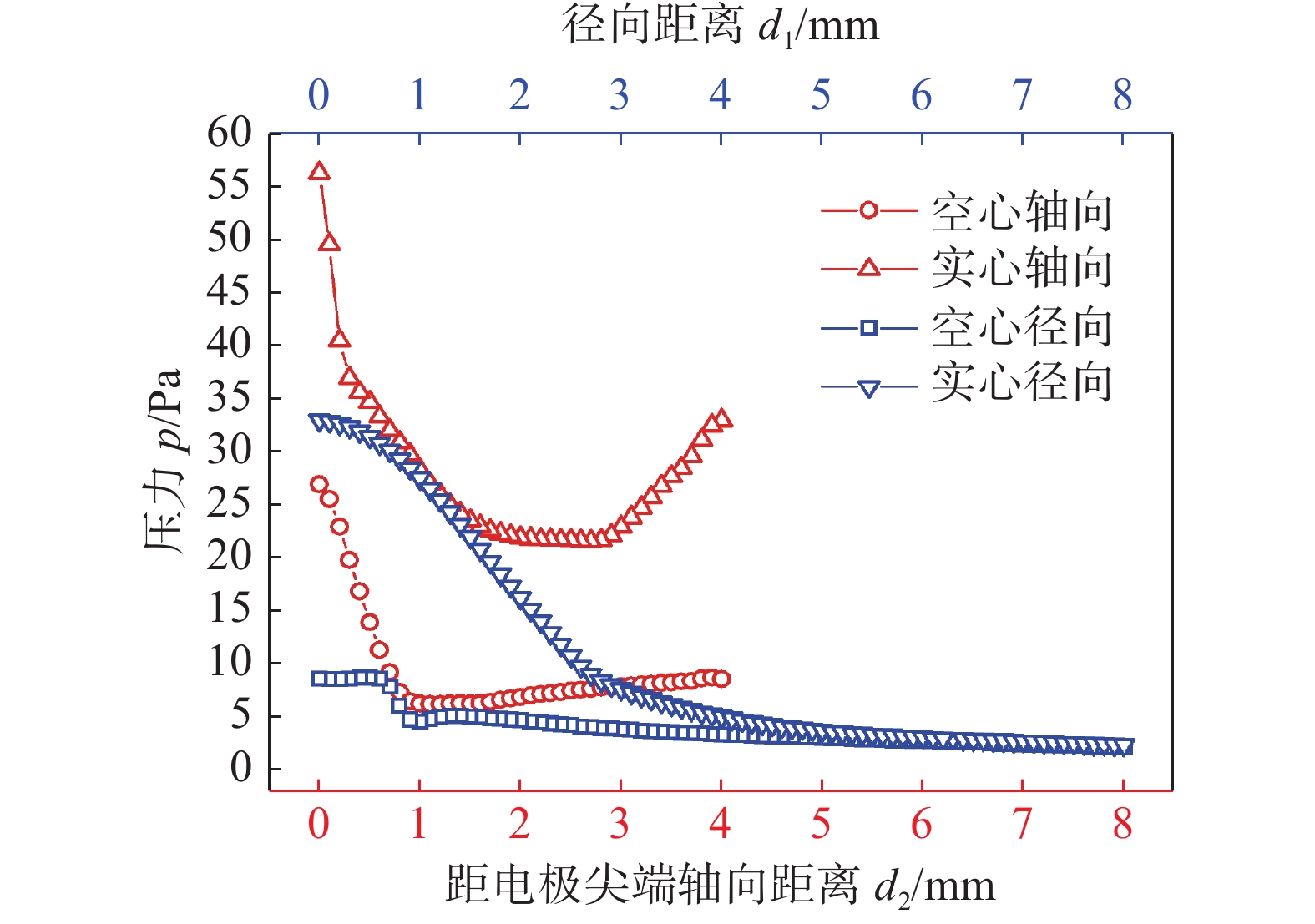
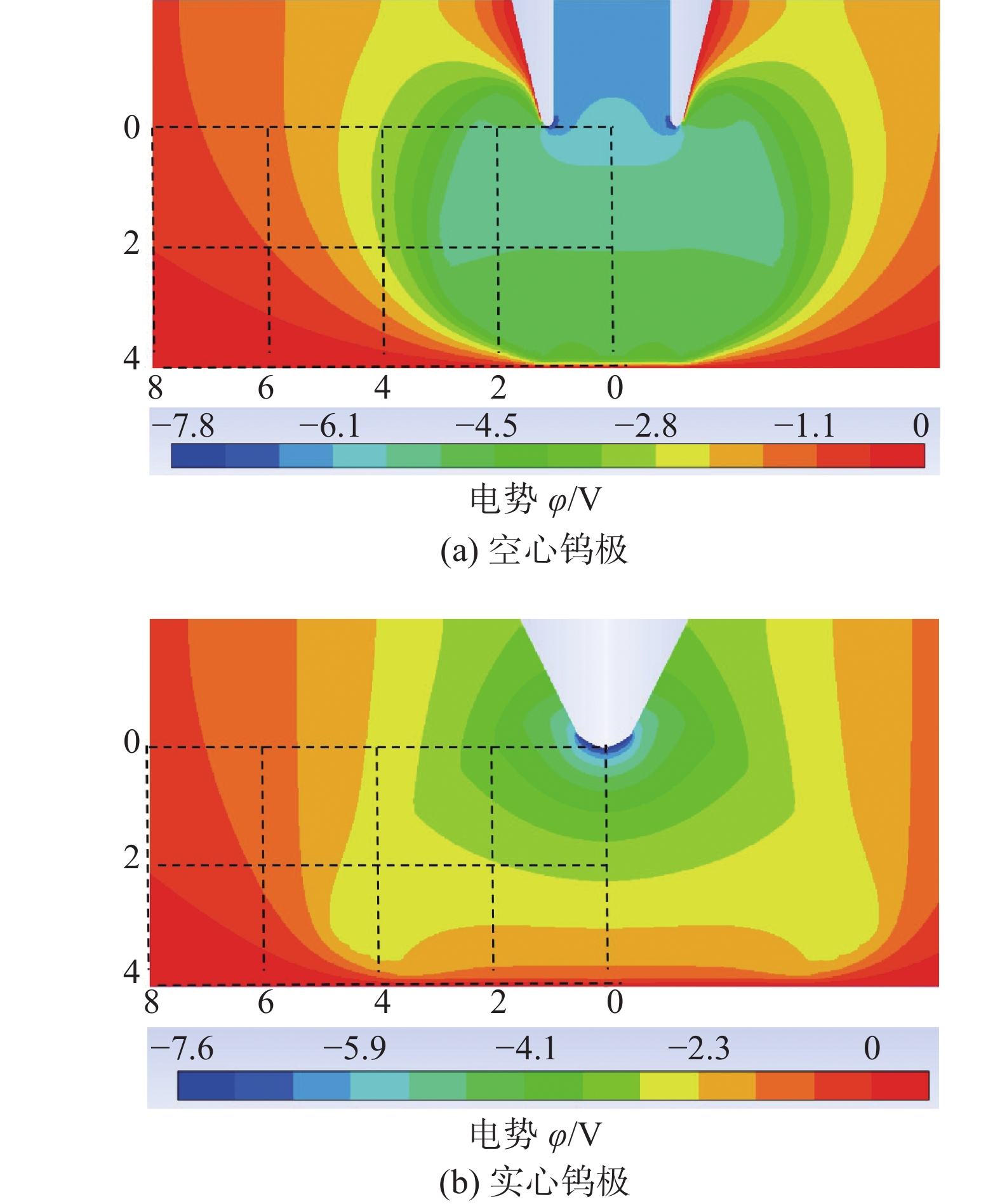
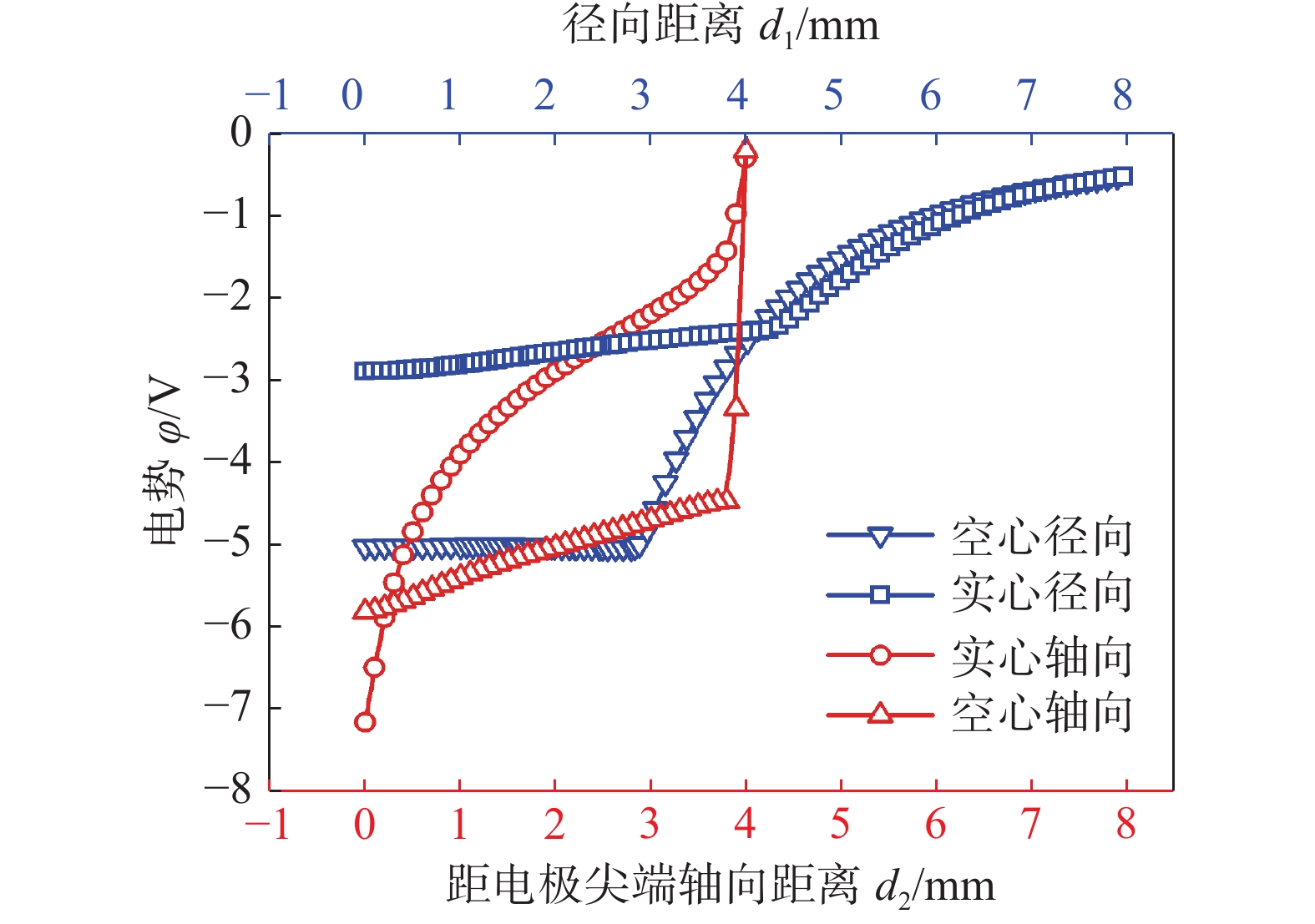
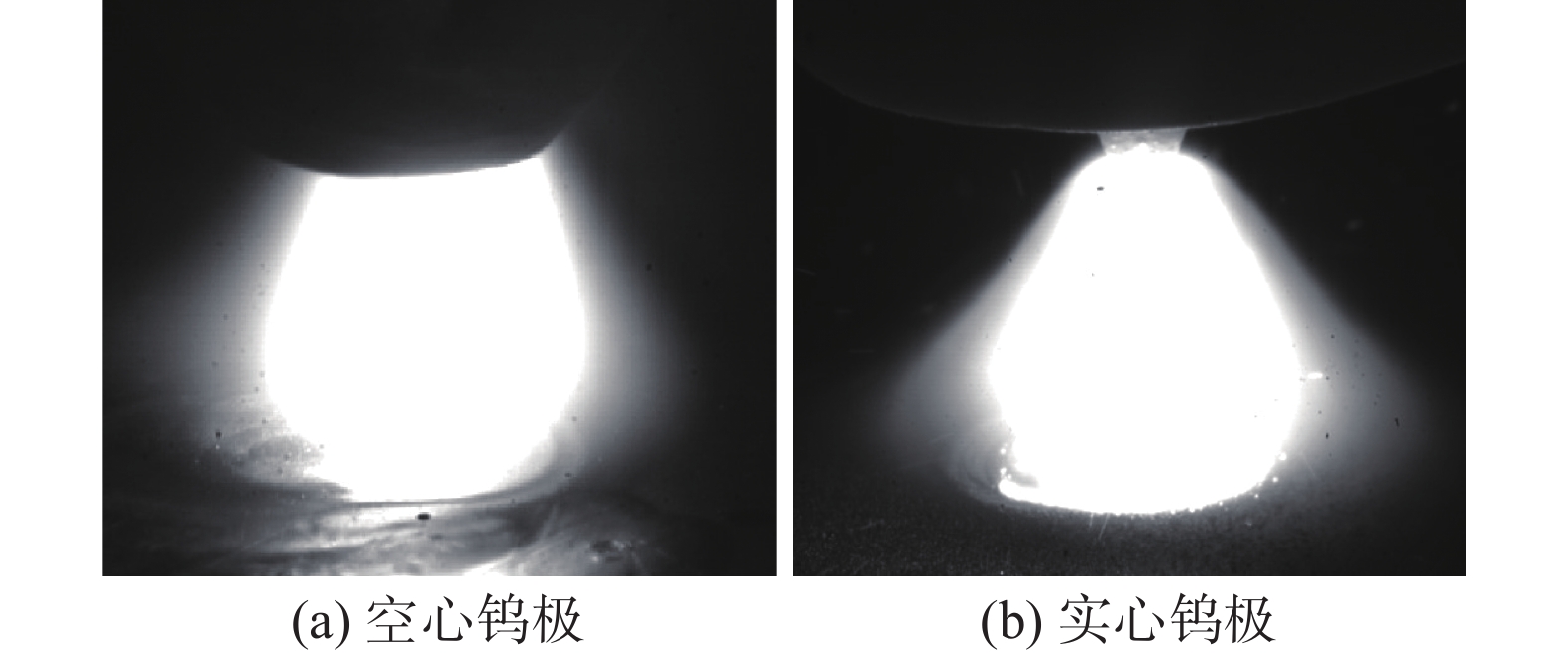
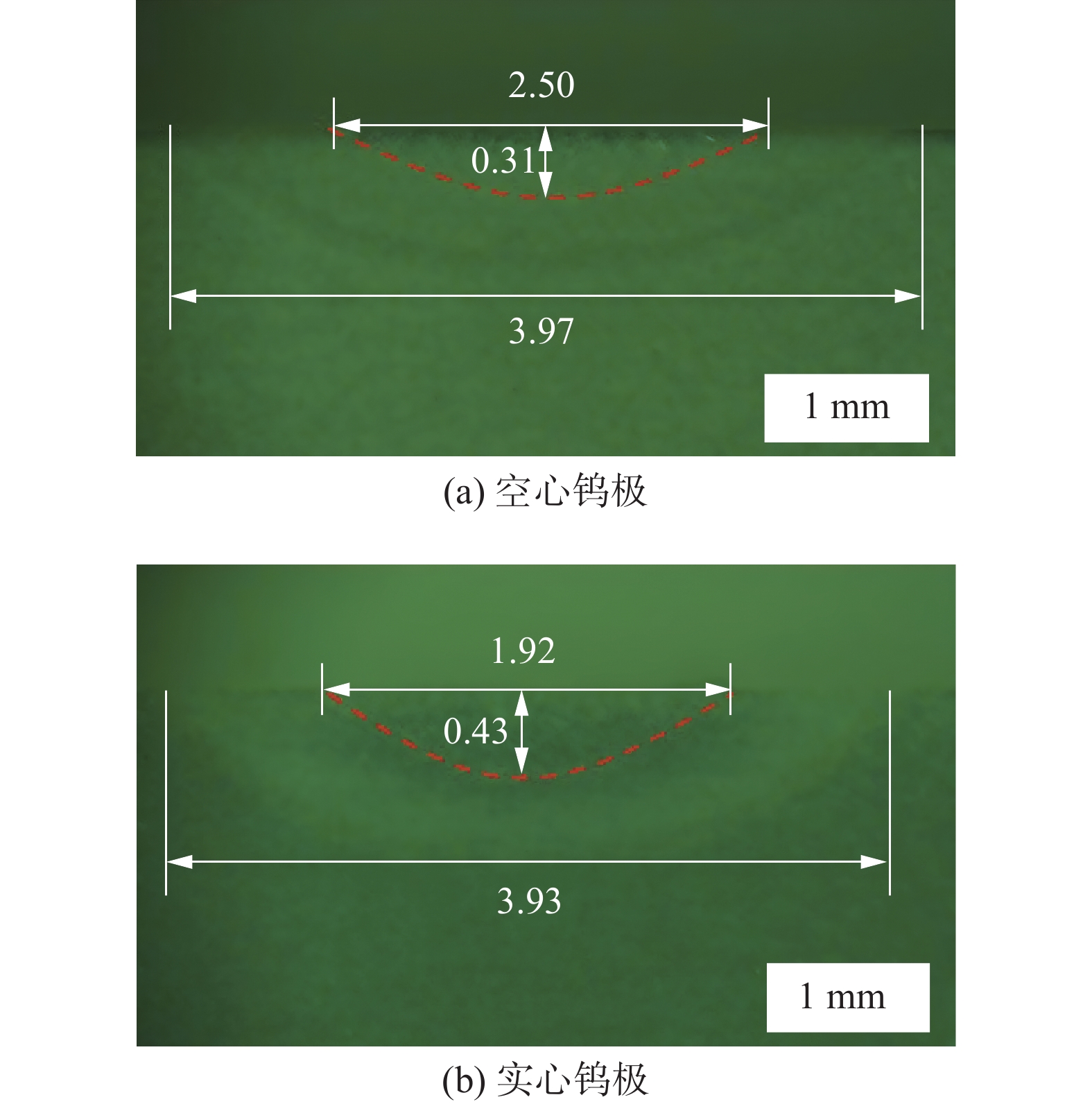
摘要: 建立了内径2 mm的空心钨极TIG焊电弧数值模型,用Fluent软件用户自定义函数(UDF)功能加载了氩气电导率、动量方程和能量方程的源项,计算了稳态下焊接电流为60 A时电弧的温度场、流场以及电弧压力,并与相同条件下实心钨极TIG焊电弧作了对比. 结果表明,空心钨极TIG焊电弧呈钟罩形,空心钨极圆环放电和钨极中心气流的冷却作用使得电弧温度分布云图顶部下凹;电弧等离子体在钨极下方运动速度较快,阳极表面电弧压力呈柱状分布,弧柱区空间压力分布比较均匀;与相同电流条件下TIG焊相比,空心钨极TIG焊电弧峰值温度降低17.3%,钨极下方2 mm位置处峰值温度降低27%,等离子体最大运动速度降低40%,电弧压力峰值降低57%,堆焊焊缝熔宽增加30%,熔深减小27.9%.Abstract: The numerical model of hollow tungsten TIG welding with inner diameter of 2 mm is developed. The source terms of momentum equation and energy equation and the conductivity of argon gas are loaded by the user defined function (UDF) of Fluent software. The temperature field, flow field and arc pressure are calculated when the welding current is 60 A in steady state. The results are compared with those of solid tungsten TIG arc under the same conditions. The results show that the shape of hollow tungsten TIG arc is bell jar shape, and the temperature field is concave at the top middle position due to the air flow and current density. The velocity of plasma below the tungsten pole is faster than other regions. The arc pressure is uniformly distributed, and the anode surface pressure is uniformly distributed in cylindrical shape. Compare with TIG welding under the same current condition, the maximum temperature, maximum plasma flow velocity and peak arc pressure of the hollow tungsten arc are reduced by 17.3%, 40% and 57%, respectively, and the peak temperature of the 2 mm cross section below the tungsten electrode is reduced by 27%. The weld width of surfacing welding increases by 30% but the weld depth decreases by 27.9%.
-
-
表 1 空心钨极TIG焊电弧模型边界条件
Table 1 Boundary condition of hollow tungsten TIG welding arc model
区域 边界类型 氩气流速v1/(m·s−1) 温度T/K 电势φ/V 磁矢量A/Wb AB 轴 — — — — BC 壁面 0 5 000 0 $\partial A{\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial A{\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ CD 压力出口 — 1 000 $\partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ 0 DE 速度进口 1.2 1 000 $\partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ $\partial A{\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial A{\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ EF 壁面 0 1 000 $\partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ $\partial A{\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial A{\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ FG 壁面 0 3 000 $ - \sigma \cdot \partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = I/{{{S}}_{\rm{c}}}$ $\partial A{\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial A{\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ GH 壁面 0 1 000 $\partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ $\partial A{\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial A{\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ HA 速度进口 1.2 1 000 $\partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial \varphi {\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ $\partial A{\rm{/}}\partial {\rm{}}z = \partial A{\rm{/}}\partial r{\rm{ = 0}}$ 表 2 焊接试验工艺参数
Table 2 Process parameters of welding test
焊接电流
I/A电弧电压
U/V焊接速度
v/(mm·min−1)气体流量
Qo/(L·min−1)弧长
l/mm60 15.9 300 10 4 -
[1] Liu Liming, Shi Jipeng, Hou Zhonglin, et al. Effect of distance between the heat sources on the molten pool stability and burn-through during the pulse laser-GTA hybrid welding process[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 34: 697 − 705. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.06.038
[2] Sridhar Raja K S, Jebith Prem J P. Sathiyaseelan P, et al. Investigation of microstructure and mechanical properties of laser and TIG welded stainless steel alloy[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2021, 44: 3578 − 3582. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.09.456
[3] Cho Y T, Cho W I, Na S J. Numerical analysis of hybrid plasma generated by Nd: YAG laser and gas tungsten arc[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2011, 43(3): 711 − 720. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2010.09.013
[4] Doi, Makoto. Coaxial hybrid process of hollow cathode TIG and YAG laser welding[J]. Welding International, 2010, 24(3): 188−196.
[5] 陈树君, 盛珊, 蒋凡, 等. 空心钨极中心负压电弧的物理性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(12): 1 − 4. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20171230 Chen Shujun, Sheng Shan, Jiang Fan, et al. Physical properties of hollow tungsten central negative pressure arc[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(12): 1 − 4. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20171230
[6] Nerovnyi V M, Khakhalev A D. Hollow cathode arc discharge as an effective energy source for welding processes in vacuum[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2008, 41(3): 1 − 8.
[7] 黄勇, 郝延召, 瞿怀宇, 等. 耦合电弧钨极TIG焊电弧压力的测量与分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(12): 33 − 36. Huang Yong, Hao Yanzhao, Qu Huaiyu, et al. Test and analysis of arc pressure measurement in coupling arc electrode TIG welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(12): 33 − 36.
[8] 张晓鸿, 陈静青, 张康, 等. 不同电流密度下的TIG焊电弧行为分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(12): 77 − 80,118. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20170730002 Zhang Xiaohong, Chen Jingqing, Zhang Kang, et al. Analysis of TIG arc behaviors under different current densities[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(12): 77 − 80,118. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20170730002
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 晏杰,胡水莲,张维维,白鹏飞,李涛. GTAW堆焊工艺参数对2A12铝合金板堆焊焊缝组织和力学性能的影响. 轻合金加工技术. 2024(09): 46-52 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 徐心洁,林文钦,胡成江,路寒,蒋洪俊. LY12角片断裂分析. 失效分析与预防. 2021(02): 139-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨帅,邢彦锋,刘文杰. 基于超声清洗的CMT焊缝质量分析. 上海工程技术大学学报. 2020(03): 284-289 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: