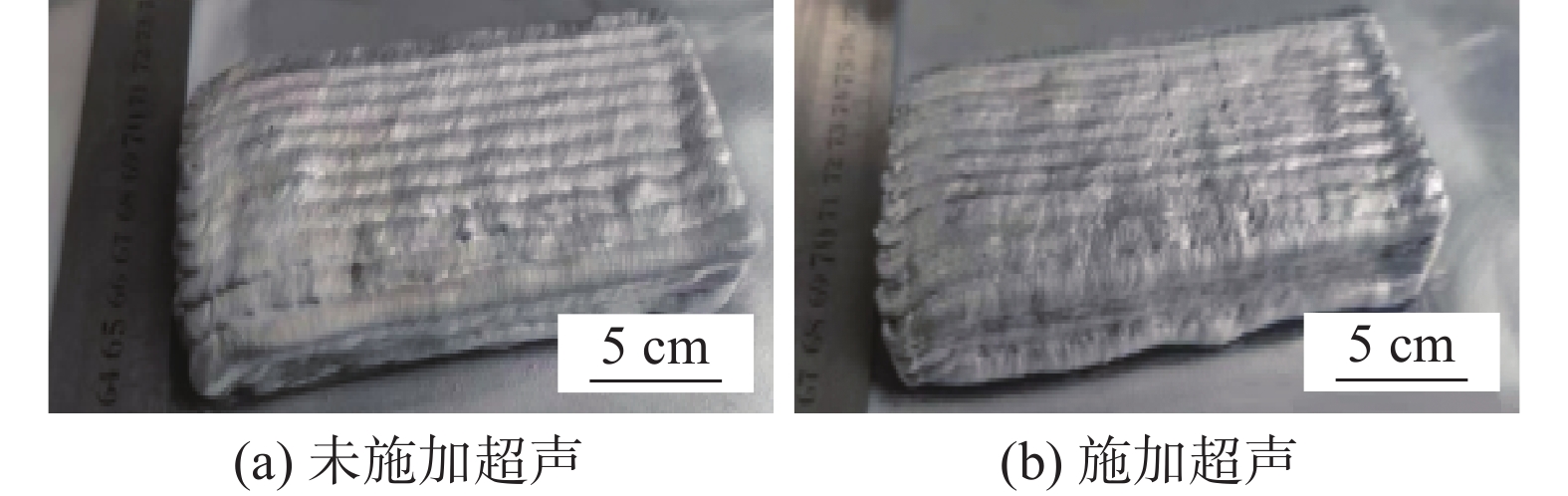
Finite element analysis of the effect of ultrasonic impact on the stress of aluminum alloy arc additive manufacturing
-
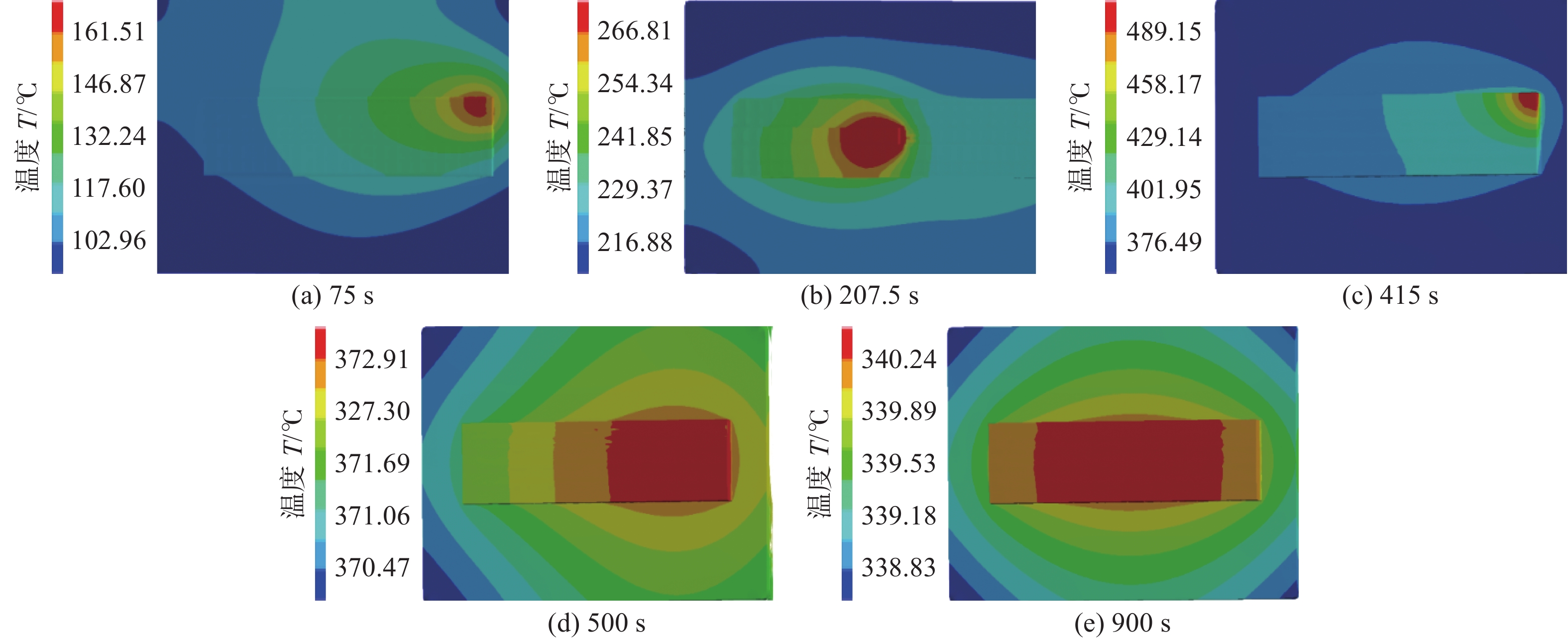
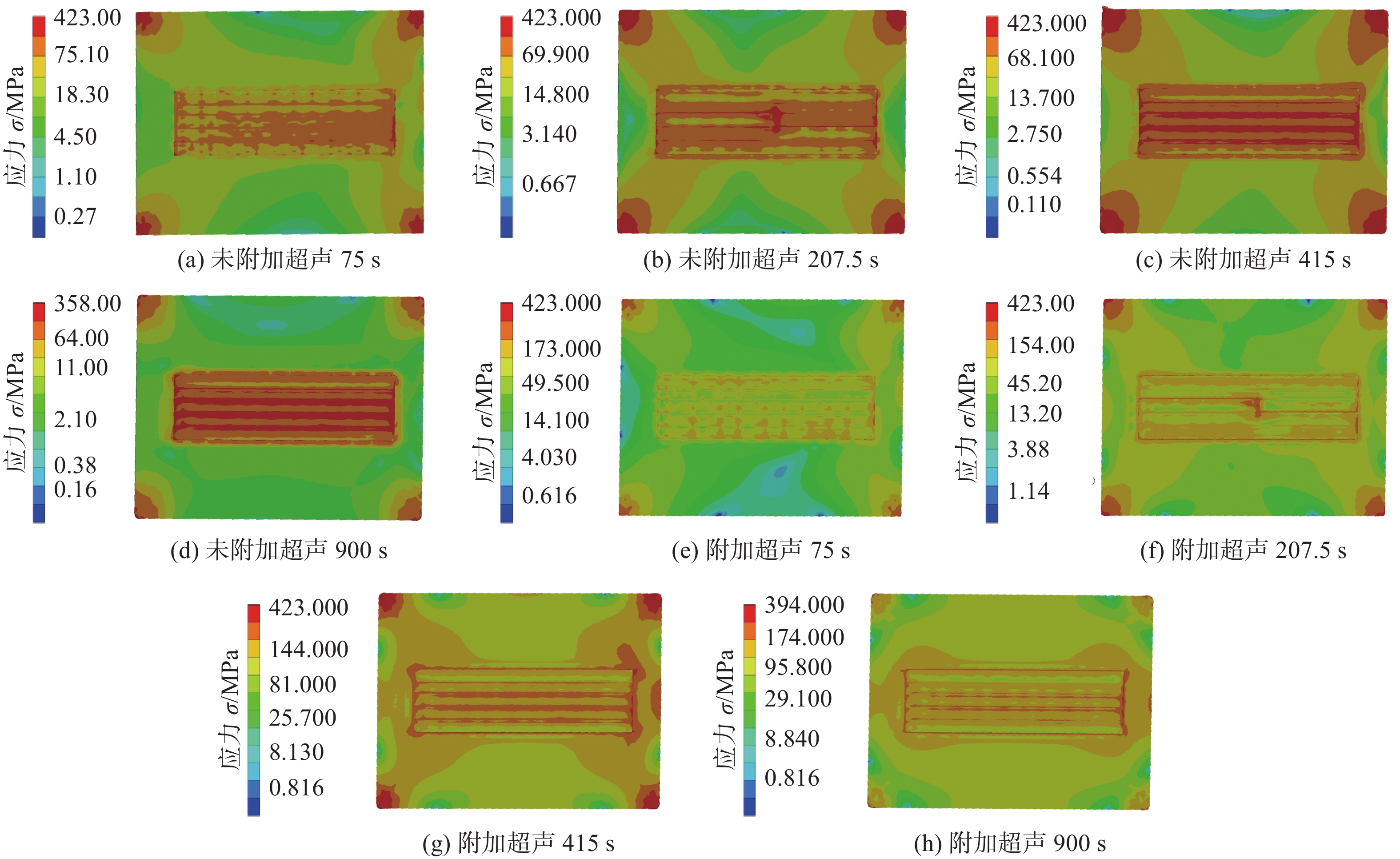
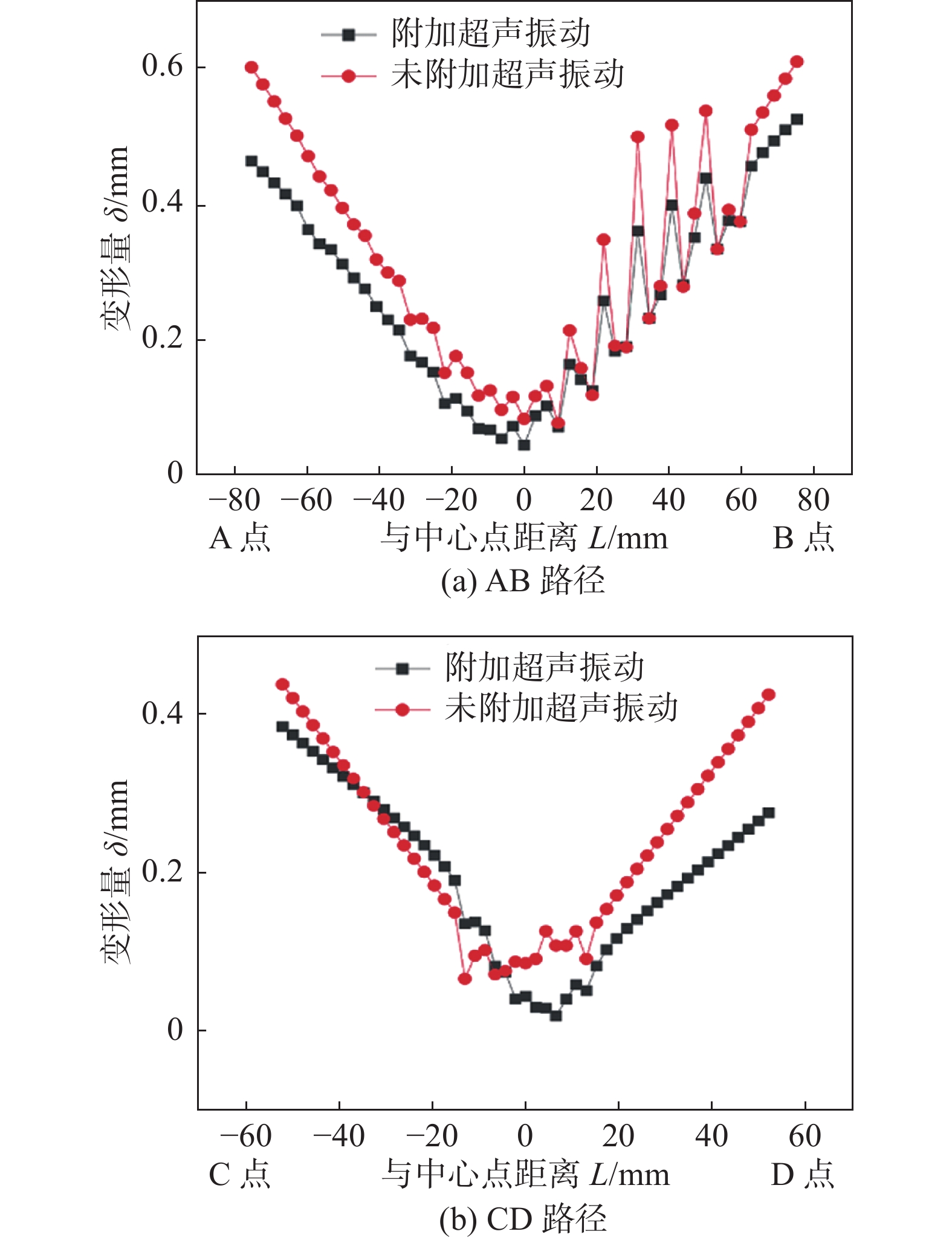
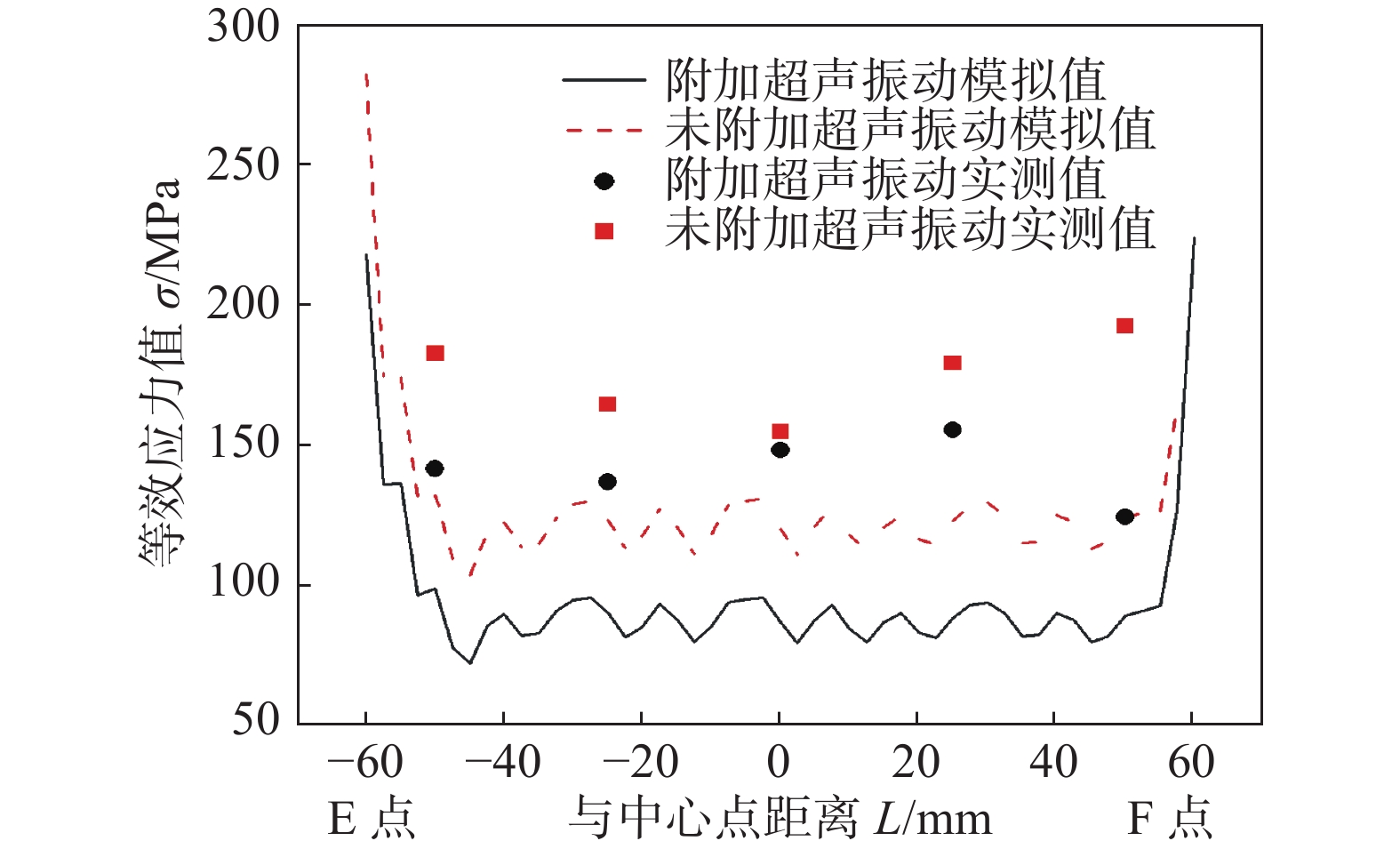
摘要: 采用有限元分析方法对附加超声冲击下电弧增材制造2219铝合金的过程进行数值模拟,并研究了其应力场变化以及工件变形情况的变化. 结果表明,附加超声冲击能使多层多道沉积过程中沉积件边缘处以及基板中靠近沉积件的区域的应力集中程度下降. 多层多道沉积过程中附加超声冲击能有效降低沉积件内部的应力. 在附加超声冲击后道间交界处的应力范围由156.1 ~ 211.6 MPa下降至138.8 ~ 181.9 MPa,表面平均残余应力下降22.3%. 附加超声冲击下,多层多道电弧增材构件最大变形量由0.61 mm下降至0.53 mm,平均变形量由0.33 mm下降至0.27 mm. 试验实际测量所得的与有限元计算的多层多道沉积件上表面的应力分布规律相近,证明模拟结果的可靠.Abstract: The finite element analysis was used to numerically simulate the process of arc additive manufacturing of 2219 aluminum alloy under ultrasonic impact, and the changes in stress fields and component deformation were studied. The results show that the additional ultrasonic impact can reduce the stress concentration at the edge of the sediment and at the area close to the sediment in the substrate during the multi-layer multi-channel deposition. Additional ultrasonic impact during multi-layer multi-channel deposition can effectively reduce the stress inside the sediment. After the ultrasonic impact, the stress range at the interface between layers decreased from 156.1 − 211.6 MPa to 138.8 − 181.9 MPa, and the average residual stress on the surface decreased by 22.3%. Under the ultrasonic impact, the maximum deformation of multi-layer multi-pass arc additive component decreased from 0.61 mm to 0.53 mm, and the average deformation decreased from 0.33 mm to 0.27 mm. The stress distribution on the upper surface of the multi-layer sediment calculated by the finite element is similar to that of the measured in actual experiment, which proves that the simulation results are reliable.
-
0. 序言
随着汽车电子、航空电子、便携式移动电子以及大功率集成电子设备向着高密度化、微型化和多功能化方向的发展,三维(3D)高密度封装逐渐成为封装技术发展的潮流[1-2]. 在电子封装技术领域,微互连凸(焊)点起着机械连接、电气导通、信号传递等核心作用[3-4],而微互连铜核焊点更是由于具有不易桥连、导电性好、导热性良和熔点高等优点而被广泛应用于高性能计算芯片、存储器等高密度3D封装领域[5-6].
在回流焊过程中,3D封装结构中铜核加入后,铜核与焊料、焊料与基板均发生化学反应,在铜核/焊料、焊料/基体金属界面处均会形成IMC层,界面IMC层作为焊点的重要和关键组成部分,它的结构及形貌对电子封装互连焊点可靠性连接有着重要的影响,薄且连续均匀的 IMC层有利于界面的良好结合[7]. 与传统锡球焊点相比,铜核焊点的界面数量、原子扩散距离、界面微观结构(即IMC层)等有较大的变化,且界面化合物占比较高,但是由于IMC层较脆,太厚的IMC层使焊点的可靠性降低[8-9]. 铜核单界面或同质界面的界面反应特征已经进行了大量研究[10-13],Jeong等人[10]采用同质双ENIG界面研究了ENIG/Cu核 SAC305/ENIG焊点在电迁移过程中的界面演变;Chen等人[13]研究了铜核Sn-Pb焊点在固态高温时效作用下的界面反应和力学性能,并研究了铜核大小对力学性能的影响. 然而,在3D封装中,铜核焊点会同时存在4个界面,即芯片/焊料、焊料/铜核、铜核/焊料和焊料/基板,在回流焊过程中,4个界面将同时发生界面反应,两端的原子可能穿过液体焊料扩散到另一端,相互影响对面的界面反应,这种状态下焊点的组织及性能在焊接和服役过程中的演变将与单界面焊点存在较大差异. 关于铜核添加的复合钎料异质基材焊点界面 IMC层在热时效过程中的生长行为和力学性能之间关系的研究还较少. 因此,研究Ni/Cu铜核 + 钎料/Cu异质焊点界面层的形貌和生长特征,更真实地模拟铜核焊点的实际应用环境具有重要指导意义. 为此,文中以Ni/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu焊点为对象,研究该焊点在不同热时效时间作下的界面反应特征及拉伸性能,通过与Cu/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu同质焊点力学性能进行对比,探讨和分析Ni/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu焊点界面IMC层生长动力学行为及焊点力学性能,为提高铜核焊点的可靠性提供理论依据.
1. 试验方法
试验采用直径d为400 μm的铜丝和镍丝(纯度均为99.9%)作为基体材料,采用商用低银无铅Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu(简称Solder)锡膏与直径为350 μm高纯度的镀镍铜核球作钎料. 首先采用线切割将铜丝和镍丝基体材料加工成长度为30 mm的小棒,再采用砂纸将基材待焊端面磨平后放置超声波仪器用无水乙醇清洗并吹干后备用,然后将镍丝、铜丝放到自制的V形夹具上,中间放入铜核和Solder锡膏,搭建Ni/Cu-core + Solder/Cu三明治线性焊点(Ni-Cu铜核焊点),焊点高度t (即两根基材中间的间隙)和试样总长度L分别控制在0.5和60 mm左右,焊点结构如图1所示. 将组装好的三明治焊点放置于温度为250 ℃的恒温炉中,待钎料熔化后在回流态保持20 s左右,立即将夹具和试样一起从炉中取出放置于空气中冷却至室温,回流后采用酒精浸泡以去除试样表面残留的助焊剂.
将焊接后的试样用砂纸打磨掉焊点表面的氧化物及多余的钎料,然后将处理后的微焊点放置于恒温箱中进行不同时长(48、120、360 h)的100 ℃等温时效试验. 将经历不同时长热时效处理后的焊点取出进行镶嵌、打磨、抛光及腐蚀后使用带X射线能谱(energy dispersive spectrometer,EDS)的扫描电镜进行显微组织观察,采用Image-pro软件对3幅SEM图片的界面IMC厚度进行测量,并结合EDS分析界面层相组成.
将热时效后的焊点在DMAQ 800设备进行常温(约25 ℃)拉伸试验,加载速率设置为1 N/min. 每个热时效时长下的焊点分别取3个进行拉伸试验,将所得数据求平均值,在SEM扫描电镜上观察拉伸断口形貌.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 热时效时间对焊点界面显微组织的影响
Ni-Cu铜核焊点在250 ℃回流焊20 s后空冷至室温的界面IMC显微组织及形貌,如图2所示. 由图2可观察到在各界面上均形成了一层很薄的连续的IMC层. 图2中A、B、C和D点的能谱分析如图3所示,除Solder/Cu基界面外,Ni基/Solder、近Ni基侧Solder/Cu铜核和近Cu基侧Cu铜核/Solder 3个界面IMC层均由Sn,Cu和Ni 3种元素组成,在Ni基/Solder界面处该相组成(摩尔分数)为44.32%Cu-14.97%Ni-40.71%Sn,其中(Cu + Ni)与Sn的原子数比为(44.32 + 14.97)∶40.71,接近6∶5,因此,将该相表征为(Cu,Ni)6Sn5,在近Ni基侧Solder/Cu铜核和近Cu基侧Cu铜核/Solder两个界面B点和C点处该相组成中,(Cu + Ni)与Sn的原子数比接近6∶5,因此,将该相表征为(Cu,Ni)6Sn5. Solder/Cu基界面D点的能谱分析,该相成分56.47%Cu-43.53%Sn,Cu与Sn的原子数比接近6∶5,因此,将该相也表征为Cu6Sn5. 从各界面的相组成来看,除Solder/Cu基界面外,其他3个界面上发生了明显的Cu-Ni交互作用. Solder/Cu基界面IMC形态呈扇贝状,其他3个界面形成近似针状的界面形貌,同时在近Cu基侧还发现有少量Cu6Sn5颗粒分布于钎料基体中,Ni基侧的IMC厚度明显比Cu基侧小,近Ni基侧的Solder/Cu铜核界面IMC厚度也略小于近Cu基侧的.
Ni-Cu铜核焊点在100 ℃热时效48、120、360 h后的界面形貌,如图4 ~ 图6所示. 可以看出,各界面IMC层的厚度均随着热时效时间的延长而增加,Ni基/Solder和近Ni基侧的Solder /Cu铜核两个界面的IMC层生长速率略低于Solder/Cu基和近Cu基侧的Cu铜核/Solder两个界面IMC层的生长速率. 随着时效时间的增加,Solder/Cu基界面处的IMC层与焊料基体的界面形貌由平坦向锯齿状转变,但齿尖深入焊料基体较浅;其他3个界面的IMC层除厚度增加外,其界面形貌变化不显著. 在近Cu基侧钎料基体中观察到有较大尺寸块状的Cu6Sn5存在,而近Ni基侧钎料基体中,发现少量尺寸较小的(Cu,Ni)6Sn5颗粒存在,可能是基体或铜核表面Ni原子扩散到钎料中形成的金属间化合物. 结果表明,在Ni-Cu铜核焊点中,采用Ni作为基体,对焊点界面IMC层过度生长起到了明显的抑制效果,有利于改善焊点服役可靠性.
此外,热时效时长的增加并未改变Ni基/Solder、近Ni基侧Solder/Cu核和近Cu基侧Cu核/Solder 3个界面IMC种类. 通常在(Cu,Ni)6Sn5/铜核间界面形成的典型Cu3Sn未被检测到,主要原因是在回流焊过程中,一定量的Ni原子从镍基体界面扩散到铜核界面,Ni原子抑制了Cu3Sn的生成,与Tian等人[14]的研究结果相同. 在经历360 h热时效的试样中,在Solder/Cu基界面处,未观察到明显的IMC分层现象,但通过对界面进行能谱分析可知,Cu-Ni铜核焊点经较长热时效后,Solder/Cu基界面IMC层由Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn两层化合物组成,即位于焊料一侧的Cu6Sn5层以及位于Cu基板和Cu6Sn5之间的Cu3Sn层,如图7所示,两种化合物中的Cu原子均来源于铜基板,Sn来自于钎料,Cu6Sn5是一种不稳定的化合物,在热时效时会发生以下反应[15]
$$ \mathrm{6Cu + 5Sn = Cu}_{ \mathrm{6}} \mathrm{Sn}_{ \mathrm{5}} $$ (1) $$ \mathrm{3Cu + Sn = Cu}_{ \mathrm{3}} \mathrm{Sn} $$ (2) $$ \mathrm{9Cu + Cu}_{ \mathrm{6}} \mathrm{Sn}_{ \mathrm{5}} \mathrm{ = 5Cu}_{ \mathrm{3}} \mathrm{Sn} $$ (3) 2.2 热时效时间对界面IMC层生长行为的影响
从热时效时间对焊点的微观组织演变可以看出,在热时效过程中,焊料与基体、焊料与铜核不断发生着反应,使界面层的厚度随着热时效时间的增加而变厚,界面IMC层厚度随时效时间的变化规律,如图8所示. 随着时效时间的延长,各界面IMC层逐渐变厚,Solder/Cu基界面的IMC厚度无论在哪个时刻均大于其他3个界面,可能是与Cu侧界面离Ni侧最远其受到Ni原子的影响最小有关. 热时效0 ~ 48 h内,Solder/Cu基界面IMC增长速率最快,随后该界面的IMC增长速率有所下降,这主要是因为Cu基界面在热时效初期形成的较厚Cu6Sn5有效的阻挡了Cu基体界面的Cu元素扩散进入钎料. 时效120 h后,Ni基/Solder、近Ni基侧Solder/Cu核和近Cu基侧Cu核/Solder 3个界面的(Cu,Ni)6Sn5生长速率均有下降趋势,这可能与界面之前已生成的(Cu,Ni)6Sn5层减缓了Ni、Sn和Cu原子的扩散速率有关. 时效360 h时,Ni基/Solder的界面IMC层厚度为5.38 μm,约为Solder/Cu基界面层厚度的一半.
根据测试界面层IMC厚度结果,得到各界面层IMC层的厚度和热时效时间的拟合关系曲线如图9所示,为
$$ \mathit{l}\mathrm{=}\mathit{l}_{\mathrm{0}}\mathrm{+}\mathit{Kt}^{\mathit{\mathrm{1/2}}} $$ (4) 式中:l是时效过程中IMC层厚度(μm);l0是时效前 IMC层厚度(μm);K是IMC层生长系数(μm2/h);t是热时效时间(h) .
从图9可以观察到4个界面IMC层厚度与热时效时间近似呈线性增长趋势,拟合线的斜率反映了界面IMC层厚度随时间的增长趋势. 显然,100 ℃时效时,Ni基/Solder界面IMC层的增长速率仅为Solder/Cu基界面的70%,近Ni基侧Solder/Cu核和近Cu基侧Cu核/Solder两个界面的IMC生长速率也明显比Solder/Cu基的低,说明在同等时效条件下,采用焊料中添加微量Ni或采用Ni作基体可显著减缓焊点界面IMC层的生长趋势. 从图9还可以看出,4个界面层在100 ℃时效时的生长指数均为0.5,表明(Cu,Ni)6Sn5层和Cu6Sn5层的生长以扩散控制为主,该研究结果与SAC焊点可靠性研究中IMC层的生长行为吻合[16].
2.3 热时效对焊点拉伸性能的影响
Cu-Cu铜核同质焊点和Ni-Cu铜核异质焊点时效前后焊点拉伸强度的变化,如图10所示. 从图10可以得到看出,随着热时效时间的延长,焊点的强度逐渐下降. 在相同时效时长下,Ni-Cu铜核焊点拉伸强度比Cu-Cu铜核焊点稍大,在时效120 h内,两种焊点的抗拉强度均下降较快,随后强度下降速率略缓,但Cu-Cu铜核焊点强度下降速率稍大于Cu-Ni焊点的.
Ni-Cu铜核焊点的抗拉强度从回流焊后的38.60 MPa下降到热时效360 h后的20.77 MPa,拉伸强度下降了46.19%. 结合Ni-Cu铜核焊点4种界面IMC层的生长曲线可知,Ni-Cu铜核焊点各界面的生长速率和厚度均有差异,在热时效48 h时,其Ni基/Solder界面IMC厚度约为3.37 μm,而热时效360 h后,其Ni基/Solder界面IMC厚度约为5.38 μm,与回流焊后Solder/Cu基侧的IMC厚度相当.很显然,焊点抗拉强度变化规律与焊点IMC层的厚度有关,界面IMC是脆性物质,过厚的界面化合物将会导致微焊点的拉伸性能降低,因此热时效引起的界面IMC厚度的增加是引起微焊点抗拉强度下降的原因之一.
试验研究发现,Cu-Cu和Ni-Cu两种铜核焊点在轴向拉伸试验中,其拉伸断裂主要在钎料/铜基界面附近和近铜基侧的钎料部分,以韧脆混合断裂为主,拉伸断口形貌如图11所示. 由于Cu-Cu铜核焊点的断裂位置与断口形貌与Ni-Cu焊点的断裂位置与断口形貌基本一致,因此图11中只列出Ni-Cu焊点的拉伸断口形貌. 从图11很明显可以看到,在断口处均发现有类似小球的颗粒状和撕裂的韧窝存在. 对颗粒状小球进行能谱分析,如图12所示,可以推断颗粒小球主要成分为Cu6Sn5,即界面IMC,这与Somidin等人[17]从IMC层侧面观察到Cu6Sn5成扇贝状相吻合.
如图11所示,焊态和热时效后的焊点断口表面均出现了一定数量的韧窝,同时断口存在少部分裸露的Cu6Sn5层,随热时效时间的延长,裸露的Cu6Sn5层占比有增大倾向,说明焊点的断裂位置在更靠近IMC的体钎料处,可能是因为随着时效时间的延长,焊点靠近铜基侧界面IMC晶粒长大导致晶粒间结合强度降低,同时界面IMC自身的脆性也使得界面处连接强度变弱[18],因此断裂位置更靠近IMC的体钎料处. 在Ni-Cu异质焊点中,Cu在焊料/Ni界面发生耦合反应,抑制了界面IMC层的生长,在一定程度上起到了减缓焊点力学性能恶化的效果,有利于提高焊点的可靠性.
3. 结论
(1) Ni-Cu铜核焊点,在Ni基/Solder、近Ni侧Solder/Cu核以及近Cu侧Solder/Cu核界面处均形成(Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMC层,表明Cu原子穿过钎料到达Ni基侧参与界面反应,Solder/Cu基界面处形成Cu6Sn5 IMC层. 焊点4个界面的IMC层平整、连续,且主要呈锯齿状.
(2) 热时效中,界面IMC厚度均随着热时效时间的延长而逐渐增大,而且生长行为以扩散控制为主. 在相同时效条件下,近Cu基侧的两个界面IMC层厚度分别小于近Ni基侧的两个IMC层的厚度.
(3) Ni-Cu铜核焊点的拉伸强度略高于Cu-Cu铜核焊点的,两种焊点的拉伸强度均随热时效时间延长而降低且断裂模式均以韧脆混合断裂为主,断裂位置主要发生在近Cu基侧IMC层厚度较大的体钎料处. 随着热时效时间的延长,断裂位置越倾向于近Cu基侧IMC层处,采用Ni替代Cu作基体,可减缓界面层的生长速度,有利于提高铜核焊点的可靠性.
-
-
[1] Davoud J, Vaneker T, Gibson I. Wire and arc additive manufacturing: Opportunities and challenges to control the quality and accuracy of manufactured parts[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 202: 109471.
[2] Evans S, Wang J, Qin J, et al. A review of WAAM for steel construction – Manufacturing, material and geometric properties, design, and future directions[J]. Structures, 2022, 44: 1506 − 1522. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2022.08.084
[3] Ou W, Mukherjeee T, Knapp G, et al. Fusion zone geometries, cooling rates and solidification parameters during wire arc additive manufacturing[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2018, 127: 1084 − 1094. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.08.111
[4] 张纪奎, 陈百汇, 张向. 电弧增材制造钛合金界面处残余应力及其影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2018, 47(3): 920 − 926. Zhang Jikui, Chen Baihui, Zhang Xiang. Residual stress and its influence at the interface of titanium alloy fabricated by electric arc additive manufacturing[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2018, 47(3): 920 − 926.
[5] 权国政, 杨焜, 盛雪, 等. 电弧熔丝增材制造残余应力控制方法综述[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2021, 28(11): 1 − 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.11.001 Quan Guozheng, Yang Kun, Sheng Xue, et al. Review of residual stress control methods for additive manufacturing of arc fuses[J]. Chinese Journal of Plastic Engineering, 2021, 28(11): 1 − 10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2021.11.001
[6] 姚波, 马良, 陈静, 等. 电弧增材制造典型构件热应力变形仿真分析[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2022, 41(6): 961 − 970. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200514 Yao Bo, Ma Liang, Chen Jing, et al. Simulation analysis of thermal stress deformation of typical components of arc additive manufacturing[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 961 − 970. doi: 10.13433/j.cnki.1003-8728.20200514
[7] Ding J, Colegrove P, Mehnen J, et al. A computationally efficient finite element model of wire and arc additive manufacture[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 70(1-4): 227 − 236. doi: 10.1007/s00170-013-5261-x
[8] Yuan T, Kou S, Luo Z. Grain refining by ultrasonic stirring of the weld pool[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 106: 144 − 154. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2016.01.016
[9] Tian Y, Shen J, Mehnen J, et al. Effects of ultrasonic vibration in the CMT process on welded joints of Al alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 259: 282 − 291. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.05.004
[10] Chen Q, Lin S, Yang C, et al. Grain fragmentation in ultrasonic-assisted TIG weld of pure aluminum[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2017, 39: 403 − 413. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.05.001
[11] 贺地求, 李剑, 李东辉等. 铝合金超声搅拌复合焊接[J]. 焊接学报, 2011, 32(12): 70 − 72,108. He Diqiu, Li Jian, Li Donghui, et al. Aluminum alloy ultrasonic stirred composite welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2011, 32(12): 70 − 72,108.
[12] Wang J, Yu C, Lu C, et al. Research status and future perspectives on ultrasonic arc welding technique[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 58: 936 − 954. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.09.005
[13] 饶德林, 陈立功, 倪纯珍等. 超声冲击对焊接结构残余应力的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2005, 26(4): 48 − 50,64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2005.04.013 Rao Delin, Chen Ligong, Ni Chunzhen, et al. Influence of ultrasonic impact on residual stress of welded structure[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2005, 26(4): 48 − 50,64. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2005.04.013
[14] Zhou C, Jiang F, Xu D, et al. A calculation model to predict the impact stress field and depth of plastic deformation zone of additive manufactured parts in the process of ultrasonic impact treatment[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 280: 116599. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116599
[15] Zhou C, Wang J, Guo C, et al. Numerical study of the ultrasonic impact on additive manufactured parts[J]. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences, 2021, 197(1): 106334.
[16] Yang Y, Jin X, Liu C, et al. Residual stress, mechanical properties, and grain morphology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy produced by ultrasonic impact treatment assisted wire and arc additive manufacturing[J]. Metals, 2018, 8(11): 934 − 934. doi: 10.3390/met8110934




 下载:
下载: