Numerical analysis and mechanism investigation of the bypass-current plasma-MIG hybrid arc and the molten pool
-
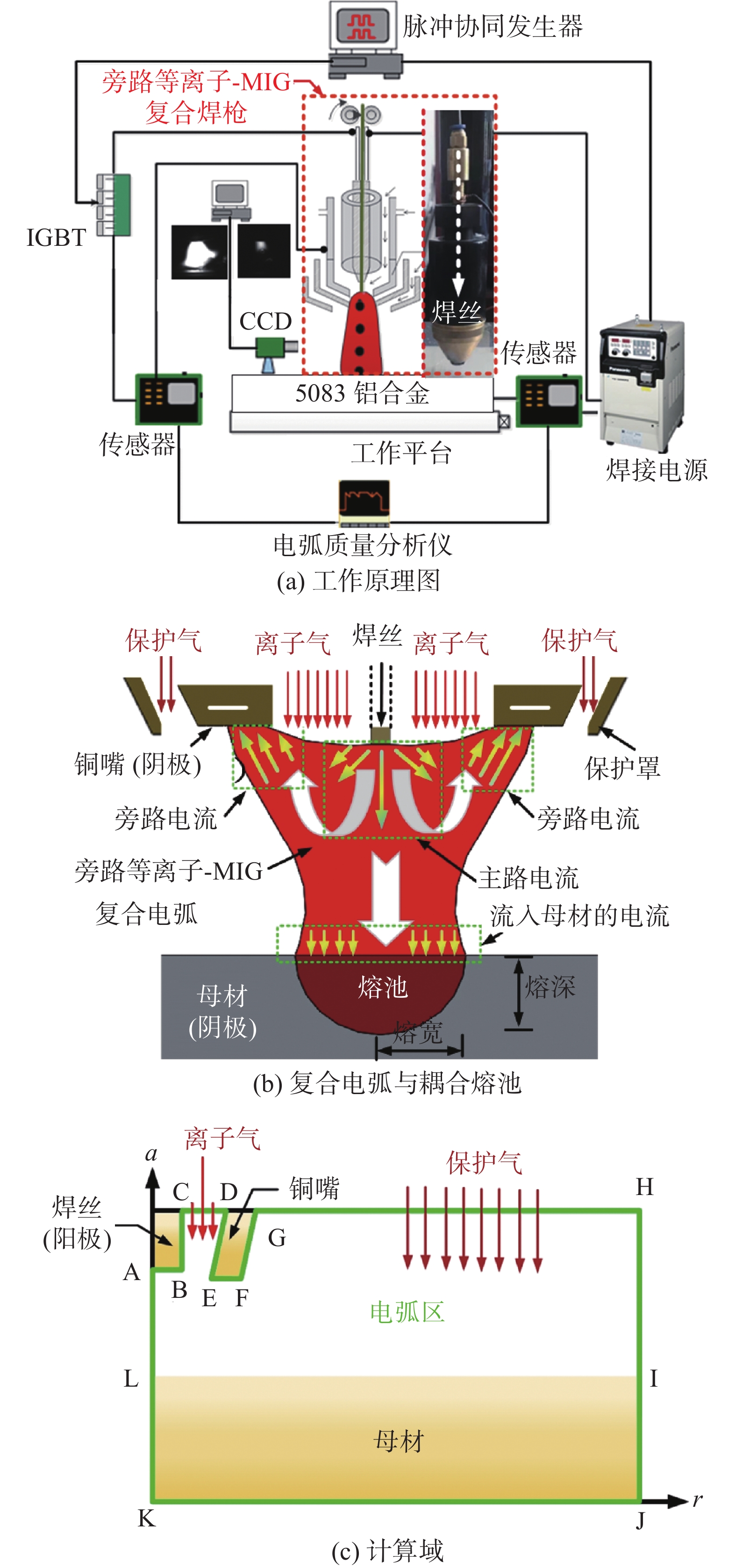
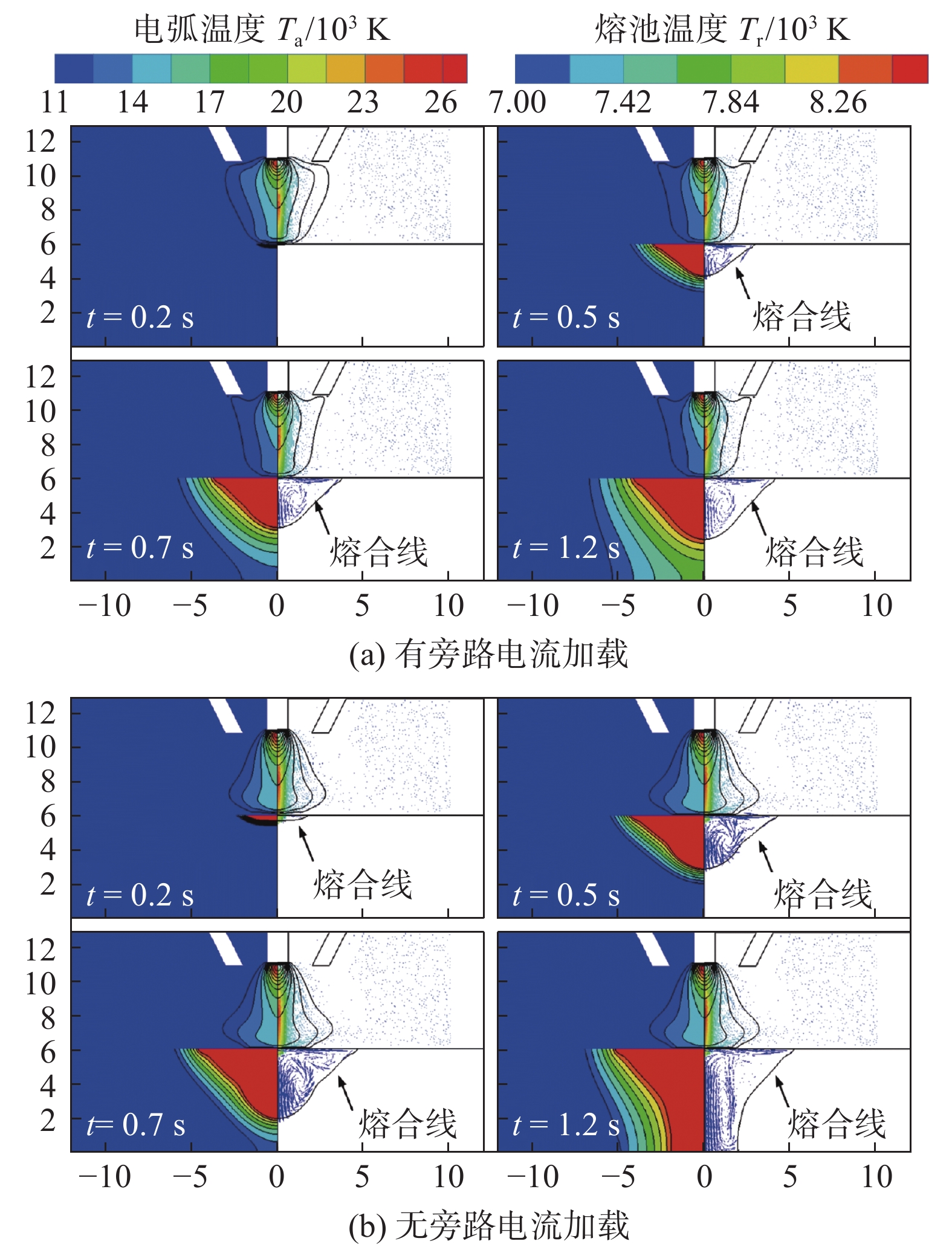
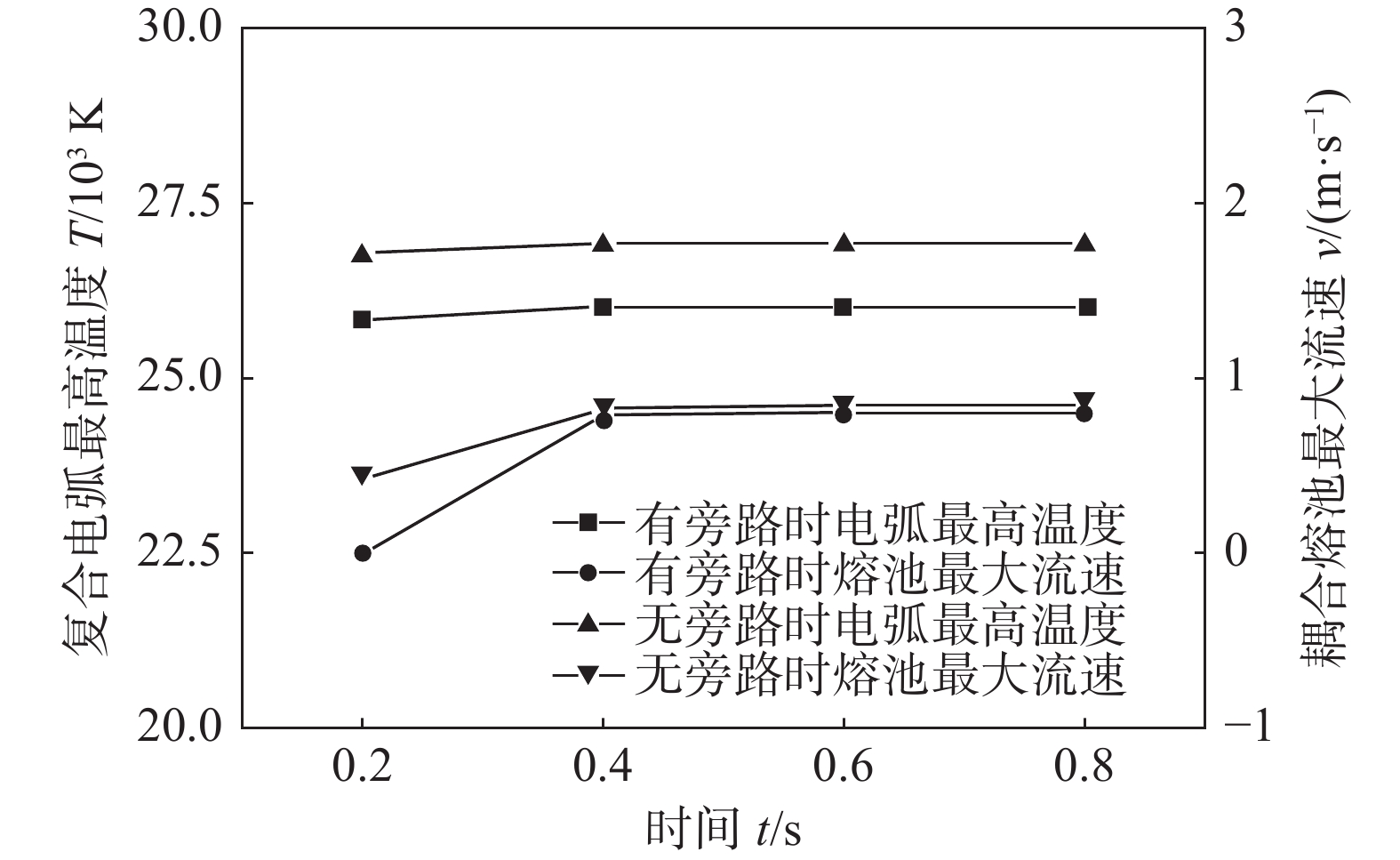
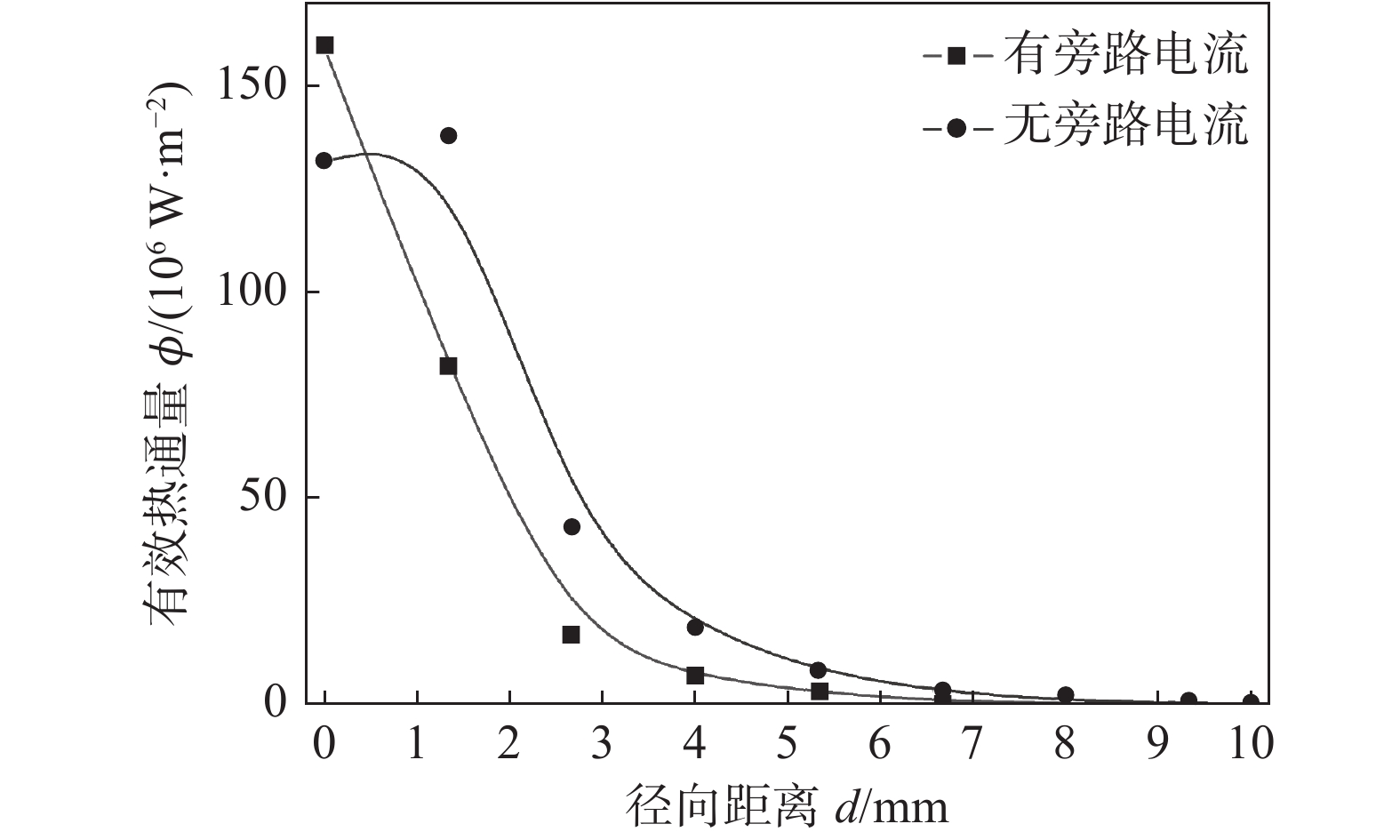
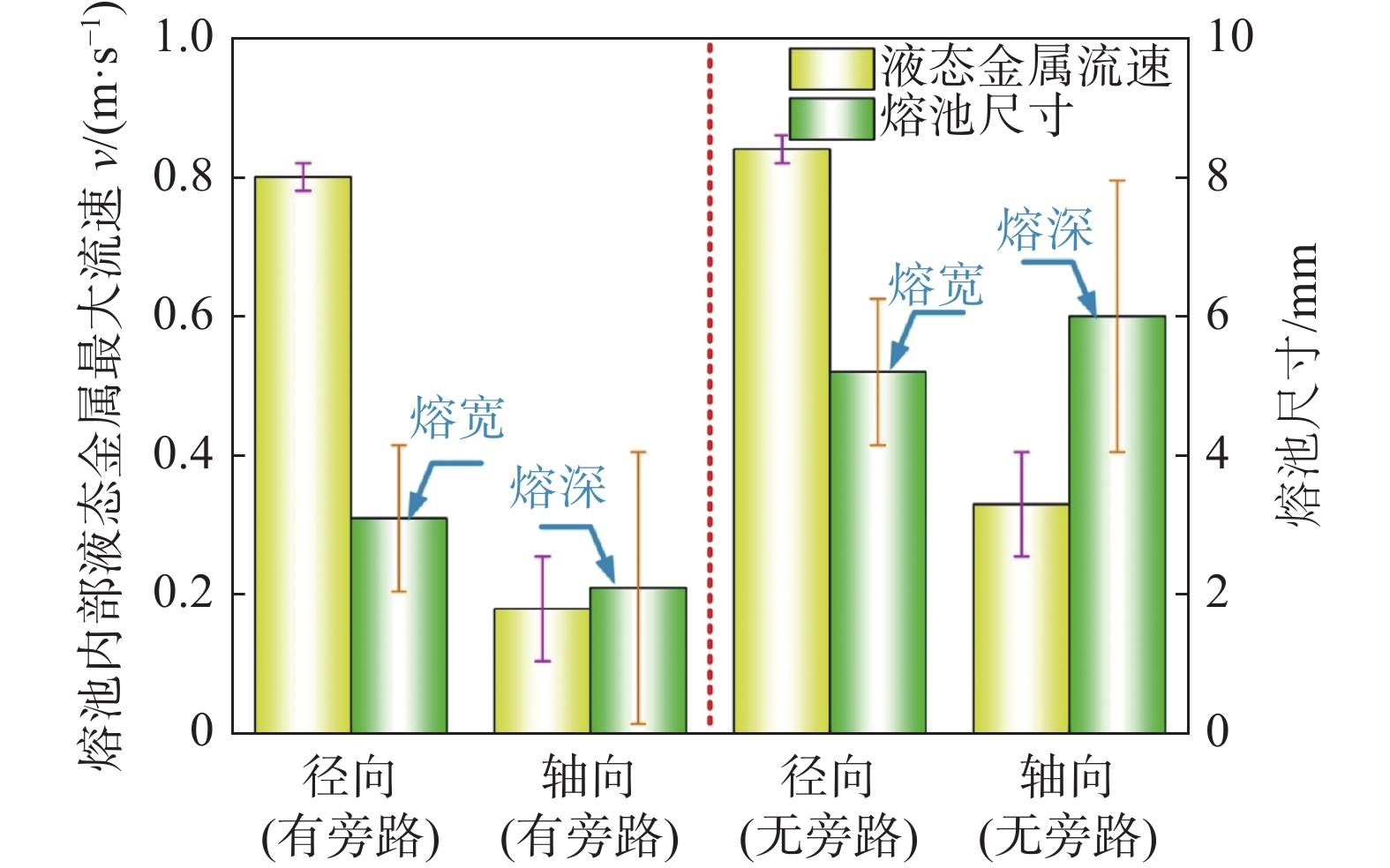
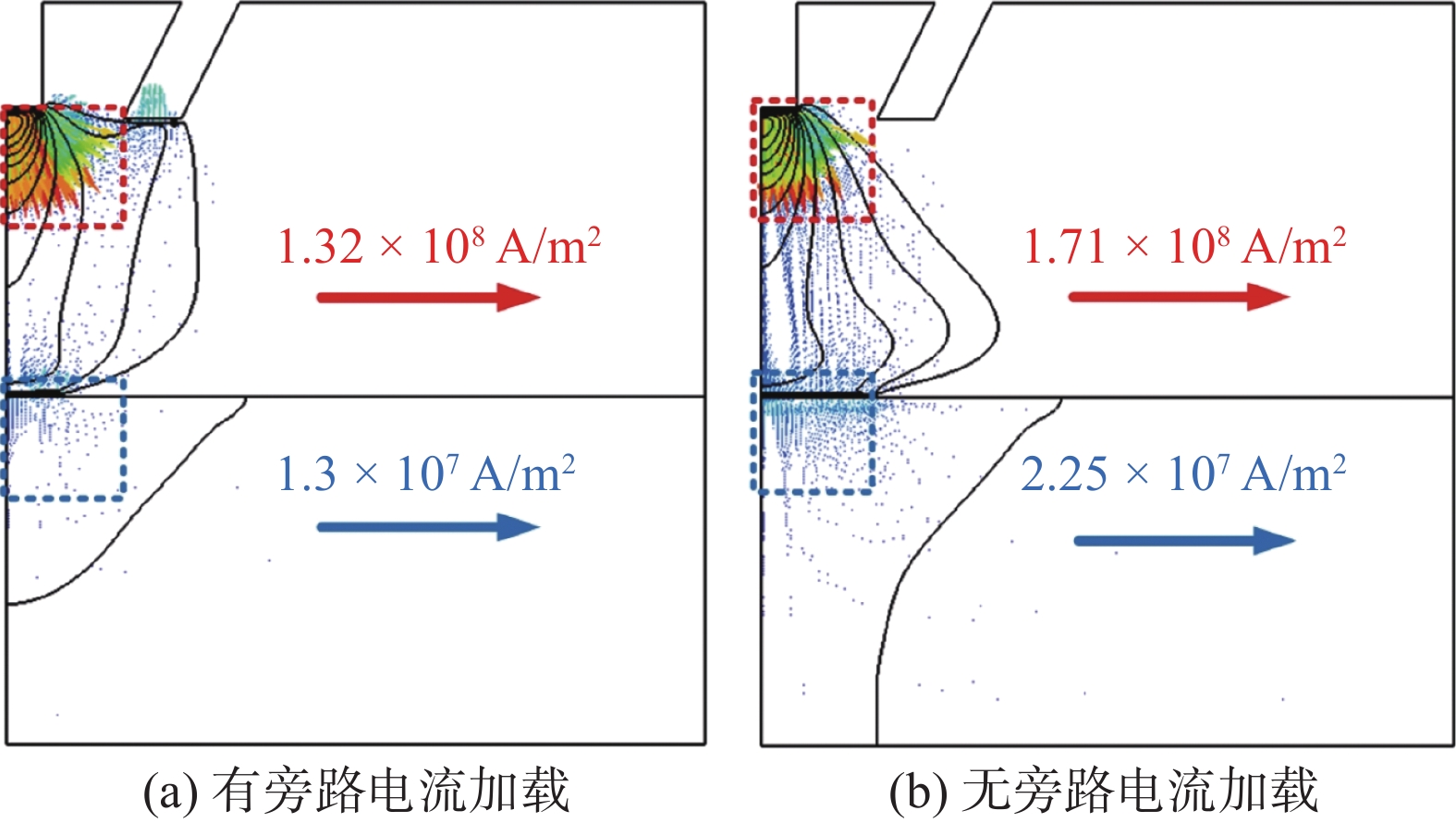
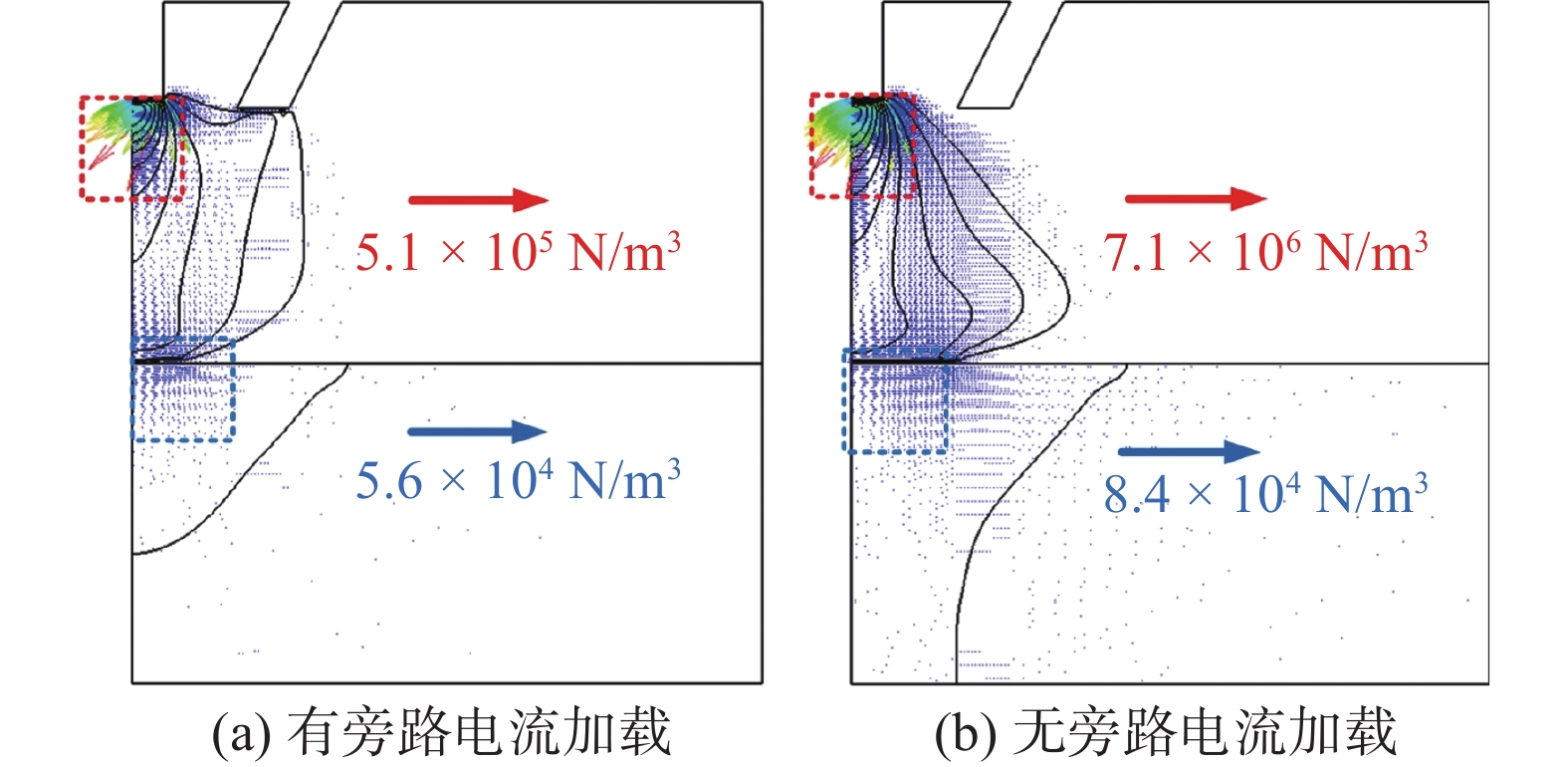
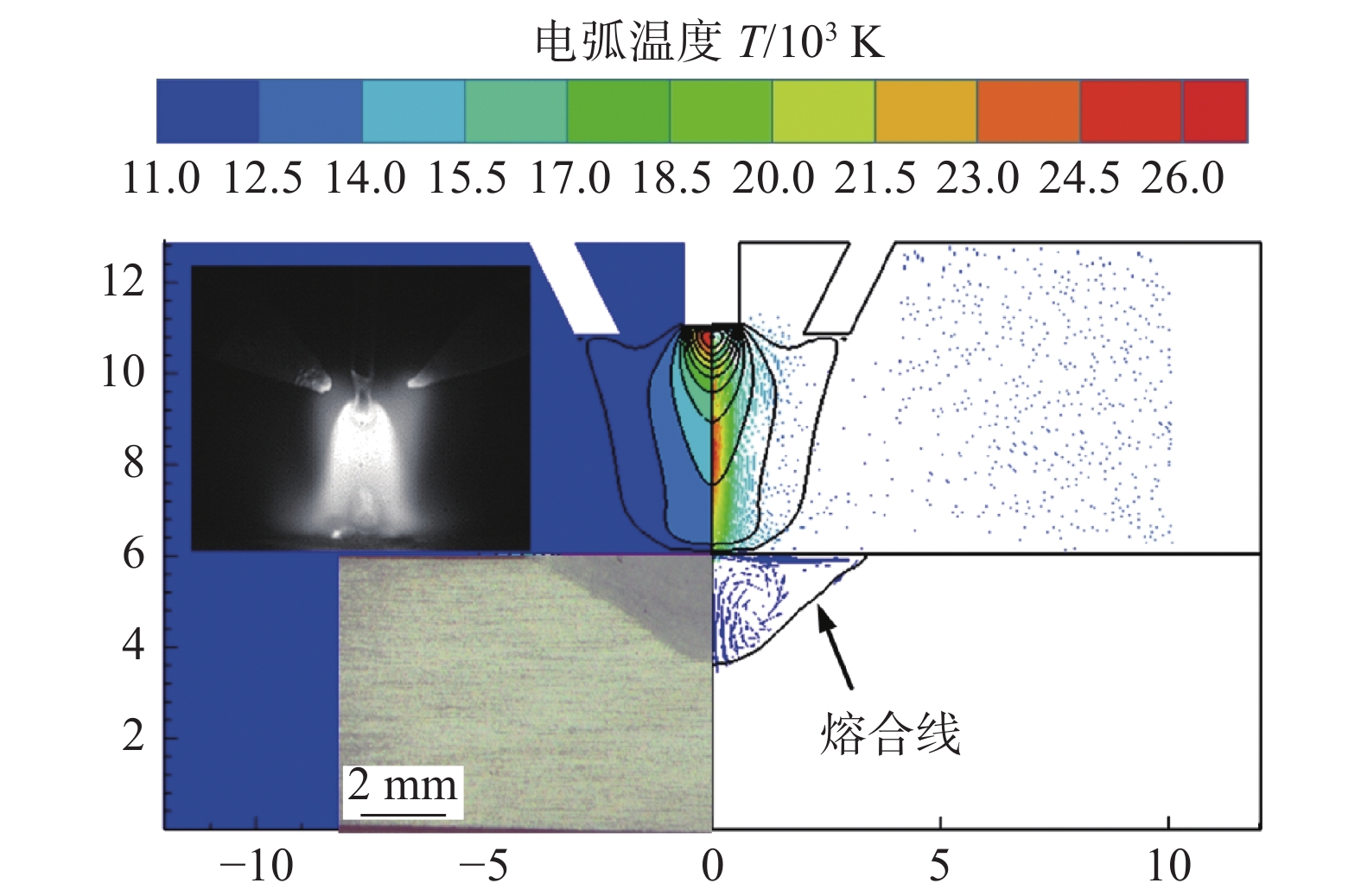
摘要: 旁路等离子-MIG复合工艺是通过等离子焊枪的导电铜嘴与焊丝之间形成的分流弧、焊丝与母材之间的主路弧同轴耦合进行焊接的新型工艺,不但保持了MIG焊的高效性,还可以通过对旁路电流的调节实现焊接过程能量的精确控制. 为了深入了解该工艺条件下复合电弧与耦合熔池的物理作用机制,通过建立流体动力学瞬态计算模型,并基于合理的试验验证,对旁路电流加载前后气液两相内部及界面处的传热传质行为进行了对比研究. 结果表明,相比未加载旁路电流时,电弧的最高温度下降约1 000 K,同时电弧与耦合熔池交界处的有效热通量整体下降;熔池内部液态金属回流速度明显下降,因此导致熔深和熔宽尺寸均有所减少;复合电弧和耦合熔池的最大电磁力方向没有改变,但数值均有所降低.
-
关键词:
- 旁路分流 /
- 等离子-MIG复合焊 /
- 复合电弧 /
- 耦合熔池 /
- 传热传质
Abstract: The bypass-current plasma-MIG hybrid welding is a new process by coaxial coupling of the shunt arc achieved between the conductive copper nozzle of the plasma torch and the welding wire and the main arc between the wire and the base material. This process not only maintains the high efficiency of MIG welding but also provides more schemes for precise control of the welding process energy through the regulation of the bypass current. In order to understand the physical mechanism of action of the hybrid arc and the molten pool under this process, a hydrodynamic transient model was developed and verified with a reasonable experiment to compare the heat and mass transfer behavior inside the gas and liquid phases, and at the interface between them before and after the bypass-current loading. The results show that the maximum temperature of the arc decreases by about 1 000 K compared to that without the bypass current, and the effective heat flux at the interface of the hybrid arc and the molten pool decreases overall; the liquid metal flow rate inside the molten pool decreases significantly, and thus leading to a decrease in both dimensions of the penetration and the width; the maximum electromagnetic force direction of the hybrid arc and the molten pool remains unchanged, but the values are reduced.-
Keywords:
- bypass-current /
- plasma-MIG hybrid welding /
- hybrid arc /
- molten pool /
- heat and mass transfer
-
0. 序言
钛合金具有优良的耐蚀性、较小的密度、较高的比强度及较好的韧性和焊接性[1-2],不锈钢具有良好的耐蚀性和较高的塑韧性[3-4],而钛合金/不锈钢复合结构由于同时具备两种合金的优点,在航空航天、化工、国防军事装备等领域得到了广泛的应用[5-6].然而,由于两种材料在晶格类型、原子半径、电负性等化学性能以及冶金兼容性方面的显著差异,钛合金/不锈钢异种材料焊接存在诸多挑战,其中最主要的难题是接头易生成脆性极高的Ti-Fe金属间化合物(intermetallic compound,IMC)[7-8],导致接头力学性能显著降低[9]. 因此,钛合金/不锈钢异种材料的优质、高效焊接问题受到研究人员的广泛关注,而过渡层金属的优化是改善焊接接头性能的有效途径之一[10-12].
目前国内外对于钛合金/不锈钢异种材料焊接用的过渡层金属方面进行了大量的研究. 研究表明,以纯Ag作为过渡层,虽然接头界面会有AgTi化合物相生成,但可获得力学性能较好的接头[13-14]. 然而,由于Ag成本的限制,Ag过渡层难以在实际工程中应用,目前主要集中在Cu,Ni等过渡层金属的研究,这是由于接头界面处形成的Cu-Ti相比Ti-Fe相具有更好的塑韧性. Zhang等人[15-16]研究了0.2和0.4 mm厚Cu箔对钛合金/不锈钢激光焊接头的影响,结果表明,添加两种厚度的Cu箔可获得抗拉强度分别为210和320 MPa的钛合金/不锈钢激光焊接头. Li等人[17]研究了添加纯Cu和Cu-Nb过渡层进行TC4钛合金/316L不锈钢激光焊接,结果表明,添加Cu-Nb过渡层接头的最高抗拉强度达到215 MPa. Wang等人[18]研究了添加0.5 mm铜片进行TA15钛合金/304不锈钢电子束焊接,获得了抗拉强度约为234 MPa的接头. 由此可见,虽然目前已有的添加Cu过渡层金属可提高钛合金/不锈钢焊接接头强度,但接头强度仍然较低,难以满足实际应用的更高强度要求.
激光焊具有能量密度高、焊接热输入低、焊接速度快、接头热影响区小、焊接应力和变形小以及光束能量及作用位置精确可控等优势[19],且不需要真空,生产中柔性高,极易实现自动化生产. 同时,激光焊接低的热输入有利于抑制接头界面IMC的形成,减小IMC层厚度,从而提高接头的力学性能[20]. 为此,采用力学性能优异的NAB取代纯Cu作为过渡层金属进行TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢对接接头的激光焊接工艺探索,分析添加NAB过渡层对TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢焊接接头微观组织和力学性能的影响,为钛/钢异种材料焊接接头力学性能的提升提供理论基础和新的研究思路.
1. 试验方法
选用的母材分别为3 mm厚的TC4钛合金板与3 mm厚的15-5PH不锈钢板,过渡层金属为NAB块体材料,厚度为2 mm. 采用X射线荧光光谱法测得3种材料的化学成分如表1所示.
表 1 材料的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of materials材料 Mn Ni Al V Cr Cu Fe Ti TC4钛合金 — — 5.5 ~ 6.8 3.5 ~ 4.5 — — ≤0.30 88.4 ~ 90.7 NAB青铜 0.5 ~ 4.0 3.0 ~ 6.0 7.0 ~ 11.0 — — 77.5 ~ 82.0 2.0 ~ 6.0 — 15-5PH不锈钢 ≤1.0 4.7 ~ 5.7 — — 14 ~ 15 1.7 ~ 2.5 75.5 ~ 78.5 0.15 ~ 0.30 采用IPG公司生产的YLS-6000系光纤激光器进行双道激光焊接,焊接过程示意图如图1所示,第1道对TC4/NAB进行激光焊接,再以相同工艺参数立即对第2道NAB/15-5PH进行激光焊接,光斑均向NAB侧偏移. 为获得全熔透焊缝,优化的激光焊接工艺参数如表2所示.
表 2 优化的激光焊接工艺参数Table 2. Optimized laser welding process parameters激光功率
P/W焊接速度
v/(mm·min−1)离焦量
Δf/mm偏移量
d(mm)氩气流量
Q/(L·min−1)3500 2500 3 0.4 20 焊接完成后,采用线切割对接头进行切割取样,镶样经过研磨、抛光和腐蚀后制备金相试样.钛合金和不锈钢采用的腐蚀剂分别为Keller试剂和王水. 采用LEXT OLS4100型激光共聚焦显微镜和扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)观察接头界面IMC组织形貌及分布;采用能谱仪(energy dispersive spectrometer,EDS)进行IMC成分分析;采用HVS-1000型显微硬度仪测试钛/钢接头显微硬度;采用液压万能材料试验机进行接头拉伸试验,试样依据GB/T 2651—2008《焊接接头拉伸试验方法》标准制样,拉伸性能结果取3个试样测试的平均值.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 钛合金/不锈钢异种材料接头的焊缝成形
添加NAB过渡层的TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢异种材料激光焊接获得了良好冶金结合的全熔透接头,其横截面形貌如图2所示. 接头由钛合金侧热影响区(heat affected zone,HAZ)、钛侧界面及近钛合金侧过渡层区A、未熔化过渡层区B、近钢侧过渡层区C、钢侧界面及钢侧HAZ组成. 钛合金侧和不锈钢侧HAZ的宽度分别为0.21 mm和0.54 mm,钛合金侧HAZ宽度小于不锈钢侧. 过渡层焊缝中部产生一个尺寸较大的气孔,直径约为185.3 μm,未见裂纹等其它焊接缺陷.
2.2 钛合金/不锈钢接头力学性能
2.2.1 接头的硬度分布
图3为TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢异种材料激光焊接头显微硬度分布曲线. 母材TC4钛合金和15-5PH不锈钢的平均硬度分别为347.6和405.7 HV. TC4钛合金及15-5PH不锈钢侧HAZ的硬度分别为390.5和 366.3 HV,中间过渡层焊缝铜合金区域硬度最低为211.9 HV. 由图3可见,接头TC4钛合金侧界面硬度最高,这是由于钛合金侧界面生成了脆硬的IMC. 然而,相对于TiFe2相的高硬度大于(1 000 HV),添加NAB过渡层钛合金侧界面IMC层硬度降低了约400 HV. 因此,添加NAB过渡层金属降低了钛合金侧界面区域的硬度,改善了钛合金侧界面IMC层的塑性.
2.2.2 接头的拉伸性能
TC4钛合金、15-5PH不锈钢、NAB过渡层及TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢接头的拉伸测试结果如表3所示. TC4钛合金、15-5PH不锈钢、NAB过渡层金属的抗拉强度分别为1012,980,638 MPa,而添加NAB过渡层的钛合金/不锈钢激光焊接头的抗拉强度为290 MPa. 与已有的添加Cu过渡层钛合金/不锈钢焊接研究结果相比[15-18],添加NAB过渡层激光焊接头获得了较高的抗拉强度. 图4为TC4/NAB/15-5PH激光焊接头拉伸断口形貌. 接头拉伸试样均断裂在钛合金侧界面的IMC层,断裂位置如图4a所示. 由图4b可见,钛合金侧拉伸断口的表面光滑平坦,塑性变形很小.图4c为高倍SEM断口形貌,呈现河流花纹图样,为典型的脆性解理断裂,而这种脆性断裂与钛合金侧界面处形成的IMC层组织的形貌及物相组成密切相关.
表 3 激光焊接接头的拉伸性能Table 3. Tensile properties of laser welded joints材料 屈服强度ReL/MPa 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 断后伸长率
A(%)TC4钛合金 865 1012 ≥10.0 15-5PH不锈钢 785 980 ≥8.0 NAB青铜 268 638 15.0 TC4/15-5PH接头试样 — 290 2.0 2.3 钛合金/不锈钢接头不同区域的微观组织
图5为TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢接头焊缝组织形貌. 靠近钛合金侧界面的NAB过渡层熔化结晶形成的焊缝(图5a)呈现了细小的等轴晶,弥散分布着球形的IMC颗粒,对该IMC颗粒进行点扫描分析,该IMC颗粒原子组成为27.52%Ti,26.50%Fe,22.06%Ni,23.92%Cu,因此,推测此球形颗粒可能为NiTi或TiFe相. 过渡层中部区域组织(图5b)有粗大的等轴晶组成,晶界上分布着细小的IMC颗粒,证实过渡层NAB金属存在未熔的区域,未熔区域的存在对钛合金与不锈钢母材可以起到屏障作用,有利于抑制Fe,Ti在接头界面中的相互扩散[21],从而抑制Fe-Ti IMC的生成. 图5c为靠近不锈钢侧过渡层NAB金属熔化凝固形成的焊缝区,显示了网状分布的等轴树枝晶组织,与钛合金侧焊缝组织明显不同.
图6为TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢异种接头不锈钢侧界面的组织形貌. 从图6可见,在不锈钢侧界面处无明显IMC生成,这是因为Cu和Fe能够相互溶解形成连续的固溶体界面. 在界面附近NAB过渡层金属中形成了较多的直径为0.5 ~ 1.0 μm的球形气孔,这些微气孔的存在可能会对接头拉伸断裂行为有一定的影响.
图7和图8为激光焊接TC4钛合金/15-5PH不锈钢异种材料钛合金侧界面的组织形貌. 由图7可见,TC4钛合金侧界面处形成了复杂的IMC层,依据IMC组织的晶粒形态分为Ⅰ,Ⅱ,Ⅲ 3个区域,其相应的高倍SEM形貌如图8所示.
采用EDS能谱对IMC进了点扫描分析,测得各合金元素的含量如表4所示. 图8显示的IMC组织厚度约为67.50 μm,靠近TC4钛合金侧的Ⅰ区IMC组织密集分布,其中标记为1 ~ 3相富集Cu,Ti元素,由原子含量计算推测形成的IMC为CuTi2和CuTi相. 临近I区的Ⅱ区IMC组织中黑色相4和灰色相5,6的晶粒明显粗大,富集Ni,Ti元素,根据原子含量计算4相可能为CuTi,NiTi2,经Gibbs free energy公式计算[22],G(NiTi2) = −49 120 + 17.21T,G(CuTi) = −17 534 + 3.37T;T = 1 023 K时,G(NiTi2)(−31.5 J/mol) < G(CuTi)(−14.1 J/mol),因此4相为NiTi2;5相为NiTi相;6相可能为FeTi2和NiTi2,经计算G(FeTi2) = −15 219 − 2.29T,T = 1 023 K时,G(FeTi2) (−17.6 J/mol) > G(NiTi2),因此6相为NiTi2. 由此可知,Ⅱ区IMC组织为NiTi和NiTi2相. 靠近不锈钢侧Ⅲ区IMC中黑色相7的晶粒尺寸显著细化,由原子含量计算7和9相可能为NiTi2,FeTi2相,G(FeTi2) > G(NiTi2),因此7和9相主要为NiTi2相,8相为Cu基固溶体,因此该层主要为少量的NiTi2相弥散在铜基体中形成. 因此,Ⅲ区IMC组织主要由CuTi2,CuTi,NiTi和NiTi2组成. 可见,添加NAB中间层接头钛合金侧界面形成了大量脆性相对较低的Cu-Ti,Ni-Ti相,Ti-Fe 相数量减少. 因此,添加NAB中间层有效地抑制了Fe和Ti在钛合金侧界面的相互扩散,界面处形成了大量塑性相对较好的Cu-Ti,Ni-Ti相,有利于改善接头的抗拉强度.
表 4 TC4侧界面IMC组织的EDS分析(原子分数,%)Table 4. EDS analysis of IMC structure of TC4 side interface区域 Ti V Cr Fe Ni Cu 可能的物相 1 57.47 1.29 1.01 1.19 1.55 37.50 CuTi2 2 40.71 1.07 0.17 2.47 3.48 52.10 CuTi 3 25.18 0.98 0.06 1.63 1.69 70.45 CuTi 4 34.15 0 0.12 12.26 14.54 38.93 CuTi,NiTi2 5 16.30 0.11 0.10 3.63 12.56 67.30 NiTi 6 4.32 0 0 2.34 2.32 91.02 FeTi2,NiTi2 7 33.69 0.25 0.24 20.56 20.50 24.76 NiTi2,FeTi2 8 6.10 0.06 0.05 3.47 3.66 86.65 Cu 基固溶体 9 33.01 0 0.14 16.35 15.68 34.83 NiTi2,FeTi2 3. 结论
(1) 添加NAB过渡层钛合金/不锈钢异种材料激光焊接可获得成形优良的全熔透钛/钢异种接头. 接头拉伸断裂于钛合金侧界面IMC层,接头的抗拉强度可达290 MPa,断后伸长率为2.0%.
(2) 接头钛合金侧界面IMC层硬度最高为547.8 HV,相对脆性高Ti-Fe相的硬度降低了400 HV以上.
(3) 接头钛合金侧界面形成的IMC层的宽度约为67.5 μm,主要由CuTi2,CuTi,NiTi,NiTi2相及少量的FeTi2相组成,脆性相对较低的Cu-Ti,Ni-Ti相数量增加,接头不锈钢侧界面未形成IMC.
-
图 8 模拟与试验结果对比[15]
Figure 8. Comparison between simulation and experiment results
表 1 5083铝合金热物理性能
Table 1 5083 aluminum alloy property parameters
环境温度Tamb/K 固相线温度Ts/K 液相线温度Tl/K 热传导率(固态)
ks/(W·m−1·K−1)热传导率(液态)
k1/(W·m−1·K−1)比热容(固态)
cs/(J·kg−1·K−1)比热容(液态)
c1/(J·kg−1·K−1)粘度μ/(kg·m−1·K−1) 密度
ρ/(103 kg·m3)300 847 933 235 90 1 050 1 200 0.004 2 2.66 辐射率
ε磁导率
μ0/(10−6 H·m−1)相变潜热
L/(105 J·kg−1)线膨胀系数
α/10−5K−1电导率
σe/ (107Ω−1·m−1)传热系数
k/(W·m−2·K−1)功函数
ϕw/eV表面张力温度梯度系数γ/(10−4 N·m−1·K−1) 0.15 1.26 3.87 2.3 1.7 20 3.0 -1.55 表 2 计算过程工艺参数
Table 2 Process parameters
序号 主路电流
I1/A旁路电流
I2/A离子气体流量
Q1/(L·min−1)保护气体流量
Q2/(L·min−1)1 140 15 1 15 2 140 0 1 15 -
[1] Zhang Zhihao, Wu Dongting, Zou Yong. Effect of bypass coupling on droplet transfer in twin-wire indirect arc welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018(262): 123 − 130.
[2] Li Yan, Wang Ling, Wu Chuansong. A novel unified model of keyhole plasma arc welding[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019(133): 885 − 894.
[3] Li Kehan, Zhang Yuming. Interval model control of consumable double-electrode gas metal arc welding process[J]. IEEE Tautom Scieng, 2010(7): 826 − 839.
[4] Bai Yan, Gao Hongming, Qiu Lin. Droplet transition for plasma-MIG welding on aluminium alloys[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2010(20): 2234 − 2239.
[5] Yang Tao, Xiong Jun, Chen Hui. Effect of process parameters on tensile strength in plasma-MIG hybrid welding for 2219 aluminum alloy[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016(84): 2413 − 2421.
[6] Yang Tao, Chen Long, Zhuang Yuan, et al. Arcs interaction mechanism in plasma-MIG hybrid welding of 2219 aluminium alloy[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020(56): 635 − 642.
[7] Miao Yugang, Wang Ziran, Liu Ji, et al. Bypass-current plasma arc welding of aluminum alloy: thermal behavior, residual stress, and distortion[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2022(119): 5365 − 5376.
[8] Zhang Y M, Jiang M, Lu W. Double electrodes improve GMAW heat input control[J]. Welding Journal, 2004(83): 39 − 41.
[9] Huang Jiankang, Liu Shen, Yu Shurong, et al. Cladding Inconel 625 on cast iron via bypass coupling micro-plasma arc welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020(56): 106 − 115.
[10] Hu Gangxu, Yang Xingya, Yu Xingbin, et al. Investigation on automated loading of dynamic 3D heat source model for welding simulation[J]. China Welding, 2022, 31(3): 48 − 52.
[11] 雷正, 朱宗涛, 李远星, 等. 空心钨极TIG焊电弧特性数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(9): 9 − 14. Lei Zheng, Zhu Zongtao, Li Yuanxing, et al. Numerical simulation of TIG arc characteristics of hollow tungsten electrode[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(9): 9 − 14.
[12] Wu Dongsheng, Tashiro Shinichi, Hua Xueming, et al. Analysis of the energy propagation in the keyhole plasma arc welding using a novel fully coupled plasma arc-keyhole-weld pool model[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019(141): 604 − 614.
[13] Wu Dongsheng, Hua Xueming, Li Fang, et al. Understanding of spatter formation in fiber laser welding of 5083 aluminum alloy[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017(113): 730 − 740.
[14] Ding Xueping, Li Huan, Wei Huiliang et al. Numerical analysis of arc plasma behavior in double-wire GMAW[J]. Vacuum, 2016(124): 46 − 54.
[15] 石玗, 陈作雁, 薛诚, 等. 双旁路耦合电弧铝合金MIG焊熔滴过渡形态研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2010, 46(20): 77 − 79. Shi Yu, Chen Zuoyan, Xue Cheng, et al. Research on metal transfer in dual bypass MIG welding of aluminum[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2010, 46(20): 77 − 79.
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 夏忠虎,张友昭,任延杰,李相伟,张书彦. 一种新型增材制造FeCoNi中熵合金的时效硬化行为. 焊接. 2024(02): 36-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 田宪华,杨晓东,刘亚,王磊. 激光熔覆涂层材料的研究现状. 热加工工艺. 2024(06): 1-5+9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张欣,蒋淑英,杨昊炎,张恒玮,胡伟伟. CoCrMnNiMo_x高熵合金涂层的组织和耐磨耐蚀性研究. 材料保护. 2023(06): 106-114+122 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 卢煜,李春燕,田霖,翟建树,寇生中. 高熵合金的性能研究进展. 稀有金属. 2022(10): 1352-1364 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 鲁铭洋,张欣,蒋淑英,冯涛,王彦芳. 激光熔覆CoCrFeMnNiMo_x高熵合金的组织和耐蚀性研究. 精密成形工程. 2022(12): 50-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 冯伟,邹力维,韩宇,陈波,徐锴. 堆焊工艺对镍基276带极堆焊晶间腐蚀的影响规律. 压力容器. 2021(03): 25-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 李晓鹏,周龙,贺涛江,程锌谋,王庆梅,张英哲. 氩弧焊接方法制备FeCoNiCrAl高熵合金焊接接头的组织和力学性能研究. 贵州农机化. 2021(04): 27-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 黄晋培,章奇,李忠文,于治水. T10钢表面FeMoCoNiCrTi_x高熵合金熔覆层组织及性能. 有色金属科学与工程. 2020(03): 39-43+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 郝文俊,孙荣禄,牛伟,谭金花,李小龙. 合金元素影响高熵合金涂层组织及力学性能综述. 材料导报. 2020(S2): 1330-1333 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)



 下载:
下载: