Properties of induction brazing diamond/Ni-based alloy composite coating
-
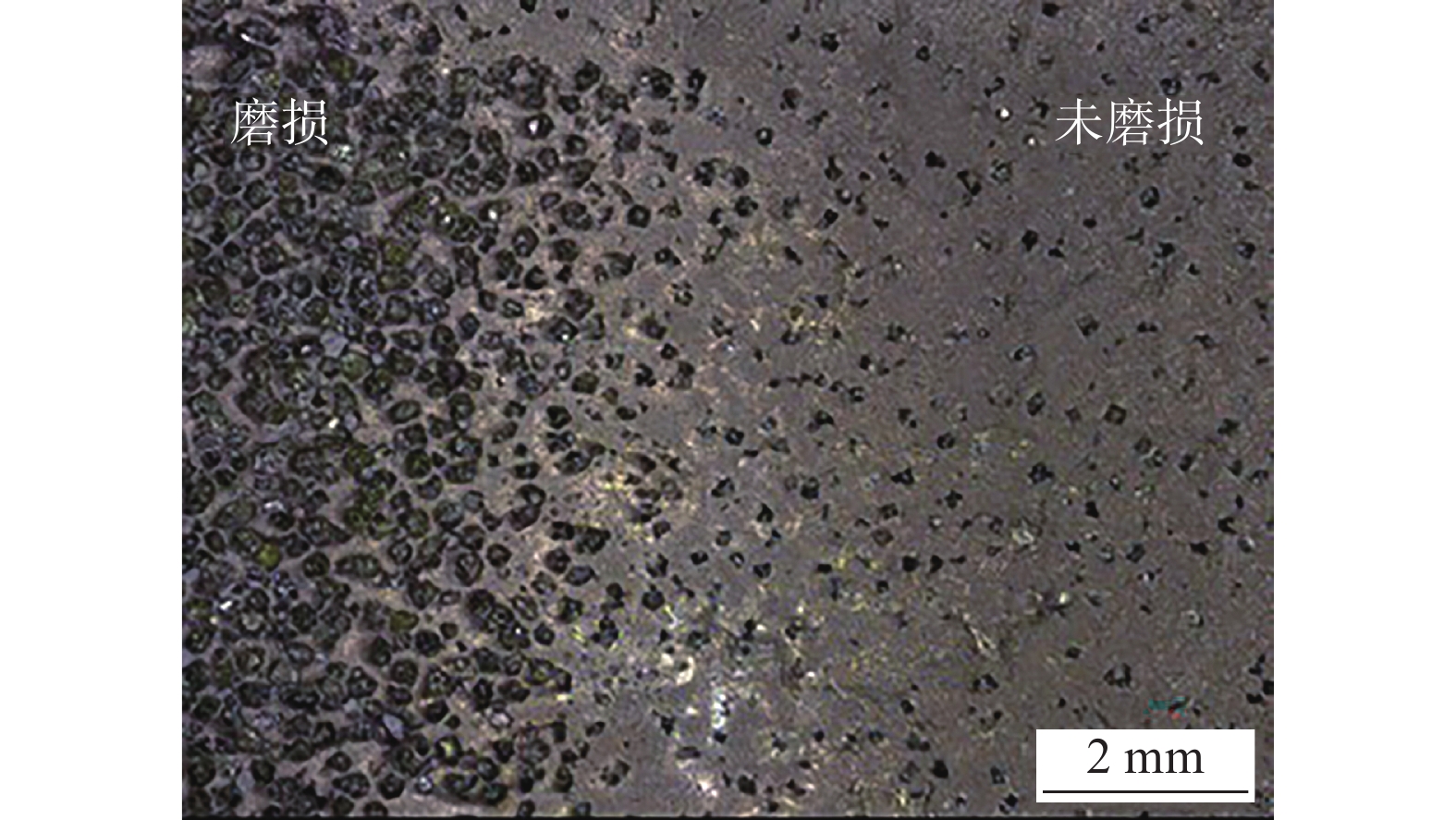
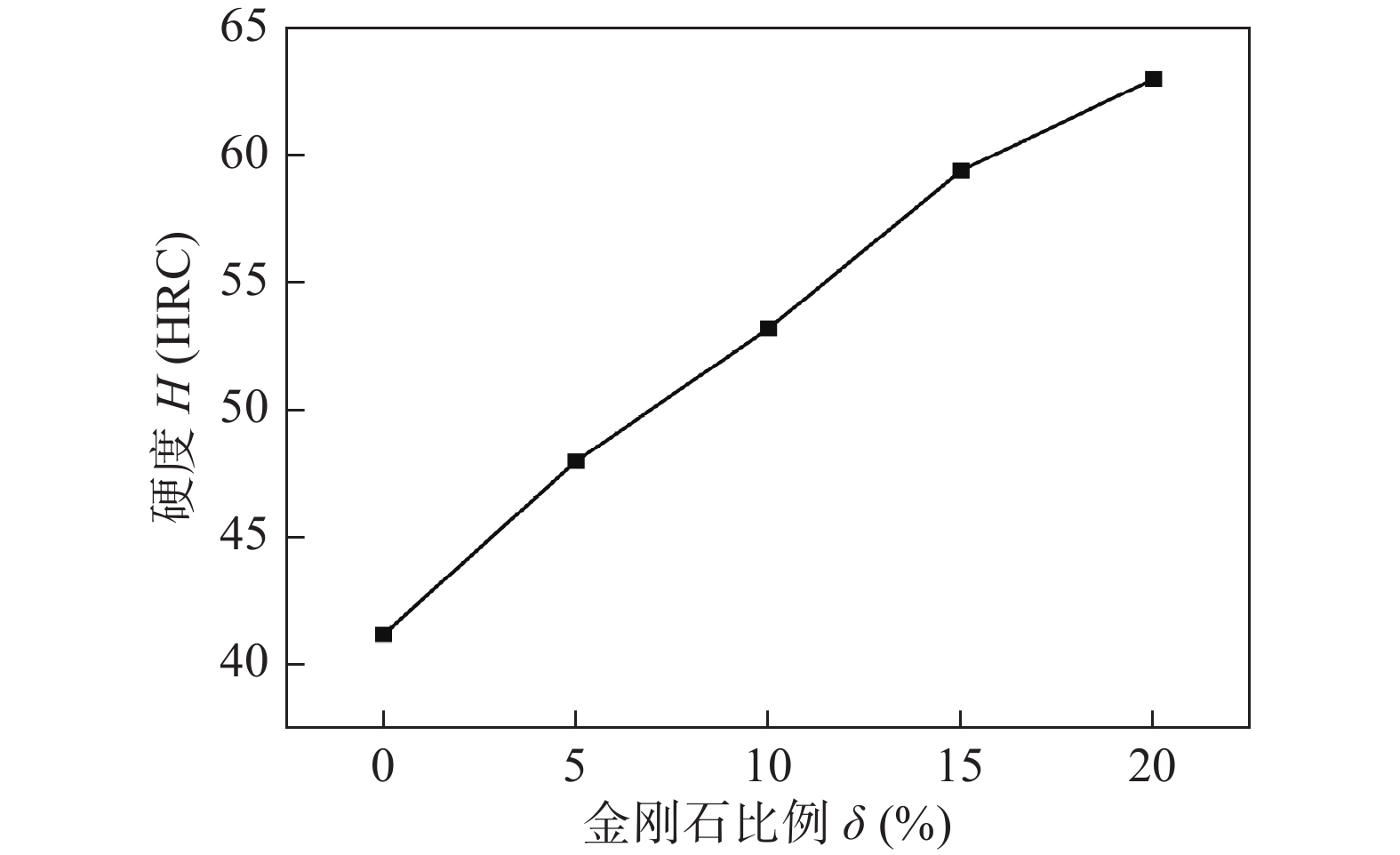
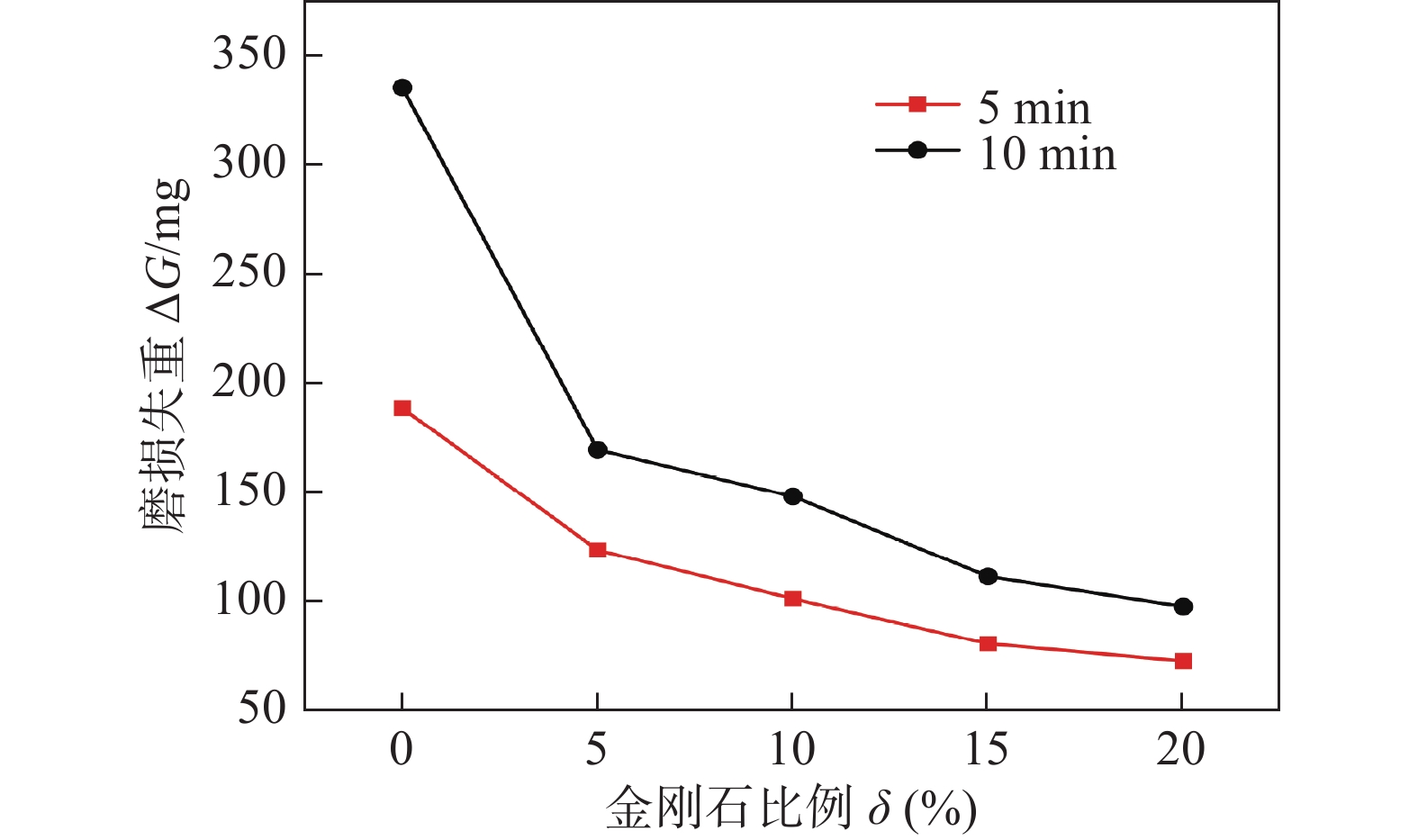
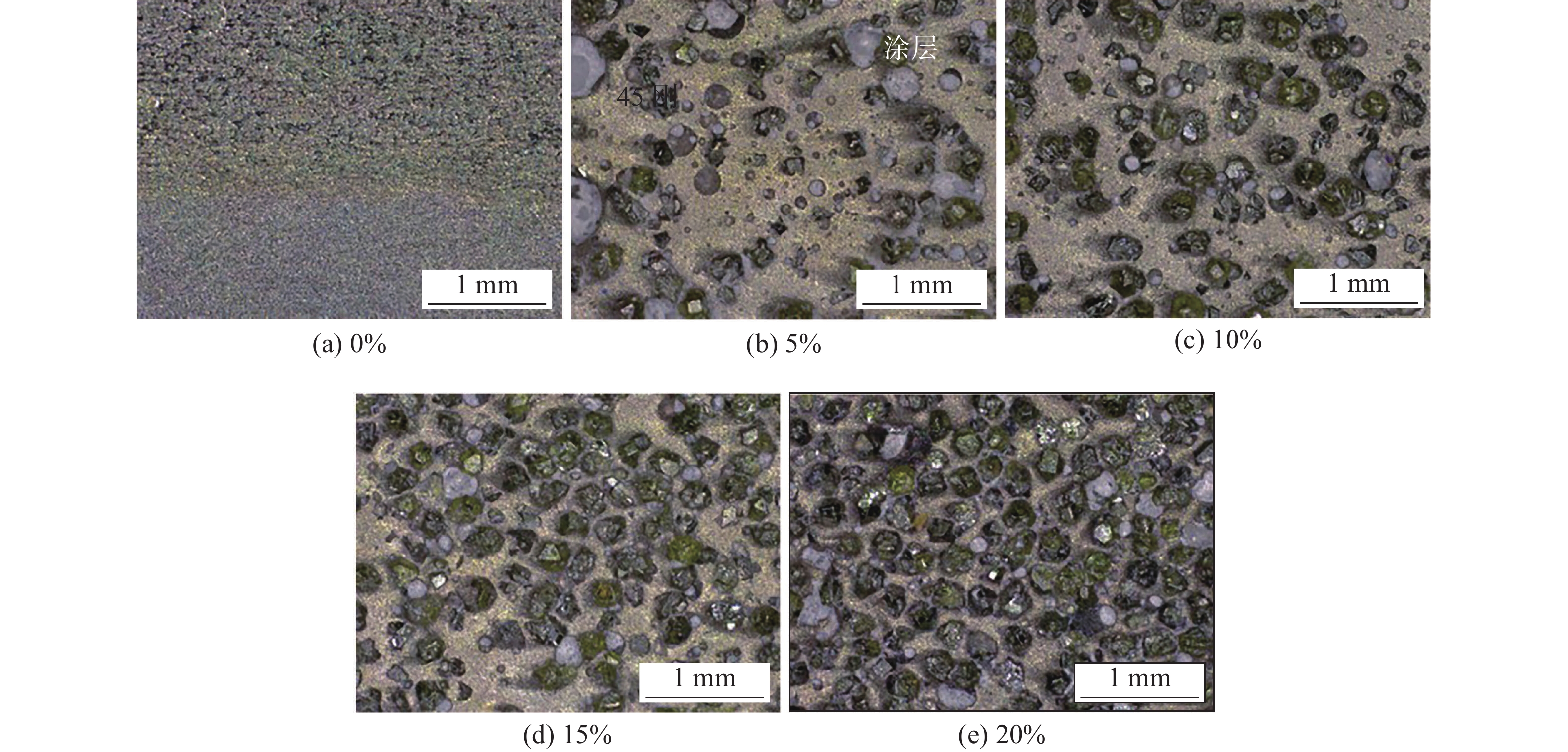
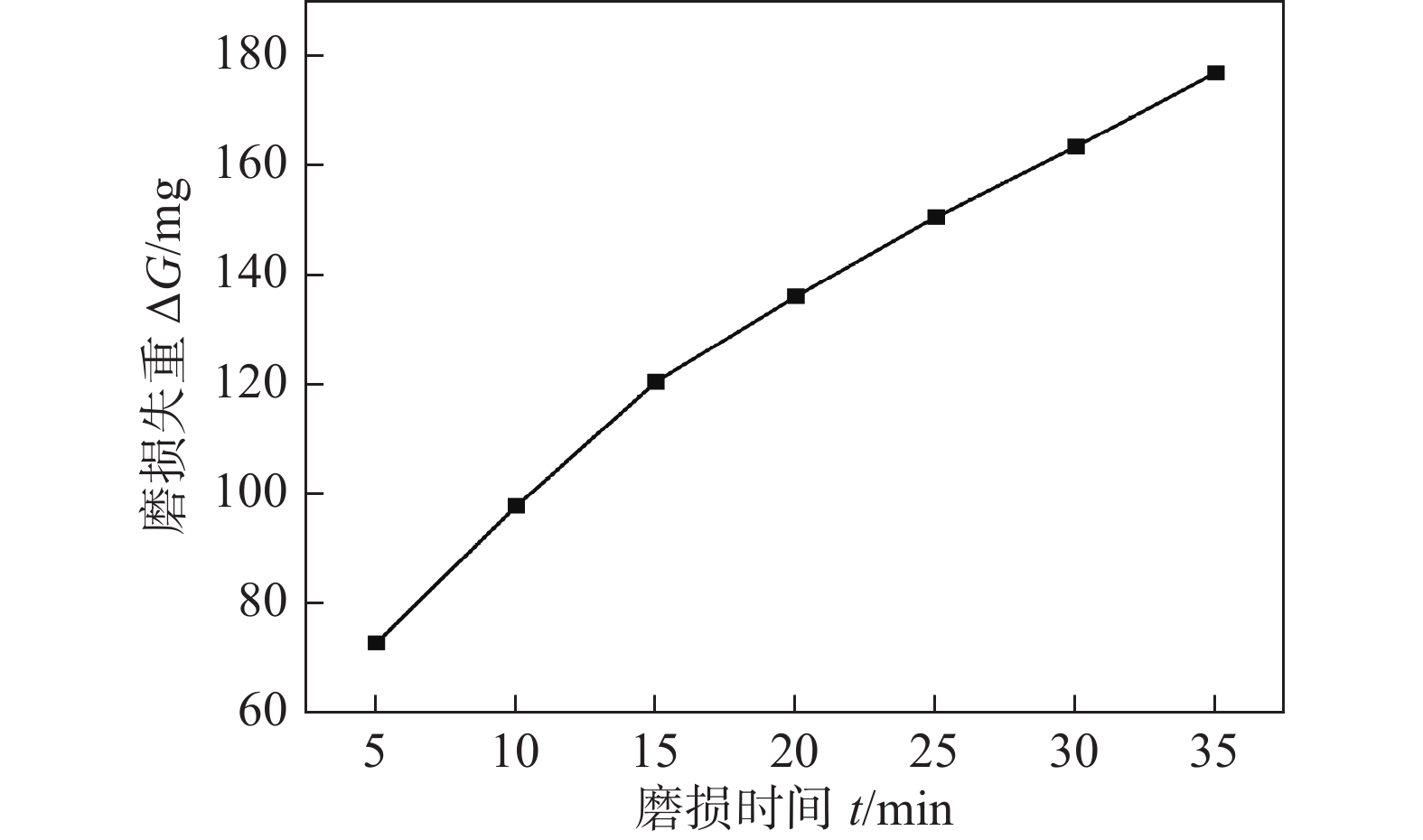
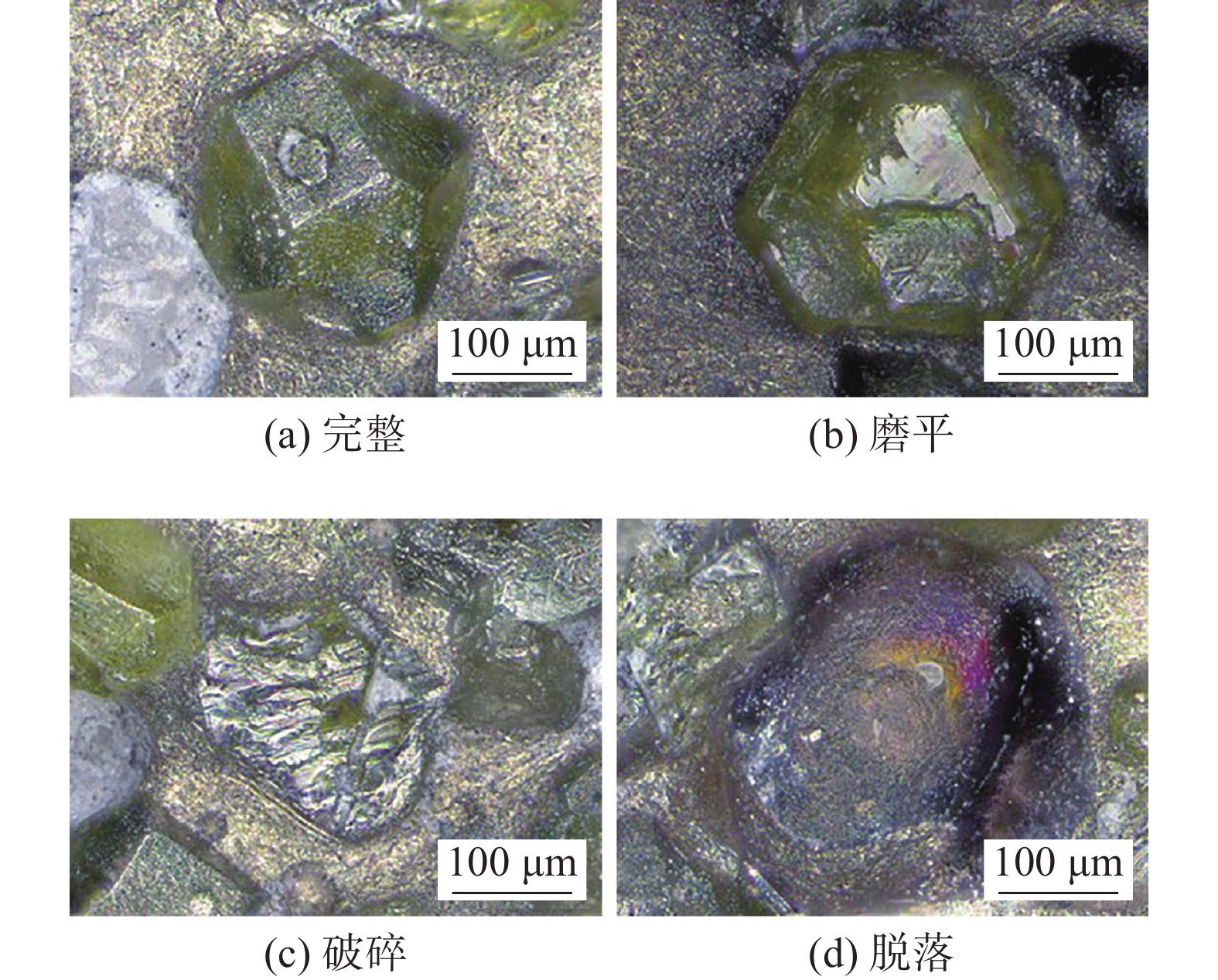
摘要: 以45钢为基体,采用感应钎涂工艺在其表面制备金刚石/镍基合金复合涂层,通过洛氏硬度计、磨粒磨损试验机对涂层进行硬度和耐磨性测试,采用超景深显微镜、扫描电子显微镜对涂层、钎料和金刚石形貌进行观察,采用EDS对金刚石表面微区进行成分分析,初步研究了复合涂层的微观形貌、磨损规律及机制. 结果表明,金刚石颗粒在镍基合金复合涂层中弥散分布,与钎料合金实现了良好的冶金结合. 随着金刚石含量增加,可显著提高复合涂层的硬度及耐磨性. 当金刚石质量分数为20%时,涂层的宏观硬度达到63 HRC,较纯钎料涂层提高1.5倍;在相同的磨损试验条件下,纯钎料涂层的磨损失重为0.335 4 g,金刚石含量为20%的复合涂层磨损失重为0.097 9 g,仅为纯钎料涂层的29.2%.Abstract: Diamond /Ni-based alloy composite coating was made on the surface of 45 steel by induction brazing process. The hardness and wear resistance of the coating were tested by Rockwell hardness tester and abrasive wear tester, and the morphology of the coating, brazing filler metal and diamond were observed by ultra-depth of field microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, the micro-region compositions on the diamond surface were analyzed by energy dispersive spectroscopy. The micro-morphology, wear laws and mechanisms of the coating were preliminarily studied. The results showed that the diamond is dispersed in the Ni-based alloy composite coating and achieved a good metallurgical bond with the brazing alloy. The increase in the content of diamond particles can significantly improve the hardness and wear resistance of the coating. When the mass fraction is 20%, the macrohardness reached 63 HRC, which was 1.5 times higher than that of the pure brazing coating; under the same wear test conditions, the wear loss of the pure brazing filler metal coating reached 0.335 4 g while the 20% diamond/Ni-based alloy composite coating was 0.097 9 g, which was only 29.2% of the pure brazing filler metal coating.
-
Keywords:
- induction brazing /
- diamond /
- Ni-based alloy /
- wear resistance
-
-
表 1 复合粉末的成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Composition of composite powder
编号 镍基钎料 金刚石 1 100 0 2 95 5 3 90 10 4 85 15 5 80 20 表 2 镍基钎料化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of Ni-based brazing
Cr B Si Fe C Ni 7 3.1 4.5 3.0 0.02 余量 -
[1] 曹忠溪, 周玉梅, 张凤林, 等. 钎焊金刚石耐磨涂层制备及其磨损性能[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2019, 39(3): 93 − 101. Cao Zhongxi, Zhou Yumei, Zhang Fenglin, et al. Preparation and wear resistance of brazed diamond wear resistant coatings[J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering, 2019, 39(3): 93 − 101.
[2] Cui Bin, Tao Shanren, Xue Xingya, et al. A brief review of brazing diamond in cutting tools[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(2): 56 − 64.
[3] Oskolkova T N, Glezer A M. Wear-resistant coatings on WC–Co hard alloys synthesized by concentrated energy flows[J]. Inorganic Materials: Applied Research, 2019, 10(1): 146 − 154.
[4] Kang A S, Cheema G S, Singla S. Wear behavior of hardfacings on rotary tiller blades[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2014, 97: 1442 − 1451. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2014.12.426
[5] 赵建国, 李建昌, 王安, 等. 喷焊余温淬火改善深松铲尖铁基涂层耐磨性[J]. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(3): 65 − 71. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.03.009 Zhao Jianguo, Li Jianchang, Wang An, et al. Improvement of wear resistance of iron base coating on deep loosen spade tip by spray-welding residual temperature quenching[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(3): 65 − 71. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.03.009
[6] Karoonboonyanan S, Salokhe V M, Niranatlumpong P. Wear resistance of thermally sprayed rotary tiller blades[J]. Wear, 2007, 263(1): 604 − 608.
[7] 宋月鹏, 王伟, 高东升, 等. 基于表面工程技术制备农机刃具的研究现状[J]. 中国农机化学报, 2018, 39(1): 27 − 31. Song Yuepeng, Wang Wei, Gao Dongsheng, et al. Research status of agricultural machinery cutting tools based on surface engineering technology[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization, 2018, 39(1): 27 − 31.
[8] 赫青山, 崔仲鸣, 傅玉灿, 等. 型面约束下的真空钎焊金刚石工艺及其等高性分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(2): 39 − 42. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20191106006 He Qingshan, Cui Zhongming, Fu Yucan, et al. brazing diamond process and contour analysis under profile constraint[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(2): 39 − 42. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20191106006
[9] 秦建, 龙伟民, 路全彬, 等. 金刚石/NiCrBSi钎涂接头组织与耐磨性能分析[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(S2): 1457 − 1461. Qin Jian, Long Weimin, Lu Quanbin, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance analysis of diamond /NiCrBSi brazing joints[J]. Materials Review, 2020, 34(S2): 1457 − 1461.
[10] Huang Guoqin, Wang Yingda, Zhang Meiqin, et al. Brazing diamond grits onto AA7075 aluminium alloy substrate with Ag–Cu–Ti filler alloy by laser heating[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(6): 67 − 78.
[11] Qin Jian, Huang Junlan, Long Weimin, et al. Evolution behavior of phase and performance in Ni-based coating layer based on high temperature thermal field[J]. China Welding, 2020, 29(4): 25 − 32.
[12] Qi Wenchun, Lu Jinbin, Li Yang, et al. Vacuum brazing diamond grits with Cu-based or Ni-based filler metal[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 26(8): 4112 − 4120. doi: 10.1007/s11665-017-2804-6
[13] Prithviraj Mukhopadhyay, D Raghava Simhan, Amitava Ghosh. Challenges in brazing large synthetic diamond grit by Ni-based filler alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 250: 390 − 400. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.08.004
[14] Long Weimin, Liu Dashuang, Wu Aiping, et al. Influence of laser scanning speed on the formation property of laser brazing diamond coating[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2020(110): 108085.
[15] Jiang Chengyu, Liu Geng, Zhang Dinghua, et al. Induction brazing diamond grinding wheel with Ni-Cr filler alloy[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2006, 51: 377 − 380.
[16] 龙伟民, 郝庆乐, 傅玉灿, 等. 金刚石工具钎焊用连接材料研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(23): 23138 − 23144. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20100102 Long Weimin, Hao Qingle, Fu Yucan, et al. Research progress of joints for brazing of diamond tools[J]. Materials Review, 2020, 34(23): 23138 − 23144. doi: 10.11896/cldb.20100102
[17] Burkhard G, Zieglich B, Poletius M, 等. 用有序排列的金刚石或立方氮化硼磨料作切削加工[J]. 超硬材料工程, 2006(3): 50 − 55. Burkhard G, Zieglich B, Poletius M, et al. Cutting with ordered array of diamond or cubic boron nitride abrasives[J]. Superhard Materials Engineering, 2006(3): 50 − 55.
[18] 李灿, 刘小萍, 郑强, 等. 等离子喷涂含金刚石微粉的Cr2O3涂层干摩擦磨损性能研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2016, 36(8): 873 − 879. Li Can, Liu Xiaoping, Zheng Qiang, et al. Study on dry friction and wear properties of Cr2O3 coating with diamond powder by plasma spraying[J]. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2016, 36(8): 873 − 879.
[19] 王志军. 激光钎焊金刚石颗粒界面结合特征及磨损性能研究[D]. 长沙: 长沙理工大学, 2020. Wang Zhijun. Research on the interface bonding characteristics and wear properties of laser brazed diamond particles[D]. Changsha: Changsha University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[20] Chen Yan, Fu Yucan, Su Honghua, et al. The effects of solder alloys on the morphologies and mechanical properties of brazed diamond grits[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2014, 42: 23 − 29. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2013.10.003
[21] 邓钺. 金刚石磨损特征评价及其对材料加工影响研究[D]. 泉州: 华侨大学, 2020. Deng Yue. Evaluation of diamond wear characteristics and its influence on material processing[D]. Quanzhou: Huaqiao University, 2020.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 邹阳,魏巍,范悦,王泽震,王强,赵亮. 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊工艺研究进展. 热加工工艺. 2024(03): 7-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈平. 2系铝合金的搅拌摩擦焊接接头微观组织与力学性能研究. 北京印刷学院学报. 2024(03): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王浡婳,张立杰. 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头微观组织和力学性能分析. 精密成形工程. 2023(01): 94-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 许辉,刘宽,徐耀钟,于文凯,刘婷,王笑含,徐雪华. 2A14铝合金FSW焊缝背部线状缺陷返修工艺. 电焊机. 2023(03): 117-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马领航,李波,赵彦广,宋建岭,高世康,李雨,许子彦,周利. 火箭贮箱焊接缺陷修复技术研究现状. 电焊机. 2023(03): 31-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李晓华,齐影,郑瑞娟,武媛,祝弘滨,崔雷. QT400球墨铸铁摩擦塞焊接头的微观组织和力学性能研究. 热加工工艺. 2023(05): 141-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 鲁克锋,殷凤仕,王文宇,滕涛,樊世冲,刘亚凡,王鸿琪,朱建,任智强. 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头缺陷及焊件结构问题控制策略的研究进展. 表面技术. 2023(07): 55-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 丁清伟,汪春能,眭怀明,赵引红,陈冬梅. 铝合金机匣预埋管处渗漏机理分析及解决措施. 铸造技术. 2023(09): 873-876 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李德福,王希靖. 6082铝合金摩擦塞补焊接头焊核区晶体特征. 兰州理工大学学报. 2022(03): 7-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 高彦军,刘西伟,刘旭升,邵震,崔雷. 2060-T8铝锂合金顶锻式摩擦塞补焊接头组织性能研究. 电焊机. 2022(07): 69-75+99 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 赵慧慧,高焓,胡蓝,董吉义,尹玉环,崔雷. 2219铝合金薄板拉拔式摩擦塞焊工艺及力学性能优化. 焊接. 2021(06): 48-55+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 胡永鹅,龙琼,韩兴科,何波,王尧,杨秀芳. 铝合金材料焊接方法研究进展. 贵州农机化. 2020(03): 15-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)




 下载:
下载: