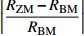Fatigue strength evaluation of Q460 weld joints based on energy dissipation
-
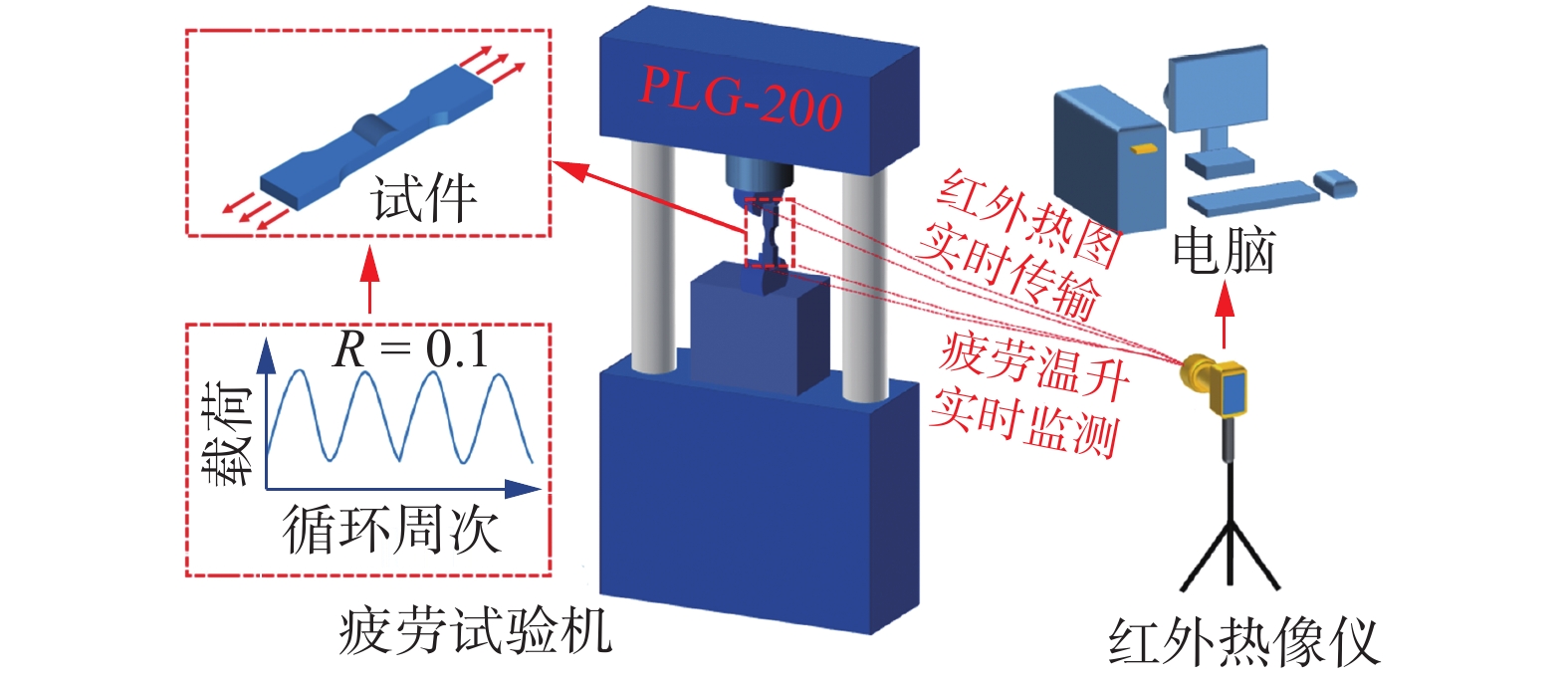
摘要: 传统基于温度数据的疲劳强度预测方法,无法揭示疲劳过程背后的不可逆能量耗散机理. 针对Q460焊接接头疲劳强度,提出一种新的基于不同载荷等级下能量耗散斜率转折的疲劳强度预测方法,即最大斜率法. 采用红外热像仪测得的试件表面实时热像数据,建立高周疲劳过程能量耗散模型,并计算不同载荷等级下的Q460焊接接头能量耗散值. 借助不同载荷等级下的能量耗散随载荷等级增加时其值存在转折点这一理论,将能量耗散作为疲劳强度的预测参量,实现其疲劳强度的快速预测. 为验证模型的准确性,将由最大斜率法得出的疲劳强度估计值分别与传统双线法和升降法的计算值进行对比. 结果表明,由最大斜率法得到的疲劳强度预测值与通过双线法和升降法得到的预测值较为接近,误差分别为0.04%和7.40%,能够为焊接接头疲劳强度预测提供一定的参考.Abstract: Traditional temperature-based fatigue strength prediction method, fail to reveal the irreversible energy dissipation behind the fatigue evolution. For the fatigue strength evaluation of Q460 welded joints, a new fatigue strength prediction method, which is based on the energy dissipation of different load levels that exists the turning point, was proposed, i.e. maximum slope method. The energy dissipation was firstly established based on the obtained real-time thermographic data of the specimen surface, and then the energy dissipation value of Q460 welded joints were calculated. Based on the theory of the energy dissipation turning point exists when the load level increases, the energy dissipation was set as an index for rapid fatigue strength estimation. To verify the accuracy of the developed model, the fatigue strength value estimated by the maximum slope method was compared with the predicted value by the traditional bi-linear and staircase methods. The results show that a good agreement is reached between the predicted fatigue strength by the maximum slope method and the traditional bi-linear and staircase methods, and the errors are 0.04% and 4.76%, respectively, which may provide a certain reference for fatigue strength prediction of welded joints.
-
Keywords:
- maximum slope method /
- welded joints of Q460 /
- energy dissipation /
- fatigue strength
-
-
表 1 Q460对接接头力学性能
Table 1 Mechanical properties of Q460 butt joints
屈服强度
ReL/MPa抗拉强度
Rm/MPa断后伸长率
A(%)冲击吸收能量
Akv/J659.4 737.9 21.5 56(−40 ℃) 表 2 能量耗散和相关参数计算值
Table 2 Calculation of energy dissipation and relevant parameters
应力幅σa/MPa 热传导因数ka/(10−2 mW·mm·K−1) 黏性系数v/(mm2·K−1) 热阻R/(10−2 (mm3·K·m−1 W−1)) 能量耗散d/(mW·mm−3) 148.5 2.46 15.7 2.00 1.52 135.0 2.46 15.6 2.10 1.44 130.5 2.45 15.6 2.12 1.42 126.0 2.45 15.6 2.12 1.42 121.5 2.45 15.6 2.14 1.41 117.0 2.44 15.5 2.21 1.37 112.5 2.44 15.5 2.22 1.36 108.0 2.44 15.5 2.38 1.26 表 3 基于不同方法的疲劳强度值
Table 3 Fatigue strength based on different methods
双线法
疲劳强度
RBM/MPa最大斜率法
疲劳强度
RZM/MPa升降法
疲劳强度
RSM/MPa$\left| {\dfrac{ { {R_{ {\rm{ZM} } } } - {R_{ {\rm{SM} } } } } }{ { {R_{ {\rm{SM} } } } } } } \right|$ $\left| {\dfrac{ { {R_{ {\rm{ZM} } } } - {R_{ {\rm{BM} } } } } }{ { {R_{ {\rm{BM} } } } } } } \right|$ 112.54 112.5 121.5 7.40% 0.04% -
[1] Zhang L, Liu X, Wu S H, et al. Rapid determination of fatigue life based on temperature evolution[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2013, 54(9): 1 − 6.
[2] Jacobsen T K, Srensen B F, Brndsted P. Measurement of uniform and localized heat dissipation induced by cyclic loading[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1998, 38(4): 289 − 294. doi: 10.1007/BF02410391
[3] 杨鑫华, 孙屹博, 邹丽. 网格不敏感结构应力的焊接疲劳数据分布[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(2): 11 − 14. Yang Xinhua, Sun Yibo, Zou Li. Data distribution in welding fatigue analysis based on mesh-insensitive structural stress[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(2): 11 − 14.
[4] Wei G Q, Ochbileg O, Xu D Y, et al. Combine S-N curve and fracture mechanics for fatigue life analysis of welded structures[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(4): 39 − 45.
[5] Fan J L, Guo X L, Wu C W. A new application of the infrared thermography for fatigue evaluation and damage assessment[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2012, 44: 1 − 7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.06.003
[6] 樊俊铃, 郭杏林, 赵延广, 等. 定量热像法预测焊接接头的S-N曲线和残余寿命[J]. 材料工程, 2011(12): 29 − 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2011.12.007 Fan Junling, Guo Xinling, Zhao Yanguang, et al. Predictions of S-N curve and residual life of welded joints by quantitative thermographic method[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2011(12): 29 − 33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2011.12.007
[7] Liu Y L, Sun Y B, Sun Y, et al. Rapid fatigue life prediction for spot-welded joint of SUS301 L-DLT stainless steel and Q235B carbon steel based on energy dissipation[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 10(11): 1 − 11.
[8] 孙杨, 刘亚良, 李赫, 等. 基于红外热像法的SUS301L-Q235B异种材料点焊接头疲劳强度快速评定[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(1): 61 − 66. Sun Yang, Liu Yaliang, Li He, et al. Rapid fatigue limit prediction of SUS301L-Q235B dissimilar materials spot-welded joint based on infrared thermography[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(1): 61 − 66.
[9] Fargione G, Geraci A, Rosa G L, et al. Rapid determination of the fatigue curve by the thermographic method[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2002, 24(1): 11 − 19. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(01)00107-4
[10] Luong M, Van K D. Metal fatigue limit evaluation using infrared thermography[C]//Proceedings of Workshop Advanced Infrared Technology and Applications. Capri (Italy), 1994: 245−253.
[11] Luong M P. Fatigue limit evaluation of metals using an infrared thermographic technique[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 1998, 28(1): 155 − 163.
[12] Yang W P, Guo X L, Guo Q, et al. Rapid evaluation for high-cycle fatigue reliability of metallic materials through quantitative thermography methodology[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2019, 124: 461 − 472.
[13] Fan J L, Guo X L, Wu C W, et al. Research on fatigue behavior evaluation and fatigue fracture mechanisms of cruciform welded joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2011, 528(29): 8417 − 8427.
[14] 刘亚良. 基于疲劳损伤熵的点焊接头累积损伤评估方法研究[D]. 大连: 大连交通大学, 2018. Liu Yaliang. Research on curnulative damage assessment method of spot welded joint based on fatigue damage entropr[D]. Dalian: Dalian Jiaotong University, 2018.
[15] Guo Q, Guo X L, Fan J L, et al. An energy method for rapid evaluation of high-cycle fatigue parameters based on intrinsic dissipation[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2015, 80(11): 136 − 144.
[16] Guo Q, Guo X L. Research on high-cycle fatigue behavior of FV520B stainless steel based on intrinsic dissipation[J]. Materials & Design, 2016, 90: 248 − 255.
[17] 郭强, 郭杏林, 樊俊铃, 等. 基于固有耗散的FV520B钢高周疲劳性能研究[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(4): 18 − 24. Guo Qiang, Guo Xinling, Fan Junling, et al. Research on high-cycle fatigue behavior of FV520B steel based on intrinsic dissipation[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(4): 18 − 24.
[18] Wei W, Li C, Sun Y, et al. Investigation of the self-heating of Q460 butt joints and an S-N curve modeling method based on infrared thermographic data for high-cycle fatigue[J]. Metals, 2021, 11(2): 232.
[19] Yang W P, Guo X L, Guo Q. A high-cycle fatigue energy dissipation accurate estimation method considering natural convection and radiation heat transfer[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2020, 138: 105717. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2020.105717
[20] Huang J, Pastor M L, Garnier C, et al. Rapid evaluation of fatigue limit on thermographic data analysis[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 104: 293 − 301. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.07.029
[21] Rosa G L, Risitano A. Thermographic methodology for rapid determination of the fatigue limit of materials and mechanical components[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2000, 22(1): 65 − 73. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(99)00088-2
[22] Montesano J, Fawaz Z, Bougherara H. Use of infrared thermography to investigate the fatigue behavior of a carbon fiber reinforced polymer composite[J]. Composite Structures, 2013, 97(5): 76 − 83.
[23] Fan J L, Zhao Y G, Guo X L, et al. A unifying energy approach for high-cycle fatigue behavior evaluation[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2018, 120(5): 15 − 25.
[24] 樊俊铃. 基于能量耗散的Q235钢高周疲劳性能评估[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(6): 1 − 9. Fan Junling. High cycle fatigue behavior evaluation of Q235 steel based on energy dissipation[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(6): 1 − 9.
[25] Holman J P. Heat transfer[M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2010.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 王磊磊,吕飞阅,高转妮,虞文军,高川云,占小红. 电弧增材制造2319铝合金交叉桁条结构微观组织与拉伸性能研究. 机械工程学报. 2023(01): 267-277 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 姚宇,张秋菊,陈宵燕,吕青,焦露. 复杂空间曲面焊接机器人自动编程系统. 焊接学报. 2023(05): 122-128+136 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 董曼淑,朱晗,张晓超,白凯,刘龙,高洪明. 矿用链轮链窝电弧增材制造路径规划. 焊接. 2021(01): 51-55+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李天旭,王天琪,李亮玉,杨壮. 典型薄壁结构件增材制造焊接路径规划优化算法. 焊接学报. 2021(02): 69-74+101-102 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 马明亮,刘苏杭,郭纯,王树军,刘茵琪. 电弧增材制造技术的研究进展. 铸造技术. 2021(03): 231-233 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 舒凤远,牛司成,何鹏,隋少华,张小东. 高熵非晶材料及其增材制造技术研究进展. 焊接学报. 2021(09): 1-8+97 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 杨东青,王小伟,黄勇,李晓鹏,王克鸿. 熔化极电弧增材制造18Ni马氏体钢组织和性能. 焊接学报. 2020(08): 6-9+21+97 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 王天琪,张宏宇,耿冬寒,李亮玉,杨壮. 金属桁架结构成形工艺分析. 焊接学报. 2020(11): 25-30+98 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)



 下载:
下载: