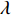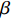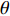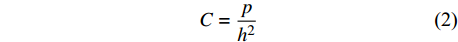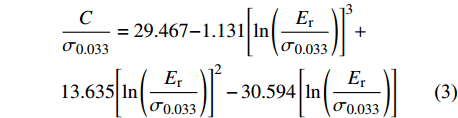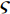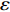Analysis of microstructure and properties and nanoindentation of nickel-based alloy heterogeneous fusion welded 9Ni steel joint
-
摘要: 采用对接焊方法,以NiCrMo-6焊条作为填充材料,对板厚9 mm的9Ni钢母材进行了焊接试验.通过光学显微镜(OM)、扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能谱分析(EDS)等方法对熔焊接头组织进行观察分析.采用纳米压痕技术对熔焊接头中母材(BM)、粗晶热影响区(CGHAZ)、熔合区(FB)和焊缝中心区域(WM)各微区之间的微观组织与力学性能的关系进行表征.辅以接头原位拉伸试验,确定焊接薄弱区.结果表明,焊缝柱状组织中,Fe-Cr,Ni-Cr-Fe等主要析出相在奥氏体基体上弥散分布,热影响区组织以粗板条马氏体及贝氏体为主,板条间逆变奥氏体相已基本消失.纳米压痕试验结果显示,熔焊接头具有突出的抗塑性流变变形能力,粗晶热影响区强度最高,而熔合区强度最低.拉伸断口观察试验进一步显示熔合线区域受撕裂应力影响易发生断裂,为接头薄弱区.Abstract: Adopting the butt welding method and using NiCrMo-6 electrode as the filler material, the welding experiment of the 9 mm thickness 9Ni steel base metal was carried out. Through optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM) and energy spectrum analysis (EDS), etc. Method Observe and analyze the structure of fusion welded joint. Nanoindentation technology is used to improve the microstructure and mechanical properties of the base metal (BM), coarse-grain heat affected zone (CGHAZ), fusion zone (FB) and weld center area (WM) in the fusion welded joint. The relationship is characterized. Supplemented by the joint in-situ tensile test to determine the weakened area. The results show that: in the columnar structure of the weld, Fe-Cr, Ni-Cr-Fe and other main precipitation phases are dispersed on the austenite matrix, and the heat-affected zone is mainly composed of coarse lath martensite and bainite. The inverted austenite phase between the bars has basically disappeared. The nanoindentation test results show that the welded joint has outstanding resistance to plastic rheological deformation. The coarse-grain heat-affected zone has the highest strength, while the fusion zone has the lowest strength. The tensile fracture observation test further shows that the fusion line area is prone to tearing stress. Fracture is the weak area of the joint.
-
Keywords:
- 9% nickel steel /
- welded joint /
- microstructure /
- nanoindentation
-
0. 序言
随着液化天然气(LNG)需求的不断增加,9%Ni钢已被广泛应用于在−196 ℃低温下使用的液化LNG盛装设备的制造. 该材料组织特征为细板条状马氏体基体上分布有5% ~ 10%的逆变奥氏体组织,其特殊的组织赋予该材料在低温下具备良好的高强和高韧性. 目前9%Ni钢焊接广泛采用镍基型合金作为填充金属. 生产过程中受现场装配结构施工条件所限,焊接结构一般不便于进行焊后热处理而服役于焊态. 现有的研究表明,焊缝热循环对9%Ni钢组织具有十分显著的影响,并造成性能的变化. 同时采用镍基合金异质焊接9%Ni钢时,母材金属与异质焊缝金属元素间的相互扩散,对熔合区微观组织及结构也具有显著的影响. 这在很大程度上造成了焊接接头的成分、微观结构及性能的不均匀性.
非均质焊接接头各微区力学性能受试样制取尺寸的限制,目前仅能从宏观上测定出接头的力学性能. 近年来,纳米压痕技术在微区力学性能分析方面显示出越来越重要的特别作用. 例如Hamad等人[1]对发生蠕变变形的镍基高温合金进行了纳米压痕测试,从而研究枝晶尺度上的偏析,并表征出各个相的力学性能. Chen,Maier和Thai-Hoan等人[2-5]使用纳米压痕技术结合光学显微镜分析了结构钢焊接区的显微组织,包括母材、热影响区和焊缝金属,较好的对接头各微区的力学性能进行了表征. 文献[6]分析了低温LNG储罐9%镍钢焊接接头的力学特性. 基于上述,采用微观分析和纳米压痕技术相结合的方法力图揭示出镍基异质合金非匀质熔焊接头各微观区域组织与力学性能间的关系,为工程设计理论依据.
1. 试验方法
试验用9%Ni钢母材成分见表1,采用对接焊,选用ϕ3.2 mm × 350 mm的ENiCrMo-6型焊条作为填充材料,其熔敷金属化学成分如表2所示. 试板尺寸为300 mm × 100 mm × 9 mm,并制备成60° 的单边V形坡口保障焊缝熔透. 试验中焊接参数为焊接电压24 V、焊接电流180 ~ 200 A、焊接热输入22 kJ/cm2、层间温度控制在100 ℃以下. 焊后采用线切割方法截取焊缝横断面分析试样(包括拉伸试样),拉伸试样按照国家标准GBT 228—2002制备. 试样经清洗打磨后用于各种微观分析[7-10].
表 1 9%Ni钢化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of 9% nickel steel材料 C Si Mn Ni S P ASME ≤0.13 0.13 ~ 0.45 ≤0.98 8.4 ~ 9.6 ≤0.035 ≤0.035 9Ni%钢 0.021 0.25 0.72 9.18 0.003 0.002 表 2 焊材熔敷金属化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 2. Chemical composition of self-developed welding consumablesC Mn P S Si Cr Mo Fe W Nb+Ta Ni 0.01 3.02 0.003 0.005 0.37 14.22 5.72 5.80 1.66 0.86 余量 采用光学显微镜和扫描电子显微镜(JSM-6360LV)观察焊接对接接头的微观组织结构,以XRD分析衍射花样并确定相结构,用透射电子显微镜(TEM,JEOLJEM-2100HR)观察熔合区形貌及晶体学特征.
采用纳米压痕仪(Nano Indenter Agilent G200)对熔焊接头焊缝金属、热影响区、熔合区以及母材4个微区在室温下的纳米硬度、弹性模量、应力—应变关系曲线、流变力学行为以及流变应力指数等[11-12]进行表征. 纳米硬度试验参数设置为:最大载荷即Pmax为100 mN、加载和卸载速度均设置为5 mN/s、保载时间20 s. 纳米压痕试样尺寸为25 mm × 15 mm × 9 mm,在熔焊接头4个微观区域分别取点,各区域取点数不少于8个以减少误差. 计算材料的塑性流变应力指数参考Stilwell等人[13]总结的经验公式.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 熔焊接头的显微组织特征
熔焊接头中9Ni钢母材、粗晶热影响区、熔合线区域和焊缝区域的光学显微组织结构如图1所示. 图1a ~ 1c中分别显示母材、粗晶热影响区和熔合区域的显微组织形貌. 观察分析可知,两相区淬火(IHT)状态下的母材显微组织主要是由均匀、细小的低碳回火马氏体和少量的逆变奥氏体组织组成. 其中逆变奥氏体镍含量较高,弥散分布在基体内,不易发生相变,且可以很好地割裂基体,从而一定程度上保证了材料的低温韧性. 靠近熔合区的粗晶热影响区域,受焊接过高热输入的影响,加热温度已超过AC3相变温度. 由图1b可明显观察到,该区域组织由完全奥氏体化冷却后转化为粗大的马氏体条组成,由XRD样品尺寸,通过Scherrer公式计算可知,图1b中冷却后热影响粗晶区的晶粒尺寸甚至达到了50 ~ 60 μm. 板条间几乎未发现有残留的逆变奥氏体相. 由于逆变奥氏体相对低温韧性具有很大的影响. 因此逆变奥氏体相的缺失势必对该区域的塑性和韧性造成一定的影响. 熔合区的显微组织既不同于粗晶热影响区,又有别于焊缝组织. 这显然与焊缝-母材间合金元素的相互扩散有关. 结合图2的SEM形貌观察,可发现在焊缝与母材间存在一条明显的过渡带. 该过度带显然对应于熔合区. 粗晶热影响区中的板条马氏体宽度在1 μm,在靠近熔合区附近板条马氏体已嵌入奥氏体内部.
$$D = k\lambda /\left( {\beta \cos \theta } \right)$$ (1) 式中:k为常数;
$\lambda $ 为XRD入射波长;$\beta $ 为衍射峰半高宽;$\theta $ 为衍射角.由图1d可观察到焊缝区域组织以奥氏体为主,由图3的透射电镜图可以观察到,奥氏体晶界界面两侧晶粒取向差大于10°,故其晶界具有较高角度特征,在晶界处分布着较多呈黑色的沉淀物,该沉淀物由镍基合金焊缝金属在结晶过程中发生了晶界偏析及晶内偏析影响而形成,其中颜色较浅的为奥氏体基体,Fe-Cr,Ni-Cr-Fe等析出相呈黑色点状和块状. 熔焊接头焊缝金属区域在SEM形貌图2d中可以明显观察到,呈现条状亮白色的析出相和大小不一弥散分布在晶界周围的点状、块状的亮白色析出相.图2d中,点A,B,C分别是不同尺寸、不同形状的析出物,由扫描电镜能谱分析数据(表3)可知,3点成分都有着不同程度的偏析现象,其中C点为Laves析出相,其成因在于C点含Nb的量明显偏高,与填充金属中所含Ni,Cr,Mo元素发生共晶反应而形成脆性金属间化合物. 条状富铬析出相A和点状富铬析出相B及靠近晶界的连续析出相呈均匀、弥散形式分布在奥氏体基体上及晶界处,对焊缝金属的强韧性有着一定的影响.
表 3 扫描电镜能谱分析Table 3. Energy spectrum analysis data table位置 质量分数w(%) 原子分数a(%) Ni Cr Mo Fe Nb Ni Cr Mo Fe Nb A 66.39 13.22 4.51 15.87 — 65.89 14.82 2.74 16.56 — B 67.06 12.08 5.54 15.32 — 66.93 13.61 3.38 16.08 — C 54.83 10.64 8.13 12.09 14.31 58.59 12.84 5.32 13.58 9.67 2.2 纳米压痕力学性能及应力—应变本构关系表征
图4给出了在熔焊接头BM,CGHAZ,FB和WM 4个区域用纳米压痕方法测得的纳米硬度和弹性模量的分布趋势,以纳米硬度的统计曲线参照可以发现,各微区间的纳米硬度由小到大顺序为BM,WM,FB,CGHAZ. 结合接头显微组织分析结果可知,在CGHAZ形成的粗大板条马氏体具有较高的硬度. 在图4中,CGHAZ和FB区域各点的纳米硬度数据起伏较大,表现出其微区力学性能分布具有不均匀的特征. 由于镍基熔池金属传热较慢,导致焊缝中心具有相当低的冷却速度,因而其组织形态为对称的等轴晶组织. 在熔合线附近部分区域由于受过冷度影响,组织形态多呈现树枝晶状,且弥散分布的析出相有着钉扎强化作用,所以虽然焊缝中心区的硬度没有粗晶热影响区和熔合线区域高,但和母材相比较,焊缝中心区的强韧性更好. 众所周知,弹性模量的大小主要取决于材料的晶体结构、微观组织和化学成分等,图4b显示统计弹性模量未出现多大的变化,但粗晶热影响区、熔合区以及焊缝由于结构的不均匀性,弹性模量的分散度较母材大得多.
纳米压痕试验测得的BM,CGHAZ,FB,WM载荷—位移曲线(p-h曲线)如图5a所示. 显而易见的,尽管各微区的p-h曲线都有着相似的加载、保载和卸载曲线特征. 在加载初始阶段,压痕的深度随着载荷的增加而快速增加,载荷增加到一定程度后,深度增加趋势逐渐放缓至最大加载载荷50 mN. 形成该现象主要是受加工硬化作用的影响,随着载荷的增加,接头加工硬化作用影响加剧,对纳米压痕试验结果的影响也愈发明显. 如图5a所示,由于各区域的微观结构和组织组成的差异,在相同载荷之下,CGHAZ表现的位移量最小,位移量最大的是BM. 结合显微组织分析可知,CGHAZ区域由于受粗板条马氏体和焊接热循环的影响,加工硬化现象最为严重. 而焊缝中心区域受到析出相的弥散强化作用,所以位移量略小于母材.图5b显示了不同区域在保载阶段产生的位移—时间的关系曲线,该曲线与塑性流动的动态曲线相关. 在0 ~ 5 s塑性流变的第一阶段,塑性流变应变现象剧烈,5 ~ 20 s塑性流变第二阶段,塑性流变应变趋于平稳,在相同保载时间内,CGHAZ,FB,WM产生的塑性流变位移量都小于BM,可知以NiCrMo-6为填充金属的熔焊接头其抵抗塑性流变变形的能力十分突出.
根据Dao 等人[14]方法推算得到加载阶段的曲率C,计算公式为
$$ C = \frac{p}{{{h^2}}} $$ (2) 式中:p和h分别为加载阶段的载荷大小和压头压入深度;C为加载阶段的曲率. 结合Cheng 等人[15]相关文献研究得出接头微区材料的特征应力(σ0.033)为
$$\begin{split} & \frac{C}{{{\sigma _{0.033}}}} = 29.467{\rm{ - }}1.131{\left[ {{\rm{ln}}\left( {\frac{{{E_{\rm{r}}}}}{{{\sigma _{0.033}}}}} \right)} \right]^3} + \\ &13.635{\left[ {{\rm{ln}}\left( {\frac{{{E_{\rm{r}}}}}{{{\sigma _{0.033}}}}} \right)} \right]^2} - 30.594\left[ {{\rm{ln}}\left( {\frac{{{E_{\rm{r}}}}}{{{\sigma _{0.033}}}}} \right)} \right] \end{split}$$ (3) 式中:Er为约化模量;σ0.033是接头特征应力. 进一步推算可得出最后的接头微区的塑性流变指数(n)为
$${\rm{log}}{\sigma _{0.003}} = \log a + n\log \varsigma $$ (4) 式中: a为硬化系数(强度系数);
$\varsigma $ 为真应变,$\varsigma = $ $ {\rm{ln}}\left( {1 + \varepsilon } \right)$ ,$\varepsilon $ 为工程应变.应力−应变本构关系表征如图6所示. 纳米压痕力学性能如表4,根据以上试验结果可以得出,粗晶热影响区和熔合线区域作为熔焊接头两个薄弱区域,受焊接热循环和元素扩散影响,其微观弹性模量、纳米硬度和塑性流变应力指数都会产生改变.
表 4 接头纳米压痕力学性能Table 4. Mechanical properties of joint nanoindentation位置 塑性流动应力指数
n屈服强度
ReL/MPa抗拉强度
Rm/MPa母材 7.19 846.4 1 317.8 粗晶热影响 6.17 1 193.7 1 826.5 熔合区 1.20 1 092.6 1 657.9 焊缝中心 5.32 854.2 1 328.6 2.3 焊接接头断裂行为分析
图7显示出熔焊接头在室温下纵向拉伸断裂的接头表面形貌,如图7a所示,NiCrMo-6焊材为填充金属的熔焊接头整体呈现出典型的韧性断裂特征.图7b中采用扫描电镜能谱分析对焊缝区域的A,B两点的第二相粒子进行成分分析的结果如表5显示,Ni,Cr元素在第二相粒子附近富集,同时还有少量Ti元素. 说明在第二相粒子中夹杂了少量的杂质. 有关第二相粒子研究,文献[16-17]证明,第二相杂质基本不对力学性能构成影响,断口处韧窝的形态、大小和分布规律仍是力学性能变化的主要影响因素. 在图7c,7d接头微观区域中显示,远离FB的区域韧窝形态以等轴韧窝为主. FB附近的区域中韧窝呈抛物线形态,该拉长韧窝受撕裂应力影响,形成图中的撕裂脊. 与9%Ni钢基板相比,靠近熔合线的粗晶区韧窝尺寸大,且分布不均匀. 这些不同的断口微观现象说明,在接头呈现韧性断裂的前提下,由于熔合边界线附近枝晶形态多样化、韧窝大小不同、分布不均匀的影响,使得熔焊接头在微观领域依旧存在脆性断裂现象,且已有微裂纹被检测到. 结合微观组织和纳米压痕试验表征结果分析,断口所形成的韧窝形态和存在的塑性变形能力都与上述的微观力学性能和塑性应力行为特征相吻合.
表 5 拉伸断口选区元素成分含量Table 5. elemental composition content table of tensile fracture selection area编号 Nb Mo Ti Cr Mn Fe Ni Si A — 1.64 1.24 25.73 7.29 8.48 55.82 — B 4.12 8.67 0.15 14.85 3.98 10.89 56.25 1.24 3. 结论
(1)在焊接热循环作用下,从9%Ni钢基板到焊缝中心的微观组织呈现细板条马氏体→粗大板条马氏体→柱状奥氏体→等轴状奥氏体的组织演变. 其中粗晶热影响区中马氏体板条间的逆变奥氏体相受过热影响几乎已消失.
(2)熔合区存在明显的结构过渡带,其成分由母材与焊缝相互扩散而形成. 断口形貌韧窝大小、分布不均匀,易产生应力集中,伴随有较多的撕裂棱形貌,是焊接接头的薄弱区.
(3)采用纳米压痕技术对非均质的焊接接头各微区的力学性能分布,包括纳米硬度、弹性模量、强度以及塑性流变指数等进行了分析. 结果显示,尽管接头各微区塑性流变存在不均匀性,但总体具有较强的抗塑性流变变形能力,其中粗晶热影响区中加工硬化现象明显,强度最高,而熔合区则为强度最低部位.
-
表 1 9%Ni钢化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of 9% nickel steel
材料 C Si Mn Ni S P ASME ≤0.13 0.13 ~ 0.45 ≤0.98 8.4 ~ 9.6 ≤0.035 ≤0.035 9Ni%钢 0.021 0.25 0.72 9.18 0.003 0.002 表 2 焊材熔敷金属化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of self-developed welding consumables
C Mn P S Si Cr Mo Fe W Nb+Ta Ni 0.01 3.02 0.003 0.005 0.37 14.22 5.72 5.80 1.66 0.86 余量 表 3 扫描电镜能谱分析
Table 3 Energy spectrum analysis data table
位置 质量分数w(%) 原子分数a(%) Ni Cr Mo Fe Nb Ni Cr Mo Fe Nb A 66.39 13.22 4.51 15.87 — 65.89 14.82 2.74 16.56 — B 67.06 12.08 5.54 15.32 — 66.93 13.61 3.38 16.08 — C 54.83 10.64 8.13 12.09 14.31 58.59 12.84 5.32 13.58 9.67 表 4 接头纳米压痕力学性能
Table 4 Mechanical properties of joint nanoindentation
位置 塑性流动应力指数
n屈服强度
ReL/MPa抗拉强度
Rm/MPa母材 7.19 846.4 1 317.8 粗晶热影响 6.17 1 193.7 1 826.5 熔合区 1.20 1 092.6 1 657.9 焊缝中心 5.32 854.2 1 328.6 表 5 拉伸断口选区元素成分含量
Table 5 elemental composition content table of tensile fracture selection area
编号 Nb Mo Ti Cr Mn Fe Ni Si A — 1.64 1.24 25.73 7.29 8.48 55.82 — B 4.12 8.67 0.15 14.85 3.98 10.89 56.25 1.24 -
[1] Hamad ur Rehman, Karsten D, Steffen N, et al. Nanoindentation studies of the mechanical properties of the phase in a creep deformed Re containing nickel-based superalloy[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2015, 634: 202 − 208.
[2] Chen Shuangjian, Ye Xiangxi, Yu Kun, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of UNS N10003 alloy welded joints[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2017, 682: 168 − 177.
[3] Maier P, Richter A, Faulkner R G, et al. Application of nanoindentation technique for structural characterisation of weld materials[J]. Materials Characterization, 2002, 48: 329 − 339. doi: 10.1016/S1044-5803(02)00274-7
[4] Thai-Hoan P, Jung J Kim, Seung-Eock Kim. Estimation of microstructural compositions in the weld zone of structural steel using nanoindentation[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2014, 99: 121 − 128. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2014.04.011
[5] Thai-Hoan P, Seung-Eock K. Nanoindentation for investigation of microstructural compositions in SM490 steel weld zone[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2015, 110: 40 − 47. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2015.02.020
[6] Yong-Keun Yoon, Jae-Hoon Kim, Kyu-Taek Shim. Mechanical characteristics of 9% Ni steel welded joint for LNG storage tank at cryogenic[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics: Conference Series, 2012(6): 355 − 360.
[7] 常川川, 张田仓, 李菊, 等. 高氧TC4/TC17钛合金线性摩擦焊接头组织特征及力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(12): 109 − 114, 120. Chang Chuanchuan, Zhang Tiancang, Li Ju, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of high-oxygen TC4/TC17 titanium alloy linear friction welded joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(12): 109 − 114, 120.
[8] 刘鸣宇, 鲁艳红. 焊接热循环对低合金钢组织及性能的影响[J]. 压力容器, 2019, 36(8): 7 − 11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2019.08.002 Liu Mingyu, Lu Yanhong. The effect of welding thermal cycle on the microstructure and properties of low alloy steel[J]. Pressure Vessel, 2019, 36(8): 7 − 11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4837.2019.08.002
[9] Wei Guoqian, Odsuren Ochbileg, Yue Xudong, et al. Combine S-N curve and fracture mechanics for fatigue life analysis of welded structures[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(4): 39 − 45.
[10] 陈虎, 王骞, 张鹏, 等. 9Ni钢大型LNG低温储罐施工及焊接技术[J]. 中国化工装备, 2019, 21(3): 24 − 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0525.2019.03.007 Chen Hu, Wang Qian, Zhang Peng, et al. Construction and welding technology of 9Ni steel large-scale LNG low-temperature storage tank[J]. China National Chemical Industry, 2019, 21(3): 24 − 35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0525.2019.03.007
[11] 王志海, 钱江蓉, 兰欣, 等. 纳米压痕法测量SAC305焊料的力学性能[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2020, 39(6): 72 − 78. Wang Zhihai, Qian Jiangrong, Lan Xin, et al. Mechanical properties of SAC305 solder measured by nanoindentation method[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2020, 39(6): 72 − 78.
[12] Peng G, Ma Y, Hu J, et al. Nanoindentation hardness distribution and strain field and fracture evolution in dissimilar friction stir-welded AA 6061-AA 5A06 aluminum alloy joints[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2018, 6: 1 − 11.
[13] Stilwell N A, Tabor D. Elastic recovery of conical indentations[J]. Proceedings of the Physical Society, 1961, 78(2): 169.
[14] Dao M, Chollacoop N, Van Vliet K, et al. Computational modeling of the forward and reverse problems in instrumented sharp indentation[J]. Acta Materialia, 2001, 49(19): 3899 − 3918. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(01)00295-6
[15] Cheng G, Choi K S, Hu X, et al. Determining individual phase properties in a multi-phase Q & P steel using multi-scale indentation tests[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2016, 652: 384 − 395.
[16] 刘芳芳, 付魁军, 王佳骥, 等. 船板钢第二相粒子在大热输入焊接热循环中的变化[J]. 上海金属, 2018, 40(2): 7 − 10, 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2018.02.002 Liu Fangfang, Fu Kuijun, Wang Jiaji, et al. Changes of second-phase particles of ship plate steel in the heat cycle of large heat input welding[J]. Shanghai Metals, 2018, 40(2): 7 − 10, 18. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7208.2018.02.002
[17] 尹桂丽, 周立岱, 林成. 微合金钢中第二相粒子在焊接HAZ溶解行为的价电子结构分析[J]. 辽宁工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 34(2): 124 − 127. Yin Guili, Zhou Lidai, Lin Cheng. Valence electron structure analysis of the dissolution behavior of the second phase particles in microalloyed steel in welding HAZ[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 34(2): 124 − 127.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 卜华全,赵伟,臧晓飞,刘海定,任明皓,连轶博. 9%Ni钢用国产镍基焊丝的焊接试验研究. 压力容器. 2022(01): 19-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈国耀,徐彤,钟继如,章骁程,关凯书. 小冲杆和压入测试技术获取材料真应力-应变曲线的对比研究. 压力容器. 2022(09): 42-49+55 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐卫军. 锅炉异种金属焊接的缺陷思考. 化纤与纺织技术. 2022(08): 94-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)



 下载:
下载: