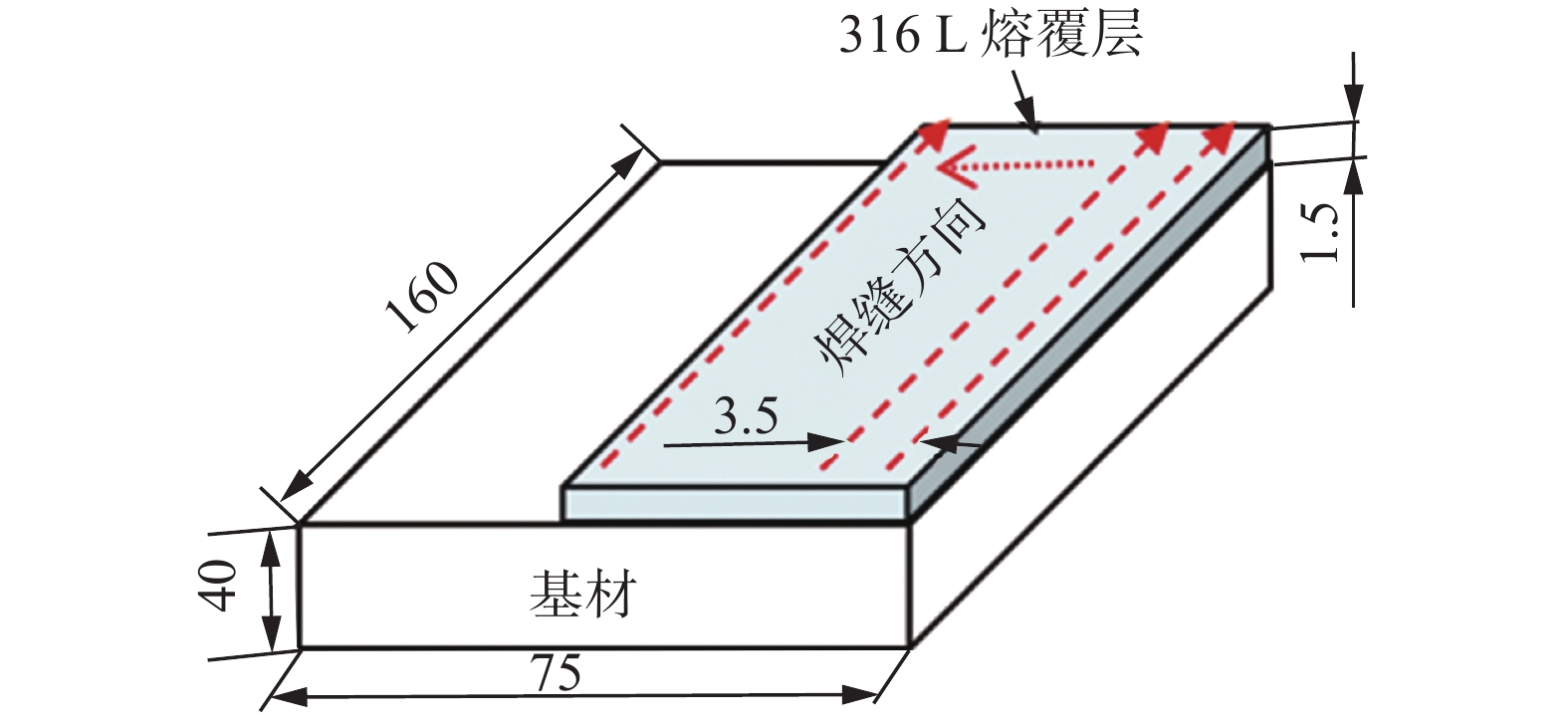
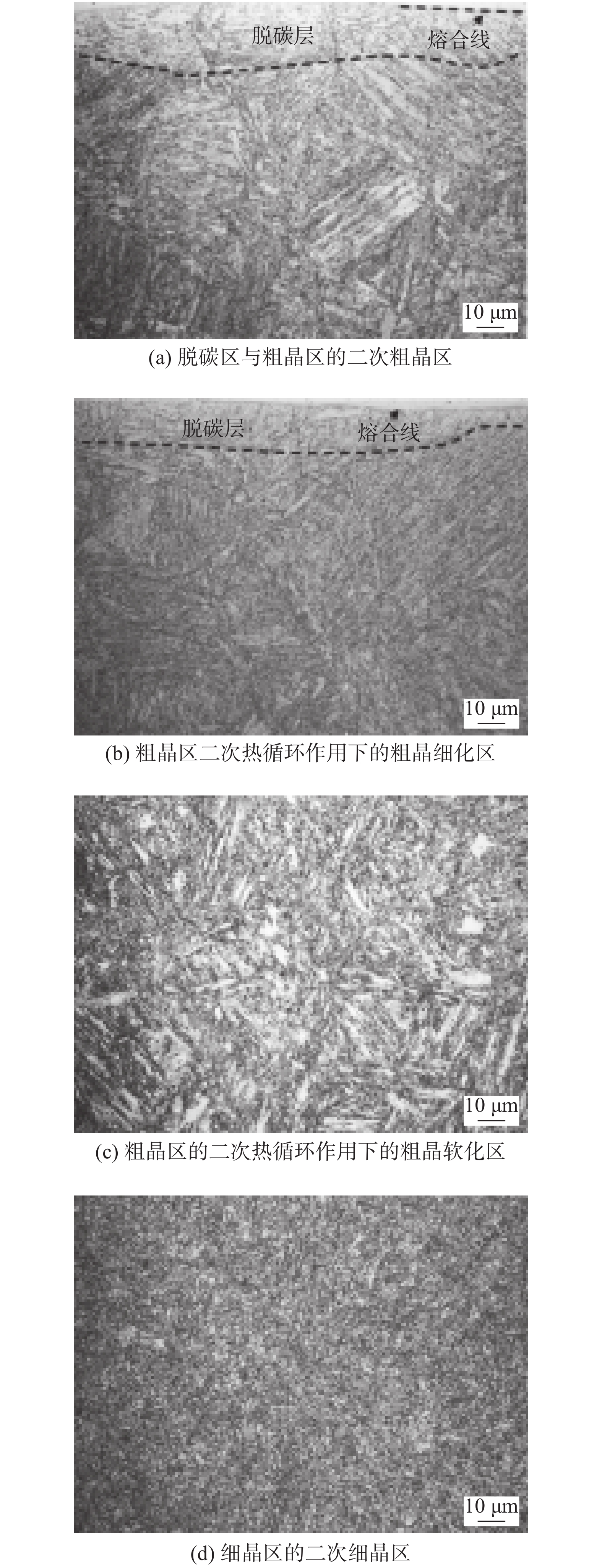
Microstructure and properties of plasma arc additive repairing depositions for the worn rotor journal of power station equipment
-
摘要: 针对电站设备转子轴颈的现场修复要求,采用微束等离子熔覆技术,在20Cr2NiMo材料表面实现了不预热单层多道增材熔覆316L合金,分析了熔覆层与热影响区的组织、硬度、化学成分和力学性能. 结果表明,熔覆层与基材完全冶金结合,熔覆层与热影响区无裂纹等缺陷;316L熔覆层组织为奥氏体 + δ铁素体,一次热影响区可分为脱碳区、粗晶区、细晶区、混晶区,且粗晶区因二次热循环而粗化、细化与软化. 316L熔覆层硬度与基材相差小,一次粗晶区硬度最高,但二次粗晶区硬度在476 HV0.3以下,热影响区宽度约为2.5 mm;热影响区抗剪强度高于基材,但基材塑性更好.Abstract: In view of the in situ repairing requirements of rotor journal of power plant equipment, a non preheating single-layer and multi-passes additive depositing 316L alloy was achieved on 20Cr2NiMo steel by Micro Plasma Arc Depositing process. The microstructure, hardness, chemical composition and mechanical properties of deposition and heat affected zone were analyzed. The results show that the deposition is metallurgical bonded with the substrate, and there is no crack in the cladding layer and heat affected zone; the microstructure of 316L deposition consists of austenite + δ ferrite, and the primary heat affected zone can be divided into decarburization zone, coarse-grained zone, fine-grained zone and mixed crystalline zone, and the primary coarse-grained zone is coarsened, refined and softened due to the secondary heat cycle. The difference of hardness between 316L deposition and substrate is small, while the hardness of primary coarse-grained zone is the highest, but that of secondary coarse-grained zone below 476HV0.3, and the width of heat affected zone is about 2.5 mm; the shear strength of heat affected zone is higher than that of substrate, but the plasticity of substrate is better.
-
Keywords:
- rotor journal /
- micro plasma arc depositing process /
- interface /
- in situ repairing /
- shear strength
-
0. 序言
疲劳是循环载荷在材料表面或近表面产生局部损伤并不断累积的过程[1]. 描述疲劳演化过程中的损伤行为一直是疲劳定量分析和寿命预测的重要问题. 自1924年以来,出现了许多疲劳损伤模型,其中,Miner法则由于操作简单、使用方便,获得了最为广泛的应用. 由于Miner法则本质上是一种线性损伤累积模型,无法考虑加载次序的影响[2],在预测变幅载荷疲劳寿命时,容易高估“高载-低载”载荷谱的疲劳寿命和低估“低载-高载”载荷谱的疲劳寿命. 为了弥补Miner法则的不足,学者们针对不同的损伤参量,提出了多种非线性损伤累积模型,如双线性模型[3]、Carten-Dolan模型[4]、M-H模型[5]、连续介质损伤模型[6]、耗散能量损伤模型[7]等. 这些非线性模型具有繁杂的材料参数,且很难通过常规力学试验精确获取,应用适用性较差.
在非线性损伤模型研究过程中,一些学者注意到疲劳损伤状态与材料S-N曲线密切相关,继而提出了一类基于材料S-N曲线的非线性损伤累积模型. 这一类模型认为材料S-N曲线能够表征疲劳损伤的临界状态,进一步可分为横轴(即N轴)收敛模型[8]、纵轴(即S轴)收敛模型[9]等. Pavlou[10]综合了上述思想,引入了疲劳损伤区概念,基于有限元方法实现了一种集成的非线性疲劳损伤计算框架. 该框架直接引用材料S-N曲线构造疲劳损伤区内的损伤分布及其演化特征,无需其它材料参数,具有操作简单、适用性广等特点.
针对焊接结构,许多行业标准和规范都给出了针对不同焊接接头的规范性S-N曲线族,为Pavlou计算框架的实施提供了极大的便利性. 然而,这些标准和规范中的S-N曲线往往是基于大量试验数据并采用统计学方法处理获得,带有鲜明的概率特性,S-N曲线的存活率(或破坏率)对焊接结构疲劳寿命预测结果有直接影响.
基于上述现状,文中首先基于BS7608标准提供的S-N曲线,研究并实现了基于Pavlou方法的疲劳损伤计算框架. 然后,针对承载型十字焊接接头、非承载型十字焊接接头和对接焊接接头开展了试验验证工作,通过对比分析多种疲劳损伤模型的疲劳寿命预测结果,验证了Pavlou方法的合理性和有效性. 最后,针对S-N曲线的存活率进行了讨论,给出了存活率选取的指导性建议.
1. 理论基础
1.1 Pavlou框架的基本思想
现有的基于S-N曲线的损伤模型可分为2种基本类型,如图1所示,由于采用了双对数坐标系,图中的等损伤曲线均可简化描述为直线形式. 在基于S-N曲线的损伤模型中,S-N曲线被认为是一种损伤极限状态,对应损伤值D = 1. 通过理论分析与推导,Subramanyan[8]认为对应其它损伤状态的等损伤直线可以由D = 1的等损伤直线绕拐点(knee point)旋转获得(图1a). 从物理上看,拐点对应的是无限寿命Ne和材料疲劳极限Se,经过拐点的水平直线对应的损伤值D = 0. 基于此,其它的等损伤直线可以在S-N曲线和经过拐点的水平线之间按一定比值获取. 图1a中各条等损伤直线与S轴的交点,其损伤值由上而下依次减小. 实际上,S轴上各点对应的循环次数均为0,从疲劳角度来看,它们的损伤值应该为0. 为此,Hashin等人[9]提出了纵轴收敛的等损伤直线分布形态(图1b). 同样,该假设在经过拐点的水平线上也存在无法合理解释的问题.
Pavlou[10]综合考虑了上述2种基本类型存在的不足,提出了基于S-N曲线的疲劳损伤区构建方法. 整个疲劳损伤区由材料S-N曲线、S轴和经过拐点的N轴平行线封闭而成,如图2所示,其中,S-N曲线对应损伤D = 1,S轴和经过拐点的N轴平行线对应损伤D = 0,其余的等损伤曲线可以看成是由D = 0的2条等损伤直线向D = 1的等损伤直线渐变获得. 即使在双对数坐标系下,Pavlou方法中的等损伤曲线也不再呈现简单的直线形式,反映出该方法能够更直接地描述疲劳损伤演化的非线性特征. 进一步观察,在靠近拐点的区域,各条等损伤曲线近似为直线分布形式,与图1a所示横轴收敛模型相似;在靠近S-N曲线与S轴交点的区域,各条等损伤曲线也表现出直线分布形式,与图1b所示纵轴收敛模型近似. 可以说,Pavlou方法综合考虑了上述2类基于S-N曲线的疲劳损伤累积模型的优势,同时避免了它们在拐点和S轴交点上的固有缺陷.
![]() 图 2 Pavlou框架的基本思想[10]Figure 2. Basic concept of Pavlou framework
图 2 Pavlou框架的基本思想[10]Figure 2. Basic concept of Pavlou framework1.2 等损伤曲线的构造
Pavlou通过对图2所示损伤区内的损伤分布进行理论推导,发现等损伤曲线可以由简单的有限元热传导分析构造获得. 根据图2所示的损伤区形状建立有限元热传导分析的几何对象(图3a). 考虑到S-N曲线对应的损伤值D = 1,将该边界的初始温度T设为T = lgD = lg1=0,针对损伤值D = 0的2个边界,为方便计算,可以取一个极小的数值如D = 10−8,则对应边界的初始温度可设为T = lgD = lg10−8=−8. 通过简单的热传导问题求解,可以获得问题域的温度场分布. 按照D = 10T,可以获得疲劳损伤区的损伤分布云图(图3b). 进一步,可以从中抽取对应的等损伤曲线(图3c).
1.3 损伤等效原理
采用非线性损伤累积模型进行变幅载荷作用下的疲劳损伤计算和寿命预测时,关键在于不同载荷谱块之间的损伤等效转移,借助图3c所示的等损伤曲线,可以直观方便地实现该种转移. 如图4所示,考虑二级载荷谱块序列的疲劳载荷谱,在经历第1个载荷谱块(S1, n1)期间,损伤点在经过S1的水平直线上移动. 当第1个载荷谱块加载完毕时,损伤值为D1,此时对应的损伤点a位于对应D1的等损伤曲线C1上. 当进入第2个载荷谱块(S2, n2)时,由于应力水平发生了改变,损伤点需要调整到经过S2的水平直线上. 由于此时材料已经具有一定的初始损伤,相应地,可以将损伤点a沿等损伤曲线C1移动到对应S2的水平直线上,即图中b点,则第2个载荷谱块期间的损伤过程可以描述为损伤点b在对应S2的水平直线上的移动,直至该载荷谱块结束,即图中c点. 后续载荷谱块的损伤过程和等效处理可依次进行.
2. 焊接接头损伤分布云图的构建
2.1 焊接接头的S-N曲线族
与金属材料的疲劳特性不同,焊接结构的疲劳性能主要取决于焊接接头构造类型[11-12],为此,不同的焊接结构疲劳设计标准或规范根据焊接接头的焊缝类型,同时考虑载荷、焊接工艺等实际情况,将焊接接头的疲劳强度划分为若干等级,并给出了对应级别的疲劳数据和S-N曲线. 疲劳性能评估时,需要根据被评估焊接接头的几何形状,确定相应的疲劳等级.
BS7608标准提供的S-N曲线族如图5所示,其中包括了B, C, D, E, F, F2, G, G2, W等疲劳等级.根据BS7608,对接焊缝一般采用D类等级,角焊缝一般采用F类等级. 实际应用中还必须根据焊缝承载情况、实际焊缝质量进行细致考虑.
![]() 图 5 焊接接头的S-N曲线族[13]Figure 5. S-N curve family of welded joints
图 5 焊接接头的S-N曲线族[13]Figure 5. S-N curve family of welded joints2.2 S-N曲线的存活率
焊接结构疲劳设计标准和规范中提供的S-N曲线来源于大量的焊接接头疲劳试验数据,不可避免地具有分散性,通过统计学处理之后,这些曲线具有显著的概率意义[14]. 以BS7608标准为例,提供了中值S-N曲线和标准基础设计S-N曲线,前者具有50%存活率,后者具有97.7%存活率(即向下两个标准偏差), 考虑到工程问题的复杂性,实际应用中通常使用后者,从设计角度来看,这种选择偏保守,预测寿命具有较高的可靠性.
从损伤角度来看,具有较高存活率的S-N曲线并不符合疲劳损伤区的构造原理. 图6为带有疲劳试验数据的S-N曲线示意图,可以看到,所有试验数据点近似对等地分布在中值S-N曲线的两侧,而具有较高存活率的基础设计S-N曲线则位于多数试验数据点的左下方. 此外,位于基础设计S-N曲线左下方的试验数据点很少,如果以该S-N曲线为衡量标准,发生疲劳破坏的试验样本数量很少. 换句话说,此时绝大多数试验样本并未发生疲劳破坏,因此,该S-N曲线无法表征具有损伤值D = 1的损伤边界.
基于上述原因,具有较低存活率的S-N曲线更适合于构造基于Pavlou方法的疲劳损伤区. 文中借鉴BS7608标准中的基础设计S-N曲线的存活率数值,采用向上2个标准偏差(即具有2.3%存活率)的S-N曲线定义构造损伤分布云图. 根据BS7608标准,S-N描述方程,即,
$$ \log N = \log {{{C}}_{\text{0}}} - {{d}} \cdot \sigma - {{m}} \cdot \log {{\Delta }}S $$ (1) 式中:C0,m是与材料、应力比、加载方式等有关的参数;σ是标准偏差;d是标准偏差数.常用疲劳等级的S-N曲线的相关参数见表1[13].
表 1 S-N曲线的相关参数Table 1. Parameters of S-N curves疲劳等级 参数m 参数C0(1012) 标准偏差σ 标准偏差数d 存活率p(%) 强度极限Su /MPa 疲劳极限Se /MPa D 3 3.988 0.2095 −2 2.3 736 53 F 3 1.726 0.2183 −2 2.3 556 40 F2 3 1.231 0.2279 −2 2.3 497 35 2.3 损伤分布云图的规则化
焊接结构疲劳设计标准或规范中提供的S-N曲线为一组相互平行的直线,拐点被定义为具有非常大的循环次数,例如BS7608标准对应的拐点横坐标被定义为1×107次,相应的纵坐标对应为该种类型焊接接头的疲劳极限.如果不考虑疲劳极限等实际参数,所有焊接接头的S-N曲线往往具有相似的形状,所有基于焊接接头S-N曲线构造而成的疲劳损伤区也具有相似的形状, 将疲劳损伤区进行规则化处理,则可生成适用性更高的损伤分布云图,并可实现不同类型焊接接头的损伤计算和寿命预测.
疲劳损伤区规则化处理如图7所示,图7a为实际S-N曲线围成的损伤区,图7b为规则化处理之后的损伤区,两者之间的坐标变换,即.
$$ {x_i} = \frac{{\lg {n_i}}}{{\lg {N_i}}} $$ (2) $$ {y_i} = \frac{{\lg {S_i} - \lg {S_{\rm{e}}}}}{{\lg {S_{\rm{u}}} - \lg {S_{\rm{e}}}}} $$ (3) 式中:(xi,yi)为点对(ni,Si)经规则化处理之后得到的坐标值;ni为第i级载荷谱块的加载次数;Si为第i级载荷谱块的应力范围;Ni为对应Si常幅载荷的疲劳寿命;Se为疲劳极限,对应拐点的纵坐标;Su为强度极限,对应S-N曲线与纵轴交点的纵坐标.
规则化之后的横坐标为对数加载次数与对数疲劳寿命的比值,纵坐标为对数载荷的相对比值,两者的取值范围均为[0, 1]. 通过规则化处理,不仅可以简化有限元热传导问题的分析模型,还可以使生成的损伤分布云图脱离与实际焊接接头类型及其对应S-N曲线之间的联系,提高损伤计算方法的适用性. 实际应用中,根据实际载荷谱块的特征参数(即ni和Si)和对应焊接接头S-N曲线的特征参数(即Se和Su),利用式(2)和式(3)获得规则化的损伤点坐标,即可在图3b所示的标准损伤分布云图中实施损伤演化和等效计算.
3. 试验验证
3.1 试验方法
为了验证上述基于Pavlou损伤计算框架的疲劳寿命预测方法,针对承载型十字焊接接头、非承载型十字焊接接头、对接焊接接头等3种形式的焊接接头试件开展了二级变幅载荷谱的拉伸疲劳试验. 试件几何构造如图8所示,其中,试件母材均采用低合金结构钢Q345B,焊前根据相关标准预制坡口以确保焊缝根部全熔透,焊后采用锤击法消除残余应力,以尽可能去除残余应力对疲劳试验的影响. 根据BS7608标准,同时考虑试件实际的焊接质量和焊趾形貌,确定3种试件的疲劳等级依次为F2类、F类和D类.
3.2 试验载荷谱
实施二级载荷谱块序列的试验载荷谱如图9所示,其中考虑“高-低”和“低-高”2种加载次序,且n =1× 104次. 考虑到F2类和F类疲劳性能接近,为承载型十字焊接接头和非承载型十字焊接接头设置了相同的载荷谱参数,对接焊接接头则设置了明显不同的载荷谱参数见表2. 需要说明,载荷谱中的应力均特指试件薄板焊趾部位的名义应力.
3.3 试验结果
在长春SDS100疲劳试验机上开展疲劳试验,每种试件类型各试验6根试件,其中3根实施“高-低”载荷谱,另外3根实施“低-高”载荷谱,共计18根试件. 试验中,加载频率设为10 Hz,将试件完全断裂对应的加载次数定义为试验疲劳寿命, 所有试件的疲劳破坏均发生于薄板焊趾部位,试验寿命见表3. 总体来看,相同类型的试件在相同载荷谱下的试验寿命具有明显的分散性,从试验寿命平均值来看,相同试件类型在“高-低”载荷谱下的试验寿命明显低于“低-高”载荷谱的试验寿命;在相同载荷谱类型下,非承载十字焊接接头较承载型十字焊接接头具有更高的试验寿命. 上述规律与已有文献报道基本一致. 针对对接焊缝接头,由于对应载荷水平不同,无法进行合理比较.
表 2 试验载荷谱参数Table 2. Parameters of loading spectrum试件类型 载荷谱块 最大应力Smax/MPa 最小应力Smin/MPa 应力范围ΔS/MPa 平均应力Sm/MPa 循环比R 承载型十字接头/非承载型十字接头 高 200 0 200 100 0 低 100 0 100 50 0 对接接头 高 280 0 280 140 0 低 140 0 140 70 0 表 3 试验寿命(万次)Table 3. Test lives (104 cycles)承载型十字接头 非承载型十字接头 对接接头 加载次序 试件
编号试验
寿命Nt平均
寿命Na试件
编号试验
寿命Nt平均
寿命Na试件
编号试验
寿命Nt平均寿命Na LCruc01 57.1 58.7 NLCruc01 70.8 83.5 Butt01 70.6 69.6 高-低 LCruc02 51.2 NLCruc02 82.5 Butt02 77.5 LCruc03 67.8 NLCruc03 97.1 Butt03 60.7 LCruc04 89.4 73.9 NLCruc04 102.4 100.6 Butt04 81.1 80.4 低-高 LCruc05 69.8 NLCruc05 88.6 Butt05 71.5 LCruc06 62.5 NLCruc06 110.8 Butt06 88.6 3.4 寿命分析
根据试件的实际接头形式,采用BS7608标准中对应构造类型的S-N曲线估算试件的疲劳寿命,相关参数可在表1中获取. 为了比较不同损伤模型的预测效果,同时考虑了Miner线性损伤模型和M-H非线性损伤模型. 其中,针对同种试件的不同模型采用相同的S-N曲线参数,Miner模型同时采用了50%和2.3%两种存活率,M-H模型与Pavlou方法仅采用了2.3%存活率,计算结果见表4.
表 4 预测寿命与试验寿命(万次)Table 4. Predicted lives and test lives (104 cycles)试件类型 加载次序 预测寿命Np 试验寿命Nt Miner模型 M-H模型 Pavlou方法 由小至大排序 平均值 50% 2.3% 2.3% 2.3% 承载型
十字接头高-低 24.2 71.6 68.2 66.7 51.2, 57.1, 67.8 58.7 低-高 32.9 79.0 78.1 77.4 62.5, 69.8, 89.4 73.9 非承载型
十字接头高-低 32.6 102.7 95.8 87.8 70.8, 82.5, 97.1 83.5 低-高 39.1 111.4 105.7 97.2 88.6, 102.4, 110.8 100.6 对接接头 高-低 26.9 82.6 77.8 66.5 60.7, 70.6, 77.5 69.6 低-高 35.6 91.4 87.7 76.6 71.5, 81.1, 88.6 80.4 从表4可以看出,以试验寿命的平均值为基准,无论是在“高-低”还是“低-高”载荷谱下,具有50%存活率的Miner模型的预测寿命均远远低于试验寿命,而具有2.3%存活率的Miner模型的预测寿命均高于试验寿命. 考虑到疲劳设计标准提供S-N曲线的偏保守性以及试验条件下试件焊接质量的较优性,上述结果具有合理性. 在2.3%存活率下,Miner模型和M-H模型的预测寿命均高于试验寿命,Pavlou方法的预测寿命存在不规律的高估和低估,但总体上看,Pavlou方法的预测寿命数值均在试验寿命平均值附近波动,且差值最小,表明Pavlou方法具有最高的预测精度.
进一步绘制预测寿命与试验寿命的误差散射图,如图10所示. 横轴为试验寿命,纵轴为预测寿命,A区域、B区域和C区域分别对应10%, 25%和50%的相对误差. 在10%的误差散射带内,Miner模型、M-H模型和Pavlou方法的数据点数量分别为5, 8和14个,在25%的误差散射带内,Miner模型、M-H模型和Pavlou方法的数据点数量分别为15, 17和18个,表明非线性损伤累积模型的预测精度明显高于线性损伤累积模型,而Pavlou方法的预测精度又明显高于M-H模型. 此外,多数数据点分布在正误差散射带区域内(即对角线左上侧),表明不同模型的预测寿命有高估疲劳寿命的趋势,且在“高-低”载荷谱下更加明显. 相比之下,Pavlou方法数据点较均匀地分布在对角线两侧,进一步表明Pavlou方法的计算结果更加合理.
3.5 进一步讨论
如前所属,S-N曲线存活率的选取对疲劳损伤区的构建和损伤分布云图的实际形态具有直接影响.为了讨论其作用,针对前述的承载型十字焊接接头、非承载型十字焊接接头和对接焊接接头试件类型,考虑“高-低”和“低-高”2种载荷谱,分别基于具有1.0%, 2.3%, 5.0%, 50.0%, 95.0%, 97.7%, 99.0%等7种存活率的S-N曲线进行疲劳寿命预测,计算结果见表5.
表 5 不同存活率下的疲劳寿命对比(万次)Table 5. Comparison of fatigue lives with different survival probabilities (104 cycles)序号 存活率p(%) 预测寿命Np 承载型十字接头 非承载型十字接头 对接接头 H-L L-H H-L L-H H-L L-H 1 1.0 81.6 90.9 105.2 112.6 80.2 88.3 2 2.3 66.7 77.4 87.8 97.2 66.5 76.6 3 5.0 49.9 64.3 74.3 85.2 57.6 68.1 4 50.0 22.7 32.1 29.5 32.5 23.9 33.6 5 95.0 6.49 15.8 9.43 18.8 8.21 17.8 6 97.7 5.38 14.7 7.89 17.1 6.9 16.6 7 99.0 4.54 13.9 6.77 16.2 5.9 15.7 试验寿命平均值 58.7 73.9 83.5 100.6 69.6 80.4 随着存活率的增加,不同试件类型和载荷谱类型下的预测寿命均逐渐减小. 相比之下,存活率为2.3%的计算结果和试验寿命平均值最为接近. 因此,采用存活率为2.3%的S-N曲线进行疲劳损伤区的构建并进一步开展焊接结构疲劳寿命预测是合理的.
4. 结论
(1)基于Pavlou提出的疲劳损伤区概念,选取BS7608标准提供的具有2.3%存活率的S-N曲线,利用有限元热传导分析技术,构建了焊接结构的损伤分布云图,提出了一种焊接结构疲劳寿命的预测方法.
(2)针对承载型十字焊接接头、非承载型十字焊接接头和对接焊接接头,开展了二级变幅载荷的拉伸疲劳试验,通过试验寿命与多种损伤累积模型预测结果的对比研究,验证了Pavlou方法的合理性和有效性.
(3)对1.0%, 2.3%, 5.0%, 50.0%, 95.0%, 97.7%, 99.0%等7种存活率的疲劳寿命预测结果进行了讨论,发现2.3%存活率具有较满意的预测效果.
-
表 1 试验用转子材料及焊接材料化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of the materials
材料 C Mn Si S P Cr Ni Cu Mo Fe 20Cr2NiMo 0.22 ~ 0.28 0.25 ~ 0.80 0.15 ~ 0.35 ≤ 0.015 ≤ 0.015 1.70 ~ 2.10 1.00 ~ 1.20 ≤ 0.15 0.75 ~ 0.90 余量 316L粉末 ≤ 0.03 1.0 ~ 2.5 0.3 ~ 0.65 ≤ 0.03 ≤ 0.03 18.0 ~ 20.0 11.0 ~ 14.0 ≤ 0.75 2.0 ~ 3.0 余量 表 2 熔覆层与316L粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of the deposition
材料 C Mn Si S P Cr Ni Cu Mo 熔覆层 0.081 1.37 0.87 — — 16.29 12.54 0.046 2.46 316L粉末 ≤ 0.03 1.0 ~ 2.5 0.3 ~ 0.65 ≤ 0.03 ≤ 0.03 18.0 ~ 20.0 11.0 ~ 14.0 ≤ 0.75 2.0 ~ 3.0 -
[1] 叶荣学, 孙伟, 张艾萍, 等. 滑动轴承油膜厚度变化对汽轮机转子稳定性的影响[C]//第九届全国振动理论及应用学术会议, 2017: 1062-1067. Ye Rongxue, Sun Wei, Zhang Aiping, et al. The influence of oil film thickness of sliding bearing on the stability of steam turbine rotor[C]//The 9th National Conference on Vibration Theory and Application, 2017: 1062-1067.
[2] Shchurova A V. Modeling the turbine rotor journal restoration located on cylindrical surface of the supporting bearer[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2017, 206: 1142 − 1147. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.608
[3] 赵景辉. 汽轮机转子轴颈划伤处理[J]. 电力安全技术, 2015(2): 10 − 11. Zhao Jinghui. Treatment of turbine rotor journal scratch[J]. Electric Safety Technology, 2015(2): 10 − 11.
[4] 何新有. 汽轮机转子轴颈损伤原因分析及修复措施[J]. 发电设备, 2009, 23(3): 170 − 172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-086X.2009.03.005 He Xinyou. Cause analysis of turbine rotor’s shaft neck damage and the repair[J]. Power Equipment, 2009, 23(3): 170 − 172. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-086X.2009.03.005
[5] Aloraie A, Al-Mazrouee A, Price J W H, et al. Weld repair practices without post weld heat treatment for ferritic alloys and their consequences on residual stresses: a review[J]. International Journal of Pressure Vessels and Piping, 2010, 87: 127 − 133. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpvp.2010.02.001
[6] 黄岚, 金硪馨. 1 000 MW汽轮机精加工转子轴颈微弧等离子堆焊研究[J]. 东方汽轮机, 2011(1): 21 − 25. Huang Lan, Jin Woxing. Study on micro-arc plasma deposition for finished rotor journal of 1 000 MW steam turbine[J]. Dongfang Turbine, 2011(1): 21 − 25.
[7] 徐俊强, 彭勇, 刘智慧, 等. 等离子弧异质异构增材制造构件的组织与力学性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(11): 119 − 124. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400298 Xu Junqiang, Peng Yong, Liu Zhihui, et al. Study on plasma arc additive manufacturing process of dissimilar steels with various composite structures[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(11): 119 − 124. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400298
[8] 中国机械工程学会焊接分会. 焊接手册[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2007. Welding Society of China Mechanical Engineering Society.Welding Manual[M]. Beijing: China Mechanical Industry Press, 2007.
[9] 钟玉, 曹天兰, 梁刚, 等. 30Cr2Ni4MoV, 20Cr2NiMo和Cr2Ni2MoV材料的焊接性研究[J]. 东方汽轮机, 2012(2): 27 − 32. Zhong Yu, Cao Tianlan, Liang Gang, et al. Study on the weldability of 30Cr2Ni4MoV, 20Cr2NiMo and Cr2Ni2MoV materials[J]. Dongfang Turbine, 2012(2): 27 − 32.
[10] Yan C Y, Jiang X Y, yuan Y, et al. Cold cracking susceptibility of X100 pipeline steel[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(3): 1 − 9.
[11] 郭伟, 牛靖, 张建勋. 试样厚度对微冲剪试验结果的影响[J]. 焊接, 2012(5): 31 − 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2012.05.008 Guo Wei, Niu Jing, Zhang Jianxun. The influence of specimen thickness on the results of micro punching shear test[J]. Welding & Joining, 2012(5): 31 − 34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2012.05.008
[12] Mohammad J E, Reza Alizadeh, Reza M. Applicability of shear punch testing to the evaluation of hot tensile deformation parameters and constitutive analyses[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 996 − 1002. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.02.014
[13] Tomasz K, Konrad G, Wojciech S, et al. Correlation between process parameters, microstructure and properties of 316 L stainless steel processed by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2018, 71: 64 − 73.
[14] Morteza S, Abbas E, Masoomeh E, et al. Interface microstructure across cladding of super duplex stainless steel with austenitic stainless steel buffer layer[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2014, 259: 532 − 542.
[15] Wu Q J, Lu F G, Cui H C, et al. Soft zone formation by carbon migration and its effect onthe high-cycle fatigue in 9%Cr–CrMoV dissimilar welded joint[J]. Materials Letters, 2015, 141: 242 − 244. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.08.158
[16] 王天剑, 黄菊, 张邦强, 等. 铬钼钢与巴氏合金摩擦磨损试验[J]. 大型铸锻件, 2009, 6: 11 − 14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5635.2009.05.004 Wang Tianjian, Huang Ju, Zhang Bangqiang, et al. Friction and wear test of Cr Mo steel and Babbitt alloy[J]. Heavy Castings and Forgings, 2009, 6: 11 − 14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5635.2009.05.004
[17] Guduru R K, Darling K A, Kishore R, et al. Evaluation of mechanical properties using shear–punch testing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2005, 395: 307 − 314. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2004.12.048
[18] Foletti S, Madia M, Cammi A, et al. Characterization of the behavior of a turbine rotor steel by inverse analysis on the small punch test[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011(10): 3628 − 3635.
[19] 潘超锋, 潘慧斌. 汽轮机转子输出端强度计算与校核[J]. 热力透平, 2017, 46(4): 46 − 49. Pan Chaofeng, Pan Huibin. Strength calculation and check of turbine rotor output end[J]. Thermal Turbine, 2017, 46(4): 46 − 49.
[20] Li S, Ren S, Zhang Y, et al. Numerical investigation of formation mechanism of welding residual stress in P92 steel multi-pass joints[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 244: 240 − 252. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.01.033
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 孙立成,毛泓霖,明驰,卫星. 承载型60°斜十字全熔透焊接接头疲劳寿命评估. 焊接学报. 2025(01): 137-144 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 陈振,陈能鹏,冉庆杰,王乔木,魏超成,鞠浩文. 耦合焊接残余应力的横波可控震源振动器平板疲劳寿命预测. 工程设计学报. 2025(01): 102-111 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐连勇,龙志平,赵雷,韩永典,彭晨涛. EH36钢焊接接头焊趾处应力集中对高低周复合疲劳的影响. 焊接学报. 2024(07): 1-9 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: