Microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joint of titanium/steel and titanium/copper/steel composite plate
-
摘要:
采用电弧焊接方法(TIG/MIG)进行钛/钢(TA1/Q345)和钛/铜/钢(TA1/T2/Q345)复合板的对接焊接,借助SEM,EBSD,TEM,显微硬度、纳米压痕和拉伸试验系统研究了对接焊缝中的显微结构和力学性能. 结果表明,钛/钢对接接头中,Cu-V焊缝主要以铜基固溶体和铁基固溶体为主,局部生成的Fe2Ti相被韧性较好的铜基固溶体包围;Cu-V/ERTi-1焊缝界面处存在多种Cu-Ti和Fe-Ti金属间化合物;Cu-V焊缝与TA1/Q345界面处,存在Fe-Ti,CuTi2和β-Ti化合物. 钛/铜/钢对接接头中,Cu/ERTi-1焊缝界面处分布着多种Cu-Ti金属间化合物,分布范围较广. 钛/钢对接焊缝中Fe2Ti脆性相的硬度较高,为20.7 GPa,但由于其尺寸相对较小,因此接头的显微硬度分布与钛/铜/钢对接焊缝类似,高硬度区域均在铜基焊缝与ERTi-1焊缝界面处,达到400 HV0.3,两种对接接头中大量分布的Cu-Ti化合物的硬度处于8 ~ 11 GPa. 钛/钢异质接头的抗拉强度为440 MPa,钛/铜/钢异质接头的抗拉强度为225 MPa,断裂位置均在焊缝区域,并且铜基焊缝与ERTi-1焊缝界面处均是脆性断裂特征. 钛/钢对接焊缝中不可避免会存在Fe-Ti脆性相,虽然采用钛/铜/钢三层复合板的形式可以避免Fe-Ti脆性相的生成,但是接头中分布较广的Cu-Ti化合物仍旧是接头的一个薄弱区域.
Abstract:The titanium/steel and titanium/copper/steel composite plates were butt joined by arc welding method. SEM, EBSD, TEM, microhardness, nanoindentation and tensile tests were applied to investigate the microstructure and mechanical properties. The results showed that in the titanium/steel butt joints Cu-V weld mainly consisted of Cu solid solution and Fe solid solution phases. Localized Fe2Ti intermetallics were surrounded by the soft Cu solid solution. Cu-Ti and Fe-Ti intermetallics were formed at Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface. Cu-V weld near the TA1/Q345 interface consisted of Fe-Ti, CuTi2 and β-Ti phases. A series of Cu-Ti compounds were widely distributed at Cu/ERTi-1 interface in titanium/copper/steel butt joints. Although Fe2Ti brittle intermetallics had high hardness (20.7 GPa), its limited size had less effect on the global microhardness distribution. These two butt joints had similar microhardness distribution, where high hardness values (400 HV0.3) were located at the Cu-base weld/ERTi-1 interface. The Cu-Ti compounds with wide distribution showed the hardness around 8 ~ 11 GPa.The tensile strength of titanium/steel butt joint and titanium/copper/steel butt joint were 440 MPa and 225 MPa, respectively. Both samples were fractured at the weld metal regions and brittle fracture morphology was observed at the Cu-based weld/ERTi-1 interface regions. Fe-Ti brittle intermetallics were inevitable in titanium/steel butt joint. These brittle phases were suppressed in titanium/copper/stee butt joints. However, the widely distributed Cu-Ti compounds region was the weak region of such joints.
-
-
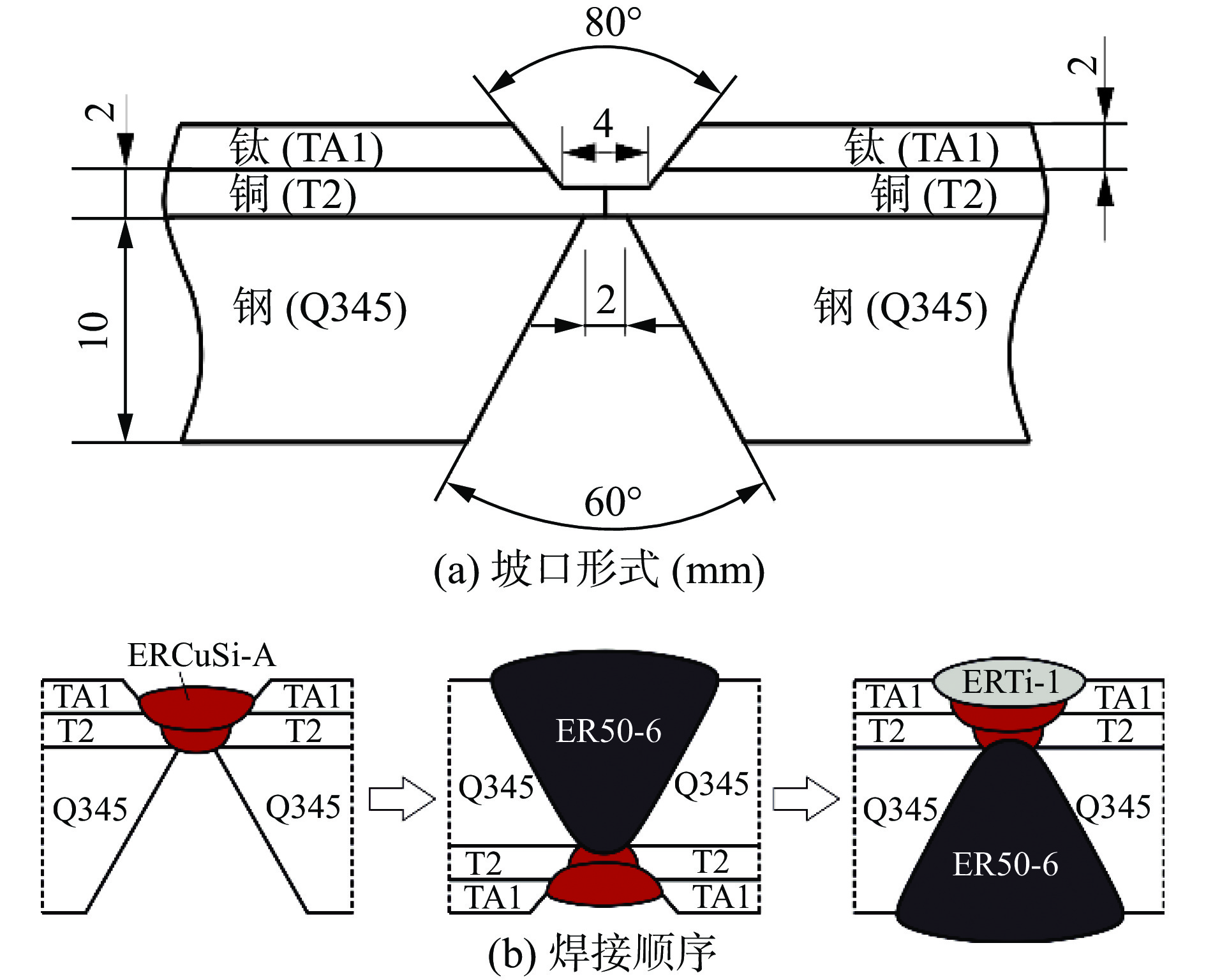
图 3 钛/钢复合板对接接头显微组织
Figure 3. Microstructure of titanium/steel butt joints. (a) ER50-6/Cu-V interface; (b) the central of Cu-V weld; (c) the phase map in the central of Cu-V weld; (d) Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface; (e) the high magnification image of Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface; (f) the phase map at Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface; (g) TA1/Cu-V/Q345 interface; (h) the high magnification image of TA1/Cu-V/Q345; (i) the phase map at TA1/Cu-V/Q345; (j) adjacent to Q345; (k) adjacent to TA1; (l) the phase map adjacent to Q345
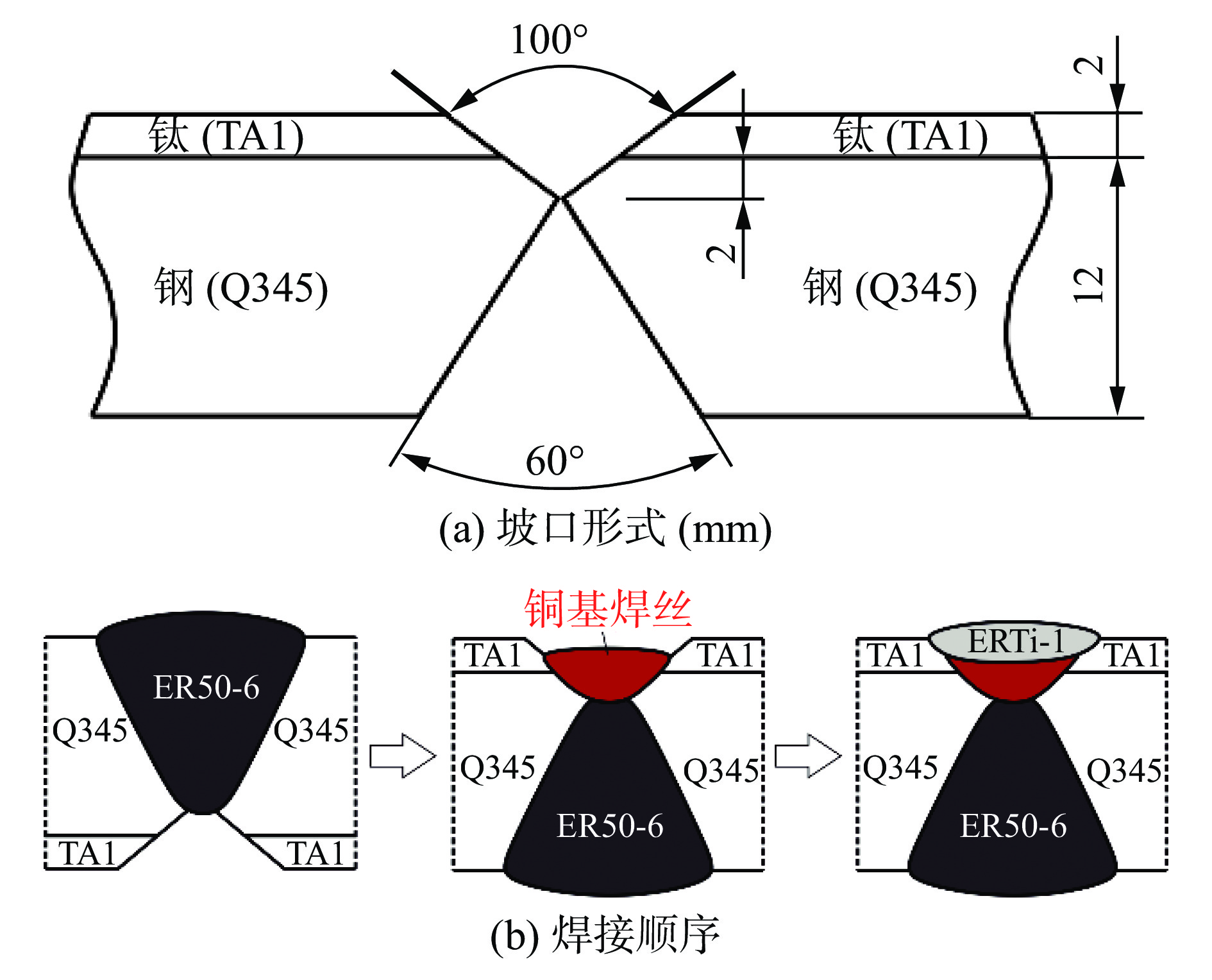
图 5 钛/铜/钢复合板对接接头显微组织
Figure 5. Microstructure of titanium/copper/steel butt joints. (a) ER50-6/Cu interface; (b) the high magnification image of ER50-6/Cu interface; (c) T2/Cu interface; (d) Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (e) the high magnification image of Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (f) ERTi-1 weld; (g) TA1/Cu/T2 interface; (h) the high magnification image of TA1/Cu/T2 interface; (i) the high magnification image of region near ERTi-1
图 6 钛/铜/钢复合板对接接头TEM分析
Figure 6. TEM results of titanium/copper/steel butt joints. (a) the bright field image of Cu/ER50-6 interface; (b) the dark field image of Cu/ER50-6 interface; (c) the diffraction of A region; (d) Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (e) the high magnification image of Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (f) the diffraction of B region
表 1 焊接材料的主要化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Main chemical composition of the welding materials
焊丝 C Si Mn Ti Cu Fe V ER50-6 0.08 0.89 1.51 — — 余量 — ERTi-1 0.03 — — 余量 — 0.10 — ERCuSi-A — 3.0 1.0 — 余量 — — Cu-V 0.01 0.30 0.50 — 余量 — 22.02 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding experiment paraments
焊丝 焊接方法 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 保护气体 ER50-6 MIG 150 ~ 180 20 ~ 24 6 ~ 7 80%Ar + 20%CO2 ERTi-1 TIG 100 ~ 120 20 ~ 22 3 ~ 4 100%Ar ERCuSi-A MIG 200 ~ 240 20 ~ 24 6 ~ 7 100%Ar Cu-V焊丝 TIG 140 ~ 160 20 ~ 24 3 ~ 4 100%Ar 表 3 钛/钢复合板对接接头典型区域EDS能谱(原子分数,%)
Table 3 EDS results of the typical regions in titanium/steel butt joints
区域 Fe Cu V Ti 主要相组成 谱图1 0.80 95.60 3.60 — Cu 谱图2 81.04 9.64 0.29 9.03 Fe + Fe2Ti 谱图3 66.53 5.22 2.51 25.74 Fe2Ti 谱图4 11.19 63.02 0.50 25.29 Cu2Ti + Cu3Ti2 谱图5 25.78 20.86 0.71 52.64 FeTi + β-Ti 谱图6 9.75 14.95 2.09 73.21 β-Ti + CuTi2 谱图7 51.07 19.21 4.00 25.72 Fe2Ti 谱图8 28.58 22.13 3.68 45.61 FeTi + Cu 谱图9 10.51 37.41 0.59 51.48 CuTi + FeTi 谱图10 5.60 30.20 0.85 63.35 CuTi2 表 4 钛/铜/钢复合板接头典型区域EDS能谱结果(原子分数,%)
Table 4 EDS results of the typical regions in titanium/copper/steel butt joints
区域 Fe Cu Si Ti 主要相组成 谱图1 0.10 98.50 0.40 — Cu 谱图2 87.78 11.77 0.45 — α-Fe 谱图3 — 52.15 — 47.85 CuTi 谱图4 — 46.17 — 53.83 CuTi + CuTi2 谱图5 — 32.70 — 67.30 CuTi2 谱图6 — 53.11 — 46.89 CuTi + Cu4Ti3 谱图7 — 12.91 — 87.09 β-Ti + CuTi2 谱图8 — 22.83 — 77.17 CuTi2 + β-Ti -
[1] 杨培智, 张钧, 杨海欧. TC4钛合金混合制造技术的研究与进展[J]. 铸造技术, 2023, 44(11): 977 − 987. Yang Peizhi, Zhang Jun, Yang Haiou. Research and progress of the hybrid manufacturing of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Foundry Technology, 2023, 44(11): 977 − 987.
[2] 南榕, 蔡建华, 杨健, 等. 钛及钛合金腐蚀行为研究进展[J]. 钛工业进展, 2023, 40(5): 40 − 48. Nan Rong, Cai Jianhua, Yang Jian, et al. A review of corrosion resistance of titanium and titanium alloys[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2023, 40(5): 40 − 48.
[3] 郑远谋. 爆炸焊接和金属复合材料及其工程应用[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2002. Zheng Yuanmou. Explosive welding and metallic composite and their engineering application[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2002.
[4] 张保奇. 异种金属爆炸焊接结合界面的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2005. Zhang Baoqi. Investigation on bonding interface of explosive welding dissimilar metal[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2005.
[5] Findik F. Recent developments in explosive welding[J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(3): 1081 − 1093. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.10.017
[6] 张柯柯, 涂益民. 特种先进连接方法[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2012. Zhang Keke, Tu Yimin. Special advanced welding and joining technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2012.
[7] 毕志雄, 李雪交, 吴勇, 等. 钛箔/钢爆炸焊接的界面结合性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(4): 81 − 85. Bi Zhixiong, Li Xuejiao, Wu Yong, et al. Interfacial bonding properties of titanium foil/steel explosive welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(4): 81 − 85.
[8] 张婷婷, 王文先, 袁晓丹, 等. Mg/Al 合金爆炸焊连接及其界面接合机制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(12): 52 − 58. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.12.052 Zang Tingting, Wang Wenxian, Yuan Xiaodan, et al. Interface bonding mechanism of Mg/Al alloy explosive welded[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(12): 52 − 58. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.12.052
[9] 武通. 脉冲TIG焊接对钛/钢复合结构中爆炸焊界面影响研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. Wu Tong. Research on the effect of pulse TIG welding on explosive welding interface in titanium/steel composite structure[D]. Harbin : Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021.
[10] Kundu S, Ghosh M, Chatterjee S. Diffusion bonding of commercially pure titanium and 17-4 precipitation hardening stainless steel[J] Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 428: 18-23.
[11] Li W, Yan L, Karnati S, et al. Ti-Fe intermetallics analysis and control in joining titanium alloy andstainless steel by laser metal deposition[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 242: 39 − 48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.11.010
[12] Xia Y Q, Dong H G, Zhang R Z, et al. Interfacial microstructure and shear strength of Ti6Al4V alloy/316 L stainless steel joint brazed with Ti33.3Zr16.7Cu50- xNi x amorphous filler metals[J]. Materials and Design, 2020, 187: 108380. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108380
[13] Adomako N K, Kim J O, Lee S H, et al. Dissimilar welding between Ti-6Al-4V and 17-4PH stainless steel using a vanadium interlayer[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 732: 378 − 397. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.015
[14] Wang T, Zhang B G, Feng J C, et al. Effect of a copper filler metal on the microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded titanium-stainless steel joint[J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 73: 104 − 113. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2012.08.004
[15] Wang T, Zhang B G, Chen G Q, et al. High strength electron beam welded titanium-steel joint with V/Cu based composite filler metals[J]. Vacuum, 2013, 94: 41 − 47. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2013.01.015
[16] Lee M K, Lee J G, Choi Y H, et al. Interlayer engineering for dissimilar bonding of titanium to stainless steel[J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 64: 1105 − 1108. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2010.02.024
[17] Chu Q L, Tong X W, Xu S, et al. The formation of intermetallics in Ti/steel dissimilar joints welded by Cu-Nb composite filler[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828: 154389. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154389
[18] Chu Q L, Zhang M, Li J H, et al. Intermetallics in CP-Ti/X65 bimetallic sheets filled with Cu-based flux-cored wires[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 90: 299 − 306. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.136
[19] Chu Q L, Zhang M, Li J H, et al. Influence of vanadium filler on the properties of titanium and steel TIG welded joints[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 240: 293 − 304. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.06.018
[20] Chu Q L, Bai R X, Zhang M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium/steel bimetallic joints[J]. Materials Characterizaiton, 2017, 132: 330 − 337. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.08.025
[21] Ning J, Zhang L J, Jiang G C, et al. Narrow gap multi-pass laser butt welding of explosion welded CP-Ti/Q235B bimetallic sheet by using a copper interlayer[J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2017, 701: 587 − 602. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.129
[22] Chu Q L, Xia T, Zhang L, et al. Structure-property correlation in weld metals and interface regions of titanium/steel dissimilar joints[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2022, 31(8): 6509 − 6522. doi: 10.1007/s11665-022-06693-9



 下载:
下载: