Effect of long term high temperature aging on CGHAZ microstructure of T23 water wall welded joint
-
摘要:
通过高温时效方法分析了焊后未热处理T23水冷壁管焊接接头粗晶热影响区(coarse grained heat affected zone,CGHAZ)在服役过程中形成再热裂纹的微观机理,揭示了工程中未热处理T23水冷壁接头在机组启机后,短期运行容易发生开裂泄漏的内在原因. 采用材料表征手段对未时效和高温时效处理后的水冷壁焊接接头CGHAZ硬度、微观组织、析出物物相等进行系统分析. 结果表明,在530 ℃时效100 h后,CGHAZ硬度出现由晶内弥散强化导致的二次硬化现象,随着时效(运行)时间增加,CGHAZ硬度逐渐降低,但时效1000 h后,CGHAZ硬度仍有319 HV高于标准要求;在600 ℃温度下,随着时效时间的增加,CGHAZ硬度随之降低,组织回复、再结晶、马氏体板条宽化、位错密度降低、C元素及合金元素从基体析出等因素导致的CGHAZ硬度降低作用高于MX碳化物在晶内弥散析出导致的硬度升高,M23C6型碳(氮)化物在晶界、亚晶界逐渐析出和长大.
Abstract:The micro-mechanism of reheat crack formation in coarse grain heat affected zone (CGHAZ) of welded joint of T23 water wall tube without heat treatment after welding was analyzed by high temperature aging method.It reveals the internal reason that T23 water wall joint without heat treatment is easy to crack and leak in short-term operation after unit startup.The hardness, microstructure and precipitates of welded joints of water wall after unaged and high temperature aging treatment were systematically analyzed by means of material characterization.The results show that after aging at 530 ℃ for 100 h, the hardness of CGHAZ appears secondary hardening caused by intragranular dispersion strengthening. With the increase of aging (running) time, the hardness of CGHAZ gradually decreases, but after aging for 1000 h, the hardness of CGHAZ is still 319 HV, which is higher than the standard requirement.After aging at 600 ℃, the hardness of CGHAZ decreases with the increase of aging time. The hardness of CGHAZ decreased due to the recovery of microstructure,recrystallization, broadening of martensite lath, reduction of dislocation density, and precipitation of C and alloy elements from the matrix, which is higher than the hardness increased due to dispersion and precipitation of MX carbide in the grain. M23C6 carbide gradually precipitates and grows at grain boundaries and subgrain boundaries.
-
Keywords:
- high temperature aging /
- T23 steel /
- water cooling wall /
- CGHAZ /
- reheat crack
-
0. 序言
T23钢是住友公司在T22的基础上以W元素部分替代Mo元素,添加少量的Nb,V和N元素研制而成的,在550 ~ 600 ℃有优异的抗高温蠕变断裂性能和高温持久性能[1],该钢种已广泛用于超临界机组的过热器、再热器以及超超临界机组的水冷壁管. 国内超超临界机组T23水冷壁服役温度在500 ~ 550 ℃,但T23钢具有较高的再热裂纹敏感性[2],国内外研究表明该钢种再热裂纹敏感性温度区间在500 ~ 700 ℃[3].
工程应用中常见的T23水冷壁规格为ϕ38.1 mm × 6.8 mm,以往对于这种壁厚小于8 mm的壁管,要求是可以不进行焊后热处理的,因此,工程现场存在大量的未经焊后热处理的T23水冷壁焊接接头. 虽然,这类焊接接头射线检验合格,但经常出现启机后短时间内水冷壁焊接接头部位泄漏,对于该类失效,原因分析多简单的归结于T23钢焊接接头粗晶热影响区(CGHAZ)的再热裂纹敏感性,但更为微观具体的失效原因却少有涉及. T23水冷壁焊接接头服役过程为在复杂应力条件下,进行的高温时效过程,因此,对于服役过程中出现的T23焊接接头开裂问题,可通过焊接接头的高温时效试验进行分析.
文中以T23水冷壁管焊接接头CGHAZ作为研究对象,对焊接接头CGHAZ进行高温时效试验,并通过与未时效的焊接接头CGHAZ显微硬度、微观组织、析出物等进行对比分析,模拟服役过程中焊接接头CGHAZ的硬度、微观组织等变化规律,分析了焊接接头CGHAZ在服役过程中再热裂纹形成的微观机理,揭示T23水冷壁管焊接接头短时服役即开裂泄漏的根本原因.
1. 试验方法
试验用T23水冷壁管材规格ϕ38.1 mm× 6.8 mm,T23钢管化学成分为(质量分数,%):0.06C,0.26Si,0.36Mn,0.008P,2.31Cr,0.08Mo,0.24V,0.051Nb,1.62W,0.0047B,余量为Fe. 为模拟真实工程中的水冷壁管屏焊接,试验采用上下管屏(每屏10根管)整体对接方式,对接接头坡口及组对尺寸如图1所示. 焊接位置2G,管屏整体采用槽钢框架固定方式模拟拘束应力,为减小焊接拘束应力对焊接接头的影响,焊前在水冷壁鳍片处切割应力释放槽,单侧应力释放槽长度不小于300 mm,如图2所示.
试验采用氩弧焊,焊丝牌号Union I P23,直径ϕ2.4 mm,焊前采用火焰预热,待焊接坡口根部达到150 ℃以上方可焊接,焊道布置为3层4道,即打底1道,填充1道、盖面2道. 为保证焊缝质量,氩弧焊时必须对管内充氩保护,气体流量6 ~ 8 L/min,具体焊接参数见表1.
表 1 焊接工艺参数Table 1. Welding parameters预热温度
T1/℃层间温度
T2/℃焊接电流
I/A电弧电压
U/V150 ℃ 200 ~ 300 100 ~130 10 ~14 焊完的试样放置48 h后,进行焊缝表面及射线探伤检测,确保无冷裂纹产生. 对焊后试样进行不同温度的高温时效试验,其中S1-Y试样作为焊态(不进行高温时效)对比试样,其余6组试验参数为S2-Y:530 ℃ × 100 h,S3-Y:530 ℃ × 500 h,S4-Y:530 ℃ × 1000 h,S5-Y:600 ℃ × 100 h,S6-Y:600 ℃ × 500 h,S7-Y:600 ℃ × 1000 h.
将焊态和高温时效后的水冷壁外壁焊缝余高去除后,对焊接接头进行打磨、抛光后,采用4%的硝酸酒精腐蚀. 用Q10A + 型全自动显微维氏硬度计,测量焊态及时效处理后水冷壁外壁焊接接头处的CGHAZ硬度,试验过程中施加载荷10 N,将试验后试样接头再次进行打磨、抛光、侵蚀后,利用Axiovert 200 MAT研究级倒置万能材料显微镜对CGHAZ进行微观组织观察,金相组织观察后,在蔡司SIGMA 300场发射扫描电镜下继续观察CGHAZ微观形貌. 采用线切割设备将焊接接头制成30 mm × 6.8 mm × 0.5 mm的薄片,并利用Tenupol-5电解双喷仪进一步制备CGHAZ金属薄膜样品,薄膜样品制备完成后,用FEI公司TecnaiG2 20透射电子显微镜对CGHAZ亚结构特征及析出碳化物进行观察,并利用设备自带的能谱仪对微观组织析出物进行能谱分析,采用划线法测量原奥氏体晶粒尺寸和板条宽度,每个试样测试3 ~ 5个视场,结果取平均值.
2. 试验结果与讨论
2.1 显微硬度
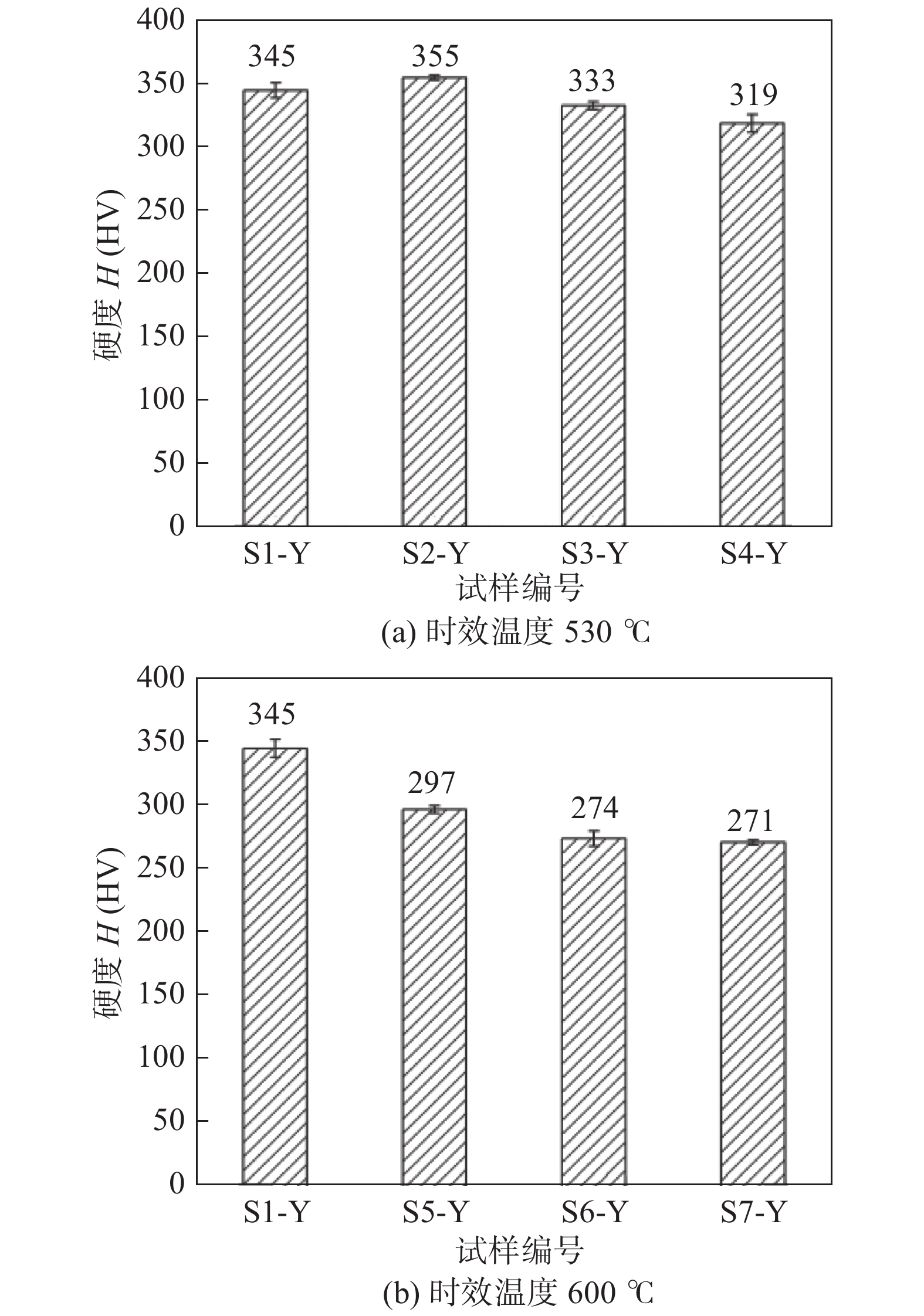
T23钢焊接接头的CGHAZ为再热裂纹敏感性最高的区域,试验检测了焊态及时效后T23水冷壁焊接接头CGHAZ显微硬度,每个试样CGHAZ检测4个值,取平均值作为最终试验结果.
不同时效参数下T23水冷壁焊接接头CGHAZ显微硬度如图3所示,观察时效温度为530 ℃的CGHAZ显微硬度发现,显微硬度先升高后降低,其中,焊态试样S1-Y的CGHAZ硬度为345 HV;530 ℃恒温100 h后(S2-Y) CGHAZ显微硬度增加至355 HV,随着时效时间的延长,CGHAZ硬度不断降低;时效时间达500 h后(S3-Y) CGHAZ硬度为333 HV;时效1000 h后(S4-Y) CGHAZ硬度降至319 HV. 观察时效温度为600 ℃的CGHAZ显微硬度,其显微硬度走势与530 ℃时效后硬度走势不同,随着时效时间的增加,CGHAZ显微硬度呈不断下降趋势,当时效时间达到1000 h后(S7-Y),CGHAZ硬度仅有271 HV. 综合对比2种不同时效温度后的CGHAZ显微硬度发现在相同时效时间条件下,时效温度为600 ℃时,CGHAZ硬度下降幅度更大,由此可见,T23钢焊接接头的CGHAZ显微硬度在600 ℃时敏感性更大.
2.2 微观组织
2.2.1 光学金相观测
T23钢焊接接头CGHAZ不同时效参数下的金相组织形貌如图4所示. 由图4(a)可以看出,焊态的CGHAZ组织为马氏体 + 贝氏体的混合组织,原奥氏体晶粒比较粗大,平均晶粒尺寸约100 μm;图4(b)~图4(d)为CGHAZ在530 ℃经过100,500,1000 h时效后的金相组织,与焊态相比,组织中出现了明显的铁素体,板条马氏体组织依然清晰可见,原奥氏体晶界均清晰可见,晶粒尺度与焊态时变化不大,此外,原奥氏体晶界或多晶粒交界处出现细小的再结晶组织;图4(e)~图4(g)为CGHAZ在600 ℃经过100, 500,1000 h时效后的金相组织,图4(e)中平均晶粒尺寸相对焊态明显更细小,晶粒尺寸约20 ~ 30 μm,随着时效温度提高至600 ℃,马氏体组织发生回复及再结晶,在原奥氏体晶界交界处形成细小的再结晶组织,而板条形态组织减少;图4(f)和图4(g)发现,虽然组织中存在板条形貌,但板条宽度增加,且随着时效时间增加,组织中出现了白色块状铁素体,平均晶粒尺寸也增加至100 μm.
2.2.2 扫描电镜分析
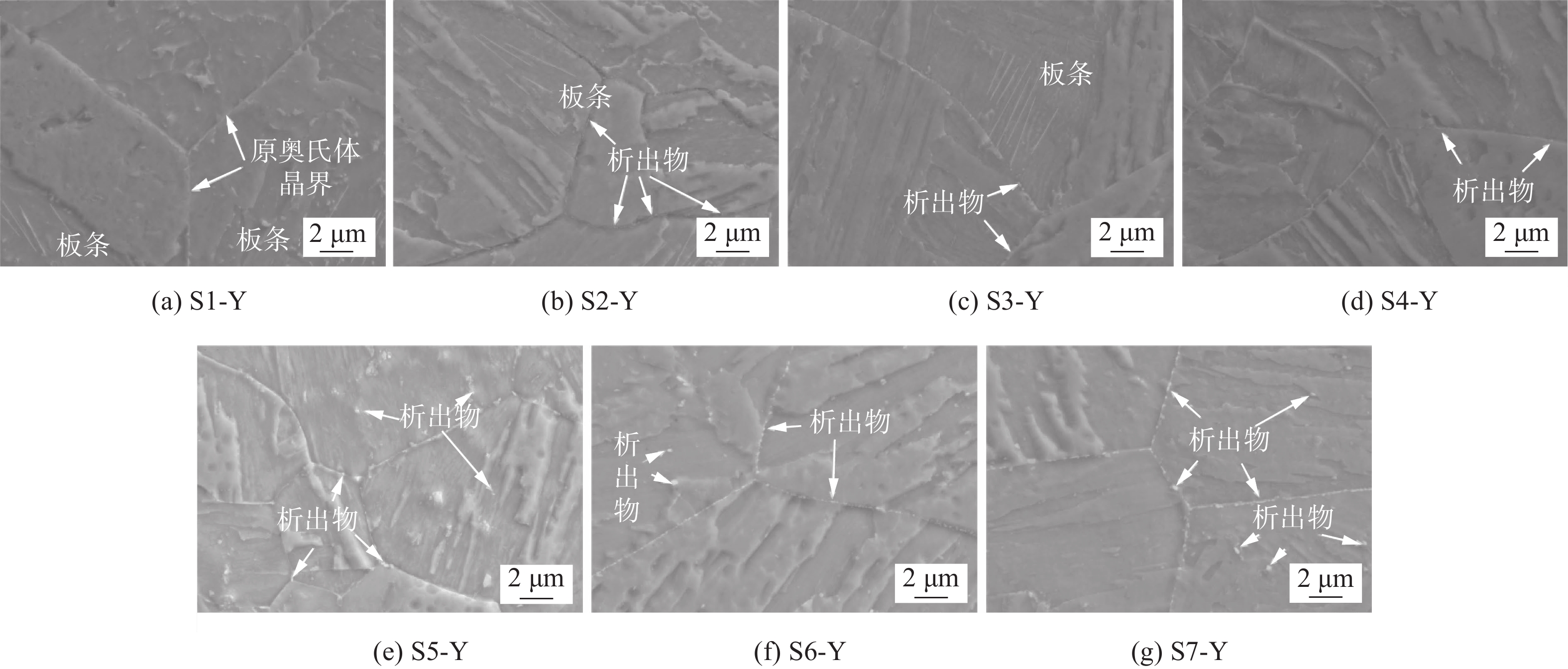
T23钢焊接接头试样CGHAZ在530 ℃和600 ℃时效不同时间后的SEM(scanning electron microscope)如图5所示,图5(a)中焊态接头CGHAZ的马氏体板条特征明显,原奥氏体晶界清晰,晶界和晶内几乎不见析出物,表明大部分合金元素均被固溶在基体中.
图5(b)~图5(d)为接头试样CGHAZ在530 ℃时效100, 500, 1000 h的SEM形貌,从图中可以看出,原奥氏体晶界清晰,在晶界处可见少量析出物,晶内无明显析出物,时效100 h和500 h后板条马氏体形貌仍然可见,板条边界清晰,但时效时间达1000 h后,随着马氏体的回复、再结晶,板条形貌已不明显. 图5(e)~图5(g)为接头试样CGHAZ在600 ℃时效100, 500, 1000 h的SEM形貌,从图中可以看出,原始晶界清晰可见,在图5(e)和图5(f)中依稀可见马氏体痕迹,但图5(g)中马氏体位相基本消失,从析出物角度来看,析出物主要在原奥氏体晶界析出,晶内也有少量析出物,随着时效时间则增加,在晶界析出的碳化物具有明显长大趋势.
2.2.3 透射电镜分析
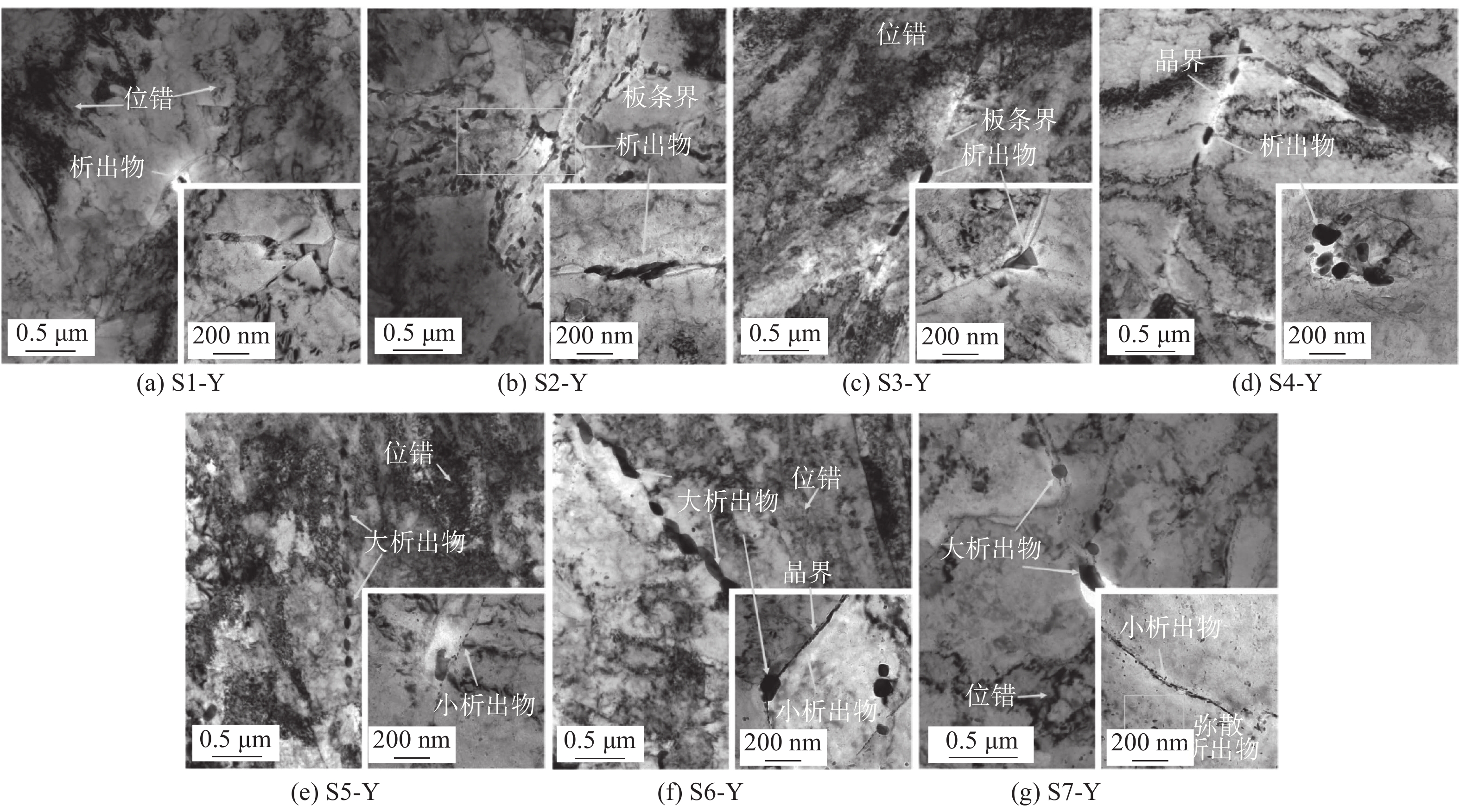
采用透射电子显微镜对焊态及不同时效参数下焊接接头CGHAZ亚结构特征及析出碳化物进行观察,焊接接头TEM(transmission electron microscope)形貌如图6所示,图6(a)为S1-Y试样CGHAZ焊态TEM形貌,CGHAZ焊态组织位错塞积明显,密度较大,析出物很少,视野可见析出物尺寸0.1 μm; 图6(b)~图6(d)为在530 ℃条件下时效100, 500, 1000 h的试样CGHAZ TEM形貌,对比3张形貌图可知,位错密度逐渐减小. 首先,时效100 h后,TEM形貌中析出物大量从板条界析出,析出物尺寸约0.1 μm见图6(b);其次,时效500 h后,有杆状析出物从板条界或晶界析出,同时在三晶粒交界部位存在三角形析出物,析出物尺寸略有长大,长度约0.2 ~ 0.3 μm,位错密度降低;当时效时间达到1000 h后,在原奥氏体晶界可见明显多个椭圆状或短杆状析出物,同时,在晶粒内部局部位置存在椭球状密集析出物,析出物尺寸约0.2 ~ 0.3 μm,位错密度进一步降低.图6(e)~图6(g)为在600 ℃条件下时效100,500 ,1000 h的试样CGHAZ TEM形貌,图6(e)中有2种规格的析出物,较大析出物沿板条界或晶界呈链状析出,析出物尺寸约0.1 μm,小析出物沿板条界呈断续线状析出,尺寸约20 nm,位错密度较高; 图6(f)中析出物相对图6(e)有一定程度长大,大析出物沿晶界断续呈杆状或椭球状析出,同时在三叉晶界处析出较大椭球状析出物,小析出物也沿板条晶界密集析出,其尺寸相对也略有长大,但长大不太明显,同时,位错密度降低;从图6(g)中可以看出,大析出物除了在奥氏体晶界析出外,在晶内也有析出,其尺寸约0.3 μm,小尺寸析出物沿板条晶界密集析出,尺寸相对图6(e)和图6(f)中明显增加,此外,在晶粒内部还存在大量弥散析出的小析出物,尺寸约10 ~ 20 nm,位错密度相对进一步降低.
2.2.4 能谱分析
采用TEM自带的能谱分析仪对图6(d)和图6(f)中的大析出物进行半定量元素成分分析,分析结果如图7所示. 对图6(e)和图6(g)中的小析出物也进行了半定量元素成分分析,结果如图8所示.从结果可知,Fe与Cr元素的原子百分比接近3∶1,W元素质量百分比为10% ~ 11.8%,W元素峰明显. 根据于在松和Zieliński等人[4-5]的研究结果:M7C3中 Fe和Cr元素峰的高度比接近1∶1;M23C6中Fe和Cr元素峰的高度比接近3∶1,且有明显的W元素峰;M3C中Fe和Cr元素峰的高度比大于5∶1,且 W 元素的峰不显著,综上,在图6(d)和图6(f)中大尺寸析出物应为M23C6型碳化物.
图8中从元素峰值占比可知,Fe元素占比最多,质量百分比分别为78.7%和87.2%,其余含量较高元素为W,Cu,C,Cr和V等. Miyata等人[6]研究表明,这些细小的沉淀相为MX相(富含V,Nb和Ti的碳氮化物),鉴于透射电镜的电子束斑较大,对于尺寸较小的析出物,束斑范围较大,元素峰值中含量较高的一般为基体中的元素含量,这是Fe元素峰值最高的原因. 从能谱分析结果并结合前人的研究结果来看,图6(e)和图6(g)中的细小析出物主要是MX相(富含V元素的碳化物).
马氏体板条束宽度与强度之间满足Hall-Petch关系,即板条束宽度增加,强度下降[7]. 因此,在600 ℃温度下,时效随着时效时间的延长,位错密度的减小和板条宽度的增加将导致CGHAZ硬度下降.过大的晶内和晶界强度差是导致T23钢产生再热裂纹的根本原因[8],焊态CGHAZ组织为马氏体 + 少量贝氏体组织,板条内有高密度位错,晶界和晶内几乎不见析出物,表明大部分合金元素均被固溶在基体中. 不论是在530 ℃还是在600 ℃时效过程中均会发生组织回复、再结晶,板条宽度增大,位错密度下降的变化;随着时效时间的增加,合金元素脱溶析出,在晶内、晶界、板条(亚晶)界及板条内均有碳化物析出.
不同电厂的工程应用表明,存在大量未经焊后热处理的T23水冷壁焊接接头,在运行较短时间后(几天至几周内)就会发生水冷壁接头开裂泄漏的案例,同时文献[9]表明,未经焊后热处理的T23接头的不稳定脆硬性马氏体-贝氏体混合组织,在运行过程中会发生脆化导致脆性蠕变断裂.
从OM(optical microscope)组织、SEM形貌以及TEM结果来看,CGHAZ焊态时,大量合金元素固溶在基体中,位错密度大、马氏体板条强化等共同作用导致CGHAZ硬度较高. 经过530 ℃ × 100 h的时效过程后,由于组织回复、再结晶、板条粗大和位错密度下降等原因,CGHAZ硬度应该下降,但由于530 ℃温度相对较低,时间相对较短,时效过程中会有部分尺寸较小的析出物在晶内析出,晶内弥散分布的析出物的析出强化作用高于高温导致的回复、位错密度下降等因素的弱化作用,由此引发CGHAZ二次硬化发生. 随着时效(运行)时间增加,CGHAZ硬度逐渐降低,但时效1000 h后,CGHAZ硬度仍有319 HV,高于标准要求硬度. 此外,结合时效1000 h后的OM组织、SEM形貌、TEM形貌可知,在530 ℃下时效(运行)并不能消除敏感性组织和有效降低CGHAZ硬度,仅能起到降低焊接残余应力的作用[10]. 金玉静[11]对比了显微硬度与纳米硬度,显微硬度能在一定程度上反映晶粒内硬度的趋势,因此,T23水冷壁较高的CGHAZ硬度表明晶内强度相对较高,而且,时效后大量与基体共格与半共格的M23C6型碳化物在晶界析出降低了晶界强度[12],导致晶内强度与晶界强度差较大,再热裂纹敏感性较高. 此外,在机组启机至稳定运行过程中,水冷壁管屏施加的拘束应力和温度变化导致的交变应力共同作用在焊接接头处,导致CGHAZ产生再热裂纹开裂. 解释了大量的未进行焊后热处理的T23水冷壁焊接接头在启机短期运行即发生开裂泄漏的原因.
在600 ℃温度下时效,随着时效时间的增加,CGHAZ硬度随之降低,在时效过程中并没有发生二次硬化现象,1000 h时效后CGHAZ硬度降至271 HV,该硬度区间的CGHAZ对再热裂纹敏感较低,这表明在600 ℃下,CGHAZ组织的回复、再结晶作用更强,位错密度降低更多,因此,由组织的回复、再结晶、马氏体板条宽化、位错密度降低、C元素及合金元素从基体析出等因素,导致的CGHAZ硬度降低作用高于MX碳化物在晶内弥散析出导致的CGHAZ整体硬度升高[13-14],整体硬度降低.
3. 结论
(1)焊态CGHAZ组织为为马氏体 + 少量贝氏体组织,板条内有高密度位错,晶界和晶内几乎不见析出物,大部分合金元素均被固溶在基体中.
(2) 530 ℃时效100 h后CGHAZ硬度会出现轻微二次硬化,晶内弥散分布的析出物导致析出强化作用高于高温回复、再结晶、位错密度下降等因素导致的弱化作用.
(3)焊态的T23水冷壁焊接接头在启机后短期运行,容易发生接头开裂泄漏的内在原因是,由于焊态CGHAZ硬度较高,在正常服役温度下短时间内出现二次硬化,导致晶内强度与晶界强度差增大,再热裂纹敏感性增高,同时叠加结构应力的作用,便形成再热裂纹而开裂.
(4)在600 ℃温度下时效,随着时效时间的增加,CGHAZ硬度随之降低;M23C6型碳(氮)化物在晶界、亚晶界逐渐析出、长大;MX型碳化物在原奥氏体晶内或亚晶界弥散析出、长大. CGHAZ硬度降低表明,由组织的回复、再结晶、马氏体板条宽化、位错密度降低等因素,导致的CGHAZ硬度降低作用高于MX型碳化物在晶内弥散析出导致的硬度升高.
致谢
文中焊接试验及试验数据的测量记录工作是在陈勇平、刘明玉、徐伟等工作人员的大力支持下完成的,在此向他(她)们表示衷心的感谢.
-
表 1 焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Welding parameters
预热温度
T1/℃层间温度
T2/℃焊接电流
I/A电弧电压
U/V150 ℃ 200 ~ 300 100 ~130 10 ~14 -
[1] 周任远, 朱丽慧, 李世贤, 等. T23钢再热裂纹敏感性的改善及其组织[J]. 钢铁, 2020, 55(3): 80 − 86. Zhou Renyuan, Zhu Lihui, Li Shixian, et al. Improvement of reheat crack sensitivity and microstructure of T23 steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(3): 80 − 86.
[2] Li Y, Wang X, Wang J Q, et al. Stress-relief cracking mechanism in simulated coarse-grained heat-affected zone of T23 steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 266: 73 − 81.
[3] 牛锐锋, 曹怡姗, 朱一乔, 等. 国产T23钢再热裂纹敏感性试验研究[J]. 兵器材料科学与工程, 2014, 37(5): 36 − 39. Niu Ruifeng, Cao Yishan, Zhu Yiqiao, et al. Experimental study on reheat crack sensitivity of domestic T23 steel[J]. Ordnance Material Science and Engineering, 2014, 37(5): 36 − 39.
[4] 于在松, 聂铭, 侯淑芳, 等. HCM2S(T23)钢中的碳化物及其演化规律[J]. 热力发电, 2012, 41(9): 1 − 6. Yu Zaisong, Nie Ming, Hou Shufang, et al. Carbides in HCM2S(T23) steel and its evolution law[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2012, 41(9): 1 − 6.
[5] Zieliński A, Golański G, Sroka M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the T23 steel after long-term ageing at elevated temperature[J]. Materials at High Temperatures, 2016, 33: 154 − 163. doi: 10.1080/09603409.2016.1139306
[6] Miyata K, Igarashi M, Sawaragi Y. Effect of trace elements on creep properties of 0.06C-2.25Cr-1.6W-0.1Mo-0.25V-0.05Nb Steel[J]. ISIJ International, 1999, 39(9): 947 − 954. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.947
[7] Morito S, Yoshida H, Maki T, et al. Effect of block size on the strength of lath martensite in low carbon steels[J]. Materials Science & Engineering, A, 2006, 438: 237 − 240.
[8] 李世贤, 朱丽慧, 周任远, 等. T23低合金耐热钢再热裂纹敏感性研究[J]. 上海金属, 2020, 42(3): 7 − 11. Li Shixian, Zhu Lihui, Zhou Renyuan et al. Study on reheat crack sensitivity of T23 low alloy heat resistant steel[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2020, 42(3): 7 − 11.
[9] 周任远, 朱丽慧, 柯志刚, 等. 回火温度对改进型T23钢冲击吸收功的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2021, 56(3): 51 − 57. Zhou Renyuan, Zhu Lihui, Ke Zhigang et al. Influence of tempering temperature on impact absorption energy of improved T23 steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(3): 51 − 57.
[10] 王学, 李勇, 王家庆, 等. 高温时效对T23钢粗晶热影响区显微组织及再热裂纹敏感性的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2021, 57(6): 736 − 748. Wang Xue, Li Yong, Wang Jiaqing, et al. Effect of high temperature aging on the microstructure and reheat crack susceptibility of T23 steel coarse-grained heat-affected zone[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2021, 57(6): 736 − 748.
[11] 金玉静. T23钢粗晶热影响区再热裂纹敏感性研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2015. Jin Yujing. Study on reheat crack sensitivity of T23 steel coarse grain heat affected zone [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2015.
[12] 金玉静, 周巍. 改良型T23钢CGHAZ再热裂纹开裂特征[J]. 金属热处理, 2017, 42(11): 191 − 197. Jin Yujing, Zhou Wei. CGHAZ reheat cracking characteristics of improved T23 steel[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2017, 42(11): 191 − 197.
[13] 周任远, 朱丽慧, 李世贤, 等. 改进型T23钢的再热裂纹敏感性[J]. 金属热处理, 2020, 45(1): 20 − 25. Zhou Renyuan, Zhu Lihui, Li Shixian. et al. Reheat crack susceptibility of improved T23 steel[J]. Metal Heat Treatment, 2020, 45(1): 20 − 25.
[14] 柯志刚, 朱丽慧, 周任远, 等. 改进型T23钢冲击韧度的改善[J]. 上海金属, 2022, 44(4): 49 − 54. Ke Zhigang, Zhu Lihui, Zhou Renyuan, et al. Improvement of impact toughness of improved T23 steel[J]. Shanghai Metal, 2022, 44(4): 49 − 54.




 下载:
下载: