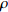Effect of power distribution on dynamic behavior of molten pool during laser oscillating welding of 5A06 aluminum alloy
-
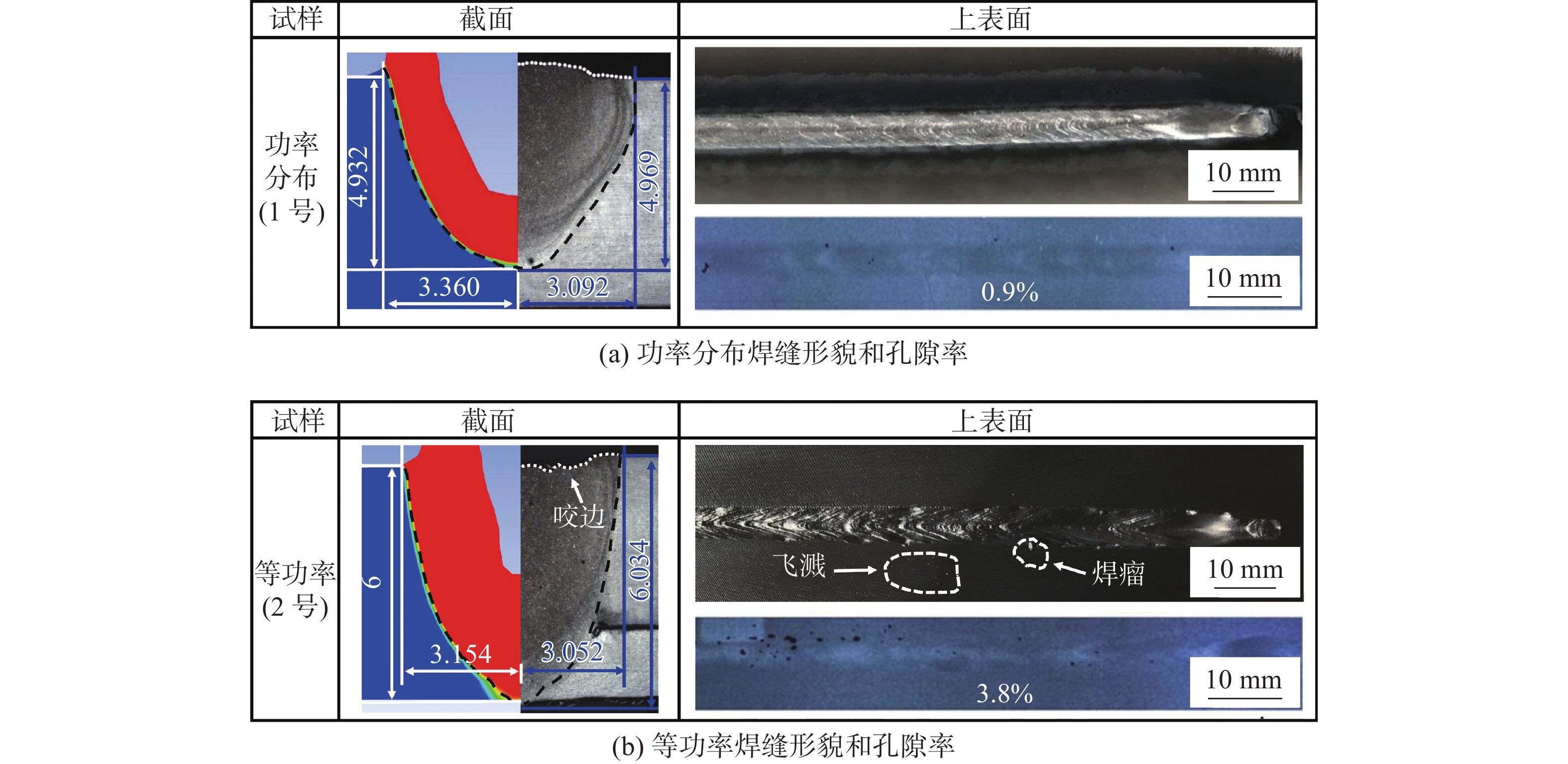
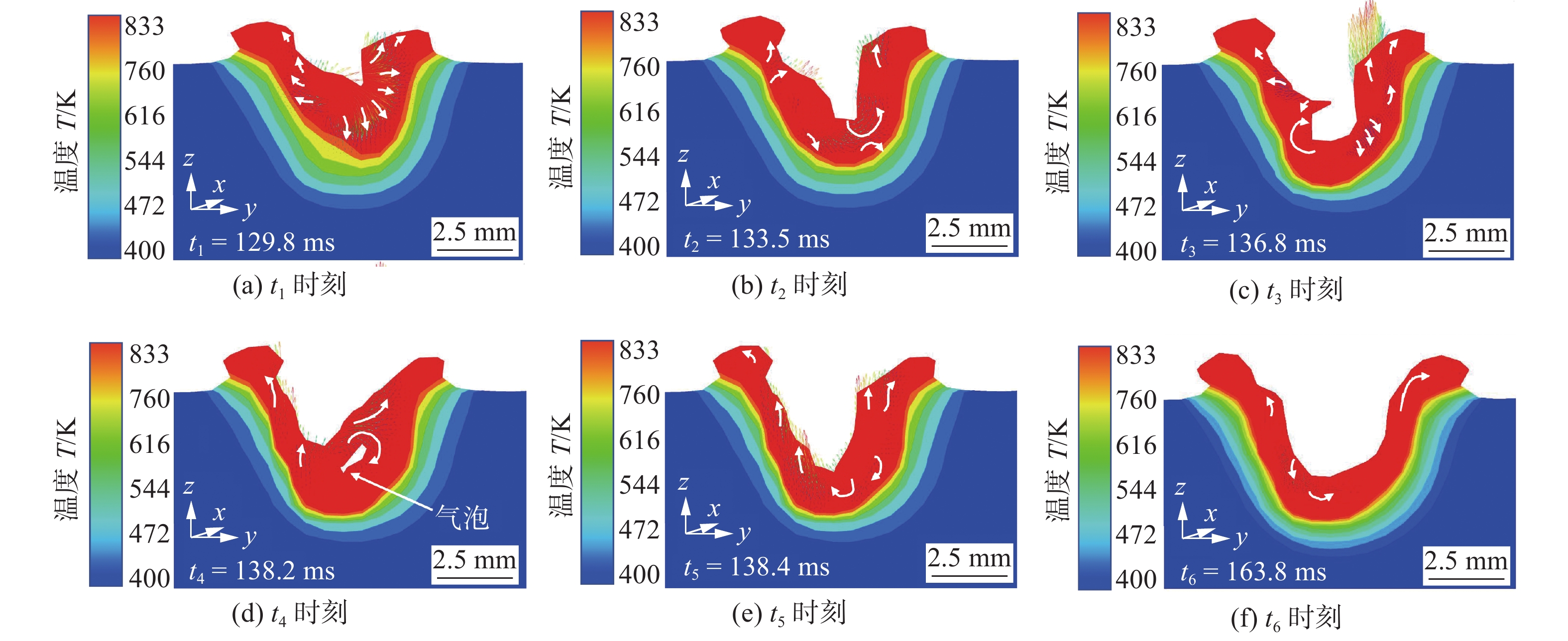
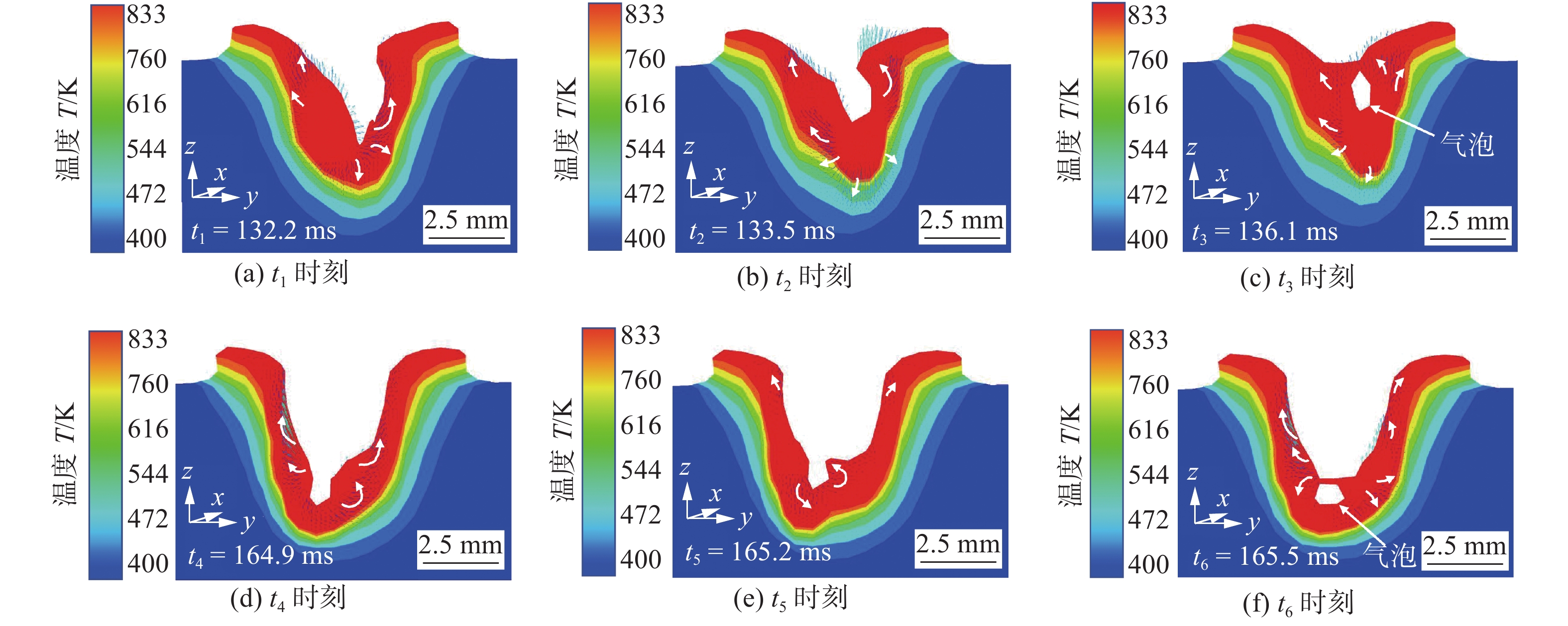
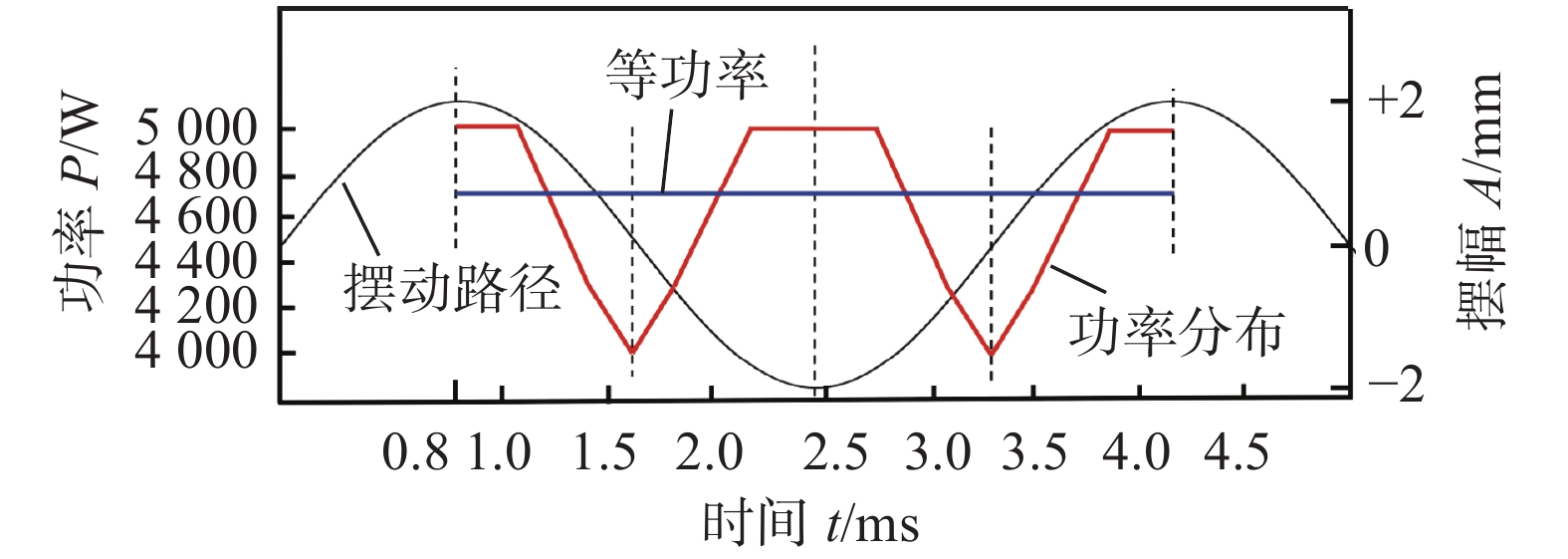
摘要: 以5A06铝合金锁底对接焊缝为研究对象,在激光束摆动的基础上引入一种沿正弦摆动路径分布的激光功率(功率分布),实现功率相对于摆动路径的动态调控. 基于FLUENT有限元软件,建立激光摆动焊接过程的流体动力学模型,研究光斑摆动与功率分布对焊缝成形的影响机制,模拟对比了施加等功率与功率分布2种工艺下的焊缝截面形貌、熔池动态行为及气孔形成过程. 结果表明,与等功率焊接相比,施加功率分布焊缝成形更优,未出现咬边和烧穿等缺陷;由于功率分布的特点,有效缓和了熔池的平均流速,熔融金属呈现更为稳定的流动行为,进一步提高了匙孔的稳定性,并获得了深宽比较小的匙孔,有效降低了焊缝的孔隙率(0.9 %).Abstract: 5A06 aluminum alloy lock butt weld was used as the research object. Based on the laser beam oscillating, a laser power (power distribution) which is distributed along the oscillating path was added to achieve the dynamic control of power relative to the path. The fluid dynamics model of laser oscillating welding process was established by the finite element software FLUENT to research the effect mechanism of laser oscillating and power distribution on weld forming. The weld section morphology, molten pool dynamic behavior and porosity formation process were simulated and compared under two processes of equal power and power distribution. The results show that compared with the equal power weld, the better formed weld is obtained by power distribution and has no defects such as undercut and burn through. Due to the characteristics of power distribution, the average flow rate of molten pool is effectively reduced, the steady flow behavior of molten metal is exhibited, further improve the stability of the keyhole, and smaller depth-to-width ratio keyhole is obtained, effectively reduce the porosity of the weld (0.9%).
-
-
表 1 5A06铝合金母材的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of base metal
Si Mg Fe Mn Zn Al 0.4 5.8 ~ 6.8 0.4 0.5 ~ 0.8 0.2 余量 表 2 激光摆动焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Laser oscillating welding process parameters
试样 激光功率P/W 摆幅A/mm 频率f/Hz 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) 1 5 000 ~ 4 300 ~ 4 000 2 300 1 200 2 4 700 2 300 1 200 表 3 5A06铝合金热物理特性参数
Table 3 Thermophysical properties of 5A06 aluminum alloy
密度 $ \rho $ /(kg· m−3)固相导热系数kS/(W·m−1·K−1) 液相导热系数kl/(W·m−1·K−1) 固相比热容CS/(J·kg−1·K−1) 液相比热容Cl/(J·kg−1·K−1) 动态粘滞度v/(kg·m−1·s−1) 固相线TS/K 液相线Tl/K 沸点Tg/K 熔化潜热LS/(105J·kg−1) 2 630 243 138 940 1 180 0.001 3 833.01 905.49 2 720 3.97 -
[1] Guo N, Fu Y L, Wang Y Z, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties in friction stir welded 5A06 aluminum alloy thick plate[J]. Materials & Design, 2017, 113: 273 − 283.
[2] Çam G, İpekoğlu G. Recent developments in joining of aluminum alloys[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 91: 1851 − 1866.
[3] Xu J J, Rong Y M, Huang Y, et al. Keyhole-induced porosity formation during laser welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 252: 720 − 727. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.10.038
[4] Wang Z M, Oliveira J P, Zeng Z, et al. Laser beam oscillating welding of 5A06 aluminum alloys: Microstructure, porosity and mechanical properties[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2019, 111: 58 − 65. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2018.09.036
[5] Wu S K, Li Z X, Qi E Y, et al. Impact of Nb on microstructure and properties of oscillating laser-CMT hybrid welding joints of A7204P-T4 aluminum alloy sheets[J]. Science and Technology of Welding & Joining, 2021, 26(4): 273 − 278.
[6] Pang X B, Dai J H, Chen S, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of fiber laser welding of aluminum alloy with beam oscillation[J]. Applied Sciences-Basel, 2019, 23(9): 5096 − 5107. doi: 10.3390/app9235096
[7] Zhang C, Yan Y, Chen C, et al. Suppressing porosity of a laser keyhole welded Al-6Mg alloy via beam oscillation[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 278: 116382 − 116389. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116382
[8] Cho J H, Na S J. Implementation of real-time multiple reflection and Fresnel absorption of laser beam in keyhole[J]. Journal of Physics D-Applied Physics, 2006, 39(24): 5372 − 5378. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/39/24/039
[9] Pang S Y, Chen W D, Wang W. A quantitative model of keyhole instability induced porosity in laser welding of titanium alloy[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A-Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2014, 45(6): 2808 − 2818. doi: 10.1007/s11661-014-2231-3
[10] Li L Q, Peng G C, Wang J M, et al. Numerical and experimental study on keyhole and melt flow dynamics during laser welding of aluminium alloys under subatmospheric pressures[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 133: 812 − 826. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2018.12.165
[11] Ke W C, Bu X Z, Oliveira J P, et al. Modeling and numerical study of keyhole-induced porosity formation in laser beam oscillating welding of 5A06 aluminum alloy[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2021, 133: 106540 − 106550. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2020.106540
[12] Tan Z J, Pang B W, Oliveira J P, et al. Effect of S-curve laser power for power distribution control on laser oscillating welding of 5A06 aluminum alloy[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2022, 149: 107909 − 107916. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.107909
[13] Xiao R S, Zhang X Y, Problems and issues in laser beam welding of aluminum-lithium alloys[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2014, 16(2): 166–175.
[14] Wang H, Shi Y, Gong S, et al. Effect of assist gas flow on the gas shielding during laser deep penetration welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2007, 184(1–3): 379–385.
[15] Xu G, Li P, Cao Q, et al. Modelling of fluid flow phenomenon in laser + GMAW hybrid welding of aluminum alloy considering three phase coupling and arc plasma shear stress[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2018, 100: 244 − 255. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2017.10.009
[16] Gueyffier D, Li J, Nadim A, et al. Volume-of-fluid interface tracking with smoothed surface stress methods for three-dimensional flows[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1999, 152(2): 423 − 456. doi: 10.1006/jcph.1998.6168
[17] Schepper S C K D, Heynderickx G J, Marin G B. Modeling the evaporation of a hydrocarbon feedstock in the convection section of a steam cracker[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2009, 33(1): 122 − 132.
[18] 陈彦宾. 现代激光焊接技术[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005. Chen Yanbin. Laser Welding Technology[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005.
[19] Liu T T, Mu Z Y, Hu R Z, et al. Sinusoidal oscillating laser welding of 7075 aluminum alloy: Hydrodynamics, porosity formation and optimization[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2019, 140: 346 − 358. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.05.111
[20] Chen L, Mi G Y, Zhang X, et al. Effects of sinusoidal oscillating laser beam on weld formation, melt flow and grain structure during aluminum alloys lap welding[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2021, 298(12): 117314 − 117328.
[21] Li S R, Mi G Y, Wang C M. A study on laser beam oscillating welding characteristics for the 5083 aluminum alloy: Morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 53: 12 − 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.018
[22] Li L Q, Gong J F, Xia H B, et al. Influence of scan paths on flow dynamics and weld formations during oscillating laser welding of 5A06 aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2021, 11: 19 − 32.
[23] Fuhrich T, Berger P, Hügel H. Marangoni effect in laser deep penetration welding of steel[J]. Journal of Laser Applications, 2001, 13(5): 178 − 186. doi: 10.2351/1.1404412
[24] Shi L, Li X, Jiang L, et al. Numerical study of keyhole-induced porosity suppression mechanism in laser welding with beam oscillation[J]. Science and Technology of Welding & Joining, 2021, 26(5): 349 − 355. doi: 10.1080/13621718.2021.1913562
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 栗振鑫,蔡创,余杰,陈梓琳,熊发帅,汤坪,陈辉. 激光摆动对TC4钛合金窄间隙焊接接头组织性能的影响. 中国激光. 2025(08): 77-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郭克星. 铝合金激光焊接技术研究进展. 热处理. 2024(06): 1-7 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)



 下载:
下载: