Microstructure and dynamic fracture behaviors of 17-4PH stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting
-
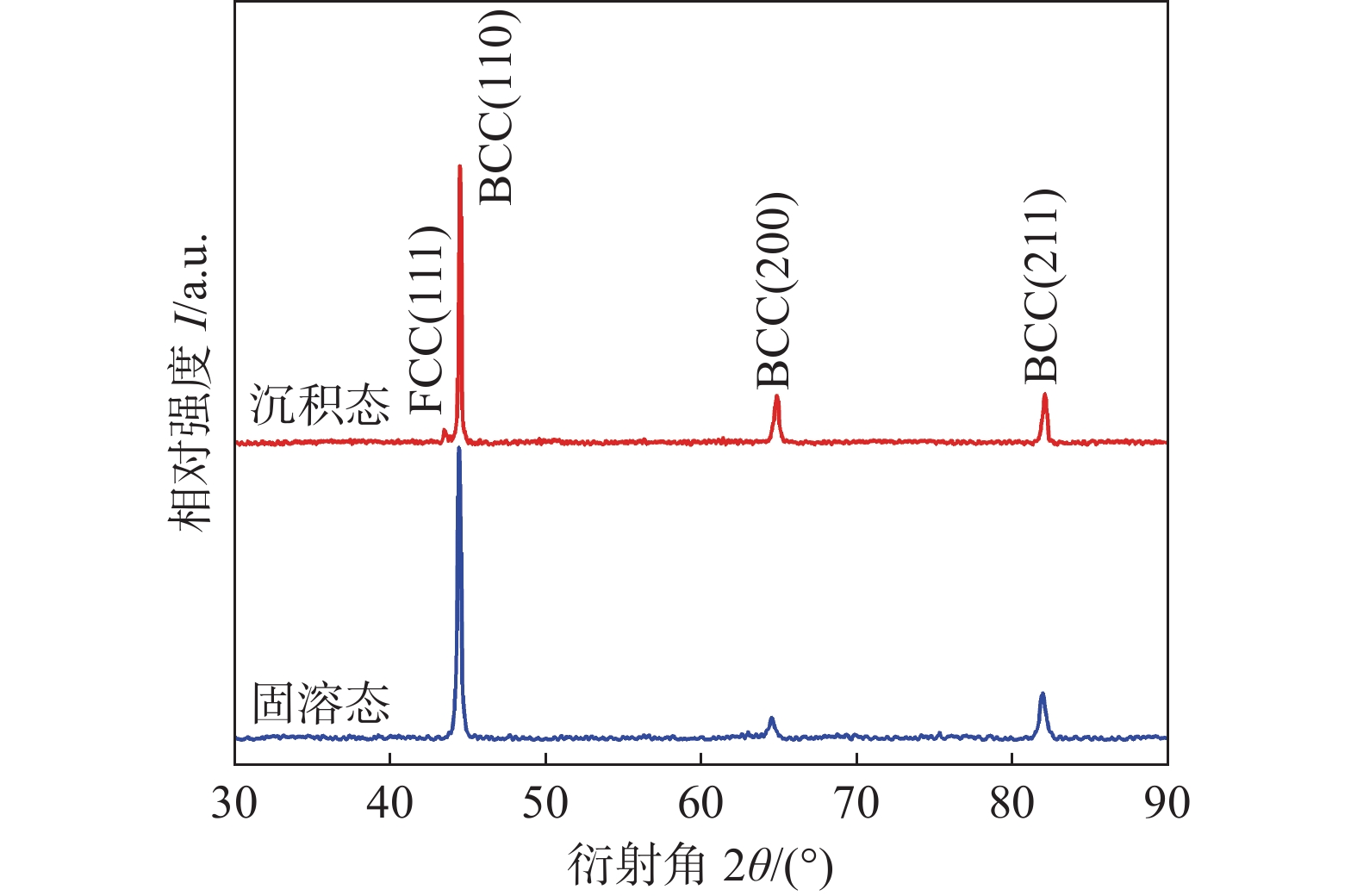
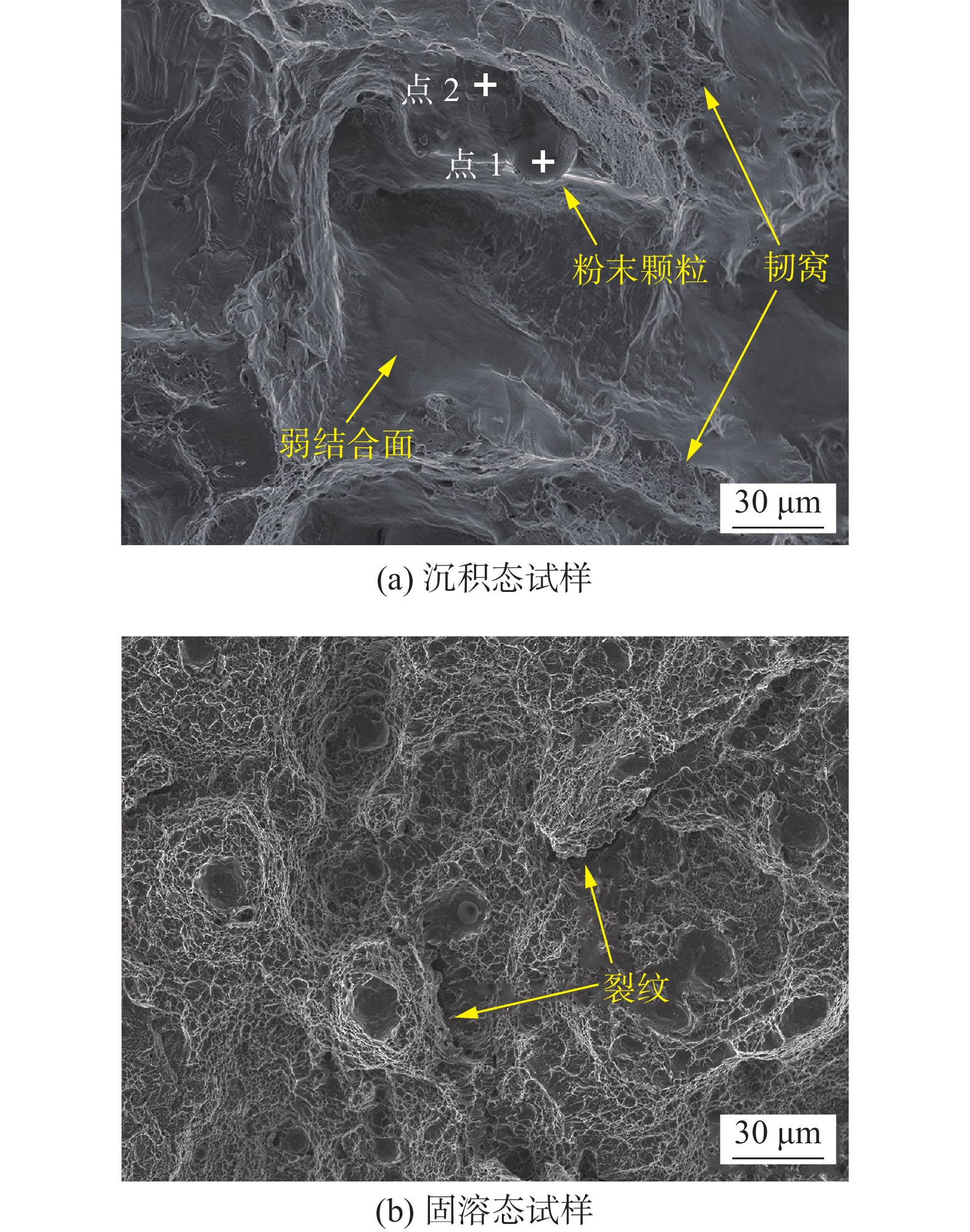
摘要: 通过激光选区熔化(selective laser melting, SLM)技术制备了17-4PH不锈钢,采用电子背散射衍射(electron backscattered diffraction, EBSD)和透射电子显微镜(transmission electron microscope, TEM)等方法对沉积态和固溶态试样微观组织结构进行了分析. 通过示波冲击试验确定了裂纹萌生扩展的特征阶段和动态裂纹扩展阻力曲线(J−R曲线),研究了微观组织与动态断裂性能之间的关系. 结果表明,沉积态试样主要由<100>择优且沿增材方向拉长的δ铁素体柱状晶、取向随机的细小马氏体,以及少量奥氏体组成,不同截面具有显著的组织各向异性;大尺寸δ铁素体柱状晶与细小晶粒的结合面作为薄弱环节,使其脆性增加,J−R曲线的撕裂模量较低,以准解理方式断裂. 固溶热处理明显弱化组织各向异性,微观组织由尺寸细小、均匀的马氏体组成,其冲击吸收能量提升1倍,动态断裂韧性优良,属于韧性断裂. 大尺寸δ铁素体柱状晶与周围细小马氏体晶粒界面结合较弱是沉积态17-4PH不锈钢动态断裂性能较差的主要原因.Abstract: 17-4PH stainless steel was fabricated by selective laser melting (SLM). The microstructure of the as-built and solution heat treated 17-4PH was analyzed by electron backscattered diffraction (EBSD) and transmission electron microscope (TEM). The relationship between microstructure and dynamic fracture behavior was investigated by performing instrumented impact test. Absorbed impact energies related to crack initiation, stable and unstable propagation were calculated and the dynamic J−R curves were estimated.The results demonstrate that as-built 17-4PH stainless steel mainly consists of coarse columnar δ ferrite grains growing along the building direction with <100> texture and fine martensitic grains with random orientation. A small amount of austinite can also be found in the as-built sample. As-built 17-4PH stainless steel displays low resistance to crack initiation and propagation, resulting in marginally rising J−R curve and quasi-cleavage fracture. After solution heat treatment, the retained ferrite transforms into martensite and microstructural anisotropy can be eliminated. The impact toughness is 1 times higher than that in as-built conditions and the dynamic J−R curve rises steeply, indicating superior dynamic mechanical properties. Fracture surfaces revealed that the inferior dynamic fracture toughness of as-built 17-4PH stainless steel can be attributed to the weak boundaries between the coarse δ ferrite grains and surrounding fine martensite grains.
-
Keywords:
- selective laser melting /
- stainless steel /
- microstructure /
- mechanical properties
-
-
表 1 17-4PH不锈钢粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 17-4PH stainless steel powder
C Cr Ni Cu Nb Si Mn N Fe 0.011 15.92 4.66 4.2 0.30 0.62 0.33 0.01 余量 表 2 示波冲击试验裂纹扩展不同阶段冲击吸收能量
Table 2 Absorbed impact energies associated with different stages of instrumented Charpy impact tests J
试样类型 裂纹萌生功Win 稳定扩展功Wstable 失稳扩展功Wunstable 总冲击吸收能量Wtotal 沉积态 4.81 ± 0.32 4.29 ± 0.45 4.74 ± 0.28 17.20 ± 1.01 固溶态 6.84 ± 0.46 15.59 ± 1.21 4.48 ± 0.36 34.86 ± 0.98 -
[1] Guennouni N, Barroux A, Grosjean C, et al. Comparative study of the microstructure between a laser beam melted 17-4PH stainless steel and its conventional counterpart[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2021, 823: 141718.
[2] 巴培培, 董志宏, 张炜, 等. 选区激光熔化成形12CrNi2合金钢的显微组织和力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(8): 8 − 17. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20210323003 Ba Peipei, Dong Zhihong, Zhang Wei, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 12CrNi2 alloy steel manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(8): 8 − 17. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20210323003
[3] 周博康, 魏正英, 李俊峰, 等. 90W-7Ni-3Fe激光选区熔化热行为及试验分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(11): 76 − 82. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200518002 Zhou Bokang, Wei Zhengying, Li Junfeng, et al. 90W-7Ni-3Fe selective laser melting heat behavior analysis and experimental research[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(11): 76 − 82. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200518002
[4] 尹燕, 刘鹏宇, 路超, 等. 选区激光熔化成形316L不锈钢微观组织及拉伸性能分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(8): 77 − 81. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390205 Yin Yan, Liu Pengyu, Lu Chao, et al. Microstructure and tensile properties of selective laser melting forming 316L stainless steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(8): 77 − 81. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390205
[5] Rafi H K, Pal D, Patil N, et al. Microstructure and mechanical behavior of 17-4 precipitation hardenable steel processed by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23(12): 4421 − 4428. doi: 10.1007/s11665-014-1226-y
[6] Ponnusamy P, Sharma B, Masood S H, et al. A study of tensile behavior of SLM processed 17-4PH stainless steel[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2021, 45: 4531 − 4534. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.12.1104
[7] Alnajjar M, Christien F, Wolski K, et al. Evidence of austenite by-passing in a stainless steel obtained from laser melting additive manufacturing[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 25: 187 − 195. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2018.11.004
[8] Sabooni S, Chabok A, Feng S C, et al. Laser powder bed fusion of 17-4 PH stainless steel: a comparative study on the effect of heat treatment on the microstructure evolution and mechanical properties[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 46: 102176. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2021.102176
[9] Lobodyuk V A, Meshkov Yu Ya, Pereloma E V. On tetragonality of the martensite crystal lattice in steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2019, 50(1): 97 − 103. doi: 10.1007/s11661-018-4999-z
[10] Ryde L. Application of EBSD to analysis of microstructures in commercial steels[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2006, 22(11): 1297 − 1306. doi: 10.1179/174328406X130948
[11] Baek M-S, Kim K-S, Park T-W, et al. Quantitative phase analysis of martensite-bainite steel using EBSD and its microstructure, tensile and high-cycle fatigue behaviors[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2020, 785: 139375. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.139375
[12] Chang Y, Lin M, Hangen U, et al. Revealing the relation between microstructural heterogeneities and local mechanical properties of complex-phase steel by correlative electron microscopy and nanoindentation characterization[J]. Materials & Design, 2021, 203: 109620.
[13] Murr L E, Martinez E, Hernandez J, et al. Microstructures and properties of 17-4 PH stainless steel fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2012, 1(3): 167 − 177. doi: 10.1016/S2238-7854(12)70029-7
[14] Hooper P A. Melt Pool Temperature and cooling rates in laser powder bed fusion[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2018, 22: 548 − 559. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2018.05.032
[15] Alexopoulos N D, Stylianos A. Impact mechanical behaviour of Al-7Si-Mg (A357) cast aluminum alloy. The effect of artificial aging[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2011, 528(19-20): 6303 − 6312.
[16] Alexopoulos N D, Stylianos A, Campbell J. Dynamic fracture toughness of Al-7Si-Mg (A357) aluminum alloy[J]. Mechanics of Materials, 2013, 58(2): 55 − 68. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmat.2012.11.005
[17] 马力深, 钟约先, 马庆贤, 等. δ铁素体对12%Cr超超临界转子钢冲击性能的影响[J]. 清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 48(11): 1887 − 1890. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2008.11.004 Ma Lishen, Zhong Yuexian, Ma Qingxian, et al. Effect of δ-ferrite on impact properties of 12%Cr rotor steel for ultra-supercritical steam conditions[J]. Journal of Tsinghua University (Science and Technology), 2008, 48(11): 1887 − 1890. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0054.2008.11.004
[18] Toshiro K, Isamu Y, Mitsuo N. Evaluation of dynamic fracture toughness parameters by instrumented charpy impact test[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 1986, 24(5): 773 − 782. doi: 10.1016/0013-7944(86)90249-3
[19] Lin Y, Yu Q, Pan J, et al. On the impact toughness of gradient-structured metals[J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 193: 125 − 137. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.04.027
[20] Tronskar J P, Mannan M A, Lai M O. Measurement of fracture initiation toughness and crack resistance in instrumented charpy impact testing[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2002, 69(3): 321 − 338. doi: 10.1016/S0013-7944(01)00077-7
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 邹阳,魏巍,范悦,王泽震,王强,赵亮. 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊工艺研究进展. 热加工工艺. 2024(03): 7-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈平. 2系铝合金的搅拌摩擦焊接接头微观组织与力学性能研究. 北京印刷学院学报. 2024(03): 32-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王浡婳,张立杰. 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头微观组织和力学性能分析. 精密成形工程. 2023(01): 94-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 许辉,刘宽,徐耀钟,于文凯,刘婷,王笑含,徐雪华. 2A14铝合金FSW焊缝背部线状缺陷返修工艺. 电焊机. 2023(03): 117-123 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马领航,李波,赵彦广,宋建岭,高世康,李雨,许子彦,周利. 火箭贮箱焊接缺陷修复技术研究现状. 电焊机. 2023(03): 31-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 李晓华,齐影,郑瑞娟,武媛,祝弘滨,崔雷. QT400球墨铸铁摩擦塞焊接头的微观组织和力学性能研究. 热加工工艺. 2023(05): 141-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 鲁克锋,殷凤仕,王文宇,滕涛,樊世冲,刘亚凡,王鸿琪,朱建,任智强. 铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头缺陷及焊件结构问题控制策略的研究进展. 表面技术. 2023(07): 55-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 丁清伟,汪春能,眭怀明,赵引红,陈冬梅. 铝合金机匣预埋管处渗漏机理分析及解决措施. 铸造技术. 2023(09): 873-876 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李德福,王希靖. 6082铝合金摩擦塞补焊接头焊核区晶体特征. 兰州理工大学学报. 2022(03): 7-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 高彦军,刘西伟,刘旭升,邵震,崔雷. 2060-T8铝锂合金顶锻式摩擦塞补焊接头组织性能研究. 电焊机. 2022(07): 69-75+99 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 赵慧慧,高焓,胡蓝,董吉义,尹玉环,崔雷. 2219铝合金薄板拉拔式摩擦塞焊工艺及力学性能优化. 焊接. 2021(06): 48-55+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 胡永鹅,龙琼,韩兴科,何波,王尧,杨秀芳. 铝合金材料焊接方法研究进展. 贵州农机化. 2020(03): 15-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)



 下载:
下载: