Effect of element distribution on the microstructure of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy coating
-
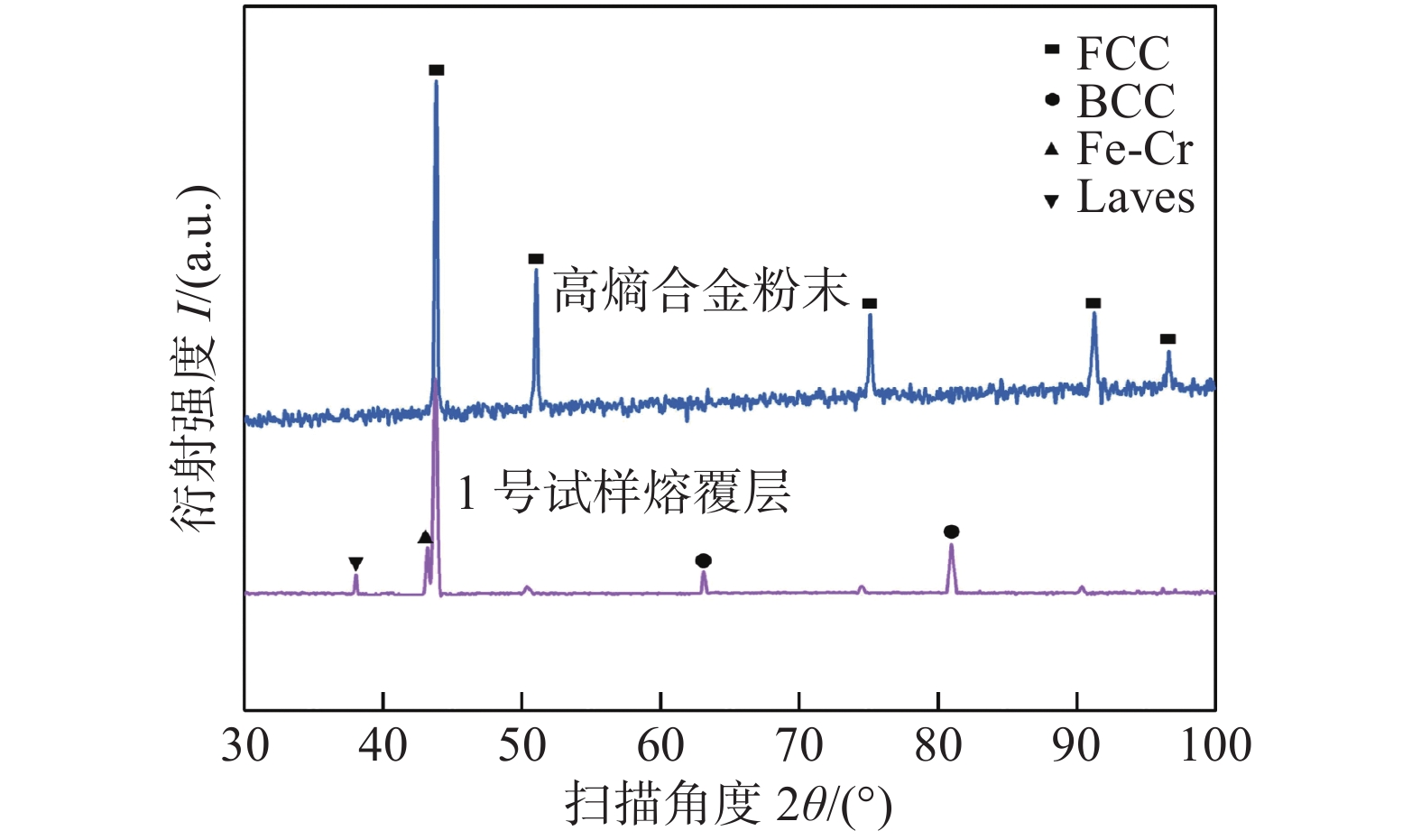
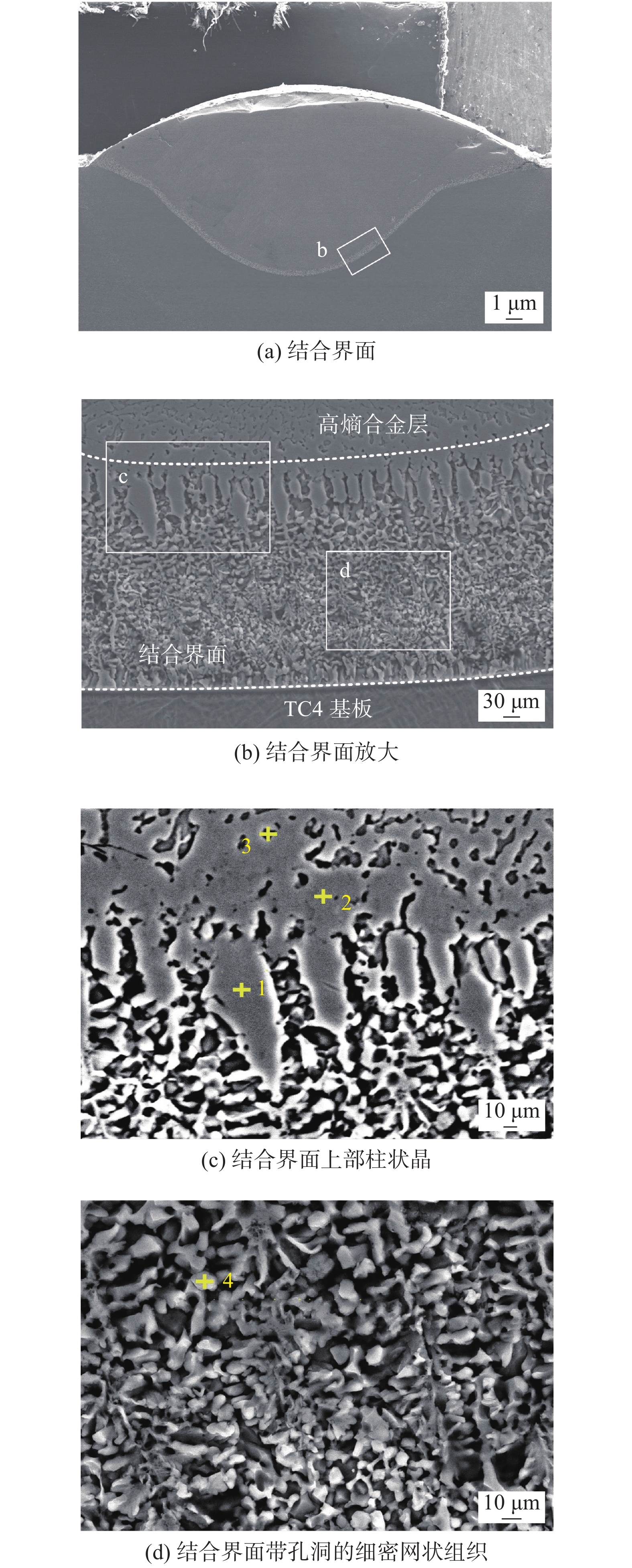
摘要: 聚焦于激光熔覆高熵合金表面强化技术,开展了6 mm厚TC4钛合金板材表面激光熔覆FeCoCrNi高熵合金涂层的研究. 首先通过X射线衍射(XRD)对FeCoCrNi高熵合金熔覆层进行物相分析,探究其相组成. 随后,利用金相显微镜和场发射扫描电子显微镜表征手段,探究了熔覆层以及其与TC4基体结合界面处的微观组织形态及物相分布. 结果表明,Ti,Ni组合和Ti,Co组合具有最大的负混合焓(∆Hmix),因此易造成部分物相中(Ti,Ni,Co)的富集,而其周围相中则会呈现出(Fe,Cr)的富集. 结合界面上部和下部主要由灰色的柱状晶组成,中部区域主要由白色网状组织和灰色收缩孔洞组成.Abstract: Laser cladding of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy coating on the surface of 6 mm thick TC4 titanium plate was studied by focusing on the surface strengthening technology of laser cladding high entropy alloy. Firstly, the phase analysis of the FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy cladding layer was carried out by X-ray diffraction to explore its phase composition. Then, the microstructure and phase distribution of the cladding layer and its interface with TC4 substrate were investigated by metallographical microscope and field emission scanning electron microscope. The results show that Ti and Ni, Ti and Co have the most significant negative mixing enthalpy (∆Hmix), so it is easy to cause the enrichment of (Ti, Ni, Co) in some phases, and the enrichment of (Fe, Cr) in the surrounding phases. The upper and lower part of the bonding interface is mainly composed of gray columnar grains, and the middle part is mainly composed of white reticulum structure and gray shrinkage cavity.
-
Keywords:
- TC4 titanium alloy /
- high entropy alloy /
- laser cladding /
- element distribution /
- microstructure
-
-
表 1 TC4基体的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of TC4 substrate
Fe Ti Al V $\leqslant $ 0.15余量 6.04 3.71 表 2 FeCoCrNi高熵合金粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical compositions of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy
Fe Co Cr Ni 24.44 26.18 22.43 余量 表 3 FeCoCrNi高熵合金激光熔覆试验工艺参数
Table 3 Experimental process parameters of FeCoCrNi high entropy alloy during laser cladding
试样
编号激光功率
P/W扫描速度
V/(mm·s−1)热输入
E/(J·mm−2)预铺层厚度
D(mm)1 800 10 40 0.5 2 900 12 37.5 1 3 900 10 45 1 表 4 熔覆层与TC4基体结合界面微观组织的元素分布(质量分数,%)
Table 4 Elements distribution of microstructure at the bonding interface of cladding layer and TC4 substrate
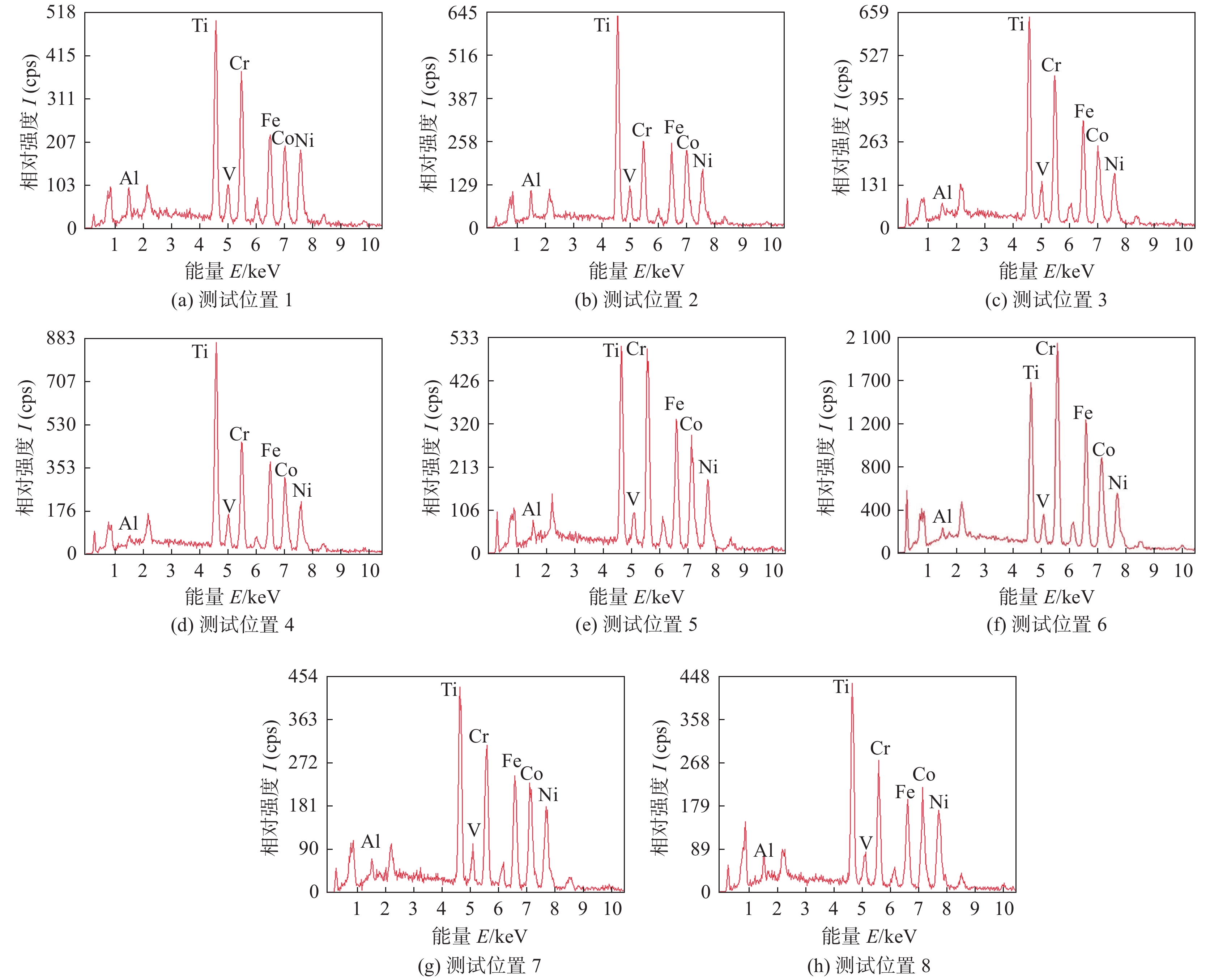
测试位置 Fe Co Cr Ni Ti Al V 1 11.61 11.43 10.57 9.36 50.63 3.52 2.85 2 9.09 12.59 8.49 11.86 52.44 3.06 2.46 3 13.96 10.07 20.11 6.78 43.09 2.56 3.42 4 3.68 3.20 53.88 5.31 30.29 2.18 1.95 -
[1] 刘世锋, 宋玺, 薛彤, 等. 钛合金及钛基复合材料在航空航天的应用和发展[J]. 航空材料学报, 2020, 40(3): 77 − 94. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000061 Liu Shifeng, Song Xi, Xue Tong, et al. Application and development of titanium alloy and titanium matrix composites in aerospace field[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2020, 40(3): 77 − 94. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1005-5053.2020.000061
[2] 张天刚, 孙荣禄. Ti811 合金表面 TC4 激光熔覆层微观组织及性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(4): 41 − 45. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400097 Zhang Tiangang, Sun Ronglu. Microstructure and properties of TC4 laser cladding coating on Ti811 titanium alloy surface[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(4): 41 − 45. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400097
[3] Yeh J, Chen S, Lin S, et al. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: novel alloy design concepts and outcomes[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2004, 6(5): 299 − 303. doi: 10.1002/adem.200300567
[4] Chookajorn T, Murdoch H A, Schuh C A. Design of stable nanocrystalline alloys[J]. Science, 2012, 337(6097): 951 − 954. doi: 10.1126/science.1224737
[5] Ma Y, Wang Q, Jiang B, et al. Controlled formation of coherent cuboidal nanoprecipitates in body-centered cubic high-entropy alloys based on Al2(Ni, Co, Fe, Cr)14 compositions[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 147: 213 − 225. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2018.01.050
[6] 赵盛举, 祁文军, 黄艳华, 等. TC4激光熔覆NiCrCoAlY热循环特性及组织性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(9): 89 − 96. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200521001 Zhao Shengju, Qi Wenjun, Huang Yanhua, et al. Research on thermal cycle characteristics and microstructure performance of TC4 laser cladding NiCrCoAlY[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(9): 89 − 96. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200521001
[7] Guo S, Hu Q, Ng C, et al. More than entropy in high-entropy alloys: Forming solid solutions or amorphous phase[J]. Intermetallics, 2013, 41: 96 − 103. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2013.05.002
[8] Cai Y, Chen Y, Manladan S M, et al. Influence of dilution rate on the microstructure and properties of FeCrCoNi high-entropy alloy coating[J]. Materials & Design, 2018, 142: 124 − 137.
[9] Guo S, Ng C, Lu J, et al. Effect of valence electron concentration on stability of fcc or bcc phase in high entropy alloys[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(10): 103505. doi: 10.1063/1.3587228
[10] Kube S A, Sohn S, Uhl D, et al. Phase selection motifs in High Entropy Alloys revealed through combinatorial methods: Large atomic size difference favors BCC over FCC[J]. Acta Materialia, 2019, 166: 677 − 686. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2019.01.023
[11] Cieslak J, Tobola J, Berent K, et al. Phase composition of AlxFeNiCrCo high entropy alloys prepared by sintering and arc-melting methods[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 740: 264 − 272. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.12.333
[12] 齐超琪. TC4表面激光熔覆FeCoCrNi高熵合金组织与性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2020. Qi, Chaoqi. Microstructure and Properties of Laser Cladded FeCoCrNi High-entropy Alloy on TC4 Surface[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020.




 下载:
下载: