Effect of process parameters on welding fume of self-shielded flux cored wire
-
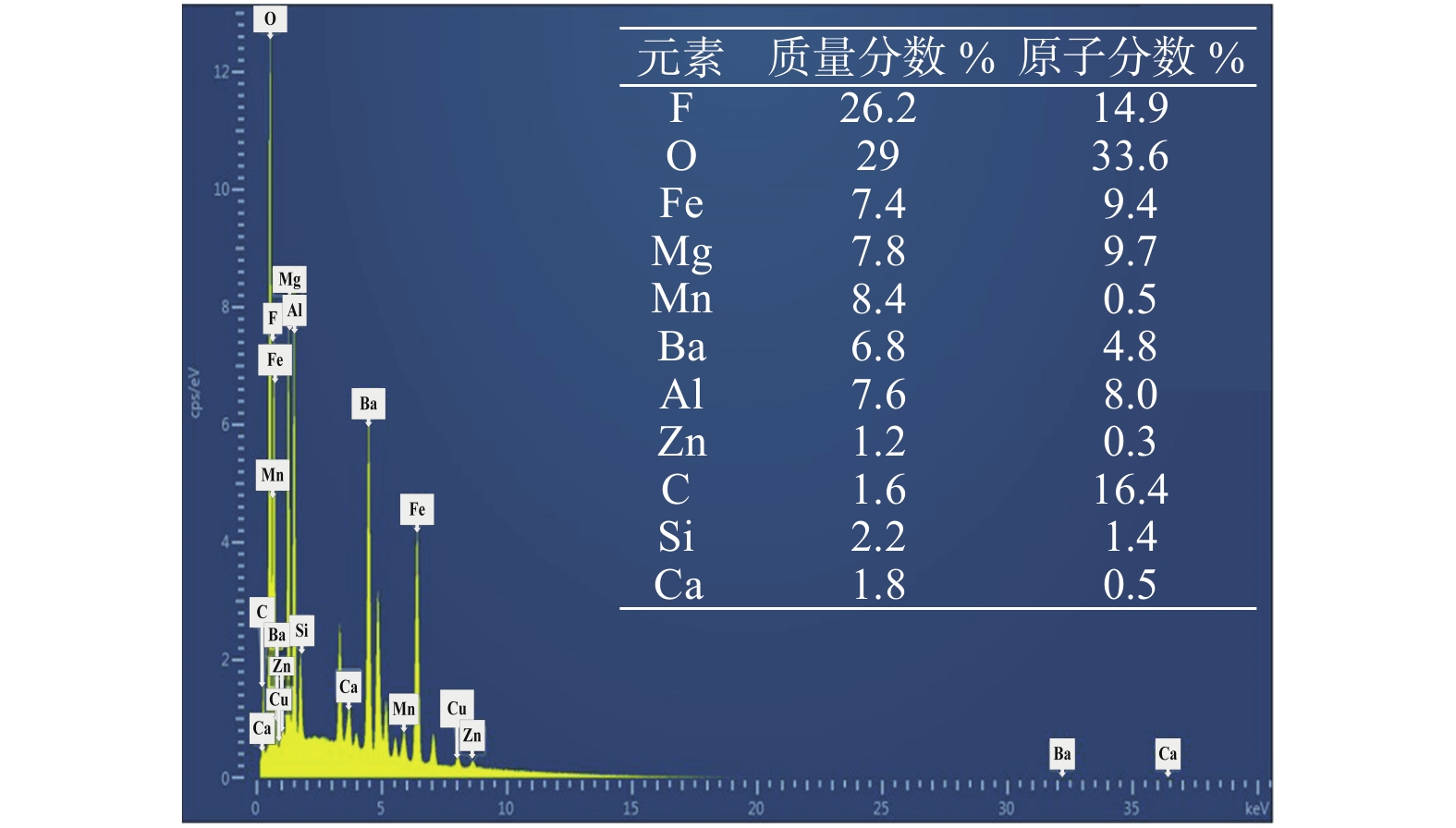
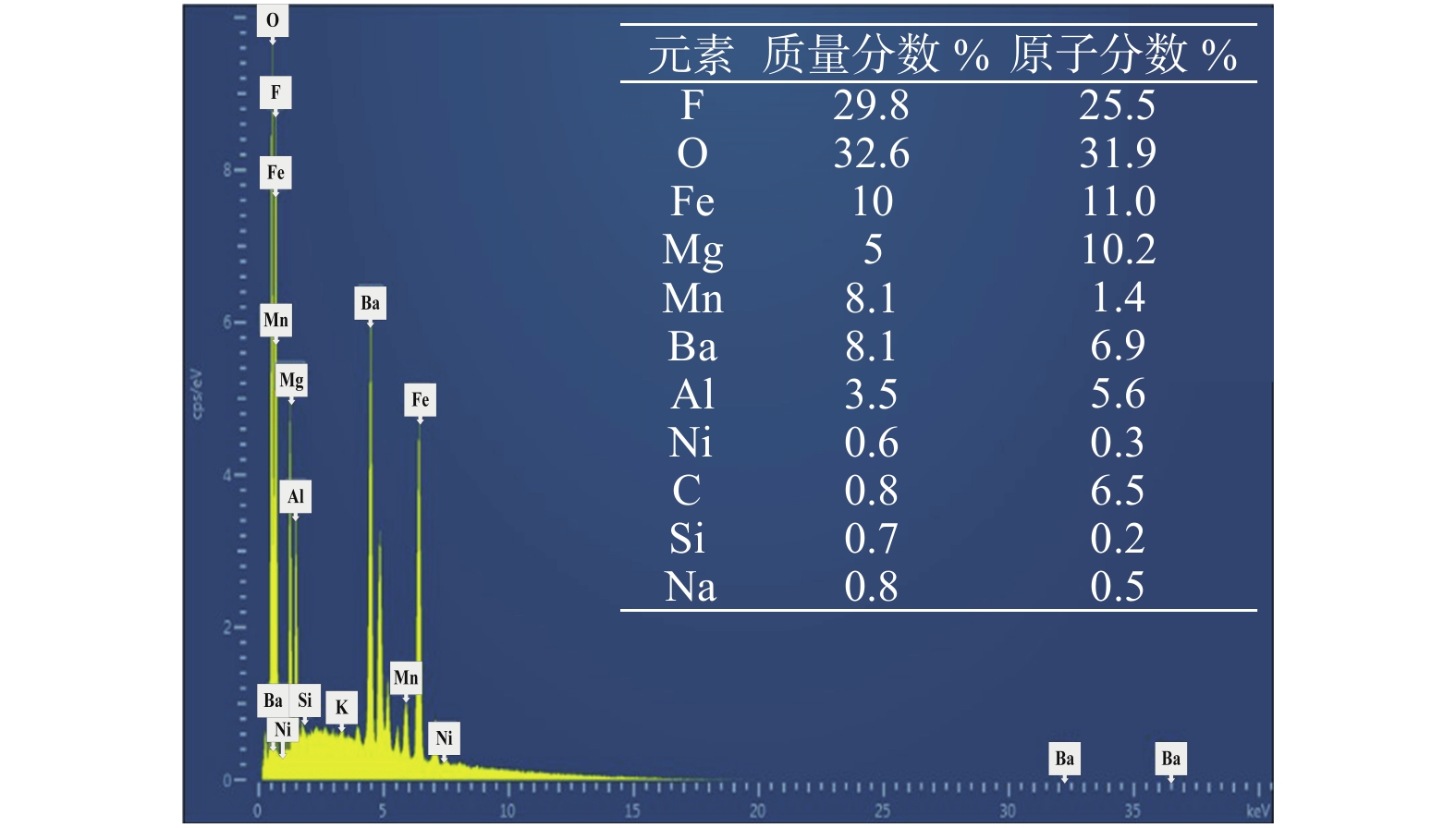
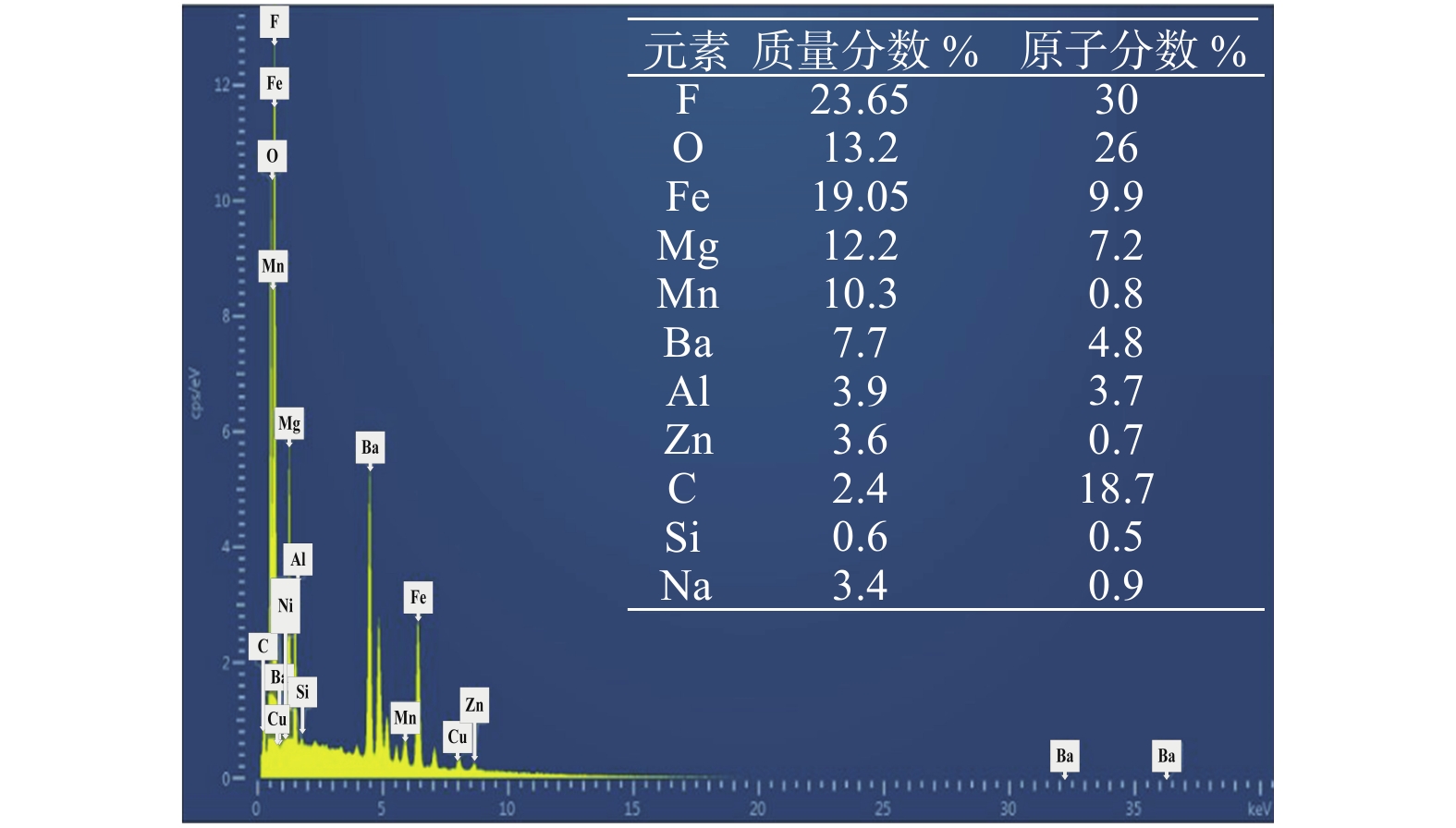
摘要: 焊接烟尘中含有大量有害物质,严重威胁到焊工的身体健康,所以针对焊接烟尘的研究具有十分重要的意义. 通过高速摄像采集系统研究了焊接时熔滴的过渡模式,通过焊接烟尘收集装置对焊接烟尘的发尘量进行测量,对不同工艺参数下产生的焊接烟尘进行了成分分析. 结果表明,在大的电参数下,熔滴过渡模式对烟尘的发尘量影响不大,但过大的热输入导致了熔滴、母材的蒸发量和焊接烟尘的增加,直流反接下,熔滴过渡主要表现为排斥过渡,出现较多的焊接飞溅颗粒,导致直流反接时的焊接烟尘增多. 不同的极性规范下,烟尘的元素类型基本一致. 由于在直流反接时,更多的低电离物质在熔滴底部燃烧蒸发,导致低电离物质元素含量相比于直流正接时较多. 而在直流正接时,阴极斑点总在氧化膜处进行燃烧,导致更多的氧化物元素蒸发,形成焊接烟尘. 因此,直流正接下氧化物元素含量比直流反接下的元素含量多.Abstract: there were a lot of harmful substances in welding fumes, and it seriously threaten the health of welders, therefore, it was significant to study welding fume. In this paper, the droplet transfer mode was captured by high-speed camera. At the same time, the fume generated in the welding process was collected by the collection device. The amounts of fumes were measured next, and the composition of welding fumes in different parameters were analyzed by EDS. The results showed that the droplet transfer mode has little effect on the amounts of fumes generated under large electrical parameters, which is mainly due to the excessive heat input, it leaded to the increase of droplet and base metal evaporation and become the main reason for the increase of fumes. Under the direct current electrode positive (DCEP), the droplet mainly performed globular repelled transfer and there was more welding spatter, it caused the welding fume increases. In addition, the element types in fumes were basically the same for different polarity specifications. However, due to the combustion and evaporation of more low ionized substances at the bottom of the droplet during DCEP, the element content of low ionized substances was more than that under direct current electrode positive (DCEN). Otherwise, the cathode spots always located at the oxide film under DCEN, which causes more oxide elements to evaporate and form fumes. Finally, the content of oxide elements under DCEN was higher than that under the DCEP.
-
-
表 1 母材成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Base material composition
母材 C Mn Si S P Fe Q235 0.14 ~ 0.22 0.30 ~ 0.65 ≤ 0.30 ≤ 0.05 ≤ 0.045 余量 表 2 直径1.0 mm自保护药芯焊丝的焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding process parameters of 1.0 mm diameter self-shielded flux cored wire
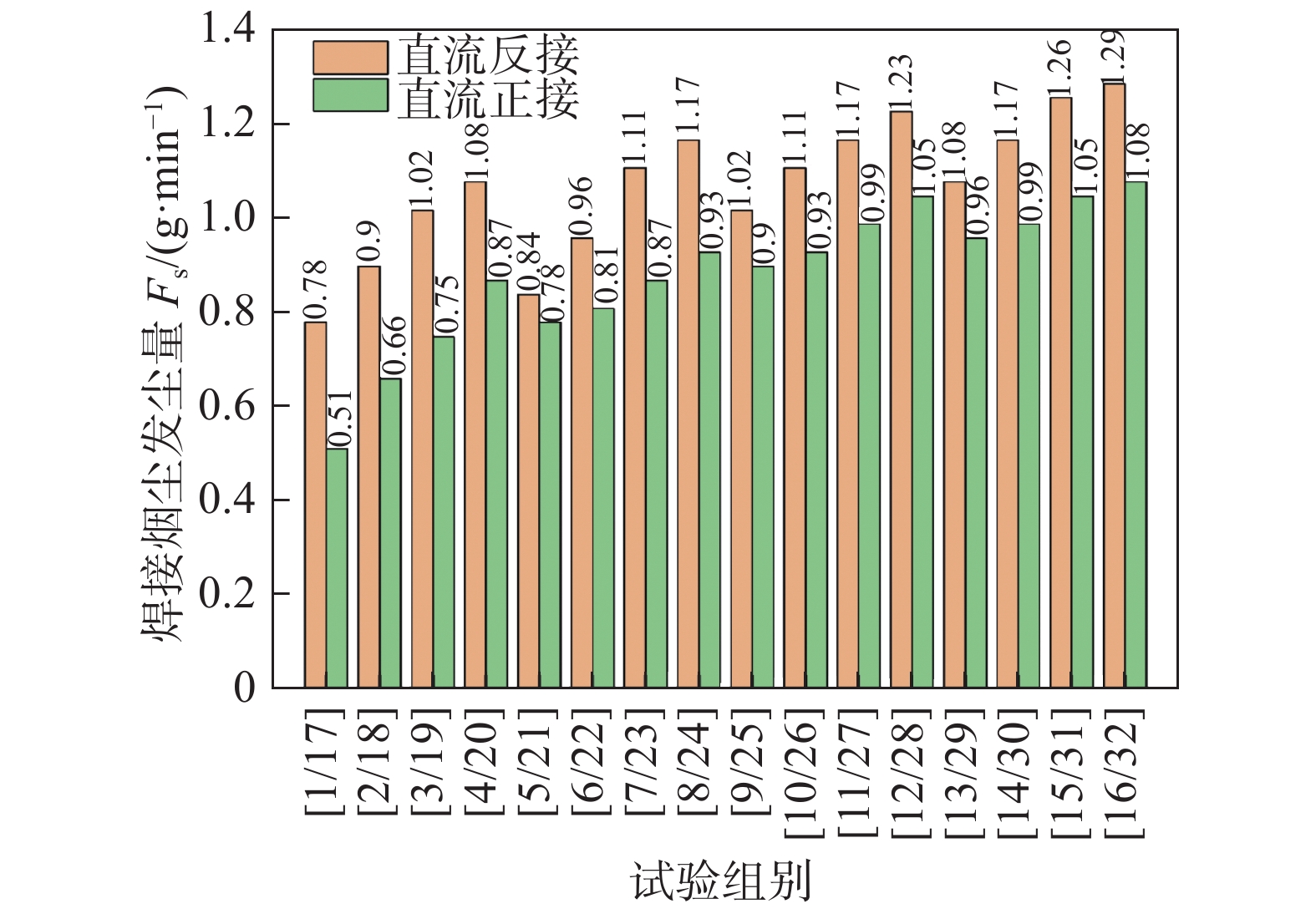
序
号电压
U/V电流
I/A焊接速度
v/(cm·min−1)熔滴过渡
模式焊接时
间t/s烟尘质
量m/g发尘量
Fs/(g·min−1)序
号电压
U/V电流
I/A焊接速度
v/(cm·min−1)熔滴过渡
模式焊接时
间t/s烟尘质
量m/g发尘量
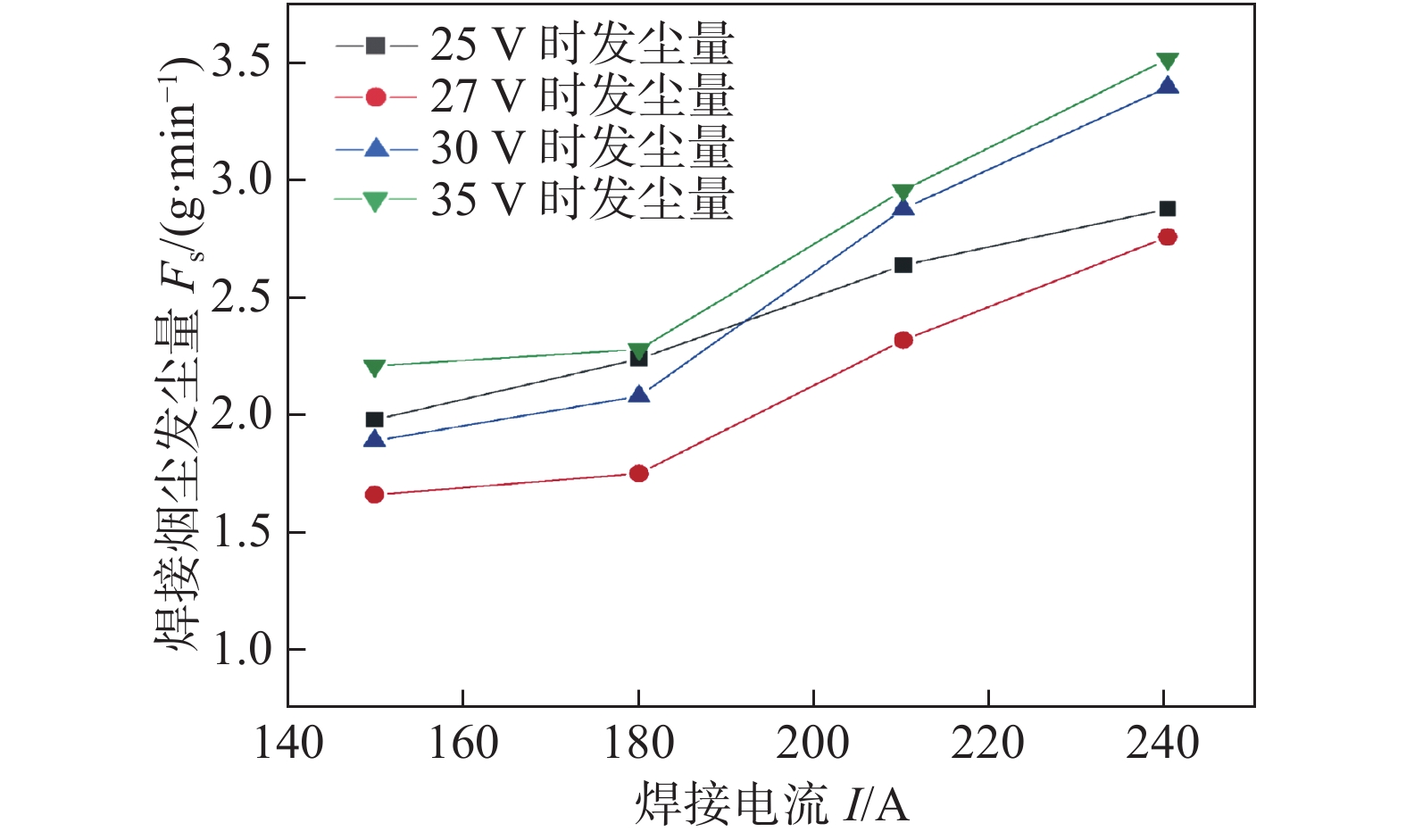
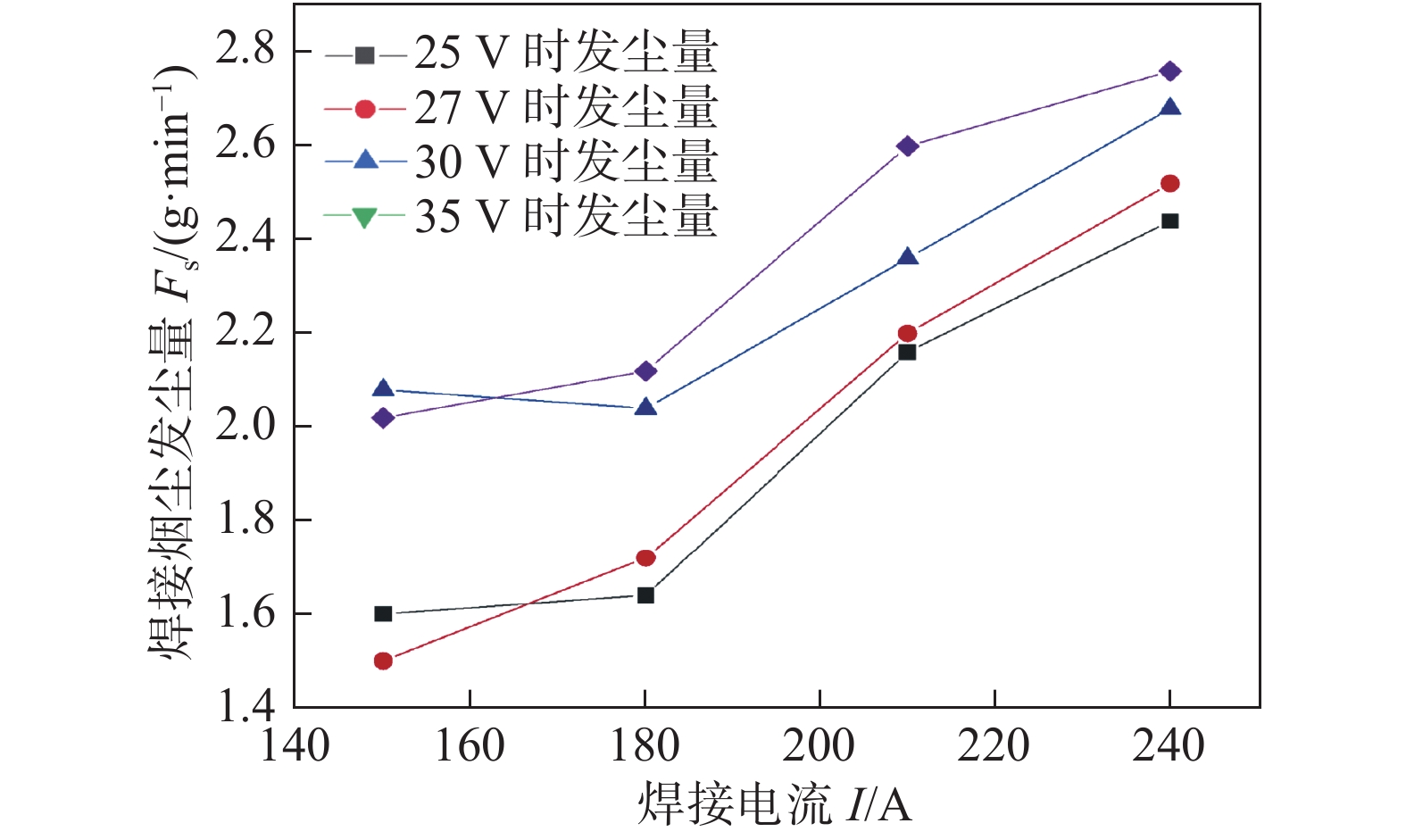
Fs/(g·min−1)1 25 120 150 排斥过渡 30 0.26 0.78 17 25 120 150 射滴过渡 30 0.17 0.51 2 25 140 175 排斥过渡 30 0.3 0.9 18 25 140 175 射滴过渡 30 0.22 0.66 3 25 160 200 排斥过渡 30 0.34 1.02 19 25 160 200 射滴过渡 30 0.25 0.75 4 25 180 250 排斥过渡 30 0.36 1.08 20 25 180 250 射滴过渡 30 0.29 0.87 5 27 120 150 排斥过渡 30 0.28 0.84 21 27 120 150 射滴过渡 30 0.26 0.78 6 27 140 175 排斥过渡 30 0.32 0.96 22 27 140 175 射滴过渡 30 0.27 0.81 7 27 160 200 排斥过渡 30 0.37 1.11 23 27 160 200 射滴过渡 30 0.29 0.87 8 27 180 250 排斥过渡 30 0.39 1.17 24 27 180 250 射滴过渡 30 0.31 0.93 9 30 120 150 排斥过渡 30 0.34 1.02 25 30 120 150 射滴过渡 30 0.3 0.9 10 30 140 175 排斥过渡 30 0.37 1.11 26 30 140 175 射滴过渡 30 0.31 0.93 11 30 160 200 排斥过渡 30 0.39 1.17 27 30 160 200 射滴过渡 30 0.33 0.99 12 30 180 250 排斥过渡 30 0.41 1.23 28 30 180 250 射滴过渡 30 0.35 1.05 13 32 120 150 排斥过渡 30 0.36 1.08 29 32 120 150 射滴过渡 30 0.32 0.96 14 32 140 175 排斥过渡 30 0.39 1.17 30 32 140 175 射滴过渡 30 0.33 0.99 15 32 160 200 排斥过渡 30 0.42 1.26 31 32 160 200 射滴过渡 30 0.35 1.05 16 32 180 250 排斥过渡 30 0.43 1.29 32 32 180 250 射滴过渡 30 0.36 1.08 表 3 直径2.0 mm自保护药芯焊丝的焊接工艺参数
Table 3 Welding process parameters of 2.0 mm diameter self-shielded flux cored wire
序
号电压
U/V电流
I/A焊接速度
v/(cm·min−1)熔滴过渡
模式焊接时
间t/s烟尘质
量m/g发尘量
Fs/(g·min−1)序
号电压
U/V电流
I/A焊接速度
v/(cm·min−1)熔滴过渡
模式焊接时
间t/s烟尘质
量m/g发尘量
Fs/(g·min−1)1 25 150 80 渣柱过渡 15 0.495 1.98 17 25 150 80 渣柱过渡 15 0.4 1.6 2 25 180 100 排斥过渡 15 0.42 1.68 18 25 180 100 射滴过渡 15 0.41 1.64 3 25 210 150 排斥过渡 15 0.56 2.24 19 25 210 150 射滴过渡 15 0.54 2.16 4 25 240 200 短路过渡 15 0.66 2.64 20 25 240 200 射滴过渡 15 0.61 2.44 5 27 150 80 排斥过渡 15 0.38 1.66 21 27 150 80 射滴过渡 15 0.375 1.5 6 27 180 100 排斥过渡 15 0.44 1.75 22 27 180 100 射滴过渡 15 0.43 1.72 7 27 210 150 排斥过渡 15 0.58 2.32 23 27 210 150 射滴过渡 15 0.55 2.2 8 27 240 200 排斥过渡 15 0.69 2.76 24 27 240 200 射滴过渡 15 0.63 2.52 9 30 150 80 排斥过渡 15 0.47 1.89 25 30 150 80 射滴过渡 15 0.52 2.08 10 30 180 100 排斥过渡 15 0.52 2.08 26 30 180 100 射滴过渡 15 0.51 2.04 11 30 210 150 排斥过渡 15 0.72 2.88 27 30 210 150 射滴过渡 15 0.59 2.36 12 30 240 200 排斥过渡 15 0.85 3.4 28 30 240 200 射滴过渡 15 0.67 2.68 13 35 150 80 排斥过渡 15 0.53 2.11 29 35 150 80 射滴过渡 15 0.505 2.02 14 35 180 100 排斥过渡 15 0.57 2.28 30 35 180 100 射滴过渡 15 0.53 2.12 15 35 210 150 排斥过渡 15 0.74 2.96 31 35 210 150 射滴过渡 15 0.65 2.6 16 35 240 200 排斥过渡 15 0.88 3.52 32 35 240 200 射滴过渡 15 0.69 2.76 -
[1] Zeidler-Erdely P C, Falcone L M, Antonini J M. Influence of welding fume metal composition on lung toxicity and tumor formation in experimental animal models[J]. Journal of Occupational and Environmental Hygiene, 2019, 16(6): 372 − 377.
[2] 李桓, 曹文山, 陈邦固, 等. 气保护药芯焊丝熔滴过渡的形式及特点[J]. 焊接学报, 2000, 21(1): 13 − 16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2000.01.006 Li Huan, Cao Wenshan, Chen Banggu, et al. Metal transfer of gas shielded flux cored wire and its characteristics[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2000, 21(1): 13 − 16. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2000.01.006
[3] 肖诗祥, 施雨湘, 杨世柏. 焊接烟尘的扩散特性[J]. 武汉交通科技大学学报, 1997(4): 40 − 44. Xiao Shixiang, Shi Yuxiang, Yang Shibo. Diffusion character of welding aerosol[J]. Journal of Wuhan Transportation University, 1997(4): 40 − 44.
[4] McCarrick S, Wei Z, Moelijker N, et al. High variability in toxicity of welding fume nanoparticles from stainless steel in lung cells and reporter cell lines: the role of particle reactivity and solubility[J]. Nanotoxicology, 2019, 13(10): 1293 − 1309. doi: 10.1080/17435390.2019.1650972
[5] Yang L, Wang Y, Sun T, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of FCTIG-welded DH36 steel with rutile-type and basic-type flux cored wires[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 275: 116363. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116363
[6] 许芙蓉. GMA焊接工艺参数对焊接烟尘产生影响的研究[D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2008. Xu Furong. Effect of GMA Welding process parameters on welding fume [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2008.
[7] Castner H R. Gas metal arc welding fume generation using pulsed current[R]. Miami: American Welding Society, 1994.
[8] Jenkins N T, Eagar T W. Chemical analysis of welding fume particles[J]. Welding Journal, 2005, 84(6): 87.
[9] Vishnyakov V I, Kiro S A, Oprya M V, et al. Effects of shielding gas temperature and flow rate on the welding fume particle size distribution[J]. Journal of Aerosol Science, 2017, 114: 55 − 61. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2017.09.010
[10] 黄勇, 张佳杰, 冉小龙, 等. 环保焊枪吸烟对小电流CO2气体保护电弧焊的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(12): 68 − 72. Huang Yong, Zhang Jiajie, Ran Xiaolong, et al. Influence of environmental protection welding gun smoking on low current CO2 gas shielded arc welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(12): 68 − 72.
[11] 蒋仲安, 兰桂, 彭亚. 焊接车间多尘源粉尘分布数学模型和验证[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(4): 67 − 72. Jiang Zhong'an, Lan Gui, Peng Ya. Mathematical model and verification of dust distribution in welding workshop[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(4): 67 − 72.
[12] Wang Shenglin, Cui Li, He Dingyong, et al. Effect of molybdenum on the microstructure and wear resistance of hypoeutectic Fe-Cr-B-C hardfacing alloys[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(4): 46 − 51.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 周浩南,孙文磊,王伟,张志虎. 面向涂层裂纹的激光熔覆预测模型研究. 热加工工艺. 2024(14): 27-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑世茂,刘玉国,王豪,王新佩,陈洪堂. 长直焊缝自动焊接设备研究. 南方农机. 2023(10): 127-128+154 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王颖,高胜,吴立明. 基于胶囊网络的TIG熔透预测. 焊接. 2023(04): 15-20+28 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 黄威威,游德勇,高向东,张艳喜,黄宇辉. 基于相关分析和神经网络的激光焊接稳态识别. 激光技术. 2022(03): 312-319 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴月玉,张弓,林群煦,侯至丞,杨文林. 机器人TIG焊接的焊缝形貌遗传神经网络预测. 制造业自动化. 2022(07): 86-90 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘秀航,黄宇辉,张艳喜,高向东. 基于BP神经网络补偿卡尔曼滤波的激光-MIG复合焊缝熔宽在线检测. 中国激光. 2022(16): 115-121 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陶永,兰江波,任帆,王田苗,江山,高赫,温宇方. 基于自适应模糊神经网络的机器人焊接焊缝外形预测方法. 计算机集成制造系统. 2022(11): 3643-3651 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘天元,鲍劲松,汪俊亮,顾俊. 融合时序信息的激光焊接熔透状态识别方法. 中国激光. 2021(06): 228-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 吴月玉,张弓,林群煦,侯至丞,杨文林,刘胜祥,徐群华,张雨航. 焊接机器人特征参数预测方法的研究综述与展望. 机床与液压. 2021(15): 168-173+199 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 成慧翔,马艳娥,李新卫. 基于改进神经网络的激光焊接偏差智能识别研究. 激光杂志. 2021(12): 165-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 火巧英,闫海宁,涂本荣,陆安进. 焊接工艺参数对Q345NQR2耐候钢激光焊焊缝成形的影响. 焊接技术. 2020(08): 16-18+105-106 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 范鹏飞,张冠. 基于线性回归和神经网络的金属陶瓷激光熔覆层形貌预测. 表面技术. 2019(12): 353-359+368 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)




 下载:
下载: