Progress and trends towards visual perception technologies in intelligent robotic welding
-
摘要:
智能化焊接在推进“工业强基”工程、支撑国家建设及国防安全中起到重要作用,从重大装备到精细结构,焊接都是不可或缺的关键技术,而机器人作为智能化焊接的重要载体,推动“以机器代替人,以机器解放人”的过程中将发挥重要作用. 文中从焊接制造全流程的场景建模、焊接过程形性原位感知、自适应调控、工艺知识构建等关键技术出发,重点阐述了焊接机器人的“免示教”编程环境感知、点云配准、焊缝轨迹规划和焊道自适应编排等共性技术的研究现状,以智能化焊接制造过程多源信息监测及控制系统为例,提出了基于IIOT-MAS(industrial internet of things-multi-agent system)焊接制造系统分层结构模型,介绍了焊接多模态信息感知、融合及工艺知识建模等共性科学问题,并介绍了工程机械部件焊接现场感知数据在线学习和模型-数据双驱动的焊接质量评价模型典型案例,探讨了机器人焊接智能化的发展趋势和所面临的挑战.
Abstract:Intelligent welding is important in promoting the "industrial base strengthening" project, supporting national construction and defense security. From major equipment to fine structures, welding is an indispensable key technology. As an important carrier of intelligent welding, robots will play an important role in promoting "replacing people with machines and liberating people with machines." Starting from the key technical perspectives of scene modeling of the entire welding manufacturing process, in-situ perception of welding process shape, adaptive regulation, and process knowledge construction, this paper focuses on the research status of common technologies such as "teaching-free" programming environment perception, point cloud registration, weld trajectory planning, and weld adaptive arrangement of welding robots. Then, taking the multi-source information monitoring and control system of the intelligent welding manufacturing process as an example, a hierarchical structure model of a welding manufacturing system based on IIOT-MAS is proposed, and common scientific problems such as welding multimodal information perception, fusion, and process knowledge modeling are introduced. In addition, the paper introduces a typical case of online learning of on-site perception data of engineering machinery parts welding and a welding quality evaluation model driven by a model-data dual drive. In conclusion, we explore the current trends and obstacles in advancing intelligent robot welding.
-
Keywords:
- welding robot /
- intelligent welding /
- visual sensor /
- weld seam tracking /
- welding quality
-
-
图 1 基于激光视觉的机器人自主焊接关键技术[17]
Figure 1. Key technologies of autonomous robotic welding based on laser vision
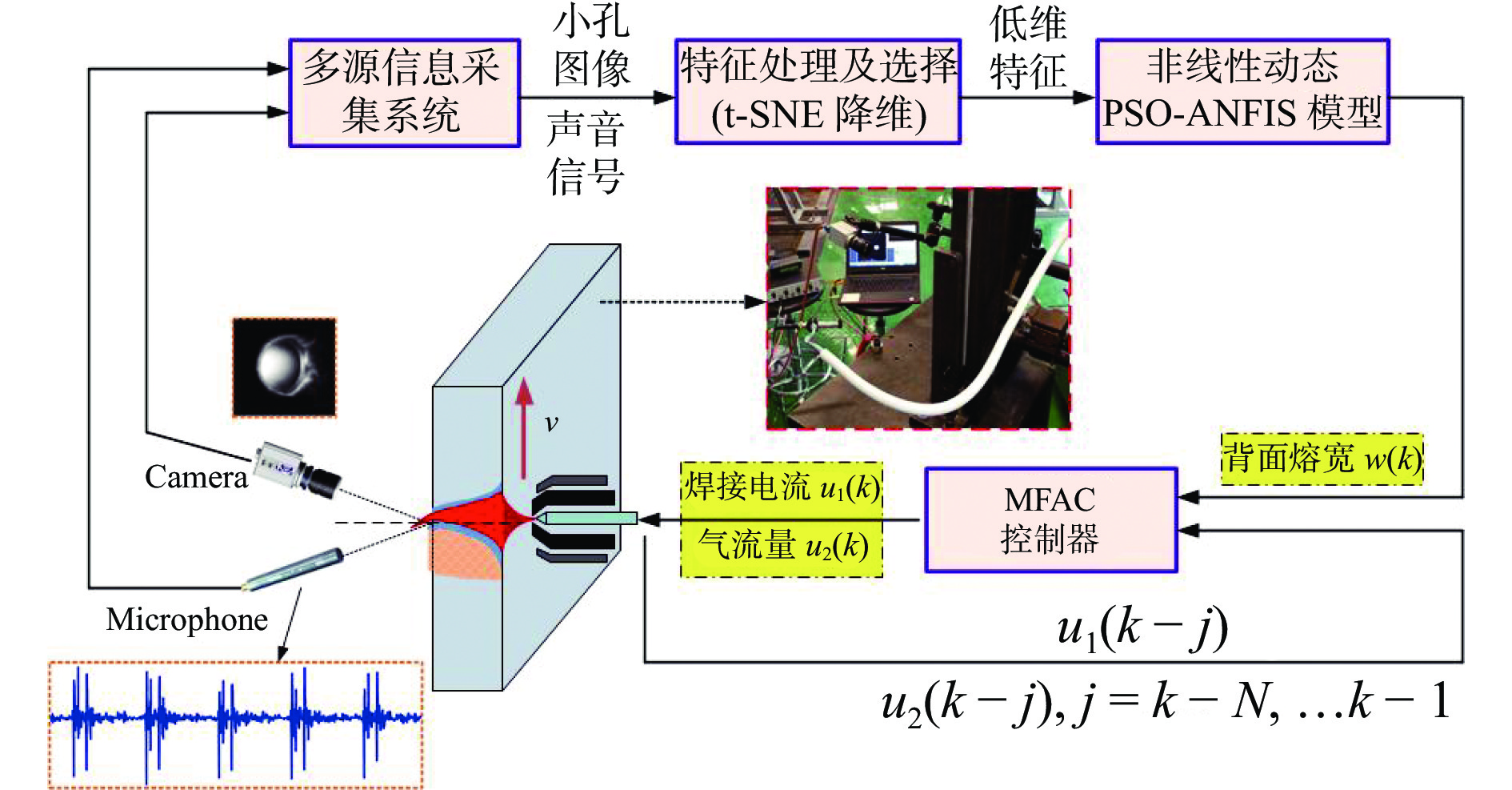
图 3 基于IOT-MAS的智能焊接制造系统[22]
Figure 3. Intelligent welding manufacturing system based on IOT-MAS
图 5 焊接HAZ高温应变视觉表征及残余应力计算[27]
Figure 5. Welding residual stress based on high temperature HAZ strain visualization
-
[1] 国家自然科学基金委员会 工程与材料科学部 机械工程学科发展战略报告[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. Department of Engineering and Materials Sciences, National Natural Science Foundation of China Engineering Mechanical Engineering Discipline Development Strategy Report[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2021.
[2] Zhou Ji, Zhou Yanhong, Wang Baicun, et al. Human-cyber-physical systems (HCPSs) in the context of new-generation intelligent manufacturing[J]. Engineering, 2019, 5: 624. doi: 10.1016/j.eng.2019.07.015
[3] 陈华斌, 陈善本. 复杂场景下的焊接智能制造中的信息感知与控制方法[J]. 金属学报, 2022, 58(4): 541 − 550. Chen Huabin, Chen Shanben. Key information perception and control Strategy of intelligent welding under complex scene[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2022, 58(4): 541 − 550.
[4] 国家制造强国建设战略咨询委员会. 中国制造2025蓝皮书[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2016. National Manufacturing Power Construction Strategy Advisory Committee. China manufacturing 2025 bluebook[M]. Beijing: Electronics Industry Press, 2016
[5] 林尚扬, 杨学勤, 徐爱杰, 等. 机器人智能化焊接技术发展综述及其在运载火箭贮箱中的应用[J]. 上海航天(中英文), 2021, 38(3): 8 − 17. Lin Shangyang, Yang Xueqin, Xu Aijie, et al. Recent advances in intelligentized robotic welding technologies and its application in launch vehicle tank[J]. Aerospace Shanghai, 2021, 38(3): 8 − 17.
[6] 王克鸿, 黄勇, 孙勇, 等. 数字化焊接技术研究现状与趋势[J]. 机械制造与自动化, 2015, 44(5): 1 − 6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5276.2015.05.001 Wang Kehong, Huang Yong, Sun Yong, et al. Research status and development of digital welding technology[J]. Machine Building & Automation, 2015, 44(5): 1 − 6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-5276.2015.05.001
[7] 张广军, 李永哲. 工业4.0语义下智能焊接技术发展综述[J]. 航空制造技术, 2016(11): 28 − 33. Zhang Guangjun, Li Yongzhe, Towards intelligent welding in the context of industry 4. 0[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2016(11): 28 − 33.
[8] 冯吉才. 中国焊接1994-2016[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2017. Feng Jicai. China Welding 1994-2016[M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2017.
[9] Liu T Y, Zheng P, Bao J S, et al. A state-of-the-art survey of welding radiographic image analysis: Challenges, technologies and applications[J]. Measurement, 2023, 214: 112821. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2023.112821
[10] 宋天虎, 刘永华, 陈树君. 关于机器人焊接技术的研发与应用之探讨[J]. 焊接, 2016(8): 1 − 10. Song Tianhu, Liu Yonghua, Chen shujun. Discussion on the development and application of robot welding technology[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016(8): 1 − 10.
[11] Song S, Chen H B, Lin T, et al. Penetration state recognition based on the double-sound-sources characteristic of VPPAW and hidden markov model[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2016, 234: 33 − 44. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.03.002
[12] Wu D, Huang Y M, Chen H B, et al. VPPAW penetration monitoring based on fusion of visual and acoustic signals using t-SNE and DBN model[J]. Materials and Design, 2017, 123: 1 − 14. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2017.03.033
[13] Huang H B, Hu M H, Xu A J, et al. In-situ strain measurement and error analysis of arc welding with 2D digital image correlation[J]. China Welding, 2022, 31(3): 17 − 23.
[14] Zhu K H, Wang Q Z, Chen W G, et al. Robotic MAG welding defects and quality assessment with a defect threshold decision model-driven method[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2025, 224: 112056. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2024.112056
[15] 王耀南, 江一鸣, 姜娇, 等. 机器人感知与控制关键技术及其智能制造应用[J]. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 494 − 513. Wang Yaonan, Jiang Yiming, Jiang Jiao, et al. Key technologies of robot perception and control and its intelligent manufacturing applications[J]. Acta automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 494 − 513.
[16] 王浩, 赵小辉, 徐龙哲, 等. 结构光视觉辅助焊接的轨迹识别与控制技术[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(6): 50 − 57. Wang Hao, Zhao Xiaohui, Xu Longzhe, et al. Research on trajectory recognition and control technology of structured light vision-assisted welding[J]. Transactions of the China welding institution, 2023, 44(6): 50 − 57.
[17] Xiao R Q, Xu Y L, Xu F J, et al. LSFP-Tracker: An autonomous laser stripe feature point extraction algorithm based on siamese network for robotic welding seam tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71: 1037 − 1048. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3243265
[18] Hou Z, Xu Y L, Xiao Runquan, et al. A teaching-free welding method based on laser visual sensing system in robotic GMAW[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 128: 2753 − 2762.
[19] Rao M Z, Liu K, Sheng Z X, et al. A novel filling strategy for robotic multi-layer and multi-pass welding based on point clouds for saddle-shaped weld seams[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2024, 121: 233 − 245. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2024.05.024
[20] Lu Y, Chen H B, Rao M Z, et al. A fast point cloud reconstruction algorithm for saddle-shaped weld seams in boiler header joints[M]. Singapore: Springer, 2022.
[21] Guo W X, Huang X K, Qi B W, Vision-guided path planning and joint configuration optimization for robot grinding of spatial surface weld beads via point cloud[J]. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2024, 61: 102465.
[22] 陈超. 基于IOT与MAS结构的智能化焊接制造过程监控及系统研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2021. Chen Chao, Research on monitoring of intelligent welding manufacturing process and systems based on IOT and MAS structure[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2021.
[23] Chen S B, Lü N. Research evolution on intelligentized technologies for arc welding process[J]. Journal of manufacturing processes, 2014, 2014,16(1): 109 − 122.
[24] Chen Z Y, Chen J, Feng Z. Welding penetration prediction with passive vision system[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 36: 224 − 230. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.10.009
[25] Zhang K, Zhang Y M, Chen J S, et al. Observation and analysis of Three-Dimensional weld pool oscillation dynamic behaviors a sensor was used to observe weld pool oscillation in three dimensions, and then the 3D data was used to analyze the oscillation behaviors[J]. Welding Journal, 2017, 96: 143s − 153s.
[26] Cheng Y C, Wang Q Y, Jiao W H, et al. Detecting dynamic development of weld pool using machine learning from innovative composite images for adaptive welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 56: 908 − 915.
[27] Chen H B, Song Y L, Chen X Q, et al. In-situ studies of full-field residual stress mapping of SS304 stainless steel welds using DIC[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 109: 45 − 55. doi: 10.1007/s00170-020-05627-w
[28] Huang Y M, Zhao D J, Chen H B, et al. Porosity detection in pulsed GTA welding of 5A06 Al alloy through spectral analysis[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 259: 332 − 340. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.05.006
[29] Zhang Z F, Chen H B, Xu Y L, et al. Multisensor-based real-time quality monitoring by means of feature extraction, selection and modeling for Al alloy in arc welding[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 60: 151 − 165.
[30] Wu D, Chen H B, Huang Y M, et al. On-line monitoring and model-free adaptive control of weld penetration in VPPAW based on extreme learning machine[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 15: 2732 − 2740.
[31] Liu W H, Chen M H, Zhu K H, et al. Online monitoring and penetration recognition in all-position TIG welding of nuclear power pipeline[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2024, 108: 889 − 902.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王振民,宋哲龙,迟鹏,廖海鹏,张芩. 类人机器人焊接技术研究现状与展望. 机电工程技术. 2025(04): 1-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: