Corrosion fatigue behavior of X65 pipeline steel welded joints under different stress ranges
-
摘要: 通过腐蚀疲劳试验研究了在H2S环境中不同应力幅下X65管线钢焊接接头的腐蚀疲劳行为及机理,对试样的微观组织、断口和裂纹扩展路径进行了观察. 结果表明,X65管线钢焊接接头焊缝的微观组织主要由先共析铁素体、粒状贝氏体和M/A组元构成,M/A组元增大了焊缝的脆性. 粗晶热影响区主要由板条贝氏体和粒状贝氏体组成,焊缝和粗晶热影响区的硬度较高,韧性较差. 在不同应力幅下X65管线钢焊接接头的腐蚀疲劳机理均为阳极溶解 + 氢脆混合机制,但低应力幅下腐蚀作用带来的损伤更加显著. 随着应力幅的增大,试样的腐蚀疲劳寿命显著降低,裂纹扩展的速率也越快. 此外,二次裂纹主要沿着贝氏体板条束的晶界扩展,裂纹尖端在针状铁素体和先共析铁素体处产生了钝化现象,这两类组织有着良好的抗氢脆能力.Abstract: The corrosion fatigue behavior and mechanism of X65 pipeline steel welded joints under different stress ranges in H2S environment were studied through corrosion fatigue experiment. The microstructure, fracture and crack propagation path of the specimens were observed. The results show that the microstructure of X65 pipeline steel weld is mainly composed of proeutectoid ferrite, granular bainite and M/A component, and the M/A component increases the brittleness of the weld. The coarse grain heat affected zone is mainly composed of lath bainite and granular bainite. The hardness of weld and coarse grain heat affected zone is high, and the toughness is low. The corrosion fatigue mechanism of X65 pipeline steel welded joints under different stress ranges is mixed of anodic dissolution and hydrogen embrittlement, but damages caused by corrosion is more significant under low stress ranges. With the increase of stress amplitude, the corrosion fatigue life of the specimens decreases significantly, and the rate of crack propagation grows rapidly. In addition, the secondary cracks mainly spread along the grain boundary of the bainite strip, and the crack tip passivates at the acicular ferrite and the proeutectoid ferrite, which have exhibited excellent resistance to hydrogen embrittlement.
-
Keywords:
- X65 pipeline steel /
- welded joint /
- microstructure /
- corrosion fatigue behavior
-
-
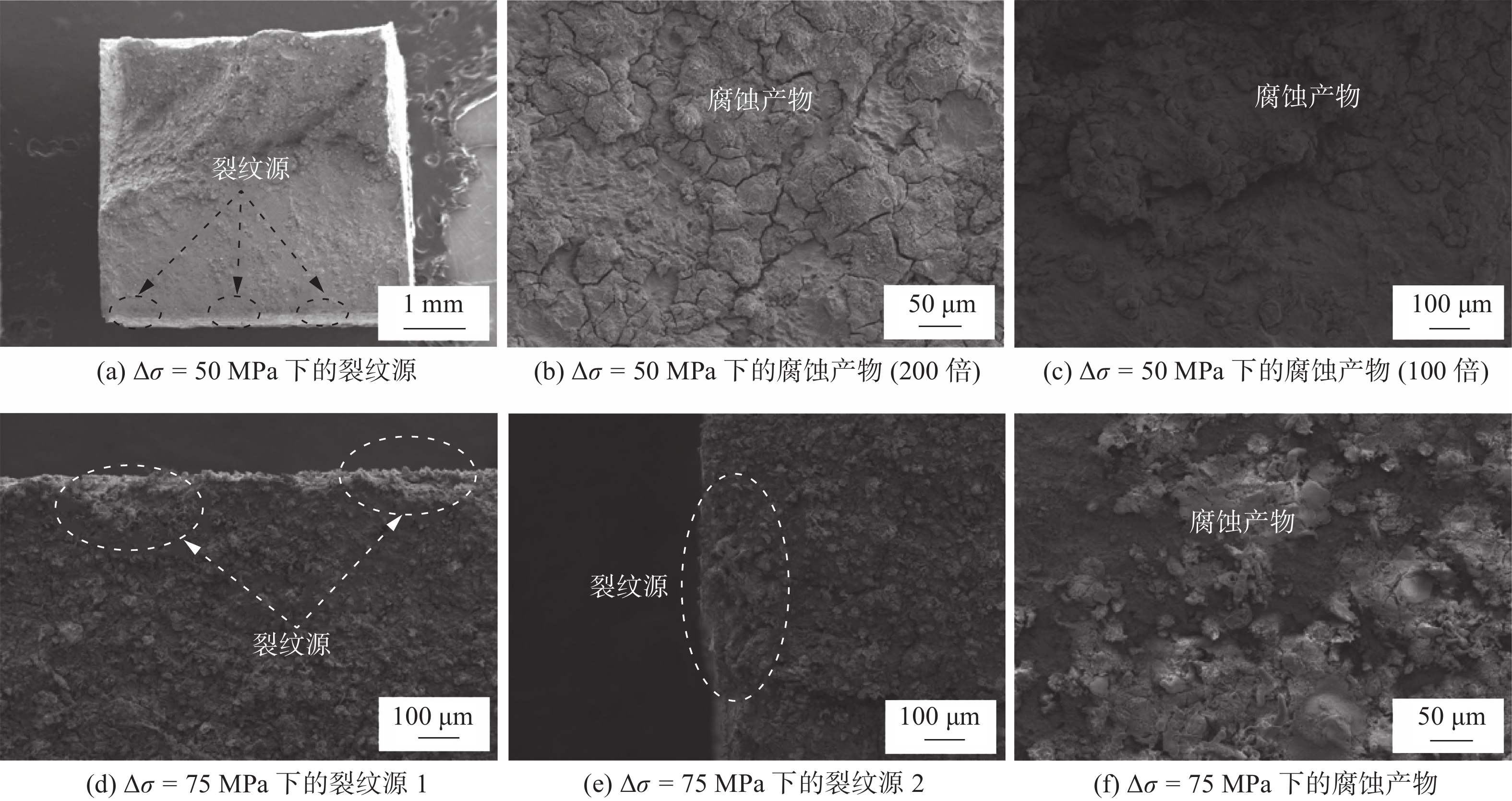
图 8 Δσ = 50,75 MPa时X65管线钢焊接接头腐蚀疲劳断口
Figure 8. Corrosion fatigue fractures of X65 pipeline steel welded joint at Δσ = 50, 75 MPa. (a) crack source at Δσ = 50 MPa; (b) corrosion products at Δσ = 50 MPa(200×); (c) corrosion products at Δσ = 50 MPa(100×); (d) crack source 1 at Δσ = 75 MPa; (e)crack source 2 at Δσ = 75 MPa; (f) corrosion products at Δσ = 75 MPa
图 9 Δσ = 100,150,200 MPa时X65管线钢焊接接头腐蚀疲劳断口
Figure 9. Corrosion fatigue fractures of X65 pipeline steel welded joint at Δσ = 100, 150, 200 MPa. (a) crack source at Δσ = 100 MPa; (b) secondary crack at Δσ = 100 MPa; (c) fatigue striation at Δσ = 100 MPa; (d) crack source at Δσ = 150 MPa; (e) secondary crack at Δσ = 150 MPa; (f) fatigue striation at Δσ = 150 MPa; (g) crack source at Δσ = 200 MPa; (h) secondary crack at Δσ = 200 MPa; (i) fatigue striation at Δσ = 200 MPa
表 1 X65管线钢和ER80S-G焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of X65 pipeline steel and ER80S-G welding wire
材料 C Si Mn Nb P S Ni Cr Cu V Ti Fe X65 0.10 0.23 1.21 0.60 0.013 0.002 0.03 0.06 0.06 0.04 — 余量 ER80S-G 0.089 0.581 1.366 0.60 0.021 0.007 0.0833 0.011 0.106 — 0.024 余量 表 2 X65管线钢和ER80S-G焊丝的力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of X65 pipeline steel and ER80S-G welding wire
材料 屈服强度
ReL/MPa抗拉强度
Rm/MPa断后伸长率
A(%)X65 465 565 30.0 ER80S-G 580 630 31.0 表 3 焊接工艺参数
Table 3 Welding process parameters
焊道 焊接电流
I/A送丝速度
vs /(cm·min−1)焊接速度
v/(cm·min−1)摆动幅度
W/mm摆停时间
ts /s摆动速度
vb /(mm·s−1)层间温度
T/℃打底 130 ~ 165 30 ~ 32 10 ~ 13 3 0.2 120 250 热焊 230 ~ 245 45 ~ 50 12 7 0.4 130 250 填充 255 ~ 290 50 ~ 70 10 ~ 11 9 ~ 23 0.5 140 250 盖面 210 ~ 230 30 ~ 32 12 11 0.1 25 250 表 4 X65管线钢焊接接头S-N曲线拟合参数
Table 4 S-N curve fitting parameters of X65 pipeline steel welded joint
测试频率
f/Hz拟合常数
m特征值Cm/1010 疲劳强度
R/MPa50%存活率 95%存活率 2 2.34 2.00 1.26 42 -
[1] 张强, 吕福亮, 贺晓苏, 等. 南海近5年油气勘探进展与启示[J]. 中国石油勘探, 2018, 23(1): 54 − 61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.006 Zhang Qiang, Lyu Fuliang, He Xiaosu, et al. Progress and enlightenment of oil and gas exploration in the South China Sea in recent five years[J]. China Petroleum Exploration, 2018, 23(1): 54 − 61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7703.2018.01.006
[2] 田野. “深海一号”傲然面世— —中国海洋石油勘探开发进入“超深水时代”[J]. 中国石油企业, 2021(6): 24 − 32,111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4267.2021.06.007 Tian Ye. “Shenhai No. 1” proudly lauched— —CNOOC’S exploration and development capabilities have entered the “ultra-deep water era”[J]. Chinese Petroleum Enterprises, 2021(6): 24 − 32,111. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4267.2021.06.007
[3] 何琦, 汪鹏. 深海能源开发现状和前景研究[J]. 海洋开发与管理, 2017, 34(12): 66 − 71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2017.12.012 He Qi, Wang Peng. Current situation and prospect of deep sea energy development[J]. Marine Development and Management, 2017, 34(12): 66 − 71. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9857.2017.12.012
[4] Cheng A, Chen N Z. An extended engineering critical assessment for corrosion fatigue of subsea pipeline steels[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2018, 84: 262 − 275. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2017.11.012
[5] Ossai C I, Boswell B, Davies I J. Pipeline failures in corrosive environments—A conceptual analysis of trends and effects[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2015, 53: 36 − 58. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2015.03.004
[6] Mansor N I I, Abdullah S, Ariffin A K, et al. A review of the fatigue failure mechanism of metallic materials under a corroded environment[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2014, 42: 353 − 365. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2014.04.016
[7] Farhad F, Smyth-Boyle D, Zhang X. Fatigue of X65 steel in the sour corrosive environment—A novel experimentation and analysis method for predicting fatigue crack initiation life from corrosion pits[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2021, 44(5): 1195 − 1208.
[8] 王歧山, 李鸿瑾, 何川, 等. 加载波形对X65钢腐蚀疲劳裂纹萌生及扩展的影响[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2022, 42(2): 227 − 234. Wang Qishan, Li Hongjin, He Chuan, et al. Effect of loading modes on initiation and propagation of corrosion fatigue cracks of X65 steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Corrosion and Protection, 2022, 42(2): 227 − 234.
[9] 王晶. H2S环境中疲劳裂纹扩展速率数学模型的建立及行为研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2010. Wang Jing. Modeling of fatigue crack growth rate and study on crack propagation behavior in H2S environment[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2010.
[10] 程攀. H2S腐蚀产物膜对MS X65管线钢氢渗透动力学行为的影响[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2017. Cheng Pan. Effect of sulfide films formed on MS X65 steel surface on hydrogen permeation in H2S environments[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[11] 张体明, 王勇, 赵卫民, 等. 模拟煤制气环境下X80管线钢及HAZ的氢脆敏感性[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(9): 43 − 46. Zhang Timing, Wang Yong, Zhao Weiming, et al. Hydrogen embrittlement susceptibility of X80 steel substrate and HAZ in simulated coal gas environment[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(9): 43 − 46.
[12] 侯双平. 微观组织及晶界结构对管线钢氢致开裂行为的影响[D]. 武汉: 武汉科技大学, 2020. Hou Shuangping. Effect of microstructure and grain boundary structure on hydrogen-induced cracking behavior of pipeline steel[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[13] 彭先华, 刘静, 黄峰, 等. 微观组织对管线钢氢致裂纹扩展方式及氢捕获效率的影响[J]. 腐蚀与防护, 2013, 34(10): 882 − 885. Peng Xianhua, Liu Jing, Huang Feng, et al. Effect of microstructure on hydrogen induced crack propagation mode and hydrogen capture efficiency of pipeline steel[J]. Corrosion and Protection, 2013, 34(10): 882 − 885.
[14] 严春妍, 张根元, 刘翠英. X80管线钢焊接接头氢分布的数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(9): 103 − 107. Yan Chunyan, Zhang Genyuan, Liu Cuiying. Numerical simulation of hydrogen distribution in welded joint of X80 pipeline steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(9): 103 − 107.
[15] 贾清松, 吕小青, 韩永典, 等. 电化学充氢条件下管线钢焊接接头对氢的吸收能力分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(9): 111 − 114. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20150813001 Jia Qingsong, Lyu Xiaoqing, Han Yongdian, et al. Hydrogen absorbing ability of pipeline steel welded joint in condition of electrochemical hydrogen[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(9): 111 − 114. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20150813001
[16] Han Yongdian, Zhong Shifang, Tian Lei, et al. Welding heat input for synergistic improvement in toughness and stress corrosion resistance of X65 pipeline steel with pre-strain[J]. Corrosion Science, 2022, 206: 110478. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2022.110478
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 闫玉升,钟史放,徐连勇,赵雷,韩永典. 焊接热输入对X65管道粗晶热影响区应力腐蚀开裂行为的影响. 机械工程学报. 2024(12): 220-227 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王朝阳,尤景泽,孟彤,张连旺,孙超,王慧,于镇洋,宋明. 预应变对X80管线钢冲击断裂行为的影响. 钢铁钒钛. 2024(04): 163-169 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 肖友福,刘永贞,孙有辉,闫玉升,徐连勇,韩永典. 预充氢对SCR焊接接头应力腐蚀敏感性影响. 焊接学报. 2024(10): 19-27 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 郭宏超,关晓迪,王铳,赵越. 多因素耦合作用下高强钢焊缝连接疲劳性能研究进展. 建筑钢结构进展. 2024(11): 1-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 侯文亮,李明勇,刘艳峰,刘鑫. 点固焊有限元建模在反变形设计中的应用. 焊接技术. 2024(12): 84-88 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: