Parameters optimization for friction stir lap welding of Al/Mg dissimilar alloys based on RBF-GA
-
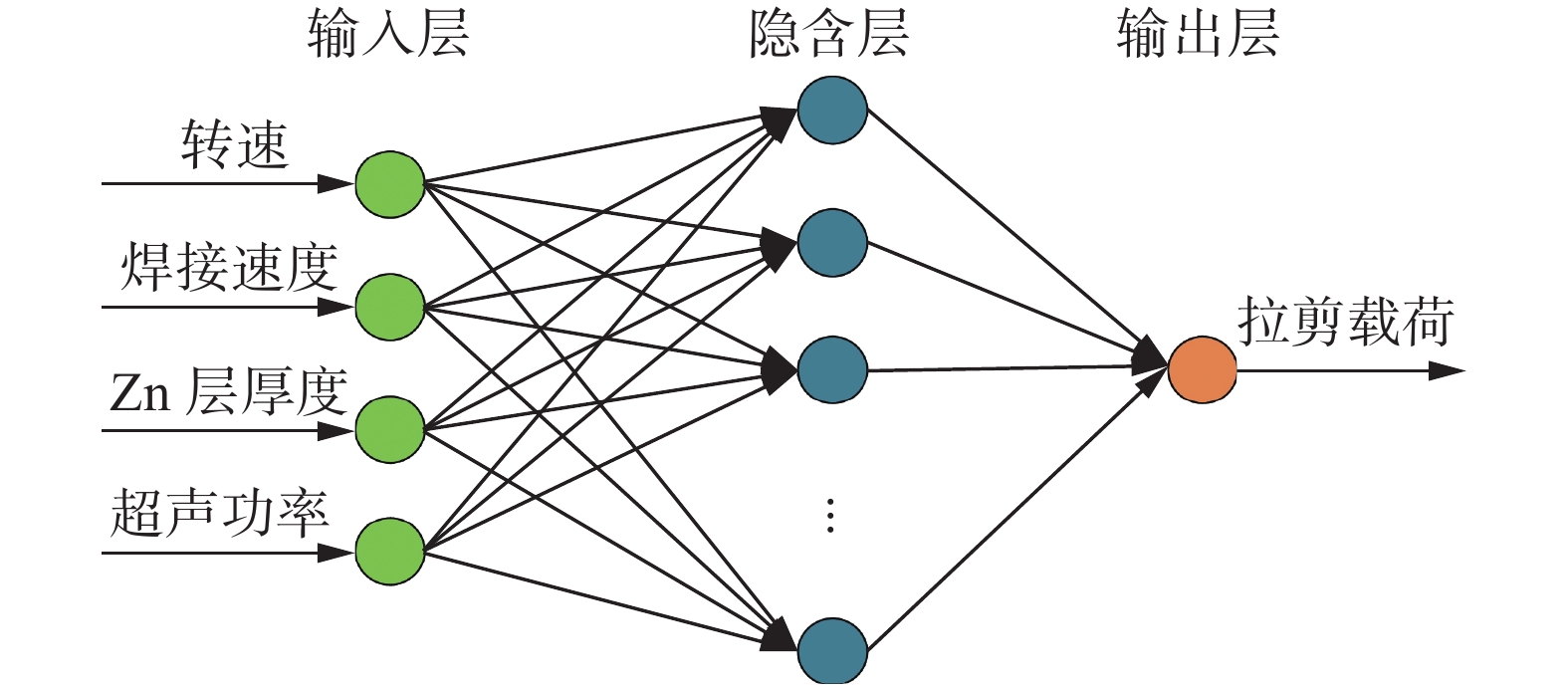
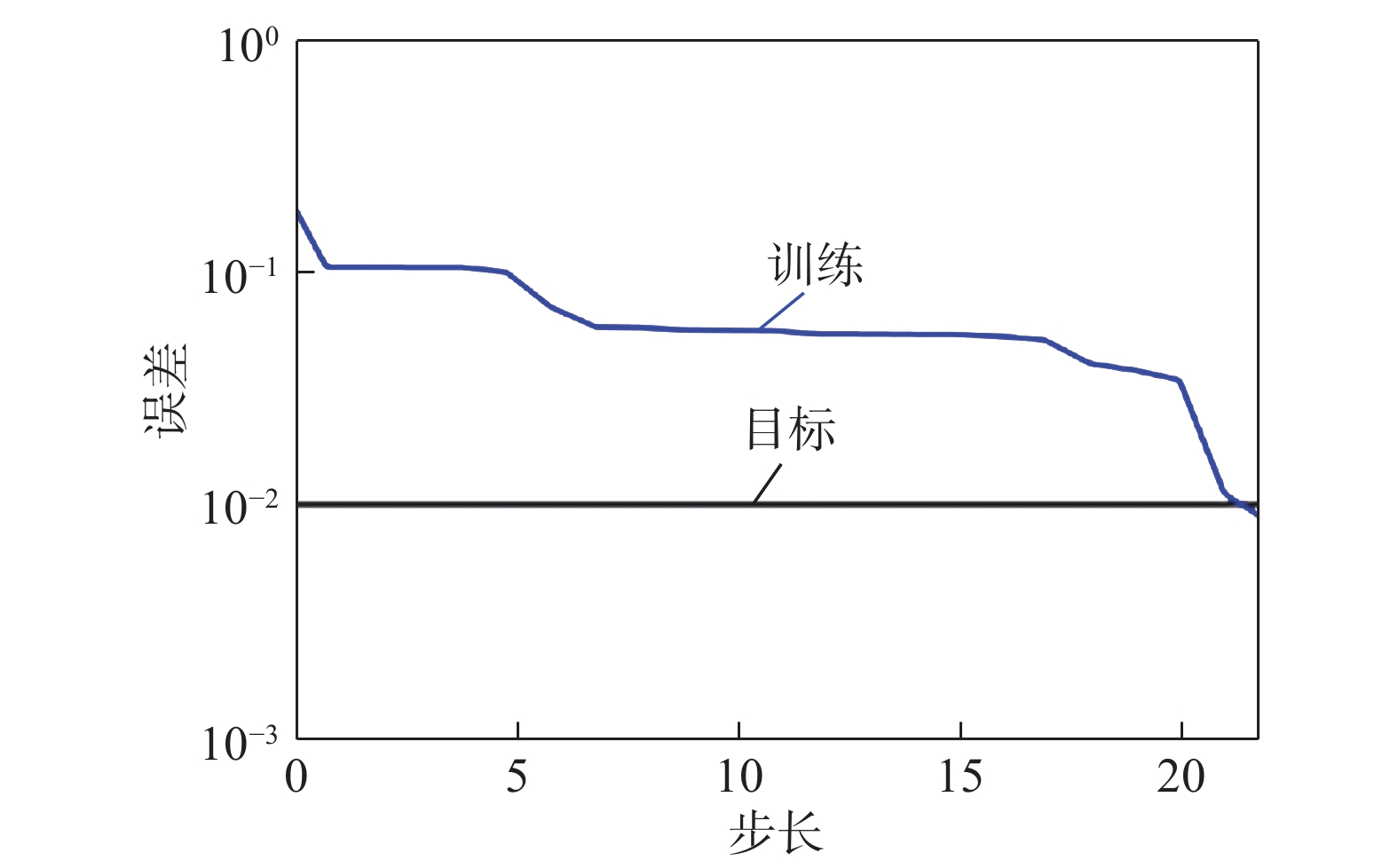
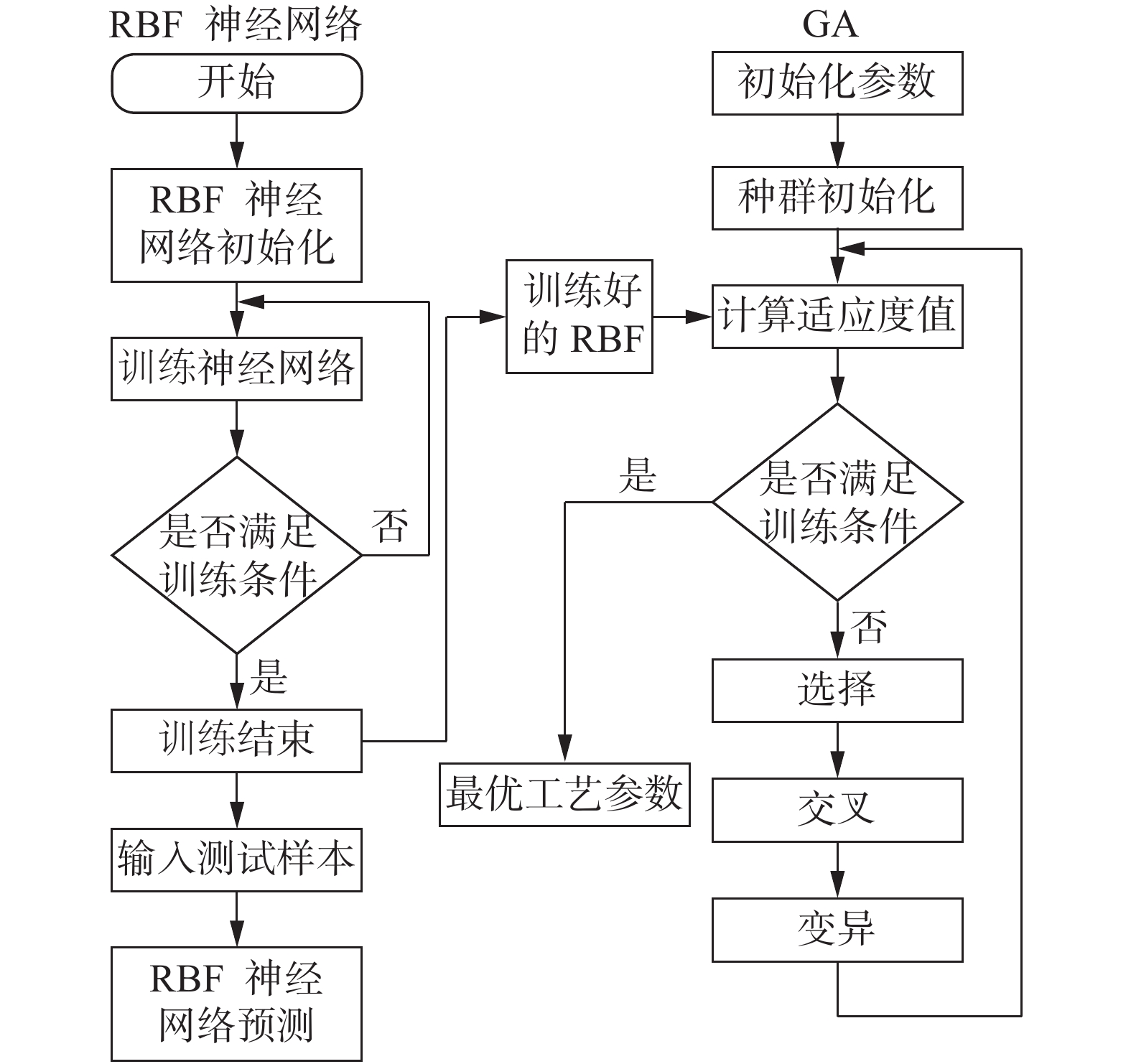
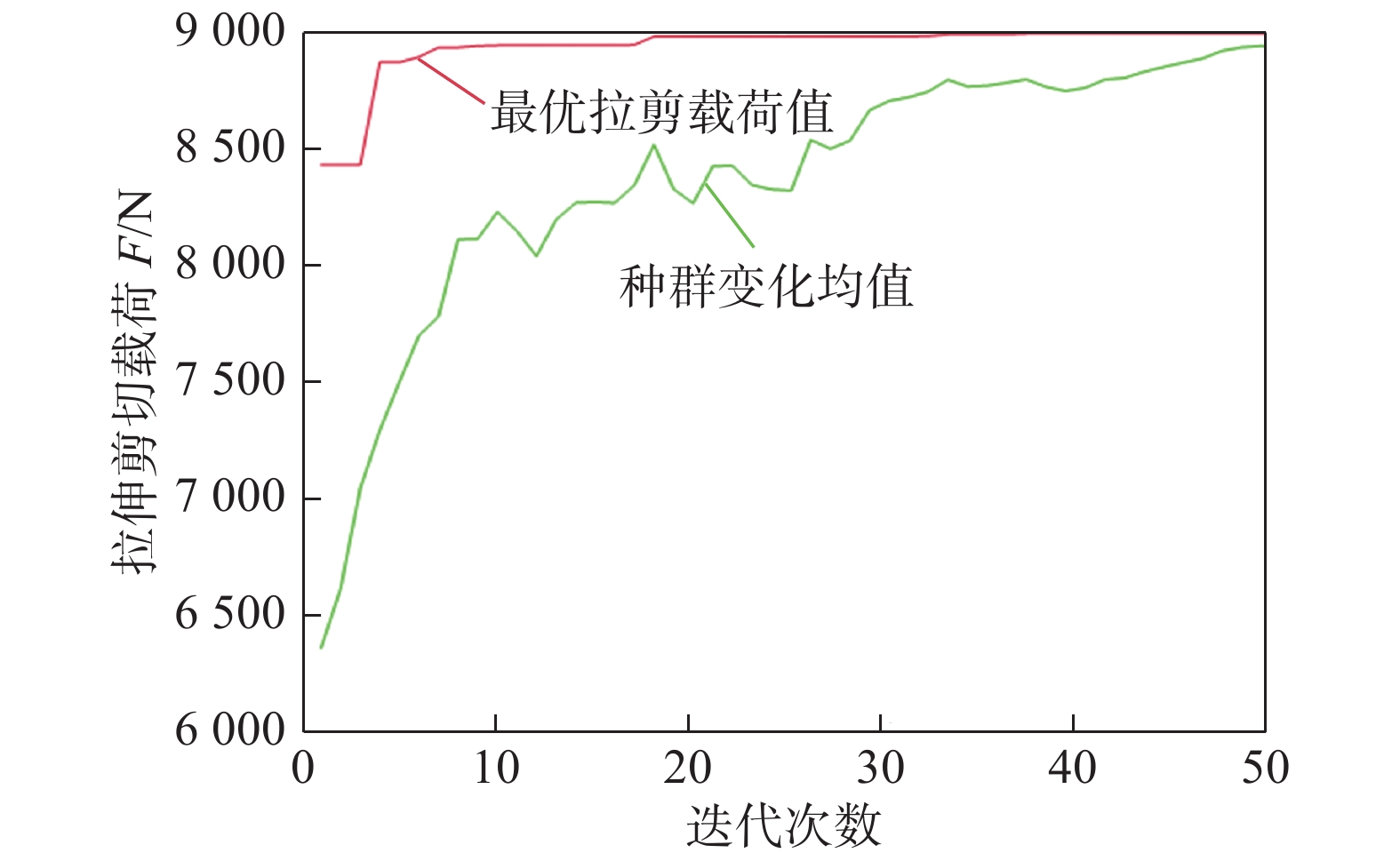
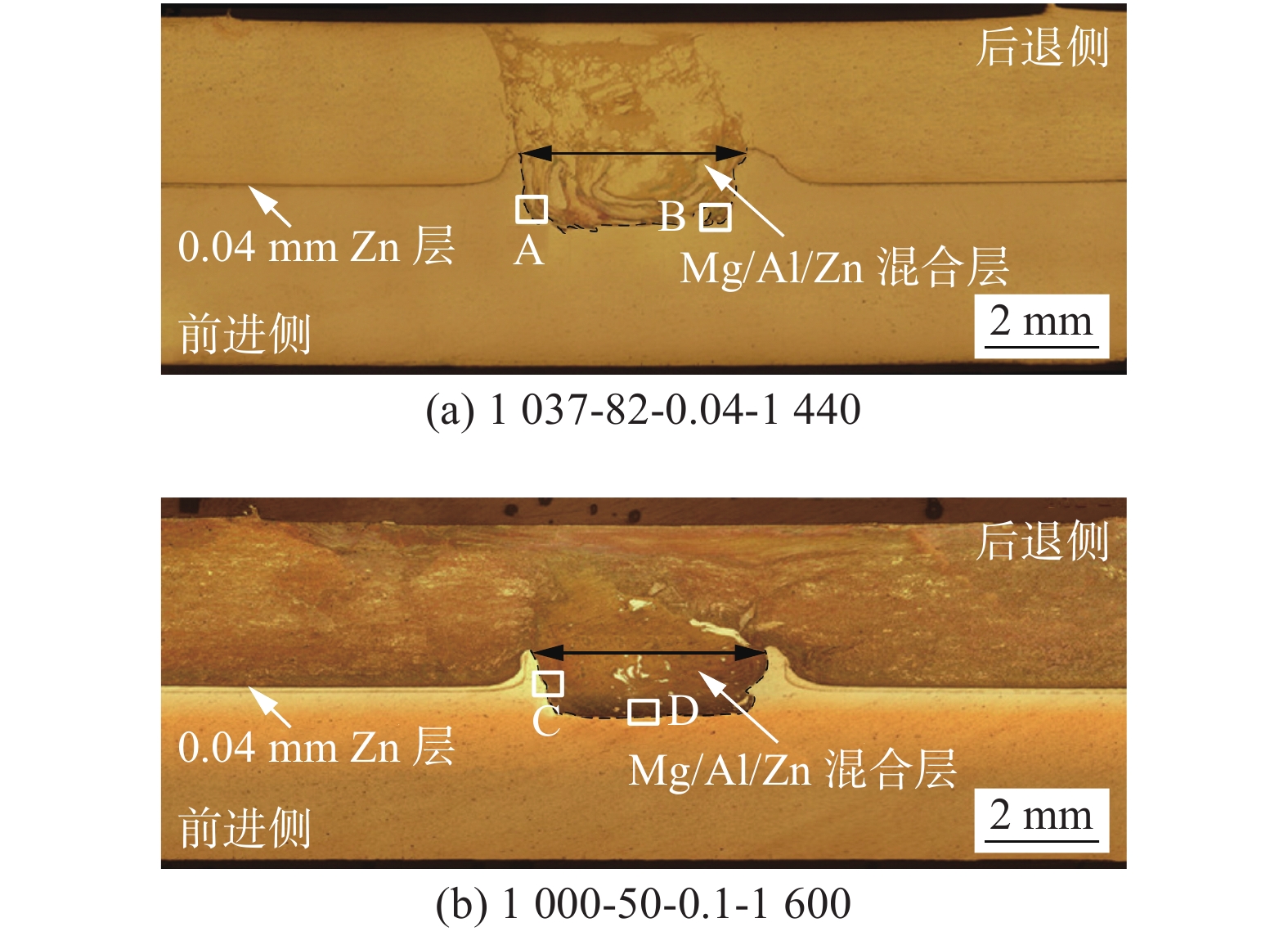
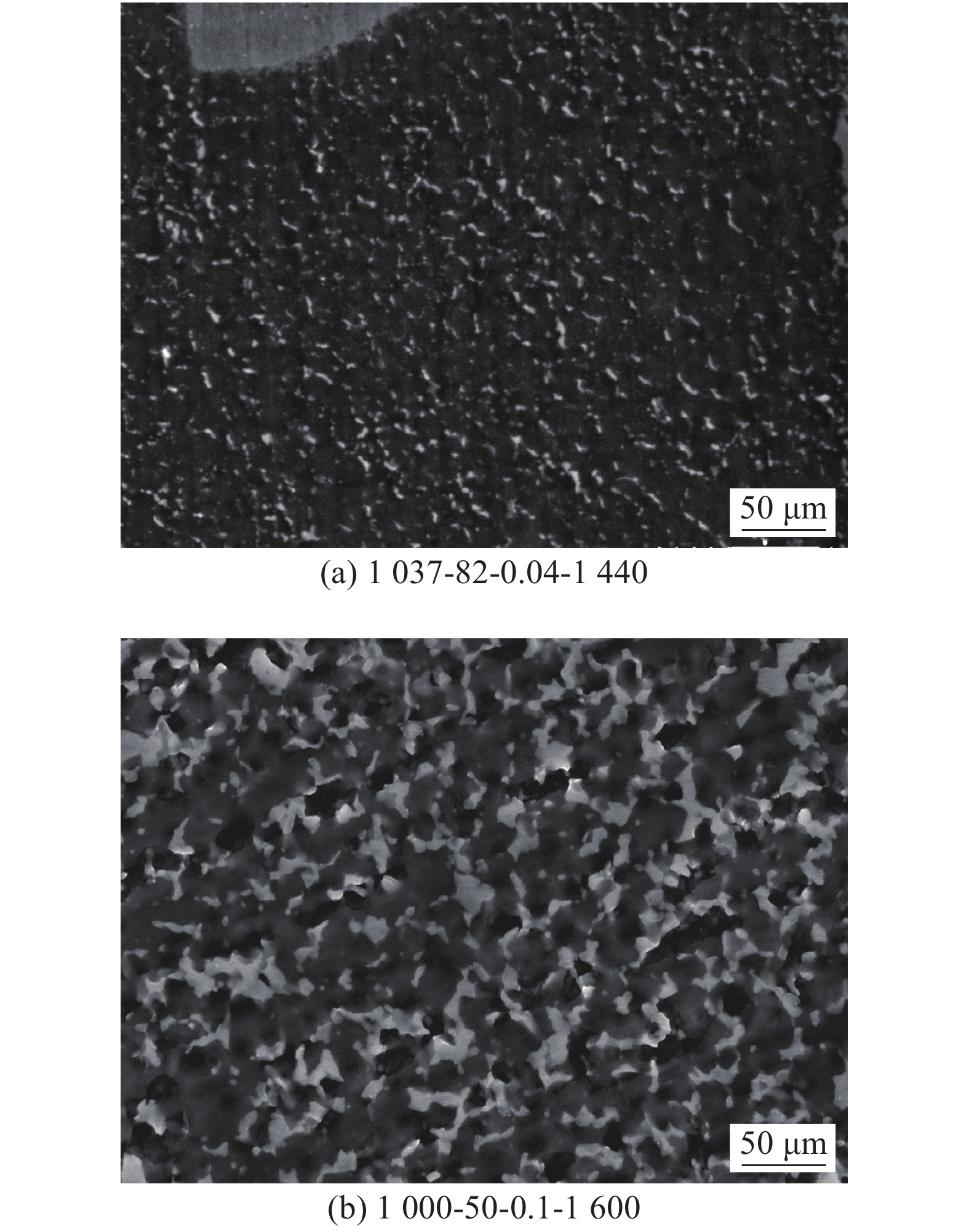
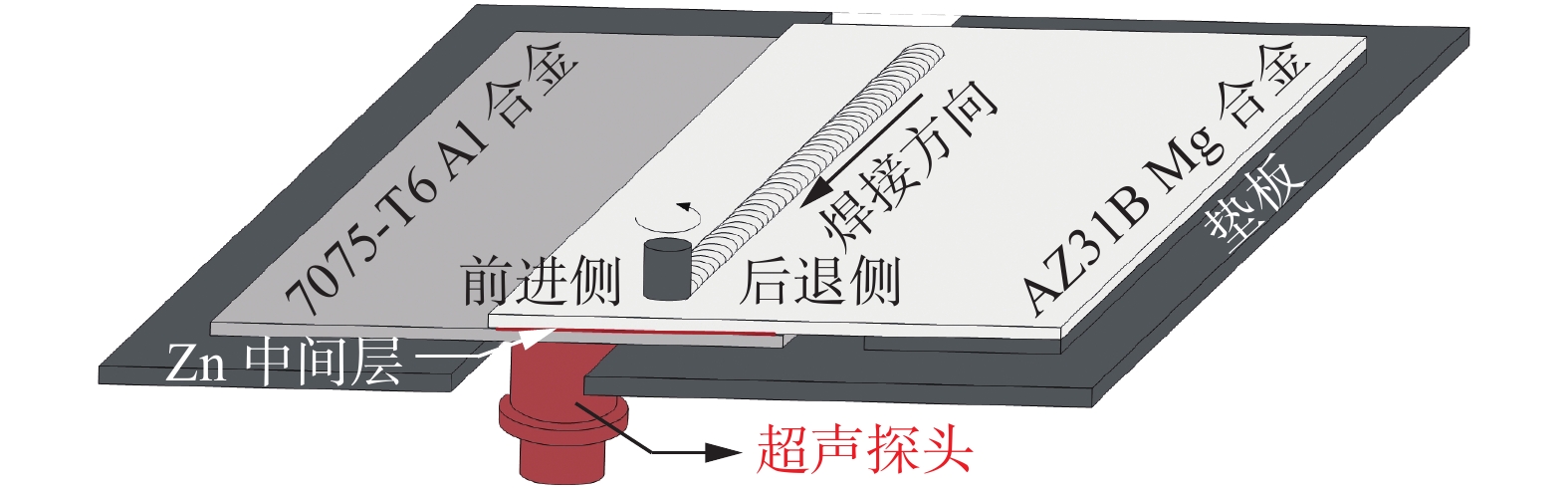
摘要: 为获得高质量的7075-T6/AZ31B异种合金Zn中间层-超声辅助FSLW接头,通过RBF-遗传算法对转速、焊接速度、Zn中间层厚度及超声功率四种工艺参数进行了优化. 结果表明,经过训练的RBF神经网络满足预测精度要求;将其与遗传算法相结合,在经多次迭代后可获得最优工艺参数组合. 取可执行最优解转速1 037 r/min、焊接速度82 mm/min、Zn层厚度0.04 mm和超声功率1 440 W进行试验验证,焊接接头拉剪载荷达到8 860 N,与已报道最优接头相比提高11.4%. RBF神经网络与遗传算法相结合的人工智能优化方法可准确预测并优化接头质量,且具有较大的时间及经济优势.Abstract: The hybrid of RBF neural network with genetic algorithm (GA) was employed to optimize process parameters of rotating velocity, welding speed, Zn interlayer thickness and ultrasound power, thus obtaining a dissimilar 7075-T6 Al/AZ31B Mg Zn-added ultrasound assisted friction stir lap welding joint with a high quality. The results stated that the prediction accuracy of the trained RBF neural network was accepted. GA was combined with RBF neural network, and the optimal combination of welding process parameters was obtained after many iterations. The verification test was performed under the executable optimal solution which consisted of the rotating velocity of 1 037 r/min, the welding speed of 82 mm/min, the Zn interlayer thickness of 0.04 mm and the ultrasound power of 1 440 W. The tensile shear load of the joint was reached 8 860 N, which was 11.4% larger than that of the reported optimal joint. The artificial intelligence optimization method of RBF neural network with GA can accurately predict and optimize the joint quality, which has great time and economic advantages.
-
-
表 1 焊接工艺参数样本
Table 1 Welding process parameters samples
序号 转速n/(r·min−1) 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) Zn层厚度h/mm 超声功率P/W 拉剪载荷F/N 1 1 200 200 0 0 4 830 2 1 200 200 0.1 0 5 680 3 1 200 150 0 0 5 790 4 1 200 150 0.1 0 6 410 5 1 200 100 0 0 6 720 6 1 200 100 0.1 0 7 230 7 1 200 50 0 0 5 620 8 1 200 50 0.1 0 6 290 9 600 50 0 0 4 420 10 600 50 0.1 0 5 510 11 800 50 0 0 5 210 12 800 50 0.1 0 5 780 13 1 000 50 0 0 5 950 14 1 000 50 0.1 0 6 600 15 1 000 50 0.1 800 6 820 16 1 000 50 0.1 1 200 7 830 17 1 000 50 0.1 1 600 7 950 18 1 000 50 0.02 0 7 340 19 1 000 50 0.05 0 8 680 20 1 000 50 0.2 0 6 210 21 1 000 100 0.1 0 6 930 22 1 000 150 0.02 0 7 110 23 1 200 100 0.02 0 7 580 24 800 50 0 1 600 7 170 25 1 200 150 0.05 0 7 370 26 1 000 100 0.1 1 600 8 120 27 800 50 0.02 1 200 7 330 28 1 200 100 0.02 1 200 7 960 29 800 50 0.2 800 6 040 30 1 200 150 0.1 1 200 7 270 31 1 200 200 0.05 1 600 6 690 32 1 200 100 0.1 1 200 7 860 33 1 200 50 0.1 1 600 7 110 34 600 50 0.05 800 6 270 35 800 50 0.05 1 600 6 860 36 1 000 50 0.02 1 200 8 130 37 1 000 50 0.05 1 200 8 740 38 1 000 50 0.2 800 6 530 39 1 000 100 0.1 1 600 7 640 40 1 200 150 0.05 1 200 8 140 表 2 RBF模型预测结果
Table 2 Prediction results of RBF model
序号 转速n/(r·min−1) 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) Zn层厚度h/mm 超声功率P/W 实测值F1/N 预测值F2/N 1 800 50 0.02 600 5 430 5 490 2 1 200 100 0.05 1 600 8 340 8 420 3 600 50 0.02 1 200 5 810 6 010 4 600 100 0.1 800 5 130 5 250 表 3 优化结果验证及对比
Table 3 Validation and comparison of optimization result
序号 转速n/(r·min−1) 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) Zn层厚度h/mm 超声频率P/W 拉剪载荷F/N 1 1 037 81.7 0.038 1 444.2 8 980 2 1 037 82 0.04 1 440 8 860 3 1 000 50 0.1 1 600 7 950 -
[1] Huang Y X, Meng X C, Zhang Y B, et al. Micro friction stir welding of ultra-thin Al-6061 sheets[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 250: 313 − 319. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.07.031
[2] Ji S D, Li Z W, Zhang L G, et al. Effect of lap configuration on magnesium/aluminum friction stir lap welding assisted by external stationary shoulder[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 103: 160 − 170. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.04.066
[3] Mohammadi J, Behnamian Y, Mostafaei A, et al. Friction stir welding joint of dissimilar materials between AZ31B magnesium and 6061 aluminum alloys: microstructure studies and mechanical characterizations[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 101: 189 − 207. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2015.01.008
[4] Liu Z L, Yang K, Ji S D. Reducing intermetallic compounds of Mg/Al joint in friction stir lap welding[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2018, 27(11): 5605 − 5612. doi: 10.1007/s11665-018-3705-z
[5] Wang X J, Zhang Z K, Da C B, et al. Microstructures and properties analysis of dissimilar metal joint in the friction stir welded copper to aluminum alloy[J]. China Welding, 2007, 16(1): 57 − 62.
[6] Bozkurt Y. The optimization of friction stir welding process parameters to achieve maximum tensile strength in polyethylene sheets[J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 35: 440 − 445.
[7] Shanavas S, Dhas J E R. Parametric optimization of friction stir welding parameters of marine grade aluminium alloy using response surface methodology[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2017(11): 24 − 34.
[8] 杨亚超, 全惠敏, 邓林峰, 等. 基于神经网络的焊机参数预测方法[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(1): 32 − 36. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390008 Yang Yachao, Quan Huimin, Deng Linfeng, et al. Prediction method of welding machine parameters based on neural network[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(1): 32 − 36. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390008
[9] Panneerselvam K, Aravindan S, Haq A N. Hybrid of ANN with genetic algorithm for optimization of frictional vibration joining process of plastics[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2009, 42(7-8): 669 − 677. doi: 10.1007/s00170-008-1641-z
[10] 龙振华, 程蓉. 基于人工智能的薄板电阻点焊数值分析及工艺参数优化[J]. 组合机床与自动化加工技术, 2013(6): 139 − 141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2265.2013.06.042 Long Zhenhua, Cheng Rong. Numerical simulation and process optimization of thin sheet resistance spot welding based on artificial intelligence[J]. Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique, 2013(6): 139 − 141. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2265.2013.06.042
[11] Nagesh D S, Datta G L. Genetic algorithm for optimization of welding variables for height to width ratio and application of ANN for prediction of bead geometry for TIG welding process[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2010, 10(3): 897 − 907. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2009.10.007
[12] Babu K K, Panneerselvam K, Sathiya P, et al. Parameter optimization of friction stir welding of cryorolled AA2219 alloy using artificial neural network modeling with genetic algorithm[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 94(9-12): 3117 − 3129. doi: 10.1007/s00170-017-0897-6
[13] Darzi Naghibi H, Shakeri M, Hosseinzadeh M. Neural network and genetic algorithm based modeling and optimization of tensile properties in FSW of AA 5052 to AISI 304 dissimilar joints[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2016, 69(4): 891 − 900. doi: 10.1007/s12666-015-0572-2
[14] Gan R, Jin Y. Friction stir-induced brazing of Al/Mg lap joints with and without Zn interlayer[J]. Science & Technology of Welding & Joining, 2018, 23: 164 − 171.
[15] Ji S, Niu S, Liu J. Dissimilar Al/Mg alloys friction stir lap welding with Zn foil assisted by ultrasonic[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019, 35: 1712 − 1718.
[16] Rai R, De A, Bhadeshia H, et al. Friction stir welding tools[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2011, 16(4): 325 − 342. doi: 10.1179/1362171811Y.0000000023
[17] Ji S, Niu S, Liu J, et al. Friction stir lap welding of Al to Mg assisted by ultrasound and a Zn interlayer[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 267: 141 − 151. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.12.010
[18] Niu S, Ji S, Yan D, et al. AZ31B/7075-T6 alloys friction stir lap welding with a zinc interlayer[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2019, 263: 82 − 90. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.08.009



 下载:
下载: