Simulation study on ultrasonic propagation characteristics of Al2O3/EP composites
-
摘要:
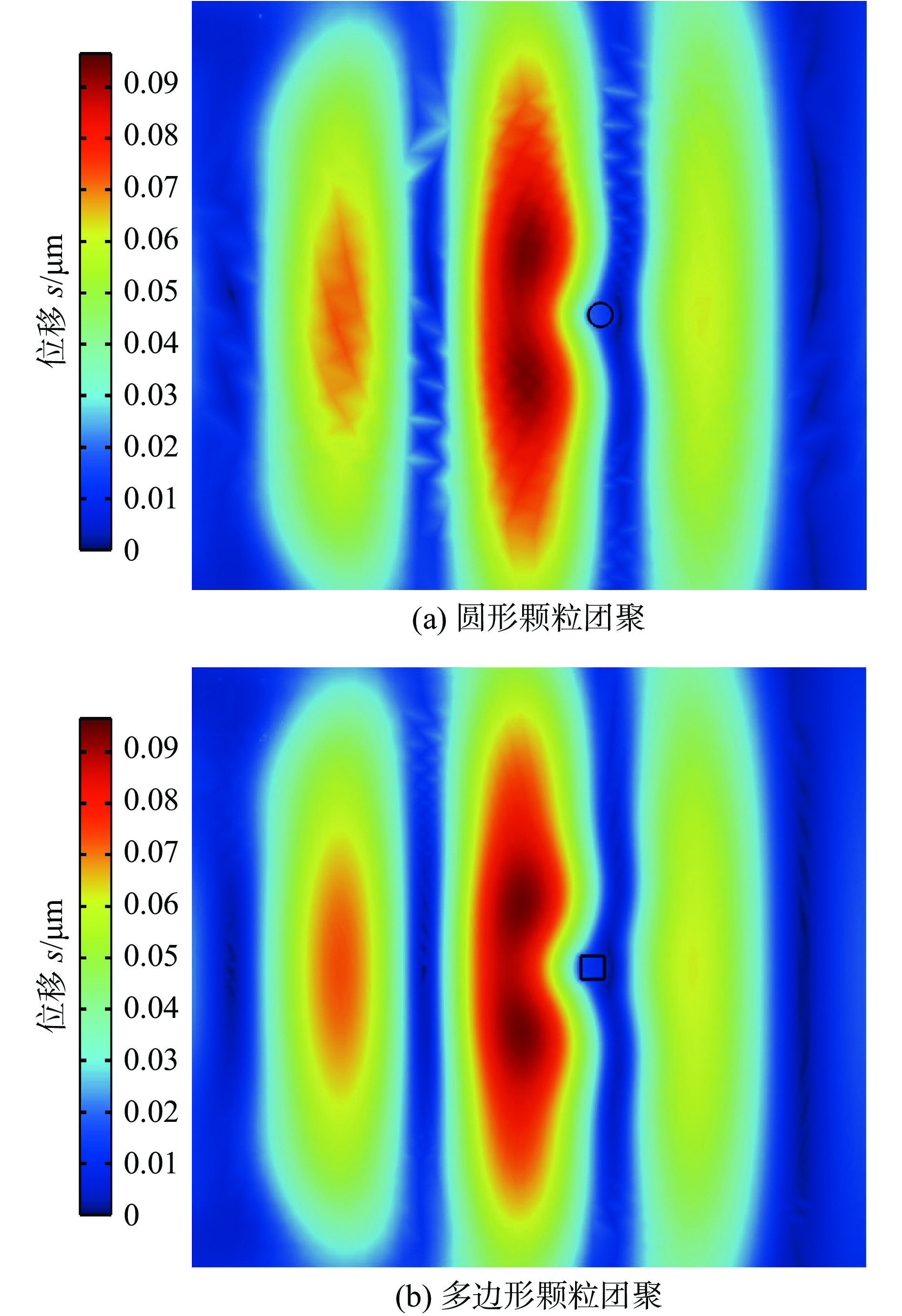
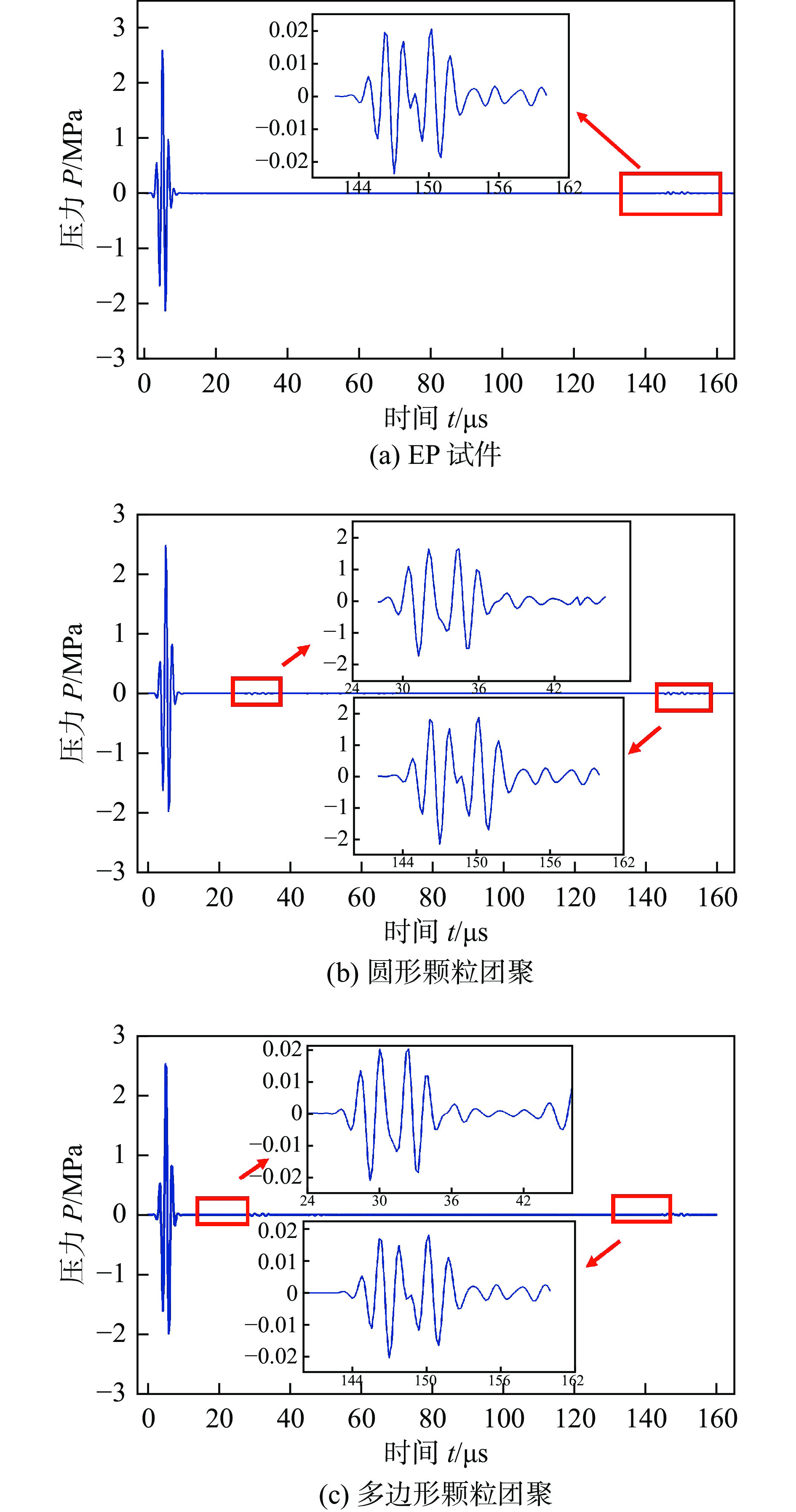
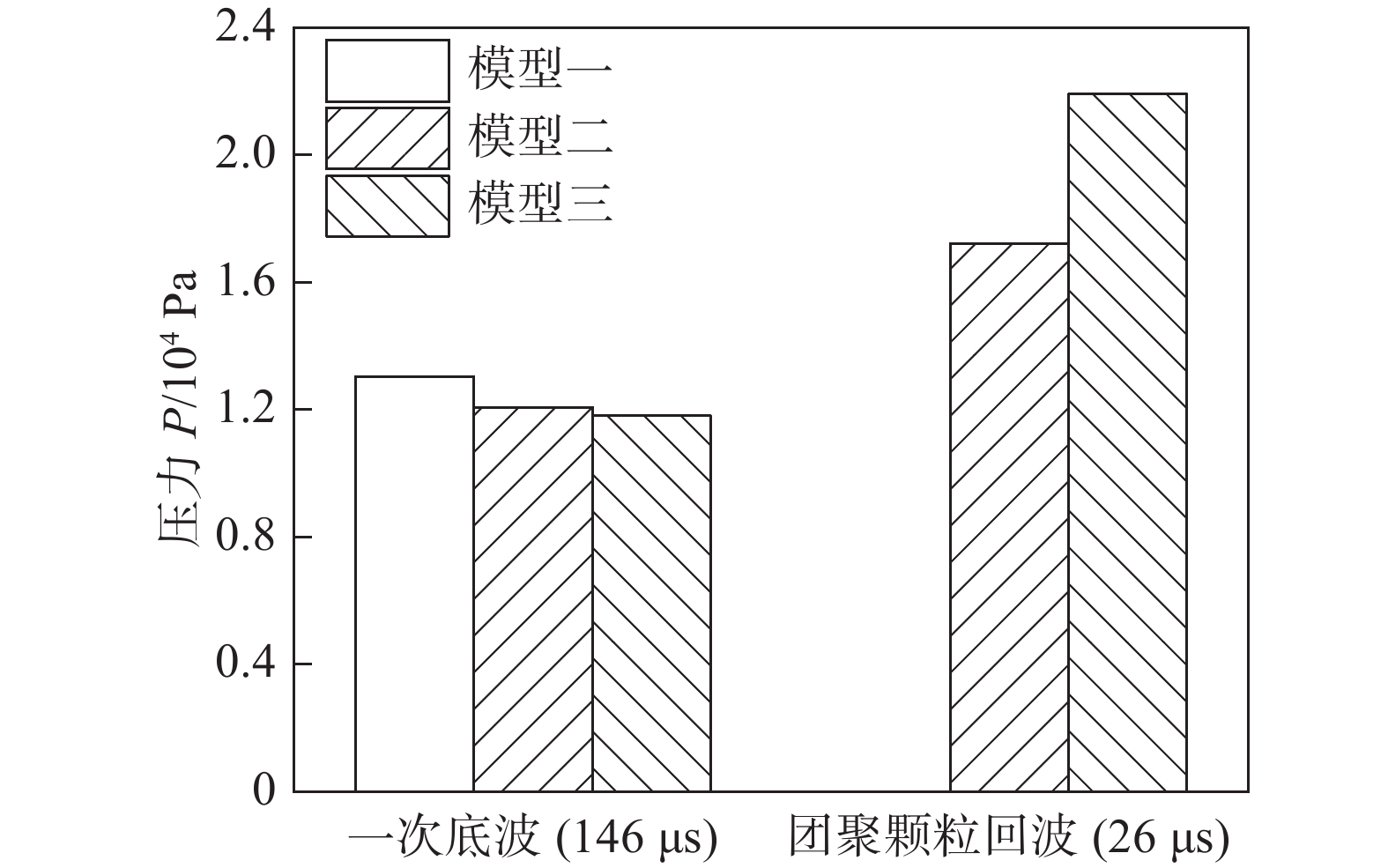
采用COMSOL Multiphysics软件,对Al2O3/环氧树脂(Al2O3/EP)复合材料的超声波传播特性进行了仿真. 对于颗粒增强的树脂基复合材料,由于树脂基体的高声衰减特性及其存在的异质颗粒和多连接界面属性,导致检测难,文中主要针对GIS用Al2O3/EP复合材料微观结构中存在的典型颗粒团聚现象和颗粒/树脂连接界面存在的间隙特征,通过建立数值仿真模型,对比Al2O3不同颗粒形状和含量对超声波传播的影响规律,以及不同界面间隙尺寸对超声波能量穿透影响规律. 结果表明,Al2O3颗粒几何形状和团聚现象对超声的传播产生一定影响,其中多边形团聚颗粒比同尺寸圆形颗粒对超声波的衰减作用更大,约高出1.9%;且随着添加Al2O3颗粒含量的增加,由于异质连接界面的增多,声波传播速度减慢,对比20%含量较10%一次底波压力信号增强了约40%左右;对颗粒与基体界面间隙尺寸的影响研究发现,随着间隙大小的增加,穿透Al2O3颗粒的超声能量大幅减弱.综合分析,Al2O3颗粒增强的树脂基复合材料GIS盆子超声检测,对超声衰减特性的影响规律由大到小依次为Al2O3/环氧树脂连接界面间隙的存在—异质连接界面—颗粒几何形状.
Abstract:In this paper, the ultrasonic propagation characteristics of Al2O3/EP composites are simulated by COMSOL Multiphysics software. For particle reinforced resin matrix composites, it is difficult to detect due to the high sound attenuation characteristics of the resin matrix and the existence of heterogeneous particles and multi-connection interface properties. In this paper, a numerical simulation model is established for the typical particle agglomeration phenomenon in the microstructure of Al2O3/EP composites for GIS and the gap characteristics at the particle/resin interface. The effects of different Al2O3 particle shapes and contents on ultrasonic propagation and the effects of different interface gap sizes on ultrasonic energy penetration were compared. The results show that the geometric shape and agglomeration of Al2O3 particles have a certain influence on the propagation of ultrasonic wave, and the polygonal agglomerated particles have a greater attenuation effect on ultrasonic wave than the circular particles of the same size, about 1.9% higher; With the increase of the content of Al2O3 particles, the acoustic wave propagation speed slows down due to the increase of the heterogeneous connection interface. Compared with the 10% primary bottom wave pressure signal, the 20% content is enhanced by about 40%. The research on the influence of the gap size on the interface between the particles and the matrix shows that the ultrasonic energy penetrating the Al2O3 particles is greatly weakened with the increase of the gap size. Comprehensive analysis, Al2O3 particle reinforced resin matrix composite GIS basin ultrasonic testing, the influence of ultrasonic attenuation characteristics from large to small in turn is the existence of Al2O3/EP interface gap— heterogeneous connection interface— particle geometry.
-
0. 序言
激光焊在焊接工艺中具备独特的工艺优势,如焊接热影响区范围小、焊接工件变形小并且焊接灵活性高等. 在应用激光焊的制造业中,需要调整焊接工艺参数完成新产品的打样工作. 例如常作为客户要求重点的抗拉强度,需要工程师首先依据经验确认参数的大致区间,随后随机调节变量完成一批样件的焊接,经对比抗拉强度测试结果后确定合适的焊接工艺参数.
学者们通过采用正交试验设计(orthogonal experimental design, OED)、响应面法(response surface methodology, RSM)等方式在减少试验次数情况下进行优化求解. 其中,OED是利用正交原理的一种数理统计分析方法. 吴晓红、曹海涛和王传洋等人[1-3]在激光焊研究中利用OED设计了3因素3水平试验方案通过分析各因素的显著性水平论证了工艺参数的作用规律. 基于单个试验点采用OED开展分析,并准确评价各因素对指标的影响程度,但难以获得确定试验点以外的更优参数组合. 但在试验因素具有较多水平数时,OED即使通过大量试验也难以在整个区域获得因素和相应目标之间的明确函数表达式[4].RSM是参数设计优化领域的一种重要的方法,通过采用多元二次回归方程的方法以确定最优工艺参数,能够有效解决一些数学与统计方法结合的多变量问题. 与OED相比,RSM能够连续对各个因素水平进行分析,优化后的参数是一个区域,使得在试验数量较少的基础上仍能够较为准确地确定更优参数组合[5]. 除直接在设计试验中确认最优解外,RSM可通过创建期望指标,将原先的响应变量转化为另一个变量期望,即通过在拟合曲面上做相应曲面分析来优化工艺参数组合. 丁亚茹等人[6]以7075铝合金激光焊为对象,基于RSM围绕激光功率等4个变量设计了29组试验,在确定各参数显著性的基础上获得了较好成形系数及焊缝截面积的所对应的优化参数. RSM所具备的减少试验次数、缩短试验周期及预测性能好等优势,使其在激光焊工艺参数组合作用机理分析和优化研究中获得了广泛的应用[7-8]. 但RSM以最小二乘法进行拟合时,所选取的试验点即使误差极小,其拟合效果对概率密度较高区域的概率计算也将有较大的影响[9]. 在实际应用过程中,需要保证每个试验点数据准确及最佳条件在所设计试验参数范围内,常由于试验结果偏差过大、响应不显著等问题而无法获得期望结果[10].
国内外学者为进一步提高效率和获得更优解,应用智能优化算法开展了焊接工艺优化研究[11-14]. 优化算法的求解方式通常有3类:一是基于RSM拟合方程,利用优化算法对拟合方程进行优化求解,如 Vedrtnam等人[12]基于RSM拟合方程预测了埋弧焊最佳工艺参数组,但该研究中未开展基因算法优化结果与RSM优化结果的差异比较;二是在RSM拟合方程的基础上,设置权重后利用优化算法进行多目标优化,如王霄等人[13]基于RSM建立了计算焊接强度、焊缝宽度和焊接成本的二阶多项式数学模型,利用遗传算法计算综合性能优异的焊接工艺参数组合;三是将OED或RSM的试验方案中的试验点作为学习样本建立神经网络模型,利用优化算法进一步求解,如余果等人[14]为确定运载火箭膜盒膜片材料的焊接工艺,依据OED结果建立了BP神经网络预测模型,结合小步长搜索法获得了较高抗拉力值对应的最佳工艺参数范围. 上述研究应用优化方法获得了较好的工艺参数组合,但这些方法仍需要通过OED或RSM建立数据模型,基于数据模型和算法进行联动求解,增加了解决问题的学习成本,不利于实际工程的应用.
OED,RSM等优化方法在实际工程中存在较高的使用门槛. 因此,工程师打样时一般依赖经验,开展一批采用类似遗传算法单点变异的参数组合试验后优选较好的工艺参数组合. 蜜蜂算法(bees algorithm, BA)是在工程领域被大量应用的一种算法,能够通过适应度评价函数对一些解决方案进行参数化表示[15]. Laili等人[16]基于BA所开发的三元蜜蜂算法(ternary bees algorithm, TBA)在机器人拆解路径规划中展现了可达成在线实时优化的快速计算能力,其特点在于能够通过少量的搜索次数进行可靠度较高的有针对性优化求解.
在目前打样方法研究的基础上,借鉴TBA的架构建立了一种仅依赖试验以求解更优工艺参数的试验方法. 该方法通过元启发式的优化求解能够有效解决RSM中最小二乘法拟合导致的概率计算问题[9]. 为验证该方法的有效性,同时比较了与RSM及基于RSM拟合方程的BA求解两种方法所获得最优工艺参数的差异. 通过该研究能够为工程师打样过程提供一种学习成本低且更快获得更优参数组合的试验方法.
1. 试验及理论方法
1.1 试验条件
试验采用通快(中国)有限公司所提供的TruLaser Robot 5020型机器人焊接系统,激光功率最大为4 kW,机器人线性轴的定位精度可达0.08 mm,旋转轴的定位精度可达0.015°. 试验所选母材为电池盒等常用的304不锈钢,经线切割将母材切割成尺寸为200 mm × 100 mm × 2 mm的板材,焊接前使用WD-40万能除锈剂对试件进行擦拭,以消除试件表面的氧化膜、杂质及油污. 如图1所示,试件经夹具定位后进行激光对接焊. 焊接过程中,采用氩气作为保护气体,气体流量为40 L/min.
研究选定抗拉强度作为优化目标,以激光功率、焊接速度和离焦量为工艺条件的设计变量.考虑到焊缝的质量、焊缝表面出现飞溅和咬边等焊接缺陷、焊接不熔或者焊接熔透等因素,结合工程师建议确定激光功率、焊接速度和离焦量3个变量的取值范围分别为1.5 ~ 3.5 kW,0.02 ~ 0.05 m/s及−2 ~ −0.5 mm.
焊接结束后,采用TruLaser 3040 fiber型激光切割机对试件进行切割,该仪器中的DetectLine和CoolLine功能可精确定位板材,对于加工余量小的板材也能高精度地进行切割. 按照标准GB/T 2651—2008《焊接接头拉伸试验方法》采用UTM5000微机控制电子万能试验机进行拉伸试验,其拉伸速率为20 mm/min.
1.2 Box-Behnken响应面法
RSM的试验种类中含有全因子试验设计、部分因子试验设计、中心复合设计和Box-Behnken Design (BBD),其中,中心复合设计和BBD是最常用的两种方法. 在相同因子个数的情况下,中心复合设计所需开展的试验次数要多于BBD. 从经济性及实际应用需求的角度考虑,该研究在最优激光焊工艺参数预估区间内采用BBD设计试验方案,将激光功率、焊接速度和离焦量作为试验变量,进行3因素3水平的响应面分析,所设计试验因素水平表如表1所示.
表 1 响应面试验的因素和水平编码Table 1. Factor and level code of response surface test编码 激光功率Q/kW 焊接速度v/(m·s−1) 离焦量f/mm −1 1.5 0.02 −0.5 0 2.5 0.035 −1.25 1 3.5 0.05 −2 1.3 基于RSM拟合方程的蜜蜂算法
BA算法中优化问题的最优解即为算法中的蜜源位置,优化过程由全局随机搜索与局部搜索相结合,由侦察蜂随机在整个搜索区域内全局搜索,寻找有价值的蜜源. 跟随蜂根据侦察蜂带回的信息,挑选其中的优质蜜源(包含精英蜜源和精选蜜源)进行局部搜索觅食. 侦察蜂在跟随蜂采集花粉的同时也开始新的搜索,从而更加高效地采集食物.
基于这一行为的BA具备两个突出的特点为明确的功能划分和并行计算,从而能够保证蜜蜂算法在寻找最优参数上发挥作用. 其中,对优质蜜源进行局部搜索的机制类似于工程师打样过程中为找到更优解时进行的参数微调. 研究中所比较的方法中包含BA的两种不同使用方法:一是基于RSM拟合方程的一般蜜蜂算法(RSM-BA)优化求解;二是类似于工程师打样思路的快速蜜蜂试验法(fast bees test method, FBTM). 其中,RSM-BA方法的伪代码如图2所示. 图2中n为侦察蜂数量,e为精英蜜源个数,m为略差于精英蜜源的精选蜜源个数,nep为精英蜜源的跟随蜂数量,nsp为精选蜜源的跟随蜂数量,itr为迭代次数.
1.4 快速蜜蜂试验法
通过优化现有工程师打样方法及借鉴三元蜜蜂算法[14]架构,研究设计了仅通过少量试验进行优化的FBTM,该试验方案设计流程图如图3所示,每轮优化所需试验次数为11次.
试验中,首先在预估工艺参数区间内执行3次全局随机搜索,测试获得抗拉强度后进行排序,将最好的解定义为精英蜜源,次好的解定义为精选蜜源,最差的舍去;其次,在精英蜜源执行3次局部搜索,在精选蜜源执行2次局部搜索,同时全局执行3次随机搜索. 每轮所有试验所获得的最佳抗拉强度所对应的工艺参数组合即为该轮优化结果.
2. RSM试验结果与分析
2.1 参数设计及试验结果
根据BBD试验方案,对激光功率(A)、焊接速度(B)和离焦量(C)开展15组试验,各组试验所采用的参数与测试结果如表2所示.
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计与结果Table 2. Box-Behnken experimental scheme and results序号 激光功率Q/kW 焊接速度v/(m·s−1) 离焦量f/mm 抗拉强度Rm /MPa 1 1.5 0.02 −1.25 637 2 3.5 0.02 −1.25 637 3 1.5 0.05 −1.25 667 4 3.5 0.05 −1.25 635 5 1.5 0.035 −0.5 671 6 3.5 0.035 −0.5 613 7 1.5 0.035 −2 630 8 3.5 0.035 −2 669 9 2.5 0.02 −0.5 635 10 2.5 0.05 −0.5 658 11 2.5 0.02 −2 661 12 2.5 0.05 −2 651 13 2.5 0.035 −1.25 663 14 2.5 0.035 −1.25 659 15 2.5 0.035 −1.25 663 2.2 响应曲面模型的检验
如表3所示, P值可用来检验各试验因素对响应值影响的显著性的高低,其值越低则否定原假设的证据越充分. 如显著性水平α所示,在模型不解释响应中的变异时得出模型对此进行解释的风险为5%. 该试验研究得出的模型显著性检验P值小于α,说明该模型显著.
表 3 响应面拟合回归方程的方差分析结果Table 3. Analysis of variance results of response surface fitting regression equation方差来源 平方和Ss 自由度f 方差Ms F值 P值 显著性水平α 回归模型 4171.09 9 463.45 37.47 0.0005 ** A 332.66 1 332.66 26.90 0.0035 ** B 219.90 1 219.90 17.78 0.0084 ** C 137.08 1 137.08 11.08 0.0208 * AB 248.54 1 248.54 20.09 0.0065 ** AC 2326.98 1 2326.98 188.14 < 0.0001 ** BC 293.74 1 293.74 23.75 0.0046 ** A2 472.95 1 472.95 38.24 0.0016 ** B2 141.08 1 141.08 11.41 0.0197 * 残差 61.84 5 12.37 失拟项 54.73 3 18.24 5.13 0.1674 纯误差 7.11 2 3.56 合计 4232.93 14 注: *代表差异显著,P值 < 0.05;**代表高度显著,P值 < 0.01. 由表3可知,工艺条件对抗拉强度影响大小顺序为:激光功率、焊接速度和离焦量. 模型的决定系数R2为0.985 4,说明模型显著,而调整系数Radj2 = 0.959 1,能够解释试验95.91%的响应值变化,预测相关系数RPred2为0.789 3,与矫正决定系数也十分接近,说明此试验模型能够较好拟合真实数据.
2.3 响应曲面模拟的拟合
如图4所示,拟合模型置信区间为0.95,在观测残差散点图中,没有发现任何升降趋势奇异的点,也未发现有无规则波动的点,由此可初步判定拟合模型正常.
2.4 提取工艺各因素响应曲面分析
从图5可以看出,激光功率和焊接速度的交互作用对抗拉强度的影响呈倾斜分布,当激光功率较小时,随着焊接速度的增加,抗拉强度呈上升趋势;而当焊接速度不变时,随着激光功率的提高,抗拉强度基本呈现先增加后减小,但是曲面波动幅度大于焊接速度的影响.
在两者交互作用下,激光功率在交互作用中的贡献更大,对抗拉强度影响也更大. 仅考虑两者因素作用下,最优提取工艺组合范围为激光功率在1.5 ~ 2.5 kW水平范围内,焊接速度在0.044 ~ 0.05 m/s水平范围内.
图6为激光功率和离焦量的交互作用对抗拉强度的影响. 激光功率和离焦量交互响应面纵向跨度较大,表明激光功率在交互作用中对抗拉强度影响较离焦量影响显著. 在实际工艺条件控制中,当激光功率位于3 ~ 3.5 kW水平且离焦量趋于−0.5 mm水平组合,或激光功率趋于1.5 kW、离焦量趋于−2 mm组合下抗拉强度较高,可控制该条件以获得合理工艺参数.
图7为焊接速度和离焦量的交互作用对抗拉强度的影响. 从图7可知,在焊接速度0.02 ~ 0.044 m/s、离焦量−2 ~ −0.8 mm水平范围内,可观察到抗拉强度随焊接速度和离焦量的增加而递增.
2.5 RSM优化结果
为进一步确定全局最优解,根据Design-Expert软件进行优化求解,在激光功率为1.595 kW、焊接速度为0.041 m/s、离焦量为−1.984 mm条件下,模型预测的抗拉强度可达到689 MPa.
3. RSM-BA运行结果与分析
3.1 优化流程
根据RSM所得到抗拉强度y与激光功率x1、焊接速度x2及离焦量x3之间的二次回归方程为
$$ \begin{split} y = & 442.929 + 108.732 {x_1} + 2\;634.24 {x_2} - 67.283\;3 {x_3} -\\& 525.5 {x_1} {x_2} + 32.159\;2 {x_1} {x_3} - 761.722 {x_2} {x_3} - \\& 11.317\;7 {x_1}^2 - 27\;473.1 {x_2}^2 - 7.625\;93 {x_3}^2 \end{split} $$ (1) 取1/y作为适应度进行最小化,按照经验和测试,所设置算法的初始值如表4所示. 在精英蜜源和精选蜜源的领域搜索中,3个工艺参数所采用的领域半径设置为工艺参数范围的25%,分别为0.5 kW,0.0075 m/s和0.375 mm. 同时,迭代次数设置为20次,即重复循环20次侦察峰及跟随蜂的搜索行为,根据产生的解计算适应度.
表 4 研究中所采用蜜蜂种群的参数Table 4. Parameters of bee population used in this study迭代次数N/次 侦察蜂数量n/个 精英蜜源数量e/个 精选蜜源数量 m/个 精英蜜源跟随蜂数量 nep/个 精选蜜源跟随蜂数量nsp/个 20 50 5 5 50 5 3.2 RSM-BA优化结果
利用BA在基于RSM拟合方程优化过程中,经20次迭代所获最优解为如图8所示的1.454,即688 MPa. 此时所预测最佳工艺参数组合为:激光功率1.5 kW、焊接速度0.05 m/s、离焦量−2 mm.
该结果与RSM模型拟合预测的抗拉强度689 MPa相比,几乎保持一致. 所存在微小差异可能来源于算法在搜索过程中的步长设置,与RSM模型原有优化方式有一定区别. 上述结果表明,研究利用RSM拟合方程与优化算法联动求解单个优化目标的方式只能局限在RSM所拟合响应面内搜索最优,难以获得其他学者所预期的优化提升价值[12].
4. 快速蜜蜂试验法结果与分析
4.1 试验流程及结果
根据FBTM的流程,确定侦察蜂的数量为3只,在表1所示激光焊参数范围所示领域中进行3次全局随机搜索, 按照随机参数进行试验后获得了表5中第一组试验结果. 根据排序结果将第3个试验点作为精英蜜源,第1个试验点作为为精选蜜源,同时舍去第2个试验点. 确定蜜源后,对精英蜜源进行3次局部搜索(领域半径与RSM-BA设置相同),对精选蜜源进行2次局部搜索,同时进行3次全局搜索. 所获得第2组试验结果如表5中第2组所示.
表 5 FBTM试验参数及结果Table 5. Experimental parameters and results of FBTM组别 激光功率P/kW 焊接速度v/(m·s−1) 离焦量f/mm 抗拉强度Rm /MPa 备注 1 2.3 0.029 −1.4 667 精选蜜源 1 2.7 0.026 −1.1 641 放弃 1 2.9 0.038 −1.85 694 精英蜜源 2 2.8 0.042 −1.9 679 精英领域 2 3.0 0.040 −1.9 706 精英领域 2 2.6 0.043 −1.6 718 精英领域 2 2.6 0.035 −1.1 707 精选领域 2 2.7 0.031 −1.1 726 精选领域 2 2.1 0.047 −1.25 720 全局随机 2 1.7 0.044 −0.65 734 全局随机 2 2.7 0.026 −1.85 690 全局随机 FBTM完成了一轮,此时所获得最优参数为激光功率1.7 kW,焊接速度0.044 m/s,离焦量−0.65 mm,所得到最大抗拉强度为734 MPa.
初期搜索结果对于FBTM找到最优解具有重要的影响. 为验证FBTM方法的普适性,开展了如表6所示的11组随机搜索试验,以探索在无针对性搜索情况下所获抗拉强度是否能满足期望值. 可观察到所获得全部抗拉强度中已有7个结果超过了660 MPa,占比63.6%,该试验值已接近另外两种方法所求最优解678 MPa. 一般情况下,抗拉强度660 MPa已基本满足客户需求.
表 6 全局随机试验结果Table 6. Experimental results of global searching组别 激光功率P/kW 焊接速度v/(m·s−1) 离焦量f/mm 抗拉强度Rm /MPa 备注 1 3.3 0.023 −1.7 662 全局随机 1 2.5 0.044 −1.4 635 全局随机 1 2.3 0.047 −1.85 672 全局随机 1 2.6 0.029 −1.42 634 全局随机 1 2.1 0.024 −2 630 全局随机 1 2.7 0.049 −1.55 665 全局随机 1 2.76 0.042 −2 633 全局随机 1 1.94 0.046 −2 663 全局随机 1 2.3 0.044 −1.25 667 全局随机 1 2.1 0.047 −1.7 664 全局随机 1 2.5 0.029 −1.1 663 全局随机 4.2 FBTM结果分析
通过比较FBTM和全局搜索各11组试验后发现,即使在没有FBTM有针对性的领域搜索机制下,全局搜索也能获得较好地发现较优工艺参数. 一定程度上可说明工程师在初期所设置合理参数范围区间内获得预期抗拉强度的概率本身较高,为尽量获得更优解可通过FBTM采取有针对性的领域搜索. 同时,可在第1次迭代后对随机参数进行优选以提高获得更优解的概率,即第2次迭代中可参考第1次迭代结果放弃部分随机蜜源.
在研究FBTM中激光功率为1.7 kW,焊接速度为0.044 m/s,离焦量为−0.65 mm时,测试获得最大抗拉强度为734 MPa. 值得注意的是,与前两种含有RSM方法所获得预测值不同的是,FBTM的结果均来自试验.
5. 试验结果与分析
如表7所示,由RSM,RSM-BA及FBTM所获最优解分别开展验证试验,所获得的最大抗拉强度分别为689,688,734 MPa. 预测结果基本一致的RSM及RSM-BA所求解激光功率、焊接速度及离焦量也具有相接近的数值. 其中,激光功率和离焦量接近RSM所选取试验点的最小值,而焊接速度接近所选取试验点的最大值. 由于RSM-BA仍是基于RSM所拟合二次回归方程所进行的参数寻优,仅能说明蜜蜂算法参数寻优有效,但无法在RSM本身单目标交互优化基础上获得更优解.
表 7 3种优化方法的参数及结果对比Table 7. Comparison of parameters and results of three optimization methods方法 激光功率P/kW 焊接速度v/(m·s−1) 离焦量f/mm 抗拉强度Rm /MPa 预测值 验证值 RSM 1.595 0.041 −1.984 689 678 RSM-BA 1.5 0.05 −2 688 695 FBA 1.7 0.044 −0.65 734 725 FBTM所求最优解相比前两种方法近似提高了45 MPa. 虽仅仅提升了约6.5%,但充分体现出不同优化机制所带来的差异. 通常情况下,仅一次迭代获得满足预期目标的概率较大. 该研究同时开展了11组随机试验,说明该方法在缺失领域搜索机制时的效果,发现63.6%的试验中抗拉强度超过了660 MPa,可证明FBTM所采用的元启发式搜索机制能够避免RSM最小二乘拟合时对试验点同等对待所忽略的概率密度问题,并在参数区间内搜索到次优解的试验点后进一步开展局部搜索以获得更优解.
为验证优化结果的准确性,分别以3组参数开展试验,3组试验与预测值或试验值的相对误差分别为−11,7,−9 MPa. 预测误差可归因为拟合模型的精度;试验误差可归因为焊接过程中两块板间隙及其它焊接环境等因素. 据此所获结果可说明3种方法优化解均有效.
6. 结论
(1) 经RSM,RSM-BA和FBTM 3种方法所优化工艺参数对比分析,FBTM所确定工艺条件中离焦量与其它两种方法存在明显差异,可证明RSM所构建响应面仍有可能丢失最优参数所在区域的部分特征.
(2) RSM和RSM-BA优化求解所预测抗拉强度最优解均近似于688 MPa. 说明利用RSM与优化算法联动方式在单一目标优化求解中,并不能获得所预期的显著优化提升效果. FBTM能够避免RSM模型建立过程中存在最小二乘拟合所忽略的不同区域中概率密度不同的问题,在求解过程中重视结果突出的试验点,研究求解中获得了734 MPa的抗拉强度.
(3) FBTM针对性的领域搜索机制类似于目前工程师打样过程中对测试结果较好的参数组合进行微调. FBTM的搜索策略具有明确的划分和针对性,能够有效提升搜索工艺参数的效率,在实际工程中采用一次迭代就可较高概率获得满意参数组合.
-
表 1 EP和Al2O3的材料参数
Table 1 Material parameters of epoxy resin and alumina ceramics
材料 密度ρ/( kg·m−3) 纵波波速v/(m·s−1) 杨氏模量E/GPa 泊松比υ 声阻抗Z/(106 kg·m−2·s−1) EP 1 200 2 390 13.17 0.35 2.9 Al2O3 3 700 9 900 111.08 0.23 0.37 表 2 空气的材料参数
Table 2 Material parameters of air
密度
ρ/(kg·m−3)声速
v/(m·s−1)杨氏模量
E/GPa泊松比
υ1.29 340 0 0 -
[1] Koch H. Introduction to the panel on gas insulated technology[J]. IEEE, 2008(1-11): 4779 − 4780.
[2] 齐波, 张贵新, 李成榕, 等. 气体绝缘金属封闭输电线路的研究现状及应用前景[J]. 高电压技术, 2015, 41(5): 1466 − 1473. Qi Bo, Zhang Guixin, Li Chengrong, et al. Research status and application prospect of gas-insulated metal-enclosed transmission lines[J]. High Voltage Technology, 2015, 41(5): 1466 − 1473.
[3] Zhang Z, Hao Y, Peng J, et al. A three-factor accelerated aging test platform of hermal, mechanical compression, pressured SF6 and a leakage test system for GIS O-Ring seals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 1 − 11.
[4] 郝艳捧, 黄盛龙, 申子魁, 等. 环氧复合绝缘内部缺陷超声自动检测系统[J]. 广东电力, 2024, 37(3): 72 − 81. Hao Yanpeng, Huang Shenglong, Shen Zikui, et al. Ultrasonic automatic detection system for internal defects of epoxy composite insulation[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2024, 37(3): 72 − 81.
[5] Lundgaard L E, Tangen G, Skyberg B, et al. Acoustic diagnoses of GIS; field experience and development of expert system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery, 1992, 7(1): 287 − 294. doi: 10.1109/61.108920
[6] Qi B, Li C, Hao Z, et al. Partial discharge detection for GIS: A comparison between UHF and acoustic methods[C]// Electrical Insulation (ISEI), Conference Record of the 2010 IEEE International Symposium on, IEEE, 2010: 1-5.
[7] 程志强. 基于太赫兹成像技术的绝缘材料缺陷检测实验研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2021. Cheng Zhiqiang. Experimental study on defect detection of insulating materials based on terahertz imaging technology [D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2021.
[8] Nsengiyumva W, Zhong S, Lin J, et al. Advances, limitations and prospects of nondestructive testing and evaluation of thick composites and sandwich structures: A state-of-the-art review[J]. Composite Structures, 2021, 256: 112951. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2020.112951
[9] 陆铭慧, 刘磨, 张雪松, 等. RTM玻璃纤维/E51环氧树脂复合材料孔隙含量对超声特征参数的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(2): 291 − 297. Lu Minghui, Liu Mo, Zhang Xuesong, et al. Effect of pore content on ultrasonic characteristic parameters of RTM glass fibre/E51 epoxy resin composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2018, 35(2): 291 − 297.
[10] 尹桂来, 李建英, 王诗航, 等. GIS用氧化铝改性环氧浇注材料的热学与力学性能研究[J]. 绝缘材料, 2014, 47(5): 50 − 54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9239.2014.05.012 Yin Guilai, Li Jianying, Wang Shihang, et al. Thermal and mechanical properties of alumina-modified epoxy castable materials for GIS[J]. Insulation Materials, 2014, 47(5): 50 − 54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9239.2014.05.012
[11] 田雨阔. 不锈钢电弧塞焊接头相控阵超声检测技术研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2023. Tian Yukuo. Research on phased array ultrasonic inspection technology of stainless steel arc plug welding head [D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2023.
[12] Sarpuen I H, Kilickaya M S. Mean grain size determination in marbles by ultrasonic first backwall echo height measurements[J]. Ndt & E International, 2006, 39(1): 82 − 86.
[13] Kováiková P, Vávro J, Dubec A. Measuring of vibration-damping properties of cast iron[J]. Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 18(1): 57 − 59. doi: 10.21062/ujep/53.2018/a/1213-2489/MT/18/1/57
[14] Guo Z, Song Y, Li X. Numerical analysis of ultrasonic wave propagation and scattering in oligo-crystalline materials[J]. Wave Motion, 2022, 115: 103048. doi: 10.1016/j.wavemoti.2022.103048
[15] Kamaraj M. , Dodson E A, Datta S. Thermal and viscoelastic behaviour of graphene nanoplatelets/flax fibre/epoxy composites[J]. Plastics, Rubber and Composites, 2021, 50(5): 219 − 227. doi: 10.1080/14658011.2020.1871241
[16] Fahad B M, Al-jadiri R S F. Acoustic impedance evaluation of the polymer–polymer hybrid composites as insulator building materials[J]. Polymers, 2023, 15: 3479.
[17] Liu Y, Tian Q, Yu P, et al. Shape and size evaluations of elongated grains using phased array ultrasound and directional backscattering method[J]. NDT & E International: Independent Nondestructive Testing and Evaluation, 2022(129): 129.
[18] Zeng Y, Himmler D, Randelzhofer P, et al. Processing of in situ Al3Ti/Al composites by advanced high shear technology: influence of mixing speed[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2020, 110(5-6): 1589 − 1599. doi: 10.1007/s00170-020-05956-w
[19] Li R, Xia H, Xu Z, et al. U-DMA measurement and dynamic analysis of ultrasonic wave propagation in particulate composites[J]. Composites Science and Technology, 2017, 151: 174 − 183. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.08.022
[20] 赵俊. 高体积分数铝合金复合材料非线性力学特性的仿真研究[J]. 铸造技术, 2013, 34(11): 1468 − 1470. Zhao Jun. Simulation study on nonlinear mechanical properties of high volume fraction aluminium alloy composites[J]. Foundry Technology, 2013, 34(11): 1468 − 1470.
[21] 吴凯, 吴少雷, 冯玉, 等. 界面接触状态和温度对电缆附件界面击穿电压和形态特性影响研究[J]. 绝缘材料, 2023, 56(12): 85 − 91. Wu Kai, Wu Shaolei, Feng Yu, et al. Study on the effects of interfacial contact state and temperature on the interfacial breakdown voltage and morphological characteristics of cable accessories[J]. Insulation Materials, 2023, 56(12): 85 − 91.
-
期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: