Microstructure and mechanical properties of welded joint of titanium/steel and titanium/copper/steel composite plate
-
摘要:
采用电弧焊接方法(TIG/MIG)进行钛/钢(TA1/Q345)和钛/铜/钢(TA1/T2/Q345)复合板的对接焊接,借助SEM,EBSD,TEM,显微硬度、纳米压痕和拉伸试验系统研究了对接焊缝中的显微结构和力学性能. 结果表明,钛/钢对接接头中,Cu-V焊缝主要以铜基固溶体和铁基固溶体为主,局部生成的Fe2Ti相被韧性较好的铜基固溶体包围;Cu-V/ERTi-1焊缝界面处存在多种Cu-Ti和Fe-Ti金属间化合物;Cu-V焊缝与TA1/Q345界面处,存在Fe-Ti,CuTi2和β-Ti化合物. 钛/铜/钢对接接头中,Cu/ERTi-1焊缝界面处分布着多种Cu-Ti金属间化合物,分布范围较广. 钛/钢对接焊缝中Fe2Ti脆性相的硬度较高,为20.7 GPa,但由于其尺寸相对较小,因此接头的显微硬度分布与钛/铜/钢对接焊缝类似,高硬度区域均在铜基焊缝与ERTi-1焊缝界面处,达到400 HV0.3,两种对接接头中大量分布的Cu-Ti化合物的硬度处于8 ~ 11 GPa. 钛/钢异质接头的抗拉强度为440 MPa,钛/铜/钢异质接头的抗拉强度为225 MPa,断裂位置均在焊缝区域,并且铜基焊缝与ERTi-1焊缝界面处均是脆性断裂特征. 钛/钢对接焊缝中不可避免会存在Fe-Ti脆性相,虽然采用钛/铜/钢三层复合板的形式可以避免Fe-Ti脆性相的生成,但是接头中分布较广的Cu-Ti化合物仍旧是接头的一个薄弱区域.
Abstract:The titanium/steel and titanium/copper/steel composite plates were butt joined by arc welding method. SEM, EBSD, TEM, microhardness, nanoindentation and tensile tests were applied to investigate the microstructure and mechanical properties. The results showed that in the titanium/steel butt joints Cu-V weld mainly consisted of Cu solid solution and Fe solid solution phases. Localized Fe2Ti intermetallics were surrounded by the soft Cu solid solution. Cu-Ti and Fe-Ti intermetallics were formed at Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface. Cu-V weld near the TA1/Q345 interface consisted of Fe-Ti, CuTi2 and β-Ti phases. A series of Cu-Ti compounds were widely distributed at Cu/ERTi-1 interface in titanium/copper/steel butt joints. Although Fe2Ti brittle intermetallics had high hardness (20.7 GPa), its limited size had less effect on the global microhardness distribution. These two butt joints had similar microhardness distribution, where high hardness values (400 HV0.3) were located at the Cu-base weld/ERTi-1 interface. The Cu-Ti compounds with wide distribution showed the hardness around 8 ~ 11 GPa.The tensile strength of titanium/steel butt joint and titanium/copper/steel butt joint were 440 MPa and 225 MPa, respectively. Both samples were fractured at the weld metal regions and brittle fracture morphology was observed at the Cu-based weld/ERTi-1 interface regions. Fe-Ti brittle intermetallics were inevitable in titanium/steel butt joint. These brittle phases were suppressed in titanium/copper/stee butt joints. However, the widely distributed Cu-Ti compounds region was the weak region of such joints.
-
0. 序言
奥氏体不锈钢在低温环境中具有优异的强度与韧性组合,使其成为低温工况常用的结构材料之一,目前已用于液氢储运容器结构材料以及国际热核反应试验堆等低温设施[1-3]. 但奥氏体不锈钢焊接接头力学性能通常略逊于母材,尤其冲击韧性随温度降低下降较大,因此,低温冲击韧性成为奥氏体不锈钢焊接接头能否安全应用的关键性能之一.
奥氏体不锈钢在焊接以及后续热处理过程中,焊缝金属易形成σ相、χ相、laves相以及碳化物、氮化物等硬脆的析出相和金属间化合物,造成焊接接头低温韧性急剧降低,严重影响低温结构的安全性[4-8]. 以往对焊缝金属中析出物的研究多集中于热处理过程中的析出行为以及对力学性能的影响,而缺乏用于低温工况的焊态焊缝金属中析出物对焊接接头韧性降低作用的研究[9-11]. 焊接接头组织和性能取决于熔焊过程焊缝金属的化学成分和凝固速度,因此,通过合理调整焊材成分可减轻或避免析出物对性能的不利影响.
在对所研制低温奥氏体不锈钢焊条的性能试验中,焊态焊缝金属性能出现了急剧降低现象,此现象将严重影响低温焊接结构的安全服役. 因此使用可获得成分及组织相似的焊条,并采用SMAW方法获得焊缝金属,进而进行对比研究焊态焊缝金属性能变化. 通过光学显微镜(optical microscope,OM)、扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)和电子背散射衍射(electron back scatter diffraction,EBSD)等方法分析了焊缝金属微观组织和析出物特征. 同时对焊缝金属的力学性能进行了系统的研究,并探讨了其显微组织对断裂行为的影响.
1. 试验方法
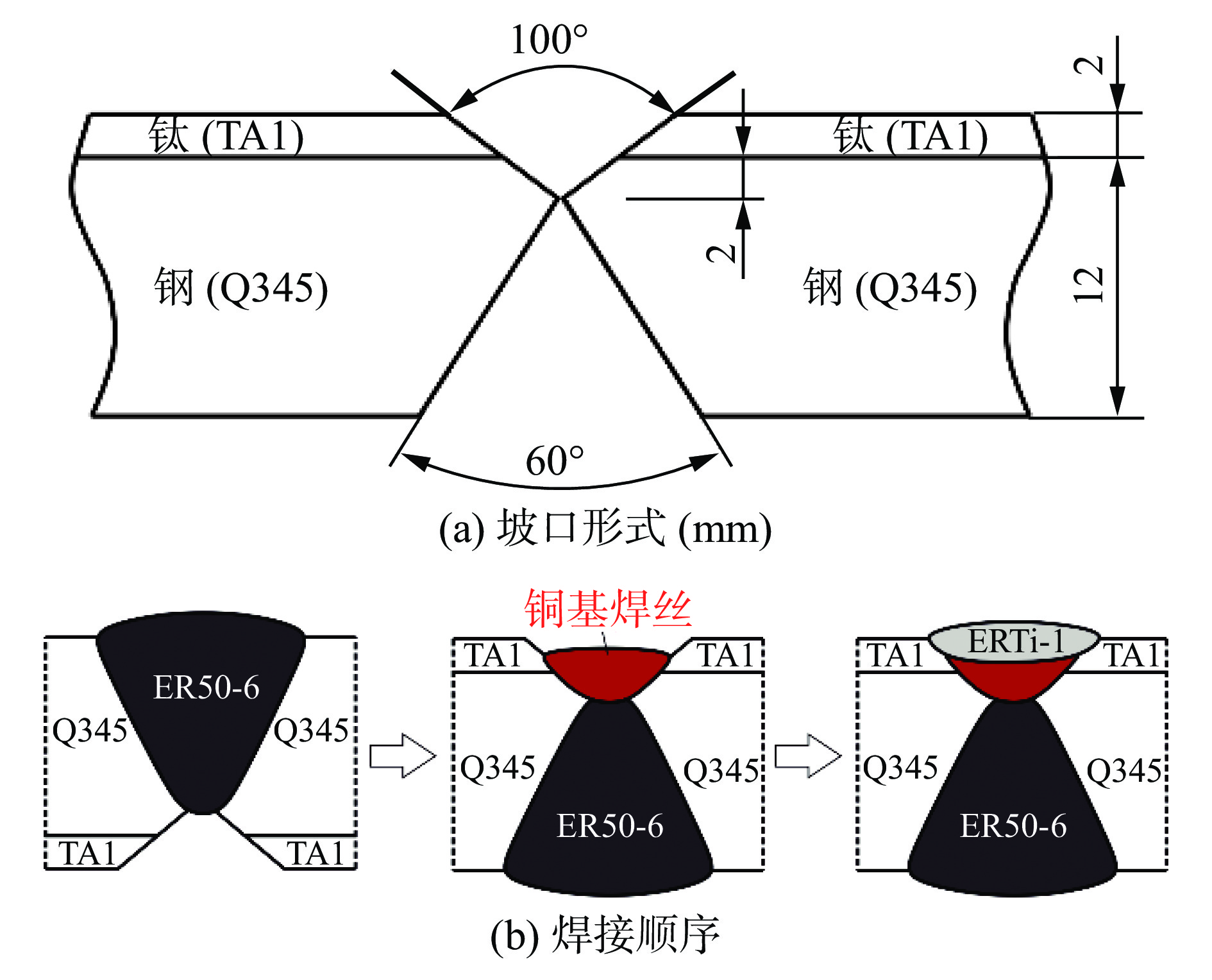
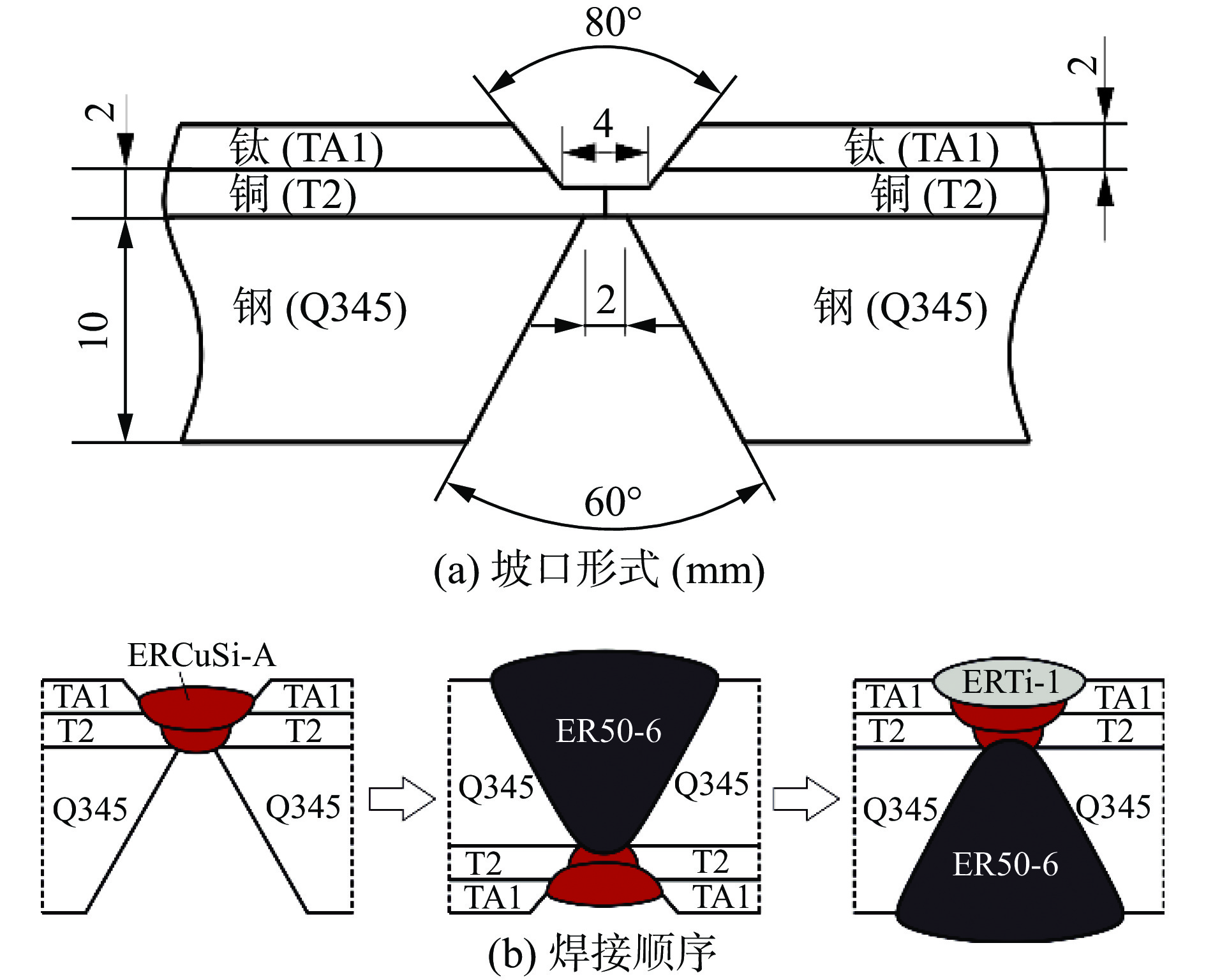
试验采用直径4.0 mmE316LMn-15焊条进行施焊,焊条采用同种焊芯,仅焊条药皮成分存在微小差异. 母材和垫板采用Q235,并在焊前使用同类型焊条堆焊过渡层以抑制元素扩散和焊缝开裂,母材尺寸为300 mm × 300 mm × 20 mm,对接焊缝坡口配置,如图1所示. 制备的焊条在经过350 ℃/1 h烘干后进行施焊,采用低热输入以避免奥氏体不锈钢焊缝过热而可能发生的裂纹等缺陷,并严格控制道间温度在100 ℃以下,详细焊接参数见表1. 试验所得4组焊缝金属化学成分见表2,其中S1和S4的Mo含量较低,而S2和S3的Mo含量高达3.5%.
表 1 焊接工艺参数Table 1. Welding process paraments电流类型 焊接电流
I / A电弧电压
U / V焊接速度
v /(mm·min−1)道间温度
T /℃DCEP 140~150 24~30 ≥150 ≤100 表 2 焊缝金属化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 2. Chemical compositions of weld metals编号 C Si Mn S P Cr Ni Mo Fe S1 0.030 0.55 6.20 0.0088 0.018 18.60 14.51 2.87 余量 S2 0.033 0.64 6.60 0.0069 0.012 19.02 14.60 3.44 余量 S3 0.039 0.63 5.98 0.0063 0.012 18.99 15.23 3.57 余量 S4 0.031 0.46 5.98 0.0041 0.015 19.41 15.34 2.16 余量 拉伸试样在焊缝中心平行于焊接方向制取,平行段长度60 mm,直径 10 mm,试验按照国家标准GB/T 228.1—2021《金属材料 拉伸试验第1部分:室温试验方法》使用WAW-300微机控制电液伺服万能试验机在室温下进行,位移控制为0.036 mm/s. 冲击试样沿焊接接头横截面切割,试样尺寸为55 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm,V形缺口加工在焊缝金属中心,冲击试样取样,如图2所示. 根据国家标准GB/T 229—2020《金属材料 夏比摆锤冲击试验方法》要求,试样在液氮中充分冷却至−196 ℃后,在5 s内转移至PTM2302摆锤式冲击试验机上并完成冲击试验,对每个焊缝金属进行3次夏比冲击试验.
焊缝金属中铁素体含量使用FICHER FMP30铁素体仪进行检测,金相试样自焊缝金属横截面进行切割,经机械研磨和抛光后,在10%铬酸溶液中进行电化学腐蚀并采用OLYMPUS GX53光学显微镜、ZEISS EVO18扫描电子显微镜对焊缝金属微观组织和冲击断面微观形貌进行观察,并通过EBSD进一步研究了焊缝金属及断面附近组织,EBSD断面试样垂直于冲击试验断后试样中心取样,采集步长为0.16 μm.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 焊缝金属室温拉伸及低温冲击性能
S1 ~ S4焊缝金属室温拉伸试验结果和−196 ℃平均冲击吸收能量,如图3所示. 室温拉伸试验中S1 ~ S4焊缝金属强度与塑性均良好,但S2和S3抗拉强度和屈服强度明显高于S1和S4,其中S2和S4屈服强度相差95 MPa,抗拉强度相差达120 MPa,而S2和S3抗拉强度和屈服强度仅分别相差25 MPa和30 MPa. 性能差异同样也表现在−196 ℃冲击试验结果中,S1和S4低温平均冲击吸收能量分别为51 J和51.33 J,S2和S3平均冲击吸收能量降低超85%,平均值均降至6.33 J. 强度的升高以及低温韧性下降可能是焊接过程中析出物的出现所导致的性能变化[12-13].
2.2 焊缝金属微观组织
奥氏体不锈钢焊缝金属组织一般由γ-奥氏体和一定量δ-铁素体组成,但δ-铁素体在−100 ℃以上就已发生韧—脆转变,造成焊接接头低温韧性劣化,因此,少量或不含δ-铁素体的焊接接头的低温韧性较好. E316LMn-15焊条可获得低铁素体的高韧性焊缝金属,铁素体仪测量S1 ~ S4中铁素体含量分别为0.6,0.9,0、0.4和S1 ~ S4典型光学显微组织,如图4所示,虽然S3试样中未检测出铁素体,但在图4(c)中仍观察到枝晶间δ-铁素体. S1 ~ S4凝固行为均符合奥氏体—铁素体(AF)凝固模式,在凝固过程中首先形成γ-奥氏体,而富含δ-铁素体形成元素的剩余液相在枝晶间形成δ-铁素体,显微组织由γ-奥氏体枝晶以及随机分布于枝晶间的δ-铁素体组成. 此外,在图4(b)和图4(c)中可明显观察到γ-奥氏体枝晶间和晶界处(见椭圆标记处)存在区别于δ-铁素体的连续条状或岛状金属间化合物,且图4(c)中金属间化合物分布密度小于图4(b).
为进一步观察焊缝金属中金属间化合物,对S2和S3进行SEM表征,如图5所示,图5(a)、图5(b)为S2中条状金属间化合物在枝晶间区域的分布和形貌. 图5(c)和图5(d)为S3金属间化合物形貌,枝晶间金属间化合物呈现片层状结构. 图5(b)、图5(d)中标记点的EDS分析结果见表3,与奥氏体基体相比,金属间化合物存在高Cr、高Mo而Ni含量较低区域,根据其成分及形貌推断枝晶间存在多种结构的混合相,包括σ相和δ-铁素体.
表 3 图5中标记点EDS分析结果(质量分数,%)Table 3. EDS analyses of the points marked in Fig. 5标记点 C Si Cr Mn Fe Ni Mo A 1.32 0.72 23.60 7.54 49.34 11.42 6.06 B 1.53 0.69 26.24 6.60 47.97 9.00 7.97 2.3 S2和S3断面形貌
S2和S3低温冲击断面形貌与冲击韧性变化具有极强相关性,如图6所示,图6(a)和图6(d)中宏观断面平直明亮且几乎无变形,表明S2和S3焊缝金属脆性断裂特征. 在较高应变速率的冲击载荷作用下,相较于韧性γ-奥氏体,由于枝晶间析出相的出现,脆硬的析出相与基体界面更容易产生裂纹,冲击试样微观断面图6(b)、图6(e)均呈现枝晶间脆性断裂特征,断面沿析出相发生,表明枝晶间区域是冲击载荷作用下的薄弱部位,可以推断枝晶间析出的σ相是裂纹源. 对断面进一步放大可更加清晰地发现图6(c)、图6(f)中断面底部分布着大量微裂纹,枝晶间区域的σ相与基体界面成为裂纹形核与扩展的场所,最终在冲击载荷下发生脆性断裂.
2.4 σ相析出机理分析
奥氏体不锈钢焊缝金属AF凝固模式以γ-奥氏体作为初生相,凝固顺序为:L→L + γ→L + γ + δ→γ + δ. 凝固组织为γ-奥氏体基体以及随机分布在枝晶间不同数量δ-铁素体. S1和S4组织完全符合这种凝固模式,而S2和S3组织中存在的析出相说明σ相形成还存在其他原因.
使用JMatPro计算了S2和S3在100 ℃/s冷却速率下的凝固路径,如图7所示. S2和S3中先凝固相γ-奥氏体的凝固温度分别为
1386.1 ℃和1388.63 ℃,接着分别在1274.2 ℃和1277.83 ℃通过共晶反应形成σ相,最终形成γ-奥氏体及σ相组织,S2和S3的计算凝固路径可归结为:L→L + γ→L + γ + σ→γ + σ,但在γ-奥氏体形成之后的冷却过程中,组织中并无δ-铁素体形成,计算结果与金相组织观察不符,说明在S2和S3凝固过程中σ相存在其他形成机制.σ相在奥氏体不锈钢凝固过程中形成方式有两种:第一种是在凝固后期,由于Mo在液相中的高度偏析,通过共晶反应形成;另一种是在δ-铁素体共析分解过程中通过固态相变形成[14]. 奥氏体不锈钢焊缝金属凝固过程液相中溶质偏析非常严重,S2和S3中Mo含量较高,而Mo在凝固过程中的再分配已被证明是这类材料性能和微观组织变化的主要原因[15-16]. 初生γ-奥氏体中Mo的偏析会导致枝晶核处Mo的贫化以及枝晶间的富集,较高浓度的Mo会在凝固结束时促进富Mo金属间化合物σ相的形成从而降低力学性能,并通过延长凝固温度范围来促进热裂. 区别于共晶反应以及时效过程中在奥氏体中直接析出的σ相,图8中枝晶间存在多种相混合结构,包括σ相、δ相以及未识别的白色区域,σ相与部分未分解的δ-铁素体,证实了S2和S3中σ相是由δ-铁素体在焊接过程中通过共析分解而形成的. 这一结果与MARIN等人[14]通过定向凝固试验证实的δ-铁素体在
1210 ℃共析分解为σ相和γ′相一致.焊接过程中,强铁素体形成元素可导致δ-铁素体快速形成,这意味着当Si,Cr,Mo在δ-铁素体中有效扩散时,可以加速δ-铁素体向σ相共析分解的发生. 在LEE等人[17]的研究中Si的添加显著增加了焊缝中σ相的体积分数和平均尺寸,而在此4组焊态焊缝金属成分中Si含量变化较小,Mo含量的增加成为σ相共析形成的主要原因. 同样的现象也出现在PERRICONE等人[18]的研究中,超过2.5%的Mo含量以A和AF模式凝固的焊缝金属枝晶间出现了σ相. 凝固过程中,σ相形成元素Mo在AF模式凝固的焊缝金属中随凝固过程的进行产生强烈偏析,γ-奥氏体形成后,由于δ-铁素体中Mo的溶解度更高,并且具有较高的扩散率,枝晶间富Mo液相凝固成为亚稳δ-铁素体,在较低的温度下共析分解为σ相以及具有与初生γ-奥氏体相不同成分的二次γ′相:δ→γ′ + σ. δ-铁素体的分解取决于其成分和冷却速率,低的冷却速率有利于γ′/σ共析结构的形核和生长,焊接厚板时,焊接热循环同样会促进高Mo亚稳δ-铁素体分解,而诸如激光焊接等高冷却速率的焊接工艺在一定程度上可以避免共析分解的发生,导致亚稳δ-铁素体相冷却后的保留[18]. 亚稳δ-铁素体共析分解的早期阶段σ相一般沿着γ/δ界面形成,导致δ-铁素体中Mo在边界处局部损耗,这促进了γ′的形核,然后σ相以某种形式与γ′相耦合生长[19]. 而δ-铁素体不完全固态转变结构在枝晶间仍然保留,这使得S2和S3的凝固顺序表现为包含共析分解的凝固模式:L→L + γ→L + γ + δ→γ + δ→γ + δ + σ + γ′. 相较于图4(b)和图4(c)展示存在于枝晶间的多种相混合结构,具有较低Mo含量的S1和S4,在焊接过程中并未发生δ-铁素体向σ和γ′相的共析转变,微观组织仅显示γ-奥氏体和极少量δ-铁素体,从而表现出较高的低温冲击韧性.
2.5 S2和S3焊缝金属断裂机理
研究冲击过程中σ相析出对焊缝金属断裂过程的影响,对断裂试样靠近断面的纵向进行切割并通过EBSD进行观察,如图9所示. 根据IPF图显示,试样存在大量孔洞多集中在枝晶间和晶界,相图中显示混合相与基体间的界面几乎全部发生断裂,孔洞周围仍保留的一定数量碎裂的δ-铁素体也证实了冲击试验前σ相的存在以及σ相在断裂过程中的作用. 图9(c)和图9(f)的KAM图被用于分析表征冲击断面附近的位错密度变化以及应变分布,S2和S3中位错高度集中于枝晶间混合相引起的裂纹和孔洞上且周边沿线的位错密度较高,而γ-奥氏体内的塑性应变较小. 焊缝金属本就存在的δ-铁素体以及通过共析分解形成的σ相,在低温冲击载荷下,脆硬的σ相以及δ-铁素体相使得局部应力更容易集中于混合相所在的位置,σ相导致不同界面位错缠结并阻碍位错运动,导致界面剥落和开裂,σ相周围出现裂纹,最终导致韧性的急剧降低,出现脆性断裂的结果.
裂纹的扩展与裂纹尖端的塑性应变有关. 在冲击载荷作用下,σ相的钉扎作用导致位错缠结和裂纹萌生,裂纹首先在σ相晶粒内形核. σ相在冲击过程中碎裂以及与δ-铁素体界面形成裂纹,为裂纹的扩展提供了优先位置,裂纹产生后向γ-奥氏体扩展,被γ-奥氏体阻断或被转至σ相边界,由于广泛分布的析出相位点使得裂纹扩展较短,微裂纹容易连接而导致断裂. 在此过程中,基体的塑性变形能力下降,导致冲击韧性急剧下降,最终表现为S2和S3光亮平直的宏观冲击断面形貌.
S2和S3中的σ相由δ-铁素体共析分解形成,σ相数量与δ-铁素体计算值相关. 而S3的Creq/Nieq大于S2,可以认为S3中σ相含量相较S2少,图9(b)和图9(e)中孔洞的密度也证实了S3中σ相较小的含量,而S2和S3平均冲击吸收能量均为6.33 J,这一结果说明即使焊缝金属中σ相的含量少,仍然会对低温冲击韧性造成极大破坏. 虽然在−196 ℃下,δ-铁素体已发生了韧—脆转变,但从S1和S4超过50 J的平均冲击吸收能量来看,以AF模式凝固的焊缝金属中少量的铁素体相并未对冲击韧性造成过大的降低作用,其韧性仍保持在较高的水平.
3. 结论
(1) 以AF模式凝固的高Mo含量焊缝金属,Mo元素在凝固后期易富集于枝晶间而形成亚稳δ-铁素体,在低速率冷却过程中发生共析分解而形成σ相和γ′相,并与未分解的δ-铁素体在枝晶间组成混合相.
(2) 枝晶间δ-铁素体共析分解形成的σ相在低温冲击载荷作用下碎裂,σ相枝晶间较高的分布密度削弱奥氏体基体协调变形能力,裂纹容易连接,从而造成焊缝金属低温冲击韧性急剧降低,与仅含有δ-铁素体未发生共析分解的试样对比,σ相造成焊缝金属低温冲击韧性下降超85%.
(3) 低Mo含量含少量铁素体组织在−196 ℃下仍能保持较高冲击韧性,通过降低焊缝金属中的Mo含量以避免枝晶间δ-铁素体共析分解形成σ相,可提高焊缝金属的低温韧性.
-
图 3 钛/钢复合板对接接头显微组织
Figure 3. Microstructure of titanium/steel butt joints. (a) ER50-6/Cu-V interface; (b) the central of Cu-V weld; (c) the phase map in the central of Cu-V weld; (d) Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface; (e) the high magnification image of Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface; (f) the phase map at Cu-V/ERTi-1 interface; (g) TA1/Cu-V/Q345 interface; (h) the high magnification image of TA1/Cu-V/Q345; (i) the phase map at TA1/Cu-V/Q345; (j) adjacent to Q345; (k) adjacent to TA1; (l) the phase map adjacent to Q345
图 5 钛/铜/钢复合板对接接头显微组织
Figure 5. Microstructure of titanium/copper/steel butt joints. (a) ER50-6/Cu interface; (b) the high magnification image of ER50-6/Cu interface; (c) T2/Cu interface; (d) Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (e) the high magnification image of Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (f) ERTi-1 weld; (g) TA1/Cu/T2 interface; (h) the high magnification image of TA1/Cu/T2 interface; (i) the high magnification image of region near ERTi-1
图 6 钛/铜/钢复合板对接接头TEM分析
Figure 6. TEM results of titanium/copper/steel butt joints. (a) the bright field image of Cu/ER50-6 interface; (b) the dark field image of Cu/ER50-6 interface; (c) the diffraction of A region; (d) Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (e) the high magnification image of Cu/ERTi-1 interface; (f) the diffraction of B region
表 1 焊接材料的主要化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Main chemical composition of the welding materials
焊丝 C Si Mn Ti Cu Fe V ER50-6 0.08 0.89 1.51 — — 余量 — ERTi-1 0.03 — — 余量 — 0.10 — ERCuSi-A — 3.0 1.0 — 余量 — — Cu-V 0.01 0.30 0.50 — 余量 — 22.02 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding experiment paraments
焊丝 焊接方法 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 保护气体 ER50-6 MIG 150 ~ 180 20 ~ 24 6 ~ 7 80%Ar + 20%CO2 ERTi-1 TIG 100 ~ 120 20 ~ 22 3 ~ 4 100%Ar ERCuSi-A MIG 200 ~ 240 20 ~ 24 6 ~ 7 100%Ar Cu-V焊丝 TIG 140 ~ 160 20 ~ 24 3 ~ 4 100%Ar 表 3 钛/钢复合板对接接头典型区域EDS能谱(原子分数,%)
Table 3 EDS results of the typical regions in titanium/steel butt joints
区域 Fe Cu V Ti 主要相组成 谱图1 0.80 95.60 3.60 — Cu 谱图2 81.04 9.64 0.29 9.03 Fe + Fe2Ti 谱图3 66.53 5.22 2.51 25.74 Fe2Ti 谱图4 11.19 63.02 0.50 25.29 Cu2Ti + Cu3Ti2 谱图5 25.78 20.86 0.71 52.64 FeTi + β-Ti 谱图6 9.75 14.95 2.09 73.21 β-Ti + CuTi2 谱图7 51.07 19.21 4.00 25.72 Fe2Ti 谱图8 28.58 22.13 3.68 45.61 FeTi + Cu 谱图9 10.51 37.41 0.59 51.48 CuTi + FeTi 谱图10 5.60 30.20 0.85 63.35 CuTi2 表 4 钛/铜/钢复合板接头典型区域EDS能谱结果(原子分数,%)
Table 4 EDS results of the typical regions in titanium/copper/steel butt joints
区域 Fe Cu Si Ti 主要相组成 谱图1 0.10 98.50 0.40 — Cu 谱图2 87.78 11.77 0.45 — α-Fe 谱图3 — 52.15 — 47.85 CuTi 谱图4 — 46.17 — 53.83 CuTi + CuTi2 谱图5 — 32.70 — 67.30 CuTi2 谱图6 — 53.11 — 46.89 CuTi + Cu4Ti3 谱图7 — 12.91 — 87.09 β-Ti + CuTi2 谱图8 — 22.83 — 77.17 CuTi2 + β-Ti -
[1] 杨培智, 张钧, 杨海欧. TC4钛合金混合制造技术的研究与进展[J]. 铸造技术, 2023, 44(11): 977 − 987. Yang Peizhi, Zhang Jun, Yang Haiou. Research and progress of the hybrid manufacturing of TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Foundry Technology, 2023, 44(11): 977 − 987.
[2] 南榕, 蔡建华, 杨健, 等. 钛及钛合金腐蚀行为研究进展[J]. 钛工业进展, 2023, 40(5): 40 − 48. Nan Rong, Cai Jianhua, Yang Jian, et al. A review of corrosion resistance of titanium and titanium alloys[J]. Titanium Industry Progress, 2023, 40(5): 40 − 48.
[3] 郑远谋. 爆炸焊接和金属复合材料及其工程应用[M]. 长沙: 中南大学出版社, 2002. Zheng Yuanmou. Explosive welding and metallic composite and their engineering application[M]. Changsha: Central South University Press, 2002.
[4] 张保奇. 异种金属爆炸焊接结合界面的研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2005. Zhang Baoqi. Investigation on bonding interface of explosive welding dissimilar metal[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2005.
[5] Findik F. Recent developments in explosive welding[J]. Materials and Design, 2011, 32(3): 1081 − 1093. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2010.10.017
[6] 张柯柯, 涂益民. 特种先进连接方法[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学出版社, 2012. Zhang Keke, Tu Yimin. Special advanced welding and joining technology[M]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology Press, 2012.
[7] 毕志雄, 李雪交, 吴勇, 等. 钛箔/钢爆炸焊接的界面结合性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(4): 81 − 85. Bi Zhixiong, Li Xuejiao, Wu Yong, et al. Interfacial bonding properties of titanium foil/steel explosive welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(4): 81 − 85.
[8] 张婷婷, 王文先, 袁晓丹, 等. Mg/Al 合金爆炸焊连接及其界面接合机制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(12): 52 − 58. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.12.052 Zang Tingting, Wang Wenxian, Yuan Xiaodan, et al. Interface bonding mechanism of Mg/Al alloy explosive welded[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(12): 52 − 58. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.12.052
[9] 武通. 脉冲TIG焊接对钛/钢复合结构中爆炸焊界面影响研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021. Wu Tong. Research on the effect of pulse TIG welding on explosive welding interface in titanium/steel composite structure[D]. Harbin : Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021.
[10] Kundu S, Ghosh M, Chatterjee S. Diffusion bonding of commercially pure titanium and 17-4 precipitation hardening stainless steel[J] Materials Science and Engineering A, 2006, 428: 18-23.
[11] Li W, Yan L, Karnati S, et al. Ti-Fe intermetallics analysis and control in joining titanium alloy andstainless steel by laser metal deposition[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 242: 39 − 48. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.11.010
[12] Xia Y Q, Dong H G, Zhang R Z, et al. Interfacial microstructure and shear strength of Ti6Al4V alloy/316 L stainless steel joint brazed with Ti33.3Zr16.7Cu50- xNi x amorphous filler metals[J]. Materials and Design, 2020, 187: 108380. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2019.108380
[13] Adomako N K, Kim J O, Lee S H, et al. Dissimilar welding between Ti-6Al-4V and 17-4PH stainless steel using a vanadium interlayer[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 732: 378 − 397. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.07.015
[14] Wang T, Zhang B G, Feng J C, et al. Effect of a copper filler metal on the microstructure and mechanical properties of electron beam welded titanium-stainless steel joint[J]. Materials Characterization, 2012, 73: 104 − 113. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2012.08.004
[15] Wang T, Zhang B G, Chen G Q, et al. High strength electron beam welded titanium-steel joint with V/Cu based composite filler metals[J]. Vacuum, 2013, 94: 41 − 47. doi: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2013.01.015
[16] Lee M K, Lee J G, Choi Y H, et al. Interlayer engineering for dissimilar bonding of titanium to stainless steel[J]. Materials Letters, 2010, 64: 1105 − 1108. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2010.02.024
[17] Chu Q L, Tong X W, Xu S, et al. The formation of intermetallics in Ti/steel dissimilar joints welded by Cu-Nb composite filler[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828: 154389. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154389
[18] Chu Q L, Zhang M, Li J H, et al. Intermetallics in CP-Ti/X65 bimetallic sheets filled with Cu-based flux-cored wires[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 90: 299 − 306. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2015.10.136
[19] Chu Q L, Zhang M, Li J H, et al. Influence of vanadium filler on the properties of titanium and steel TIG welded joints[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2017, 240: 293 − 304. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2016.06.018
[20] Chu Q L, Bai R X, Zhang M, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of titanium/steel bimetallic joints[J]. Materials Characterizaiton, 2017, 132: 330 − 337. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2017.08.025
[21] Ning J, Zhang L J, Jiang G C, et al. Narrow gap multi-pass laser butt welding of explosion welded CP-Ti/Q235B bimetallic sheet by using a copper interlayer[J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2017, 701: 587 − 602. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.01.129
[22] Chu Q L, Xia T, Zhang L, et al. Structure-property correlation in weld metals and interface regions of titanium/steel dissimilar joints[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2022, 31(8): 6509 − 6522. doi: 10.1007/s11665-022-06693-9




 下载:
下载: