Magnetic pole weld identification and robot trajectory generation technology based on 3D point cloud
-
摘要:
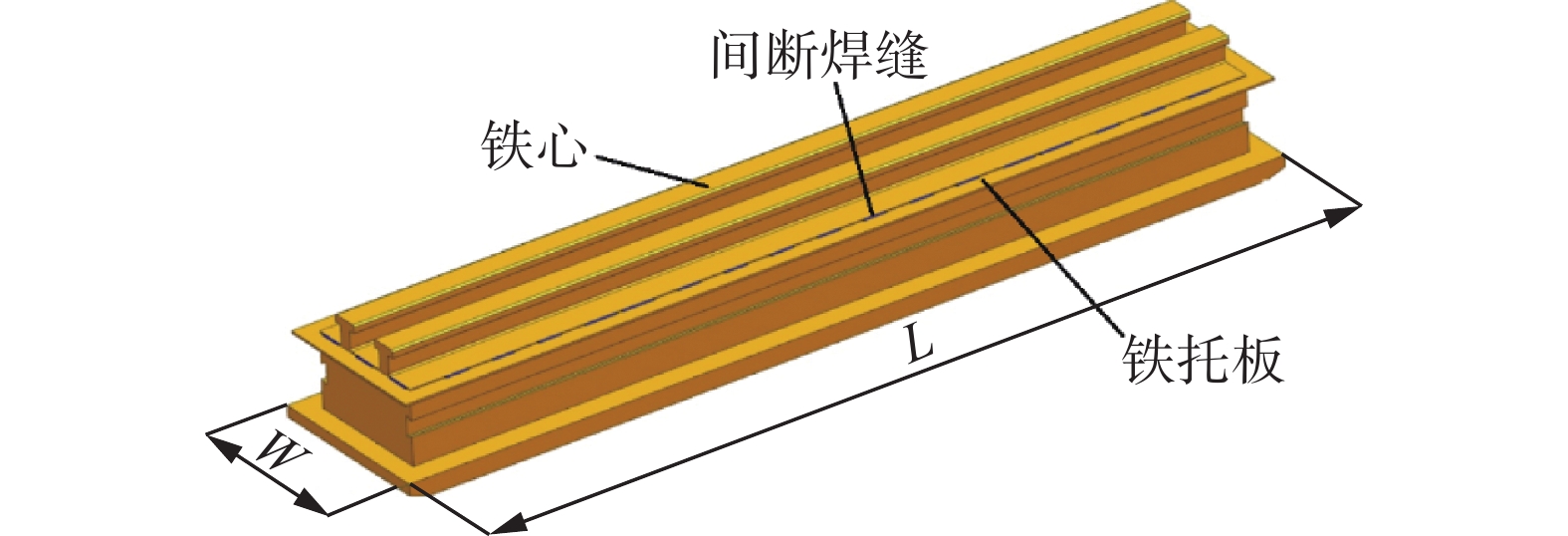
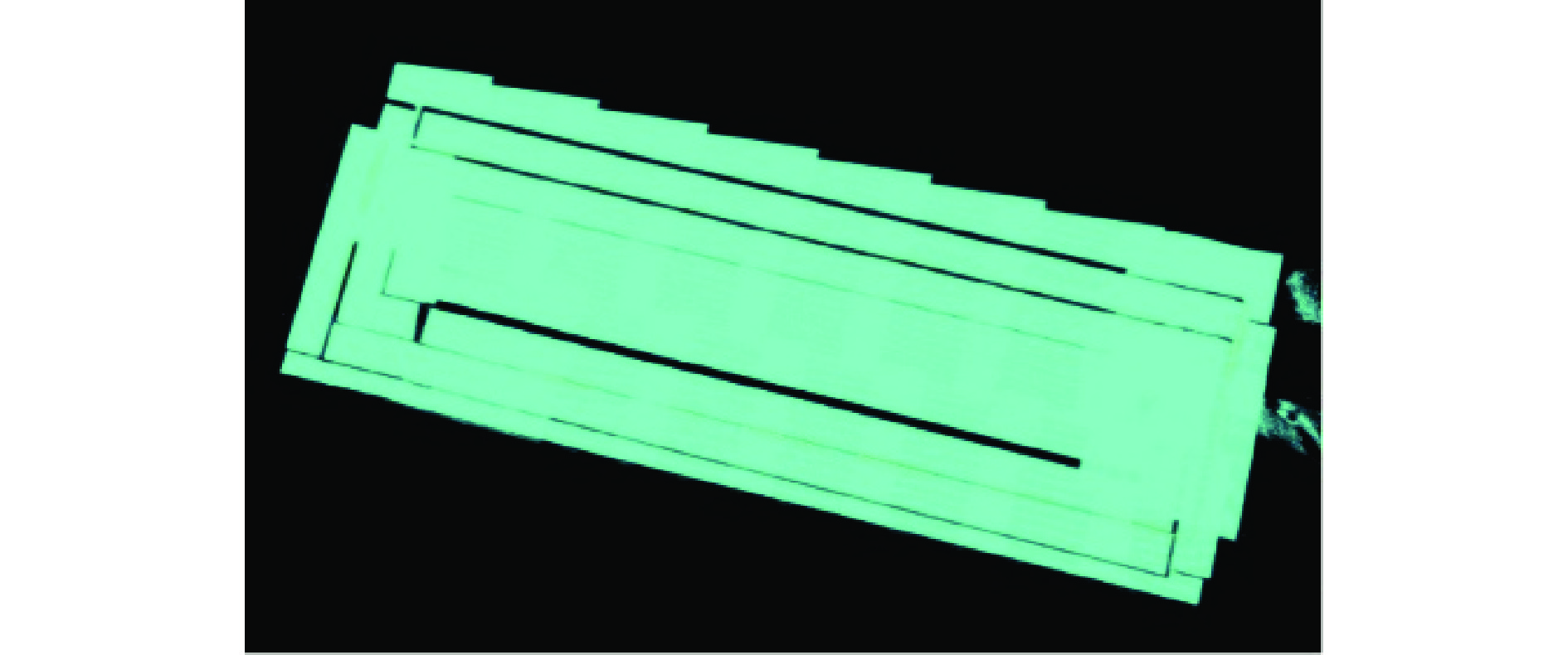
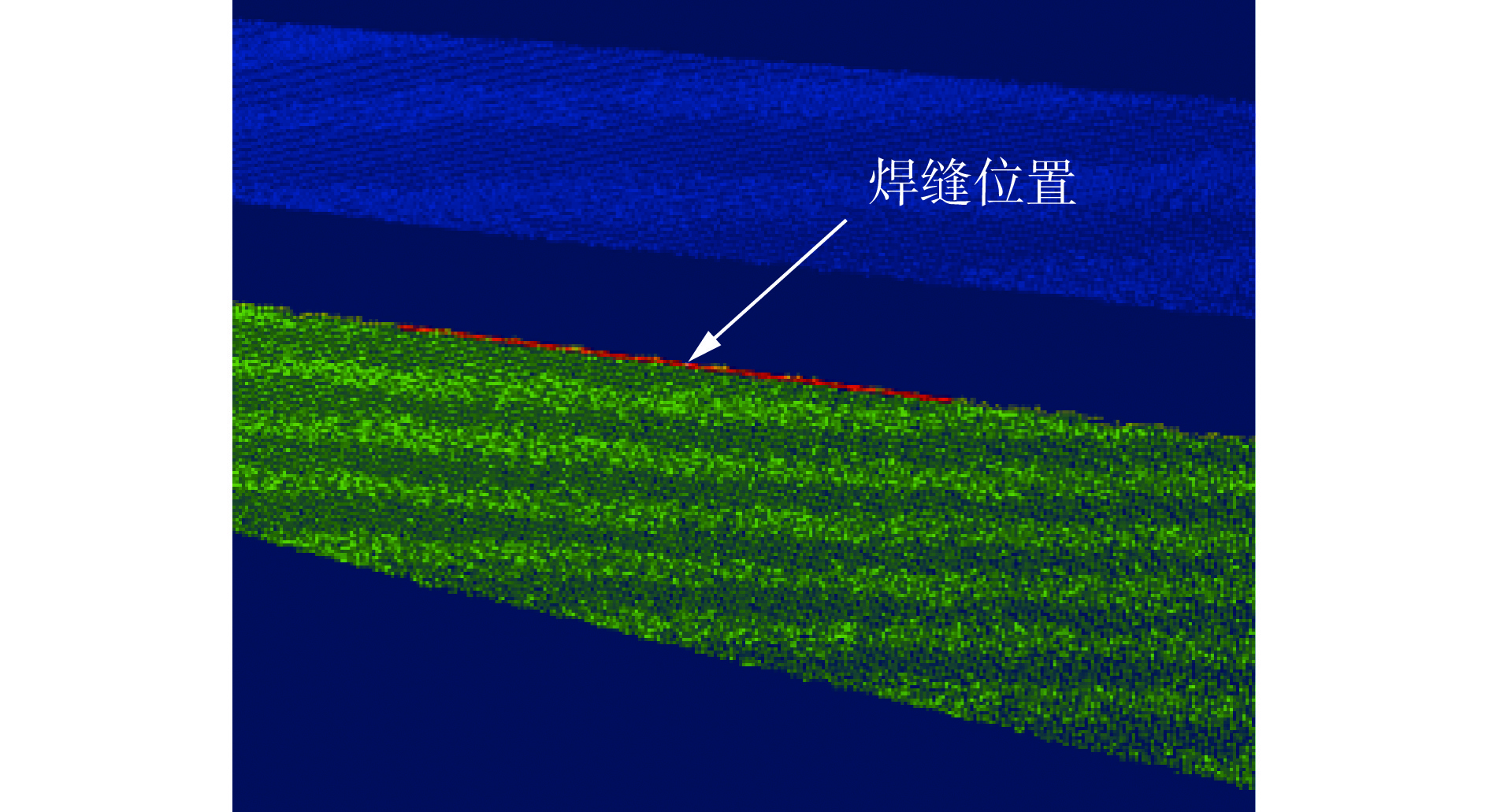
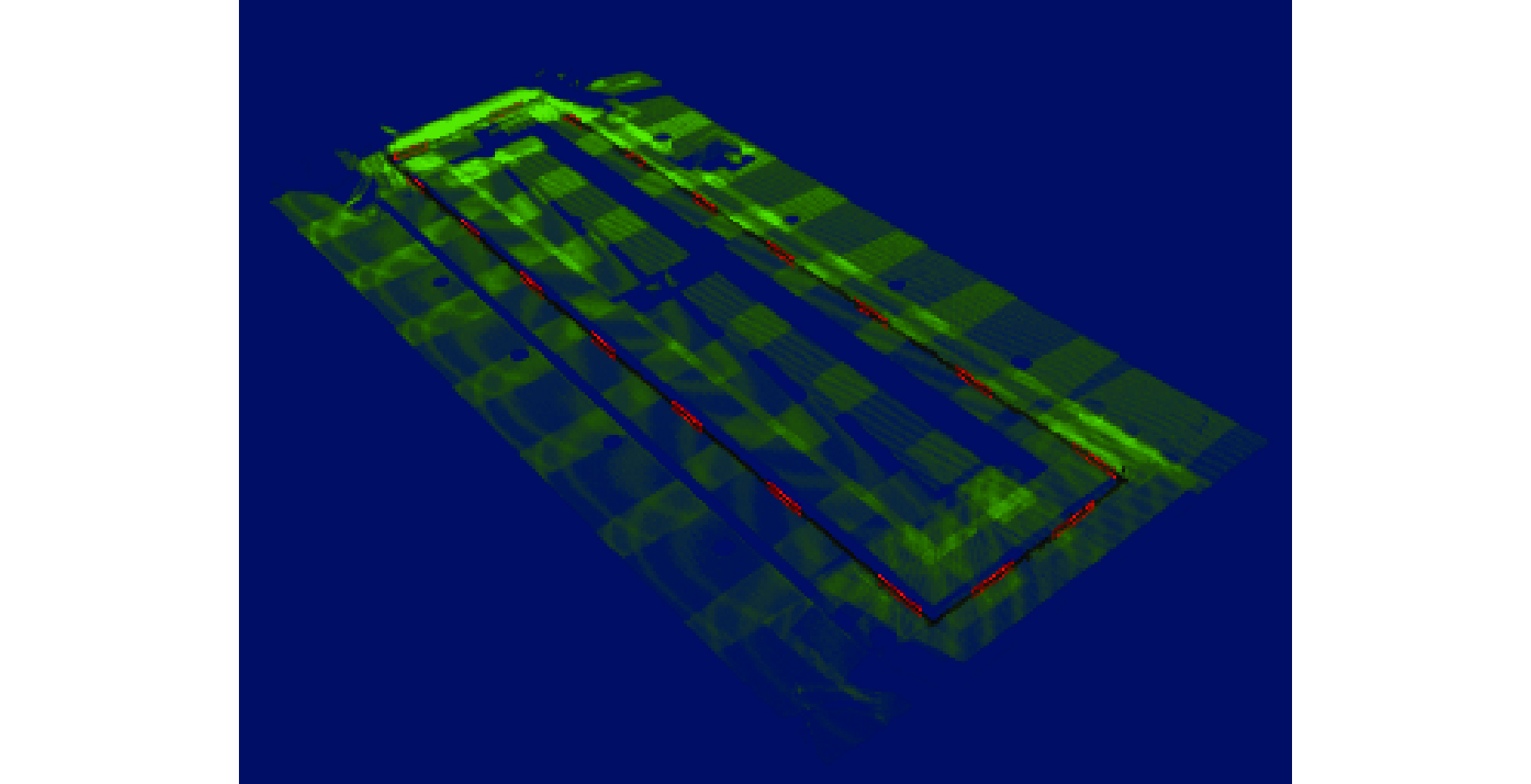
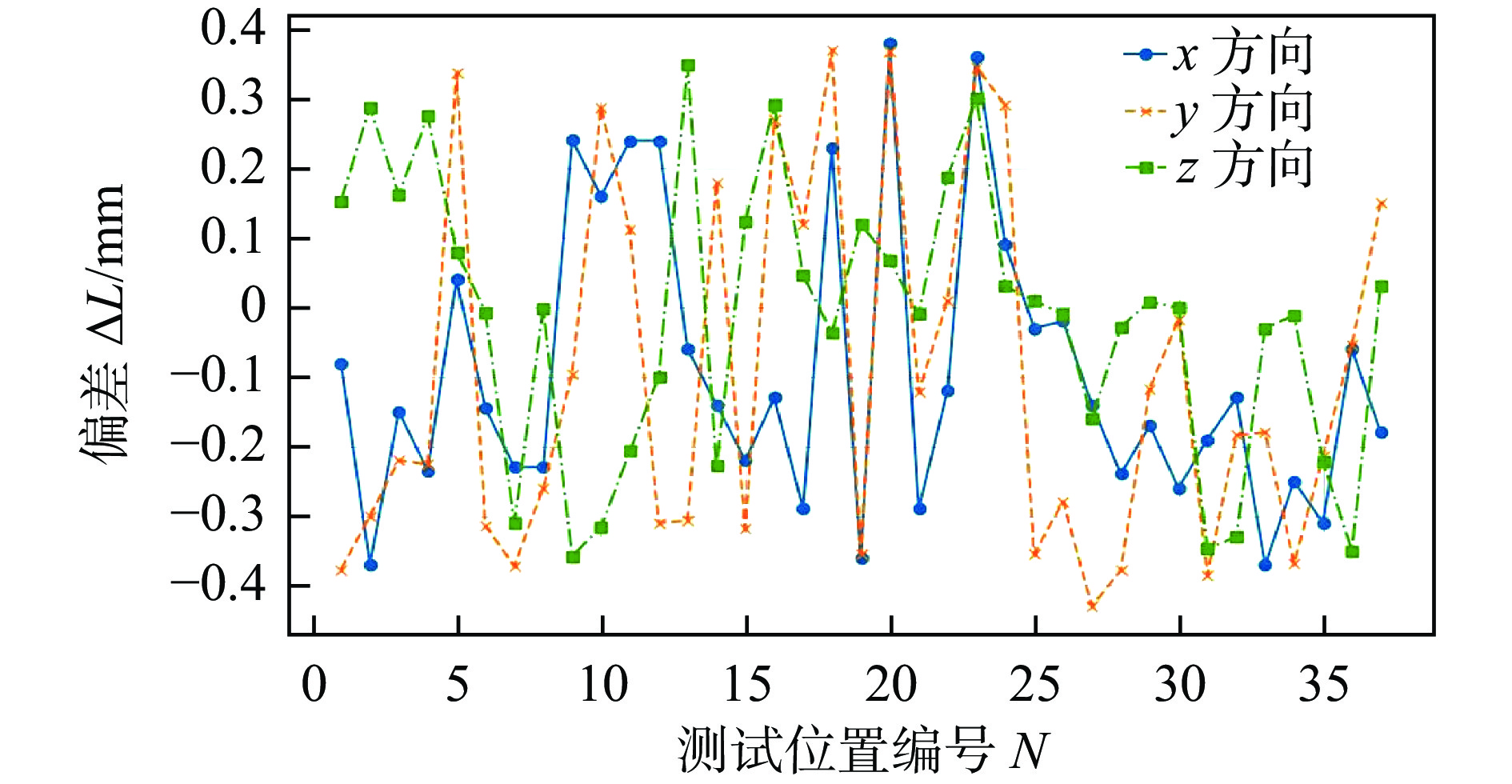
针对大型水电站发电机磁极变长度、变间隙的复杂焊缝存在的示教编程效率低、精度差的问题,开发了一种基于光栅视觉传感的焊缝识别及机器人轨迹免示教生成技术. 采用安装于机器人末端的光栅传感器获取不同部位的磁极焊缝点云,提出了一种结合机器人工具位姿变换矩阵和迭代最近点算法(ICP)的点云配准算法,得到大尺寸磁极焊缝完整点云数据. 基于随机采样一致性(RANSAC)开发了焊缝识别算法,实现了机器人焊接轨迹的自动生成. 结果表明,该算法可识别出多种复杂工况的磁极焊缝,识别率高,抗干扰能力强,平均识别误差在±0.4 mm范围内,满足焊接要求.
Abstract:Aiming at the problems of low efficiency and poor accuracy of teaching programming in complex welds with variable magnetic pole length and gap of large hydropower generators, a technology of welding seam identification and robot track generation without teaching was developed based on grating visual sensing. A grating sensor installed at the end of the robot was used to obtain the point cloud of the magnetic pole weld at different positions. A point cloud registration algorithm combining the robot tool pose transformation matrix and iterative closest point algorithm (ICP) was proposed to obtain the complete point cloud data of the large size magnetic pole weld. Based on random sampling consistency (RANSAC), a weld recognition algorithm was developed to realize the automatic generation of robot welding trajectories. The results show that the algorithm can identify a variety of complex magnetic pole welds with high recognition rate and strong anti-interference ability, and the average recognition error is with in ± 0.4 mm, which meets the welding requirements.
-
-
[1] 王慧. 向心磁极铁托板焊接质量的分析[J]. 防爆电机, 2016, 51(4): 52 − 54. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1008-7281.2016.04.17 Wang Hui. Analysis of welding quality of centripetal pole iron plate[J]. Explosion-Proof Electric Machine, 2016, 51(4): 52 − 54. doi: 10.3969/J.ISSN.1008-7281.2016.04.17
[2] 魏方锴, 贾瑞燕, 周宇飞, 等. 一种基于视觉定位的磁极铁托板自动化焊接方法, CN202210543971.5 [P]. 2024-02-13. Wei Fangkai, Jia Ruiyan, Zhou Yufei, et al. An automatic welding method of magnetic pole iron plate based on visual positioning, CN202210543971.5[P]. 2024-02-13.
[3] Li G, Hong Y, Gao J, et al. Welding seam trajectory recognition for automated skip welding guidance of a spatially intermittent welding seam based on laser vision sensor[J]. Sensors, 2020, 20(13): 36 − 57.
[4] 郭忠峰, 刘俊池, 杨钧麟. 基于关键点检测方法的焊缝识别[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(1): 88 − 93. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230204001 Guo Zhongfeng, Liu Junchi, Yang Junlin. Weld identification based on key point detection method[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(1): 88 − 93. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230204001
[5] 修延飞, 李海超, 胡广泽, 等. 一种用于穿孔塞焊焊缝特征提取的视觉识别算法[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(2): 75 − 79. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20190927002 Xiu Yanfei, Li Haichao, Hu Guangze, et al. A visual recognition algorithm for feature extraction of perforated plug welding seams[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(2): 75 − 79. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20190927002
[6] Zhang K, Yan M, Huang T, et al. 3D reconstruction of complex spatial weld seam for autonomous welding by laser structured light scanning[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 39: 200 − 207. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.02.010
[7] Tian Y Z, Liu H F, Li L, et al. Robust identification of weld seam based on region of interest operation[J]. Advances in Manufacturing, 2020, 8(4): 473 − 485. doi: 10.1007/s40436-020-00325-y
[8] 梁志敏, 高旭, 任政, 等. 基于变分立体匹配算法的GMAW熔池形貌三维重建[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(2): 61 − 66. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230224001 Liang Zhimin, Gao Xu, Ren Zheng, et al. Three-dimensional reconstruction of GMAW molten pool morphology based on variational stereo matching algorithm[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(2): 61 − 66. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230224001
[9] Zhang G, Zhang Y, Tuo S, et al. A novel seam tracking technique with a four-step method and experimental investigation of robotic welding oriented to complex welding seam[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21(9): 30 − 67.
[10] 余佳杰, 周建平, 薛瑞雷, 等. 基于结构光视觉和光照模型的焊 缝表面质量检测[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(16): 2 − 4. Yu Jiajie, Zhou Jianping, Xue Ruilei, et al. Weld surface quality detection based on structured light and illumination model[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(16): 2 − 4.
[11] 魏小保. 基于数字光栅投影的三维测量关键技术研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. Wei Xiaobao. Research on key technology of 3D measurement based on digital raster projection[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019.
[12] 王曦. 基于数字光栅投影结构光的三维重建技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017. Wang Xi. Research on 3D reconstruction technique based on digital grating projection structured light[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王永祥,何柏林,李力. 超声冲击改善P355NL1钢焊接接头腐蚀疲劳性能研究. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2022(01): 120-126 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 万里平,董汪平. EN 13445标准的焊接接头疲劳评定方法及其与ASME Ⅷ-2疲劳评定的对比. 压力容器. 2021(08): 66-75 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载: