MIG weld seam tracking system based on image automatic enhancement and attention mechanism deep learning
-
摘要:
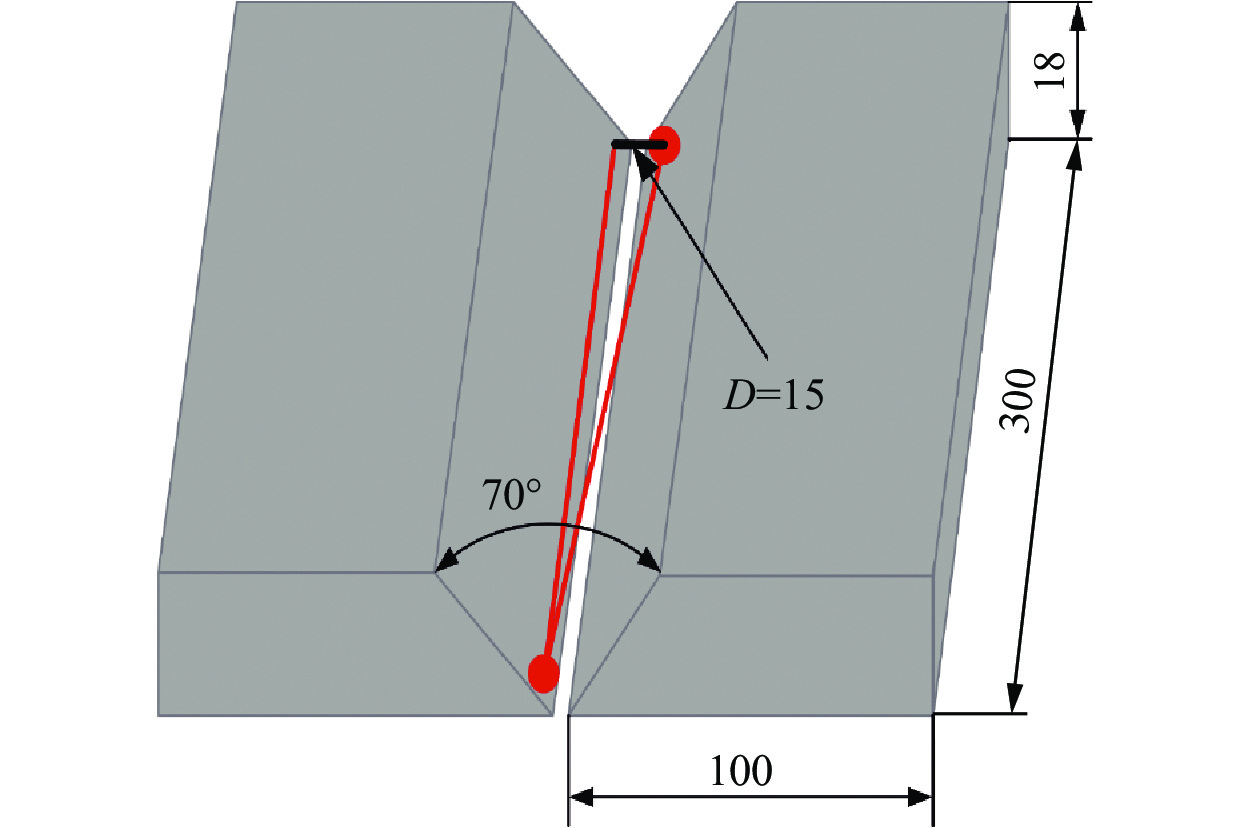
针对常规MIG焊难以根据组对偏差及热积累变形实时调整焊接位置的难题,提出并建立了被动视觉MIG焊缝跟踪试验系统,通过图像空间域滤波及自动增强算法,采用添加注意力机制的YOLO v7深度学习模型,在感兴区内对坡口的对中位置、电弧位置进行实时提取与分析;并采用模糊控制算法对预设偏差时的MIG焊过程进行实时控制. 结果表明,采用图像自动增强算法完成了对图像的预处理,边缘位置的像素灰度值由40增大到110左右,显著提高了边缘位置信息提取的精度;基于YOLO v7 网络结构添加注意力机制模块,提升目标检测效率,整体平均精度值mAP指标达到99.27%;预设偏差试验表明,对中偏差检测像素误差在8个像素以内,对中偏差距离控制在 ± 0.5 mm之间.
Abstract:Aiming at the problem that conventional MIG welding is difficult to adjust the welding position in real time according to the group deviation and thermal accumulation deformation, a weld seam tracking method based on passive vision is proposed. Through the image spatial domain filtering and automatic enhancement algorithm, the YOLO v7 deep learning model with attention mechanism is used to extract and analyze the groove alignment position and arc position in the region of interest in real time. The fuzzy control algorithm is used to control the MIG welding process in real time when the preset deviation occurs. The results show that, the image automatic enhancement algorithm is used to complete the preprocessing of the image, and the pixel gray value of the edge position is increased from 40 to about 110, which significantly improves the accuracy of the edge position information extraction; Based on the YOLO v7 network structure, the attention mechanism module is added to improve the efficiency of target detection, and the mAP index is as high as 99.27%. The preset deviation test shows that the pixel error of the alignment deviation detection is within 8 pixels, and the alignment deviation distance is controlled between ± 0.5 mm.
-
Keywords:
- weld tracking /
- passive vision /
- image enhancement /
- deep learning
-
-
表 1 模糊控制规则
Table 1 Rules of fuzzy controller
偏差距离D 偏差变化率Dcr NB NM NS ZO PS PM PB NB PB PB PB PB PM PS ZO NM PB PB PB PM PS ZO ZO NS PB PM PM PS ZO NS NM ZO PB PM PS ZO NS NM NB PS PM PS ZO NS NM NM NB PM ZO ZO NS NM NB NB NB PB ZO NS NM NB NB NB NB 注:NB为负方向大偏差,NM为负方向中等偏差,NS为负方向小偏差,ZO为无偏差,PS为正方向小偏差,PM为正方向中等偏差,PB为正方向大偏差 -
[1] 韩庆璘, 李大用, 李鑫磊, 等. 基于分区减光的电弧增材制造熔敷道尺寸主被动联合视觉检测[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(9): 28 − 32. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200418001 Han Qinglin, Li Dayong, Li Xinlei, et al. Bead geometry measurement for wire and arc additive manufacturing using active-passive composite vision sensing based on regional filter[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(9): 28 − 32. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200418001
[2] 陈华斌, 陈善本. 复杂场景下的焊接智能制造中的信息感知与控制方法[J]. 金属学报, 2022, 58(4): 541 − 550. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2021.00528 Chen Huabin, Chen Shanben. Key information perception and control strategy of intellignet welding under complex scene[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2022, 58(4): 541 − 550. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2021.00528
[3] Xia Lei, Zhou Jianping, Xue Ruilei, et al. Real-time seam tracking during narrow gap GMAW process based on the wide dynamic vision sensing method[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 101: 820 − 834. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2023.06.045
[4] Xiao Runquan, Xu Yanling, Hou Zhen, et al. A feature extraction algorithm based on improved Snake model for multi-pass seam tracking in robotic arc welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 72: 48 − 60. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.10.005
[5] 张广军, 冷孝宇, 吴林. 弧焊机器人结构光视觉传感焊缝跟踪[J]. 焊接学报, 2008, 29(9): 8 − 10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2008.09.003 Zhang Guangjun, Len Xiaoyu, Wu Lin. Robotic welding seam tracing system based on structure light vision sensor[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2008, 29(9): 8 − 10. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2008.09.003
[6] Wang Weixi, Yamane Satoshi, Wang Qi, et al. Visual sensing and quality control in plasma MIG welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2023, 86: 163 − 176. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.12.041
[7] Zhang Zhifen, Wen Guangrui, Chen Shanben. Weld image deep learning-based on-line defects detection using convolutional neural networks for Al alloy in robotic arc welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 45: 208 − 216. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2019.06.023




 下载:
下载: