A-TIG weld shaping and joint mechanical properties of austenitic stainless steel
-
摘要:
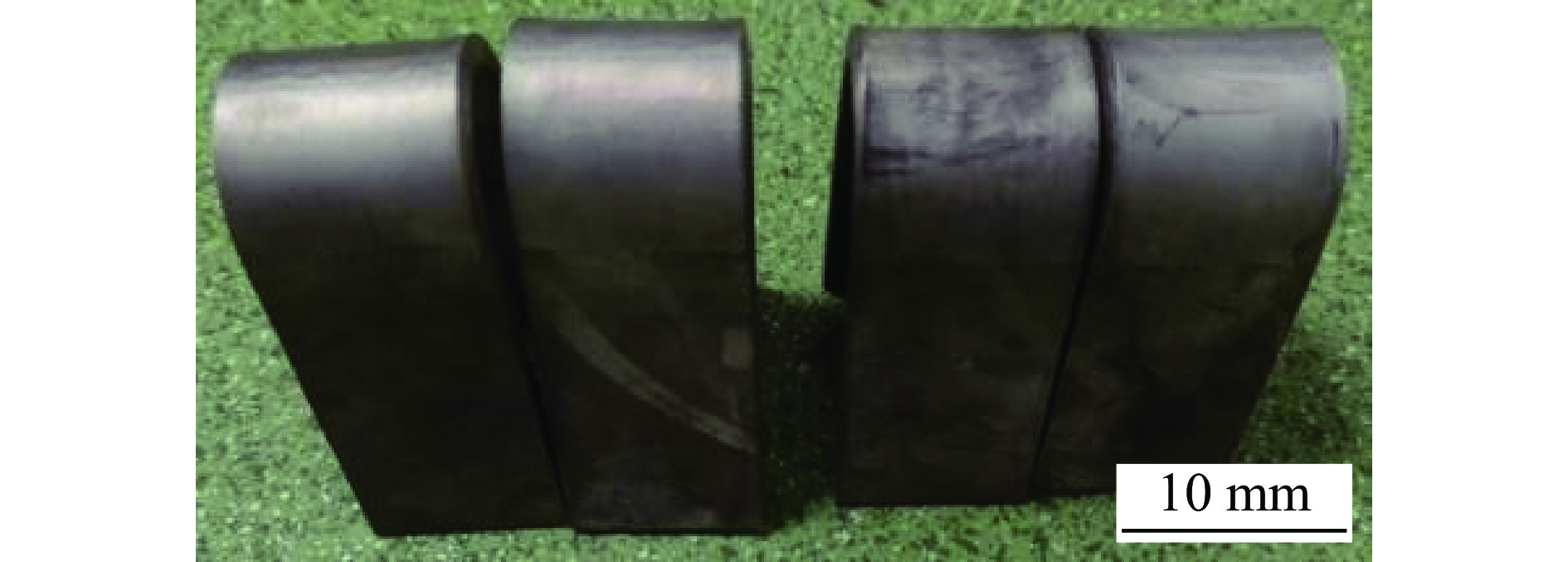
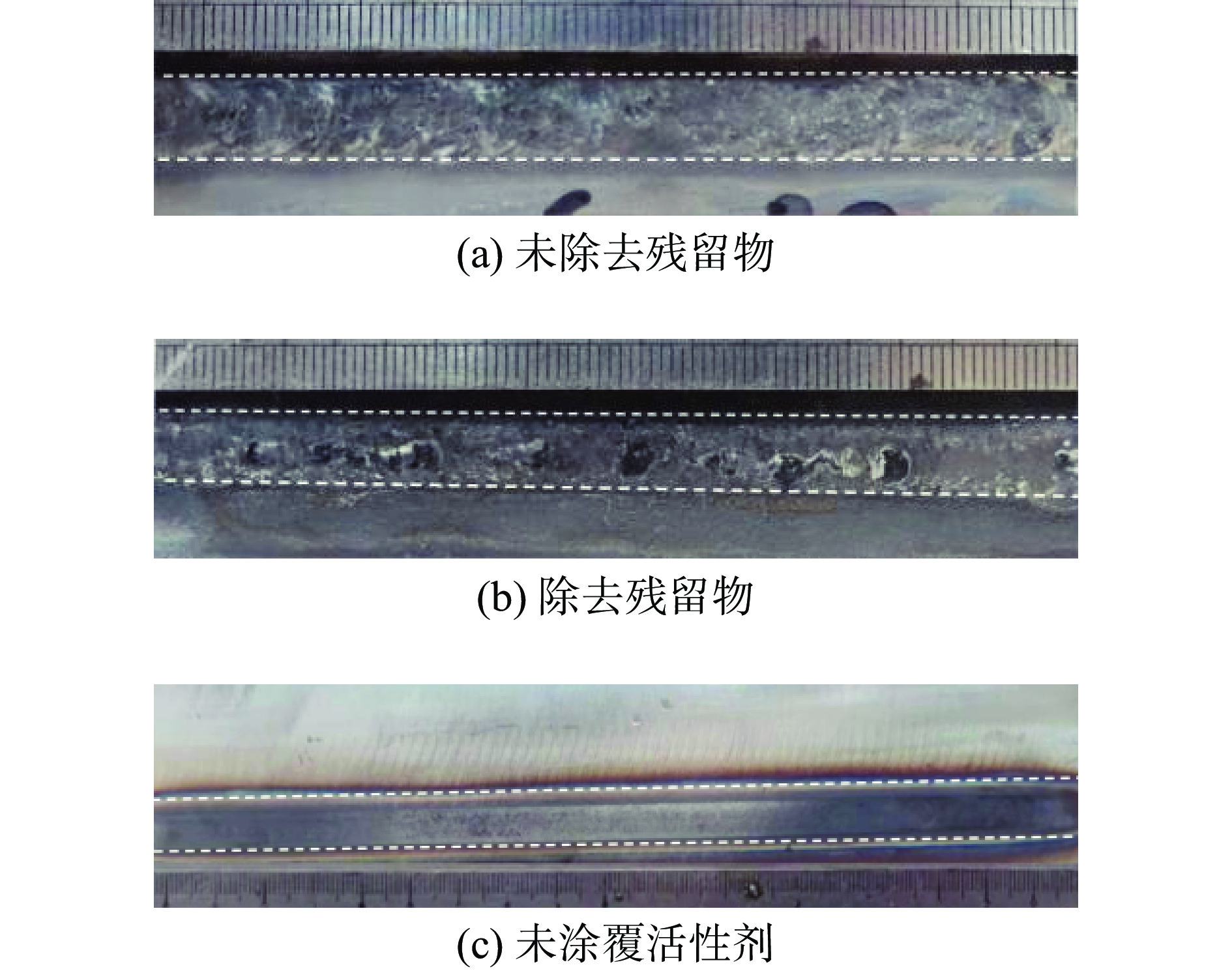
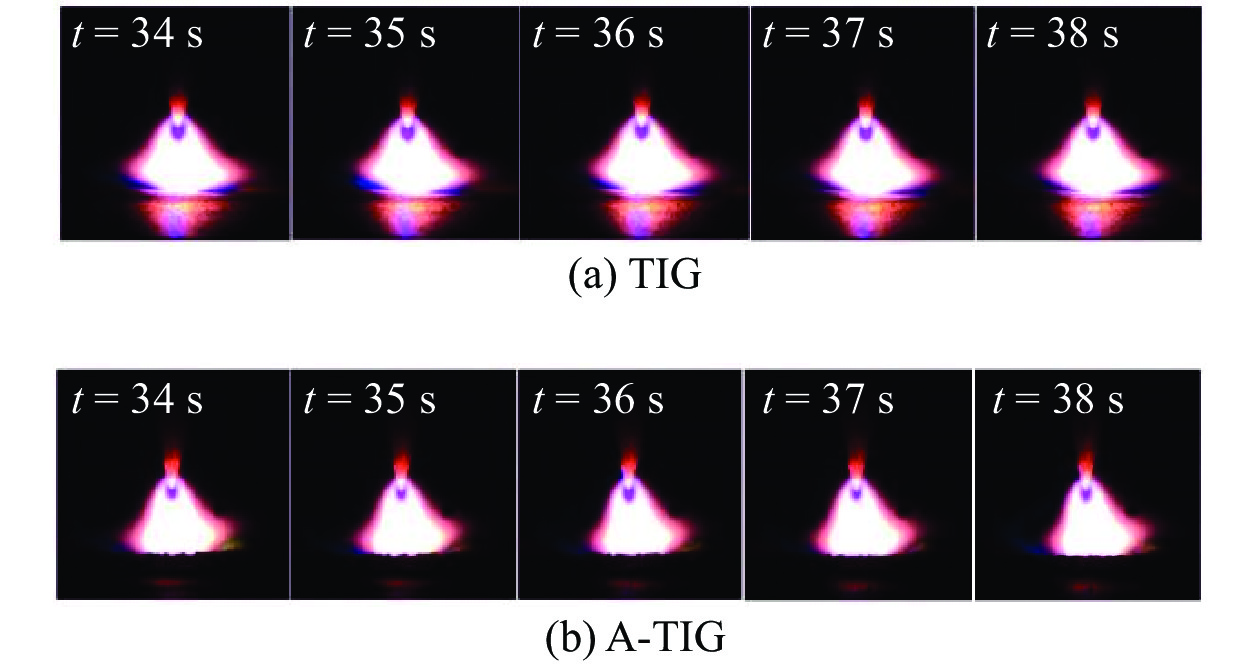
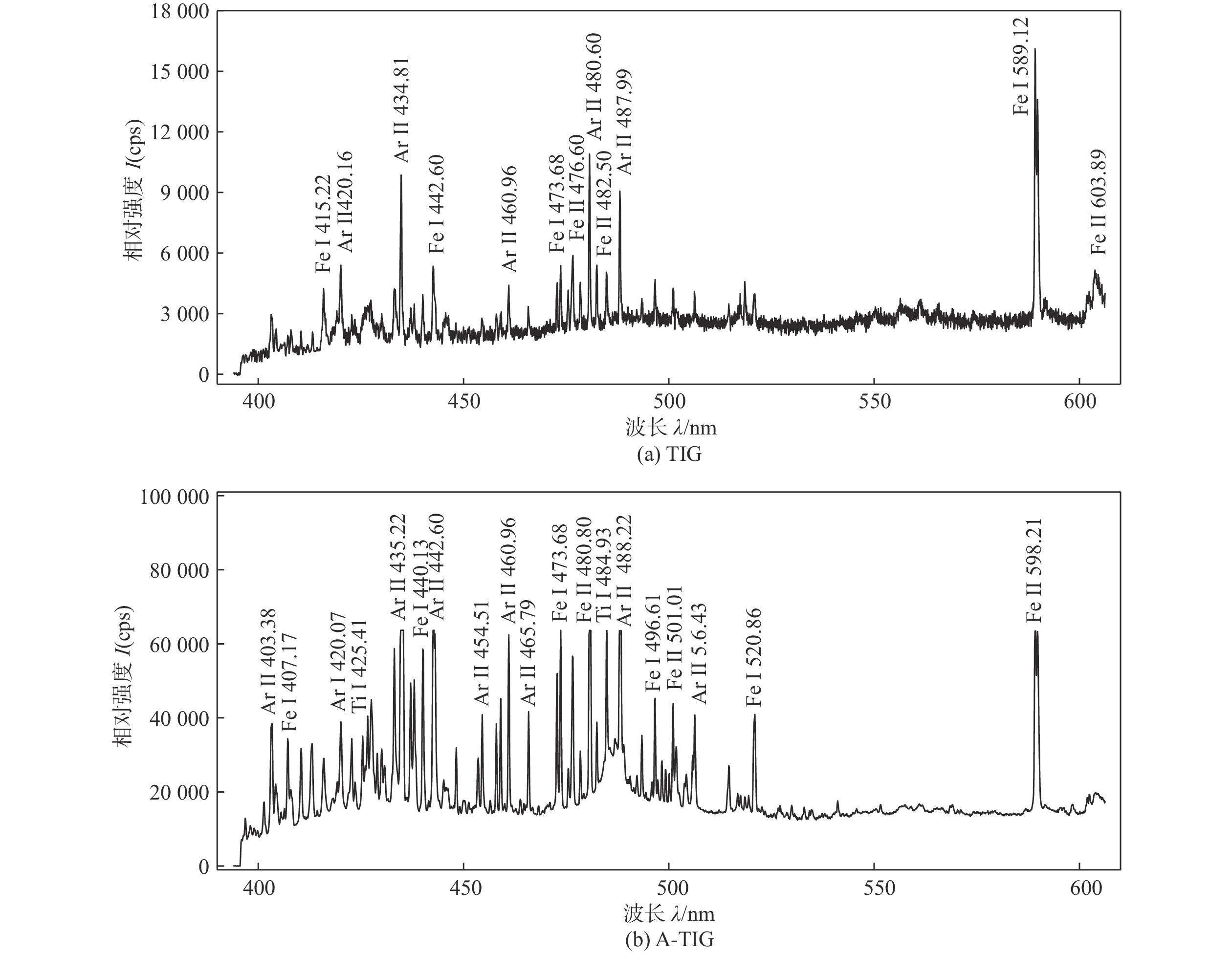
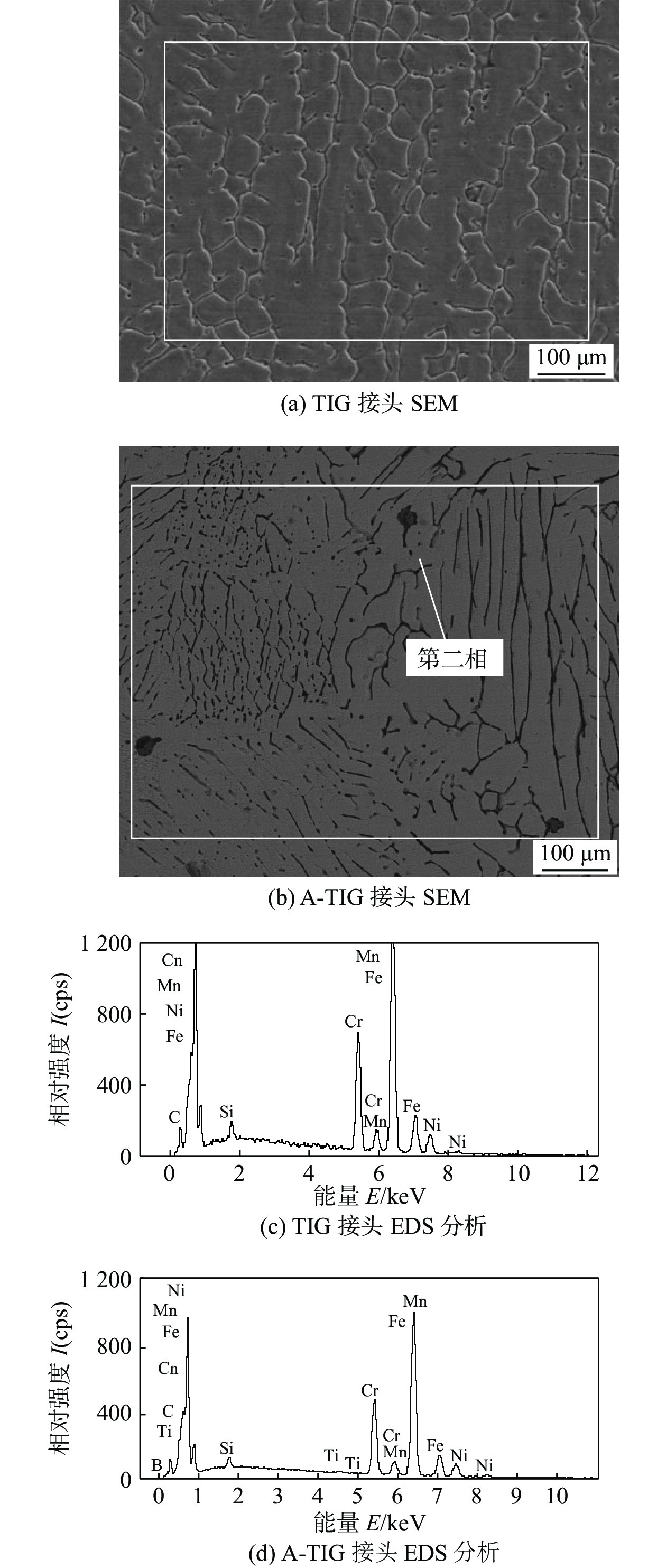
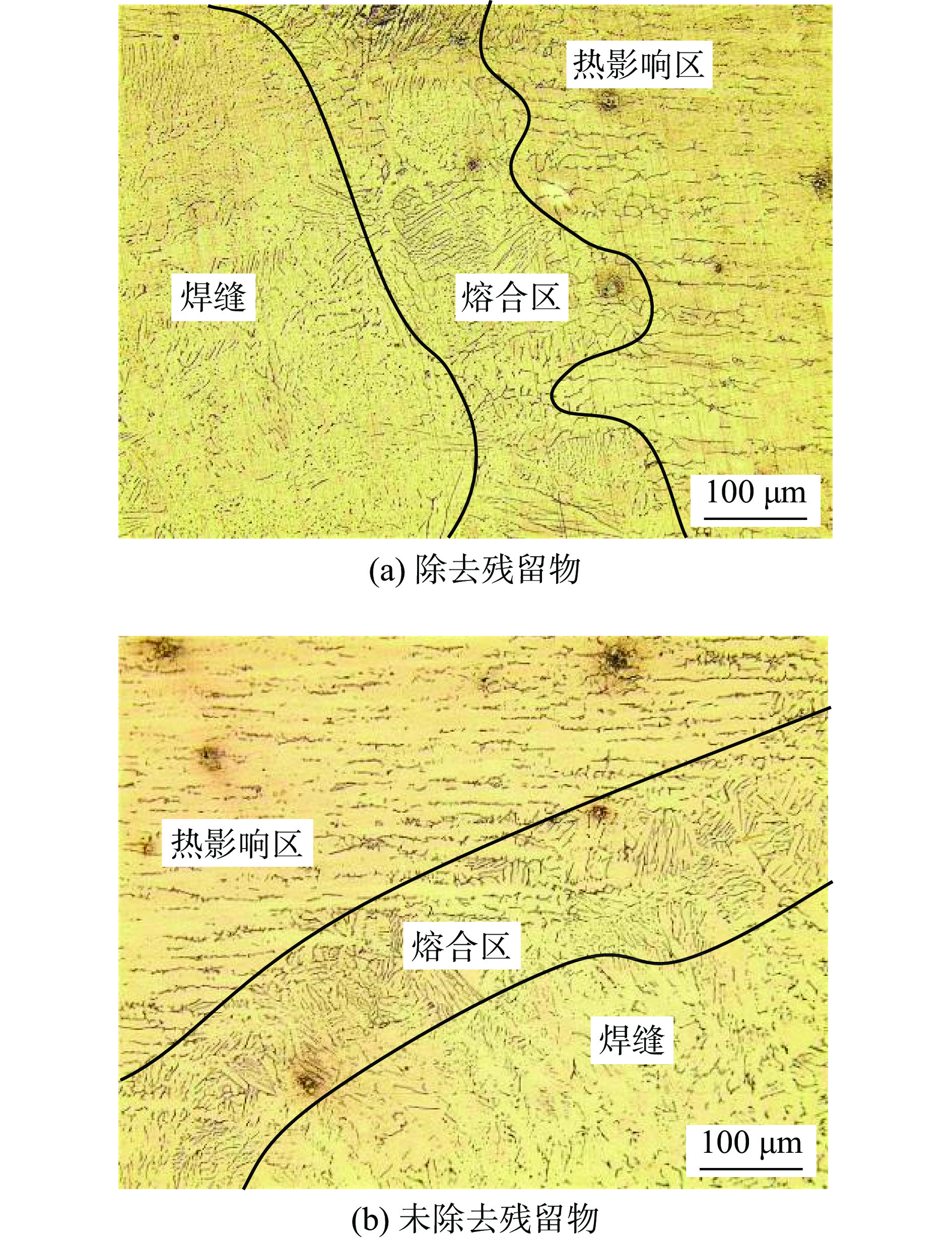
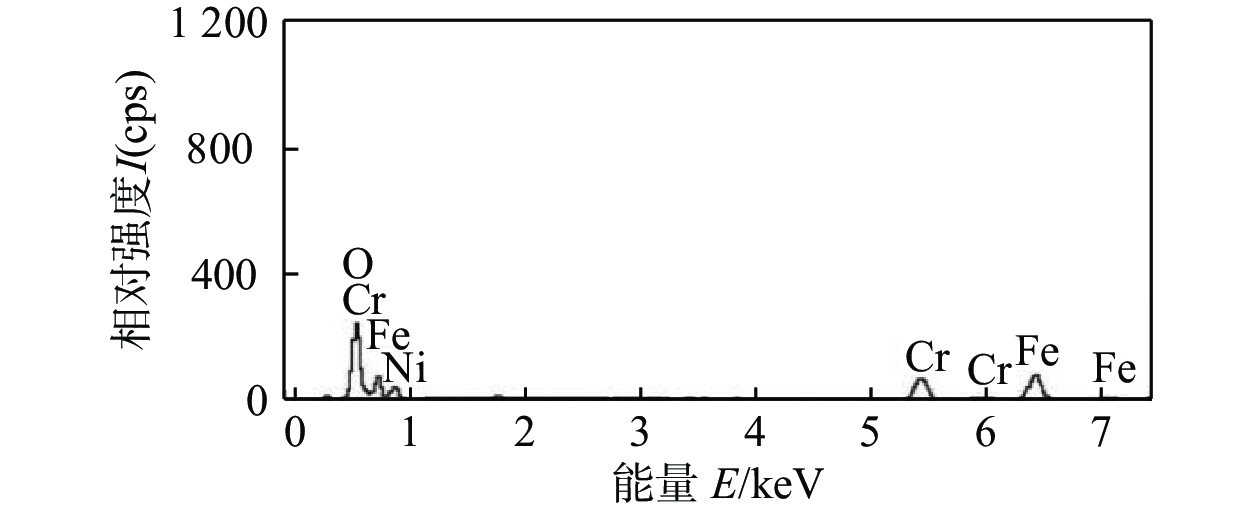
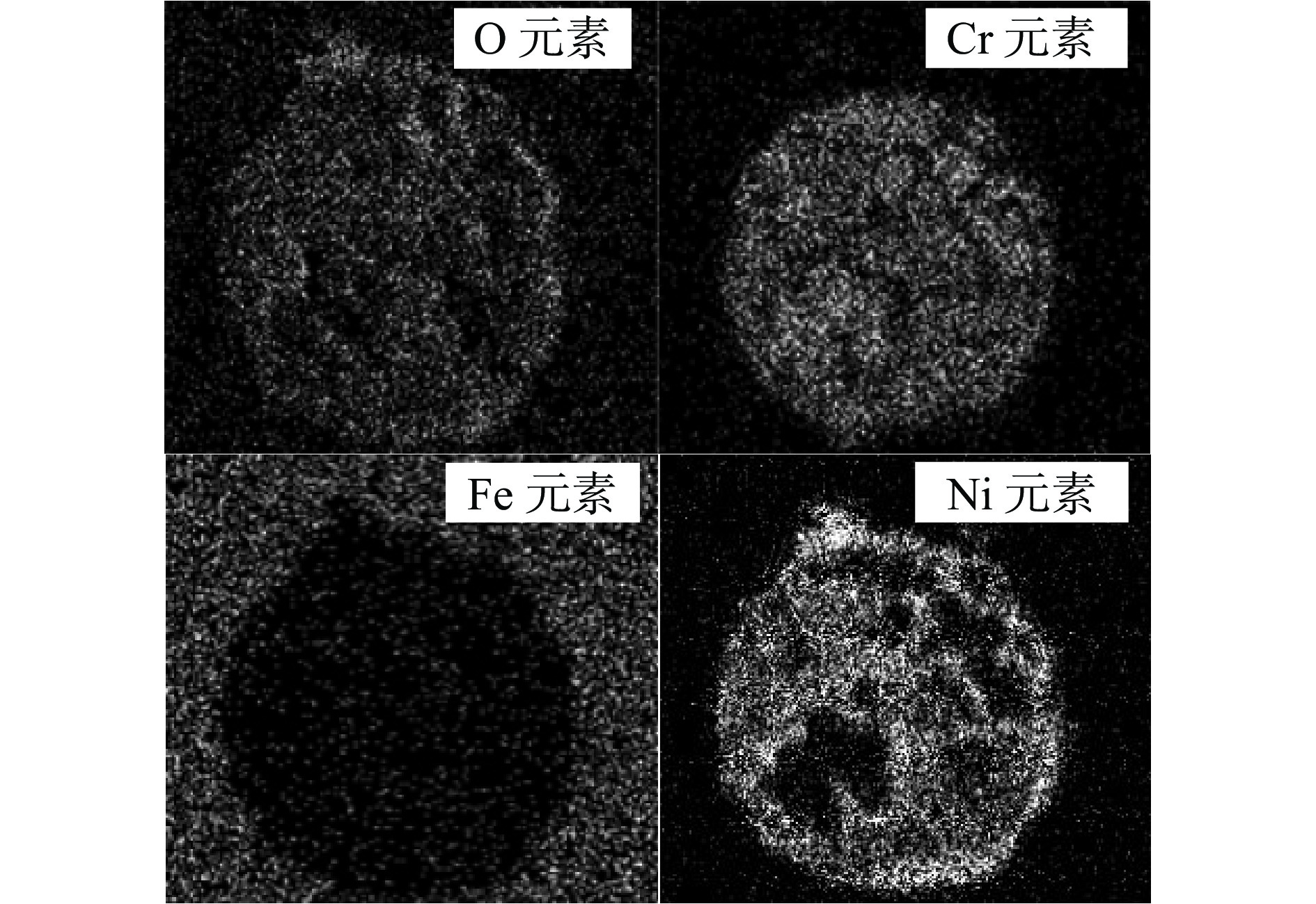
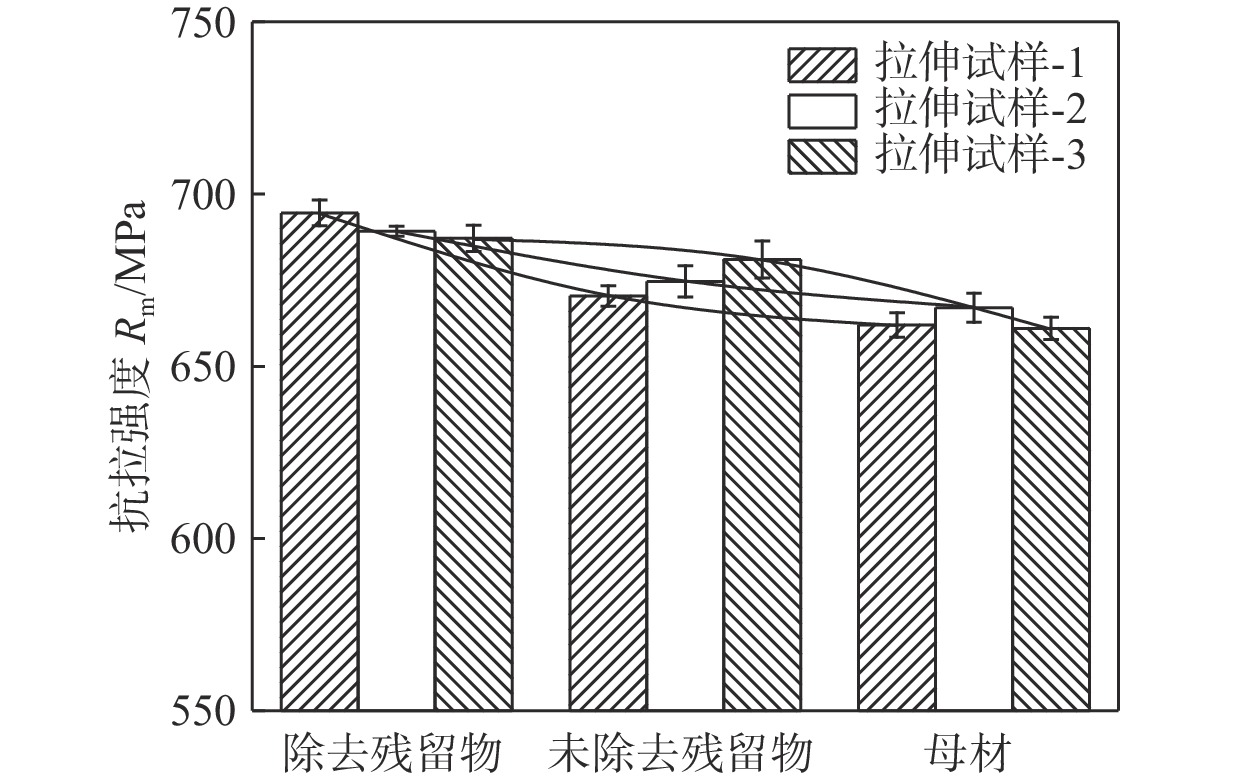
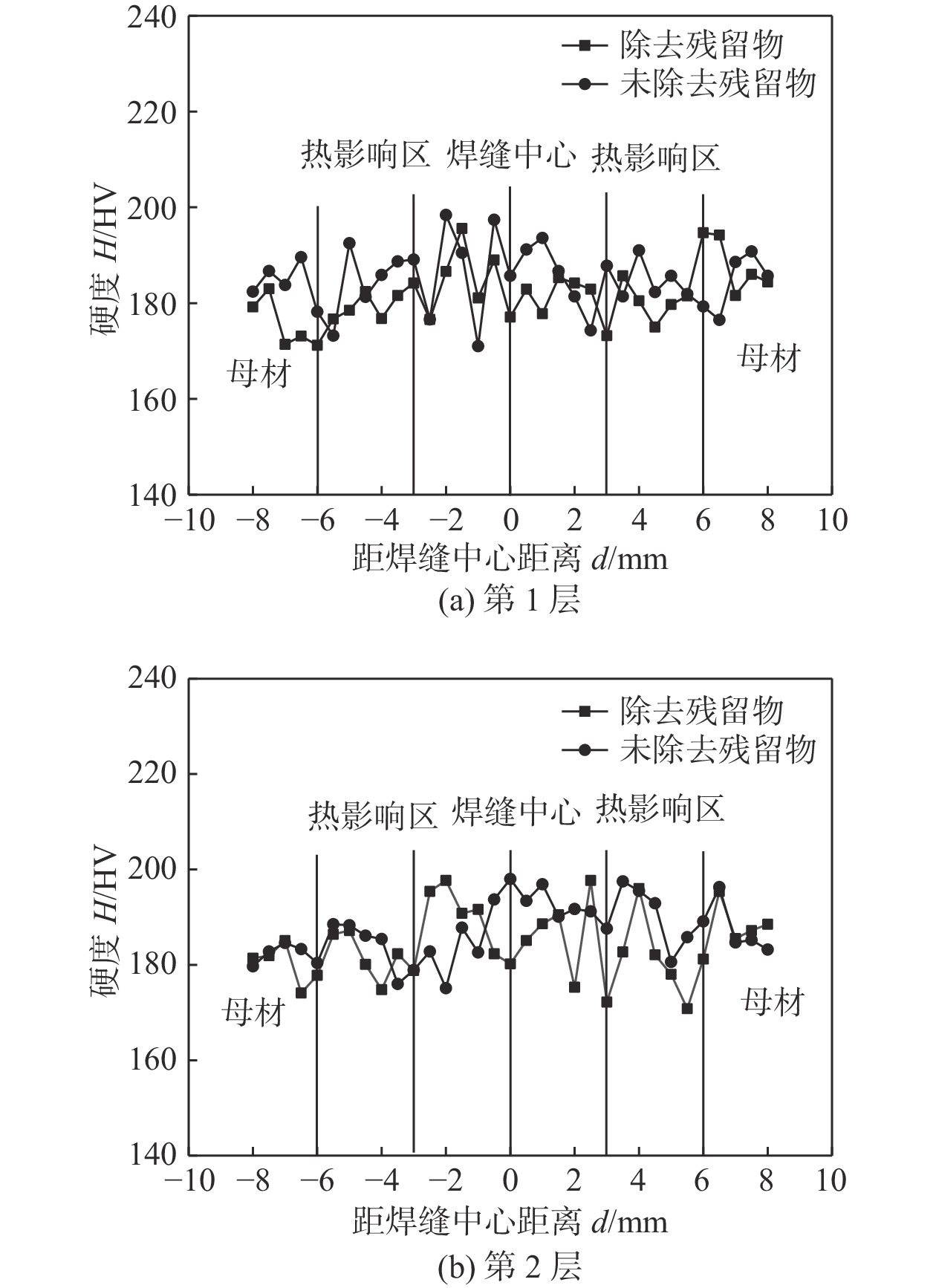
采用自主研发的C5活性剂进行活性剂钨极惰性气体保护焊(activating flux tungsten inert gas,A-TIG)试验,研究活性剂对A-TIG焊缝成形、电弧光谱和电弧形貌的影响. 同时,利用扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)观察黑色残留物的形貌,并对A-TIG焊后的黑色残留物成分进行分析,确定黑色残留物形成的原因. 结果表明,活性剂有助于提高电弧温度和穿透力,促进电弧电离,改变表面张力梯度和熔池流动方向,从而增加焊接熔深. 与焊缝基体相比,O元素、Cr元素和Ti元素在残留物中的分布更为密集,其他元素弥散分布在残留物内部. 在观察焊缝的组织和性能时发现,焊缝中心都是以奥氏体和铁素体为主要组织的等轴晶,而在接头熔合区都呈现为柱状晶. 未去除残留物试样平均抗拉强度为675.36 MPa,与母材强度相比提高了2%. 焊缝和母材的硬度曲线交错,是否除去残留物对接头的硬度影响不大. 弯曲180°后两组试样表面无任何裂纹. 采用A-TIG工艺焊接的焊缝具有良好的延展性和韧性. 此外,未除去残留物试件焊缝表面存在凹陷现象,但焊缝宽度均匀,焊缝成形系数为1.97,采用该工艺可以获得较大范围的焊缝等轴晶和较为细小的焊缝组织,较钨极氩弧焊(tungsten inert gas,TIG)拥有更小的变形.
Abstract:Activating flux tungsten inert gas (A-TIG) tests were conducted using a self-developed C5 active agent to study the effects of the active agent on the A-TIG weld formation, arc spectrum and arc morphology. At the same time, scanning electron microscope (SEM) was used to observe the morphology of the black residue, and the composition of the black residue after A-TIG welding was analyzed to determine the reasons for the formation of the black residue. The results showed that the active agent helped to increase the arc temperature and penetrative capacity, promote arc ionization, and change the surface tension gradient and the direction of melt pool flow, thus increasing the welding depth. Compared with the weld matrix, oxygen, chromium and titanium elements were more densely distributed in the residue, while other elements were diffusely distributed inside the residue. When observing the microstructure and properties of the welds, it was found that the weld centers were all equiaxial crystals with austenite and ferrite as the main tissues, while the fusion zones of the joints all showed columnar crystals. The average tensile strength of the specimen without residue removal was 675.36 MPa.Compared with the strength of the base metal, the strength was increased by 2%. The hardness curves of the weld and the base metal were staggered, and whether or not the residue was removed had little effect on the hardness of the joint. There was no crack on the surface of the two groups of specimens after bending 180°. The welds welded by A-TIG had good ductility and toughness. In addition, the weld surface of the specimen without residue removal had a concave phenomenon, but the weld width was uniform, and the weld shaping coefficient was 1.97, which could obtain a wide range of weld equiaxial crystals and relatively fine weld microstructure, and had smaller deformation than that of tungsten inert gas (TIG).
-
Keywords:
- stainless steel /
- A-TIG /
- arc spectrum /
- microstructure /
- mechanical properties
-
-
表 1 1Cr18Ni9 Ti奥氏体不锈钢TIG参数
Table 1 TIG parameters of 1Cr18Ni9 Ti austenitic stainless steel
组别 焊接层数 钨极直径
D/mm保护气体流量
Q/(L·min−1)焊接电流
I/A电弧电压
U/V焊接速度
v/(mm·min−1)1 2 3.2 15 180 14 80 2 2 3.2 15 180 14 80 3 1 3.2 15 180 14 80 表 2 1Cr18Ni9 Ti奥氏体不锈钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical composition of 1Cr18Ni9 Ti austenitic stainless steel
C Si Mn S P Cr Ni Ti Fe ≤0.12 ≤1.00 ≤2.00 ≤0.030 ≤0.035 17.00 ~ 19.00 8.00 ~ 11.00 0.80 余量 表 3 涂覆活性剂前后接头的元素含量
Table 3 Elemental content of joints before and after coating with active agent
元素 元素含量(质量分数,%) 涂覆活性剂前 涂覆活性剂后 B K — 5.34 C K 4.76 5.56 Si K 0.58 0.63 O K — 1.21 Ti K — 0.20 Cr K 17.12 17.26 Mn K 1.28 1.44 Fe K 68.08 60.07 Ni K 8.18 8.29 表 4 未除去残留物焊缝中金属间化合物元素含量
Table 4 Elemental content of intermetallic compounds in welds with residues not removal
元素 质量分数w(%) 原子分数a(%) O K 23.75 51.81 Cr K 21.13 14.18 Fe K 40.82 25.51 Ni K 14.30 8.50 -
[1] Bhanu V, Gupta A, Pandey C. Role of A-TIG process in joining of martensitic and austenitic steels for ultra-supercritical power plants -a state of the art review[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2022, 54(8): 2755 − 2770. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2022.03.003
[2] Deep A, Singh V, Ashutosh S, et al. Welding investigation on penetration and mechanical property of AISI 201 during A-TIG welding[J]. Engineering Research Express, 2022, 4(3): 035031. doi: 10.1088/2631-8695/ac863f
[3] Sunny K T, Korra N N, Vasudevan M, et al. Parameter optimization and experimental validation of A-TIG welding of super austenitic stainless steel AISI 904L using response surface methodology[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, 2022, 236(6): 2608 − 2617. doi: 10.1177/09544089221095671
[4] Patel D, Jani S, Singh V, et al. Develop a sustainable welding procedure for chromium manganese austenitic stainless steel using the ATIG process[J]. Engineering Research Express, 2021, 3(4): 045032. doi: 10.1088/2631-8695/ac3934
[5] Pandya D, Badgujar A, Ghetiya N. A novel perception toward welding of stainless steel by activated TIG welding: a review[J]. Materials and Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 36(8): 877 − 903.
[6] Kumaresan A, Sundar A, Annamalai A, et al. Effect of welding current on properties of activated gas tungsten arc super duplex stainless steel welds[J]. Materialpruefung, 2022, 64(8): 1242 − 1253.
[7] 高辉, 周灿丰, 胡晓慧, 等. 316L不锈钢掺杂SiC环状同轴送粉TIG熔覆层组织结构与性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(4): 49 − 56. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230424001 Gao Hui, Zhou Canfeng, Hu Xiaohui, et al. Microstructure and properties of annular coaxial powder feeding TIG cladding layer doped with SiC for 316L stainless steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(4): 49 − 56. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230424001
[8] 杜军, 王谦元, 何冀淼, 等. TIG电弧辅助熔滴沉积增材制造中熔滴偏距对熔池形貌的影响机制研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2024, 60(5): 219 − 230. Du Jun, Wang Qianyuan, He Jimiao, et al. Influence of the offset distance between droplet and molten pool on the molten pool morphology in TIG-assisted hroplet heposition manufacturing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2024, 60(5): 219 − 230.
[9] Touileb K, Hedhibi A C, Djoudjou R, et al. Mechanical, microstructure, and corrosion characterization of dissimilar austenitic 316L and duplex 2205 stainless-steel aTIG welded joints[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(7): 2470 − 2490. doi: 10.3390/ma15072470
[10] Liu X T, Su Y H, Zhang G Q, et al. Effect of longitudinal magnetic field on the microstructure and properties of A-TIG welding with different TiO2 coating amounts[J]. Crystals, 2022, 13(1): 66 − 76. doi: 10.3390/cryst13010066
[11] Sivateja P, Vidyarthy R S. Influence of activating fluxes on weld bead geometry, microstructures and mechanical properties of IRSM 41 A-TIG weldments[J]. Manufacturing Technology Today, 2023, 22(1): 7 − 12. doi: 10.58368/MTT.22.1.2023.7-12
[12] Baskoro A S, Amat M A, Widyianto A, et al. Investigation of weld geometry, mechanical properties, and metallurgical observations of activated flux tungsten inert gas (A-TIG) welding on 304 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Transactions of the Indian Institute of Metals, 2024, 77(3): 897 − 906. doi: 10.1007/s12666-023-03180-0
[13] Patil H S, Patel D C. Al2O3 and TiO2 flux enabling activated tungsten inert gas welding of 304 austenitic stainless steel plates[J]. Frattura ed Integrità Strutturale, 2022, 16(61): 59 − 68.
[14] Huang Y D, Wang B Y, Guo J, et al. Investigation of the mechanism of powder pool coupled activating TIG welding[J]. Metals, 2023, 13(5): 830 − 849. doi: 10.3390/met13050830
[15] Sancheti V, Patel D, Ghetiya N. Study the effect of fluxes on weld penetration during activated TIG welding of SS304[J]. Key Engineering Materials, 2023, 965: 21 − 28. doi: 10.4028/p-sX4ydX
[16] Touileb K, Djoudjou R, Ouis A, et al. Particle swarm method for optimization of ATIG welding process to joint mild steel to 316L stainless steel[J]. Crystals, 2023, 13(9): 1377 − 1397. doi: 10.3390/cryst13091377
[17] Touileb K, Djoudjou R, Hedhibi A C, et al. Comparative microstructural, mechanical and corrosion study between dissimilar ATIG and conventional TIG weldments of 316L stainless steel and mild steel[J]. Metals, 2022, 12(4): 635 − 656. doi: 10.3390/met12040635
[18] Dagur H, Kumar R, Singh V, et al. Effect of TIG and activated flux TIG welding processes on weld bead geometry, microstructure, and hardness of SAF 2507 grade super duplex stainless steel joints[J]. Engineering Research Express, 2023, 5(3): 035010. doi: 10.1088/2631-8695/ace2af
[19] Pydi H P, Pasupulla A P, Vijayakumar S, et al. Study on microstructure, behavior and Al2O3 content flux A-TIG weldment of SS-316L steel[J]. Materials Today, 2022, 51(1): 728 − 734.
[20] Qin B, Qu R, Xie Y F, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study on the TIG (A-TIG) welding of dissimilar magnesium alloys[J]. Materials, 2022, 15(14): 4922 − 4943. doi: 10.3390/ma15144922
[21] Busic M, Solic S, Tropsa V, et al. Influence of flux agent composition on the ionization potential in A-TIG welding of the electrolytic tough pitch copper (Cu-ETP) sheets[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2024, 29: 1253 − 1261. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2024.01.155
[22] Sridhar S P, Kumar S A, Sathiya P. A study on the effect of different activating flux on A-TIG welding process of Incoloy 800H[J]. Advances in Materials Science, 2016, 16(3): 26 − 37. doi: 10.1515/adms-2016-0014
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 陈昕航,徐新胜,曹立,吴松泽,陆弘毅. 基于残差修正的产品质量预测方法. 制造技术与机床. 2025(02): 177-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 沈植诚,王宾,程军辉. 基于SMA-BP算法的焊件动态电阻预测. 中国新技术新产品. 2024(21): 18-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: