Interfacial reaction at Cu-core heterogenous solder joints and its effects on mechanical properties during isothermal aging
-
摘要:
研究了Ni/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu异质铜核焊点(Ni-Cu铜核焊点)在100 ℃时效0、48、120和360 h下界面金属间化合物(intermetallic compound, IMC)的生长与演化行为,以及热时效作用下焊点的拉伸性能与断裂行为. 结果表明,在Ni-Cu铜核焊点中,在Ni基/Solder、Solder/Cu铜核以及Cu铜核/Solder界面处均形成(Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMC层,表明Cu原子穿过钎料到达Ni基侧参与界面反应,Solder/Cu基界面处形成Cu6Sn5 IMC层,4个界面的IMC层均平整连续,且主要呈锯齿状. 界面IMC层厚度均随着热时效时间的延长而逐渐增大,其生长行为以扩散控制为主. 在相同时效条件下,近Cu基侧的两个界面IMC层厚度分别大于近Ni基侧的IMC层的厚度,Ni-Cu铜核焊点的拉伸强度略高于Cu/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu(Cu-Cu铜核焊点)焊点的,两种焊点的拉伸强度均随热时效时间延长而降低,且断裂模式均以韧脆混合断裂为主,其断裂位置主要发生在近Cu基侧IMC层厚度较大的体钎料处,随着热时效时间的延长,断裂位置越倾向于近Cu基侧IMC层处,采用Ni替代Cu作基体,可减缓界面层的生长速度,有利于提高铜核焊点的可靠性.
Abstract:Ni/Cu-core + Solder/Cu heterogenous Cu-core solder joints (Ni-Cu Cu-core joints) were subjected to aging experiments at 100 ℃ for 0 h, 48 h, 120 h, and 360 h, respectively. The microstructure evolution of interfacial intermetallic compound (IMC), tensile properties and fracture behavior of Ni-Cu Cu-core joints were investigated. The results show that, at as-reflowed joints, the ternary (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 phases are formed at the Ni/Solder and Solder/Cu-core interface and the Cu6Sn5 phases are formed at the Solder/Cu interface in Ni-Cu Cu-core joints. Interfacial reaction occurs at Solder/Ni interfaces in Ni-Cu Cu-core joints by Cu atoms diffusing to the Ni base through solder. The IMC layers are flat, continuous, and mainly serrated at all interfaces. During the isothermal aging, the thicknesses of the IMC layers monotonically increase with increasing aging time and the interface growth behavior is mainly controlled by diffusion. At the same aging conditions, the thicknesses of the IMC layers on the near Cu base side are greater than that on the near Ni base side, respectively. The tensile strength of Ni-Cu joints is slightly higher than that of Cu/Cu-core + Solder/Cu (Cu-Cu) joints. The tensile strength of Ni-Cu and Cu-Cu solder joints decreases with aging time prolonged, and the fracture mode is mainly ductile brittle mixed fracture. The fracture location mainly occurs at the bulk solder with larger thickness of IMC layer near the Cu base side. With the increase of the aging time, the fracture location tends to be closer to the IMC layer near the Cu base side. Ni instead of Cu as the matrix can slow down the growth rate of the interface layer, and improve the reliability of Cu-core solder joints.
-
Keywords:
- Cu-core solder joints /
- interfacial reaction /
- IMC /
- growth behavior /
- thermal aging
-
0. 序言
随着汽车电子、航空电子、便携式移动电子以及大功率集成电子设备向着高密度化、微型化和多功能化方向的发展,三维(3D)高密度封装逐渐成为封装技术发展的潮流[1-2]. 在电子封装技术领域,微互连凸(焊)点起着机械连接、电气导通、信号传递等核心作用[3-4],而微互连铜核焊点更是由于具有不易桥连、导电性好、导热性良和熔点高等优点而被广泛应用于高性能计算芯片、存储器等高密度3D封装领域[5-6].
在回流焊过程中,3D封装结构中铜核加入后,铜核与焊料、焊料与基板均发生化学反应,在铜核/焊料、焊料/基体金属界面处均会形成IMC层,界面IMC层作为焊点的重要和关键组成部分,它的结构及形貌对电子封装互连焊点可靠性连接有着重要的影响,薄且连续均匀的 IMC层有利于界面的良好结合[7]. 与传统锡球焊点相比,铜核焊点的界面数量、原子扩散距离、界面微观结构(即IMC层)等有较大的变化,且界面化合物占比较高,但是由于IMC层较脆,太厚的IMC层使焊点的可靠性降低[8-9]. 铜核单界面或同质界面的界面反应特征已经进行了大量研究[10-13],Jeong等人[10]采用同质双ENIG界面研究了ENIG/Cu核 SAC305/ENIG焊点在电迁移过程中的界面演变;Chen等人[13]研究了铜核Sn-Pb焊点在固态高温时效作用下的界面反应和力学性能,并研究了铜核大小对力学性能的影响. 然而,在3D封装中,铜核焊点会同时存在4个界面,即芯片/焊料、焊料/铜核、铜核/焊料和焊料/基板,在回流焊过程中,4个界面将同时发生界面反应,两端的原子可能穿过液体焊料扩散到另一端,相互影响对面的界面反应,这种状态下焊点的组织及性能在焊接和服役过程中的演变将与单界面焊点存在较大差异. 关于铜核添加的复合钎料异质基材焊点界面 IMC层在热时效过程中的生长行为和力学性能之间关系的研究还较少. 因此,研究Ni/Cu铜核 + 钎料/Cu异质焊点界面层的形貌和生长特征,更真实地模拟铜核焊点的实际应用环境具有重要指导意义. 为此,文中以Ni/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu焊点为对象,研究该焊点在不同热时效时间作下的界面反应特征及拉伸性能,通过与Cu/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu同质焊点力学性能进行对比,探讨和分析Ni/Cu铜核 + Solder/Cu焊点界面IMC层生长动力学行为及焊点力学性能,为提高铜核焊点的可靠性提供理论依据.
1. 试验方法
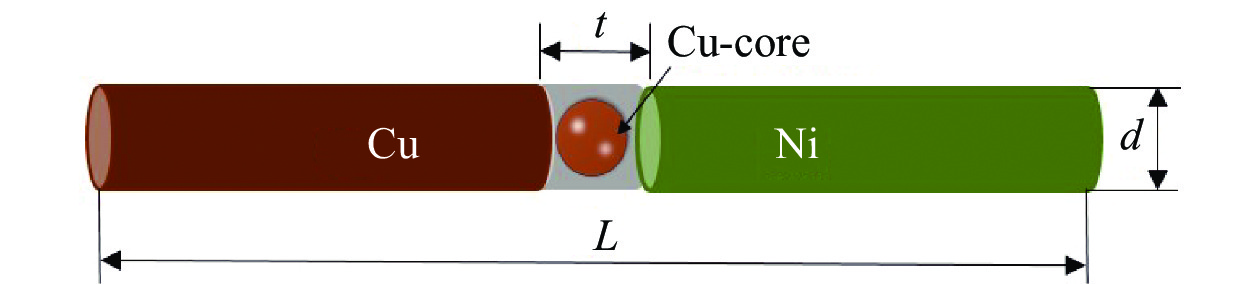
试验采用直径d为400 μm的铜丝和镍丝(纯度均为99.9%)作为基体材料,采用商用低银无铅Sn-0.3Ag-0.7Cu(简称Solder)锡膏与直径为350 μm高纯度的镀镍铜核球作钎料. 首先采用线切割将铜丝和镍丝基体材料加工成长度为30 mm的小棒,再采用砂纸将基材待焊端面磨平后放置超声波仪器用无水乙醇清洗并吹干后备用,然后将镍丝、铜丝放到自制的V形夹具上,中间放入铜核和Solder锡膏,搭建Ni/Cu-core + Solder/Cu三明治线性焊点(Ni-Cu铜核焊点),焊点高度t (即两根基材中间的间隙)和试样总长度L分别控制在0.5和60 mm左右,焊点结构如图1所示. 将组装好的三明治焊点放置于温度为250 ℃的恒温炉中,待钎料熔化后在回流态保持20 s左右,立即将夹具和试样一起从炉中取出放置于空气中冷却至室温,回流后采用酒精浸泡以去除试样表面残留的助焊剂.
将焊接后的试样用砂纸打磨掉焊点表面的氧化物及多余的钎料,然后将处理后的微焊点放置于恒温箱中进行不同时长(48、120、360 h)的100 ℃等温时效试验. 将经历不同时长热时效处理后的焊点取出进行镶嵌、打磨、抛光及腐蚀后使用带X射线能谱(energy dispersive spectrometer,EDS)的扫描电镜进行显微组织观察,采用Image-pro软件对3幅SEM图片的界面IMC厚度进行测量,并结合EDS分析界面层相组成.
将热时效后的焊点在DMAQ 800设备进行常温(约25 ℃)拉伸试验,加载速率设置为1 N/min. 每个热时效时长下的焊点分别取3个进行拉伸试验,将所得数据求平均值,在SEM扫描电镜上观察拉伸断口形貌.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 热时效时间对焊点界面显微组织的影响
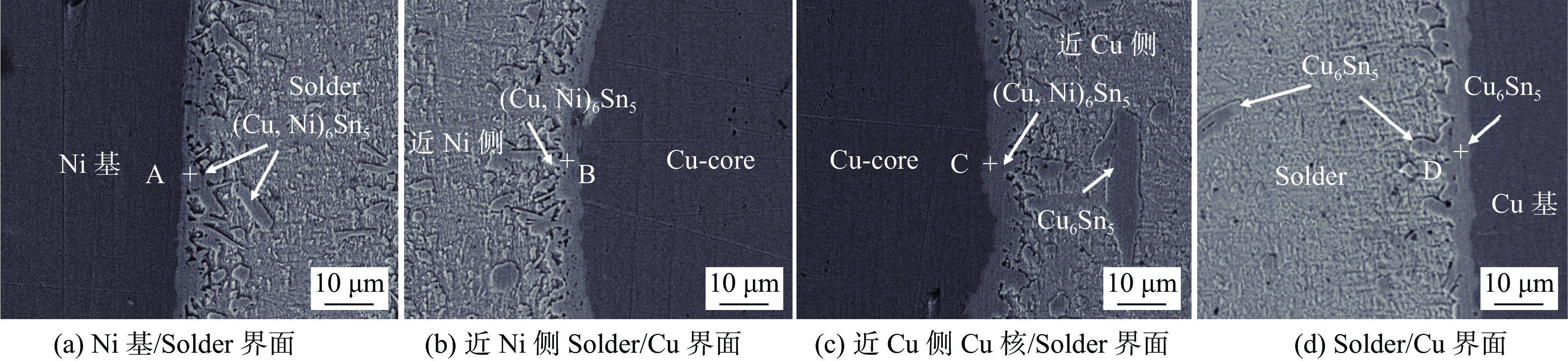
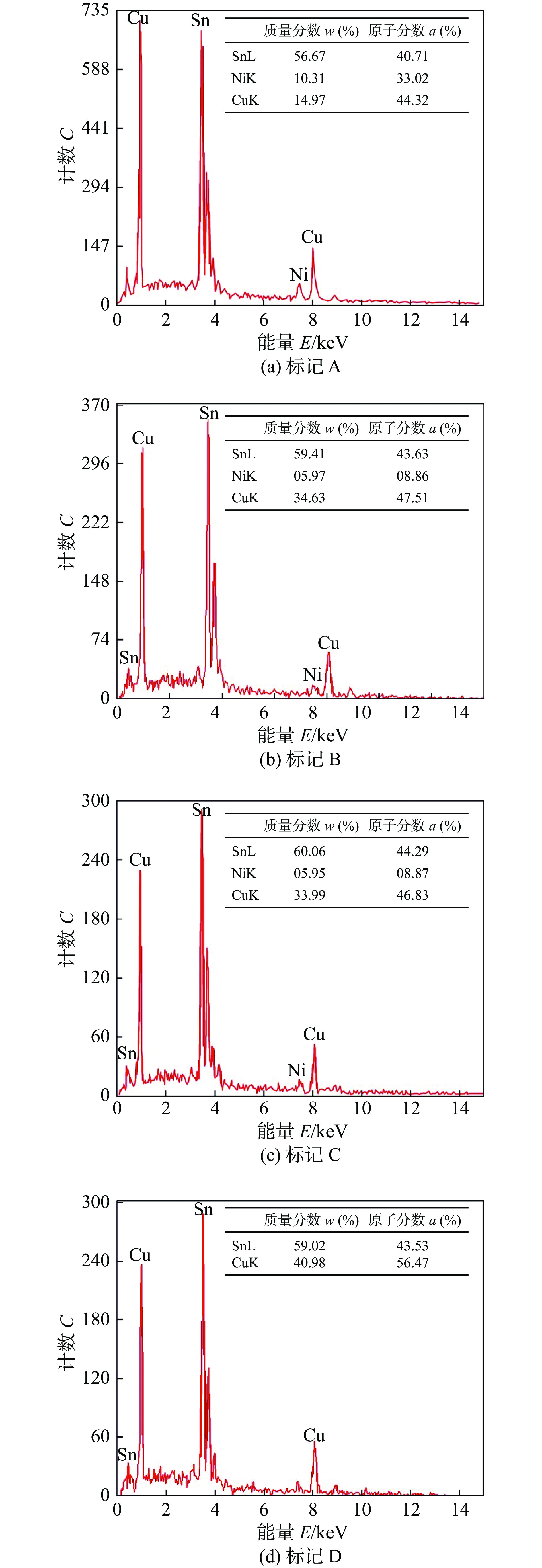
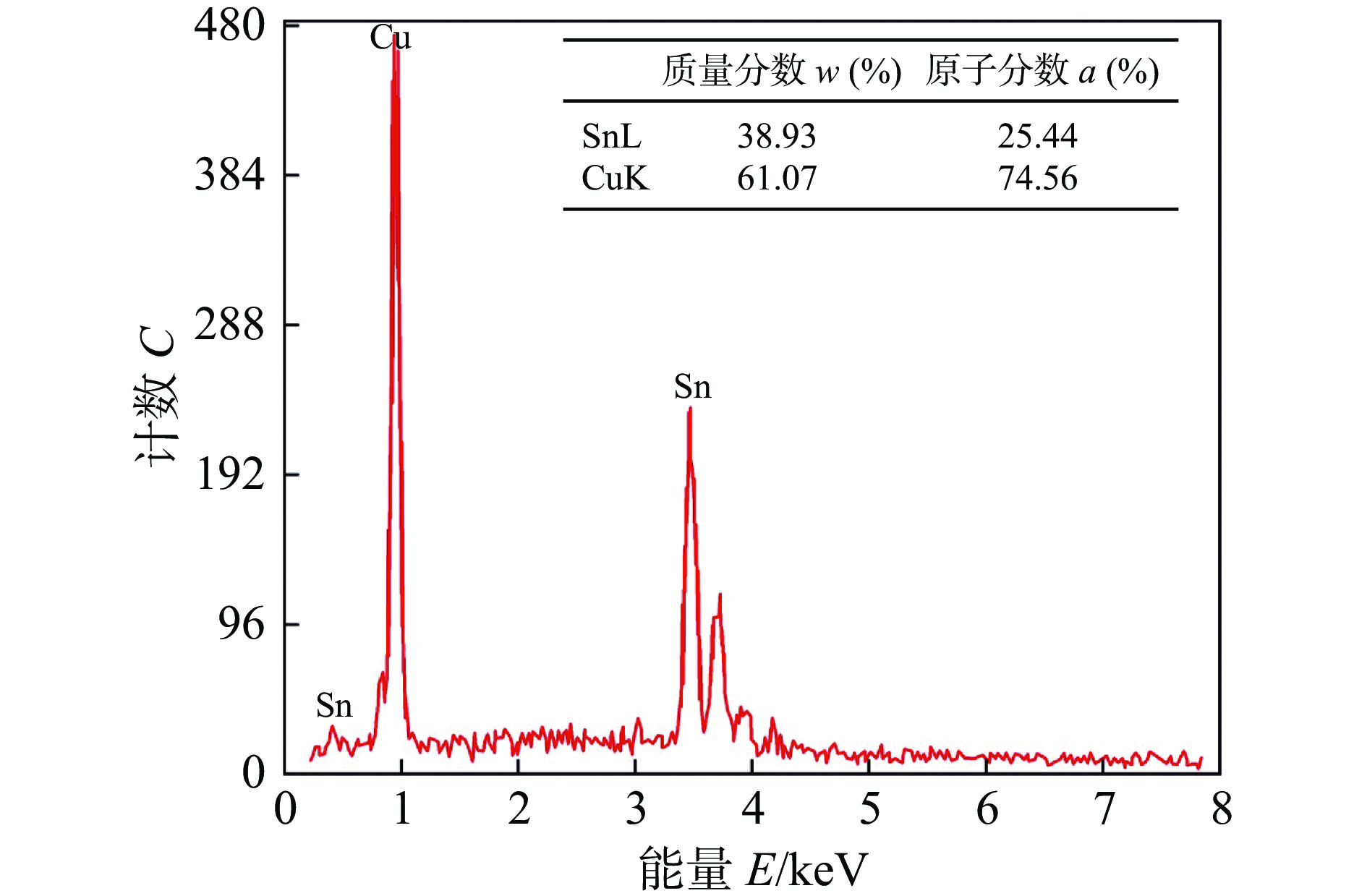
Ni-Cu铜核焊点在250 ℃回流焊20 s后空冷至室温的界面IMC显微组织及形貌,如图2所示. 由图2可观察到在各界面上均形成了一层很薄的连续的IMC层. 图2中A、B、C和D点的能谱分析如图3所示,除Solder/Cu基界面外,Ni基/Solder、近Ni基侧Solder/Cu铜核和近Cu基侧Cu铜核/Solder 3个界面IMC层均由Sn,Cu和Ni 3种元素组成,在Ni基/Solder界面处该相组成(摩尔分数)为44.32%Cu-14.97%Ni-40.71%Sn,其中(Cu + Ni)与Sn的原子数比为(44.32 + 14.97)∶40.71,接近6∶5,因此,将该相表征为(Cu,Ni)6Sn5,在近Ni基侧Solder/Cu铜核和近Cu基侧Cu铜核/Solder两个界面B点和C点处该相组成中,(Cu + Ni)与Sn的原子数比接近6∶5,因此,将该相表征为(Cu,Ni)6Sn5. Solder/Cu基界面D点的能谱分析,该相成分56.47%Cu-43.53%Sn,Cu与Sn的原子数比接近6∶5,因此,将该相也表征为Cu6Sn5. 从各界面的相组成来看,除Solder/Cu基界面外,其他3个界面上发生了明显的Cu-Ni交互作用. Solder/Cu基界面IMC形态呈扇贝状,其他3个界面形成近似针状的界面形貌,同时在近Cu基侧还发现有少量Cu6Sn5颗粒分布于钎料基体中,Ni基侧的IMC厚度明显比Cu基侧小,近Ni基侧的Solder/Cu铜核界面IMC厚度也略小于近Cu基侧的.
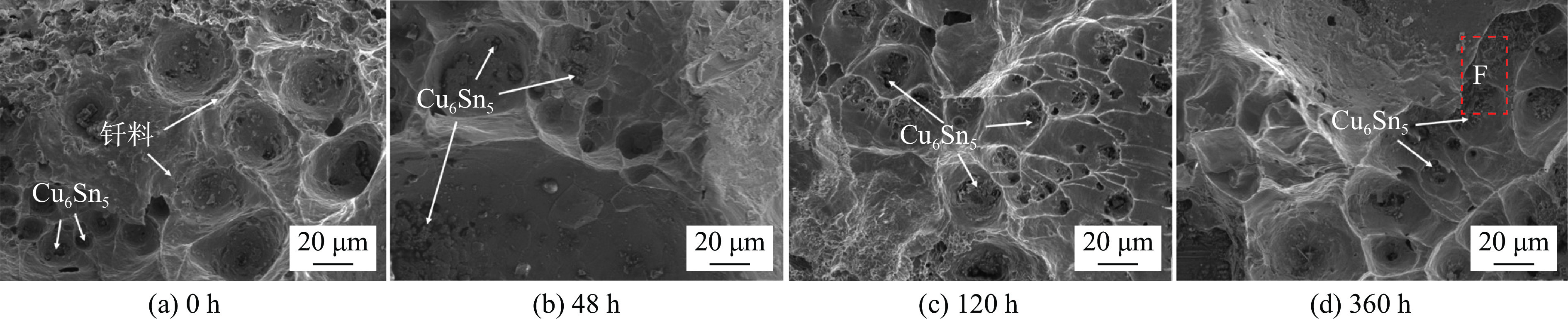
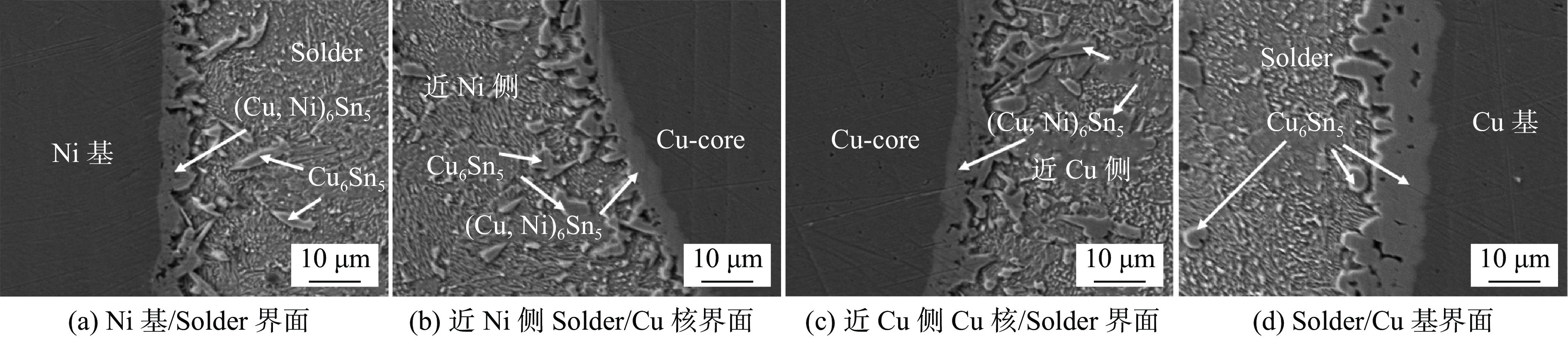
Ni-Cu铜核焊点在100 ℃热时效48、120、360 h后的界面形貌,如图4 ~ 图6所示. 可以看出,各界面IMC层的厚度均随着热时效时间的延长而增加,Ni基/Solder和近Ni基侧的Solder /Cu铜核两个界面的IMC层生长速率略低于Solder/Cu基和近Cu基侧的Cu铜核/Solder两个界面IMC层的生长速率. 随着时效时间的增加,Solder/Cu基界面处的IMC层与焊料基体的界面形貌由平坦向锯齿状转变,但齿尖深入焊料基体较浅;其他3个界面的IMC层除厚度增加外,其界面形貌变化不显著. 在近Cu基侧钎料基体中观察到有较大尺寸块状的Cu6Sn5存在,而近Ni基侧钎料基体中,发现少量尺寸较小的(Cu,Ni)6Sn5颗粒存在,可能是基体或铜核表面Ni原子扩散到钎料中形成的金属间化合物. 结果表明,在Ni-Cu铜核焊点中,采用Ni作为基体,对焊点界面IMC层过度生长起到了明显的抑制效果,有利于改善焊点服役可靠性.
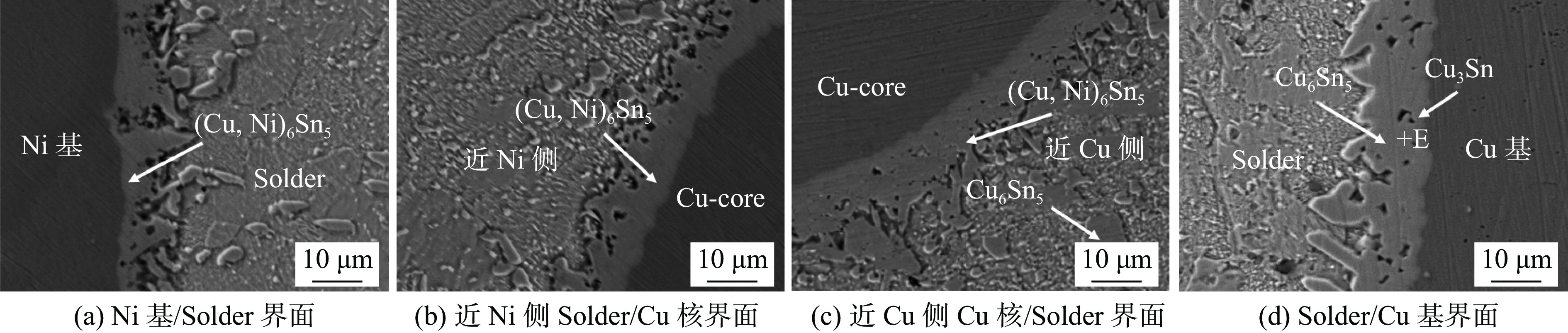
此外,热时效时长的增加并未改变Ni基/Solder、近Ni基侧Solder/Cu核和近Cu基侧Cu核/Solder 3个界面IMC种类. 通常在(Cu,Ni)6Sn5/铜核间界面形成的典型Cu3Sn未被检测到,主要原因是在回流焊过程中,一定量的Ni原子从镍基体界面扩散到铜核界面,Ni原子抑制了Cu3Sn的生成,与Tian等人[14]的研究结果相同. 在经历360 h热时效的试样中,在Solder/Cu基界面处,未观察到明显的IMC分层现象,但通过对界面进行能谱分析可知,Cu-Ni铜核焊点经较长热时效后,Solder/Cu基界面IMC层由Cu6Sn5和Cu3Sn两层化合物组成,即位于焊料一侧的Cu6Sn5层以及位于Cu基板和Cu6Sn5之间的Cu3Sn层,如图7所示,两种化合物中的Cu原子均来源于铜基板,Sn来自于钎料,Cu6Sn5是一种不稳定的化合物,在热时效时会发生以下反应[15]
$$ \mathrm{6Cu + 5Sn = Cu}_{ \mathrm{6}} \mathrm{Sn}_{ \mathrm{5}} $$ (1) $$ \mathrm{3Cu + Sn = Cu}_{ \mathrm{3}} \mathrm{Sn} $$ (2) $$ \mathrm{9Cu + Cu}_{ \mathrm{6}} \mathrm{Sn}_{ \mathrm{5}} \mathrm{ = 5Cu}_{ \mathrm{3}} \mathrm{Sn} $$ (3) 2.2 热时效时间对界面IMC层生长行为的影响
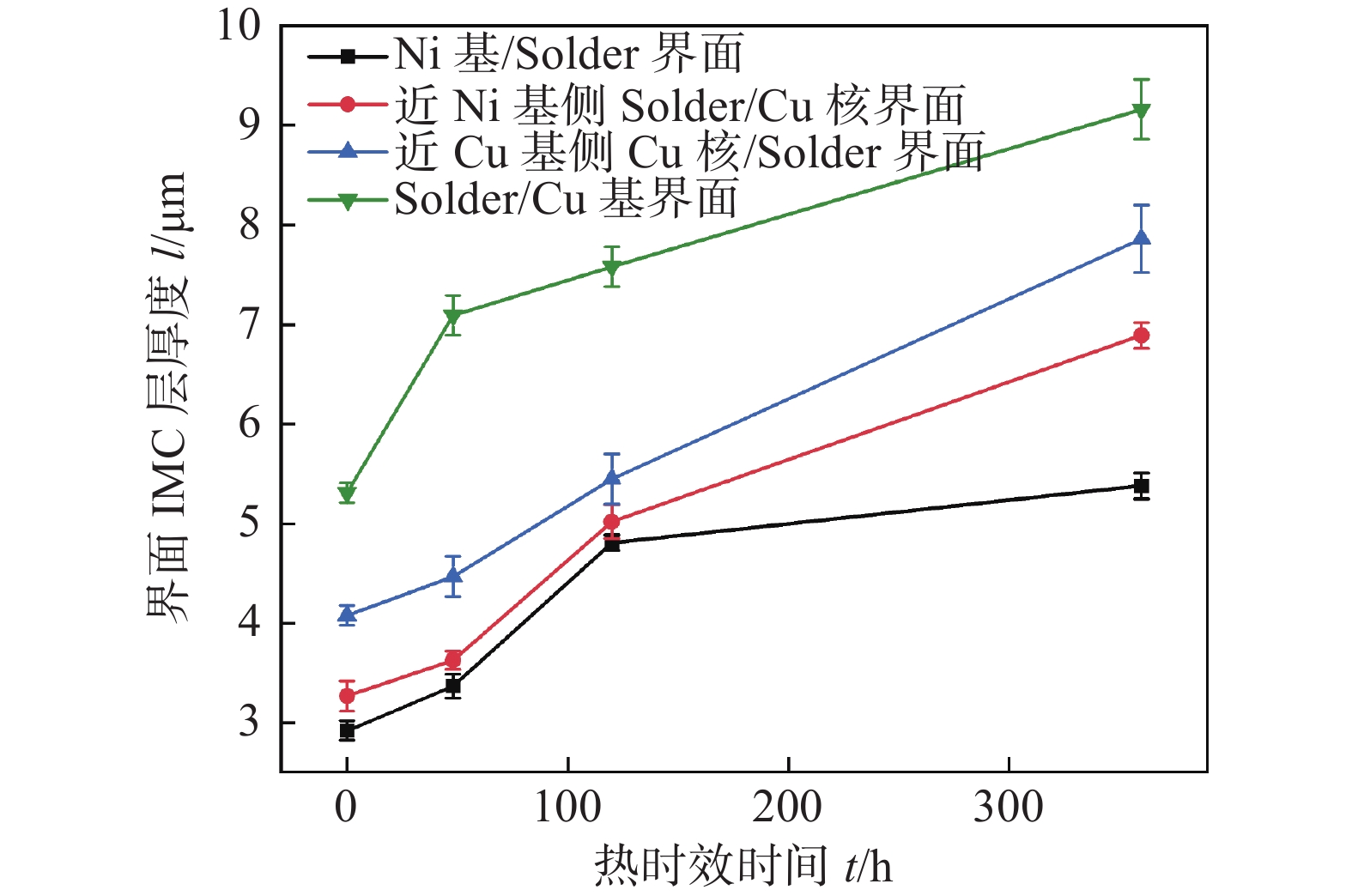
从热时效时间对焊点的微观组织演变可以看出,在热时效过程中,焊料与基体、焊料与铜核不断发生着反应,使界面层的厚度随着热时效时间的增加而变厚,界面IMC层厚度随时效时间的变化规律,如图8所示. 随着时效时间的延长,各界面IMC层逐渐变厚,Solder/Cu基界面的IMC厚度无论在哪个时刻均大于其他3个界面,可能是与Cu侧界面离Ni侧最远其受到Ni原子的影响最小有关. 热时效0 ~ 48 h内,Solder/Cu基界面IMC增长速率最快,随后该界面的IMC增长速率有所下降,这主要是因为Cu基界面在热时效初期形成的较厚Cu6Sn5有效的阻挡了Cu基体界面的Cu元素扩散进入钎料. 时效120 h后,Ni基/Solder、近Ni基侧Solder/Cu核和近Cu基侧Cu核/Solder 3个界面的(Cu,Ni)6Sn5生长速率均有下降趋势,这可能与界面之前已生成的(Cu,Ni)6Sn5层减缓了Ni、Sn和Cu原子的扩散速率有关. 时效360 h时,Ni基/Solder的界面IMC层厚度为5.38 μm,约为Solder/Cu基界面层厚度的一半.
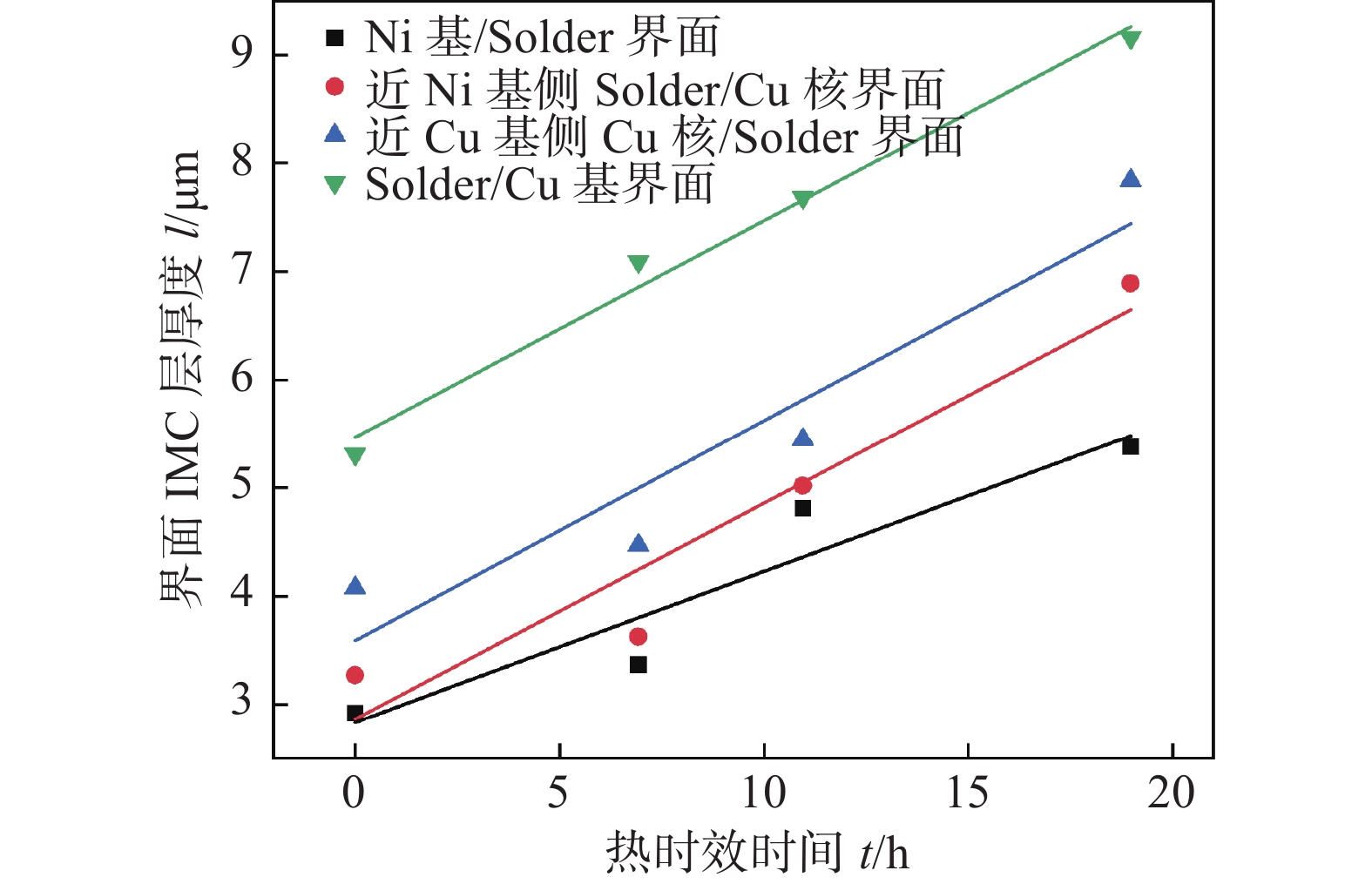
根据测试界面层IMC厚度结果,得到各界面层IMC层的厚度和热时效时间的拟合关系曲线如图9所示,为
$$ \mathit{l}\mathrm{=}\mathit{l}_{\mathrm{0}}\mathrm{+}\mathit{Kt}^{\mathit{\mathrm{1/2}}} $$ (4) 式中:l是时效过程中IMC层厚度(μm);l0是时效前 IMC层厚度(μm);K是IMC层生长系数(μm2/h);t是热时效时间(h) .
从图9可以观察到4个界面IMC层厚度与热时效时间近似呈线性增长趋势,拟合线的斜率反映了界面IMC层厚度随时间的增长趋势. 显然,100 ℃时效时,Ni基/Solder界面IMC层的增长速率仅为Solder/Cu基界面的70%,近Ni基侧Solder/Cu核和近Cu基侧Cu核/Solder两个界面的IMC生长速率也明显比Solder/Cu基的低,说明在同等时效条件下,采用焊料中添加微量Ni或采用Ni作基体可显著减缓焊点界面IMC层的生长趋势. 从图9还可以看出,4个界面层在100 ℃时效时的生长指数均为0.5,表明(Cu,Ni)6Sn5层和Cu6Sn5层的生长以扩散控制为主,该研究结果与SAC焊点可靠性研究中IMC层的生长行为吻合[16].
2.3 热时效对焊点拉伸性能的影响
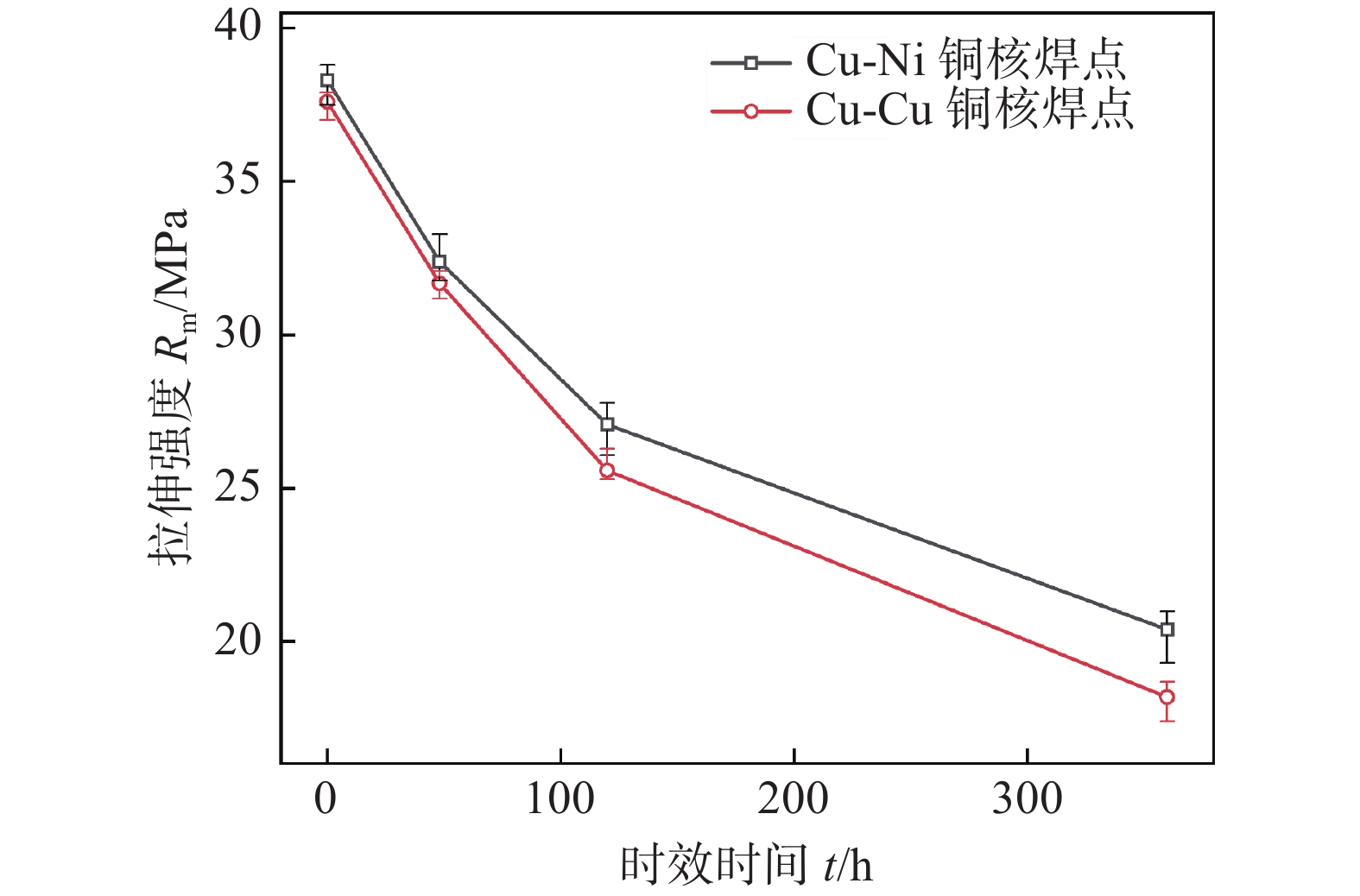
Cu-Cu铜核同质焊点和Ni-Cu铜核异质焊点时效前后焊点拉伸强度的变化,如图10所示. 从图10可以得到看出,随着热时效时间的延长,焊点的强度逐渐下降. 在相同时效时长下,Ni-Cu铜核焊点拉伸强度比Cu-Cu铜核焊点稍大,在时效120 h内,两种焊点的抗拉强度均下降较快,随后强度下降速率略缓,但Cu-Cu铜核焊点强度下降速率稍大于Cu-Ni焊点的.
Ni-Cu铜核焊点的抗拉强度从回流焊后的38.60 MPa下降到热时效360 h后的20.77 MPa,拉伸强度下降了46.19%. 结合Ni-Cu铜核焊点4种界面IMC层的生长曲线可知,Ni-Cu铜核焊点各界面的生长速率和厚度均有差异,在热时效48 h时,其Ni基/Solder界面IMC厚度约为3.37 μm,而热时效360 h后,其Ni基/Solder界面IMC厚度约为5.38 μm,与回流焊后Solder/Cu基侧的IMC厚度相当.很显然,焊点抗拉强度变化规律与焊点IMC层的厚度有关,界面IMC是脆性物质,过厚的界面化合物将会导致微焊点的拉伸性能降低,因此热时效引起的界面IMC厚度的增加是引起微焊点抗拉强度下降的原因之一.
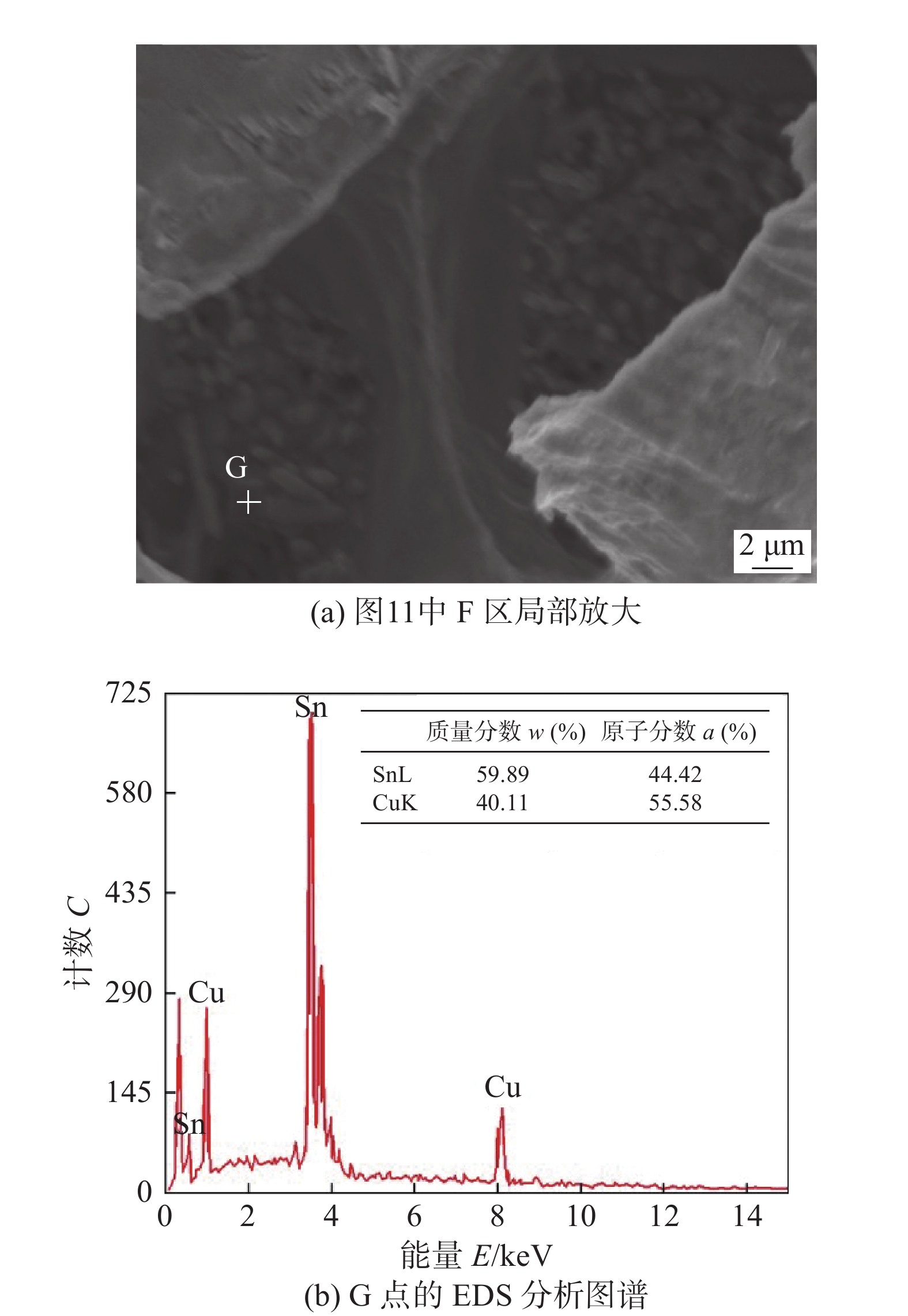
试验研究发现,Cu-Cu和Ni-Cu两种铜核焊点在轴向拉伸试验中,其拉伸断裂主要在钎料/铜基界面附近和近铜基侧的钎料部分,以韧脆混合断裂为主,拉伸断口形貌如图11所示. 由于Cu-Cu铜核焊点的断裂位置与断口形貌与Ni-Cu焊点的断裂位置与断口形貌基本一致,因此图11中只列出Ni-Cu焊点的拉伸断口形貌. 从图11很明显可以看到,在断口处均发现有类似小球的颗粒状和撕裂的韧窝存在. 对颗粒状小球进行能谱分析,如图12所示,可以推断颗粒小球主要成分为Cu6Sn5,即界面IMC,这与Somidin等人[17]从IMC层侧面观察到Cu6Sn5成扇贝状相吻合.
如图11所示,焊态和热时效后的焊点断口表面均出现了一定数量的韧窝,同时断口存在少部分裸露的Cu6Sn5层,随热时效时间的延长,裸露的Cu6Sn5层占比有增大倾向,说明焊点的断裂位置在更靠近IMC的体钎料处,可能是因为随着时效时间的延长,焊点靠近铜基侧界面IMC晶粒长大导致晶粒间结合强度降低,同时界面IMC自身的脆性也使得界面处连接强度变弱[18],因此断裂位置更靠近IMC的体钎料处. 在Ni-Cu异质焊点中,Cu在焊料/Ni界面发生耦合反应,抑制了界面IMC层的生长,在一定程度上起到了减缓焊点力学性能恶化的效果,有利于提高焊点的可靠性.
3. 结论
(1) Ni-Cu铜核焊点,在Ni基/Solder、近Ni侧Solder/Cu核以及近Cu侧Solder/Cu核界面处均形成(Cu,Ni)6Sn5 IMC层,表明Cu原子穿过钎料到达Ni基侧参与界面反应,Solder/Cu基界面处形成Cu6Sn5 IMC层. 焊点4个界面的IMC层平整、连续,且主要呈锯齿状.
(2) 热时效中,界面IMC厚度均随着热时效时间的延长而逐渐增大,而且生长行为以扩散控制为主. 在相同时效条件下,近Cu基侧的两个界面IMC层厚度分别小于近Ni基侧的两个IMC层的厚度.
(3) Ni-Cu铜核焊点的拉伸强度略高于Cu-Cu铜核焊点的,两种焊点的拉伸强度均随热时效时间延长而降低且断裂模式均以韧脆混合断裂为主,断裂位置主要发生在近Cu基侧IMC层厚度较大的体钎料处. 随着热时效时间的延长,断裂位置越倾向于近Cu基侧IMC层处,采用Ni替代Cu作基体,可减缓界面层的生长速度,有利于提高铜核焊点的可靠性.
-
-
[1] 王小伟, 王凤江. Sn-58Bi微焊点组织与力学性能的尺寸效应行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(12): 70 − 74. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230613008 Wang Xiaowei, Wang Fengjiang. Size effect behavior of microstructure and mechanical properties in Sn-58Bi micro solder joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(12): 70 − 74. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230613008
[2] 杨晓军, 李晓光, 贺定勇, 等. 环氧基Sn-Bi焊膏的焊点热稳定性[J]. 北京工业大学学报, 2025, 51(2): 140 − 147. Yang Xiaojun, Li Xiaoguang, He Dingyong, et al. Study on the thermal stability of solder joints of epoxy-based Sn-Bi solder paste[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Technology, 2025, 51(2): 140 − 147.
[3] 周敏波, 赵星飞, 陈明强, 等. 电子封装跨尺度凸点结构Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu微互连焊点界面IMC生长与演化及力学行为的尺寸效应[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(2): 259 − 268. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.02.259 Zhou Minbo, Zhao Xingfei, Chen Mingqiang, et al. Size effects of growth and evolution of interfacial intermetallic compound and the mechanical behavior of bump structure Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu/Cu cross-scale joints in electronic packages[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(2): 259 − 268. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.02.259
[4] Yao Z X, Jiang S, Yin L M, et al. Effects of joint height on the interfacial microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu-cored SAC305 solder joints[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2020, 49(9): 5391 − 5398. doi: 10.1007/s11664-020-08273-w
[5] 谢俊, 黄春跃, 梁颖, 等. 三维堆叠封装TSV互连结构热扭耦合与优化[J]. 电子元件与材料, 2023, 42(9): 1129 − 1135. Xie Jun, Huang Chunyue, Liang Ying, et al. Analysis and optimization of thermal-torsional coupling stress of 3D stacked packaged TSV interconnect structure[J]. Electronic Components and Materials, 2023, 42(9): 1129 − 1135.
[6] Song R W, Fleshman C J, Wu Z Y, et al. Increasing mechanical strength and refining grains of Cu-core solder joints with pressurized bonding[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2020, 31: 22966 − 22972. doi: 10.1007/s10854-020-04824-3
[7] Yao Z X, Zhang Y, Ling D Y, et al. Effect of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the microstructure and properties of Sn-58Bi solder alloys[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology, 2023, 38(7): 1 − 13.
[8] 张欣, 秦俊虎, 龙登成, 等. 高银系 Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu界面金属间化合物生长行为[J]. 焊接, 2024(3): 38 − 46. doi: 10.12073/j.hj.20220419001 Zhang Xin, Qin Junhu, Long Dengcheng, et al. Growth behavior of Sn-Ag-Cu/Cu intermetallic compounds in high silver series[J]. Welding & Joining, 2024(3): 38 − 46. doi: 10.12073/j.hj.20220419001
[9] 张贺, 冯佳运, 丛森, 等. 62Sn36Pb2Ag组装焊点长期贮存界面化合物生长动力学及寿命预测[J]. 工程科学学报, 2023, 45(3): 400 − 406. Zhang He, Feng Jiayun, Cong Sen, et al. Long-term storage life prediction and growth kinetics of intermetallic compounds in 62Sn36Pb2Ag solder joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2023, 45(3): 400 − 406.
[10] Jeong H, Lee C J, Kim J H, et al. Electromigration behavior of Cu core solder joints under high current density[J]. Electronic Materials Letters, 2020(4): 2641 − 2647.
[11] Jeong H, Lee C J, Min K D, et al. Mechanical properties of Cu-core solder balls with ENEPIG surface finish[J]. Research Policy: A Journal Devoted to Research Policy, Research Management and Planning, 2020, 49(10): 6073 − 6079.
[12] Fleshman C, Song R W, Tsai S Y, et al. Phase identification and interface evolution of ENIG/Cu-core SAC305/ENIG solder joints after the thermal-electrical coupling reliability test[J]. Materials Letters, 2020, 275: 128104. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128104
[13] C M Chen, H C Lin. Interfacial reactions and mechanical properties of ball-grid-array solder joints using Cu-cored solder balls[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2006, 35(11): 1937 − 1947. doi: 10.1007/s11664-006-0297-4
[14] Tian Y, Liu X, Chow J, et al. Comparison of Sn-Ag-Cu solder alloy intermetallic compound growth under different thermal excursions for fine-pitch flip-chip assemblies[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2013, 42(8): 2724 − 2731. doi: 10.1007/s11664-013-2639-3
[15] 杨蔚然, 季童童, 丁毓, 等. 热老化与热循环条件下Bi对Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu无铅焊点界面组织与性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(11): 157 − 162. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220709003 Yang Weiran, Ji Tongtong, Ding Yu, et al. Effect of Bi addition on interfacial microstructures and properties of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu Pb-free solder joints during isothermal aging and thermal cycling[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(11): 157 − 162. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220709003
[16] 谢仕芳, 韦习成, 鞠国魁, 等. Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu0.05Cr/Cu焊点界面IMC层热时效形貌及生长行为研究[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2015, 44(9): 2234 − 2239. Xie Shifang, Wei Xicheng, Ju Guokui, et al. Interfacial IMC layer morphology and growth behavior of Sn3.0Ag0.5Cu0.05Cr/Cu solder joints during isothermal aging[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2015, 44(9): 2234 − 2239.
[17] Somidin F, Mcdonald S D, Ye X, et al. Reducing cracking in solder joint interfacial Cu6Sn5 with modified reflow profile[J]. Transactions of the Japan Institute of Electronics Packaging, 2020, 13: E19-004-1-E19-004-11.
[18] 李霞, 孙凤莲, 刘洋, 等. SAC-Bi-Ni焊点抗热冲击及抗热时效性能研究[J]. 中国体视学与图像分析, 2012, 17(4): 341 − 347. Li Xia, Sun Fenglian, Liu Yang, et al. Thermal shock and thermal aging performance of SAC-Bi-Ni solder joint[J]. Chinese Journal of Stereology and Image Analysis, 2012, 17(4): 341 − 347.



 下载:
下载: