Front-side monitoring technology for back-side keyhole state in VPPAW
-
摘要:
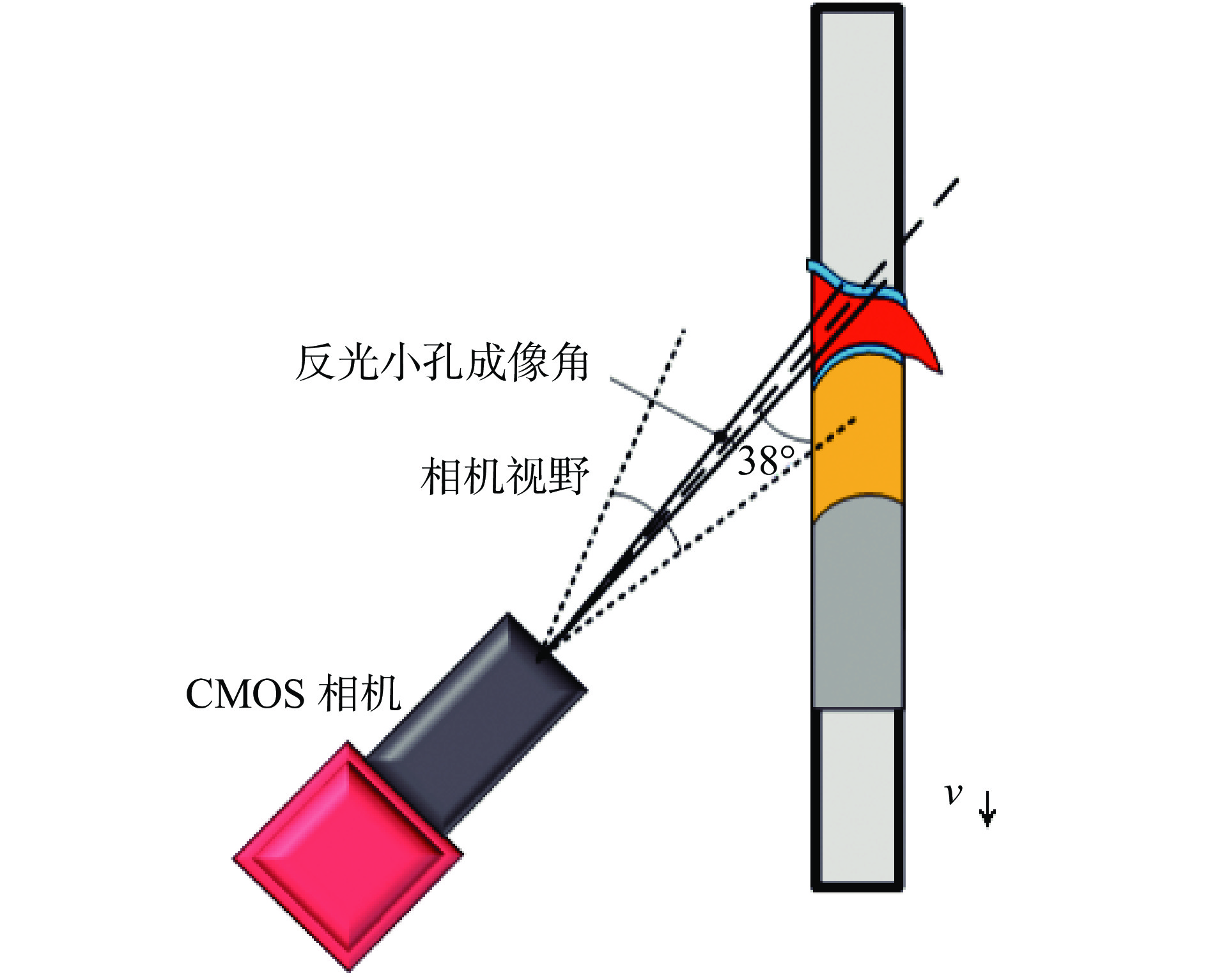
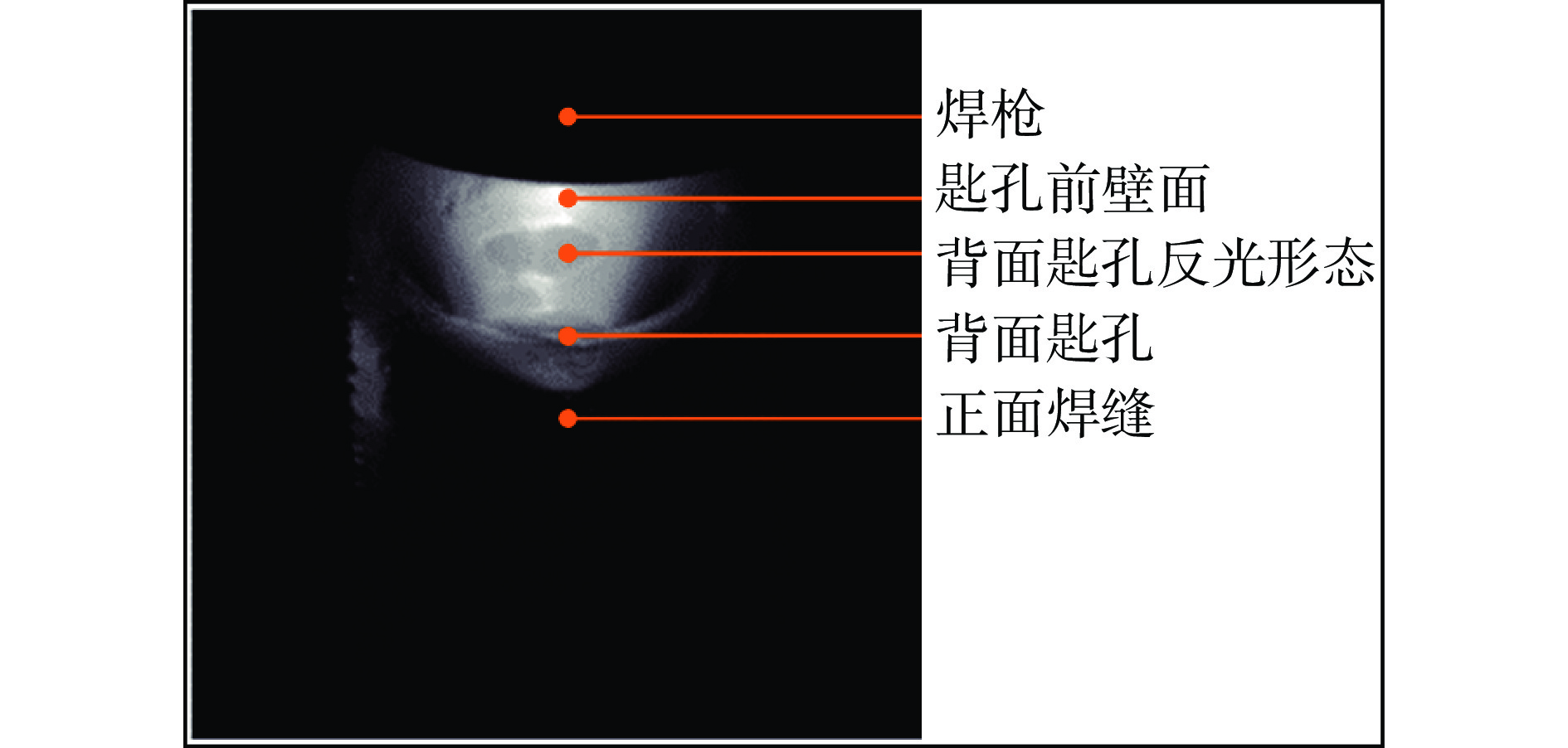
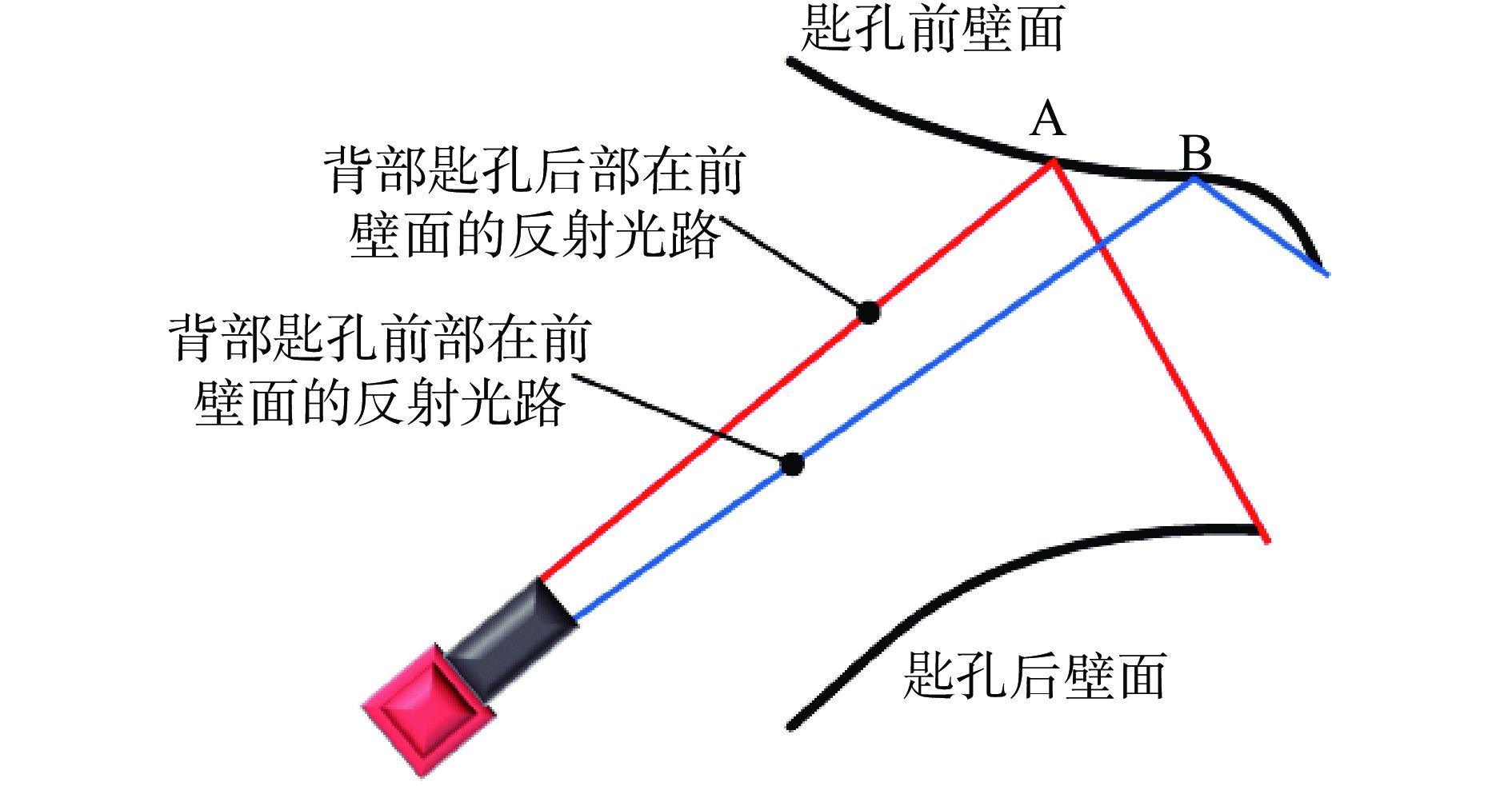
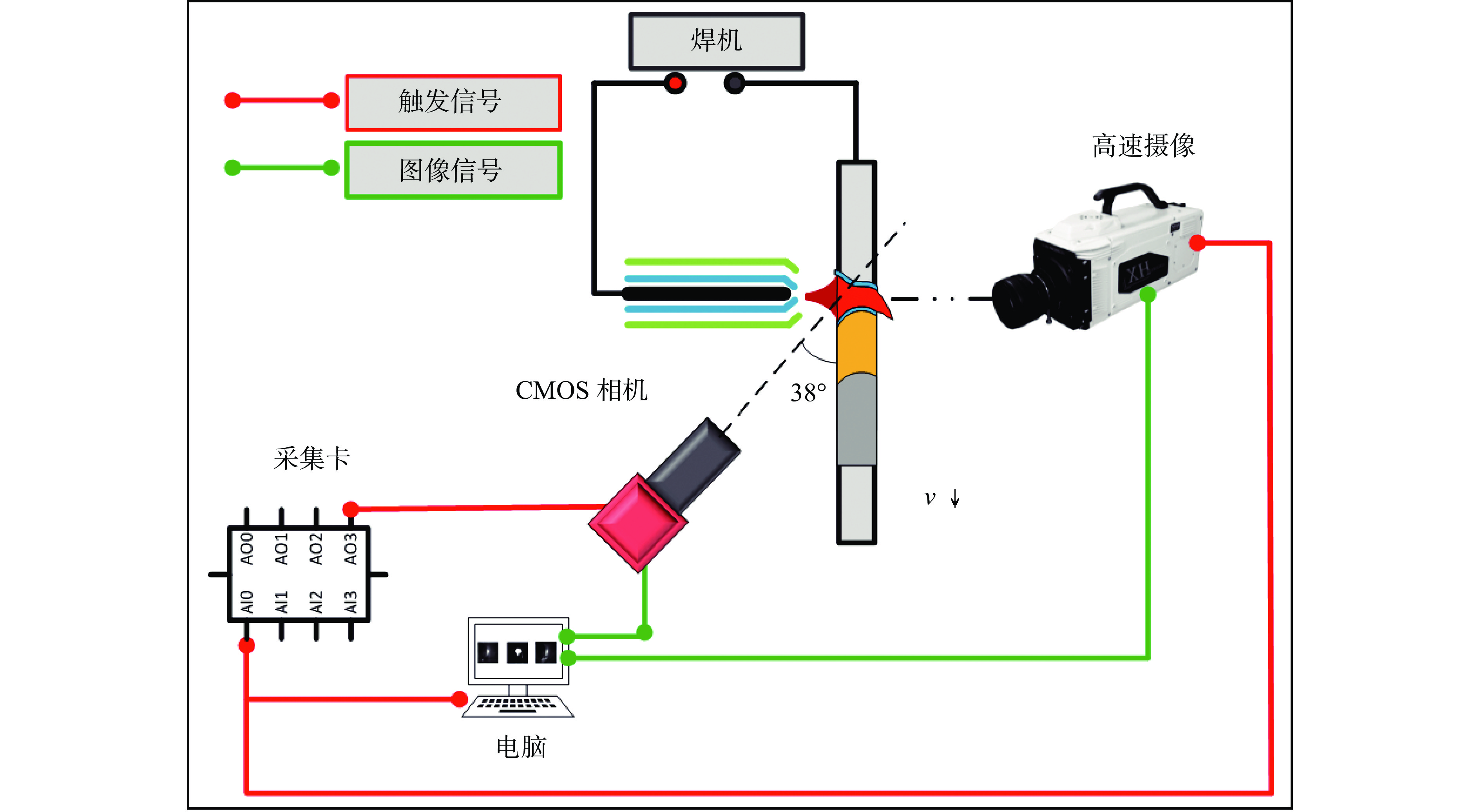
变极性等离子弧焊接(variable polarity plasma arc welding, VPPAW)过程中匙孔状态,特别是背面匙孔状态是决定焊缝成形质量的核心要素. 在实际焊接过程中,背面放置传感器检测匙孔状态存在难度. 文中提出了一种基于匙孔前壁面反光的等离子弧焊接背面匙孔正面检测方法. 在合适的拍摄角度下,该方法可以同时获得正面匙孔图像和背面匙孔在前壁面的反光成像. 通过不同焊接电流下的工艺试验,建立了焊接质量与匙孔反光形态的联系. 随着焊接电流的增大,检测到的前壁面匙孔图像位置逐渐向上偏移. 焊接出现切割时,背面匙孔反光形态消失;干扰稳定焊接状态,背面匙孔反光形态同时发生改变. 匙孔稳定与否与焊接状态稳定直接关联. 背面匙孔在前壁面的反光成像状态受焊接状态和熔池状态影响. 为等离子焊接正面检测焊接质量提供了指导意义.
Abstract:In the process of variable polarity plasma arc welding (VPPAW), the state of the keyhole, particularly the back-side keyhole, was a critical factor influencing the weld formation quality. However, in practical welding operations, monitoring the keyhole state from the backside with sensors presented significant challenges. Therefore, this paper proposed a method for detecting the back-side keyhole on the front view using plasma arc welding based on the reflection from the front wall of the molten pool. With appropriate shooting angles, this method could simultaneously capture both the front-side keyhole images and the reflected shape of the back-side keyhole on the front wall. The relationship between the welding quality and the reflective shape of the keyhole was established through experiments at different welding currents. With the increase of welding current, the position of the detected keyhole image on the front wall was gradually shifted upward. When the weld appeared to be cut, the reflective shape of the keyhole on the back disappeared; when the stable weld state was disturbed, the reflective shape of the keyhole on the back changed at the same time. The stability of the keyhole was directly related to the stability of the welding states. The reflective shape of the backside keyhole on the front wall was affected by the welding state and the molten pool state. This provided important guidance for establishing the correlation between the reflective shape of the keyhole on the back and the welding quality.
-
Keywords:
- plasma arc welding /
- keyhole /
- weld quality /
- reflection
-
-
表 1 焊接试验参数
Table 1 Paraments of welding experiment
组别 EN电流
I1/AEP电流
I2/A成形状态 1 120 150 正常 2 130 160 正常 3 140 170 正常 4 150 180 正常 5 160 190 正常 6 170 200 成形不良 7 150 180 成形不良—切割 8 150 180 正常—干扰 9 150 180 正常—切割 -
[1] 王小伟, 张斌, 曾如川, 等. 铝合金VPPAW穿孔焊接匙孔闭合处的微观组织与力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(3): 1 − 6. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230402001 Wang Xiaowei, Zhang Bin, Zeng Ruchuan, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of welds at keyhole closures in variable-polarity plasma arc welding of Al alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(3): 1 − 6. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20230402001
[2] 韩蛟, 韩永全, 洪海涛, 等. 基于光谱诊断的VPPA-MIG复合电弧耦合机理分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(11): 104 − 109. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20221211001 Han Jiao, Han Yongquan, Hong Haitao, et al. Analysis of VPPA-MIG hybrid arc coupling mechanism based on spectral diagnosis[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(11): 104 − 109. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20221211001
[3] Jiao W H, Wang Q Y, Cheng Y C, et al. End-to-end prediction of weld penetration: a deep learning and transfer learning based method[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 63: 191 − 197. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.044
[4] Zhou F Z, Liu X F, Zhang X F, et al. Keyhole status prediction based on voting ensemble convolutional neural networks and visualization by grad-CAM in PAW[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 80: 805 − 815. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.06.034
[5] Nomura K, Fukushima K, Matsumura T, et al. Burn-through prediction and weld depth estimation by deep learning model monitoring the molten pool in gas metal arc welding with gap fluctuation[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 61: 590 − 600. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.10.019
[6] 陈宸, 周方正, 李成龙, 等. 融合空间和通道特征的等离子弧焊熔池熔透状态预测方法[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(4): 30 − 38. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220516001 Chen Chen, Zhou Fangzheng, Li Chenglong, et al. Prediction method of plasma arc welding molten pool melting state based on spatial and channel characteristics[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(4): 30 − 38. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220516001
[7] Kim H, Nam K, Oh S, et al. Deep-learning-based real-time monitoring of full-penetration laser keyhole welding by using the synchronized coaxial observation method[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 68: 1018 − 1030. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.06.029
[8] Kim H, Nam K, Kim Y, et al. Analysis of laser-beam absorptance and keyhole behavior during laser keyhole welding of aluminum alloy using a deep-learning-based monitoring system[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 80: 75 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.05.044
[9] 樊重建. 变间隙铝合金脉冲GTAW熔池视觉特征获取及其智能控制研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2008. Fan Chongjian. Weld pool characters extraction visual sensing and intelligent control during varied gap aluminum alloy pulsed GTAW process[D] Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2008.
[10] 吴頔. 基于多源信息融合的铝合金VPPAW成形预测和智能控制研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. Wu Di. Research on predicting and intelligent control for weld formation during VPPAW process using multi-information fusion[D] Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2018.
[11] Liu Z M, Wu C S, Cui S L, et al. Correlation of keyhole exit deviation distance and weld pool thermo-state in plasma arc welding process[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 104: 310 − 317. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2016.08.069
[12] Liu Z M, Wu C S, Chen M A. Experimental sensing of the keyhole exit deviation from the torch axis in plasma arc welding[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2014, 71(3): 1209 − 1219.



 下载:
下载: