Mechanism of heat treatment temperature on microstructure and properties in deposited metal of 1000 MPa grade high strength steel
-
摘要:
采用丝级埋弧焊方法制备
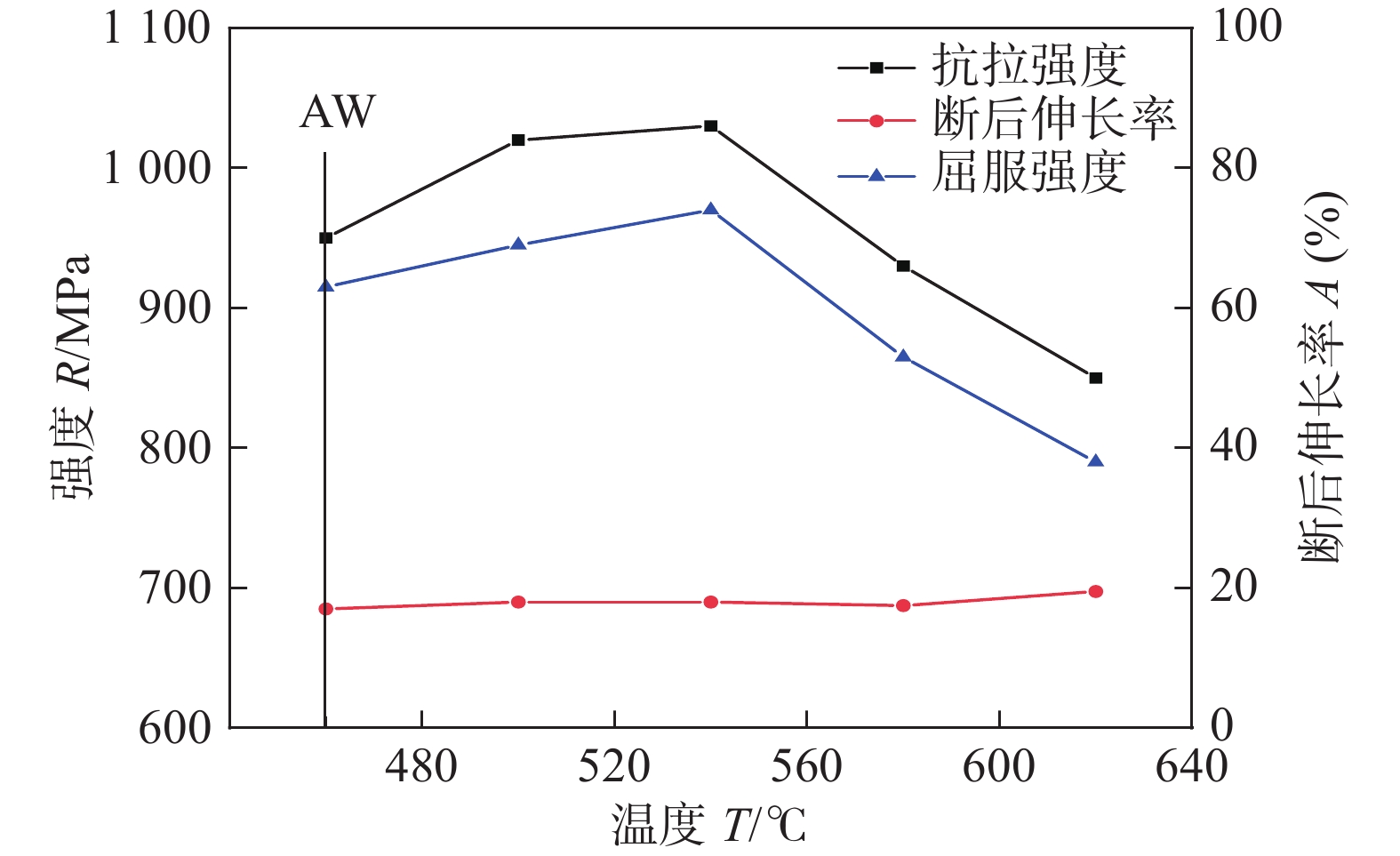
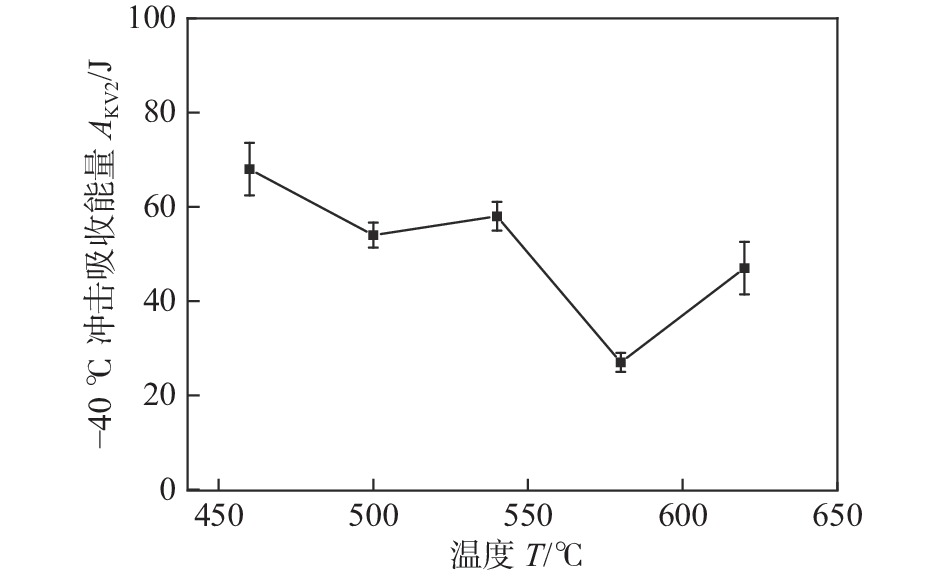
1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属,利用SEM、EBSD、XRD和TEM等微观分析方法研究了焊后热处理温度(500 ~ 620 ℃)对1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属组织演变的影响,并通过拉伸和冲击试验评估其力学性能. 结果表明,随着热处理温度升高,1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属抗拉强度和屈服强度对比焊态(as welded,AW)先升高后降低,熔敷金属热处理后比AW韧性降低.1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属在540 ℃热处理时获得较好强韧匹配效果,抗拉强度1030 MPa,屈服强度970 MPa,−40 ℃冲击韧性58 J.1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属在500 ~ 620 ℃热处理过程中M/A组元中的A逐渐分解为碳化物和铁素体,M在620 ℃热处理时生成逆转变奥氏体并保留至室温. 碳化物对于位错具有钉扎作用,但随热处理温度升高碳化物对位错的钉扎作用减弱,位错通过滑移和攀移不断减少. 熔敷金属析出的碳化物对位错的钉扎作用强于位错滑移的软化作用时,熔敷金属强度提高,碳化物对位错的钉扎作用弱于位错滑移的软化作用时基体组织软化,熔敷金属强度降低. 析出的碳化物导致位错塞积,产生的应力集中区域成为裂纹源,使热处理态熔敷金属韧性低于AW.-
关键词:
-
1000 MPa级高强钢 / - 熔敷金属 /
- 焊后热处理 /
- 埋弧焊 /
- 碳化物
Abstract:1000 MPa high strength steel deposited metal is prepared by wire submerged arc welding. The effect of post-weld heat treatment temperature (500 ~ 620 ℃) on the microstructural evolution in deposited metal of1000 MPa grade high strength steels has been investigated using microanalytical methods such as SEM, EBSD, XRD and TEM. Evaluate their mechanical properties by tensile and impact tests. The results show that with the increase of heat treatment temperature, 1000MPa grade high-strength steel deposited metal tensile strength and yield strength of heat-treated state than the AW first increase and then reduce. The heat-treated state deposited metal toughness is lower than the AW. The strength and toughness matching effect of1000 MPa grade high strength steel deposited metal is good at 540 ℃ heat treatment, the tensile strength is1030 MPa, the yield strength is 970 MPa, and the impact toughness is 58 J at −40 ℃.1000 MPa grade high strength steel fused metal in 500 ~ 620 ℃ heat treatment process in the M/A group element A gradually decomposed into carbides and ferrite. During heat treatment at 620 ℃, reverse austenite is generated and retained to room temperature. Carbide for dislocations has a pinning effect, but with the increase of heat treatment temperature carbide on the dislocation of the pinning effect is weakened, dislocations through the slip and climb constantly reduced. Deposited metal precipitation of carbide on the dislocation pinning effect is stronger than the softening effect of dislocation slip, the deposited metal strength, carbides on the dislocation pinning effect is weaker than the softening effect of dislocation slip when the matrix microstructure softens, the deposited metal strength is reduced. The precipitated carbide leads to dislocation plugging, and the stress concentration area becomes the crack source, which makes the toughness of the heat-treated deposited metal lower than the AW. -
-
0. 序言
在熔焊中,焊缝微观组织受温度场和热影响区晶粒结构的影响. 在焊接热源高温作用下形成的焊缝与热影响区中的微观组织形貌将影响焊接结构的性能和质量[1]. 因此,微观组织的控制是保证焊接接头力学性能的重要因素. 由于焊接是一个高温、瞬时、动态的复杂过程,采用试验法研究焊接接头组织的演变过程具有一定的限制. 随着计算机技术和材料科学的发展,通过数值模拟技术已经能够再现焊接熔池枝晶演变和热影响区晶粒长大的动态过程[2-7].
Pavlyk等人[3]首次利用有限差分-元胞自动机(FD-CA)模型对惰性气体钨极氩弧焊定向凝固过程中具有相同取向的枝晶生长进行了预测. Zhan等人[4]建立FD-CA模型对焊接熔池中的柱状树枝晶和等轴树枝晶进行了模拟,并提出了“对角线模拟角度”方法实现了具有不同结晶学主轴的柱状树枝晶间的竞争生长. Han等人[5]模拟了焊接熔池内不同区域的枝晶竞争生长过程,并研究了基体晶粒尺寸对柱状晶形貌的影响. 张敏等人[6-7]采用熔池凝固模型实现了焊缝横截面上的枝晶生长模拟. 宋奎晶[8]基于CA模型,并提出粗网格划分方法和相似原理实现了钛合金焊接热影响区晶粒长大的多尺度模拟.
目前的焊接接头微观组织模拟主要集中在焊接熔池枝晶生长或者热影响区晶粒长大,将二者同时考虑的模拟较少. 鉴于此,针对镍基合金TIG焊接过程,建立了枝晶生长模型与晶粒长大模型来模拟焊接温度场作用下的焊接接头微观组织演变过程.
1. 模型建立
1.1 凝固模型
焊接熔池凝固过程主要包括枝晶形核和枝晶生长. 熔池内的晶核数量采用Rappaz等人[9]提出的连续形核模型确定,单位时间步长内,形核密度n(ΔT)可表示为
$$ \begin{split} & n(\Delta T) = \frac{{{n_{\max }}}}{{\sqrt {2{\text π} } \Delta {T_{\text{σ}} }}}\\ & \int_{\Delta T}^{\Delta T + \delta (\Delta T')} {\exp \left[ { - \frac{1}{2}{{(\frac{{\Delta T' - \Delta {T_{\rm{N}}}}}{{\Delta {T_{\text{σ}} }}})}^2}} \right]} {\rm{d}}(\Delta {{T}}') \end{split} $$ (1) 式中:nmax为最大异质形核衬底密度;ΔTσ为标准曲率过冷度;ΔT ′为平均形核过冷度;ΔTN为最大形核过冷度;δ(ΔT ′)为单位时间步长过冷度的变化量. 式(1)可用于描述熔池边缘与中心的非均匀形核.
晶核形成后,开始进入生长阶段. 考虑成分过冷和曲率过冷,固/液界面处液相的溶质浓度可表示为
$$ C_{\rm{L}}^* = {C_0} - \frac{1}{{{m_{\rm{L}}}}}({T_{\rm{L}}} - T - \Gamma \kappa f(\varphi ,\theta )) $$ (2) 式中:mL,TL,Γ为常数;T为局部温度;κ为界面曲率;f(φ,θ)为各项异性函数[10].
模型中假设固/液界面存在局部平衡,通过式(3)进行溶质分配.
$$ C_{\rm{S}}^* = kC_{\rm{L}}^* $$ (3) 式中:k为溶质分配系数;
$C_{\rm{S}}^*$ 和$C_{\rm{L}}^*$ 分别是固/液界面两侧固相和液相中的溶质浓度.固/液界面生长态元胞中的液相溶质浓度为
$$ {C_{\rm{L}}} = C_{\rm{L}}^* - \frac{1}{2}(1 - {f_{\rm{S}}})\Delta x{G_{\rm{L}}} $$ (4) 式中:fS为固相分数[10];Δx为元胞尺寸;GL为液相溶质浓度梯度.
浓度梯度的存在使溶质发生扩散,液相和固相中溶质扩散控制方程为
$$ \frac{{\partial {C_{\rm{L}}}}}{{\partial {\rm{t}}}} = \frac{\partial }{{\partial x}}\left[{D_{\rm{L}}}\frac{{\partial {C_{\rm{L}}}}}{{\partial x}}\right] + \frac{\partial }{{\partial y}}\left[{D_{\rm{L}}}\frac{{\partial {C_{\rm{L}}}}}{{\partial y}}\right] $$ (5) $$ \frac{{\partial {C_{\rm{D}}}}}{{\partial {\rm{t}}}} = \frac{\partial }{{\partial x}}\left[ {{D_{\rm{D}}}\frac{{\partial {C_{\rm{D}}}}}{{\partial x}}} \right] + \frac{\partial }{{\partial y}}\left[ {{D_{\rm{D}}}\frac{{\partial {C_{\rm{D}}}}}{{\partial y}}} \right] $$ (6) 式中:CS为固相中的溶质浓度;CL为液相中的溶质浓度;DS为固相中的溶质扩散系数;DL为液相中的溶质扩散系数.
1.2 热影响区晶粒长大模型
热影响区晶粒长大是通过晶界迁移实现的,通常晶界迁移速度可通过晶界迁移率M和晶界迁移驱动力F [11]计算.
$$ v = MF $$ (7) 考虑到相邻晶粒的位向差,晶界迁移率M可表示为
$$ M = \left\{ {\begin{aligned} & {{M_0}{{\left(\frac{\theta }{{{\theta _{\rm{m}}}}}\right)}^5}},\quad{\theta < {\theta _{\rm{m}}}}\\ & {{M_0} = \frac{{{A_2}{n_1}{v_1}V_{\rm{m}}^2}}{{{N_{\rm{a}}}RT}}\exp \left( { - \frac{{\Delta {G_{\rm{A}}}}}{{RT}}} \right)},\quad{\theta > {\theta _{\rm{m}}}} \end{aligned}} \right. $$ (8) 式中:A2为晶粒接纳原子的概率;n1为单位面积上处于有利跳跃位置的原子数;v1为原子跳跃频率;Vm为原子摩尔体积;Na为阿伏伽德罗常数;R为气体常量;ΔGA为激活能;θ为晶粒的取向差,θm取15°.
晶界迁移驱动力可通过晶界曲率表示为
$$ F = \gamma \cdot \kappa $$ (9) 式中:γ为单位面积的晶界能;κ为晶界曲率. 其中γ服从Read-Shockley公式,κ可通过等效模型法计算得到[12].
中心元胞状态转变为邻居元胞状态的概率P为
$$ P = \left\{ {\begin{split} & 0,\quad{{G_{\rm{T,i}}} < \Delta {G_{\rm{A}}} - \sum {\Delta {G_{\rm{i}}}} }\\ & {\frac{{{M_{\rm{i}}}{{F_{\rm{i}}}}}}{{{M_{\max }}{F_{\max }}}}},\;\;{{G_{\rm{T,i}}} > \Delta {G_{\rm{A}}} - \sum {\Delta {G_{\rm{i}}}} } \end{split}} \right. $$ (10) 式中:GT,i为元胞内能;
$\sum {\Delta {G_{\rm{i}}}}$ 为元胞转变前后的自由能差. 给元胞赋予随机数r (0 ≤ r ≤ 1),若P > r,则元胞状态发生转变.1.3 初始条件
温度场模型中采用的构件尺寸为100 mm × 50 mm × 2 mm,材料为镍基合金GH3039,计算所用的热物性参数详见文献[13]. 焊接方式为TIG焊,焊接电流为75 A,电弧电压为10 V,焊接速度为2 mm/s. 针对薄板TIG焊,选用高斯热源模型,通过商业有限元软件计算获得焊接温度场,并将节点热循环曲线通过双线性插值计算得到元胞自动机模型中温度条件.
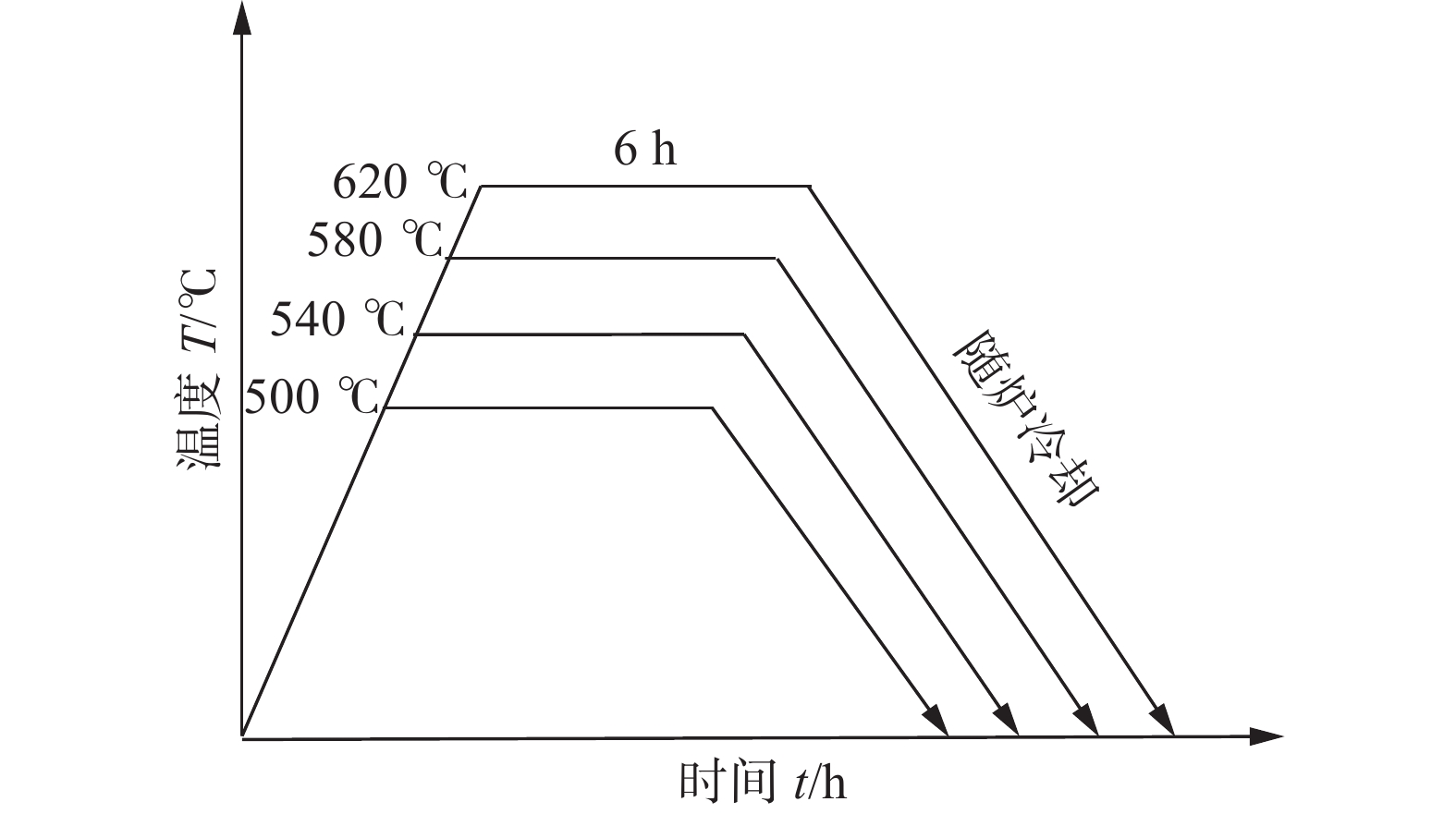
CA模型中选择焊缝横截面上的微观组织演变过程作为研究对象,选取的计算域尺寸为1 mm × 2 mm. 母材晶粒结构通过等轴晶形核和生长获得,其中母材晶粒尺寸设为32 μm(该值由试验测量得到). 晶粒取向总数设为48,其值在1 ~ 48之间随机给出,晶粒的择优生长取向随机赋予−45° ~ 45°之间的角度. 热影响区晶粒长大模型中的元胞尺寸设为4 μm,凝固模型中的元胞尺寸设为2 μm,时间步长设为0.000 1 s. 凝固枝晶生长模型中的初始参数如表1所示[14].
表 1 微观组织模拟参数Table 1. Parameters used in the Microscopic Simulation液相线温度TL/K 液相线斜率mL 溶质分配系数k 液相扩散系数DL/(m2·s−1) 固相扩散系数DS/(m2·s−1) Gibbs Thomson系数Γ/(K·m) 初始溶质浓度C0(%) 1 640 −2.1 0.714 2.0 × 10−9 3.7 × 10−12 2.0 × 10−7 20 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 温度场模拟结果
图1为宏观有限元模型计算得到的焊接过程某一时刻构件上表面、焊缝横截面及微观组织计算区域内插值后的温度场分布情况. 为了将熔池部分区分出来,将高于熔池边界温度的区域用灰色表示,熔池边界温度为1 367 ℃. 由构件上表面温度场云图可以看出熔池呈现椭圆形,熔池前方的等温线较为密集,温度梯度大,熔池后端的等温线稀疏,温度梯度较小. 由图1b中的温度分布可以看出不同区域的温度分布和最大温度梯度方向是不一致的. 选取图中黑色线框中的区域作为微观组织的计算范围,将该区域中节点的热循环曲线进行双线性插值可以得到任意时刻任一元胞的温度值,某一时间步微观尺度上的温度场分布如图1c所示.
2.2 焊接接头微观组织模拟结果
焊接接头微观组织模拟结果如图2所示. 图2a表示焊接构件横截面上的母材晶粒分布情况. 随着热源的靠近,母材熔化形成熔池,如图2b中深色区域所示. 熔池附近的晶粒在热作用下开始长大,距离熔合线越近,晶粒生长越明显. 当晶粒长大到一定程度后将基本不再变化,如图2c所示.晶粒生长过程主要是通过大晶粒吞噬小晶粒完成的. 随着热源的离开,构件的整体温度逐渐下降,熔池开始凝固. 由于熔池边缘散热较快且易于形核,在此处率先形成的晶核开始以柱状树枝晶的形式向熔池中心生长. 图中用不同灰度表示具有不同择优生长取向的晶粒,这些具有不同取向的枝晶在生长过程中逐渐靠近并发生竞争生长,择优取向与最大温度梯度方向相近的枝晶更易于生长,竞争优势较弱的枝晶在生长过程逐渐被挤压,直至停止生长,如图2d所示.由同一母材晶粒联生结晶形成的枝晶簇具有相同的择优生长方向,其凝固后在焊缝中表现为完整的柱状晶粒. 当熔池中的最大过冷度增大到足以形成新的晶核时,大量具有随机取向的晶核在柱状晶前沿形成并阻碍柱状晶的生长,因此在凝固后焊缝中心形成了连续的等轴晶区,如图2e所示.图2f为联生结晶与柱状晶向等轴晶转变过程. 熔池内的柱状晶结构和宽度主要与热影响区中的晶粒取向和尺寸有关,热影响区的晶粒粗化现象越明显,熔合线附近的母材晶粒数量越少,由同一晶粒联生结晶形成的柱状树枝晶数量增多,使得焊缝中的柱状晶变得粗大.
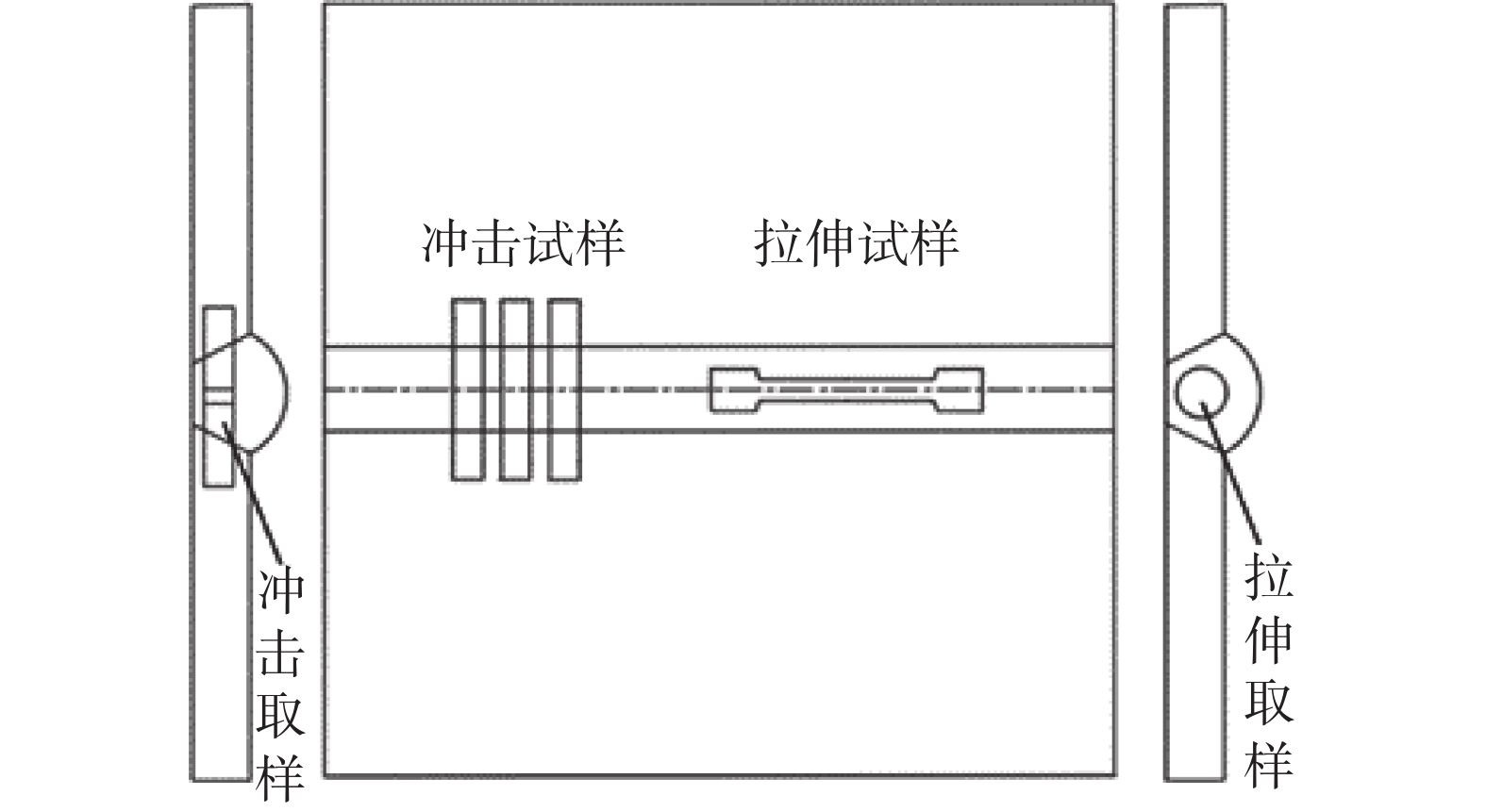
为了验证模拟结果的可靠性,选取2 mm厚的GH3039镍基合金进行TIG焊接试验,选用的焊丝牌号为HGH3039. 通过金相试验获得的焊接接头微观组织如图3所示.由图3a可以看出,熔池内部主要的枝晶形态为柱状树枝晶和等轴树枝晶.柱状树枝晶前沿为大量的等轴晶组织. 由图3b可以看到热影响区的晶粒与母材相比发生了明显的粗化,通过截线法测量得到该区域的晶粒平均尺寸约为132 μm. 同理可得模拟的热影响区晶粒平均尺寸约为129 μm,模拟结果与试验结果吻合较好,说明了该模型可用于焊接熔池及热影响区的微观组织演变过程模拟.
3. 结论
(1)所建立的热影响区晶粒长大模型能够较好的模拟热作用下的晶粒粗化过程.
(2)所建立的枝晶生长模型能够对焊接熔池凝固过程中半熔化母材边缘的联生结晶,不同枝晶间的竞争生长和熔池中心的等轴晶生长过程进行模拟,可以完整的再现焊接接头微观组织的动态演变过程.
(3)模拟结果能够较好的体现焊接热影响区晶粒尺寸与焊缝柱状晶宽度之间的关系.
(4)模拟得到熔池微观组织和热影响区晶粒分布与试验结果吻合较好,由此验证了模型的可靠性.
-
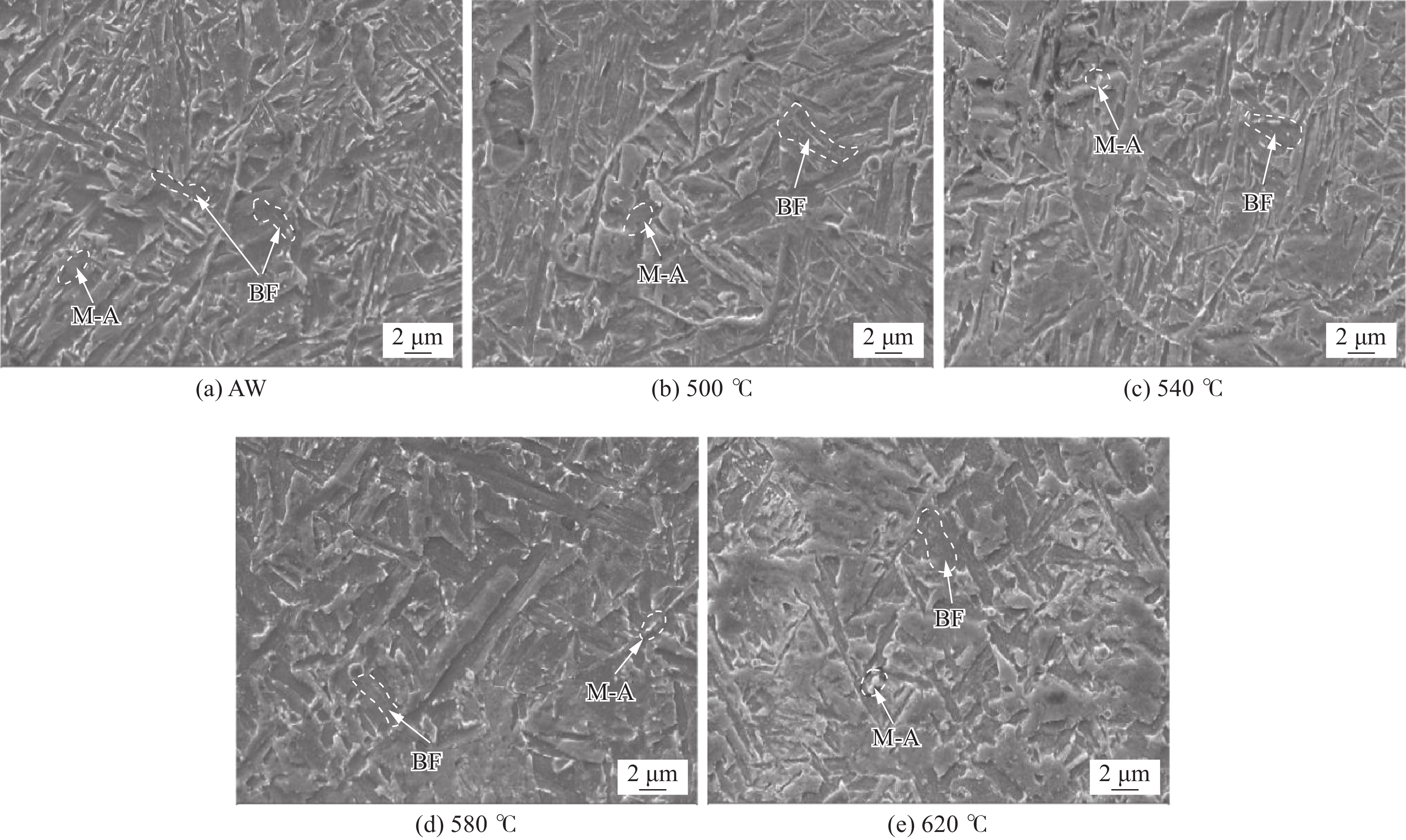
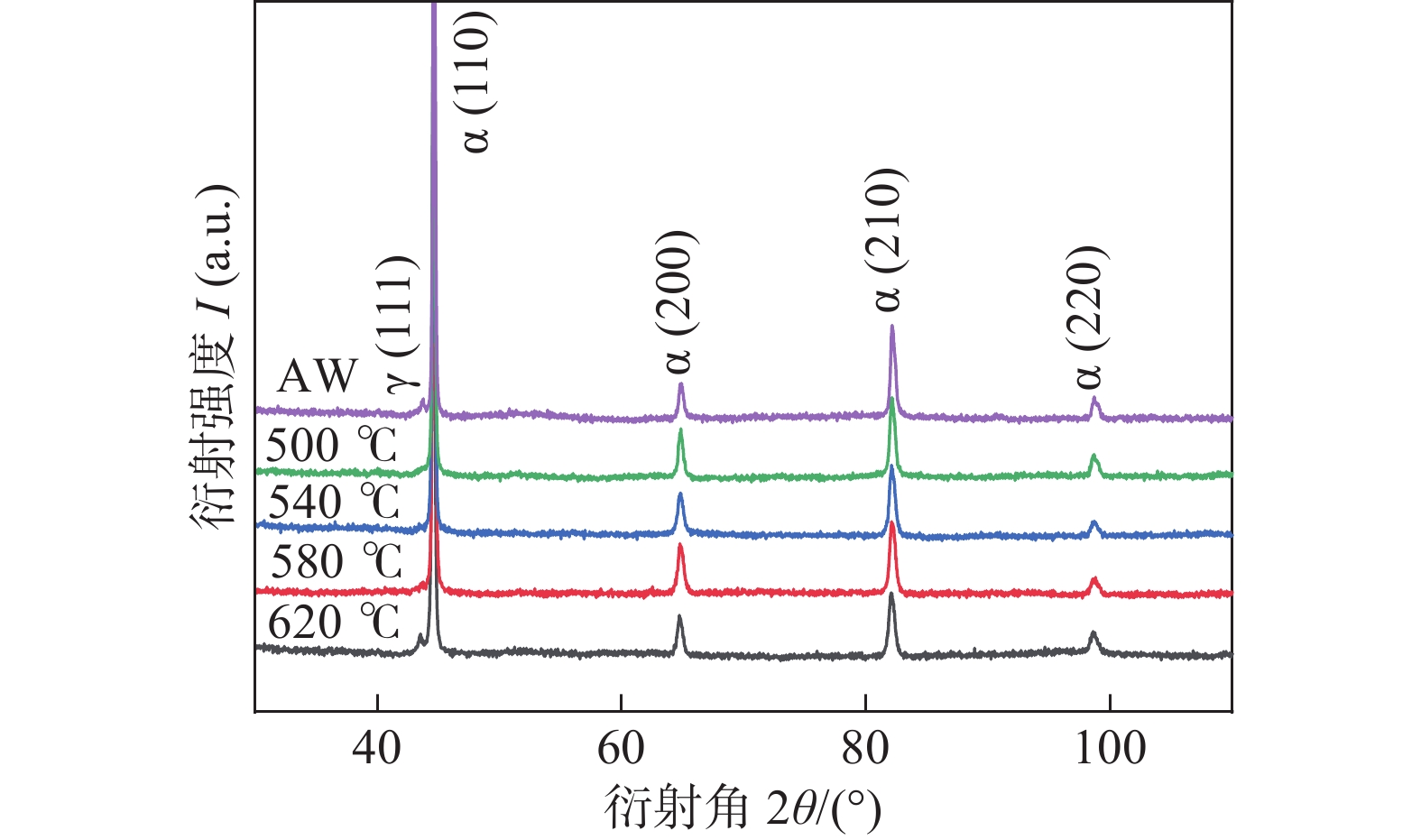
图 8 AW和不同热处理温度
1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属TEM像和SAED花样Figure 8. TEM images and SAED patterns of deposited metal with
1000 MPa grade high strength steel in AW and different heat treatment temperatures. (a) TEM image of deposited metal AW; (b) TEM image of deposited metal at 540 °C heat-treated; (c) TEM image of deposited metal at 620 °C heat-treated; (d) TEM and SAED patterns of austenite in heat-treated deposited metal at 620 ℃表 1 熔敷金属的化学成分 (质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of deposited metal
C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo Fe 0.08 0.15 1.6 0.008 0.005 0.7 2.8 1.0 余量 -
[1] Xie H, Du L X, Hu J, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of a novel
1000 MPa grade TMCP low carbon microalloyed steel with combination of high strength and excellent toughness[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 612: 123 − 130. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.06.033[2] Tumer M, Schneider-Broskamp C, Enzinger N. Fusion welding of ultra-high strength structural steels-a review[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 82: 203 − 229. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.07.049
[3] Li K, Yang T B, Gong N, et al. Additive manufacturing of ultra-high strength steels: a review[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023, 965: 171390. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.171390
[4] 曹志龙, 朱浩, 安同邦, 等. 1 000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属强韧化机理分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(7): 116 − 122. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220609002 Cao Zhilong, Zhu Hao, An Tongbang, et al. Analysis of the strengthening and toughening mechanism of deposited metal of 1000 MPa grade high strength steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(7): 116 − 122. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220609002
[5] Schnitzer R, Zuegner D, Haslberger P, et al. Influence of alloying elements on the mechanical properties of high-strength weld metal[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2017, 22(6): 536 − 543. doi: 10.1080/13621718.2016.1274095
[6] 张成竹, 陈辉. B950CF高强钢超窄间隙激光焊接头组织对残余应力的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(6): 43 − 54. Zhang Chengzhu, Chen Hui. Effect of microstructures of ultranarrow gap laser welded B950CF steel joints on residual stress distribution[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(6): 43 − 54.
[7] Gomes A J, Jorge J C, Souza L F, et al. Influence of chemical composition and post welding heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength steel weld metals[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2013, 758: 21 − 32. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.758.21
[8] Mao G J, Cao R, Yang J, et al. Effect of nickel contents on the microstructure and mechanical properties for low-carbon bainitic weld metals[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2017, 26(5): 2057 − 2071. doi: 10.1007/s11665-017-2638-2
[9] Jorge J C, Monteiro J L, Gomes A J, et al. Influence of welding procedure and PWHT on HSLA steel weld metals[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 561 − 571. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.05.007
[10] Lee S, Kim S, Hwang B, et al. Effect of carbide distribution on the fracture toughness in the transition temperature region of an SA 508 steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(19): 4755 − 4762. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00313-0
[11] 蒋中华, 杜军毅, 王培, 等. M-A岛高温回火转变产物对核电SA508-3钢冲击韧性影响机制[J]. 金属学报, 2021, 57(7): 891 − 902. Jiang Zhonghua, Du Junyi, Wang Pei, et al. Mechanism of improving the impact toughness of SA508-3 steel used for nuclear power by pre-transformation of M-A islands[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2021, 57(7): 891 − 902.
[12] 李学达, 尚成嘉, 韩昌柴, 等. X100管线钢焊接热影响区中链状M-A组元对冲击韧性和断裂机制的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(9): 1025 − 1035. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00610 Li Xueda, Shang Chengjia, Han Changchai, et al. Influence of necklace-type M-A constituent on impact toughness and fracture mechanism in the heat affected zone of X100 pipeline steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(9): 1025 − 1035. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2015.00610
[13] 温涛, 胡小锋, 宋元元, 等. 回火温度对一种Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo高强钢碳化物及其力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(4): 447 − 453. Wen Tao, Hu Xiaofeng, Song Yuanyuan, et al. Effect of tempering tempurature on carbide and mechanical properties in a Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo high-strength steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(4): 447 − 453.
[14] 屈岳波, 黄欣泉, 曹彬, 等. 残余奥氏体对2.25Cr-1Mo钢焊缝冲击性能的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2011, 47(14): 44 − 48. doi: 10.3901/JME.2011.14.044 Qu Yuebo, Huang Xinquan, Cao Bin, et al. Effect of residual austenite content on impact toughness of the filler metal of 2.25Cr-1Mo steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(14): 44 − 48. doi: 10.3901/JME.2011.14.044
[15] 周成, 赵坦, 叶其斌, 等. 回火温度对1000 MPa级NiCrMoV低碳合金钢微观组织和低温韧性的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2022, 58(12): 1557 − 1569. Zhou Cheng, Zhao Tan, Ye Qibin, et al. Effects of tempering temperature on microstructure and low-temperature toughness of 1000 MPa grade NiCrMoV low carbon alloyed steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2022, 58(12): 1557 − 1569.
[16] Luo Y, Peng J M, Wang H B, et al. Effect of tempering on microstructure and mechanical properties of a non-quenched bainitic steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2010, 527(15): 3433 − 3437. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2010.02.010
[17] Kuzmina M, Ponge D, Raabe D. Grain boundary segregation engineering and austenite reversion turn embrittlement into toughness: example of a 9 wt. % medium Mn steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2015, 86: 182 − 192. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.12.021
[18] 孙树文, 茅建富, 雷廷权, 等. 低合金Cr-Mo-V钢中VC沉淀相的精细结构[J]. 金属学报, 2000, 36(10): 1009 − 1014. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2000.10.001 Sun Shuwen, Mao Jianfu, Lei Tingquan, et al. Microstructural characterization of VC precipitates in a low alloy Cr-Mo-V steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2000, 36(10): 1009 − 1014. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2000.10.001
[19] 蒋中华, 王培, 李殿中, 等. 回火温度对2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V钢粒状贝氏体显微组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2015, 51(8): 925 − 934. Jiang Zhonghua, Wang Pei, Li Dianzhong, et al. Effects of tempering temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of granular bainite in 2.25Cr-1Mo-0.25V steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2015, 51(8): 925 − 934.
[20] 刘政军, 裘荣鹏, 武丹, 等. 960 MPa高强钢金属粉芯型药芯焊丝焊缝金属韧化机理[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(1): 102 − 106. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390023 Liu Zhengjun, Qiu Rongpeng, Wu Dan, et al. Research on toughening mechanism of weld metal with metal powder flux-cored wire for 960 MPa high strength steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(1): 102 − 106. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390023
[21] Srivatsa K, Srinivas P, Balachandran G, et al. Room temperature microstructure and property evaluation of a heat treated fully bainitic 20CrMoVTiB410 steel[J]. Journal of the Minerals, Metals & Materals Society, 2016, 68(10): 2704 − 2712. doi: 10.1007/s11837-016-2063-2
[22] Soleimani M, Kalhor A, Mirzadeh H. Transformation-induced plasticity (TRIP) in advanced steels: a review[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2020, 795: 140023. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2020.140023
[23] Lambert A, Drillet J, et al. Microstructure of martensite–austenite constituents in heat affected zones of high strength low alloy steel welds in relation to toughness properties[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2000, 5(3): 168 − 173. doi: 10.1179/136217100101538164
[24] 陈剑虹, 曹睿. 焊缝金属解理断裂微观机理[J]. 金属学报, 2017, 53(11): 1427 − 1444. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00145 Chen Jianhong, Cao Rui. Micromechanism of cleavage fracture of weld metals[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2017, 53(11): 1427 − 1444. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2017.00145
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 肖扬,高炜欣,邓国浩. 小径管X射线焊缝图像缺陷识别算法. 焊接学报. 2024(02): 82-88+133-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 张婷,王登武. 基于空洞分层注意力胶囊网络的X射线焊缝缺陷识别方法. 宇航计测技术. 2024(02): 45-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邓克剑,王艺澔,李璐,武志华. 核电站密集型穿孔塞焊自动焊技术研究. 建筑机械. 2024(07): 154-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 贾瑞燕,李海超,魏方锴,徐勇,周宇飞. 基于三维点云的磁极焊缝识别及机器人轨迹生成技术. 焊接学报. 2024(11): 50-54 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 梁小虎. 基于傅里叶变换的焊缝表面裂纹图像识别技术研究. 中国特种设备安全. 2024(12): 49-54+60 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张晓冬,张国范,刘金平,李竹渊,潘国伟,王毅. 钢筋预埋件焊接技术综述. 金属加工(热加工). 2023(01): 26-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 罗辉,崔亚飞. 改进粒子群的机器人焊缝轨迹高效识别及精确路径规划算法研究. 自动化与仪器仪表. 2023(10): 191-195 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王睿,胡云雷,刘卫朋,李海涛. 基于边缘AI的焊缝X射线图像缺陷检测. 焊接学报. 2022(01): 79-84+118 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 董亚男. 基于机器视觉的光电传感器焊缝自动识别方法. 制造业自动化. 2022(03): 180-184 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张帆,泮佳俊,刘腾,张浩,李佩齐. 基于机器视觉的焊缝识别研究现状与发展趋势. 电焊机. 2022(07): 24-33+61 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 夏攀,马飞,王中任. 基于改进U-Net模型的焊缝特征提取. 激光与红外. 2022(08): 1259-1264 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(10)
















 下载:
下载: