Influence of laser power and scanning strategy on the cracking behavior of TiC reinforced high carbon steel alloy
-
摘要:
TiC增强高碳钢硬质合金是一种在工业领域得到广泛应用的耐磨材料,但在激光熔覆制备过程中容易产生裂纹. 文中采用仿真分析和熔覆试验确定了激光功率和扫描策略对硬质合金裂纹行为的影响规律. 借助ANSYS软件采用有限元法确定激光熔覆后熔覆层中的温度梯度和残余应力分布,采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对显微组织进行分析,结果表明,激光功率和扫描策略不同会导致在熔覆层内产生不同的热梯度分布、残余应力分布以及物相组织演变,这是造成熔覆层具有不同开裂倾向性的主要原因. 高激光功率结合往复扫描策略带来了高热输入和低温度梯度,可有效减少开裂倾向. 随着激光功率的增加,TiC陶瓷相会熔化溶解,合金明显呈现回火组织特征,逐渐形成贝氏体组织和回火马氏体组织,进一步有利于降低裂纹产生的倾向.
Abstract:TiC reinforced high carbon steel hard alloy is a widely used wear-resistant material in the industrial field, but cracks are prone to occur during laser cladding preparation. The influence of laser power and scanning strategy on the crack behavior of hard alloy was investigated through simulation analysis and cladding experiments in the article. Using ANSYS software and finite element method, the temperature gradient and residual stress distribution in the laser cladding layer were investigated. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was used to analyze the microstructure. The results showed that different laser power and scanning strategies would lead to different thermal gradient distribution, residual stress distribution, and microstructure evolution in the cladding layer. This is the main reason for the different cracking tendencies of the cladding layer. The combination of high laser power and reciprocating scanning strategy brings high heat input and low temperature gradient, which can effectively reduce the tendency of cracking. With the increase of laser power, TiC ceramic phase will melt and dissolve, and the alloy will exhibit obvious tempering microstructure characteristics, gradually forming bainite and tempering martensite structures, which further helps to reduce the tendency of crack generation
-
0. 序言
耐磨性好的材料通常在采矿工业、工程领域和医疗领域有很大的需求[1-4]. 在常规部件上制备耐磨涂层是提高耐磨性的最有效、最经济的方法之一. 陶瓷-金属复合材料因其良好的硬度和耐磨性而被广泛用作涂层材料[5-6]. 其中,硬质合金钢因其硬度高、润湿性好且便宜经济而广受欢迎[7-10]. 电弧增材、电弧喷涂、等离子喷涂和激光熔覆是制备硬质合金钢涂层常用的方法[11-14]. 硬质合金增强体与基体热物理性能差异很大,非均匀热输入会使硬质合金熔覆层产生应力集中,导致硬质合金增强的复合材料熔覆层或涂层极易开裂[15-17]. 因此,相比于激光增材方法,温度梯度更低的电弧增材和放电等离子烧结制备硬质合金层更为常见,例如,Tang等人[18]采用TIG方法在304不锈钢上制备了TiB2增强硬质合金钢涂层,TiB2颗粒在涂层分布均匀且无裂纹. Sekhar等人[19]采用TIG方法制备坚硬耐磨的TiC增强硬质合金钢涂层. Li等人[20]采用放电等离子烧结技术制备了TiB2-TiC增强硬质合金钢涂层,该涂层在重载、干滑动条件下表现出优异的耐磨性. Zhang等人[21]采用放电等离子烧结技术制备了WC/Fe复合涂层,涂层表现出优异的耐磨性能. 此外,还有学者研究了采用摩擦焊增材方法制备硬质合金熔覆层. 例如,Ghasemi- Kahrizsangi等人[22]采用搅拌摩擦焊方法在中碳钢基体上制备了晶粒小于600 nm的TiC增强铁基纳米复合材料涂层,耐磨性和抗开裂性能显著提升. Guo等人[23]采用表面摩擦制备不锈钢316L/TiB2硬质合金涂层,结果表明可以该方法也可以一定程度抑制开裂.
激光增材方法在硬质合金层引起的热梯度大和应力集中程度较大,导致采用该方法制备硬质合金层容易产生裂纹,众多学者采用了成分设计和辅助加热等方法控制硬质合金层裂纹产生倾向[24],并且取得了相关成果,Kang等人[25]采用选区激光熔化方法在H13热作模具钢上制备了不同WC含量的硬质合金钢涂层,涂层相比基材表现出更高的耐磨性和更低的摩擦系数.
陶瓷颗粒增材高碳钢硬质熔覆层具备较高的耐磨性[26],然而,高碳钢和陶瓷颗粒的热膨胀系数相差较大,两者熔合极易在熔覆层中产生裂纹,目前采用激光熔覆方法制备TiC陶瓷颗粒增强高碳钢复合熔覆层的研究较少,文中采用激光熔覆方法在高碳钢表面制备了TiC增强的硬质合金钢熔覆层,旨在揭示激光功率和扫描策略对其开裂行为的影响规律,并讨论相关机理.
1. 试验方法
文中使用球形高碳钢粉末,粒度为在50-130 μm,使用TiC陶瓷颗粒,粒度为50-150 μm. TiC颗粒为非球形,但流动性较好. 图1给出了TiC颗粒形貌的SEM图像. 熔覆粉末由重量百分比为40%的高碳钢粉末和60%的TiC陶瓷颗粒组成. 这些粉末在激光熔覆前先用粉末混合机混合并干燥. 表1给出了高碳钢粉末的化学成分. 文中使用的基板的化学成分和粉末一致,基板尺寸为100 mm × 100 mm × 10 mm.
表 1 高碳钢粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of high carbon steel powdersC Si Mo Ni Fe 0.6 0.8 0.3 2.0 余量 采用波长为1064 nm、聚焦光斑为3.5 mm的连续光纤激光器和同轴送粉系统. 激光熔覆系统和激光扫描策略示意图分别如图2和图3所示. 图3中箭头方向表示每道次熔覆层激光扫描的方向,扫描策略包括扫描策略1(SP1)、扫描策略2(SP2)和扫描策略3(SP3). 每个样品包括两层熔覆层. 表2给出了试样代号和加工参数. 在熔覆过程中,采用氩气来输送熔覆粉末并保护熔池不被氧化. 在熔覆之前,样品的表面用砂纸打磨并用乙醇和丙酮清洗以除去污染物. 最后,试样被切割成小样品进行SEM观察和EDS分析.
表 2 试样编号和工艺参数Table 2. Sample designations and process conditions样品
代号激光功率
P/W扫描速度
v/(mm·s−1)送粉量
g/min扫描
程序S1 1500 4 11 SP1 S2 2000 4 11 SP1 S3 2500 4 11 SP1 S4 1500 4 11 SP2 S5 2000 4 11 SP2 S6 2500 4 11 SP2 S7 1500 4 11 SP3 S8 2500 4 11 SP3 SEM观察和EDS分析的试样用400号 ~ 1200号砂纸打磨和抛光机抛光,然后用4%硝酸的酒精溶液腐蚀15 s. 采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM、Quanta 200)观察显微组织形貌,并确定元素分布.
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 开裂行为分析
图4展示了着色检测试验的结果,熔覆层的厚度为3 mm左右. 从图中可以看出所有熔覆层中均出现裂纹. 但使用低激光功率的样品裂纹更明显. 使用低激光功率和SP1方法制备的样品S1中的裂纹显示出网状形态,在垂直于扫描的方向上可以发现许多贯穿的裂纹,这主要是由于平行于扫描方向试样的尺寸较大带来较高的残余应力造成的. 使用SP1、SP2和SP3方法时,裂纹表现出不同的形态特征. 采用SP2和SP3方法时裂纹扩展的方向性更加明显,如图3所示,这主要跟不同扫描策略的温度梯度分布和残余应力分布差异有关. 即使试样S7和S8的激光功率达到2500 W,但仍然存在明显的贯穿裂纹,这意味着扫描程序SP3不能减少穿透裂纹. 当采用SP2扫描程序时,裂纹总是沿扫描方向发生,垂直于扫描方向的方向几乎没有裂纹,这表明该方法可以有效减少垂直于扫描方向的裂纹.
为了确定开裂行为,开发了基于ANSYS软件包的顺序解耦3D有限元模型来计算温度和残余应力分布. 采用瞬态能量守恒方程作为热分析的控制方程[27-28],即
$$ \begin{split} &\quad \frac{{\partial (\rho (T) \times {C_P}(T) \times T)}}{{\partial t}} = \frac{\partial }{{\partial x}}\left( {{K_x}(T) \times \frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial x}}} \right) + \\& \frac{\partial }{{\partial y}}\left( {{K_y}(T) \times \frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial y}}} \right) + \frac{\partial }{{\partial {\textit{z}}}}\left( {{K_z}(T) \times \frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}}} \right) + {{\mathop q\limits^ \cdot}_{gen}}(x,y,{\textit{z}},t) \end{split} $$ 式中:$ \rho (T) $为与温度相关的材料密度,$ {C_P} $为与温度相关的比值,$ {K_x}(T) $,$ {K_y}(T) $和$ {K_{\textit{z}}}(T) $为与温度和方向相关的热导率(各向异性),$ {{\mathop q\limits^ \cdot}_{gen}}(x,y,{\textit{z}},t) $为体积热源项.
可以通过以下公式计算熔覆过程中熔池的温度分布[29-30],即
$$ \begin{split} &\qquad\qquad T\left(x,y,z\right) = {T}_{0} + \frac{{P}_{w}}{{\text{π} }^{3/2}kr}{\int }_{0}^{\mathrm{\infty }}\\&\left(\frac{1}{1 + {s}^{2}}\mathrm{exp}\left\{-\frac{{s}^{2}}{1 + {s}^{2}}\left[{\left(\frac{x}{r}-\frac{\rho cVr}{4k{s}^{2}}\right)}^{2} + {\left(\frac{y}{r}\right)}^{2}\right]-{s}^{2{\left(\tfrac{z}{r}\right)}^{2}}\right\}\right)ds \end{split}$$ 式中:T0为环境温度,r为激光半径点,k是热导率,ρ是密度,c是热容量,s为熔覆道宽度.
温度梯度由激光功率决定,残余应力由扫描策略决定. 图5给出了刚刚完成试样熔覆时的温度梯度. 当增加激光功率时,温度梯度明显减小. 与其他方法相比,使用SP2方法的温度梯度较低. 使用SP3方法温度梯度没有明显升高. 温度梯度是决定残余应力分布特征的重要因素之一. 图6展示了试件冷却至室温后的残余应力分布. 残余应力分布结果与温度梯度的结果基本一致,增加激光功率,峰值残余应力明显降低. 提取采用SP1工艺参数,当激光功率为1500 W时最大残余应力为363 MPa. 扫描策略对残余应力分布也有很大影响. 如图6所示,对比SP3、SP6、SP9三种方法,由于较低的温度梯度和独特的扫描策略,试样S6的最大残余应力仅为259 MPa. 图7展示了图3中的中心横截面沿x轴的残余应力分布. 当激光功率增大时,熔覆层中的残余应力明显减小. 相反,基板中的应力明显升高,这和图4中的着色检测试验结果相符合.
2.2 显微组织特征
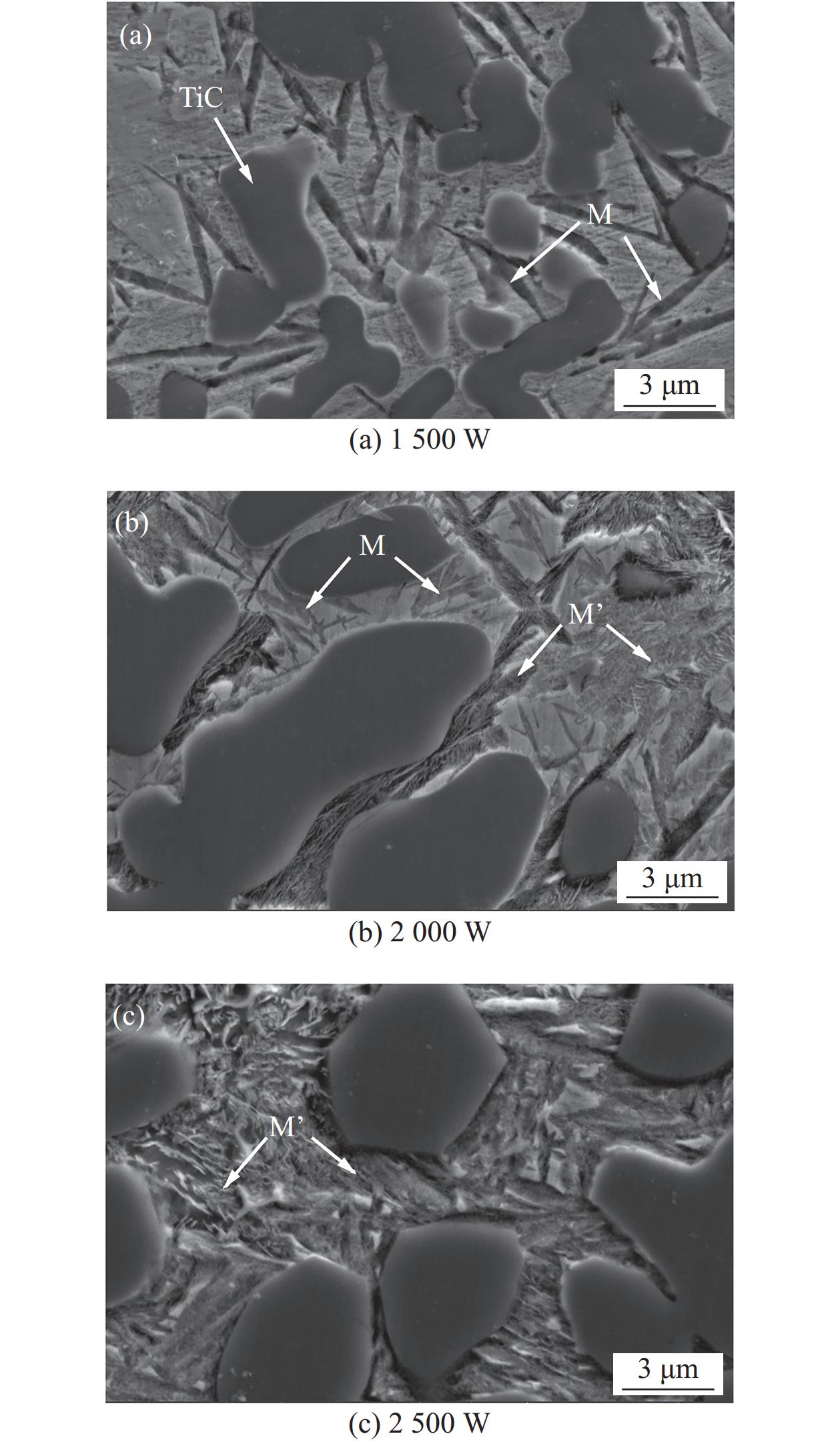
图8为不同激光功率制备熔覆层的SEM图. 从低倍放大图中可以看出,当激光功率提高时,熔覆层厚度显著增加. 这是因为不同激光功率带来的热量输入不同,导致发生熔化的粉末比例升高[31]. 随着激光功率的增加,大尺寸陶瓷颗粒的数量明显减少. 熔覆粉末中原始陶瓷颗粒明显熔化溶解,陶瓷颗粒尺寸减小. 形成的二次陶瓷颗粒随着激光功率的增加变得越来越小,细小的陶瓷颗粒有助于降低熔覆层的开裂倾向. 陶瓷颗粒沿基体内部方向熔化溶解,因此靠近熔覆层表面的陶瓷颗粒密度较高. 图9为熔覆层的能谱分析(EDS)结果,主要元素为Fe、Ti及C等. 从图中可以看出,随着激光功率的增加,元素分布越来越均匀,这归功于大尺寸的TiC陶瓷颗粒的熔化和溶解.
不同的激光功率会在熔覆层中形成不同热循环过程,从而产生不同的组织演变过程,导致熔覆层内部金相组织形貌和尺寸不同,这是造成熔覆层残余应力分布差异的原因,是影响熔覆层开裂行为的关键因素之一. 针对图8所示的显微组织进一步放大,得到了图10所示的不同激光功率制备熔覆层的显微组织形貌. 当激光功率为1500 W时,从图10(a)中可以明显地发现马氏体组织. 这主要是由于激光功率较低时冷却速度过快造成的. 当激光功率增大时,冷却速率降低,逐渐出现回火现象,如图10(b)和(c)所示. 随着激光功率的增加,逐渐形成贝氏体组织和回火马氏体组织. 马氏体通常表现出很大的脆性,这也是激光功率较低时容易产生裂纹的重要原因之一[32].
根据上述试验结果和仿真分析,高激光功率带来高热输入、低温度梯度和低残余应力,在TiC增强高碳钢硬质合金熔覆层中贝氏体组织和回火马氏体组织数量较多,最终形成熔覆层裂纹数量较少. 而低激光功率与之相反,会在熔覆层中形成高温度梯度和高残余应力,形成的熔覆层主要以马氏体为主. 此外,激光扫描策略对熔覆层显微组织形貌有明显的影响. 因此,激光功率和扫描策略对残余应力和显微组织形貌和尺寸调控有显著作用,这些规律可以为实际应用提供参考.
3. 结论
(1) 激光功率和扫描路径是影响TiC增强高碳钢硬质合金熔覆层开裂行为的关键因素. 低激光功率往往会带来明显的温度梯度,最终产生大的残余应力. 与低激光功率相比,高激光功率可以减少有效地裂纹倾向.
(2) 激光功率对熔覆过程中的TiC的组织特征和尺寸有重要影响,当增加激光功率时,陶瓷颗粒会熔化溶解,元素分布更加均匀.
(3) 激光功率对熔覆过程中硬质合金熔覆层的显微组织特征有显著的影响. 随着激光功率的增加,合金明显呈现回火组织特征,最终影响熔覆层的显微组织,缓解开裂行为.
(4) 不同扫描策略导致熔覆层温度梯度分布和残余应力分布存在差异,导致熔覆层中裂纹数量形貌不同,相比于同方向扫描策略,采用交叉式扫描路径可以有效减少垂直于扫描方向的裂纹数量.
-
表 1 高碳钢粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of high carbon steel powders
C Si Mo Ni Fe 0.6 0.8 0.3 2.0 余量 表 2 试样编号和工艺参数
Table 2 Sample designations and process conditions
样品
代号激光功率
P/W扫描速度
v/(mm·s−1)送粉量
g/min扫描
程序S1 1500 4 11 SP1 S2 2000 4 11 SP1 S3 2500 4 11 SP1 S4 1500 4 11 SP2 S5 2000 4 11 SP2 S6 2500 4 11 SP2 S7 1500 4 11 SP3 S8 2500 4 11 SP3 -
[1] Yun Xiao, Wang Jing, Zhu Qinghai, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of Fe-based and Co-based coating of AISI H13[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(3): 54 − 60. doi: 10.12073/j.cw.20190623001
[2] Peng B, Xu Y X, Du J W, et al. Influence of preliminary metal-ion etching on the topography and mechanical behavior of TiAlN coatings on cemented carbides[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 432: 128040.
[3] Chen Chong, Dong Yongzhuang, Hu Can, et al. Fabrication of gradient cemented carbide with Ni3Al binder: Simulations and experiments[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 9: 48.
[4] Vilardell A M, Cinca C, Tarrés E, et al, Iron aluminides as an alternative binder for cemented carbides: A review and perspective towards additive manufacturing[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 31: 103335.
[5] Emma M, Natasha S, Maritha T, Crack mitigation in laser engineered net shaping of WC-10wt%FeCr cemented carbides[J]. Additive Manufacturing Letters, 2022, 2: 100028.
[6] Hu Hui, Wen Shifeng, Duan Longchen, et al. Enhanced corrosion behavior of selective laser melting S136 mould steel reinforced with nano-TiB2[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2019, 119: 105588.
[7] Almangour B, Grzesiak D, Yang J M. Selective laser melting of TiB2/316L stainless steel composites: The roles of powder preparation and hot isostatic pressing post-treatment[J]. Powder Technology, 2017, 309: 37 − 48.
[8] Sahoo C K, Masanta M. Effect of pulse laser parameters on TiC reinforced AISI 304 stainless steel composite coating by laser surface engineering process[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2015, 67: 36 − 48.
[9] Yan Xingchen, Huang Chunjie, Chen Chaoyue, et al. Additive manufacturing of WC reinforced maraging steel 300 composites by cold spraying and selective laser melting[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 371: 161 − 171.
[10] 魏炜, 黄智泉, 张海燕, 等. 钢结硬质合金与钢连接技术的研究现状[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(5): 119 − 128. Wei Wei, Huang Zhiquan, Zhang Haiyan, et al. Research status on cermet/steel welding and joining[J]. Transactions of The China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(5): 119 − 128.
[11] Moghaddam H Z, Sharifitabar M, Roudini G. Microstructure and wear properties of Fe–TiC composite coatings produced by submerged arc cladding process using ferroalloy powder mixtures[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019, 361: 91 − 101.
[12] Lu J Z, Cao Z J, Lu H F, et al. Wear properties and microstructural analyses of Fe-based coatings with various WC contents on H13 die steel by laser cladding[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2019, 369: 228 − 237.
[13] Salman O O, Gammer C, Eckert J, et al. Selective laser melting of 316L stainless steel: Influence of TiB2 addition on microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2019, 21: 100615. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2019.100615
[14] 雷阿利, 冯拉俊, 沈文宁, 等. 等离子喷涂法制备铁基硬质涂层的力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(4): 27 − 30,114. Lei Ali, Feng Lajun, Shen Wenning, et al. Mechanical properties of iron-based hard coatings prepared by plasma spraying method[J]. Transactions of The China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(4): 27 − 30,114.
[15] Wu Xian, Shen Jianyun, Jiang Feng, et al. Study on the oxidation of WC-Co cemented carbide under different conditions[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2021, 94: 105381.
[16] Li Chenwei, Chang Kai-Chun, Yeh An-Chou. On the microstructure and properties of an advanced cemented carbide system processed by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 782: 440 − 450.
[17] Kumar S. Process chain development for additive manufacturing of cemented carbide[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 34: 121 − 130.
[18] Tang Xu, Zhang Song, Cui Xue, et al. Tribological and cavitation erosion behaviors of nickel-based and iron-based coatings deposited on AISI 304 stainless steel by cold metal transfer[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(3): 6665 − 6681.
[19] Sekhar B R, Nayak R K, Rout S R, et al. Wear characteristic of TiC coated AISI 1020 mild steel fabricated by TIG cladding method[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2020, 26: 3288 − 3291. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.466
[20] Li Binghong, Liu Ying, Li Jun, et al. Effect of sintering process on the microstructures and properties of in situ TiB2–TiC reinforced steel matrix composites produced by spark plasma sintering[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210(1): 91 − 95.
[21] Zhanzhan Zhang, Yunbo Chen, Lingli Zuo, et al. The effect of volume fraction of WC particles on wear behavior of in-situ WC/Fe composites by spark plasma sintering[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials, 2017, 69: 196 − 208.
[22] Ghasemi-Kahrizsangi A, Kashani-Bozorg S F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of steel/TiC nano-composite surface layer produced by friction stir processing[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2012, 209: 15 − 22.
[23] D. Guo, C. T. Kwok, S. L. I. Chan, Fabrication of stainless steel 316L/TiB2 composite coating via friction surfacing[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2018, 350: 936 − 948. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.03.065
[24] Fetni S, Enrici T M, Niccolini T, et al. 2D thermal finite element analysis of laser cladding of 316L + WC composite coatings[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2020, 50: 86 − 92. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.08.016
[25] Nan Kang, Wenyou Ma, Fu hai Li, et al. Microstructure and wear properties of selective laser melted WC reinforced 18Ni-300 steel matrix composite[J]. Vacuum, 2018, 154: 69 − 74.
[26] 周承商, 易健宏, 罗述东, 等. 硬质合金与Cr12冷作钢的微波焊接工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(4): 41 − 44 + 115. Zhou Chengshang, Yi Jianhong, Luo Shudong, et al. Welding Process of Hard Alloy and Cr12 Cold Working Steel[J]. Transactions of The China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(4): 41 − 44 + 115.
[27] Farahmand P, Kovacevic R. An experimental-numerical investigation of heat distribution and stress field in single-and multi-track laser cladding by a high-power direct diode laser[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2014, 63: 154 − 168.
[28] Lepore M, Carlone P, Berto F, et al. A FEM based methodology to simulate multiple crack propagation in friction stir welds[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2017, 184: 154 − 167. doi: 10.1016/j.engfracmech.2017.08.024
[29] Dai Xiaoqin, Zhou Shengfeng, Wang Meifeng, et al. Microstructure evolution of phase separated Fe-Cu-Cr-C composite coatings by laser induction hybrid cladding[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2017, 324: 518 − 525.
[30] Picasso M, Marsden C F, Wagniere J D, et al. A simple but realistic model for laser cladding[J]. Metallurgical and materials transactions B, 1994, 25: 281 − 291. doi: 10.1007/BF02665211
[31] Ebrahimnia M, Ghaini F M, Gholizade S, et al. Effect of cooling rate and powder characteristics on the soundness of heat affected zone in powder welding of ductile cast iron[J]. Materials & Design, 2012, 33: 551 − 556.
[32] Zeng Xianbin, Wang Qianting, Chen Changrong, et al. Effects of WC addition on the morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe50/TiC/WC laser claddings on AISI 1045 steel[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2021, 427: 127781.




 下载:
下载: