Effects of Si element on the weld formation and microstructure of titanium/steel dissimilar joints
-
摘要:
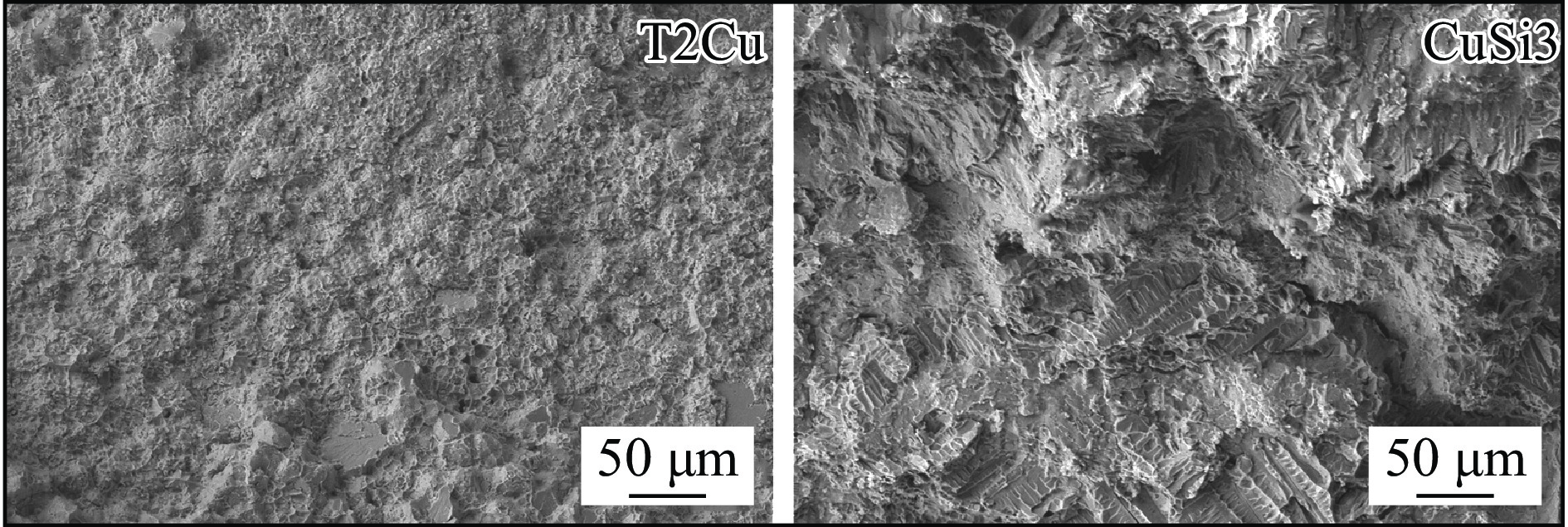
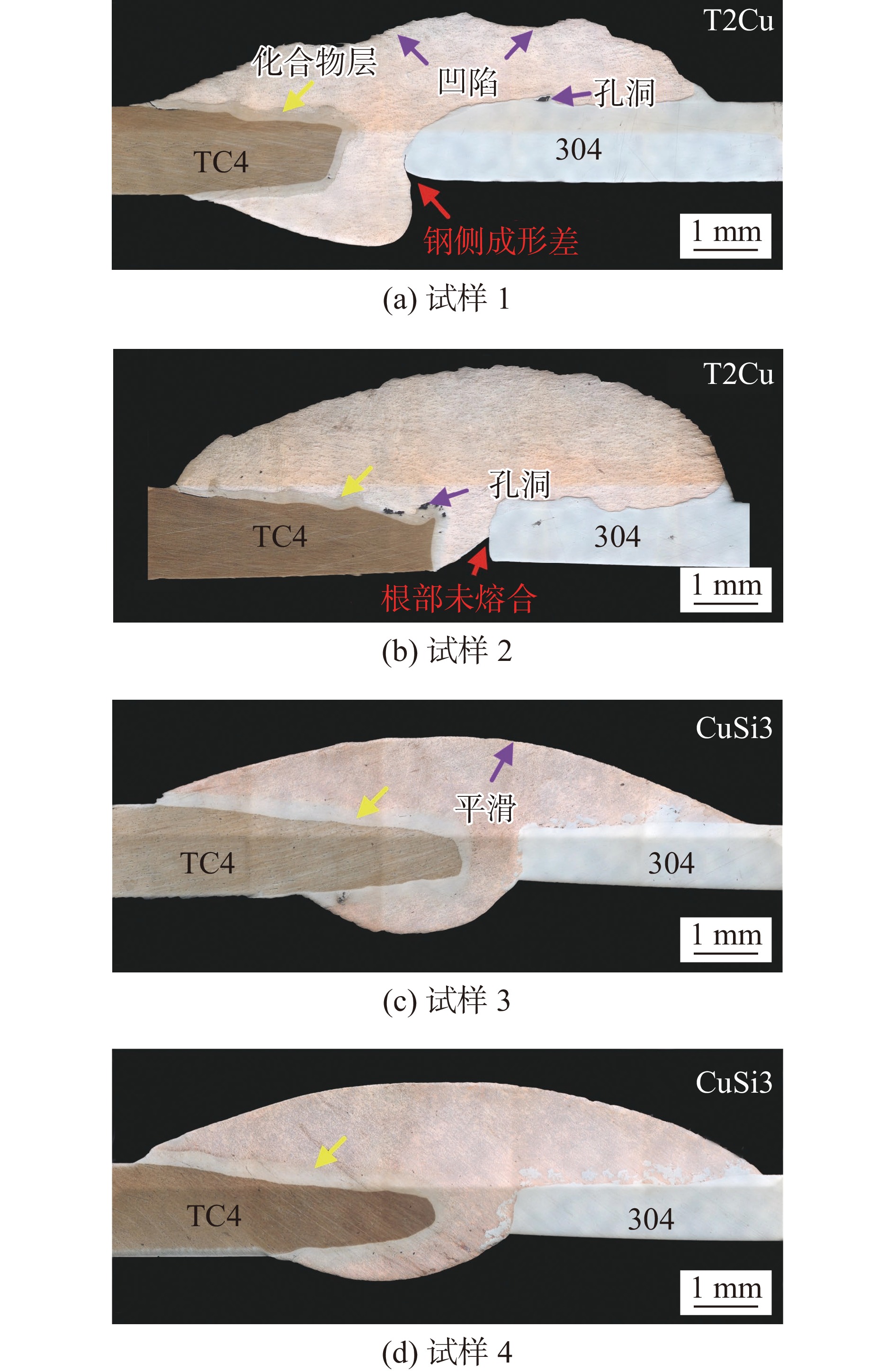
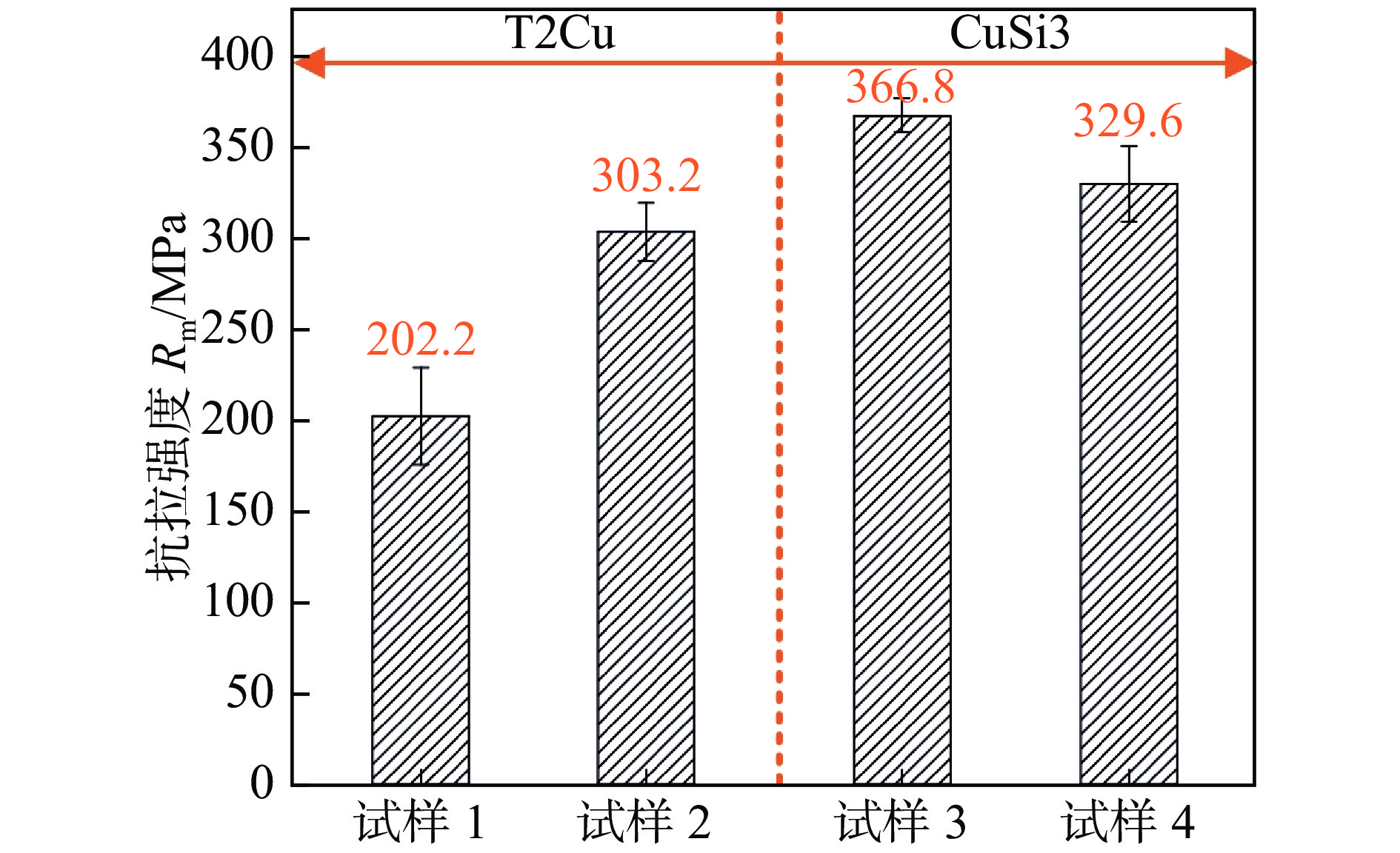
采用T2Cu和CuSi3焊丝在相同工艺参数下对厚度为1 mm的TC4钛合金及304不锈钢进行焊接,并借助光学显微镜(optical microscopy, OM)和扫描电镜(scanning electron microscopy, SEM)研究了两种焊丝下的TC4/304异种金属焊接熔池冶金行为. 对比分析了不同焊丝成分,尤其是Si元素的加入对TC4/304异种金属接头宏观成形、界面微观组织和力学性能的影响. 结果表明,Si元素的加入使液态熔池流动性显著增强,消除了凹陷和孔洞等缺陷,解决了焊缝背部熔合不良问题,焊缝宏观成形显著改善. 两种焊丝均有效阻隔了Ti,Fe原子,钛/铜界面未生成Ti-Fe化合物,但在焊缝中心以及铜/钢界面处生成了少量Ti-Fe相. CuSi3焊丝中充足的Si元素不仅使Ti5Si3相形核生长的更加充分,在熔池流动的作用下均匀分布于焊缝中,对接头起到弥散强化作用. 与T2Cu焊丝相比,CuSi3焊丝所得接头的抗拉强度提升了81.4%,最高达到366.8 MPa.
Abstract:Welding of 1mm thick TC4 titanium alloy and 304 stainless steel was performed using T2Cu and CuSi3 welding wires under the same process parameters. The metallurgical behavior of the TC4/304 dissimilar metal weld pool was studied using optical microscopy(OM) and scanning electron microscopy(SEM). A comparative analysis was conducted on the effects of different wire compositions, particularly the addition of silicon (Si), on the macro formation of the TC4/304 dissimilar metal joints, the microstructure at the interface, and the mechanical properties. The results showed that the addition of Si significantly enhanced the fluidity of the liquid weld pool, eliminated defects such as depressions and pores, and addressed issues of poor fusion at the back of the weld, leading to substantial improvements in macro formation of the welds. Both types of welding wires effectively hindered the diffusion of Ti and Fe atoms, preventing the formation of Ti-Fe compounds at the Ti/Cu interface, although a small amount of Ti-Fe phase was present at the center of the weld and at the Cu/Fe interface. The sufficient Si content in CuSi3 welding wire not only promoted more effective nucleation and growth of the Ti5Si3 phase but also allowed for its uniform distribution throughout the weld due to the flow of the weld pool, providing a dispersion strengthening effect for the joint. Compared to T2Cu welding wire, the joints obtained with CuSi3 welding wire exhibited a tensile strength increase of 81.4%, reaching a maximum of 366.8 MPa.
-
0. 序言
激光同轴送粉增材制造技术作为大型关键金属构件高质量直接沉积制造不可或缺的主流工艺方法,制造过程涉及复杂的多因素[1-2]、多流场之间的相互耦合,深刻理解工艺涉及到的关键工艺过程并加以控制,是优化和促进该技术进一步发展的基础[3-4]. 相关研究表明,粉末束流粉末从环形同轴喷嘴送出后,其空间分布特征,即粉末束流的汇聚性会直接影响到熔覆层的尺寸特征,进而对增材制造效率和构件的成形质量产生重要影响[5-6]. 粉末束流是由气体和固体粉末颗粒组成的气-固两相流,将汇聚后的粉末束流精准、可控、稳定的送进激光辐照所形成的液态熔池中,是实现该制造方法高精度、高质量和批量化生产的先决条件.
粉末颗粒从环形喷嘴送出后,先汇聚再发散,在空间上是一种离散的三维轴对称结构,常规的检测方法很难精准获取粉末束流的关键特征,并给出合理评价,这为激光同轴送粉增材制造技术关键过程的全面认识和全流程调控增加了难度. 实现对粉末束流关键特征的识别与调控已成为当前学术界和工业界共同关注的热点问题,也是该技术走向批量化生产亟需解决的关键难题之一[7].目前关于激光同轴送粉增材制造相关的研究多集中在成形件尺寸精度及组织、性能等方面[8-9],关于零部件加工过程中粉末束流关键特征表征与调控相关的研究涉及较少[10],迄今为止仍缺乏系统性认识. 为了实现对粉末束流关键特征的分析,相关研究人员尝试利用灰度表征法分析粉末束流的关键特征,并对灰度表征法的可行性进行了详细论证,但对粉末束流汇聚性相关的研究未有涉及[11]. 数值模拟作为一种重要分析方法,近年来在粉末束流关键特征分析方面也发挥了重要作用[12-14].
基于已经构建的激光同轴送粉增材制造用粉末束流表征体系,以粉末束流的焦距和有效粉斑直径为研究对象,详尽分析载气、同轴保护气、送粉速率对粉末束流关键特征的影响规律,在加深对粉末束流认识基础上,为粉末束流的调控提供依据,进而对激光同轴送粉增材制造工艺的优化提供数据支撑.
1. 试验方法
采用同向增效瞬态成像技术,将亮度均匀的背景光源和高速摄像机以较小的角度直射粉末束流,使粉末颗粒反射光尽可能多、且分布均匀的进入到CCD内部,提高背景和粉末束流之间的亮度差异. 同时采用高分辨率高速摄像机,提高时空分辨率,更加精准的捕获粉末束流的实时状态,拍摄方法及效果如图1所示.
试验用粉末颗粒为气雾化法制备的08Cr19Mn6Ni3Cu2N不锈钢球形粉末. 其原始粒度介于45 ~ 100 μm之间. 送粉器为德国GTV公司生产的双料斗载气式送粉器,型号为MF-PF2/2,送粉熔覆头为德国Fraunhofer公司生产的高精度同轴环形喷嘴,型号为COAX-40-S/F,粉末束流的理论焦点位置为6.8 mm. 高速摄像拍摄帧数为100 fps.
借助图像灰度处理技术,获取每一帧图像对应像素点的灰度值,定量表征粉末束流在不同空间位置处浓度分布特点. 粉末束流沿喷嘴中轴线方向呈环形对称分布特征,在该方向上灰度值最高区域即为粉末束流焦点位置,该位置同送粉喷嘴末端之间的距离称之为焦距,沿着焦点位置的横截面进行灰度值分析即可获得焦点位置处的粉斑直径以及粉末束流的浓度分布特征,其效果如图2所示.
对焦点位置粉末束流的空间浓度分布特征进行分析,如图3所示. 利用高斯方程对图3a中焦点位置处的灰度分布实际曲线对应的数据做多元非线性回归分析,得到相应的拟合曲线,如图3b所示. 高斯方程如式(1)所示.
$$ y=y_{0} + \frac{A}{w \sqrt{{\text{π}} / 2}} e^{-2 \tfrac{\left(x-x_{{\rm{c}}}\right)^{2}}{w^{2}}} $$ (1) 式中:y表示不同位置处灰度值大小;y0表示背景灰度值大小;xc表示粉末束流中心线位置;w为一个标准差[−σ∶ σ]对应的宽度,该宽度对应的面积占整个高斯分布曲线所占面积的68.4%. 将一个标准差对应的宽度w定义为粉末束流的有效粉斑直径,理论上w值越大,粉末颗粒在空间上的分布就越发散,粉末束流的汇聚性就越差;相反,则说明粉末束流的汇聚性较好.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 同轴保护气对粉末束流关键特征的影响
同轴保护气一方面保护高温液态熔池不被活性气体氧化,此外防止反弹的粉末颗粒和烟尘污染光学系统. 同轴保护气体流量大小对粉末束流宏观形貌的影响如图4所示,可以清晰看出,随着同轴保护气流量增加,粉末束流宏观形貌发生较大变化.
利用灰度表征法,沿着粉末束流中轴线方向对其浓度分布特征进行处理,气体流量对粉末束流焦点位置的影响规律如图5所示. 同轴保护气流量增加,灰度值最大值出现位置下移,气流量为3 L/min时,对应的粉末束流焦距为6.4 mm左右,当气流量增加到23 L/min时,粉末束流的焦距增加到9.8 mm左右,这说明同轴保护气流量对粉末束流的焦距影响较大,与此同时,灰度值最大值逐渐减小.
利用式(1)对不同同轴保护气流量大小对应的粉末束流焦点位置处的浓度分布数据进行多元非线性回归分析,回归方程相关系数如表1所示,其决定系数均在0.98以上,这说明同轴保护气流量改变并未影响到粉末束流焦点位置处的浓度特征.
表 1 同轴保护气流量对应的回归方程系数Table 1. Regression equation coefficients corresponding to shielding gas flow rates同轴保护气流量
QT/(L·min−1)有效粉斑直径
w/mm系数
A系数
H决定系数
R25 0.98 89.3 75.3 0.98 8 0.96 86.6 67.4 0.98 12 1.01 74.3 62.04 0.99 16 0.96 61.2 51.7 0.99 23 1.03 51.3 39.0 0.98 同轴保护气对粉末束流有效粉斑直径影响规律如图6所示,可以看出,同轴保护气流量增加,有效粉斑直径在1.0 mm上下波动,最大偏差在4.0%,这说明同轴保护气对有效粉斑直径影响较小.
2.2 载气流量对粉末束流关键特征的影响
载气在激光同轴送粉增材制造过程中主要起到将粉末颗粒从送粉器中以一定的速度稳定的送进熔池,此外载气对熔池也起到一定的防护作用.因此载气流量对粉末束流形态、粉末束流焦点位置以及该位置处的浓度分布都会产生一定影响,不同载气流量对应的粉末束流宏观形貌如图7所示.
沿着粉末束流中轴线方向对不同载气流量对应的焦点位置进行分析,其结果如图8所示.可以看出,载气流量越大,粉末束流焦点位置逐渐靠近喷嘴,粉末束流焦距变小,这与同轴保护气流量对焦点位置的影响规律恰好相反. 载气流量为2 L/min时,粉末束流的焦距为9 mm左右,当载气流量提高到10 L/min时,粉末束流的焦距为6.8 mm左右,这说明载气流量同样对粉末束流焦点位置影响较大.
回归分析结果如表2所示,可以看出随着载气流量增加,粉末束流焦点位置处的有效粉斑直径w逐渐变大,最大灰度值逐渐降低,决定系数R2均在0.98以上,这说明载气同样只是改变粉末束流的焦点位置,但是不改变焦点位置处的浓度分布特征.
表 2 载气流量对应的回归方程系数Table 2. Regression equation coefficients corresponding to carrier gas flow rates载气流量
QZ/(L·min−1)有效粉斑直径
w/mm系数
A系数
H决定系数
R22 0.88 149.5 134.4 0.99 5 1.02 128.55 97.3 0.99 7 1.13 106.55 82.04 0.98 9 1.24 95.15 60.3 0.99 10 1.32 83.85 50.2 0.98 载气流量对粉末束流有效粉斑直径w的影响规律如图9所示,随着载气流量增加,粉末束流有效粉斑直径以接近线性的规律提升,这说明载气流量提高粉末束流汇聚性下降.
2.3 送粉速率对粉末束流关键特征的影响
送粉速率对粉末束流宏观形貌的影响如图10所示,可以看出随着送粉速率提高,粉末束流不同区域亮度信息逐步提升,但送粉速率对粉末束流焦点位置影响不大,粉末束流最高点出现的位置均在7 mm左右,结果如图11所示.
高斯多元非线性回归方程关键系数如表3和图12所示,可以看出送粉速率提高,粉末束流焦点位置处的有效粉斑直径w在0.98 mm上下,整个过程较为一致,这说明送粉速率对粉末束流汇聚性影响不大.
表 3 送粉速率对回归方程关键系数的影响规律Table 3. Regression equation coefficients corresponding to powder feeding rates送粉速率
QP/(g·min−1)有效粉斑直径
w/mm系数
A系数
H决定系数
R29.90 0.97 71 58.4 0.98 16.50 0.99 103.5 83.6 0.99 23.10 0.99 141.1 113.8 0.99 29.60 0.98 173.5 145.7 0.99 32.90 0.98 182.1 148.1 0.99 3. 结论
(1)建立了激光同轴送粉增材制造用粉末束流焦距和焦点位置处粉末颗粒空间分布的表征与分析方法,实现了粉末束流关键特征的定量化分析.
(2)同轴保护气流量和载气流量是影响粉末束流焦距的主要工艺参数,同轴保护气流量从3 L/min提高到23 L/min时,焦距从6.4 mm提高到9.8 mm;载气流量由2 L/min提高到10 L/min时,焦距从9 mm降低到6.8 mm,两者对粉末束流焦距的影响规律恰好相反.
(3)工艺参数的改变几乎不影响粉末束流焦点位置处粉末颗粒空间分布呈典型的高斯分布这一特征,但载气流量增加,有效粉斑直径w变大,从2 L/min时的0.88 mm,提高到10 L/min时的1.32 mm,增幅高达50%.
-
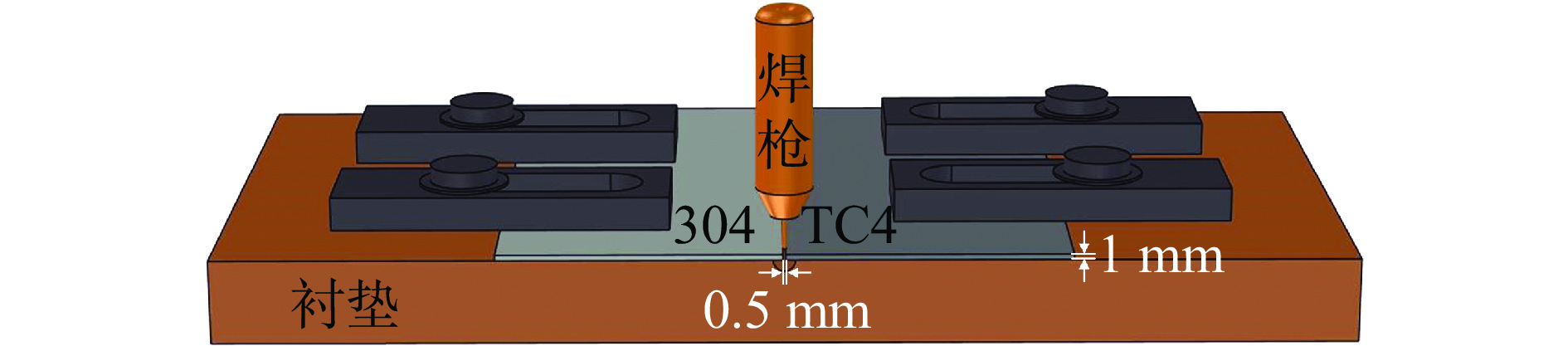
表 1 母材的元素成分 (质量分数,%)
Table 1 Base material compositions
材料 Cr Ni Al V Cu Si Fe Ti TC4 — — 5.6 ~ 5.8 3.5 ~ 4.5 0.3 — — 余量 304 18 ~ 20 8 ~ 11 — — 0.15 0.1 余量 0.15 表 2 焊丝的元素成分 (质量分数,%)
Table 2 Welding wire compositions
材料 Fe Al Si Cu T2Cu — — 0.3 余量 CuSi3 0.3 0.01 2.8 ~ 4.0 余量 表 3 焊接过程工艺参数
Table 3 Parameters and details of welding process
试样 焊接电流
I/A焊接电压
U/V焊接速度
v/(mm·s−1)热输入
H/(J·mm−1)送丝速度
vw/(m·min−1)焊丝 1 65 9.6 8 66.3 3.2 T2Cu 2 65 9.6 6 88.4 3.2 T2Cu 3 65 9.6 8 66.3 3.2 CuSi3 4 65 9.6 6 88.4 3.2 CuSi3 表 4 钛侧界面点扫描分析结果
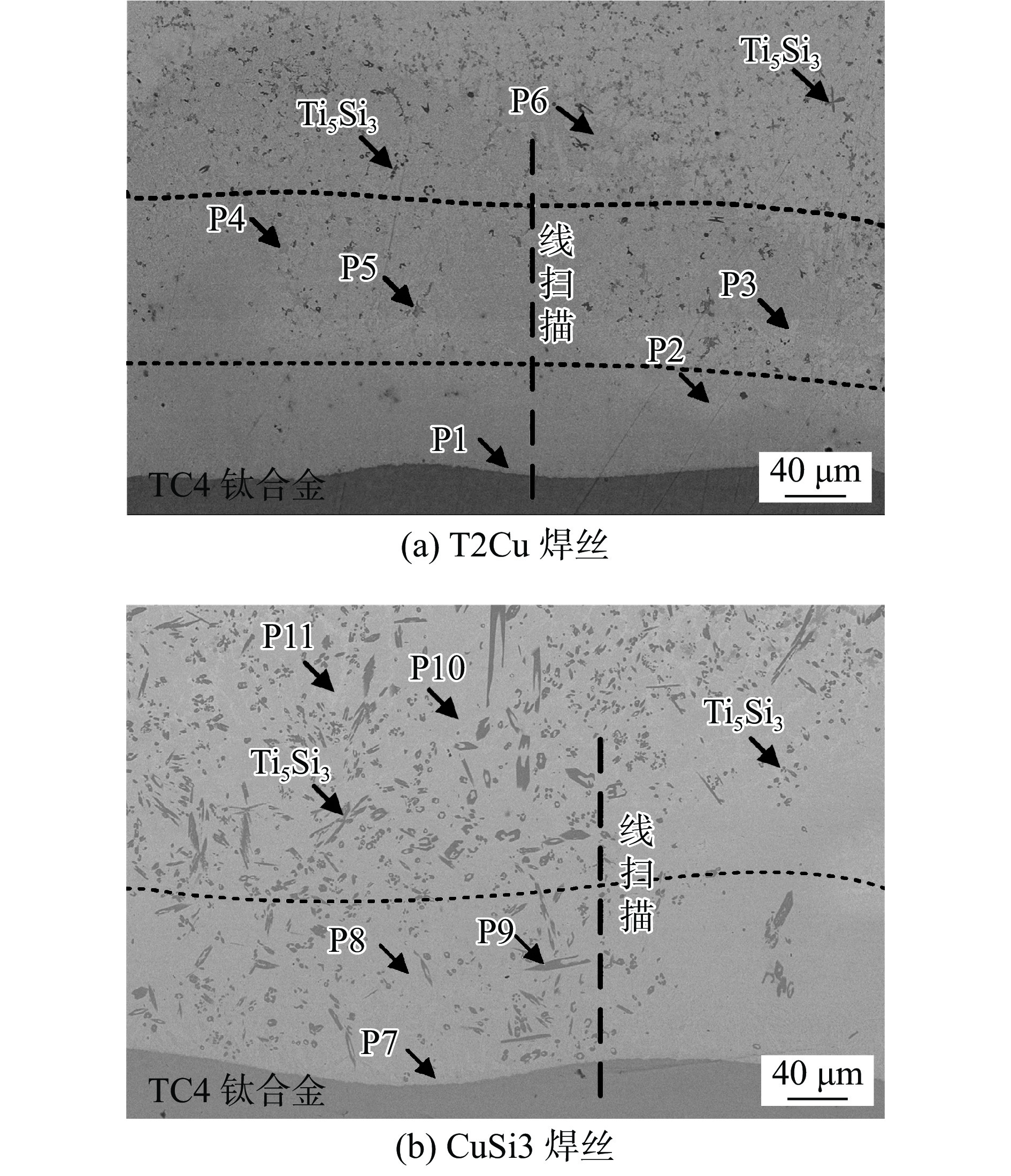
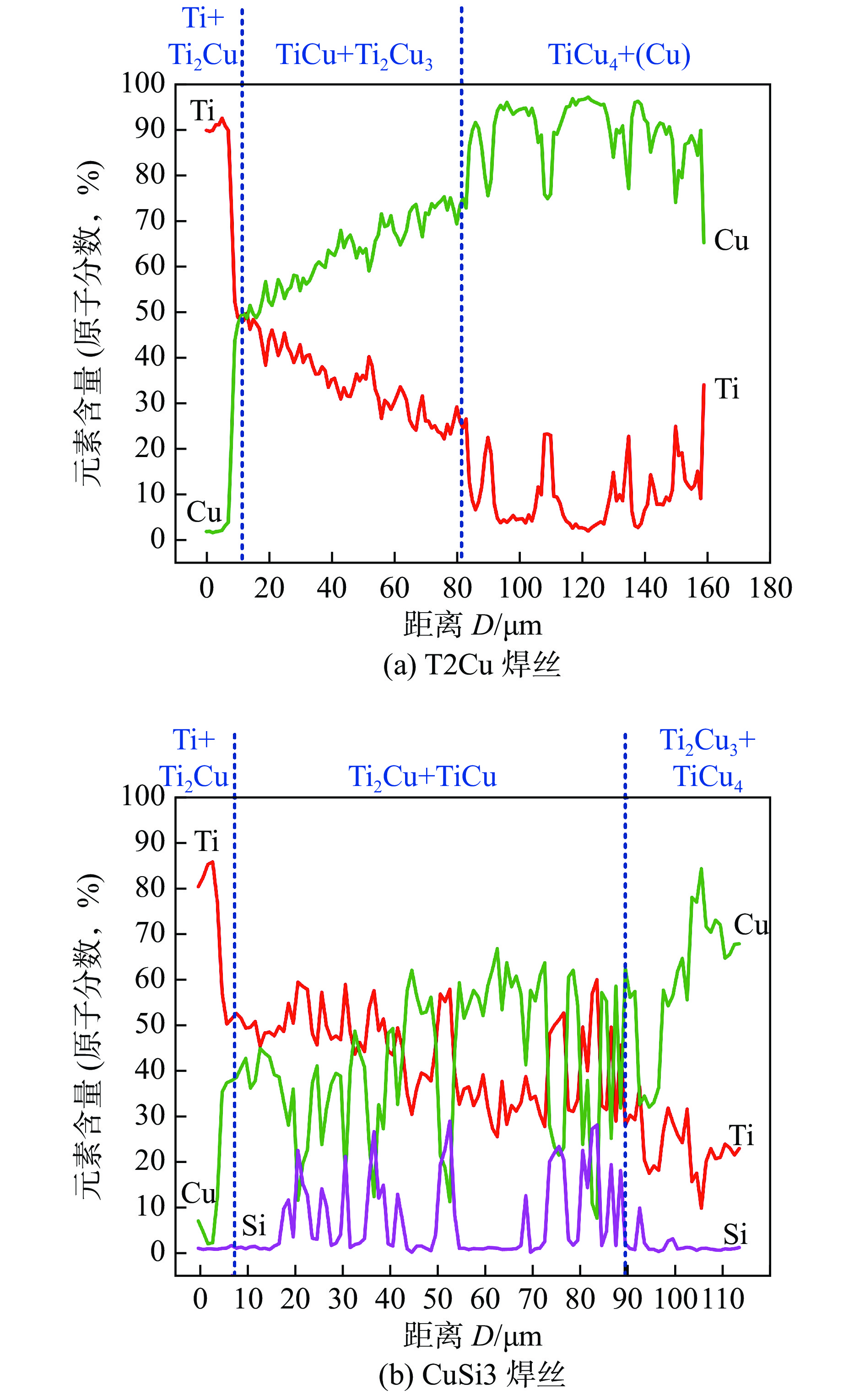
Table 4 EDS spots results of Ti/Cu interfaces
位置 元素含量(原子分数,%) 可能的相 Ti Cu Fe Al Si P1 82.09 10.65 1.31 5.94 — Ti + Ti2Cu P2 38.79 50.68 1.97 8.56 — TiCu P3 15.23 79.21 2.31 3.22 — TiCu4 P4 28.02 66.17 1.00 4.80 — Ti2Cu3 + TiCu4 P5 50.39 9.59 — 1.02 34.89 Ti5Si3 P6 17.58 80.37 — 2.05 — TiCu4 P7 52.24 35.77 4.07 7.91 — TiCu + Ti2Cu P8 41.73 49.11 3.90 5.26 — TiCu P9 54.02 9.42 — — 36.56 Ti5Si3 P10 20.10 79.90 — — — TiCu4 P11 12.13 87.87 — — — TiCu4 + (Cu) 表 5 焊缝中心及铜/钢界面点扫描分析结果
Table 5 EDS spots results of weld seams and Cu/steel interfaces
位置 元素(原子分数,%) 可能的相 Ti Cu Fe Cr Si P1 37.20 49.30 6.70 — 5.10 Ti2Cu3 P2 30.53 10.43 41.44 — 17.60 TiFe2 + Ti5Si3 P3 54.02 — — — 36.56 Ti5Si3 P4 33.61 10.61 26.83 — 23.76 TiFe2 + Ti5Si3 表 6 铜/钢界面点扫描分析结果
Table 6 EDS spots results of Cu/steel interfaces
位置 元素(原子分数,%) 可能的相 Ti Cu Fe Cr Si P5 25.09 4.30 51.49 11.51 7.58 TiFe2 + (Fe) P6 25.71 4.13 51.20 11.70 7.30 TiFe2 + (Fe) P7 3.75 4.22 67.88 19.54 — (Fe) -
[1] 毕志雄, 李雪交, 吴勇, 等. 钛箔/钢爆炸焊接的界面结合性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(4): 81 − 85. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20211105002 Bi Zhixiong, Li Xuejiao, Wu Yong, et al. Interfacial bonding properties of titanium foil/steel explosive welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(4): 81 − 85. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20211105002
[2] Shi C G, Sun Z R, Fang Z H, et al. Design and test of a protective structure for the double vertical explosive welding of large titanium/steel plate[J]. China Welding, 2019, 28(3): 7 − 14.
[3] 胡奉雅, 许国敬, 陈伟, 等. 钛/钢复合板焊接技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(6): 30 − 43. Hu Fengya, Xu Guojing, Chen Wei, et al. Research status and development trend of titanium/steel bimetallic composite plates of welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(6): 30 − 43.
[4] Chu Q L, Tong X W, Xu S, et al. The formation of intermetallics in Ti/steel dissimilar joints welded by Cu-Nb composite filler[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 828: 154389. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154389
[5] Ren G Z, Zhang Y, Zhou J P, et al. Titanium/steel composites were prepared by composite interlayer and two pass laser welding[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2023, 27: 6367 − 6375. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2023.11.118
[6] Hao X H, Wei X L, Li S H, et al. Joining mechanism evolution of fusion welded TC4 titanium alloy/304 stainless steel dissimilar joint by GTAW[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2023, 28(9): 1031 − 1040. doi: 10.1080/13621718.2023.2264572
[7] Zhang Y, Chen Y K, Zhou J P, et al. Experimental and numerical study on microstructure and mechanical properties for laser welding-brazing of TC4 titanium alloy and 304 stainless steel with Cu-base filler metal[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(1): 465 − 477. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.10.075
[8] Li J Z, Liu Y B, Zhen Z Y, et al. Weld formation mechanism and microstructural evolution of TC4/304 stainless steel joint with Cu-based filler wire and preheating[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(19): 3071. doi: 10.3390/ma12193071
[9] Jin P, Liu Y B, Sun Q J, et al. Wetting mechanism and microstructure evolution of TC4/304 stainless steel joined by CMT with an assisted hybrid magnetic field[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 819: 152951. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.152951
[10] Chang J H, Cao R, Yan Y J. The joining behavior of titanium and Q235 steel joined by cold metal transfer joining technology[J]. Materials, 2019, 12(15): 2413. doi: 10.3390/ma12152413
[11] Mou G, Hua X M, Wang M, et al. Effect of axial magnetic field on cold metal transfer arc-brazing of Ti6Al4V to 304L steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 275: 116322. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116322
[12] Cheng Z, Huang J H, Ye Z, et al. Butt brazing of titanium alloys/stainless steel plates by MIG-TIG double-sided arc welding process with copper filler metal[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2019, 8(1): 1566 − 1570. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2018.06.009
[13] Hao X H, Dong H G, Li P, et al. Dissimilar joining of TC4 alloy to ST16 steel by GTAW[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 37: 413 − 417. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.12.016
[14] 陈夏明, 王晓南, 董其鹏, 等. 焊丝Si含量对铝合金激光-CMT复合焊接头组织性能的影响[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(22): 30 − 38. Chen Xiaming, Wang Xiaonan, Dong Qipeng, et al. Effect of filling material with different Si content on microstructure and properties of laser-CMT aluminum alloy joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2021, 48(22): 30 − 38.
[15] Hu Y, Shi Y H, Sun K, et al. Effect of filler Si content on the microstructure and properties of underwater hyperbaric welded duplex stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 279: 116548.
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 张普,曹四龙. Al_2O_3+TiO_2复合颗粒对激光熔覆Inconel 718基润滑涂层显微组织及高温磨损行为的影响研究. 材料保护. 2024(06): 8-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏来,李丹,董振. 原位自生(Ti, V)C堆焊层的耐磨性能. 沈阳工业大学学报. 2023(01): 43-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘海浪,卢儒学,陈健,徐珖韬,张倩. 镍基合金电子束熔覆表面改性及高温耐磨性研究. 金属热处理. 2021(04): 161-166 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 吴雁楠,黄诗铭,朱平,马振一,兰博,何翰伟,郝博文. 原位碳化钛颗粒增强镍基喷焊层的组织与性能. 热加工工艺. 2021(22): 96-98+102 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 马强,陈明宣,孟君晟,李成硕,史晓萍,彭欣. 纯铜表面氩弧熔覆TiB_2/Ni复合涂层组织及耐磨性能. 焊接学报. 2021(09): 90-96+102 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 王永东,杨在林,张宇鹏,朱艳. Y_2O_3对原位自生TiC增强Ni基涂层组织和性能影响. 焊接学报. 2020(02): 53-57+100 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 陈鹏涛,曹梅青,吕萧,仇楠楠. 氩弧熔敷原位合成ZrC-TiB_2增强铁基涂层的组织与性能. 上海金属. 2020(05): 15-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: