Fatigue life assessment of load-carrying 60° oblique cruciform full-penetration welded joints
-
摘要:
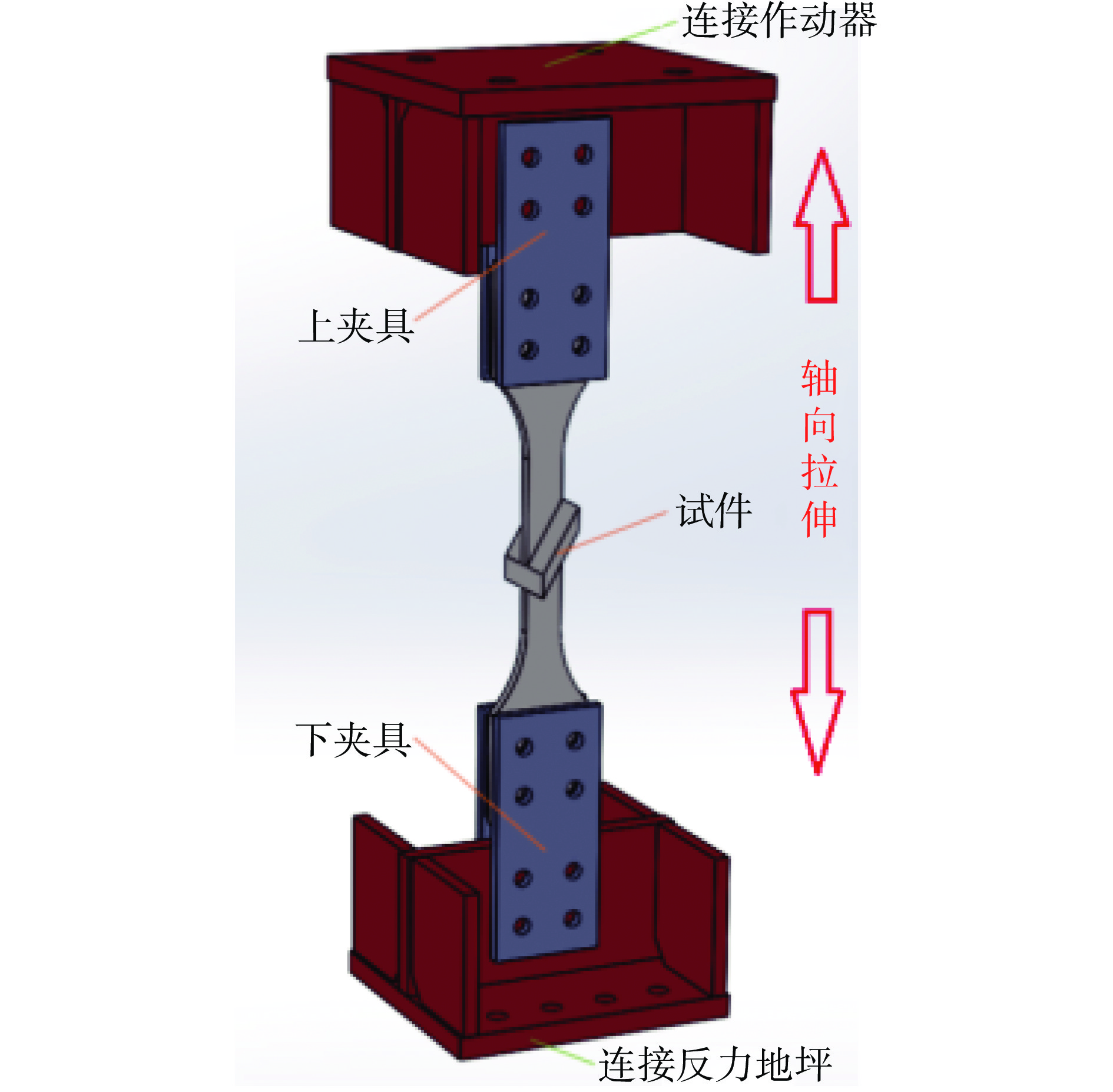
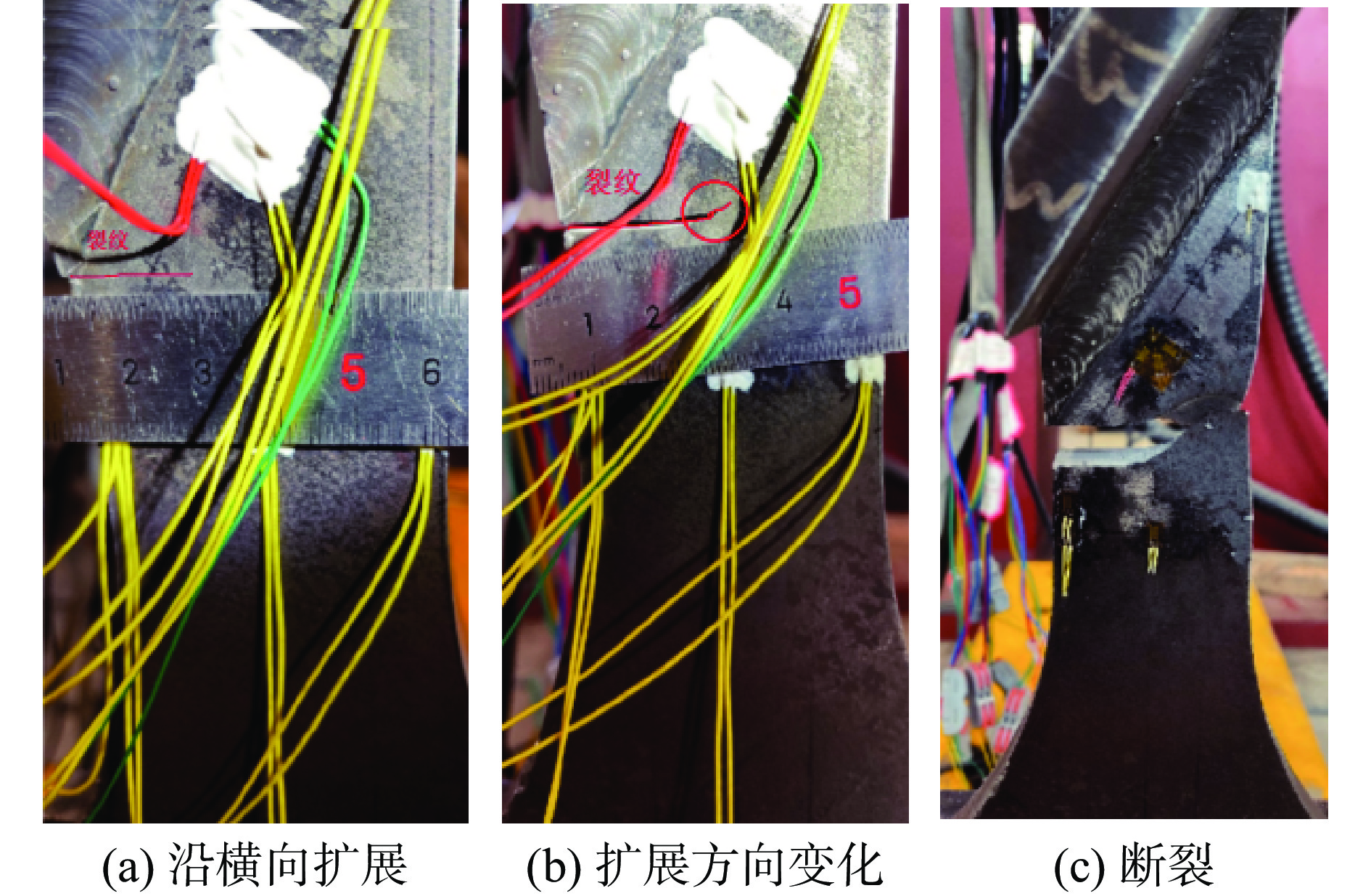
为研究承载型60°斜十字全熔透焊接接头 (oblique cruciform full-penetration welded joints,OCFWJs)局部应力分布及疲劳性能,设计3个试验模型完成3种名义应力幅水平下的疲劳试验,得到试件疲劳破坏时的循环次数. 利用ABAQUS软件建立60° OCFWJs有限元模型,计算得到焊趾处热点正应力、热点剪应力及等效热点应力. 基于规范中的名义应力S-N曲线和热点应力S-N曲线,分别采用名义主应力法、等效热点应力法和相互作用方程方法对拉—剪联合作用下60° OCFWJs疲劳寿命进行了评估. 结果表明,采用名义应力幅、名义拉应力幅或名义剪应力幅均无法对60° OCFWJs疲劳寿命进行可靠评估. 依据国际焊接学会(International Institute of Welding,IIW)规范无论采用热点拉应力幅或热点剪应力幅也无法对60° OCFWJs疲劳寿命进行可靠评估. 按欧洲钢结构设计规范Eurocode3相互作用方程方法预测的疲劳寿命远低于试验值,按等效热点应力方法预测的疲劳寿命与试验值符合良好.
Abstract:To study the local stress distributions and fatigue performance of load-carrying 60° oblique cruciform full-penetration welded joints (OCFWJs), three test specimens were designed for fatigue tests under three nominal stress amplitude levels, and the numbers of loading cycles until fatigue failure of the specimens were obtained. Using ABAQUS finite element software, the finite element models of 60°OCFWJs were established, and the hot spot normal stress, hot spot shear stress, and equivalent hot spot stress at the weld toe were calculated. Based on the nominal stress S-N curves and the hot spot stress S-N curves defined in the specifications, the fatigue life of 60° OCWJs under the combined action of tensile and shear stress were evaluated by using the nominal principal stress method, the equivalent hot spot stress method, and the interaction equation method, respectively. The results showed that whether the nominal stress range, the nominal tensile stress range, or the nominal shear stress range were used, the fatigue life of 60° OCWJs couldn't reliably evaluated. According to the International Institute of Welding specification, whether the hot spot tensile stress ranges or the hot spot shear stress ranges couldn't be used to evaluate the fatigue life of 60° OCFWJs reliably. The fatigue lives predicted by the interaction equation method in Eurocode 3:Design of Steel Structures were much lower than the experimental values , and the fatigue lives predicted by the equivalent hot spot stress method were in good agreement with the experimental values .
-
-
表 1 名义应力幅及疲劳寿命
Table 1 Nominal stress range and fatigue life
试件 最大荷载
Fmax/kN最小荷载
Fmin/kN名义应力幅
Δσnom/MPa实测疲劳寿命
Nt/104周次B1 220 22.0 247.0 24.7995 B2 136 13.6 153.0 88.9259 B3 172 17.2 193.5 33.0092 表 2 不同的名义应力幅
Table 2 Different nominal stress amplitudes
名义应力幅
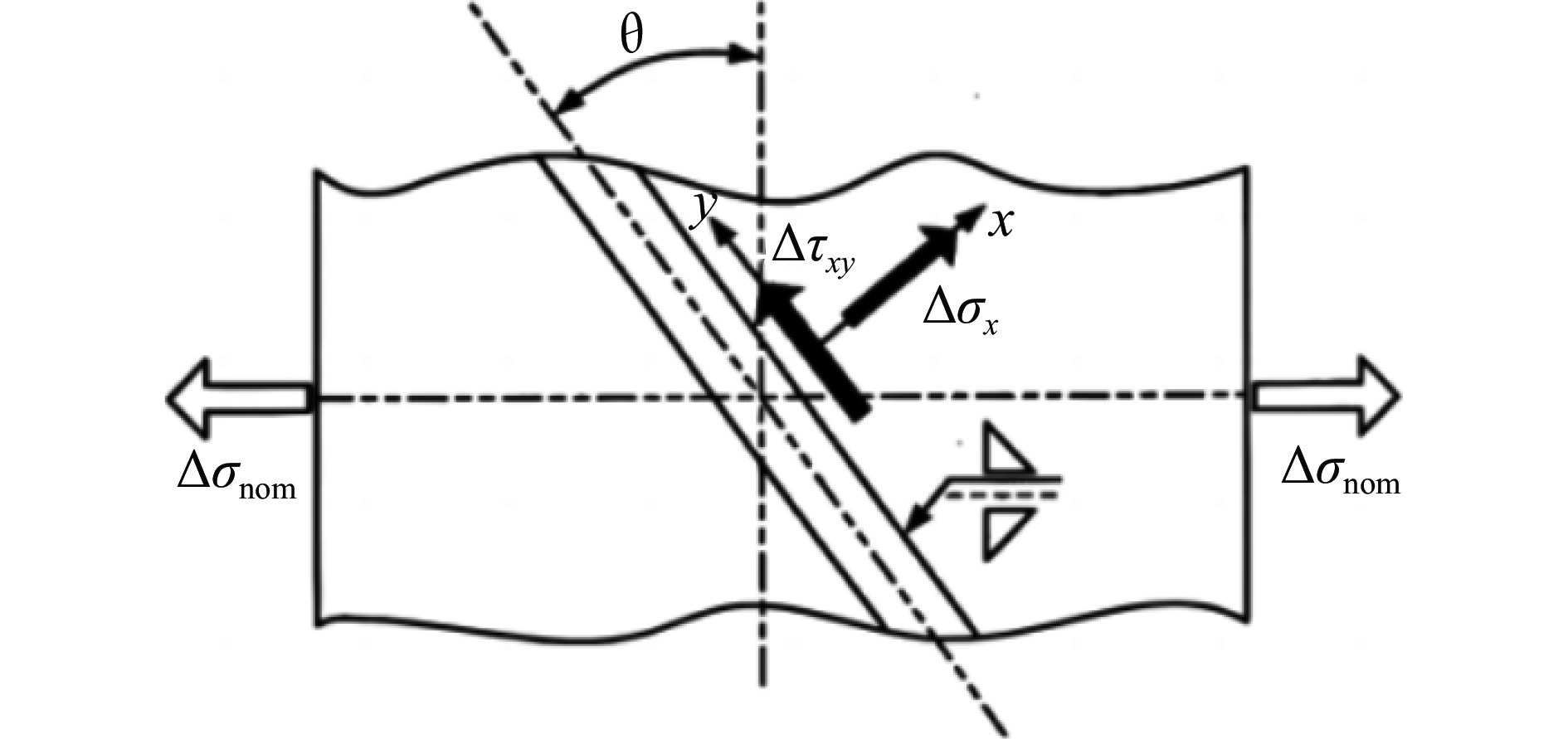
Δσnom/MPa名义正应力幅
Δσx/MPa名义剪应力幅
Δτxy/MPa最大主应力幅
Δσ1/MPa153.0 38.25 66.25 88.08 193.5 48.38 83.79 111.40 247.0 61.75 106.95 142.19 表 3 焊趾处的热点应力幅及疲劳寿命
Table 3 Hot spot stress range at the weld toe and fatigue life
试件 正应力幅
Δσx/MPa剪应力幅
Δτxy/MPa热点正应力幅
Δσh/MPa热点剪应力幅
Δτh/MPa等效热点应力幅
Δσhe/MPa基于Δσhe
疲劳寿命计算值
Nc1/104周次实测循环次数
Nt/104周次距焊趾
0.4 t距焊趾
1.0 t距焊趾
0.4 t距焊趾
1.0 tB1 71.4 66.0 199.1 197.7 75.02 200.04 213.64 20.5107 24.7995 B2 44.2 40.9 123.5 120.6 46.41 125.44 133.75 83.5889 88.9259 B3 55.9 51.7 156.0 152.6 58.71 158.28 168.82 41.5679 33.0092 表 4 基于最大主应力幅的疲劳寿命
Table 4 Fatigue life based on Δσ1
试件 最大主应力幅
Δσ1/MPa基于Δσ1疲劳寿命计算值
Nc2/104周次实测循环次数
Nt/104周次B1 142.19 35.6199 24.7995 B2 88.08 150.1093 88.9259 B3 111.40 74.0703 33.0092 表 5 基于相互作用方程法的疲劳寿命
Table 5 Fatigue life based on the interaction equation method
试件 热点正应力
$ \Delta {\sigma }_{\mathrm{h}} $/MPa热点剪应力
$ \Delta {\tau }_{\mathrm{h}} $/MPa疲劳寿命
Nc3/104周次实测循环次数
Nt/104周次B1 75.02 200.04 6.1625 24.7995 B2 46.41 125.44 62.3867 88.9259 B3 58.71 158.28 19.7306 33.0092 -
[1] 马景平, 曹睿, 周鑫. 高强钢焊接接头疲劳寿命的提高方法进展[J]. 焊接学报, 2024, 45(10): 115 − 128. Ma Jingping, Cao Rui, Zhou Xin. Development on improving fatigue life of high strength steel welded joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2024, 45(10): 115 − 128.
[2] Timar I, Arpad I W. Optimal design of the fillet weld fastening the wind turbine column[J]. China Welding, 2024, 33(3): 39 − 43.
[3] Xiao L, Wei X, Zhao J M, et al. Hot spot stress concentration factor of CFST T/Y joints based on modified equivalent thickness[J]. Structures, 2023(51): 910 − 925.
[4] 高杰, 鞠晓臣, 左照坤, 等人. 基于等效结构应力法的高强钢焊接结构低温主S-N曲线[J]. 船舶力学, 2024, 28(4): 571 − 581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2024.04.009 Gao Jie, Ju Xiaochen, Zuo Zhaokun, et al. Low temperature master S-N curve of high strength steel welded structure based on equivalent structural stress method[J]. Journal of Ship Mechanics, 2024, 28(4): 571 − 581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7294.2024.04.009
[5] 宋威, 满铮, 徐杰, 等. 含错位效应十字焊接接头疲劳可靠性评估[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(6): 20 − 26,34. Song Wei, Man Zheng, Xu Jie, et al. Fatigue reliability analysis of load-carrying cruciform joints with misalignment effects[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(6): 20 − 26,34.
[6] Song W, Man Z, Xu J, et al. Fatigue reliability assessment of load-carrying cruciform welded joints with undercuts and misalignments[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2024, 47(2): 511 − 531.
[7] Laher B , Buzzi C , Leitner M, et al. Effect of angular distortion and axial misalignment on the fatigue strength of welded and ground mild steel cruciform joints[J]. Welding in the World, 2024, 68(5): 1169 − 1186.
[8] 苏庆田, 沈翀. 错位缺陷对钢桥中厚板斜十字接头静力性能影响研究[J]. 桥梁建设, 2023, 53(5): 17 − 23. Su Qingtian, Shen Chong. Research on influence of staggering defects on static performance of thick plate skew cross joints in steel bridge[J]. Bridge Construction, 2023, 53(5): 17 − 23.
[9] Soligo M, Campagnolo A, Meneghetti G, et al. Misalignment factors to affect the fatigue of welded load-carrying joints[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2024, 178: 107996. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2023.107996
[10] Bartsch H, Feldmann M. Fatigue strength of cruciform joints with weld imperfections: a comprehensive numerical study[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2024, 157: 107866. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2023.107866
[11] Raftar H R, Ahola A, Lipiainen K, et al. Fatigue behavior of load-carrying cruciform fillet weld joints under variable amplitude load[J]. Journal of Constructional Steel Research, 2024, 215: 108559. doi: 10.1016/j.jcsr.2024.108559
[12] 魏国前, 郭子贤, 闫梦煜, 等. 基于Pavlou方法的焊接结构疲劳寿命预测[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(9): 16 − 23. Wei Guoqian, Guo Zixian, Yan Mengyu, et al. Pavlou approach based fatigue life prediction for welded structures[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(9): 16 − 23.
[13] Wang W Z, Shi W Z, Li B, et al. High-cycle fatigue life assessment of welded cruciform joints of Q460D steel[J]. Structures, 2023, 57: 105163. doi: 10.1016/j.istruc.2023.105163
[14] 聂春戈, 张旭, 管明珠, 等. 非承载角焊缝十字接头疲劳性能[J]. 焊接, 2021(1): 8 − 12,61. Nie Chunge, Zhang Xu, Guan Minzhu, et al. Fatigue property of non-load-carrying fillet welds in cruciform joint[J]. Welding & Joining, 2021(1): 8 − 12,61.
[15] European Committee for Standardization. Eurocode 3: design of steel structures, part 1-9: fatigue, EN 1993-1-9-2005[S]. Bruxelles: European Committee for Standardization, 2007.
[16] Hobbacher A. Recommendations for fatigue design of welded joints and components[S]. Paris: International Institute of Welding, 2008
[17] Zhao J M, Xiao L, Wei X, et al. Parametric study and neural network-based prediction for stress concentration factor of concrete-filled steel tubular T-joint[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2024, 305: 117972. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2024.117972
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王守明,高振坤,陈建华,丁韦,许蕊,刘国庆,谭锦红. U71Mn钢闪光-摩擦复合焊接头组织及性能研究. 金属加工(热加工). 2025(04): 67-73+78 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: