Effect of joint property differences on residual stresses in electron beam welded joints of Zr-Sn-Nb alloys
-
摘要:
为了提升Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊残余应力计算精度,对Zr-Sn-Nb合金及焊接接头热物性参数与力学性能进行测量,研究接头性能差异对电子束焊接头残余应力影响规律,建立了电子束焊复合热源模型,采用热弹塑性有限元方法对4.45mm厚Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊应力进行数值模拟,并进行焊缝形貌验证. 结果表明,考虑焊缝与母材属性差异时,试板上表面焊缝及热影响区区域的横向残余应力峰值高于二者属性相同时的模拟结果,峰值分别为319 MPa和296 MPa,进一步考虑热影响区属性与母材及焊缝差异对接头残余应力影响不大,峰值纵向应力为318 MPa.
-
关键词:
- Zr-Sn-Nb合金 /
- 接头性能差异 /
- 电子束焊 /
- 残余应力
Abstract:In order to improve residual stress numerical simulation accuracy of Zr-Sn-Nb alloy electron beam, thermophysical parameters and mechanical properties of Zr-Sn-Nb alloys and welded joints were measured. and the influence of the difference in joint properties on the residual stress of electron beam welded joints was investigated. The hybrid heat source model of electron beam welding is established, and the thermoelastic-plastic finite element method is used to numerically simulate the stress of electron beam welded 4.45 mm thick Zr-Sn-Nb alloy. The simulation model was verify by weld morphology. The results show that the peak transverse residual stresses in the weld and heat-affected zone region on the upper surface of the test plate are higher than those simulated when the properties of the two are the same, with peaks of 319 MPa and 296 MPa, respectively. The peak longitudinal stress was 318 MPa when the differences in the properties of heat-affected zone and the base material and weld are considered, which has little effect on the residual stresses in the joint.
-
0. 序言
在Zr-Sn-Nb合金的基础上通过加入多种合金元素进一步提高锆合金的耐腐蚀性能和力学性能,成为新型锆合金研发的主要趋势,如Zirlo合金、E635合金和N36合金等[1-2]. Zr-Sn-Nb合金具有耐水腐蚀性能好、高温力学性优异、中子吸收截面低等特点,成为核工业的关键材料[3],随着核反应堆的发展,在保证反应堆安全、高效和经济的前提下,其服役寿命及可靠性能需求不断提升,其中锆合金的焊接技术对于提高锆合金件的制造质量和生产效率具有重要意义[4-5]. 由于锆合金化学性质活泼,导热系数相比于铜、铝等金属低,在高温焊接过程中接头易被空气中的氧、氮、氢等气体元素所污染,也易因为焊接熔池热量积聚多而出现晶粒尺寸大,接头性能恶化[6],采用真空保护的电子束焊有助于提升锆合金焊接质量[7].
焊接残余应力会导致氢化物在锆合金焊缝及热影响区诱发氢致延迟裂纹,增加接头腐蚀开裂速率,降低接头疲劳寿命,严重制约了核燃料组件长期运行的可靠性[8]. 随着有限元数值模拟和计算机技术的发展,数值模拟也逐步发展为焊接应力研究的主流方法[9-10],模型参数的准确性决定了焊接应力模拟的精度,焊接过程中焊缝及热影响区的组织转变导致性能的变化,直接影响了焊接过程中接头的应力演变和焊后残余应力[11]. 张开元[12]考虑高强钢固态相变引起的材料力学性能变化、相变应力和相变塑性开发“热-冶金-力学”模型提升应力计算模型的精度;Banik等人[13]研究了焊缝和母材屈服强度差异对变形和残余应力分布的影响.文中对Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊接头不同区域的热物性参数与力学性能进行测量,对比焊接接头处焊缝、热影响区及母材性能差异对接头应力演化及残余应力的影响规律,为Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊应力精准预测提供指导.
1. 试验方法
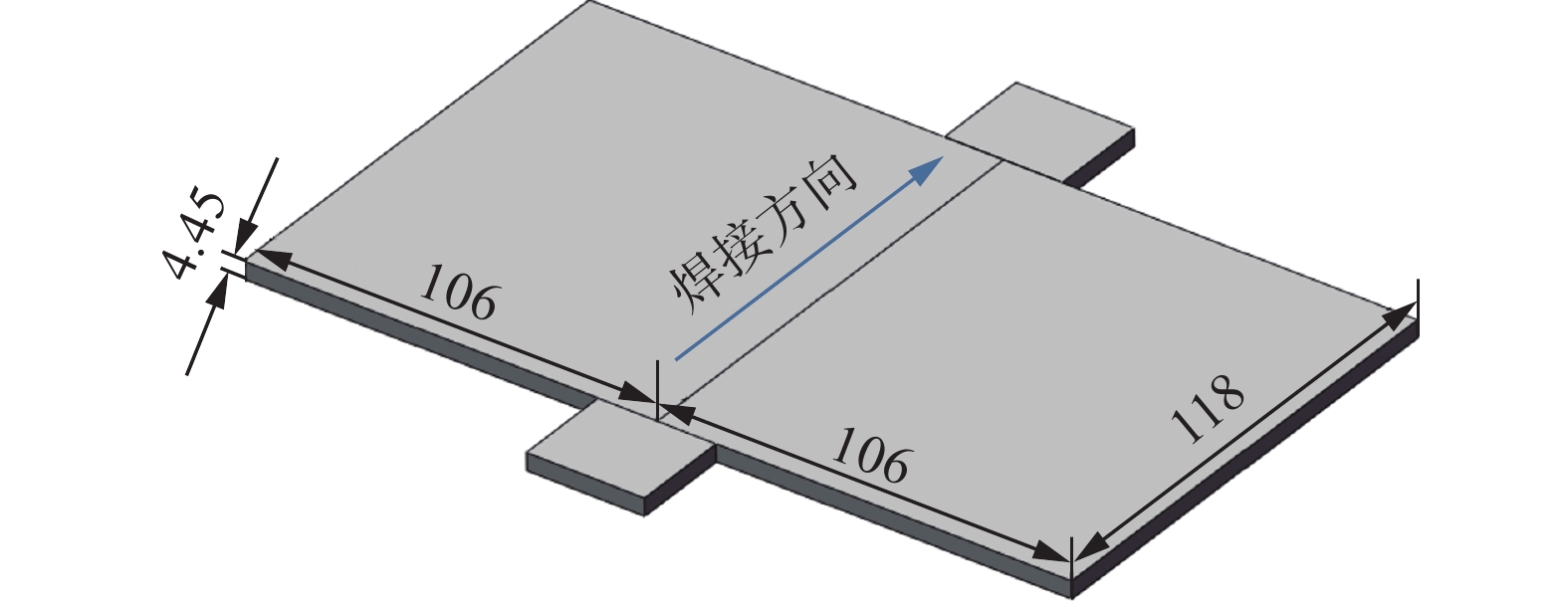
采用昆塔EBM-30H电子束焊机进行电子束焊接工艺试验,焊前抽真空至1.0 × 10−3 Pa,防止Zr-Sn-Nb合金高温下与O元素和N元素发生反应,试验采用冷轧退火态Zr-Sn-Nb合金,合金组分与文献[14]相同,将两块尺寸为118 mm × 106 mm × 4.45 mm的平板沿长度(垂直轧制)方向进行对接焊接,焊接装配如图1所示,焊接参数见表1,焊后在真空室内冷却10分钟后打开真空室取件,以避免高温取件氧化.
表 1 Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊接工艺参数Table 1. Zr-Sn-Nb alloy electron beam welding parameters加速电压
U/kV聚焦电流
If /mA焊接束流
Ib /mA焊接速度
vs /(mm·s−1)工作距离
d/mm60 706* + 8 27 480 190.5 *706 mA为试板上表面聚焦电流. 焊后对母材及焊缝(焊接接头)的热物性参数进行测量,将带有焊缝金属的接头与母材分别制成两个直径12.7 mm × 2 mm的圆柱形试样,采用LFA45703061408型激光热导仪测试室温,100 ℃,300 ℃,500 ℃,700 ℃ 5个温度点的热导率与比热容. 将带有焊缝金属的接头与母材分别制成两个80 mm × 30 mm × 3 mm的平板试样,采用RFDA-HTVP1750C高温弹性模量与阻尼测试仪测试室温、100 ℃ ~ 500 ℃焊接接头与母材的弹性模量,将带有焊缝金属的接头与母材分别制成25 mm × 3 mm × 4 mm的长方体试样,采用402 Expedis Supreme 03030217型热膨胀仪在Ar气保护下测量焊缝及母材室温至800 ℃的热膨胀系数. 制备微小拉伸试样使得试样的平行段分别位于焊缝、热影响区和母材区域,采用岛津AG-X plus拉伸试验机测试接头各区域的屈服强度,将测试值作为Zr-Sn-Nb合金焊接应力模拟的材料属性输入参数.
2. 模型的建立
2.1 几何模型与网格划分
采用与焊接试板相同尺寸的几何模型,焊缝及热影响区的尺寸根据焊缝横截面测量进行提取划分,其中焊缝为漏斗形,上表面宽度为4.3 mm,热影响区上表面宽度为1.5 mm,当考虑热影响区时,将热影响区、母材和焊缝进行分别建模,如图2所示. 总网格数量29 200,总节点数量37 819,所有的计算单元均指定为C3D8R热-力耦合单元,焊缝及热影响区采用细小网格,最小网格尺寸为0.5 mm,母材区域经小尺寸网格过渡后外围采用粗网格,以平衡计算精度和计算时长,不考虑热影响区时将母材与热影响区作为一个整体建模.
2.2 模型求解与设置
焊缝区域采用生死单元,采用Simufact Welding软件,基于热-弹塑性模型,通过顺序耦合对Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊接过程温度场及应力场进行求解,材料为各向同性,其屈服行为符合米塞斯屈服准则.考虑热影响区与母材及焊缝属性差异时,将母材与热影响区界面进行粘接处理,保持二者之间应力与变形传递的连续性,初始温度为20 ℃,计算起始时刻工件内部无应力,将实际夹具等效为长方体支撑,将实际的压块等效为长方体压块,如图3所示. 等效压块对试件施加刚性约束,力的方向垂直于试件表面,力的大小为100 N. 支撑及压块与工件接触换热系数设置为1 000 W·m2·s−1, 工件与环境间的辐射散热,辐射散热系数为0.6,焊接过程计算结束后,继续计算焊后冷却过程10分钟,保证试板最高温度低于30 ℃后,释放夹具约束,结束计算.
2.3 材料属性
材料参数是有限元模拟过程中所必需的性能参数,为了提高有限元模拟的准确性,对材料的比热容、热导率、杨氏模量、线膨胀系数随温度的变化情况进行实测,测量结果如图4所示. 图中实线为比热容、热导率、线膨胀系数实测值,虚线为外延值,测试点之间分段线性分布.
Zr-Sn-Nb合金母材与焊缝屈服强度实测值分别为360 MPa和345 MPa,结合文献[15]中锆合金不同温度和不同应变速率下测量的真应力-真应变曲线,按照屈服强度比例进行等比例换算,建立Zr-Sn-Nb合金及焊缝的流变曲线模型.
在考虑焊缝与母材属性相同时(第1组计算),焊缝采用与母材相同的参数;考虑焊缝与母材属性不同时(第2组计算),分别将焊缝属性赋予给焊缝、母材属性赋予给母材. 由于热影响区尺寸较窄且不规则,无法测试热影响区属性,考虑焊缝、热影响区、母材属性均不相同时(第3组计算),设置热影响区的属性为母材与焊缝的平均值. 模拟过程中需要的其他物理参数包括:熔化温度区间1 842 ℃ ~ 1 852 ℃,熔化潜热185.26 kJ/kg,泊松比0.36,密度6 510 kg/m3.
2.4 热源模型及验证
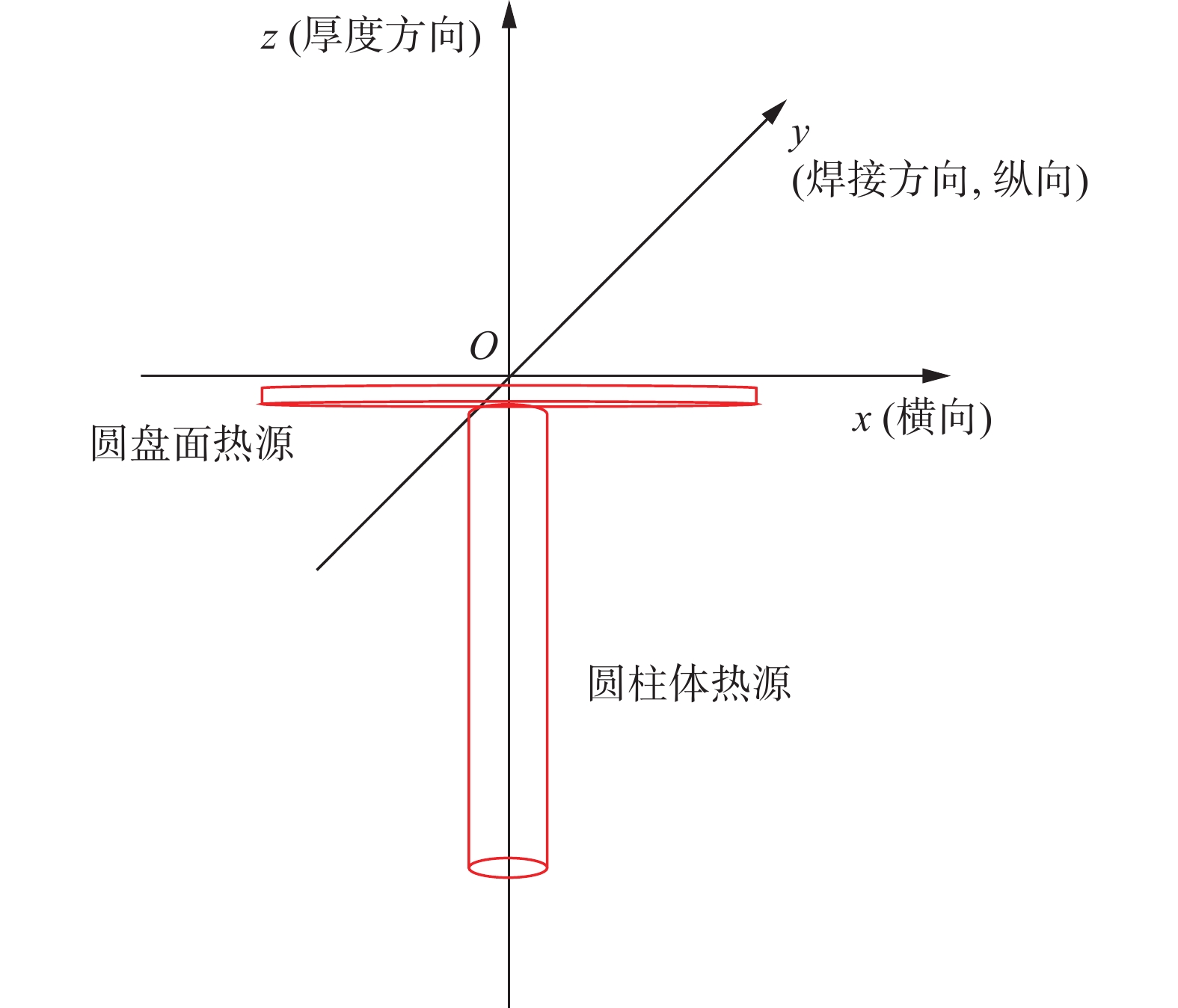
采用圆盘面热源与圆柱体热源组合的复合热源进行焊接,圆盘面热源主要反映电子束焊接时束斑外围对试件的加热,等效马拉高尼引起的对流效应,而圆柱体热源则反映了在电子束束斑中心作用下沿熔深方向上的能量分布,建立的热源模型如图5所示. 面热源直径为2.8 mm,深度为0.2 mm,圆柱体热源直径为1.4 mm,高度4.4 mm,面热源与体热源高斯分布系数均为3,能量分别为电子束焊总热输入的30%和60%,总能量利用率为0.9.
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 焊缝形貌与焊接残余应力校核
焊接接头横截面形貌如图6所示,焊缝上下表面平整,横截面呈漏斗形,上表面焊缝宽度为4.4 mm. 考虑母材与焊缝属性相同、母材与焊缝属性不同、母材、热影响区与焊缝属性均不同开展3组数值模拟,对3组计算获得的焊缝横截面轮廓形貌进行提取,并与金相照片对比. 3种情况下仿真结果与金相的尺寸一致性均较好,焊缝横截面形貌均呈漏斗形,3者上表面熔宽与实际焊接基本一致. 母材、热影响区与焊缝属性不同时,试板中部的熔宽增加,这是由于焊缝及热影响区的比热容及热导率比母材低,该情况下焊缝截面形貌与实际焊接更为接近.
基于小孔法对Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊接残余应力数值模拟结果进行校核,依据GB/T 31310-2014《金属材料残余应力测定钻孔应变法》采用BE120-2CA电阻应变片和信恒CM-1J-10静态电阻应变仪对平板Zr-Sn-Nb焊接件的焊缝、热影响区、母材残余应力进行测量,测试试板及测试点位置如图7所示.
对数值模拟相同位置的残余应力进行提取,与小孔法测量结果对比见表2,从中可以看出,焊缝区测量点x方向为压应力、y方向为拉应力,热影响区测量点x方向与y方向均为拉应力,母材测量点x方向为拉应力、y方向为压应力,3组仿真结果在测量点位置的应力方向与测量结果相一致. 第3组计算数据与测量值一致性最好,考虑焊缝、母材与热影响区属性差异有助于提高残余应力计算精度,但数值结果与测量结果在数值上存在一定的差异,一方面小孔法测量忽略了厚度方向应力,另一方面焊接接头应力波动大,位置的略微差异会引起较大的应力差异.
表 2 Zr-Sn-Nb合金焊接残余应力数值模拟与测试对比Table 2. Comparison between numerical simulation and test of welding residual stress of Zr-Sn-Nb alloy验证位置 应力方向 应力测量值δ1/MPa 应力模拟值δ2/MPa 第1组 第2组 第3组 焊缝 σx −109.3 −60.8 −112.8 −82.6 σy 114.8 103 151.6 143.3 热影响区 σx 67.5 46 52.2 87.3 σy 265.8 268 273.8 259.7 母材 σx 46.7 31 22.3 34.8 σy −47.3 −48 −50.4 −47.5 3.2 接头应力分布规律
考虑接头属性差异模拟获得的电子束焊接头应力分布规律相同,为此结合接头属性相同的模拟结果分析接头应力分布规律. 焊接试板整体残余应力分布如图8所示. 焊缝两端存在较大的横向压应力,中部区域为拉应力,焊接板厚方向应力水平较低,平行焊缝方向的焊缝及热影响区存在大范围拉应力区域,高达200 MPa以上,直接导致该区域存在较高水平的等效应力,为焊接接头最危险的应力状态.
3.3 材料属性对接头应力影响的对比分析
提取焊接冷却后(t = 10 min)焊接试板上表面焊缝中心处(纵向)和垂直焊缝试板中心处(横向)应力特征参数. 对提取的焊缝与母材材料属性相同(第1组)、焊缝与母材材料属性不同(第2组)、焊缝、热影响区、母材材料属性均不同(第3组)的3组计算进行对比,分析焊缝、热影响区及母材材料属性对锆合金电子束焊接接头应力场的影响.
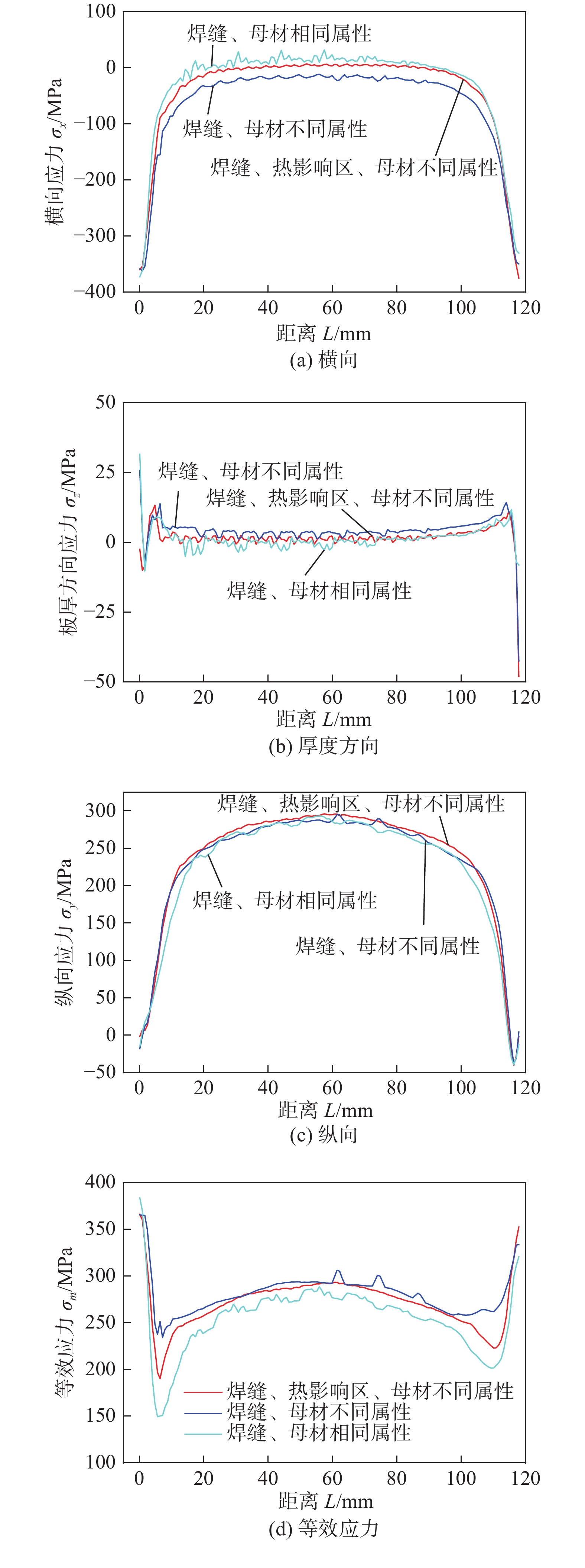
焊缝中心上表面沿焊接方向的应力分布如图9所示,电子束焊焊缝两端存在较大的应力波动,中心较长范围的应力水平较为稳定. 应力稳定段存在横向压应力(应力为负值,如图9(a)所示);由于试板较薄,板厚方向的应力水平较低,在20 MPa以下,如图9(b)所示;纵向存在着较高的拉应力,为危险应力状态,如图9(c)所示,其应力水平显著高于横向和板厚方向应力,直接决定了稳定段的等效应力水平,如图9(d)所示. 第3组计算的纵向应力最高为296 MPa,高于200 MPa的高应力水平区域长度为86 mm,占试板总长度73%.
2组与第3组的各方向应力水平整体高于第1组,这与考虑焊缝(及热影响区)与母材属性差异时,焊缝区域的屈服强度(及热影响区)较母材区域增加,使得其残余应力水平略有增加,同时考虑接头各区域物性差异后,接头区域的温度梯度增大,也会使得残余应力水平增加.
焊缝中心上表面垂直焊接方向应力分布如图10所示,电子束焊焊缝位置残余应力水平较高,母材残余应力水平低,在热影响区附近存在较大应力波动. 3组计算应力分布规律基本相同,横向和板厚方向的应力水平低,纵向的应力水平高,直接决定了等效应力水平. 纵向应力最高值出现在热影响区,第2组与第3组焊缝及热影响区应力水平高于第1组计算,3组计算最高应力分别为296,319,318 MPa.
4. 结论
(1) 基于实际测量和合理的线性插值及外延,建立了Zr-Sn-Nb合金及焊缝的比热容、热导率、线膨胀系数等热物理及力学性能参数随温度变化的模型.
(2) 基于热弹塑性模型,采用Simufact Welding软件建立了Zr-Sn-Nb合金焊接仿真模拟模型,该模型考虑了试板的几何模型与网格、初始条件、材料属性、热源模型及边界条件,考虑焊缝、母材、热影响区属性不同时,数值模拟结果与工艺试验获得的焊缝形貌一致性较好,焊缝呈漏斗形,上表面熔宽分别为4.15 mm和4.3 mm.
(3) Zr-Sn-Nb合金平板焊缝及热影响区存在大范围的高纵向应力区域,200 MPa以上区域占焊缝长度的73%,为焊接接头最危险的应力状态,直接导致该区域等效应力水平较高.
(4) 电子束焊Zr-Sn-Nb合金焊应力模拟考虑母材与焊缝残余应力不同时,焊缝及热影响区沿垂直焊缝方向的纵向残余应力,高于二者属性相同时的模拟结果,峰值残余应力分别为296 MPa和319 MPa,进一步考虑热影响区属性差异时,引起的接头应力分布规律和应力值变化较小,峰值残余应力为318 MPa.
-
表 1 Zr-Sn-Nb合金电子束焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Zr-Sn-Nb alloy electron beam welding parameters
加速电压
U/kV聚焦电流
If /mA焊接束流
Ib /mA焊接速度
vs /(mm·s−1)工作距离
d/mm60 706* + 8 27 480 190.5 *706 mA为试板上表面聚焦电流. 表 2 Zr-Sn-Nb合金焊接残余应力数值模拟与测试对比
Table 2 Comparison between numerical simulation and test of welding residual stress of Zr-Sn-Nb alloy
验证位置 应力方向 应力测量值δ1/MPa 应力模拟值δ2/MPa 第1组 第2组 第3组 焊缝 σx −109.3 −60.8 −112.8 −82.6 σy 114.8 103 151.6 143.3 热影响区 σx 67.5 46 52.2 87.3 σy 265.8 268 273.8 259.7 母材 σx 46.7 31 22.3 34.8 σy −47.3 −48 −50.4 −47.5 -
[1] 贾豫婕, 林希衡, 邹小伟, 等. 锆合金的研发历史、现状及发展趋势[J]. 中国材料进展, 2022, 41(5): 354 − 370. Jia Yujie, Lin Xiheng, Zou Xiaowei, et al. Research & development history, status and prospect of zirconium alloys[J]. Materials China, 2022, 41(5): 354 − 370.
[2] 王旭峰, 李中奎, 周军, 等. 锆合金在核工业中的应用及研究进展[J]. 热加工工艺, 2012, 41(2): 71 − 74. Wang Xufeng, Li Zhongkui, Zhou Jun, et al. Application and research progress of zirconium alloy in nuclear industry[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2012, 41(2): 71 − 74.
[3] Zhao Wanqian, Song Pengcheng, Peng Xiaoming, et al. Fracture mode analysis of Zr-Sn-Nb alloy under simulated LOCA condition in advanced nuclear reactors[J]. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2022, 137: 106392. doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2022.106392
[4] 邢硕, 蒲曾坪, 张坤, 等. 新型锆合金包壳蠕变性能评价方法研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2023, 44(4): 234 − 239. Xing Shuo, Pu Zengping, Zhang Kun, et al. Study on evaluation method for creep performance of new zirconium alloy cladding[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2023, 44(4): 234 − 239.
[5] 钟建伟, 安军靖, 丁怀博, 等. Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe-Cr与Zr-Nb-Fe锆合金电阻点焊工艺及显微组织[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(8): 82 − 90. Zhong Jianwei, An Junjing, Ding Huaibo, et al. Welding processes and microstructures of weld bead of Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe-Cr and Zr-Nb-Fe zirconium alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(8): 82 − 90.
[6] Slobodyan M S. Arc welding of zirconium and its alloys: a review[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2021, 133: 103630. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2021.103630
[7] Slobodyan M S. Resistance, electron and laser-beam welding of zirconium alloys for nuclear applications: A review[J]. Nuclear Engineering and Technology, 2021, 53(4): 1049 − 1078. doi: 10.1016/j.net.2020.10.005
[8] 王博, 包陈, 魏连峰, 等. 氢化物对锆合金薄板焊缝断裂行为的影响[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(20): 133 − 140. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.20.133 Wang Bo, Bao Chen, Wei Lianfeng, et al. Effect of hydride on fracture behavior of zirconium alloy platy welds[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(20): 133 − 140. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.20.133
[9] 杨建国, 谢浩, 闫德俊, 等. 随焊干冰激冷冷源尺寸对焊接残余应力影响的有限元分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(2): 14 − 18. Yang Jianguo, Xie Hao, Yan Dejun, et al. FEM analysis about effect of cooling source size during welding with dry ice on welding residual stress[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(2): 14 − 18.
[10] 杨帆, 陈芙蓉. A-UIT处理对7075铝合金焊接应力影响的数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(12): 91 − 96. Yang Fan, Chen Furong. Numerical simulation of effect of A-UIT treatment on welding stress of 7075 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(12): 91 − 96.
[11] 许谦, 胡广旭, 董志波, 等. 基于相变与收缩耦合的1Cr12焊缝冷却动态力学行为[J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(3): 341 − 347. Xu Qian, Hu Guangxu, Dong Zhibo, et al. Dynamic mechanics behaviors of 1Cr12 weld cooling based on coupling of phase transformation and contraction[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(3): 341 − 347.
[12] 张开元. 固态相变对超高强钢焊接-热处理过程应力变形的影响[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2022. Zhang Kaiyuan. Effect of solid-state phase transformation on stress deformation of ultra-high strength steel during weld-heat treatment [D]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2022.
[13] Banik S D, Kumar S, Singh P K, et al. Distortion and residual stresses in thick plate weld joint of austenitic stainless steel: Experiments and analysis[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2021, 289: 116944. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2020.116944
[14] 吴婧, 陈静, 蒋亦岚, 等. 冷变形N18合金再结晶过程中的织构演变[J]. 金属热处理, 2021, 46(5): 38 − 46. Wu Jing, Chen Jing, Jiang Yilan, et al. Texture evolution of cold-rolled N18 alloy during recrystallization[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2021, 46(5): 38 − 46.
[15] 张建军, 李中奎, 周军, 等. 新锆合金高温变形行为[C]//中国有色金属学会合金加工学术委员会. 中国有色金属学会第十二届材料科学与合金加工学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国有色金属学会, 2007: 374 − 378. Zhang Jianjun, Li Zhongkui, JiangYilan, et al. High temperature deformation behavior of new zirconium alloy [C]// Alloy Processing Academic Committee of China Nonferrous Metals Society. Proceedings of the 12th Annual Conference of Materials Science and Alloy Processing of the Chinese Non-Ferrous Metals Society. Beijing: Nonferrous Metals in China, 2007: 347 − 378.



 下载:
下载: