Effect of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal of 690 MPa grade HSLA steel
-
摘要:
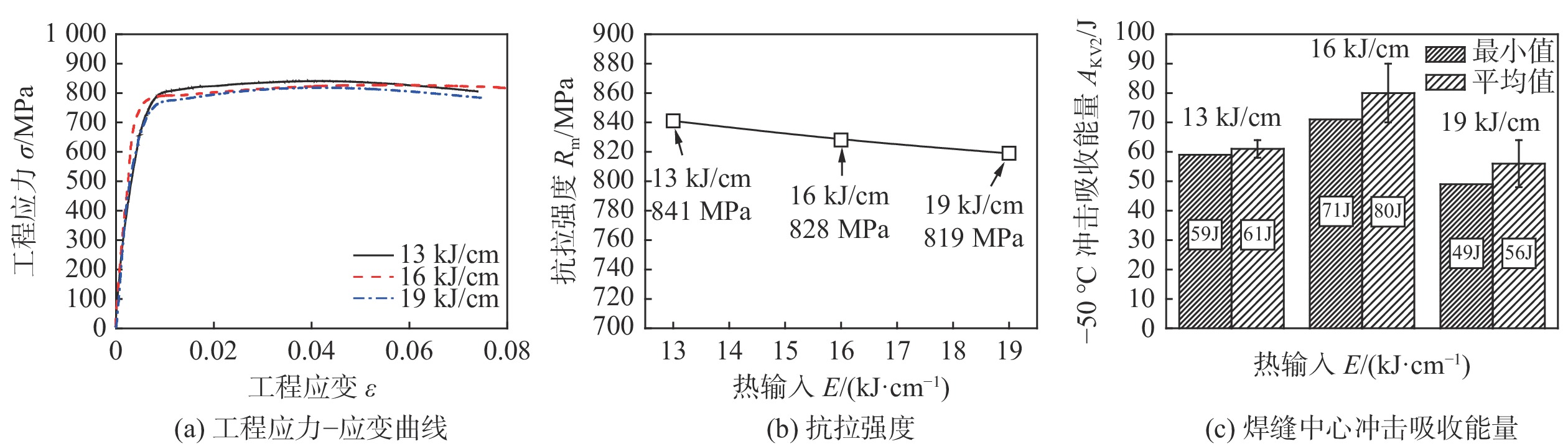
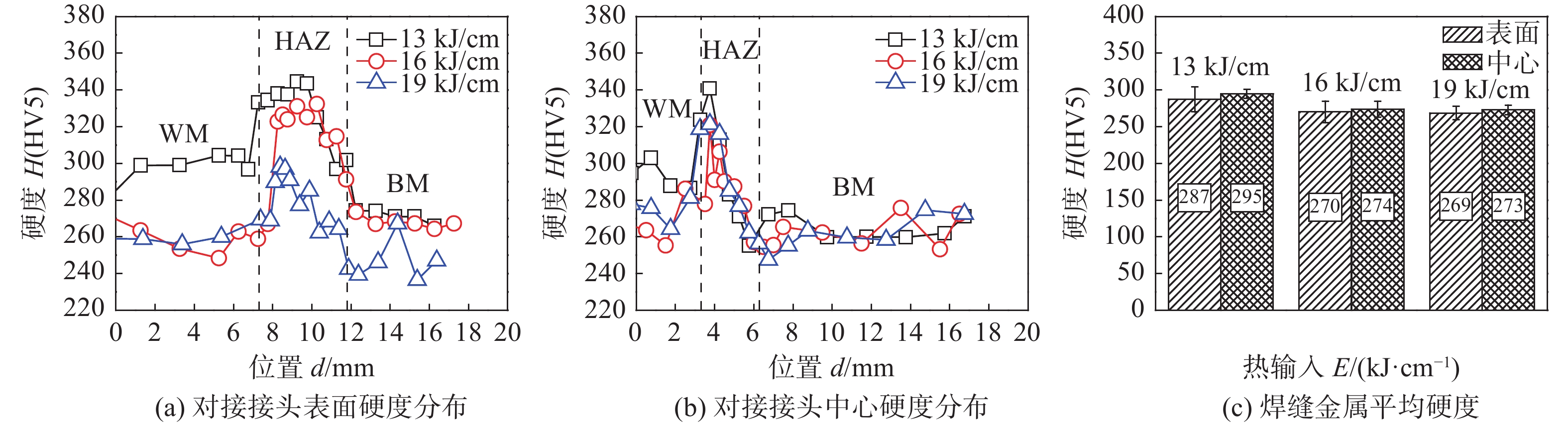
采用自研直径4.0 mm的焊条对厚度为27 mm的690 MPa级HSLA钢进行不预热焊接,研究了焊接热输入对焊缝金属组织和性能的影响及强韧化机理. 结果表明,焊接热输入由13 kJ/cm提高至19 kJ/cm对焊缝金属组织结构及其强韧性产生了显著影响,对接接头抗拉强度、硬度呈现降低趋势,焊缝金属−50 ℃冲击吸收能量呈现先升高后降低趋势. 16 kJ/cm热输入条件下获得了良好的强韧性,对接接头抗拉强度为828 MPa,焊缝中心−50 ℃冲击吸收能量为71 ~ 90 J,均值为80 J. 13 kJ/cm及19 kJ/cm热输入条件下焊缝金属强韧性较低,前者与焊缝金属中板条贝氏体及侧板条铁素体形成有关,后者与其中粗大的M-A组元形成相关. 热输入16 kJ/cm条件下,充分形成了塑性良好的针状铁素体组织,针状铁素体和贝氏体呈交织分布,同时,细小弥散分布的M-A组元并未对其韧性产生显著的负面作用,焊缝金属获得了良好的强韧性配合.
-
关键词:
- 690 MPa级HSLA钢 /
- 焊接热输入 /
- 焊缝金属 /
- 强韧化机理
Abstract:690 MPa grade high strength low alloy (HSLA) steel of 27 mm in thickness was welded by self-developed electrode of 4.0 mm in diameter without preheating. The effects of heat input on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal were studied and the mechanism of strength-toughness was revealed. The results show that heat input had significant effect on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal, which increased from 13 kJ/cm to 19 kJ/cm. With the increasing of heat input, tensile strength and hardness of butt joint decreased, −50 ℃ impact energy firstly increased and then decreased. Good strength-toughness was obtained under the heat input condition of 16 kJ/cm. The tensile strength of butt joint was 828 MPa, −50 ℃ impact energy of weld metal was 71 ~ 90 J, the average value was 80 J. The lower strength-toughness properties of weld metal under 13 kJ/cm and 19 kJ/cm heat input conditions were related with the formation of lath bainite and ferrite side plates, the formation of coarse M-A, respectively. Under the 16 kJ/cm heat input condition, good plasticity acicular ferrite was sufficiently formed and acicular ferrite and bainite were distributed in an interwoven pattern. Meanwhile, small and dispersively distributed M-A had no obviously negative effect on toughness of weld metal. Therefore, weld metal with excellent strength-toughness had been obtained.
-
0. 序言
高熵合金具有高强度、高硬度、优异的耐磨性和耐腐蚀性等[1-2].由于高熵合金涂层含有多种主元元素使得高熵合金的种类繁多[3],但目前更多研究的是对特定性能的强化以此改善高熵合金涂层的力学性能,使其能够增强结构件的综合性能,延长其使用寿命[4-5].
Nb元素具有较高的熔点,较大的原子半径,与其他元素结合具有更小的混合焓且互溶性较差[6],由于Nb元素具有这些特点可以改变复合涂层的微观组织,所以在液/固界面处会产生聚集,阻碍晶粒的生长[7].一般来说在复合涂层中加入Nb元素,不仅会在高熵合金涂层内部产生晶格畸变,导致显著的固溶强化和弥散强化[8],而且可以改善BCC固溶相的稳定性,促进析出细小弥散的第二相[9],有助于提高硬度和耐磨性,改善复合涂层的力学性能.
Xiang等人[10]在纯钛表面制备出CoCrFeNiNbx (x = 0,1)涂层,添加Nb元素之前涂层相结构为BCC相和Cr2Ti型Laves相.添加Nb后涂层中又出现了Cr2Nb型Laves相,涂层硬度达到1008 HV,是基体的8倍多.Cheng等人[11]利用等离子转移电弧法制备了CoNiCuFeCrNb涂层,涂层中包含FCC相和(CoCr)Nb型的Laves相,研究发现,在相同的磨损环境下,加入Nb元素可以使涂层的耐磨性能提高1.5倍左右.
为探究Nb元素对高熵合金涂层组织与力学性能的影响,设计4组Nb元素含量,制备CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby(y = 0.25,0.5,0.75,1.0),分析Nb元素对熔覆涂层组织结构、硬度和耐磨性的影响. 为提升高熵合金的耐磨性能与硬度提供试验参数.
1. 试验方法
熔覆粉末的化学成分见表1.在XQM-2型的立式行星球磨机中进行球磨,采用干磨的方法,球磨时间为90 min,得到混合均匀的预制涂层粉末.把混合好的合金粉末在干燥箱中烘干60 min,烘干温度为80 ℃.
表 1 熔覆合金粉末成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Compositions of cladding alloy powderCoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby Cr Fe Co Ni Ti Nb CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.25 18.12 19.46 20.53 20.45 13.34 8.10 CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.5 16.76 18.00 19.00 18.92 12.34 14.98 CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75 15.59 16.75 17.67 17.60 11.49 20.90 CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb1.0 14.58 15.66 16.52 16.45 10.74 26.05 试验采用预制粉末法,将球磨后的合金粉末均匀涂覆在Q235母材表面.利用YLS-3000型激光器制备CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby(y = 0.25,0.5,0.75,1.0)高熵合金复合涂层,其工艺参数如表2所示.
表 2 制备涂层工艺参数Table 2. Preparation of coating process parameters激光功率 P/W 光斑直径 d/mm 扫描速度 v/(mm·s−1) 1 600 3 6 对熔覆好的试样进行切割,尺寸为10 mm × 10 mm × 10 mm,将熔覆层截面打磨抛光后,使用氢氟酸与硝酸的混合溶液进行腐蚀.利用Zeiss Lab.A1型光学显微镜(optical microscope, OM)、CamScan2600FE型扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope, SEM)分析涂层微观组织;采用DX-2700B型X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffractomer, XRD)分析熔覆涂层的相结构;利用HVS-1000型显微维氏硬度计进行硬度试验,试验力为2.942 N,加载10 s后卸载,多次测量取其平均值;采用MMW-1型摩擦磨损试验机,加载载荷为100 N,试验加载时间为40 min,对试样的耐磨性进行测试.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 熔覆层组织结构
图1为在Q235表面制备的CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75高熵合金复合熔覆层的形貌,其中图1(a)是CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75的涂层截面宏观形貌,图1(b)是熔合线处的微观组织.
激光熔覆具有快速加热、快速冷却的特点,形成的微观组织晶粒细小,并且晶粒呈现规律性生长趋势.在与基体的结合处同样有一条亮白色的线条,说明与基体有良好的冶金结合.在熔合线处的温度梯度较大,冷却速度较小,导致过冷度较大,所以促进了平面晶的形成.通常导热方向与涂层和基体之间的界面垂直,所以底层的胞状晶与界面相垂直,并向内延伸生长[12].
2.2 熔覆层微观组织
图2是CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby(y = 0.25,0.5,0.75,1.0)高熵合金涂层在光学显微镜下的微观组织.其中当Nb元素含量为0.25时,晶粒尺寸较大,呈现典型的树枝晶结构,枝晶的主干相对较长,如图2(a)所示.随着Nb元素含量的增加可以看出涂层微观组织发生明显变化,组织尺寸逐渐减小,如图2(b)~(d)所示. Nb元素含量增加到0.75时,从图2(e)可以看出高熵合金涂层中的枝晶组织发生了明显的细化.这种现象可能是由于Nb元素含量的增加促使了合金的晶格发生了严重的畸变,使体系的能量增加,进而促进了形核的速率,合金的形核数增多,合金的晶粒更为细小[13].在该体系的合金中,Nb元素的熔点相对较高,所以在凝固过程中,会增加合金过冷度,从而促使枝晶快速生长,使枝晶细化. 因为随着成分过冷的进行,具有较大原子半径的Nb元素与其他原子的固溶度变小,更易聚集到固/液界面前沿,随着Nb含量的持续增加,晶粒生长受到阻碍,使树枝晶成为向各方向均匀生长的细小的等轴晶.
对CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75高熵合金涂层的微观组织成分进行分析,图3显示了CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75高熵合金涂层的SEM结果和能谱图.表3为CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75涂层中不同位置的元素含量分析的结果,可以发现,A点处富含Fe和Nb元素,B点处富含Fe,Ti,Nb元素,C点处Fe含量较多,Co,Cr,Ni,Ti,Nb分布较为均匀.B点处可以推断出是富含Ti,Nb的Laves相.这是由于Ti,Nb元素的原子半径与其他元素相比是相对较大的,使体系的晶格畸变严重,能量的提高使晶体结构发生改变,所以固溶能力有限的体系中Ti,Nb元素有一部分能被溶解在到高熵合金涂层中,由于高熵合金本身具有迟滞扩散效应,Ti,Nb元素就容易被排斥到枝晶间的区域,从而其余的Ti,Nb元素则形成了富含Ti,Nb的Laves相[14].
表 3 能谱分析结果(质量分数,%)Table 3. Results of energy spectrum analysis测量点 Co Cr Fe Ni Ti Nb A 9.42 7.77 42.94 6.32 4.77 28.78 B 7.78 7.68 35.19 7.57 22.04 19.74 C 10.73 10.98 51.56 11.32 4.86 10.55 2.3 X射线衍射试验
图4为不同Nb元素含量下的CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby高熵合金复合涂层的XRD.通过对XRD的结果分析可知,高熵合金涂层的相结构是由BCC相、FCC相和Laves相组成的.能够看出随着Nb元素含量的增加,高熵合金涂层中产生了新的金属间化合物Laves相.由于高熵合金具有高熵效应使其更容易形成固溶体相,当Nb元素含量为0.25时,涂层以BCC相为主,固溶体相较多,Laves相较少.随着Nb元素含量的增加,Laves相略微增多,FCC固溶体相先略微增加后减小,而BCC固溶体相强逐渐增多.可以判断出涂层中Nb元素含量的增加,促进了Laves相的形成.通过结合Jade软件确定其为Fe2(Ti,Nb)结构的Laves相.结合能谱分析可知,所添加的Nb元素主要以化合物的形态存在于高熵合金的涂层组织中,少部分固溶到高熵合金涂层中.
2.4 硬度试验
图5为CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby(y = 0.25,0.5,0.75,1.0)高熵合金涂层的显微硬度,从涂层到基体按一定间隔进行测量的数据.可以看出,各涂层的硬度呈降低的趋势.相较于基体,涂层的硬度有显著提高.随着Nb含量的增加,涂层硬度先升高后降低.在CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75的涂层中,硬度最高可达710 HV,是基体硬度的4倍多.
结合涂层的微观组织尺寸可以看出,因为涂层微观组织受到热源和激光扰动的缘故,产生了细晶强化的作用,同时受成分过冷的影响,涂层内部组织结构的变化对硬度有一定的影响,又由于添加适量的Nb元素对显微硬度的提升有促进作用[15].
Nb原子在与原本其他元素发生置换时会导致晶格发生扭曲,产生严重的晶格畸变,晶格之间转变为互相挤压的状态,因此可能会产生位错交割,进一步阻碍了位错的滑移,从而产生固溶强化的效果[16].其次,随着Nb元素含量的增加,在枝晶间Nb元素能促进合金中Laves相的形成,在合金体系中析出的Laves相与位错起到第二相强化的作用[17].因此,Nb元素含量的增加能提高涂层的显微硬度是在于细晶强化、固溶强化与第二相强化的共同作用所产生的结果.
2.5 耐磨性试验
从图6中可以看出,随着Nb元素含量的增大,涂层的磨损量先降低后升高.其中当Nb元素含量为0.75时,高熵合金涂层磨损量最小,此时Nb元素的磨损失重为3.2 mg.
通过对各组分的高熵合金复合涂层进行摩擦磨损试验,得到光学显微镜下不同Nb元素含量的涂层磨损形貌和扫描电镜下的磨痕形貌,分别如图7和图8所示.观察磨损形貌图可知,不同Nb元素含量下的磨损形貌都有或深或浅的犁沟,同时由于在摩擦副表面产生的相对滑动,使其在粘着效应所形成的粘着结点处发生了剪切和断裂,从而形成了这样的磨损形貌.Nb元素含量为0.25与0.5时,涂层磨损形式主要为磨粒磨损和粘着磨损.其中CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.25的磨损表面存在严重的剥落,产生了更多的磨损碎片. CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nb0.5涂层具有深浅不一的犁沟,涂层磨损表面的沟槽分布密集,形成的凹槽深而宽.同时在磨损形貌中也可以看出在沟的边缘发生了严重的塑性变形.在磨损的过程中,由于涂层中存在硬质Laves相,在对磨环和涂层表面之间反复的摩擦,磨损表面产生了犁沟,对磨环与涂层表面的往复运动使其接触面温度逐渐升高,致使磨损表面发生氧化.当Nb元素含量为0.75时,高熵合金涂层的犁沟更浅更均匀且涂层的硬度相对较高,抑制了摩擦副对涂层表面的切割,磨损量相对较小.当Nb元素的含量为1.0时,此时涂层中硬质相较多,致使涂层表面产生较多的犁沟,高熵合金涂层表面因犁沟的增加而产生了更多的剥落,使磨损加剧.因此,磨损加剧的原因一方面在摩擦磨损试验机上通过施加设定的载荷,摩擦副中的微突将硬的颗粒或凸出物压入涂层并冲刷摩擦表面.而试验中相对滑动的硬质颗粒在涂层表面产生了犁沟效应,使得磨损表面出现了磨痕[18];另一方面,由于硬质相颗粒脆性大的缘故,摩擦副和涂层之间持续的相对运动和反复切应力作用下导致沟槽两边的材料被破坏,更容易从涂层表面脱落.结合不同Nb元素含量涂层扫描电镜下的磨痕形貌如图8所示,从图中可以看出不同成分下的高熵合金涂层其磨损表面有着明显的犁沟和磨粒磨屑,表现出了较为严重的磨粒磨损和粘着磨损.随着复合涂层中Nb元素含量的增加,产生更多的高硬度Laves相,使涂层耐磨性提升.
以上试验结果表明,Nb元素含量增多时,使复合涂层中析出金属间化合物等硬质相,可以阻止犁削切削过程的进行,进而提高了涂层的耐磨性能.当Nb含量为0.75时,涂层的硬度最高,磨痕最轻,耐磨性最好.
图9所示为CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby高熵合金涂层的摩擦系数.Nb元素含量为0.25,0.5,0.75和1.0的高熵合金涂层的平均摩擦系数分别为0.563,0.497,0.363和0.455.此外,随着Nb元素含量的增加,平均摩擦系数先降低后增加.这也与硬度的变化趋势相似,随着硬度的提高,耐磨性也随之增强.其中CoCeFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75高熵合金涂层的显微硬度最高,随着加载过程的进行摩擦系数曲线也更为平滑.
3. 结论
(1)利用激光熔覆技术制备CoCrFeNiTi0.8Nby高熵合金涂层. 涂层由BCC相、FCC相和Laves相构成,其中Laves相为Fe2(Nb,Ti)型;微观组织主要受过冷度的影响,同时随着Nb元素含量的增加促使合金的晶格发生畸变,促进了形核率,使得组织的晶粒更为细小;
(2)随着Nb元素含量的增加,熔覆层硬度先增加后降低,CoCeFeNiTi0.8Nb0.75涂层的硬度最高,可达到710 HV,这是细晶强化、固溶强化与第二相强化的共同作用所产生的结果;耐磨性随着Nb元素含量的增加,呈现出先增加后降低的趋势,磨损机理主要为磨粒磨损和粘着磨损,当Nb元素含量为0.75时涂层的耐磨性最好.
-
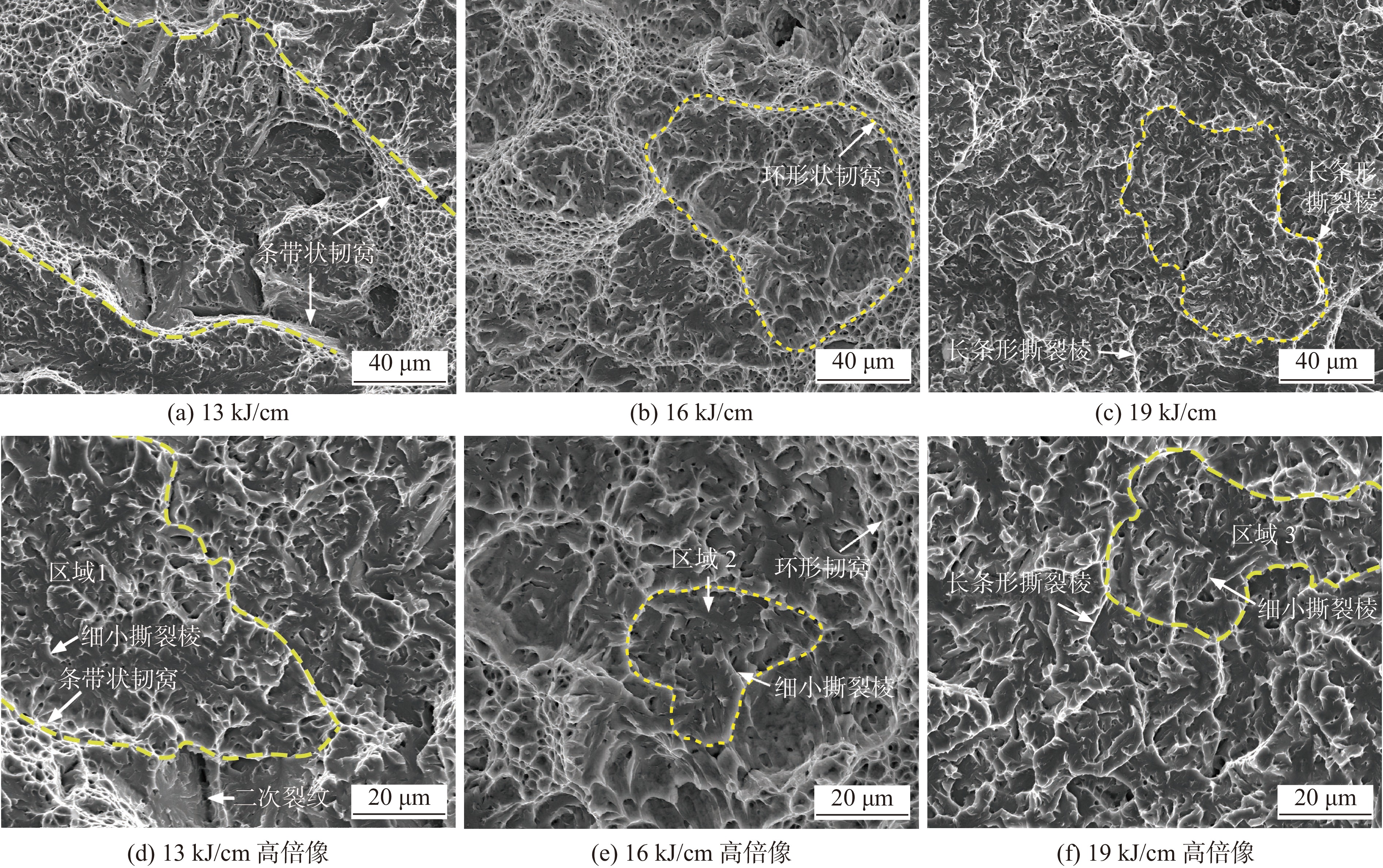
图 9 焊缝金属冲击断口中微孔及微裂纹SEM像
Figure 9. SEM of micro-voids and micro-cracks in impact fracture of weld metals. (a) 13 kJ/cm; (b) circle region in figure 9a; (c) another observation region of 13 kJ/cm; (d) circle region in figure 9(c); (e) secondary crack of 13 kJ/cm; (f) 16 kJ/cm; (g) elliptic region in figure 9(f); (h) circle region in figure 9(f); (i) backscattered electron image corresponding to figure 9(h); (j) 19 kJ/cm; (k) elliptic region in figure 9(j); (l) backscattered electron image corresponding to figure 9(k)
表 1 对接接头焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Welding parameters of butt joints
类型 道间温度 T/℃ 焊接电流
I/A电弧电压
U/V焊接速度v/(cm·min−1) 焊接热输入E/(kJ·cm−1) 实测值 平均值 实测值 平均值 对接接头No.1 104 ~ 120 114 165 ~ 171 22 ~ 32 21 11 ~ 16 13 对接接头No.2 102 ~ 117 108 164 ~ 167 24 ~ 28 16 14 ~ 18 16 对接接头No.3 100 ~ 119 112 169 ~ 173 23 ~ 32 15 16 ~ 21 19 熔敷金属 101 ~ 118 111 166 ~ 168 24 ~ 28 15 12 ~ 21 17 表 2 熔敷金属的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical compositions of deposited metal
C Si Mn + Ni + Cr Mo Ti等 P S 0.034 0.20 4.99 0.40 微量 0.007 9 0.004 8 -
[1] 栗卓新, 苏小虎, 李红, 等. 690 MPa级以上高强钢焊接熔敷金属微观组织及其联合贝氏体的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2019, 38(12): 1169 − 1176. Li Zhuoxin, Su Xiaohu, Li Hong, et al. Research progress on microstructure and coalesced bainite of welded deposited metal to high-strength steel with tensile strength above 690 MPa[J]. Materials China, 2019, 38(12): 1169 − 1176.
[2] 彭云, 宋亮, 赵琳, 等. 先进钢铁材料焊接性研究进展[J]. 金属学报, 2020, 56(4): 601 − 618. Peng Yun, Song Liang, Zhao Lin, et al. Research status of weldability of advanced steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 56(4): 601 − 618.
[3] 曹志龙, 朱浩, 安同邦, 等. 1000 MPa级高强钢熔敷金属强韧化机理分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(7): 116 − 122. Cao Zhilong, Zhu Hao, An Tongbang, et al. Study on mechanism of strengthening and toughening of deposited metal of 1000 MPa grade high strength steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(7): 116 − 122.
[4] 曾道平, 安同邦, 郑韶先, 等. 热输入对船用440 MPa级低合金高强度钢焊缝组织及性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(8): 74 − 82. Zeng Daoping, An Tongbang, Zheng Shaoxian, et al. Effect of heat input on microstructure and properties of weld seam of marine 440 MPa grade HSLA steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(8): 74 − 82.
[5] 安同邦, 郑庆, 张永林, 等. 1300 MPa级低合金高强钢SH-CCT曲线及冷裂敏感性分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(9): 75 − 81. An Tongbang, Zheng Qing, Zhang Yonglin, et al. SH-CCT diagram and cold cracking sensitivity of a 1300 MPa grade high strength low alloy steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(9): 75 − 81.
[6] Dhua S K, Mukerjee D, Sarma D S. Weldability and microstructural aspects of shielded metal arc welded HSLA-100 steel plates[J]. ISIJ International, 2002, 42(3): 290 − 298. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.42.290
[7] Lis A K, Lis J, Jeziorski L. Advanced ultra-low carbon bainitic steels with high toughness[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1997, 64(1-3): 255 − 266. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(96)02575-7
[8] Christein J P, Warren J L. Implementation of HSLA-100 steel in aircraft carrier Construction-CVN 74[J]. Journal of Ship Production, 1995, 11(2): 97 − 101. doi: 10.5957/jsp.1995.11.2.97
[9] Evans G M. Effects of silicon on the microstructure and properties of C-Mn all-weld-metal deposits[J]. Metal Construction, 1986, 18(7): 438r − 444r.
[10] Kang B Y, Kim H J, Hwang S K. Effect of Mn and Ni on the variation of the microstructure and mechanical properties of low-carbon weld metals[J]. ISIJ International, 2000, 40(12): 1237 − 1245. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.40.1237
[11] Zhang Z, Farrar R A. Influence of Mn and Ni on the microstructure and toughness of C-Mn-Ni weld metals[J]. Welding Journal, 1997, 76(5): 183s − 196s.
[12] Bhole S D, Nemade J B, Collins L, et al. Effect of nickel and molybdenum additions on weld metal toughness in a submerged arc welded HSLA line-pipe steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006, 173(1): 92 − 100. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.10.028
[13] 王学林, 董利明, 杨玮玮, 等. Mn/Ni/Mo配比对K65管线钢焊缝金属组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2016, 52(6): 649 − 660. Wang Xuelin, Dong Liming, Yang Weiwei, et al. Effect of Mn, Ni, Mo proportion on microstructure and mechanical properties of weld metal of K65 pipeline steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2016, 52(6): 649 − 660.
[14] 娄宇航, 肖红军, 彭云, 等. 690 MPa级低合金高强钢焊接接头组织性能[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2012, 20(2): 101 − 107. Lou Yuhang, Xiao Hongjun, Peng Yun, et al. Study on microstructure and properties of welded joints of a 690 MPa grade HSLA steel[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2012, 20(2): 101 − 107.
[15] Lan L, Kong X, Qiu C. Characterization of coarse bainite transformation in low carbon steel during simulated welding thermal cycles[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015, 105: 95 − 103. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2015.05.010
[16] Babu S S. The mechanism of acicular ferrite in weld deposits[J]. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science, 2004, 8(3-4): 267 − 278. doi: 10.1016/j.cossms.2004.10.001
[17] Terasaki H, Yamada T, Komizo Y. In-situ observation of nucleation and growth of acicular ferrite in weld metal[J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 2007, 93(1): 27 − 32. doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane.93.27
[18] 王学林, 李学达, 尚成嘉. 高强度管线钢焊接热影响区显微组织精细表征[J]. 焊管, 2019, 42(7): 26 − 38. Wang Xuelin, Li Xueda, Shang Chengjia. Fine characterization of high strength pipeline steel welding HAZ microstructure[J]. Welded Pipe and Tube, 2019, 42(7): 26 − 38.
[19] 杨宇龙, 贾潇, 朱伏先, 等. 大线能量焊接用钢粗晶热影响区针状铁素体形成过程控制技术的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(5): 145 − 155. Yang Yulong, Jia Xiao, Zhu Fuxian, et al. Research progeress on control technology of acicular ferrite in CGHAZ for large heat-input welding steels[J]. Materials Reports, 2022, 36(5): 145 − 155.
[20] 张德勤, 云绍辉, 田志凌, 等. 微合金钢焊缝组织中针状铁素体形核与长大驱动力[J]. 焊接学报, 2005, 26(1): 12 − 16. Zhang Deqin, Yun Shaohui, Tian Zhiling, et al. Driving force of acicular ferrite nucleation and growth in weld metal of microalloyed steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2005, 26(1): 12 − 16.
[21] 钟群鹏, 张峥, 王守凯, 等. 碳钢韧脆转变温度与组织参量和解理断裂单元尺寸的关系[J]. 钢铁, 1993, 28(10): 49 − 64. Zhong Qunpeng, Zhang Zheng, Wang Shoukai, et al. Relation of ductile-brittle transition temperature to microstructure parameter and size of cleavage fracture element[J]. Iron and Steel, 1993, 28(10): 49 − 64.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 沈虎,李先芬,叶俊洋,张雅婷,华鹏,刘大双. SiC-Ni60涂层中添加nano-Cu包覆MoS_2对其组织和摩擦磨损性能的影响. 焊接学报. 2024(09): 69-75 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 马凯,冯力,赵燕春,刘建军. 激光重熔合成FeCrAlCu(Ni, Co)高熵合金涂层组织与耐磨性能(英文). 稀有金属材料与工程. 2024(10): 2747-2754 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: