Interfacial characterization and properties of Ti6Al4V/NiTi laser additive manufactured functional gradient materials
-
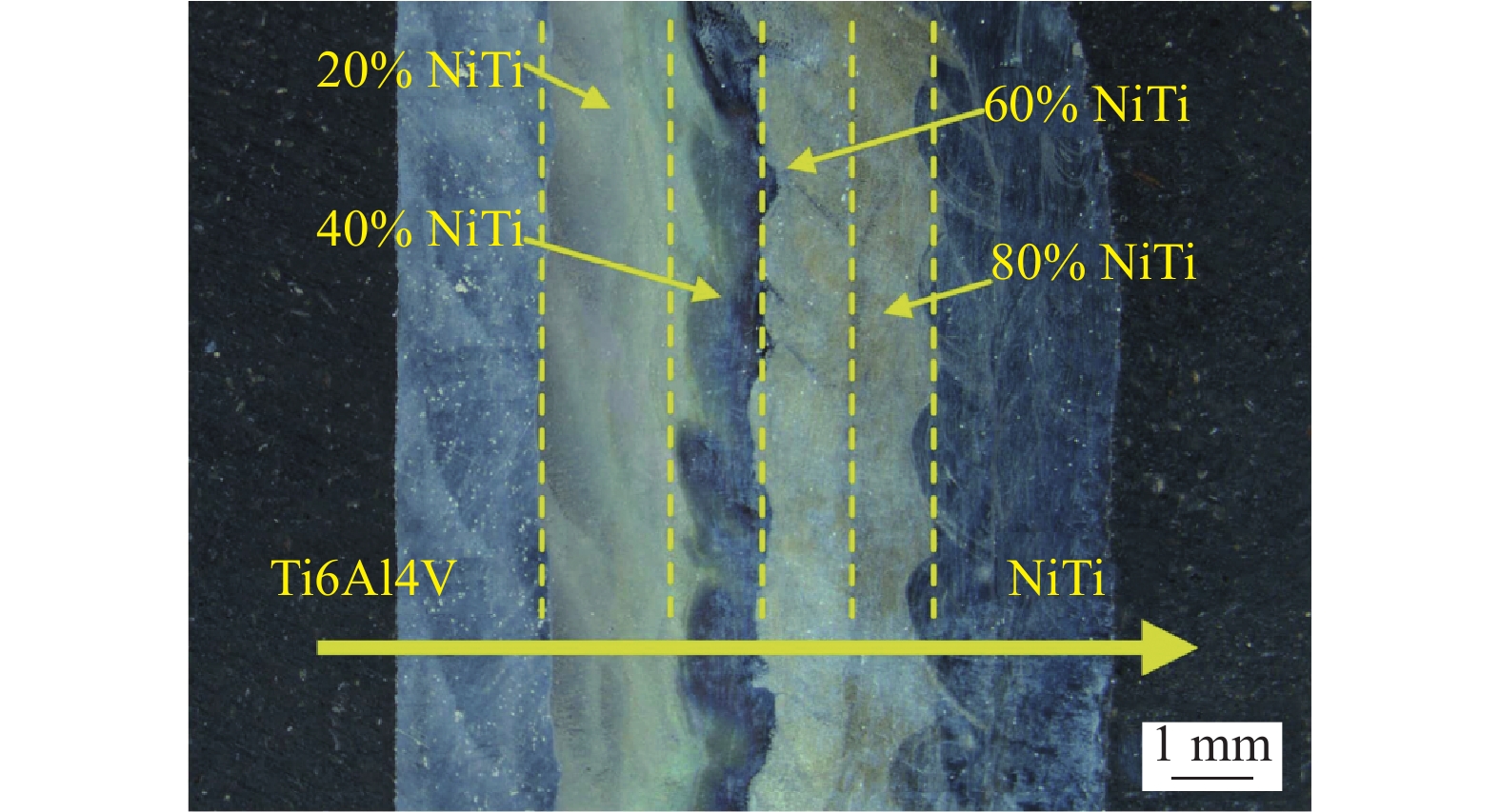
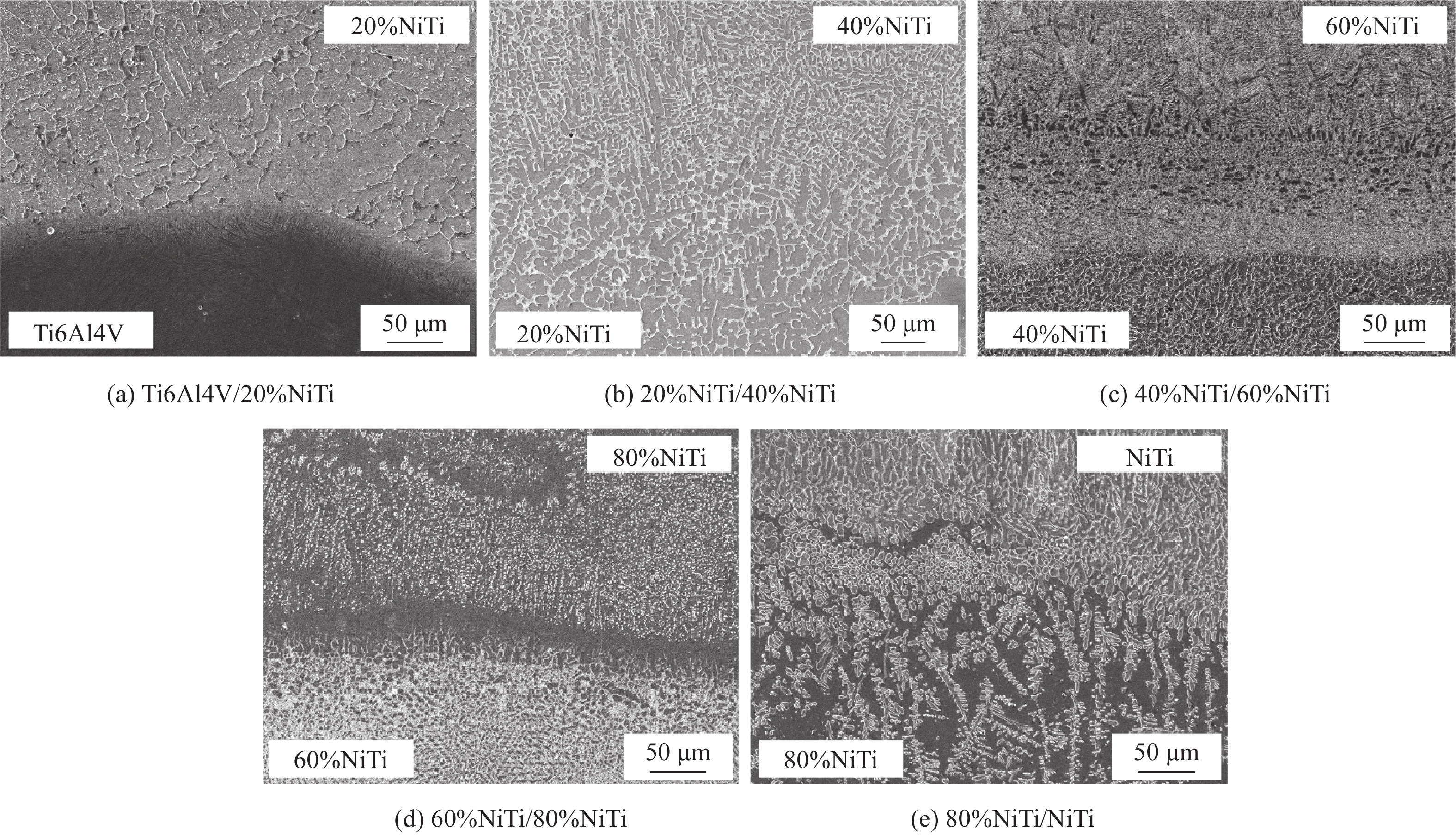
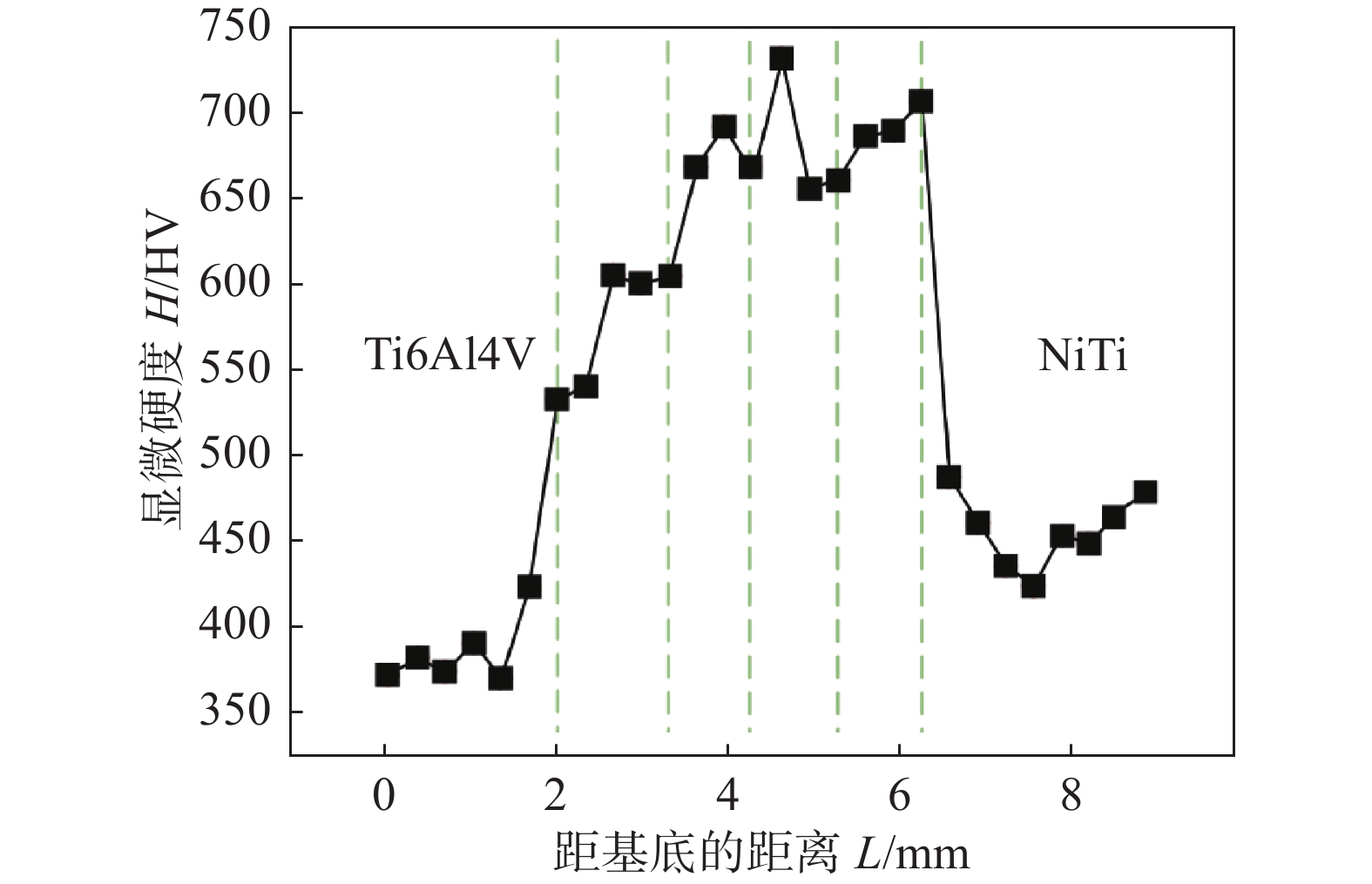
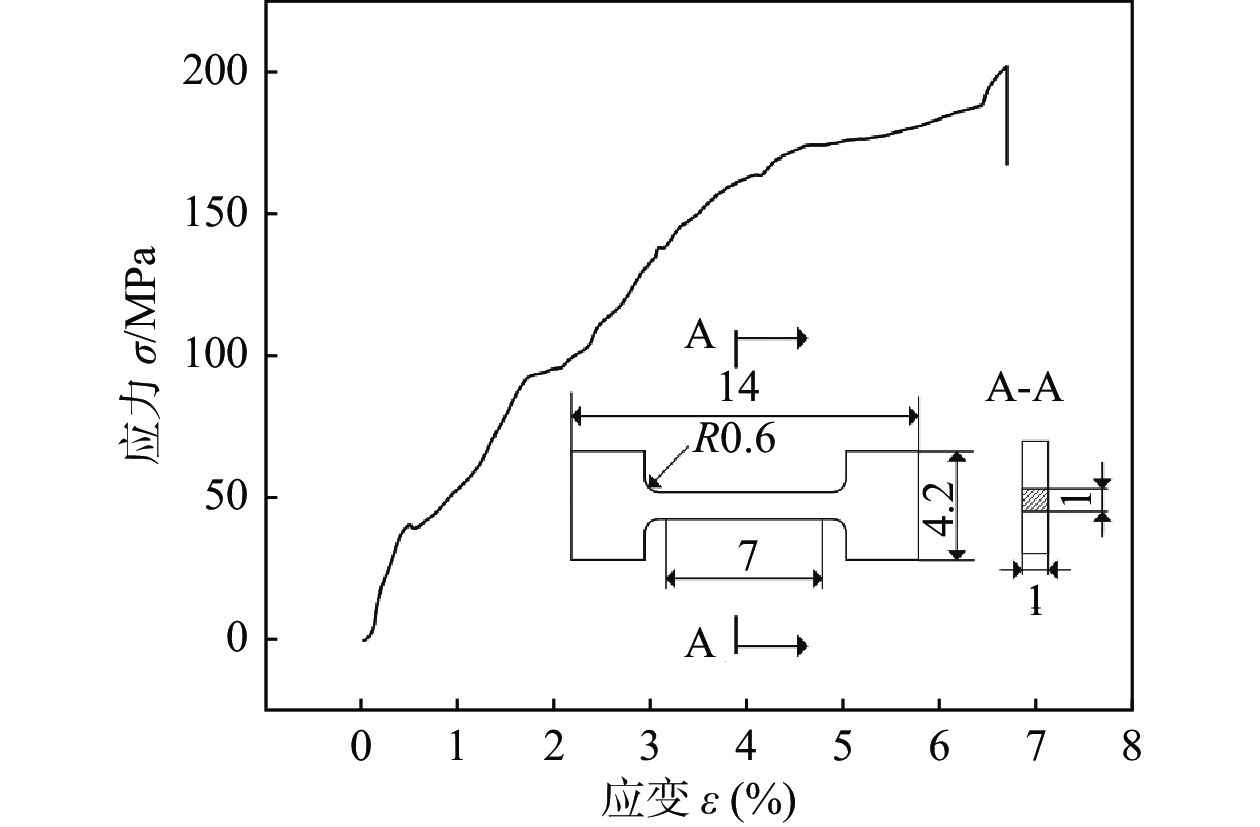
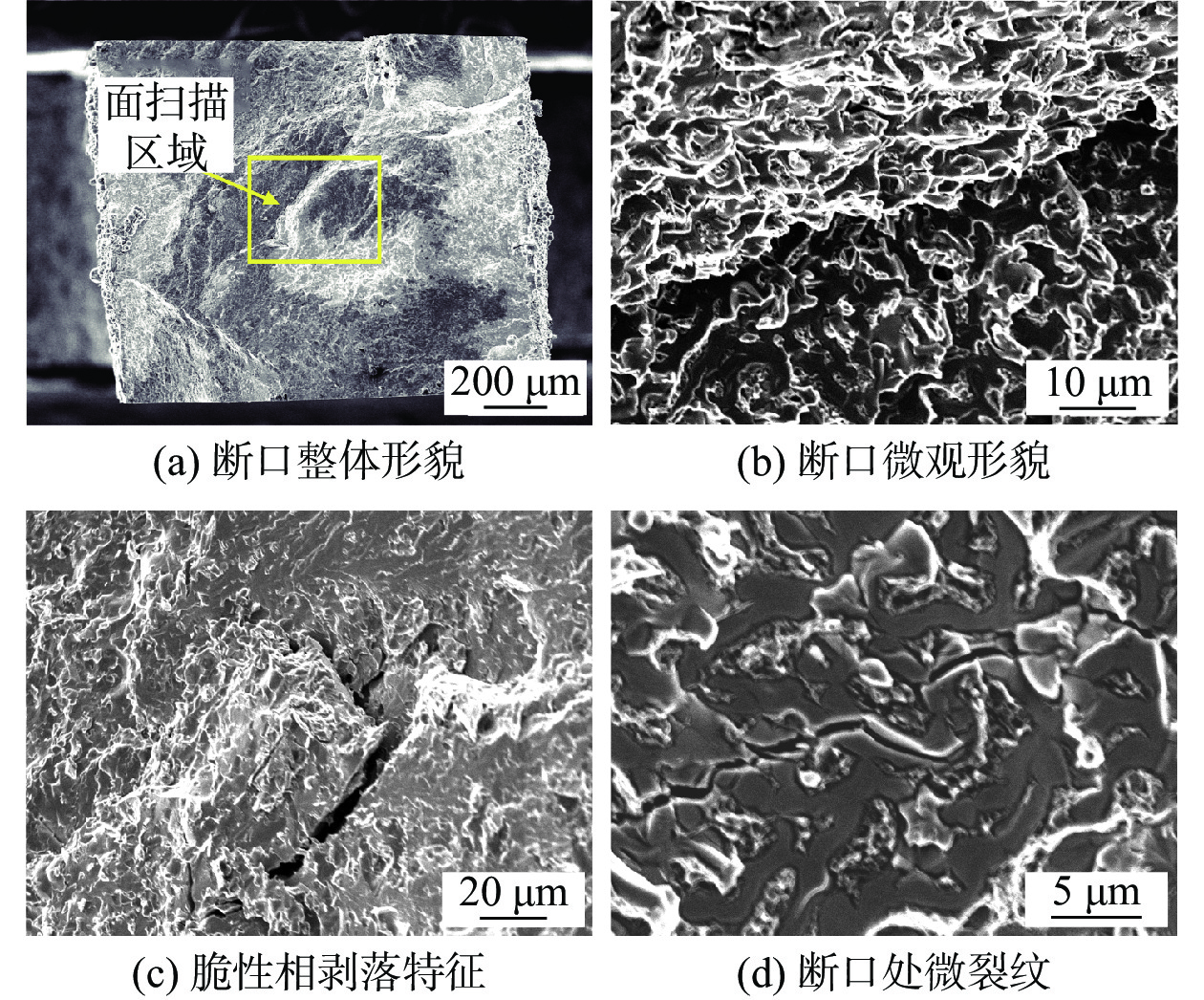
摘要: 采用激光增材制造技术制备了组织致密且无缺陷的Ti6Al4V/NiTi仿生功能梯度材料 (bionic function graded materials, BFGM),并对其界面微观结构、析出相特征和力学性能进行了研究. 结果表明,Ti6Al4V/NiTi BFGM呈现由多种晶粒形貌和不规则异常共晶组织组成的非均匀组织,主要为富钛和富镍的固溶体以及(Ti, Ni)化合物. 随着 NiTi合金含量增加,不同沉积层中析出相的数量和形态发生了显著变化. BFGM的显微结构发生了一系列转变:α + β双相组织→柱状晶 + 不规则共晶结构→柱状晶→等轴晶→等轴晶 + 柱状晶. 凝固过程中的相聚集、分离和偏析现象严重影响BFGM的力学性能,BFGM最大显微硬度为730.9 HV,归因于脆性Ti2Ni相的存在. BFGM的抗拉强度为202 MPa,断后伸长率为6.5%,显著高于直接连接的Ti6Al4V/NiTi异种材料. 拉伸断口具有脆性断裂特征,多个次级裂纹沿晶扩展.Abstract: Ti6Al4V/NiTi bionic function graded materials (BFGM) with dense and defect-free microstucture were prepared by laser additive manufacturing technology, and their interfacial microstructure, precipitation phase characteristics and mechanical properties were investigated. The results show that the Ti6Al4V/NiTi BFGM exhibits a non-uniform microstructure consisting of various grain morphologies and irregular and abnormal eutectic tissues, which are mainly titanium-rich and nickel-rich solid solutions and (Ti, Ni) compounds. As the content of NiTi alloy increases, the number and morphology of precipitated phases in different deposition layers change significantly. The microstructure of BFGM undergoes a series of transformations: α + β biphasic microstructure → columnar crystals + irregular eutectic structure → columnar crystals → equiaxial crystals → equiaxial crystals + columnar crystals. Phase aggregation, separation and segregation during solidification have significantly affected the mechanical properties of BFGM. The maximum microhardness of BFGM is 730.9 HV, which is attributed to the presence of brittle Ti2Ni phase. The tensile strength is 202 MPa and the elongation is 6.5%, which is significantly higher than that of the directly connected Ti6Al4V/NiTi heterogeneous material. The tensile fracture is characterized by brittle fracture with multiple secondary cracks extending along the crystal.
-
-
表 1 Ti6Al4V和NiTi粉末的化学成分 (质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Ti6Al4V and NiTi powders
材料 Ni Al V Fe C O N H Ti Ti6Al4V — 5.8300 3.7800 0.0350 0.0160 0.0830 0.0210 0.0031 余量 NiTi 55.12 — — ≤0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 — 余量 表 2 试验工艺参数
Table 2 Experimental process parameters
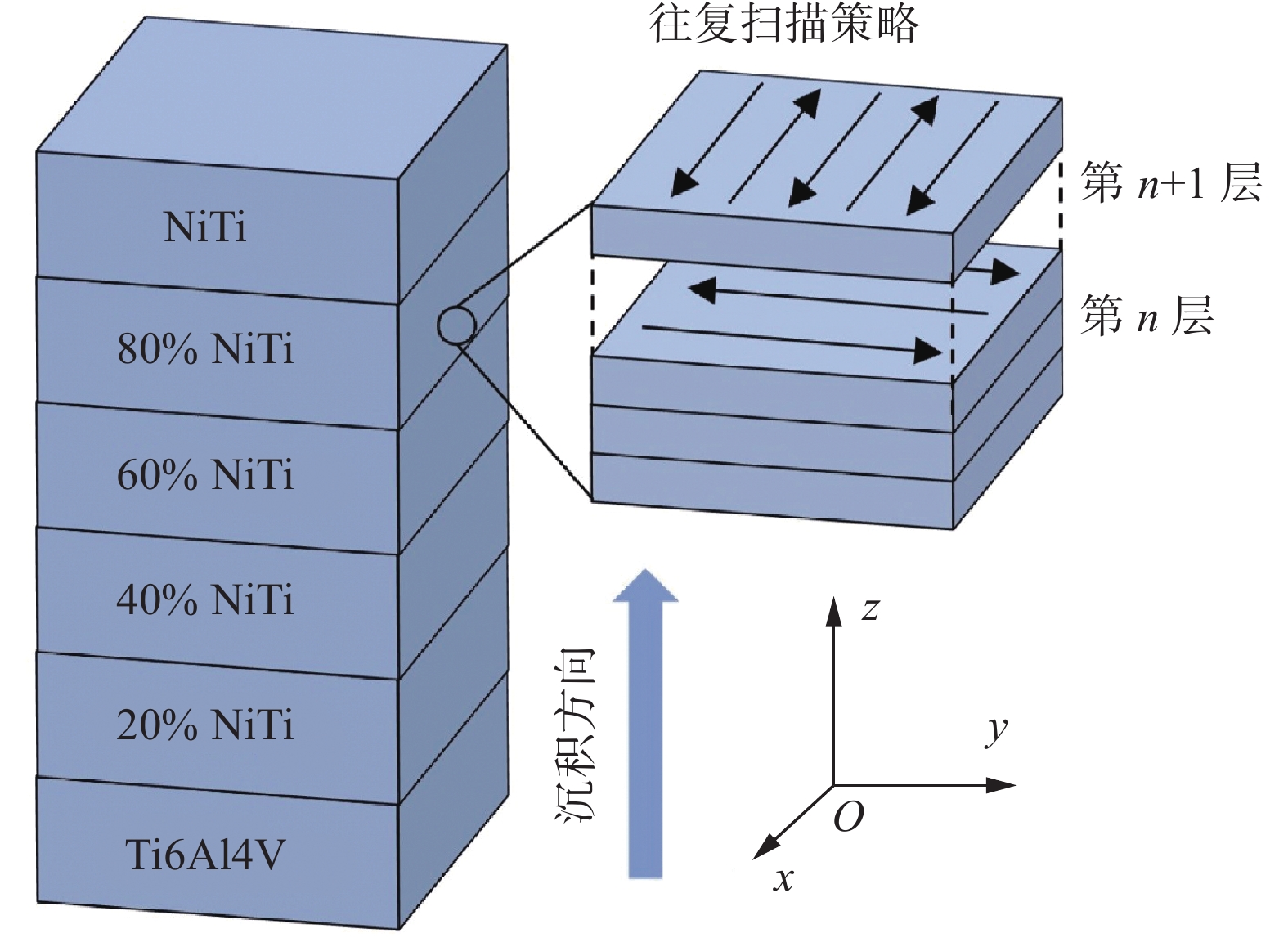
沉积层数n/层 Ti6Al4V体积分数 V1(%) NiTi体积分数 V2(%) 激光功率 P/W 扫描速度 v/(mm·s−1) 设定层厚 δ/mm 4 100 0 800 350 0.5 1 80 20 750 250 1.4 1 60 40 700 250 1.0 1 40 60 600 350 1.1 1 20 80 450 350 1.0 4 0 100 400 350 0.8 表 3 图 2 中 EDS 点扫描分析结果 (原子分数,%)
Table 3 EDS point scanning analysis results in Fig.2
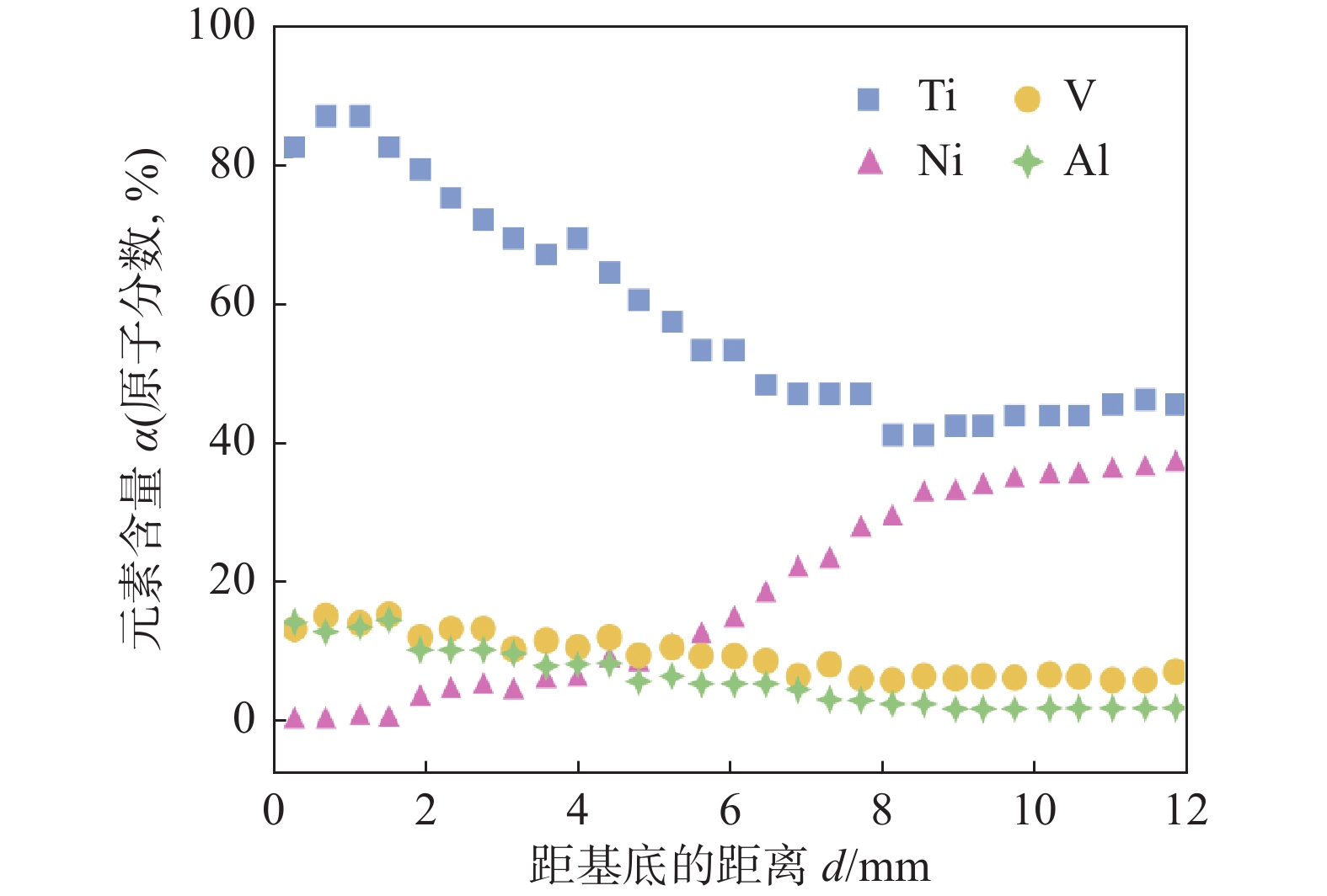
位置 Ti Ni Al V 1 87.56 0.12 8.74 3.58 2 82.13 11.24 3.83 2.80 3 72.43 23.85 2.26 1.46 4 73.26 23.29 2.20 1.25 5 67.53 28.85 2.36 1.26 6 67.24 28.61 2.71 1.44 7 53.78 44.65 0.55 1.02 8 61.24 36.28 1.44 1.04 9 54.08 45.92 — — -
[1] 董鹏, 梁晓康, 赵衍华, 等. 激光增材制造技术在航天构件整体化轻量化制造中的应用现状与展望[J]. 航天制造技术, 2018, 207(1): 7 − 11. Dong Peng, Liang Xiaokang, Zhao Yanhua, et al. Research status of laser additive manufacturing in integrity and lightweight[J]. Aerospace Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 207(1): 7 − 11.
[2] 邹吉鹏, 陈健, 黄瑞生, 等. 厚板Ti6Al4V合金低真空激光焊接接头组织及力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(8): 54 − 60. Zou Jipeng, Chen Jian, Huang Ruisheng, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of thick Ti6Al4V alloy welded joint by low vacuum laser welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(8): 54 − 60.
[3] 黄雄荣, 邵若男, 朱淋淋. NiTi合金与增材制造—下一代航空航天轴承用材料[J]. 热处理, 2022, 37(6): 1 − 4. Huang Xiongrong, Shao Ruonan, Zhu Linlin. NiTi alloys and additive manufacturing—materials for next generation aerospace bearings[J]. Heat Treatment, 2022, 37(6): 1 − 4.
[4] Oliveira J P, Panton B, Zeng Z, et al. Laser joining of NiTi to Ti6Al4V using a niobium interlayer[J]. Acta Materialia, 2016, 105: 9 − 15.
[5] Cavaleiro A J, Ramos A S, Fernandes F M, et al. Follow-up structural evolution of Ni/Ti reactive nano and microlayers during diffusion bonding of NiTi to Ti6Al4V in a synchrotron beamline[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2020, 275: 116354. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2019.116354
[6] Deng H, Chen Y, Jia Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of dissimilar NiTi/Ti6Al4V joints via back-heating assisted friction stir welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 64: 379 − 391. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.01.024
[7] Xie J, Chen Y, Yin L, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of ultrasonic spot welding TiNi/Ti6Al4V dissimilar materials using pure Al coating[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2021, 64: 473 − 480. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2021.02.009
[8] Zhong Y, Xie J, Chen Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of micro laser welding NiTiNb/Ti6Al4V dissimilar alloys lap joints with nickel interlayer[J]. Materials Letters, 2022, 306: 130896. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2021.130896
[9] Miranda R M, Assuncao E, Silva R J, et al. Fiber laser welding of NiTi to Ti-6Al-4V[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2015, 81: 1533 − 1538. doi: 10.1007/s00170-015-7307-8
[10] 崔雪, 张松, 张春华, 等. 高性能梯度功能材料激光增材制造研究现状及展望[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(9): 13 − 23. Cui Xue, Zhang Song, Zhang Chunhua, et al. Research status and prospect of laser additive manufacturing technology for high performance gradient functional materials[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2020, 48(9): 13 − 23.
[11] 白玉超, 王迪, 李朝将. 激光定向能量沉积制造A131 EH36/AISI 1045双金属结构性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(14): 244 − 258. Bai Yuchao, Wang Di, Li Chaojiang. Research on A131 EH36/AISI 1045 bimetallic material fabricated by laser directed energy deposition[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(14): 244 − 258.
[12] 张敏, 王新宝, 王浩军, 等. 激光熔覆TC4/Inconel 625/316L不锈钢梯度材料组织与性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(7): 16 − 23. Zhang Min, Wang Xinbao, Wang Haojun, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladding TC4/Inconel 625/316L stainless steel gradient material[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(7): 16 − 23.
[13] 王佳杰, 宋晓国, 武鹏博, 等. 铝/钛异种金属激光/激光-CMT复合熔钎焊工艺及其组织与力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2023, 44(2): 54 − 60. Wang Jiajie, Song Xiaoguo, Wu Pengbo, et al. Process, microstructures and mechanical properties of Al/Ti dissimilar metals with laser/laser-CMT hybrid welding-brazing[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2023, 44(2): 54 − 60.
[14] Lin X, Yue T M, Yang H O, et al. Microstructure and phase evolution in laser rapid forming of a functionally graded Ti-Rene88DT alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2006, 54(7): 1901 − 1915. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2005.12.019
[15] Stallard J C, Wheatcroft L, Booth S G, et al. Mechanical properties of cathode materials for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Joule, 2022, 6(5): 984 − 1007. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2022.04.001
[16] Lu H, Wu L, Wei H, et al. Microstructural evolution and tensile property enhancement of remanufactured Ti6Al4V using hybrid manufacturing of laser directed energy deposition with laser shock peening[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2022, 55: 102877. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2022.102877
[17] Zheng D, Li R, Yuan T, et al. Microstructure and mechanical property of additively manufactured NiTi alloys: A comparison between selective laser melting and directed energy deposition[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2021, 28(4): 1028 − 1042. doi: 10.1007/s11771-021-4677-y
[18] Xu G, Wu L, Su Y, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of directed energy deposited 316L/Ti6Al4V functionally graded materials via constant/gradient power[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2022, 839: 142870.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 刘景城,叶晗哲,徐贵峰,娄昊,耿海滨. 不同基板热沉的铝合金电弧增材控形. 福州大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(01): 91-97 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 邢松龄,李充,周海鹏,陈高强,史清宇. 铝合金型材搅拌摩擦焊无减薄接头组织和性能. 焊接学报. 2023(11): 124-128+136 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 姜淑馨,李峰光. 丝材电弧增材制造技术的研究与应用. 铸造技术. 2022(05): 369-374 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 石玗,朱珍文,张刚,李璐鹏. 金属电弧增材成形控制关键技术及研究现状. 材料导报. 2022(12): 135-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王轲,张元彬. ER5356铝合金双脉冲电弧增材制造成型工艺及组织研究. 热加工工艺. 2021(09): 20-23+28 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王磊磊,张占辉,徐得伟,薛家祥,曾敏. 双脉冲电弧增材制造数值模拟与晶粒细化机理. 焊接学报. 2019(04): 137-140+147+167 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 张炼,张兆栋,刘黎明. 316不锈钢TIG电弧增材制造成形规律研究. 焊接技术. 2018(04): 10-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 柏久阳,范成磊,杨雨晨,徐艳利,李瑞,林三宝,王计辉. 2219铝合金TIG填丝堆焊成形薄壁试样组织特征. 焊接学报. 2016(06): 124-128+134 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: