Friction stir welding process microstructure and property of weld for Zr-Sn-Nb-Cr-Fe zirconium alloys
-
摘要:
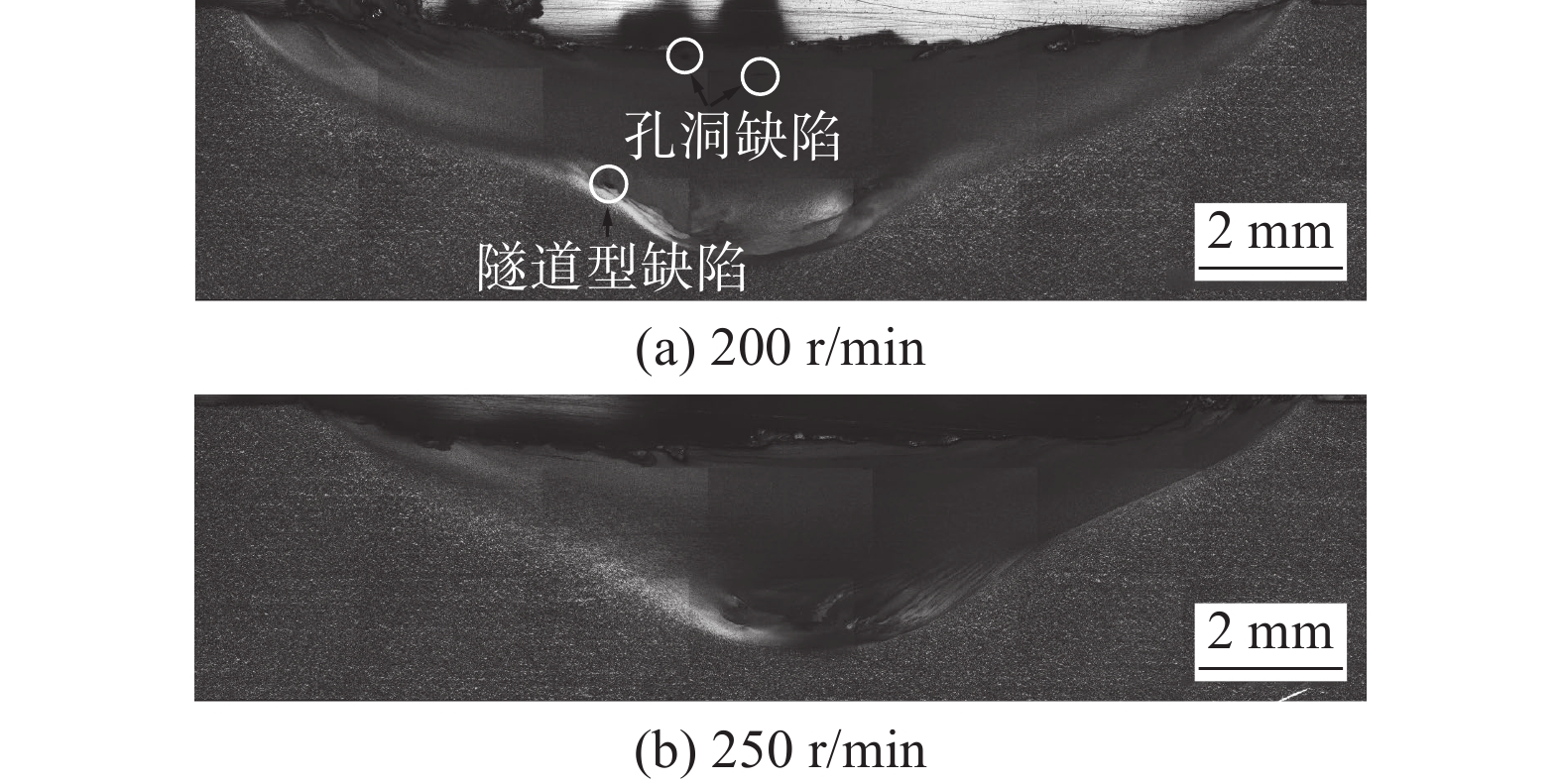
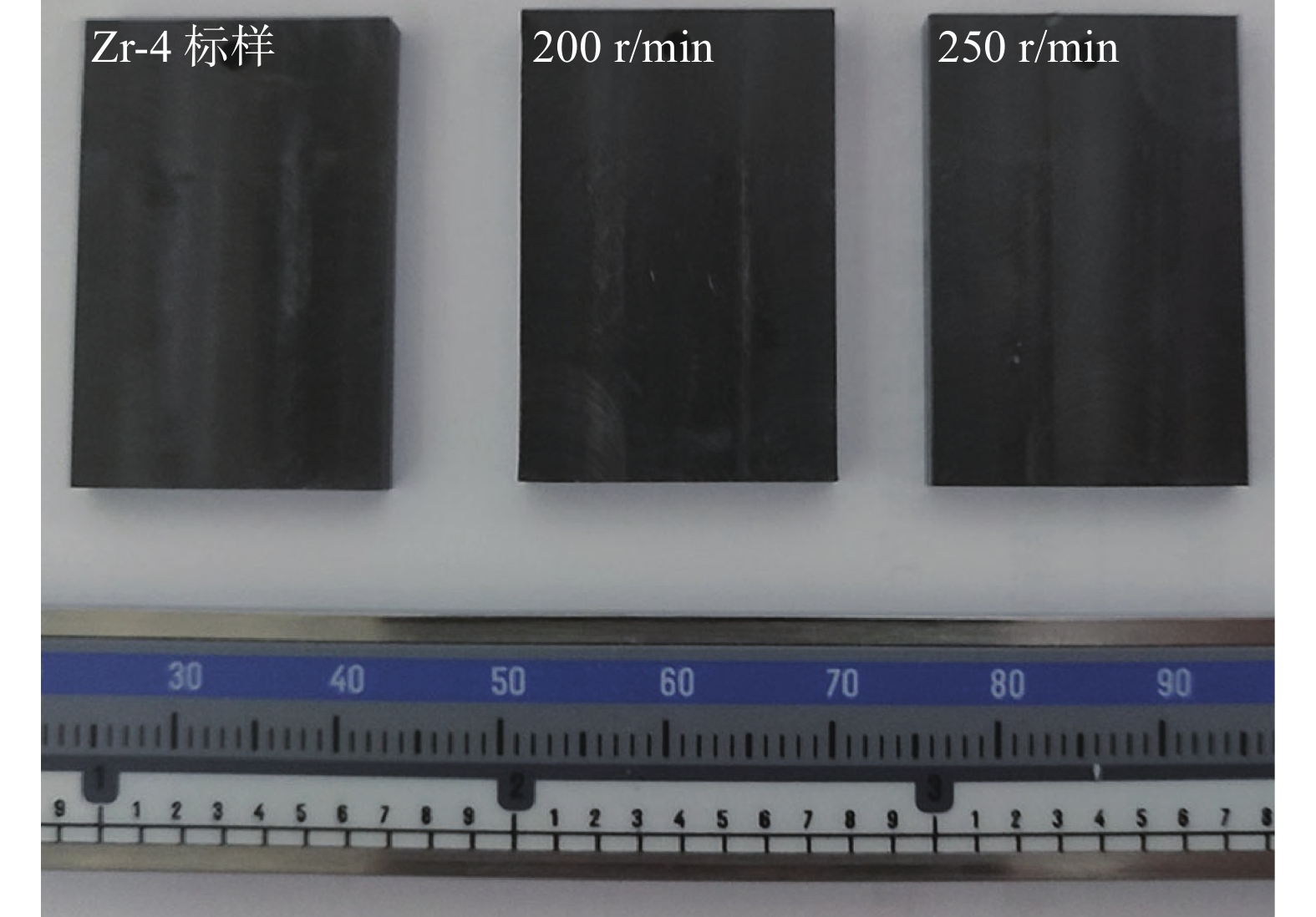
文中对Zr-Sn-Nb-Cr-Fe锆合金搅拌摩擦焊(friction stir welding,FSW)工艺、微观组织和腐蚀性能进行了分析. 结果表明,采用W-25%Re的搅拌工具在转速250 r/min、焊接速度40 mm/min、顶锻压力10 kN、氩气保护条件下可以获得成形良好且无焊接缺陷的锆合金FSW接头. 搅拌区(stir zone,SZ)剧烈的塑性变形促进动态再结晶、合金元素扩散和晶粒细化,晶粒尺寸随着转速增加而增大,同时SZ内在晶界位置处析出大量的形状不规则的第二相粒子. 不同焊接参数制备的FSW接头在360 ℃、18.6 MPa中性水中腐蚀72 h后均表现为黑色、光亮、致密的氧化膜,但随着转速增加接头耐腐蚀性能降低.
Abstract:Process performance, microstructure and corrosion properties of friction stir welded (FSW) joints of Zr-Sn-Nb-Cr-Fe zirconium alloys were studied in the present paper. The results indicate that the recommended zirconium alloys FSW joints with good shape and no welding defects were obtained by W-25%Re stir tool under the conditions of 250 rpm rotational speed, 40 mm/min welding speed, 10 kN axial force and argon protection. In stir zone (SZ), the severe plastic deformation leads to dynamic recrystallization, diffusion of alloying element and grain refinement and grain size increases with the increase of rotational speed. As the same time, a large number of irregularly shaped second phase particles were precipitated at the grain boundaries. These FSW joints prepared by different welding parameters exhibited black, bright and dense oxide film after being corroded in neutral water at 360 ℃, 18.6 MPa for 72 hours. However, the corrosion resistance of FSW joints decreases with the increase of rotational speed.
-
-
表 1 Zr-Sn-Nb-Cr-Fe锆合金化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of the Zr-Sn-Nb-Cr-Fe zirconium alloy
Sn Nb Fe Cr O Zr 1.0 0.30 0.35 0.10 0.10 余量 表 2 腐蚀试验后FSW接头腐蚀增重结果
Table 2 Corrosion weight gain results of FSW joint after corrosion test
转速n/(r∙min−1) 单位增重△m/(mg∙dm−2) 200 4.59 250 11.64 -
[1] 钟建伟, 安军靖, 丁怀博, 等. Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe-Cr与Zr-Nb-Fe锆合金电阻点焊工艺及显微组织[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(8): 82 − 90. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20210305002 Zhong Jianwei, An Junjing, Ding Huaibo, et al. Welding processes and microstructures of weld bead of Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe-Cr and Zr-Nb-Fe zirconium alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(8): 82 − 90. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20210305002
[2] Konishi T. Birth and infancy period of zircaloy materials[J]. Journal of the Atomic Energy Society of Japan, 2003, 45(7): 418 − 423.
[3] Bordoni R A, Olmedo A M. Microstructure in the weld region in seam welded and resistance welded Zircaloy 4 tubing[J]. Journal Materials Science, 1981, 16: 1527 − 1572. doi: 10.1007/BF02396870
[4] Yao M Y, Zhou B X, Li Q, et al. The effect of alloying modifications on hydrogen uptake of zirconium-alloy welding specimens during corrosion tests[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2006, 350: 195 − 201. doi: 10.1016/j.jnucmat.2005.12.005
[5] 左小涛. 锆R60702焊接接头性能研究 [D]. 合肥: 合肥工业大学, 2011. Zuo Xiaotao. Study on properties of zirconium R60702 welded joint [D]. Hefei: Hefei University of Technology, 2011.
[6] 吴宏伟, 杭逸夫, 徐宇皓, 等. 锆R60702 TIG 焊焊接工艺及接头性能研究[J]. 热加工工艺, 2008, 37(5): 83 − 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2008.05.027 Wu Hongwei, Hang Yifu, Xu Yuhao, et al. Study on TIG welding procedure of Zr R60702 and properties of welded joints[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2008, 37(5): 83 − 84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3814.2008.05.027
[7] 薛海峰, 夏宁, 金文涛, 等. 不同焊接方法下AZ31B 镁合金焊接接头组织性能研究[J]. 焊接技术, 2019, 48(5): 77 − 80. Xue Haifeng, Xia Ning, Jin Wentao, et al. Study on microstructures and properties of welded joints of AZ31B magnesium alloy welded by different welding methods[J]. Welding Technology, 2019, 48(5): 77 − 80.
[8] Xue P, Komizo Y, Ueji R, et al. Enhanced mechanical properties in friction stir welded low alloy steel joints via structure refining[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2014, 606: 322 − 329.
[9] Han W, Chen D, Ha Y, et al. Modifications of grain-boundary structure by friction stir welding in the joint of nano-structured oxide dispersion strengthened ferritic steel and reduced activation martensitic steel[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2015, 105: 2 − 5. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2015.04.012
[10] Kalvala P, Akram J, Misra M, et al. Low temperature friction stir welding of P91 steel[J]. Defence Technology, 2016, 12: 285 − 289. doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2015.11.003
[11] 张成聪, 常保华, 陶军, 等. 2024铝合金搅拌摩擦焊过程组织演化分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(3): 57 − 60. Zhang Chengcong, Chang Baohua, Tao Jun, et al. Microstructure evolution during friction stir welding of 2024 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(3): 57 − 60.
[12] Schmidt H B, Hattel J H. Thermal modelling of friction stir welding[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2008, 58: 332 − 337. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2007.10.008
[13] Song M, Kovacevic R. Thermal modeling of friction stir welding in a moving coordinate system and its validation[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2003, 43: 605 − 615. doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(03)00022-1
[14] Heurtier P, Jones M J, Desrayaud C, et al. Mechanical and thermal modelling of friction stir welding[J]. Journal Materials Process Technology, 2006, 171: 348 − 357. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.07.014
[15] Zhang C, Cui L, Liu YC, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of friction stir welds on 9%Cr reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steel[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 34: 756 − 766. doi: 10.1016/j.jmst.2017.11.049
[16] 张超. 低活化铁素体/马氏体钢搅拌摩擦焊接组织与力学性能研究 [D]. 天津: 天津大学, 2018. Zhang Chao. Study on microstructure and properties of friction stir welds on reduced activation ferritic/martensitic steels [D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2018.
[17] Xu Nan, Song Qining, Bao Yefeng, et al. Achieving an excellent strength–ductility synergy in zircaloy-4 by FSW with rapid cooling[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 2018, 34: 20 − 28. doi: 10.1080/02670836.2017.1320861
[18] 李中奎, 周廉, 张建军, 等. Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe 合金中铌的存在方式及其与热处理的关系[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2004, 33(12): 1362 − 1364. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.12.032 Li Zhongkui, Zhou Lian, Zhang Jianjun, et al. The existing form of Nb in Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe alloys and its dependence on intermediate annealing[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2004, 33(12): 1362 − 1364. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-185X.2004.12.032
[19] Tang R, Yang X. Dissolution and precipitation behaviors of hydrides in N18, Zr-4 and M5 alloys[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2009, 34(17): 7269 − 7274. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.07.018
[20] 范清松, 杨忠波, 周军, 等. Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe系锆合金中第二相粒子研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2016, 44(4): 110 − 118. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.04.017 Fan Qingsong, Yang Zhongbo, Zhou Jun, et al. Research progress of second phase particles on Zr-Sn-Nb-Fe zirconium alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2016, 44(4): 110 − 118. doi: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2016.04.017
[21] Guanghai B, Rongshan W, Yanwei Z, et al. Effect of processing techniques on precipitation behavior of secondary phase particles in Zr-1Nb-0.01Cu alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(10): 2473 − 2479. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5372(17)30018-8
[22] 李强, 黄昌军, 杨艳平, 等. N18锆合金疖状腐蚀问题研究[J]. 核动力工程, 2012, 33(S2): 22 − 27. Li Qiang, Huang Changjun, Yang Yanping, et al. Nodular corrosion investigation of N18 zirconium alloys[J]. Nuclear Power Engineering, 2012, 33(S2): 22 − 27.
[23] Kruger R M, Adamson R B, Brenner S S. Effects of microchemistry and precipitate size on nodular corrosion resistance of Zircaloy-2[J]. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 1992, 189(2): 193 − 200. doi: 10.1016/0022-3115(92)90532-P
[24] 武丹花. 新锆合金第二相粒子结构特征及显微组织演变 [D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2019. Wu Danhua. Structural characteristics of second phase particle and microstructure evolution of new zirconium alloys [D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2019.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 黄宗伟. 无线通信的远程信道分布仿真研究. 山东农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(04): 705-707 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 黄俊, 宋恺, 陈雨昕, 刘其蒙, 江俊龙, 王克鸿. 高氮钢激光-MIG复合焊温度场数值模拟. 焊接技术. 2018(04): 22-26+7-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: