Droplet transfer characteristics and mechanical properties of deposited metal as welded matching with cryogenic temperature steel for nickel based consumables
-
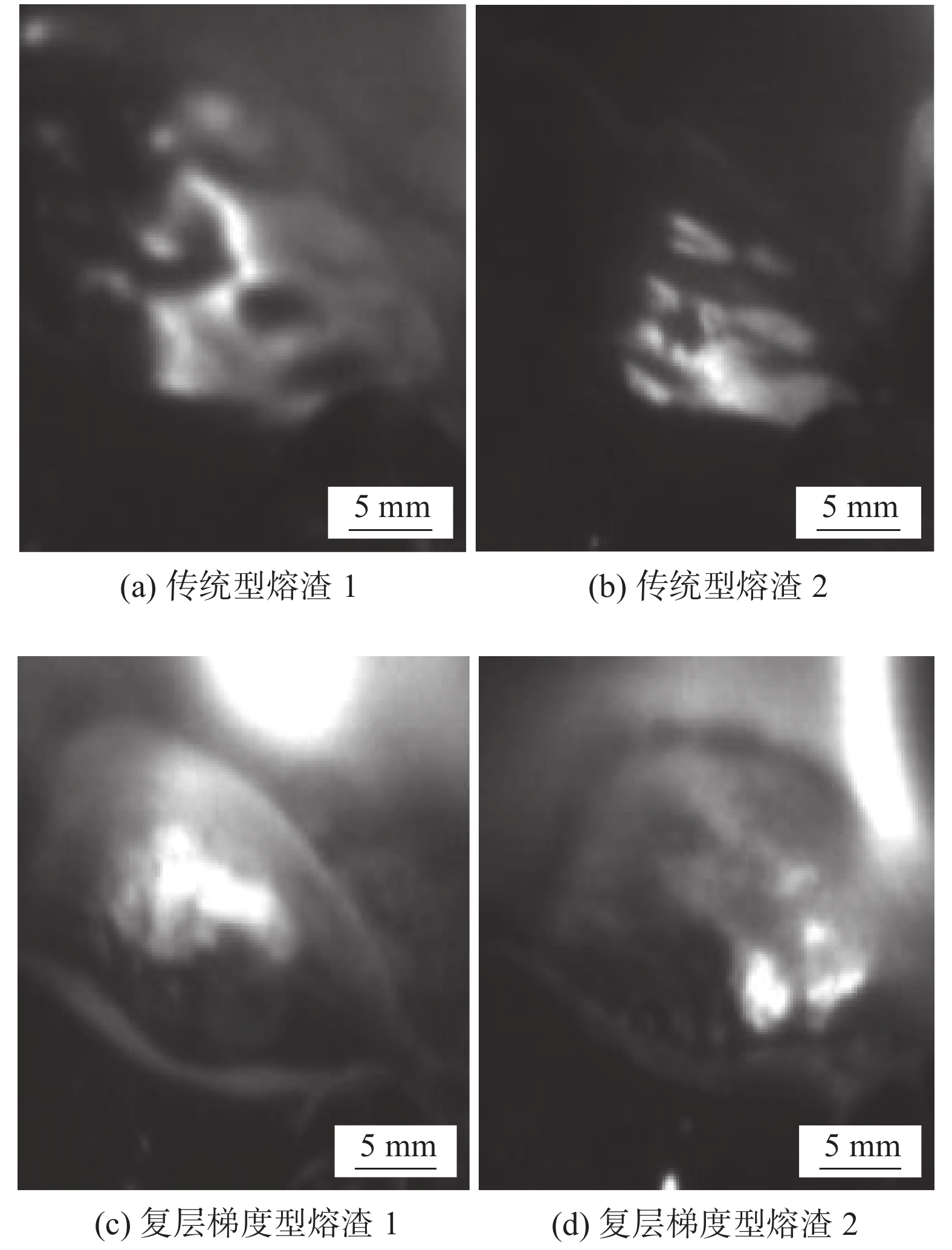
摘要: 以真空冶炼 + 电渣重熔二步法制取镍合金焊芯,设计高碱度药皮形成复层梯度型熔渣,并研制出ENiCrMo-6深冷镍合金专用焊条. 对研制焊条熔敷金属和采用ENiCrMo-6型异质材料焊接9Ni钢接头的力学性能进行试验. 借助Acuteye高速摄像技术研究熔滴过渡及熔池流动特性,采用JSM-6360LV型扫描电子显微镜分析复层熔渣结构. 对焊缝和热影响区进行观察和分析以从不同角度探讨低温断裂行为. 结果表明,针对液态镍合金熔滴过渡颗粒粗大、流动性差、焊缝成形困难问题,通过药皮设计形成复层梯度型熔渣可有效解决焊缝成形. 焊缝组织中,抑制奥氏体柱状晶粗化、减小超低温条件下的塑性损伤是保证低温韧性的重要条件. 采用ENiCrMo-6型焊条焊接9Ni钢,其焊态热影响区过热对板条马氏体和逆变奥氏体相的影响并不显著. 通常情况下,焊接加热不致严重降低过热区中板条马氏体间残留逆变奥氏体相,从而对过热薄弱区低温韧性具有组织保证作用.Abstract: The ENiCrMo-6 electrode for cryogenic temperature application was developed which was made of nickel alloy core wires obtained by duplex refining of vacuum melting and electroslag remelting, and specially designed coatings with high basicity allowing the formation of gradient composite slag. Mechanical property tests were carried out on the deposited metal and the welding joint of 9Ni steel welded by ENiCrMo-6 electrode. With the aid of Acuteye high speed photograph technology, the characteristics of the droplet transfer and the molten metal flow have been studied, and the microstructure of the composite slag layer has been observed by JSM-6360LV scanning electron microscope. The weld and heat affected zone are observed and analyzed to investigate the low-temperature fracture behavior from different perspectives. The results show that large shaped molten droplets of nickel alloy and the poor fluidity result in difficulties in weld formation, while special designed coatings is an effective solution, which allows the formation of a gradient composite slag layer to accelerate the forming of weld. To ensure joint ductility in cryogenic conditions, it is critical to avoid the coarsening of austenite columnar grains and reduce the ductility loss in weld metal as welded. The experiment results has proved that when welding 9Ni steel with ENiCrMo-6 electrode, the effect of overheat on lath martensite or reversed austenite in the as-welded heat affect zone is insignificant. Generally, overheat will not largely reduce the number of reversed austenite or retained austenite within the lath martensites, which guaranteed the ductility of joint under cryogenic condition.
-
-
表 1 ENiCrMo-6焊条焊芯化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of core wire for ENiCrMo-6 electrode
C Mn Si Cr Ni Mo Fe W Cu Nb + Ta S P ≤0.015 2.5 ~ 4.5 ≤0.5 14.0 ~ 18.0 ≥60 6.0 ~ 9.5 1.0 ~ 4.0 1.2 ~ 2.0 ≤0.50 1.0 ~ 2.0 ≤0.010 ≤0.015 表 2 ENiCrMo-6焊条药皮配方组成(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Coating compositions of ENiCrMo-6 electrode
大理石 碳酸钡 萤石 氟化钡 钛酸钾 长石 金红石 金属合金 25 ~ 45 5 ~ 10 15 ~ 30 4 ~ 10 2 ~ 6 4 ~ 10 3 ~ 7 4 ~ 12 表 3 熔敷金属力学性能试验结果
Table 3 Mechanical properties results of deposited metal
项目 屈服强度
Rp0.2 /MPa抗拉强度
Rm /MPa断后伸长率
A(%)冲击吸收能量
(−196 ℃)AKV2/J要求值 ≥410 ≥620 ≥27 ≥47 实测值 458 702 45.5 123 表 4 9Ni钢接头的力学性能试验结果
Table 4 Mechanical properties results of 9Ni steel joint
项目 抗拉强度
Rm /MPa面弯/背弯
(α = 180°)熔合区冲击吸收能量
(−196 ℃)AKV2/J射线
探伤要求值 ≥620 无裂纹 ≥47 Ⅰ级 实测值 728 试样无开口缺陷 127 Ⅰ级 -
[1] 刘东风, 杨秀利, 侯利锋, 等. 液化天然气储罐用超低温9Ni钢的研究及应用[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2009, 21(9): 1 − 5. Liu Dongfeng, Yang Xiuli, Hou Lifeng, et al. Research and application of ultralow temperature 9Ni steel for LNG storage tank[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2009, 21(9): 1 − 5.
[2] 谢章龙, 刘振宇, 陈俊, 等. 9Ni钢薄板的奥氏体化温度及强韧化因素分析[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2011, 23(9): 37 − 41. Xie Zhanglong, Liu Zhenyu, Chen Jun, et al. Austenitizing temperature for 9Ni steel thin plate and analysis of strengthening and toughening factors[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2011, 23(9): 37 − 41.
[3] Kobe Steel, Ltd. Kobelco's welding consumables for LNG storage tanks made of 9%Ni steel[EB/OL]. https://www.kobelco.co.jp/english/welding/files/kwt2011-02.pdf.
[4] Yong-Keun Yoon, Jae-Hoon Kim, Kyu-Taek Shim. Mechanical characteristics of 9% Ni steel welded joint for LNG storage tank at cryogenic[J]. International Journal of Modern Physics:Conference Series, 2012(6): 355 − 360.
[5] Khourshid A E F M, Ghanem M A. The influence of welding conditions on mechanical properties of 9% Ni steel welded joints of liquefied natural gas tank[J]. The International Journal of Engineering and Science, 2013, 2(2): 179 − 185.
[6] Jae-il Jang, Jang-Bog Ju, Baik-Woo Lee, et al. Effects of microstructural change on fracture characteristics in coarse-grained heat-affected zones of QLT-processed 9%Ni steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2003, 340: 68 − 79.
[7] Farias F W C, Filho J D C P, Daniel A S J, et al. Microstructural characterization of Ni-based superalloy 625 clad welded on a 9% Ni steel pipe by plasma powder transferred arc[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2019, 374: 1034 − 1037.
[8] Nako H, Okazaki Y, Takeda H, et al. Comparison of microstructures at as welded zone in 9%Ni steel similar composition weld metal[J]. Materials Science Forum, 2010, 638-642: 3693 − 3698. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.638-642.3693
[9] 张敏, 张明, 李继红. 9Ni钢自保护药芯焊丝的研制及分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(11): 13 − 16. Zhang Min, Zhang Ming, Li Jihong. Development and performance analysis of self-shielded flux cored wire for 9%Ni steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(11): 13 − 16.
[10] Ahsan Q, Haseeb A S M A, Hussein N I S B, et al. 9% nickel steels and their welding behavior[J]. Comprehensive Materials Processing, 2014, 6: 135 − 149.
[11] Qin Renyao, He Guo. Mass transfer of nickel-base alloy covered electrode during shielded metal arc welding[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions, 2012, 44(3): 1475 − 1484.
[12] Qin Renyao, He Guo. Mass transfer of the nickel-base alloy covered electrode with neutral flux coating during shielded metal arc welding[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 78: 1095 − 1104.
[13] 刘海定, 王东哲, 魏捍东, 等. 高性能镍基耐腐蚀合金的开发进展[J]. 材料导报, 2003, 27(3): 99 − 105. Liu Haiding, Wang Dongzhe, Wei Handong, et al. Development progress of high-performance nickel-based corrosion-resistant alloys[J]. Materials Reports, 2003, 27(3): 99 − 105.
[14] 王学东. ENiCrMo-3镍基焊条的研制及其熔敷金属性能的研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2016. Wang Xuedong. Development of nickel-based electrode ENiCrMo-3 and research of deposited metal [D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2016.
[15] 汪中玮, 张清辉, 肖逸锋. 镍基高温耐磨无渣堆焊焊条及其热处理工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2006, 27(1): 109 − 112,118. Wang Zhongwei, Zhang Qinghui, Xiao Yifeng. Nickel-based high-temperature wear-resistant non-slag hardfacing electrode and its heat treatment process[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2006, 27(1): 109 − 112,118.
[16] 孙咸. 氟化物对不锈钢焊条工艺性及熔滴过渡特性的影响[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 1997, 5(4): 1 − 5. Sun Xian. Effect of fluoride on technology and droplet transition characteristics of stainless steel electrode[J]. Materials Science and Technology, 1997, 5(4): 1 − 5.
[17] 杨拓宇, 孟工戈, 杨德云, 等. 药皮辅料的交互作用对不锈钢焊条脱渣性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2007, 28(5): 85 − 88. Yang Tuoyu, Meng Gongge, Yang Deyun, et al. Effect of interactions among coating components on slag detachability of stainless steel electrode[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2007, 28(5): 85 − 88.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 牛宗冉,莫文剑,袁志钟,易翠,王致远. 铜磷锡镍粉末钎料的钎焊性能和显微组织. 粉末冶金工业. 2025(01): 31-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 钟素娟,秦建,王蒙,崔大田,龙伟民. CuSn预合金粉芯复合银钎料的润湿铺展机理. 焊接学报. 2023(02): 16-21+129-130 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 郭亚东,陈明亮. 黄铜Type-C接口绿激光焊接工艺研究. 热加工工艺. 2022(09): 148-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张冠星,钟素娟,董媛媛,刘晓芳,常云峰,薛行雁. 焊后钎剂残渣腐蚀行为分析. 焊接. 2022(11): 47-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王蒙,张冠星,钟素娟,沈元勋,龙伟民,董宏伟,刘晓芳. 低熔合金粉末对药芯银钎料钎焊过程的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程. 2021(08): 2859-2866 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘捷,黄建林,任刚,黄映杰. 黄铜-钢异种金属激光熔覆技术研究及应用. 江西科学. 2021(06): 1077-1079 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘晓芳,张冠星,常云峰,王蒙,钟素娟. 干燥过滤器焊后泄露原因. 焊接. 2021(10): 34-37+62-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李华晨,周广涛,陈梅峰,刘雪松,崔贺鹏,杨浩. 分步气体介质下低功率激光焊接薄板紫铜成形及组织和性能. 焊接学报. 2020(10): 65-72+101 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 王毅. 黄铜与铝合金纳秒激光焊接的工艺研究. 材料保护. 2020(12): 91-94+105 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张敏霞,潘光勇,鲍熠朗. 空调四通阀焊缝泄漏原因分析. 理化检验(物理分册). 2019(12): 859-863 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 于奇,潘建军,于新泉,纠永涛,鲍丽. 微量硅元素对铜磷锡粉状钎料性能的影响. 焊接. 2019(10): 17-20+66 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘文东,李红. 黄铜与不锈钢异种金属激光焊接工艺研究. 应用激光. 2019(06): 966-969 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)




 下载:
下载: