Microstructure and mechanical properties of NAB/steel composite structures by additive manufacturing with BC-MIG wire arc
-
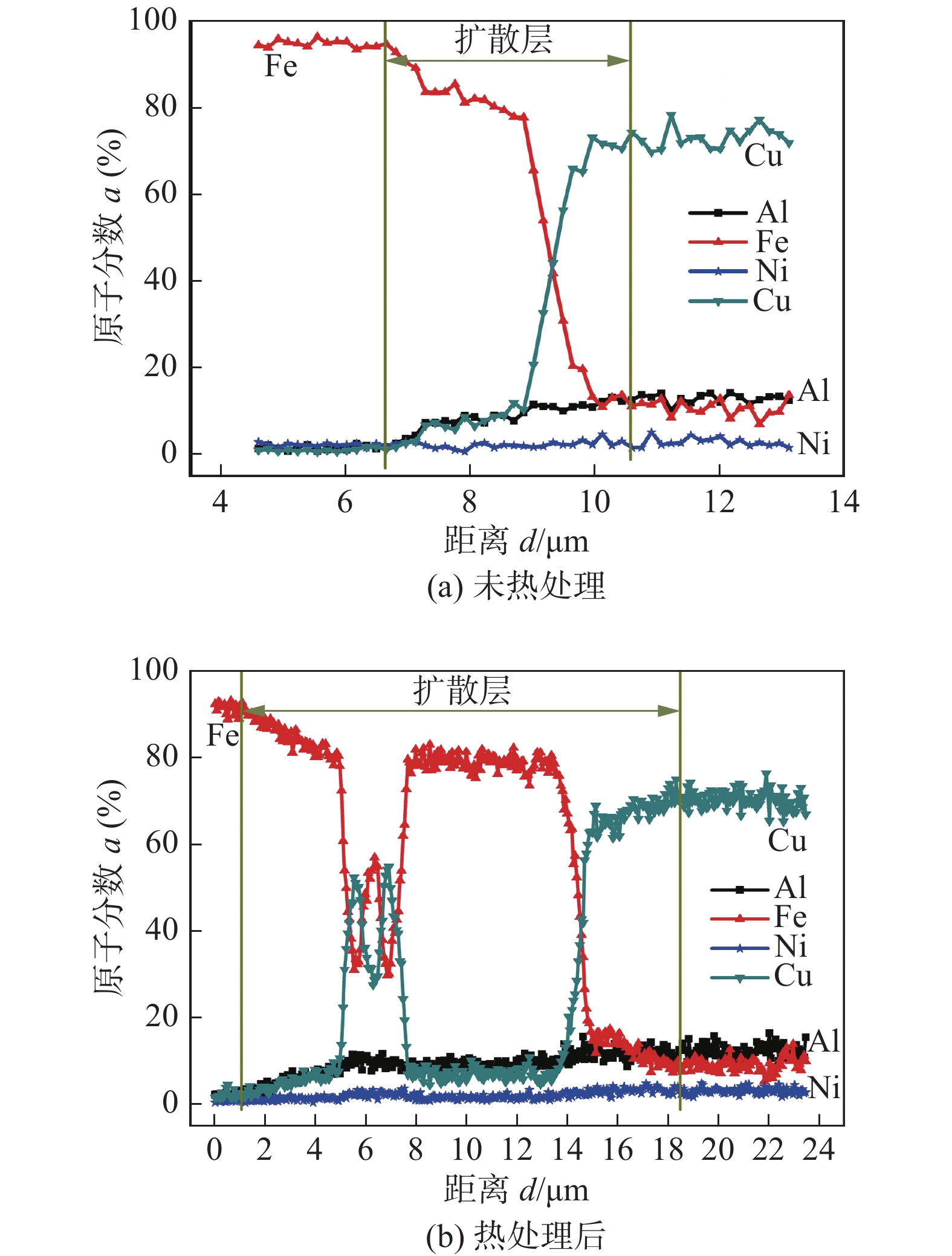
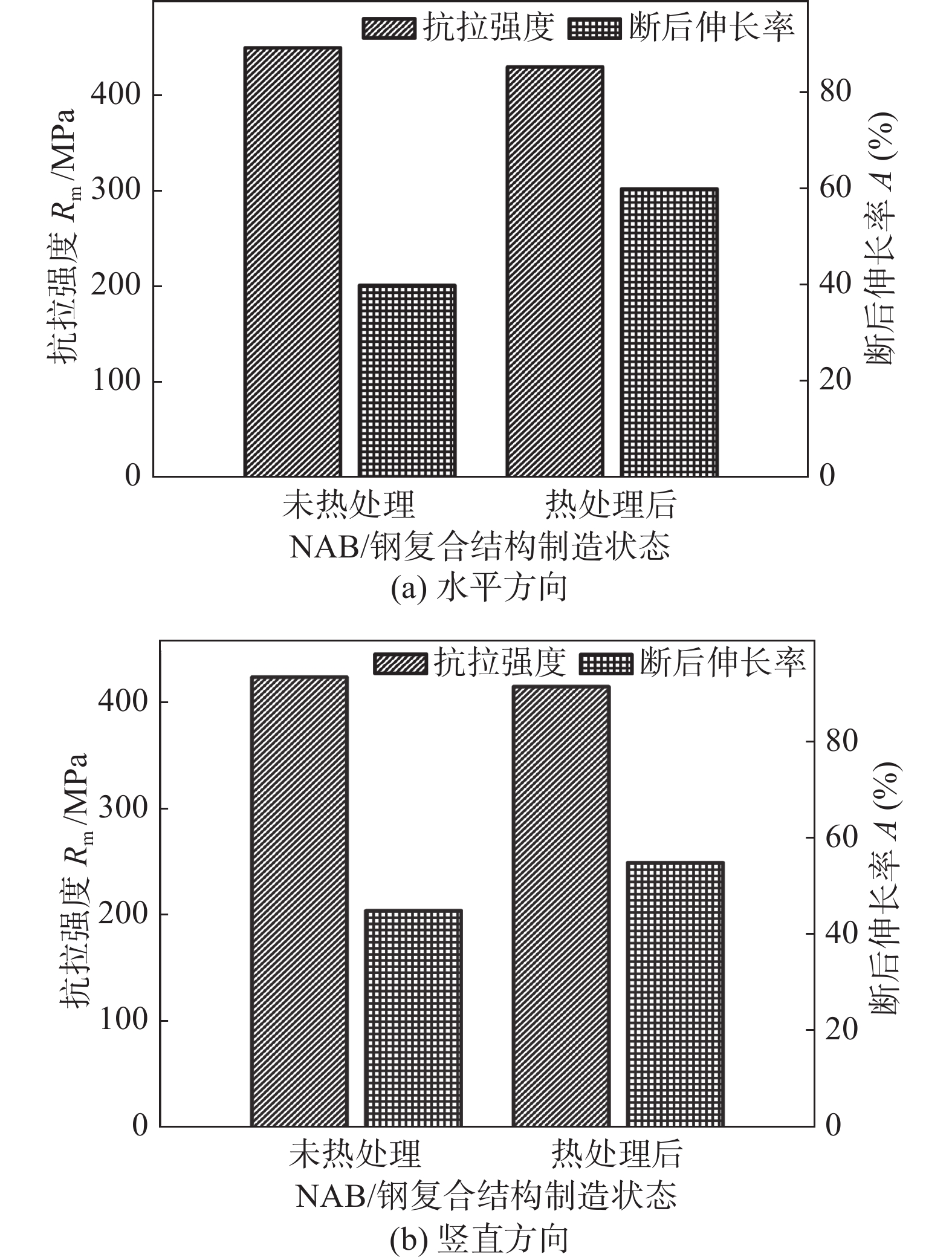
摘要: 使用旁路分流熔化极惰性气体保护焊(bypass current metal inert gas welding,BC-MIG焊)在水冷条件下增材制造镍铝青铜(nickel aluminum bronze,NAB)和25号钢复合结构,以评估异种金属增材制造的可行性. 通过光学显微镜、扫描电子显微镜、万能试验机和硬度测试仪研究了热处理前后复合结构的微观组织和力学性能的影响. 通过X射线衍射仪研究了界面附近残余应力,结果表明,在BC-MIG焊的低热输入和水冷的高冷却速率下,结构件表面成形良好且自由变形较小,接头未发现缺陷和裂纹. 热处理促进了Cu, Fe元素的相互扩散,扩散层由4 μm提高到了17 μm,但界面没有形成Fe-Al金属间化合物层. 在水冷条件下,钢的残余应力分布在−350 ~ −250 MPa之间,而NAB的残余应力差异较大,在−550 ~ 90 MPa之间. 拉伸试验结果表明,热处理后,由于残余应力降低,结构的抗拉强度略微降低,但断后伸长率明显提高.Abstract: Nickel-aluminum bronze (NAB) and grade 25 steel composite structures were fabricated using bypass current metal inert gas(BC-MIG)welding arc additive manufacturing technology under water-cooled conditions to evaluate the feasibility of dissimilar metal additive manufacturing. The results showed that under low heat input of BC-MIG welding and high water cooling rate, the surface of the additive manufacturing structure was well-formed with minimal deformation and no defects or cracks were found in the joints. The influence of heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties was studied. Heat treatment promoted the mutual diffusion of Cu and Fe elements, and the diffusion layer increased from 4 μm to 17 μm, and no Fe-Al intermetallic compound layer was formed at the interface. Residual stresses near the interface were studied by X-ray diffractometer. The results showed that under water-cooling conditions, the residual stresses of steel were distributed among −350 MPa to −250 MPa, while the residual stresses of NAB varied significantly from −550 MPa to 90 MPa. Tensile test results showed that after heat treatment, the tensile strength of the structure decreased slightly due to the reduction of residual stress, but the elongation was significantly improved.
-
Keywords:
- bypass current /
- nickel-aluminum bronze /
- steel /
- wire arc additive manufacturing /
- heat treatment
-
0. 序言
电弧增材制造技术是一种利用电弧产生的热量熔化金属丝材,并按照规划路径自下而上逐层沉积制造零部件的新技术[1]. 该技术与传统的等材制造技术及减材制造技术相比,具有材料利用率高、价格相对低廉及成形尺寸不受限制等优点,因此在水电、桥梁等领域有着较为广泛的应用,但目前电弧增材制造技术仍存在一定的问题,制约了该技术的发展[2-3].众所周知,在电弧增材制造的沉积过程中,复杂的热循环过程会导致沉积层不同位置的微观组织呈现出不同的特征,而这种微观组织的不均匀性则会最终影响沉积件的力学性能,从而导致沉积件力学性能的各向异性,因此电弧增材制造过程中微观组织的不均匀性和力学性能的各向异性成为了制约电弧增材制造技术推广应用的主要因素.
研究学者们针对电弧增材制造微观组织及力学性能的各向异性问题,分别采取了超声冲击、激光冲击、层间锤击、层间滚压等方法以改善组织形态、消除应力集中、细化晶粒等[4-7],上述这些通过外加能量场辅助电弧增材制造的方法[8],均可以在不同程度上改善沉积件的微观组织和力学性能,但也均存在一定的局限性,超声冲击和激光冲击强化均存在作用深度较小的缺点,其难以实现大熔覆效率的电弧增材沉积件全位置的强化处理. 层间锤击和层间滚压强化方法作用范围较大,但这类对沉积件进行变形处理以起到强化效果的方法均会对沉积层的沉积形貌产生影响,同时复杂的处理过程也会影响整体的沉积效率[9].
目前,现有的改善增材制造组织及力学性能各向异性的方法均存在一定的局限性,在通常情况下,沉积层的部分区域在多层沉积层的原位热处理作用下,发生柱状晶向等轴晶转变过程[10-11],因此提出一种基于大热输入、高效熔覆原位热处理的增材制造强化方法,借助四钨极电弧热源可以承载较大熔覆电流的特点,采用双丝送进的送丝方式,进行了沉积件的制造,并对沉积件不同位置的微观组织特征进行分析,通过拉伸试验与冲击试验对沉积件各向异性程度进行试验,以期探索出一种通过原位热处理方式改善电弧增材制造沉积件微观组织不均匀性与力学性能各向异性,为相关领域的研究提供数据支撑.
1. 试验方法
试验以30 mm厚的304不锈钢作为基板,尺寸为300 mm × 200 mm × 30 mm,金属丝材选用哈尔滨焊接研究所有限公司自研的00Cr13Ni5Mo(HS13/5L)不锈钢焊丝,焊丝直径为1.2 mm,基板和焊丝的化学成分见表1.
表 1 304不锈钢与HS13/5L焊丝化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chimecal compositions of 304 stainless steel and HS13/5L welding wire材料 C Si Mn S P Cr Ni Mo Fe 304不锈钢 0.0400 0.4300 1.1700 0.001 4 0.028 0 18.0500 8.0800 0.0540 余量 HS13/5L焊丝 0.0160 0.4600 0.5400 0.008 3 0.001 9 12.3000 4.5100 0.4800 余量 试验设计了一套四钨极电弧双丝增材制造系统,主要由焊接电源、送丝装置、四钨极焊接电源控制系统、三维行走试验台及自主研发的四钨极焊枪组成.
四钨极焊枪主要由4个相互绝缘的特制钨极氩弧焊枪组成,采用水冷的方式进行冷却以保证四钨极焊枪可以实现长时间无故障工作.四钨极焊枪4根钨极采用正方形的排布方式,试验中每两个钨极尖端的间距为2 mm.现对四钨极电弧增材制造的工作原理进行简要描述,图1为增材制造设备示意图,图1(b)右下角为四钨极电弧形貌(钨极间距为2 mm),在自磁收缩的作用下,4个钨极产生的电弧相互吸引汇聚形成一个电弧,因此四钨极电弧可以承载更高的沉积电流以提高热输入,从而实现文中提出的原位热处理过程.
焊接电源采用4台EWM Tetrix 352型直流焊接电源;送丝机为2台EWM TS drive型送丝机,采用前送丝的送丝方式,两根金属丝材采用同向两侧位置排布,金属丝材间夹角为20°,金属丝材与基板表面夹角为15°.
沉积过程采用的具体工艺参数见表2,试验前,首先去除基板表面氧化皮,并用酒精对基板进行清洗,去除表面油污,沉积过程采用纯度为99.9%的氩气进行保护,同时为了保证沉积件的成形质量,采用往复堆积的沉积方式进行沉积,沉积件的尺寸为160 mm$ \times $60 mm$ \times $60 mm,共沉积40层,每层共搭接7道沉积层.
表 2 增材制造工艺参数Table 2. Process parameters of additive manufacturing焊接电流I/A 送丝速度vs/(m·min−1) 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) 电弧电压U/V 气流量Q/(L·min−1) 150 × 4 3 ~ 5 200 ~ 400 14.5 15 沉积过程结束后,采用电火花线切割机对沉积层不同位置切取金相试样、拉伸试样及冲击试样,取样示位置如图2所示.
为了考量沉积件力学性能的各向异性程度,选取x,y,z 3个方向;顶部、中部与底部3个位置切取2个拉伸试件与3个冲击试件,根据国家标准GB/T 288.1—2021《金属材料拉伸试验》采用AG-X plus型电子拉力试验机进行拉伸试验;根据国家标准GB/T 229—2020《金属材料焊缝破坏性试验 冲击试验》采用ZBC2452-C型摆锤式冲击试验机进行冲击试验,试验温度为0 ℃,拉伸试样与冲击试样均为标准尺寸;金相试样分别从沉积件顶部、中部与底部切割获得,试样经金相砂纸、研磨机抛光后采用HNO3-CH3CH2OH溶液进行腐蚀,并使用OLYMPUS GX51型金相显微镜观察试样的微观组织,采用牛津EBSD模块分析试样微观组织的晶体取向关系.
根据国家标准GB/T
2654 《焊接接头硬度试验方法》采用HVS-50型数显维氏硬度仪进行硬度测试(HV10);采用EVO18型扫描电子显微镜对拉伸试件及冲击试件的断口进行观察,并采用OXFORD型能谱仪对断口中夹杂物进行分析.图3为原位热处理过程示意图,根据参考文献[12]可知,HS13/5L焊丝的Ac1温度为628 ℃,Ac3温度为771 ℃.利用四钨极电弧沉积过程热循环曲线与工艺参数相关性,沉积过程中通过对多层多道四钨极热源及层间热量累积的控制,实现HS13/5L焊丝增材制造原位热处理,作用原理为:第n层的沉积过程中,四钨极热源首先对第n-1层沉积层的部分区域进行正火处理,对第n-1层剩余区域进行1次退火处理,对第n-2层沉积层进行1次高温回火处理.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 微观组织
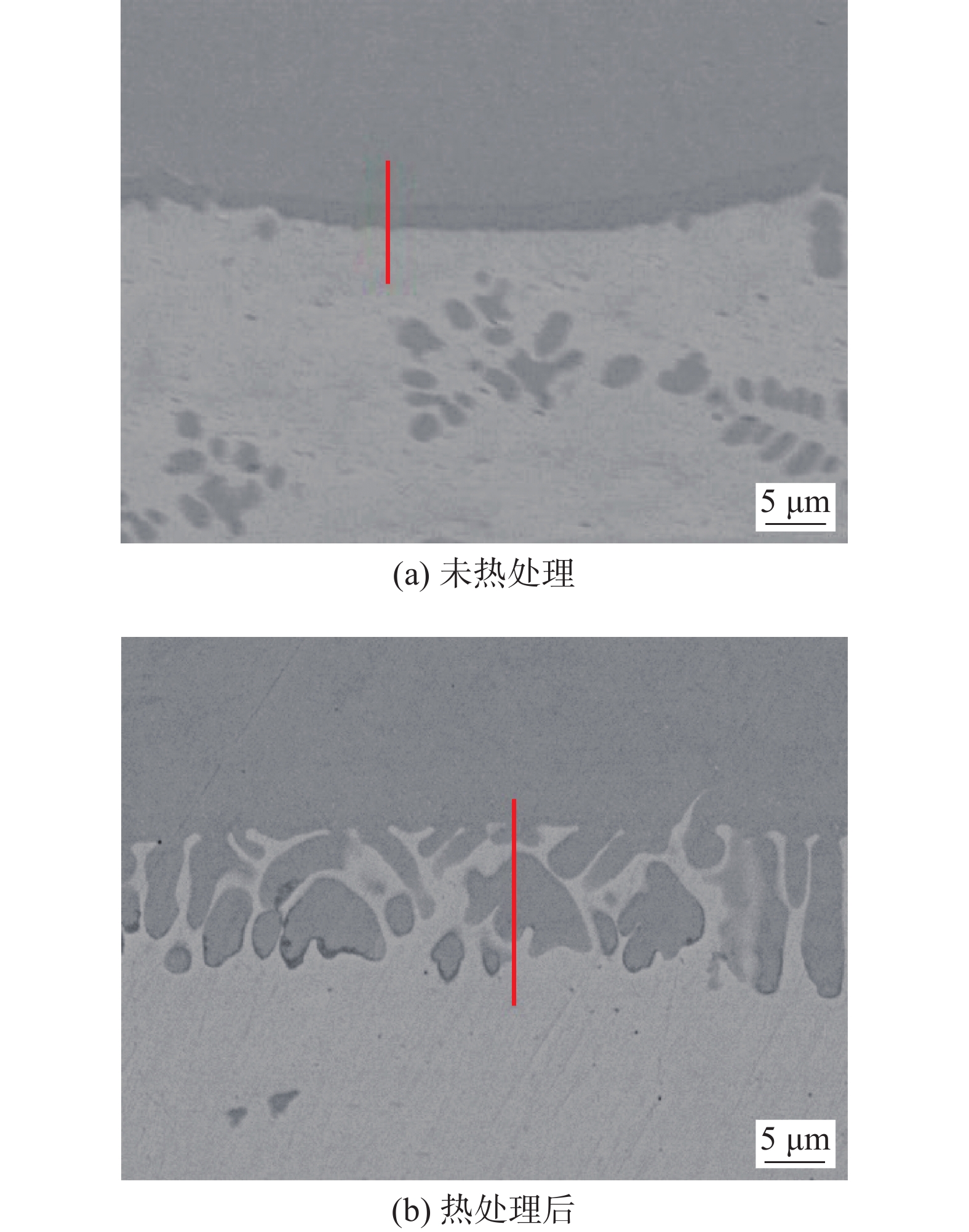
图4为第40层沉积层(顶部位置,距增材制件上表面3 mm位置)、第39层沉积层、第38层沉积层和第20层沉积层(中部位置,距增材制件上表面30 mm位置)的微观组织.
第40层沉积层为沉积件顶部区域,晶粒形状为柱状晶,其微观组织由回火马氏体、回火索氏体、碳化物及逆变奥氏体组成.分析认为,在四钨极热源的作用下,区域温度梯度相对较高,凝固速率相对较低,造成成分过冷的程度相对较大,晶粒沿温度梯度方向择优生长,因此呈现出柱状晶的形貌特征;在四钨极热源高热输入作用下,经历了1次高温自回火过程,促使部分回火马氏体继续转变为回火索氏体及碳化物,同时为逆变奥氏体的逆转变过程提供了形核驱动力,并且碳化物的析出为逆变奥氏体提供了有利形核位置,因此,该区域有部分逆变奥氏体形成.
第39层沉积层呈现出柱状晶与等轴晶的混合形貌特征,越靠近第38层沉积层的区域,其等轴晶的占比也随之增加,推测原因为凭借四钨极热源提供的热量,使该区域经历了正火、临界退火处理,而快速冷却过程也促进了柱状晶向等轴晶的转变;同时,靠近第38层沉积层的区域温度梯度较低,为等轴晶的形成创造了有利条件,越靠近第38层沉积层,等轴晶占比也随之增加.该区域组织同样由回火马氏体、回火索氏体、碳化物以及逆变奥氏体组成.
第38层沉积层的晶粒形状为等轴晶,相较于第39层沉积层,该区域等轴晶晶粒尺寸更小,推测原因为高温回火处理使晶粒进一步细化.该区域微观组织由回火索氏体、碳化物及逆变奥氏体组成,其原因为高温回火处理使回火马氏体全部转变为回火索氏体及碳化物;逆变奥氏体具有极佳的稳定性,因此在高温回火处理中得到保留.
第20层沉积层为沉积件中部区域,该区域晶粒形状为等轴晶,该区域经历了完整的原位热处理过程,并经历了多次高温回火过程,因此该区域晶粒较第38层沉积层更细,微观组织由回火索氏体、碳化物及逆变奥氏体组成.
通过沉积件典型部位(第40层、第39层、第38层)微观组织演变全过程分析可知,在四钨极耦合热源作用下,沉积件微观组织由柱状晶向等轴晶转变;为进一步验证原位热处理过程的均匀性,对中间层区域(第20层)进行微观组织分析,其全部为等轴晶,证明了四钨极原位热处理过程可以改善沉积件组织各向异性程度.
2.2 晶体取向分析
对沉积层不同位置进行电子背散射衍射(electron back-scattering diffraction, EBSD)分析,其结果如图5所示. 由图5(a)、图5(b)可知,第40层沉积层柱状晶平均长度为44.28 μm,第39层沉积层等轴晶平均长度为4.86 μm,相较于第40层沉积层,第39层沉积层等轴晶平均长度为其1/8,即在正火+退火的原位热处理作用下,沉积层晶粒平均长度明显减小.第20层沉积层等轴晶平均长度为3.24 μm.根据Hall-Petch公式可知,材料的屈服强度与晶粒平均长度的平方根成负相关的关系,即晶粒平均长度越小,材料的屈服强度越高,因此沉积件具有较好的强度.
![]() 图 5 沉积件不同位置的EBSD分析Figure 5. EBSD analyses of the additive manufacturing samples at different positions. (a) inverse pole figure of the 40th and 39th; (b) inverse pole figure of the 20th and 19th; (c) grain boundary figure of the 40th and 39th; (d) grain boundary figure of the 20th and 19th; (e) pole figure of the 40th and 39th; (f) pole figure of the 20th and 19th
图 5 沉积件不同位置的EBSD分析Figure 5. EBSD analyses of the additive manufacturing samples at different positions. (a) inverse pole figure of the 40th and 39th; (b) inverse pole figure of the 20th and 19th; (c) grain boundary figure of the 40th and 39th; (d) grain boundary figure of the 20th and 19th; (e) pole figure of the 40th and 39th; (f) pole figure of the 20th and 19th图5(c)和图5(d)为沉积件不同位置微观组织的晶界角度差分布图,通过不同颜色代指晶粒取向差分布,其中绿色为小角度晶界(<15°),黑色为大角度晶界(>15°),其中沉积件顶部区域(第40层)小角度晶界占比为80.1%;沉积件中部区域(第20层)小角度晶界占比为61.8%,小角度晶界晶格畸变相对较小,原子排布更接近,因此具有较高的结构连续性,其可以通过阻碍位错运动,有效增加材料的强度和韧性.
织构与材料各向异性之间存在密切的关系,由图5(e)和图5(f)可知,顶层区域织构强度最大值为3.19;中部区域织构强度最大值为3.1,沉积层顶部、中部区域无明显织构取向,即沉积件微观组织呈现出较好的各向同性,通过原位热处理过程可以很好的减弱增材制造沉积件的各向异性程度,使沉积件微观组织呈现出较好的各向同性.
2.3 维氏硬度
图6为沉积件纵向由底部位置至顶部位置的维氏硬度(HV10)测量结果.根据上述试验结果可知,沉积件内部各部分硬度波动范围较小,整体上在(279.4±10) HV10范围内波动,一般认为硬度与组织的种类、形态特征有关,而在文中,沉积件内部各部分微观组织均由回火索氏体、逆变奥氏体及碳化物组成,只有顶层区域有部分回火马氏体;同时沉积件各部分晶粒尺寸变化较小,因此宏观表现为沉积件各部分硬度波动较小.
2.4 拉伸性能
图7和图8分别为沉积件不同方向和不同位置的拉伸性能.x向屈服强度平均值为913.0 MPa, z向屈服强度平均值为906.0 MPa,y向(底部区域)屈服强度平均值为905.0 MPa,中部区域屈服强度平均值为905.0 MPa,顶部区域屈服强度平均值为894.5 MPa,由上述试验数据可知,x,y,z 3个方向屈服强度的最大差值为1.5%;顶部、中部与底部屈服强度的最大差值为1%,由此可以说明沉积件的拉伸性能无论是在x,y,z 3个方向,还是在顶部区域、中部区域与底部区域3个位置上均呈现出较弱的各向异性.
图9为不同方向及不同位置的拉伸断口的扫描电镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)图像.不同方向、不同位置的断口呈现出较为典型的韧性断裂断口形貌,断口只观察到纤维区及剪切唇,均未观察到放射区,同时各个方向、各个位置的拉伸断口形貌无较大差异,均呈现出等轴韧窝的形貌,同时韧窝的尺寸基本一致,因此可以认为沉积件在不同方向、不同位置的拉伸性能呈现出较弱的各向异性.
![]() 图 9 不同方向与不同位置的拉伸断口SEM图像Figure 9. SEM figure of fracture surfaces at different directions and different positions. (a) fracture surface of x-direction; (b) fracture surface of y-direction; (c) fracture surface of z-direction; (d) fracture surface of top; (e) fracture surface of middle; (f) fracture surface of bottom
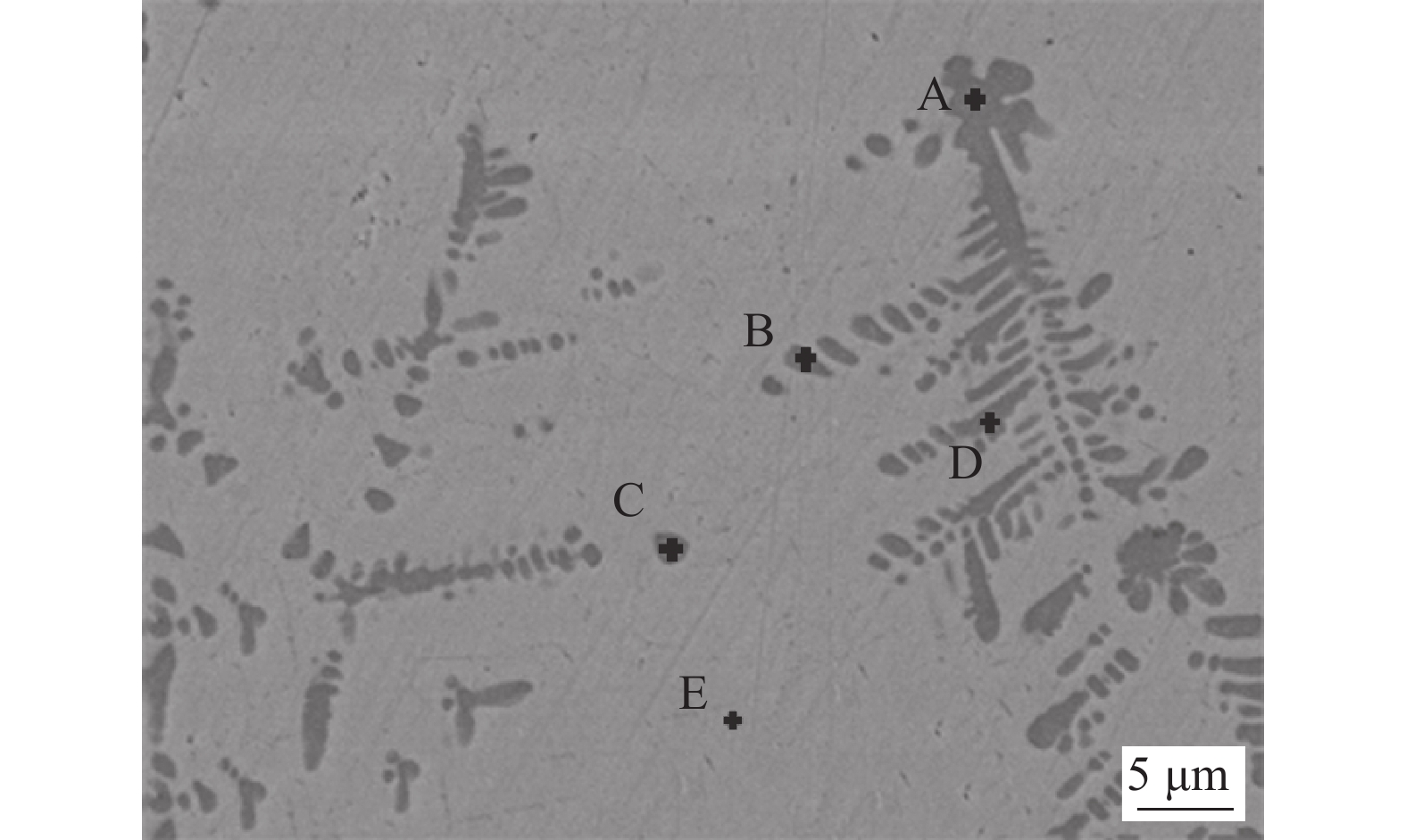
图 9 不同方向与不同位置的拉伸断口SEM图像Figure 9. SEM figure of fracture surfaces at different directions and different positions. (a) fracture surface of x-direction; (b) fracture surface of y-direction; (c) fracture surface of z-direction; (d) fracture surface of top; (e) fracture surface of middle; (f) fracture surface of bottom通过能谱仪(energy dispersive spectrometer, EDS)对拉伸断口韧窝内夹杂物的元素组成进行分析,如图10所示,沉积件各个位置的拉伸断口韧窝中均有少量夹杂物存在,根据EDS结果可知夹杂物为Al2O3.
2.5 冲击性能分析
图11为沉积件不同方向的冲击性能,图12为不同位置的冲击性能.x向冲击吸收能量平均值为211.3 J, z向冲击吸收能量平均值为202.8 J,y向(底部区域)冲击功平均值为213.3 J,中部区域冲击能量平均值为198.0 J,顶部区域冲击能量平均值为214.0 J,由上述数据可知,x,y,z 3个方向冲击性能的最大差值为10.5 J;顶部、中部与底部冲击能量的最大差值为16 J,由此可以认为沉积件不同方向、不同位置冲击性能的各向异性程度较弱.
综上试验结果可知,借助四钨极热源大熔覆电流下的原位热处理过程,可以使沉积件微观组织由柱状晶转变为等轴晶,从而改善沉积件力学性能的各向异性,并在一定程度上提高沉积件的力学性能.
3. 结论
(1) 采用四钨极双丝增材制造系统,利用四钨极热源大热输入对00Cr13Ni5Mo不锈钢沉积件进行原位热处理,使沉积件微观组织由柱状晶向等轴晶转变,从而显著地改善沉积件的各向异性.
(2)四钨极增材制造沉积件微观组织平均晶粒长度由44.28 μm降低至4.86 μm,沉积件微观组织呈现为等轴晶,因此具有较显著的微观组织各向同性,四钨极沉积件微观组织由回火索氏体、逆变奥氏体及碳化物组成.
(3) 四钨极增材制造沉积件的平均维氏硬度为(279.4±10) HV10,室温屈服强度为(903.7±11) MPa,0 ℃冲击吸收能量为(207.6±10) J,即沉积件力学性能呈现出较弱的各向异性.
-
表 1 25号钢和镍铝青铜焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 25 steel and NAB wire
材料 C Si Mn Cr Ni Cu Al Zn Fe 25号钢 0. 25 0. 8 0. 3 0. 05 0. 05 0. 15 0. 1 0. 05 余量 NAB焊丝 — 0. 04 1. 0 — 4. 0 余量 8. 5 0. 003 3. 0 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding process parameters
总电流
I/AMIG焊电流
Im /AMIG焊电压
U/V旁路TIG焊电流
It /A焊接速度
v/(m·min−1)气体流量Q/(L·min−1) MIG焊喷嘴高度
h/mm钨极高度
h2/mmMIG焊 TIG焊 200 160 21 40 0.7 15 5 8 5 表 3 残余应力测试参数
Table 3 Residual stress test parameters
测量方法 衍射晶面 辐射 X光管电压
U0 /kVX光管电流
Ix /mA扫描步
距α/(°)XRD Cu (311),
Fe (211)Crkα 20.0 5.0 0.1 -
[1] Tomar B, Shiva S, Nath T. A review on wire arc additive manufacturing: Processing parameters, defects, quality improvement and recent advances[J]. Materials Today Communications, 2022, 31: 103739. doi: 10.1016/j.mtcomm.2022.103739
[2] Liu L, Zhuang Z, Fei L. Additive manufacturing of steel-bronze bimetal by shaped metal deposition: interface characteristics and tensile properties[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 69(9-12): 2131 − 2137. doi: 10.1007/s00170-013-5191-7
[3] 花雷生. 镍铝青铜堆焊工艺及堆焊层组织与性能研究 [D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2015. Hua Leisheng. Nickel-aluminum bronze overlay process and microstructure and properties of overlayer[D]. Xi'an: Xi'an University of Technology, 2015.
[4] 吕玉廷, 王立强, 毛建伟, 等. 镍铝青铜合金(NAB)的研究进展[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2016, 45(3): 815 − 820. Lyu Yuting, Wang Liqiang, Mao Jianwei, et al. Recent advances of nickel-aluminum bronze (NAB)[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2016, 45(3): 815 − 820.
[5] 阎楚良, 王志, 张鑫, 等. 淡水介质环境的25号钢疲劳性能试验研究[J]. 农业机械学报, 2002(5): 89 − 92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1298.2002.05.028 Yan Chuliang, Wang Zhi, Zhang Xin, et al. Study on fatigue performance test for 25 steel in fresh water[J]. Journal of Agricultural Machinery, 2002(5): 89 − 92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1298.2002.05.028
[6] 徐杨. 碳钢表面堆焊铝青铜组织性能研究 [D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2021. Xu Yang. Research on microstructure and properties of aluminum bronze surfacing on carbon steel[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[7] Tian Y B, Shen J Q, Hu S S, et al. Effects of cold metal transfer mode on the reaction layer of wire and arc additive-manufactured Ti-6Al-4V/Al-6.25Cu dissimilar alloys[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2021, 74: 35 − 45.
[8] Zhang X C, Sun C, Pan T, et al. Additive manufacturing of copper – H13 tool steel bi-metallic structures via Ni-based multi-interlayer[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2020, 36: 101474. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2020.101474
[9] Rodrigues T A, Bairrão N, Farias F, et al. Steel-copper functionally graded material produced by twin-wire and arc additive manufacturing (T-WAAM)[J]. Materials & Design, 2022, 213: 110270.
[10] Chen S, Huang J, Xia J, et al. Microstructural characteristics of a stainless steel/copper dissimilar joint made by laser welding[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2013, 44(8): 3690 − 3696.
[11] 黄本生, 陈权, 杨江, 等. Q345/316L异种钢焊接残余应力与变形数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(2): 138 − 144. Huang Bensheng, Chen Quan, Yang Jiang, et al. Numerical simulation of welding residual stress and deformation in Q345/316L dissimilar steel welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(2): 138 − 144.
[12] Jiang C, Long W M, Feng J, et al. Thermal fatigue behavior of copper/stainless steel explosive welding joint[J]. China Welding, 2021, 30(4): 25 − 29.
[13] Tong Z P, Ren X D, Jiao J F, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of FeCrCoMnNi high-entropy alloy: Effect of heat treatment on microstructure, residual stress and mechanical property[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 785: 1144 − 1159. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2019.01.213



 下载:
下载: