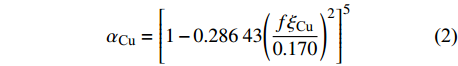Effect of vibration amplitude on ultrasonic welding of Cu/Al
-
摘要: 焊接振幅是超声波焊接的主要参数,但目前关于焊接振幅对超声波焊接影响机制的认识较少. 研究了焊接振幅对铜/铝超声波焊接过程,包括工件的振幅分配、界面温度、中间相分布、材料塑性变形以及接头性能的影响. 结果表明,在焊接压力1 575 N、焊接时间0.5 s时,随着焊接振幅增大,上工件振幅呈现近似线性增长;下工件振幅在焊接过程中均呈现逐渐近似线性增加的趋势. 在整个焊接过程中,焊接振幅越大,下工件的振幅越高. 在焊接振幅为25 μm时,获得了最大拉剪力为3150 N的铜/铝接头. 高的焊接振幅提升了焊头与上工件以及工件之间的相对运动速度,加速了焊接界面的温度升高及材料的塑性变形,增强了界面原子的扩散,最终促进了较高质量的铜/铝超声波焊接接头的形成.Abstract: Vibration amplitude is an important parameter of ultrasonic welding, but insights into the influence mechanism of vibration amplitude on ultrasonic welding are few. The effects of vibration amplitude on the process of Cu/Al ultrasonic welding were investigated in this study, including vibration amplitude distribution of specimens, interfacial temperature, intermediate phase distribution, materials plastic deformation, and properties of joint. The results show that under the welding pressure of 1575 N and welding time of 0.5 s, with the increase of welding amplitude, the vibration amplitudes of the upper specimen exhibit a linear growth, and the amplitudes of the lower specimen tend to show a near-linear growth. During the welding process, the higher the vibration amplitude, the higher the vibration amplitude of the lower specimen is. When the vibration amplitude is set at 25 μm, a Cu/Al joint is obtained with a maximum tensile-shear force of 3150 N. High vibration amplitude has increased the relative motion speed among the sonotrode, the upper specimen and the specimen, which has sped up the temperature rise in the welding interface and the plastic deformation of the material, thus accelerated the interfacial atoms diffusion and promoted the formation of high quality Cu/Al ultrasonic welding joints.
-
Keywords:
- ultrasonic welding /
- amplitude /
- plastic deformation /
- microstructure /
- mechanical property
-
0. 序言
为缓解目前面临的能源与环境危机,在碳中和背景下,以单纯锂电池组作为动力的纯电动汽车有望取代传统燃油汽车[1]. 锂电池组由大量单体锂电池串联而成,且锂电池极耳材料多采用铜、铝,因此锂电池组的制造需要焊接大量铜/铝接头[2-3]. 高质量的铜/铝异质接头对于电动汽车锂电池的制造较重要.目前锂电池极耳连接中常用的焊接方法有激光焊、电阻点焊等. 然而,由于铜、铝具有高导热性、导电性使得电阻点焊的铜/铝接头性能较差[4].尽管目前采用激光焊得到了较高质量的铜/铝异种接头[5],但其焊接界面处会生成较厚的中间相(intermetallic compound, IMC),而IMC的电阻率明显高于母材,这将很大程度增加了锂电池的极耳电阻[6-7],导致电池使用中能量损耗较大,影响了锂电池组的推广.超声波焊接是一种固相连接技术,不需要添加任何焊接材料[8-9],没有弧光和烟尘产生,具有绿色环保的特点[10-11]. 因此,超声波焊接是锂电池组的关键制造技术[12].
超声波焊接工艺参数有焊接振幅、焊接时间和压力. Kong等人[13]开展了6061铝合金超声波焊接试验,研究发现高的焊接振幅促进了连接面的形成. Shin等人[14] 获得了A5052铝合金超声焊接接头,研究发现,较高的焊接振幅在较短的焊接时间内得到了较高的焊接质量,但未解释高强度的原因. 目前相关的研究主要在焊接振幅对工件界面微观组织和力学性能的试验方面,对于高振幅下获得良好焊接质量的机制认识不足,开展焊接振幅对铜/铝超声波焊接的研究也很少;并且,关于焊接振幅对工件的振动分配、塑性变形的影响研究报道极少. 因此,研究焊接振幅对铜/铝大功率(>2.5 kW)超声波焊接的工件振幅分配、界面温度、中间相生成及接头性能的影响,以进一步明晰焊接振幅在超声波焊接中的作用机制. 该研究结果为下一步得到更高质量的铜/铝接头提供了指导.
1. 试验方法
采用TELSONIC公司的M5000型大功率超声波焊机,额定功率为4 kW,频率为19.99 kHz.焊头端面为7 mm × 5 mm的矩形. 焊头和底座的齿为梯形状. 工件选用T2纯铜和6061-T6铝合金,其尺寸为100 mm × 25 mm × 0.8 mm,工件的搭接区域为25 mm × 25 mm.为防止焊头粘铝导致其失效,将铜作为上工件. 在实际焊接中,设置焊接压力恒定为1 575 N,焊接时间0.5 s. 焊接振幅(即焊头振幅)的变化通过调整振幅比例来实现,其范围为70% ~ 100%,而振幅比例通过调整超声电功率实现.
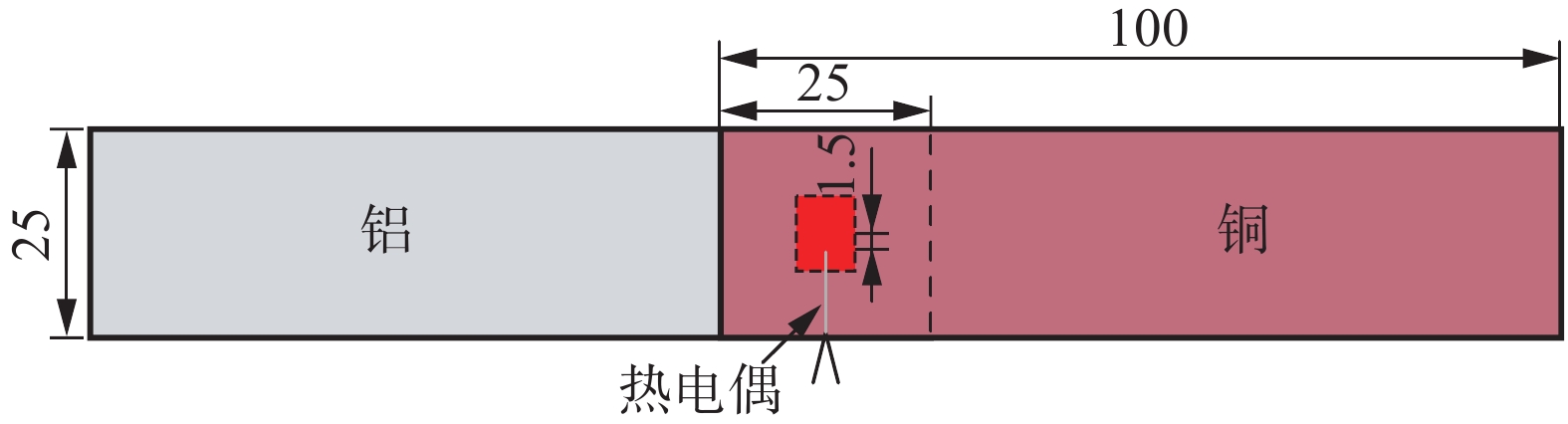
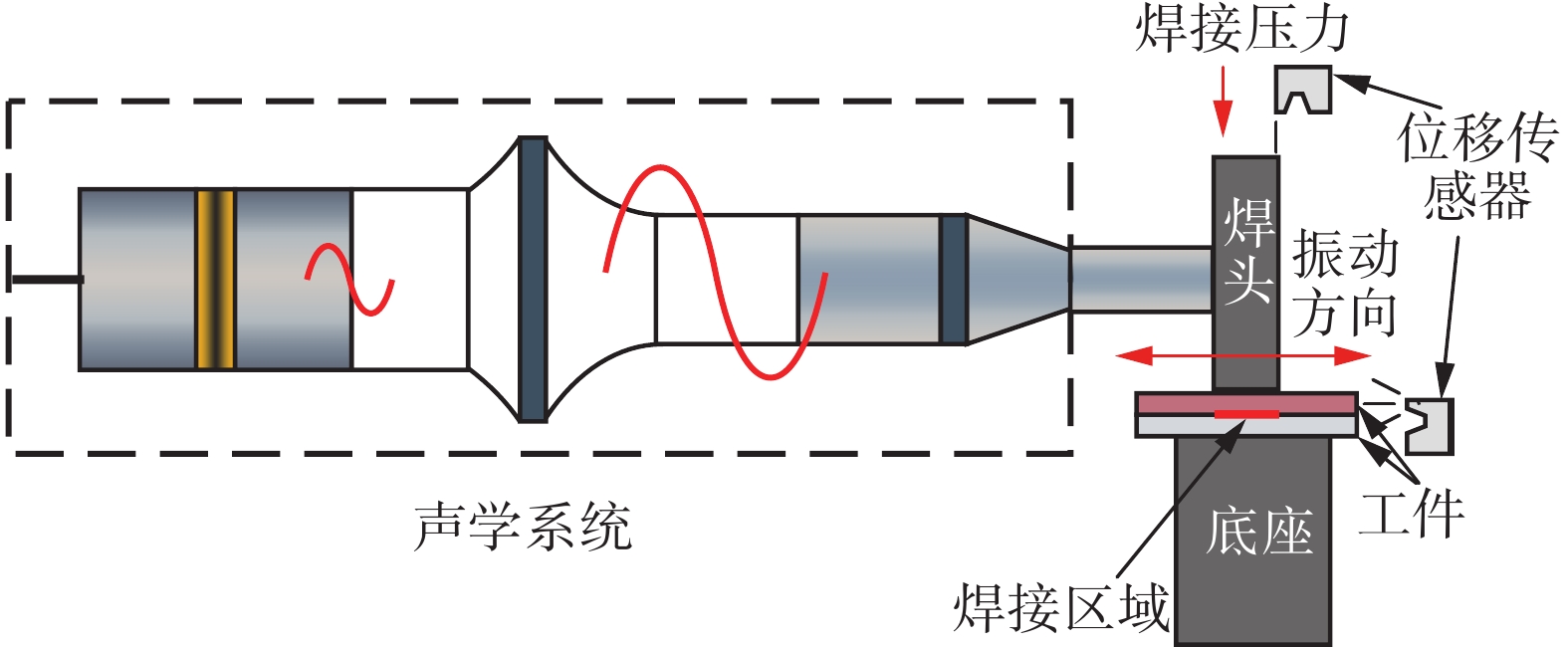
采用基恩士LG-K5001型激光位移传感器测量了焊头和工件的振幅以及焊头的下压位移,如图1所示. 首先,进行振幅测量,设置采样频率为2 MHz;然后,进行焊头下压位移的测量,设置采样频率为10 kHz. 采用直径为0.1 mm的K型热电偶测量界面温度,在铝板上表面制作半径为0.5 mm的半圆形凹槽,并将热电偶嵌入槽内,测温位置为距离焊接中心区域1.5 mm处,如图2所示.
采用配备有能谱仪(energy dispersive spectroscopy,EDS)的Phenom Pro X型场发射扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscope,SEM)来观测界面的微观组织. 采用Malvern PANalytical型X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction,XRD)分析进一步明确焊接界面中间相的组成. XRD光谱测量范围为20° ~ 90°,步长为0.02°,每步扫描时间为0.1 s. 采用岛津AGS-X型电子万能试验机测试拉剪力,设定拉伸速度为1 mm/min. 对于不同振幅参数分别做3次试验,取其平均值.
2. 有限元模型
利用ANSYS有限元软件建立了一个三维的有限元模型,如图3所示. 考虑到结构具有对称性,取实际模型的一半进行分析.由于钢的热导率相对较低,只考虑部分工具头.为提高计算精度和效率,工件网格选用六面体网格,焊接区域网格较密,远离焊接区域网格较稀疏,网格总数为41 648个.
设置铝合金的密度为2 700 kg/m3,泊松比为0.33;纯铜的密度为8 900 kg/m3,泊松比为0.35. 焊头、底座和工件材料的物理属性如图4所示[15];未给定温度的物理参数在ANSYS软件中通过线性插值得到.
![]() 图 4 材料物理属性[15]Figure 4. Material properties. (a) thermophysical properties; (b) mechanical properties
图 4 材料物理属性[15]Figure 4. Material properties. (a) thermophysical properties; (b) mechanical properties热分析时,设定环境温度为25 ℃,对流换热系数为15 J/(m2·℃). 焊接热源包括摩擦热、塑性变形热[15]. 其中, 摩擦热与塑性变形热均与各接触面的相对运动速度有关,工具头及工件取测量得到的焊头、工件的近似恒定振幅来计算摩擦热与塑性变形热. 将摩擦热和塑性变形热分别加载于摩擦区域和塑性变形区域;设置接触面的初始接触热阻为2 000 W/(m2·℃),在焊接结束时达到最大接触热阻TCCmax,即
$$ {T_{{\rm{CC}}}}_{\max } = \frac{{1\;000 \; {K_{\max }}}}{{{L_{{\rm{ag}}}}}} $$ (1) 式中:Kmax为材料最大热导率;Lag为所构建的三维模型的对角线长度. 结构分析中压力施加在焊头顶端面,底座约束y方向位移,对称面施加对称位移约束.
超声波焊接过程中材料的软化包括温度软化和超声软化.超声波焊接使用的振幅较大(一般数十微米),材料屈服强度会明显降低[16]. 为了模拟与实际接近的材料塑性变形,在模型中考虑了工件超声变软的影响.铜和铝的超声变软率为[15]
$$ {\alpha _{{\text{Cu}}}} = {\left[ {1 - 0.286\;43{{\left( {\frac{{f {\xi _{{\text{Cu}}}}}}{{0.170}}} \right)}^2}} \right]^5} $$ (2) $$ {\alpha _{{\text{Al}}}} = {\left[ {1 - 0.105\;6{{\left( {\frac{{f {\xi _{{\text{Al}}}}}}{{0.112}}} \right)}^2}} \right]^2} $$ (3) 式中:αCu和αAl分别为铜和铝的超声变软率;f为振动频率;ξCu和ξAl分别为铜和铝的振幅.
$$ {q_{\rm{f}}} = \frac{{4 \mu f \Delta \xi {F_{\text{N}}}}}{{{A_{\rm{f}}}}} $$ (4) $$ {q_{\rm{p}}} = \frac{{4 {\sigma _{ \rm{s}}} f \Delta \xi }}{{\sqrt 3 }} $$ (5) 式中:qf和qp分别为摩擦热和塑性变形热;μ为摩擦系数;Δξ为相对振幅;Af为摩擦面积;FN为焊接压力;σs为材料的屈服强度.
3. 结果与讨论
3.1 焊接振幅对焊接结构位移的影响
图5为测量得到的不同振幅比例对应的焊头振幅. 从图5可以看出,焊接初始时,在不同振幅条件下,焊头的振幅呈现逐渐增大,之后幅值有略微减小,整个焊接过程呈现不规则的变化,最后在焊接结束时焊头由于惯性会持续约0.1 s后振动逐渐停止. 在振幅比例70%时,焊头振幅变化不大,这是因为振幅比例较小,对焊接结构影响较小. 随着振幅比例从70%增至100%时,对应焊头振幅也随之增加,即从16 μm增至25 μm,焊头振幅与振幅比例呈现近似线性增长关系. 随着振幅比例的增加,超声电功率也随之呈近似的线性增加,在声−电效应后,变幅杆放大后的振幅也对应增加.
图6为焊接振幅16,18.5,22 μm和25 μm(对应的振幅比例分别为70%,80%,90%,100%)时的上工件的振幅. 从图6可以看出,上工件的振幅在焊接初期也经历了先逐渐变大后小幅度降低的过程,随着焊接振幅逐渐增大,上工件的振幅随之增大,这是因为随着焊接振幅的增加,焊头往复运动的历程越长,在压力作用下使焊头/上工件的接触面积越大,焊头传递声能的路径也越大;此外,高的振幅促进了材料的软化,铜/铝接头的互锁变强,焊头的声传递也随之增加,导致了上工件的振幅也越高.
图7为焊接振幅16 μm和25 μm时的下工件的振幅.下工件振幅在焊接过程中均呈现逐渐近似线性增加的趋势. 在整个焊接过程中,随着焊接振幅增大,下工件的振幅随之变高,这是因为此时上工件振幅越大(图6),传递至下工件的振动能量也越大. 此外,高的振幅也会使焊接区域附近出现更多的“微连接”,振动能量传递至下工件的路径也随之变大,因此下工件振幅也越高. 在焊接结束时,由于此时的工件间的机械互锁程度最大,因此下工件振幅达到峰值,焊接振幅16 μm和25 μm 对应的分别为9 μm和12 μm. 因此,高的焊接振幅提高了工件之间的相对运动速度.
3.2 焊接振幅对界面温度影响
界面温度影响母材的塑性变形程度和焊接微观组织. 图8为测量的不同焊接振幅下温度与模拟得到的温度对比. 焊接振幅从16 μm增加到25 μm时,测量的界面温度从358.9 ℃增加至452.9 ℃. 界面温度随着焊接振幅的增大而变高,这是因为较高的焊接振幅,铜/铝接触面之间的相对速度也变大,摩擦热和塑性变形热均提高. 此外,模拟结果与试验结果基本一致,模拟结果与试验结果的平均误差为2.6%.
图9为模拟的不同焊接振幅下工件接触面铝侧的温度分布. 在焊接时间为0.5 s时,焊接振幅为16 , 18.5, 22 μm和25 μm的焊接界面中心处温度分别为355.6 , 402.7 , 431.2 , 450.1 ℃. 考虑到铝和铜的动态再结晶温度约为250 ℃[18],振幅的增大使动态再结晶程度也变大. 随着焊接振幅的增大,焊接区域外的动态再结晶区域,即热影响区(HAZ)也越大,改善了铜/铝的接头性能.
3.3 焊接振幅对工件塑性变形影响
超声波焊接过程中,工具头的齿嵌入工件,导致材料塑性变形. 图10为不同焊接振幅下焊接横截面的宏观形貌. 焊接振幅的增加,导致工件焊接横截面越薄,这是因为下工件的齿嵌入工件深度随振幅的变大而增加.随着焊接振幅的增加,超声和温度使材料软化程度变高,工具头更容易嵌入工件. 此外,随着焊接振幅的变大,材料变软促进了母材的流动,导致焊头边缘下方的材料挤出堆积在焊头外,此时焊头与工件相对滑动较弱,促进焊接界面的结合[19].
图11为模拟的不同焊接振幅下焊接横截面塑性应变分布. 从图11可以看出,工件最大塑性应变均发生在焊头边缘齿下方材料上.随着焊接振幅从16 μm增加至22 μm,模拟的工件最大塑性应变从0.681增加至0.770,这是因为随着焊接振幅增加,工件更容易塑性变形.相比焊接振幅22 μm条件,焊接振幅25 μm下的最大塑性应变增加不明显,但在焊接界面的塑性应变增加明显. 高的塑性变形说明界面的机械互锁程度增强.
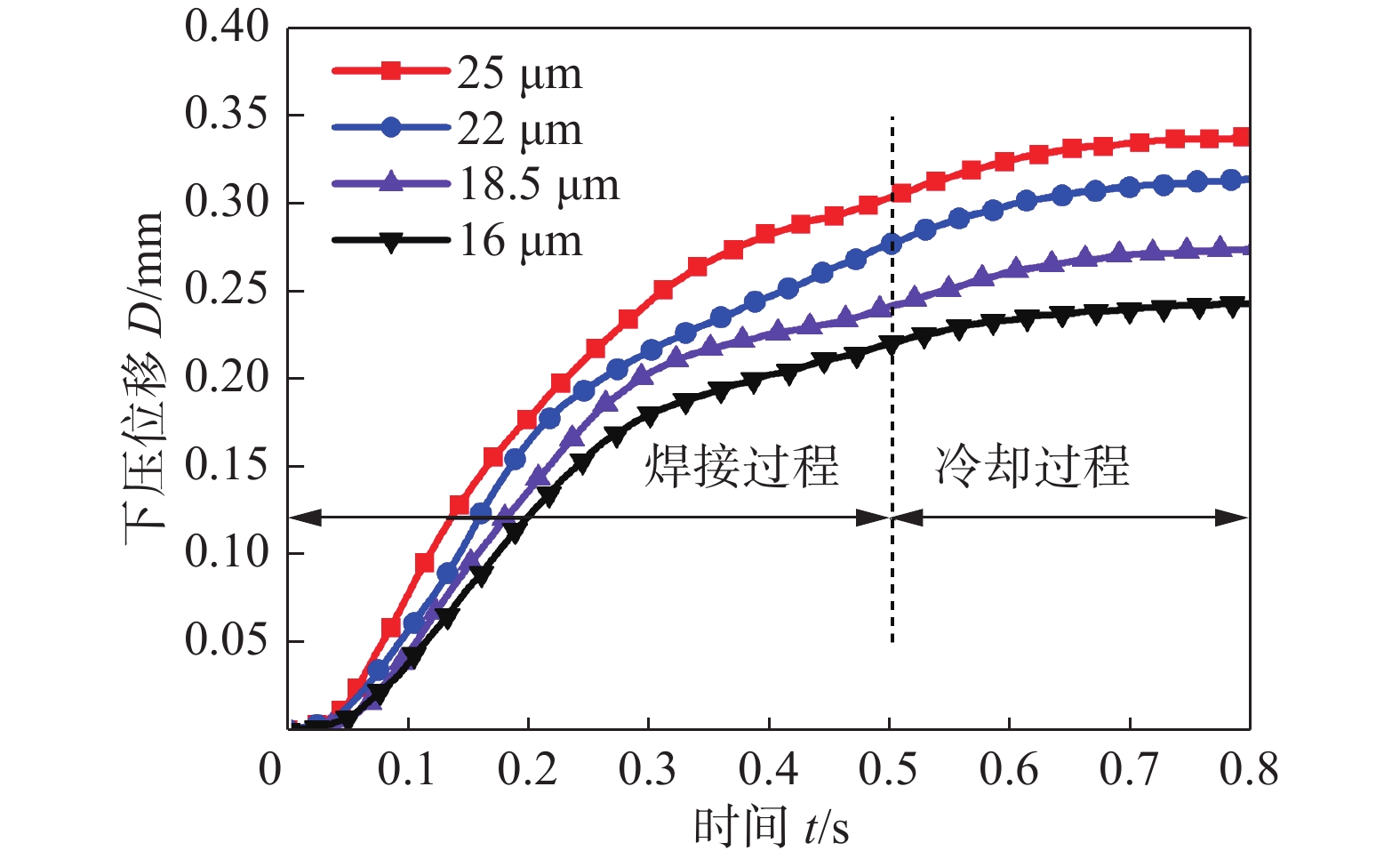
图12为随时间变化不同焊接振幅的焊头下压位移曲线. 在焊接时间为0.5 s、焊接振幅分别为16,18.5,22 μm和25 μm时,对应的焊头下压位移分别为0.221,0.242,0.277 mm和0.304 mm. 焊头下压位移随焊接振幅的增加而增大,这是因为更高的焊接振幅下温度更高,工件材料软化程度更高,因此焊头和底座的齿端更容易嵌入工件. 由于焊头下压位移与焊接区域总应变呈近似线性关系[15],因此焊头下压位移越大,焊接区域内材料塑性应变率更大,空位浓度也越高,促进了接头的冶金结合.
3.4 焊接振幅对焊接界面微观组织的影响
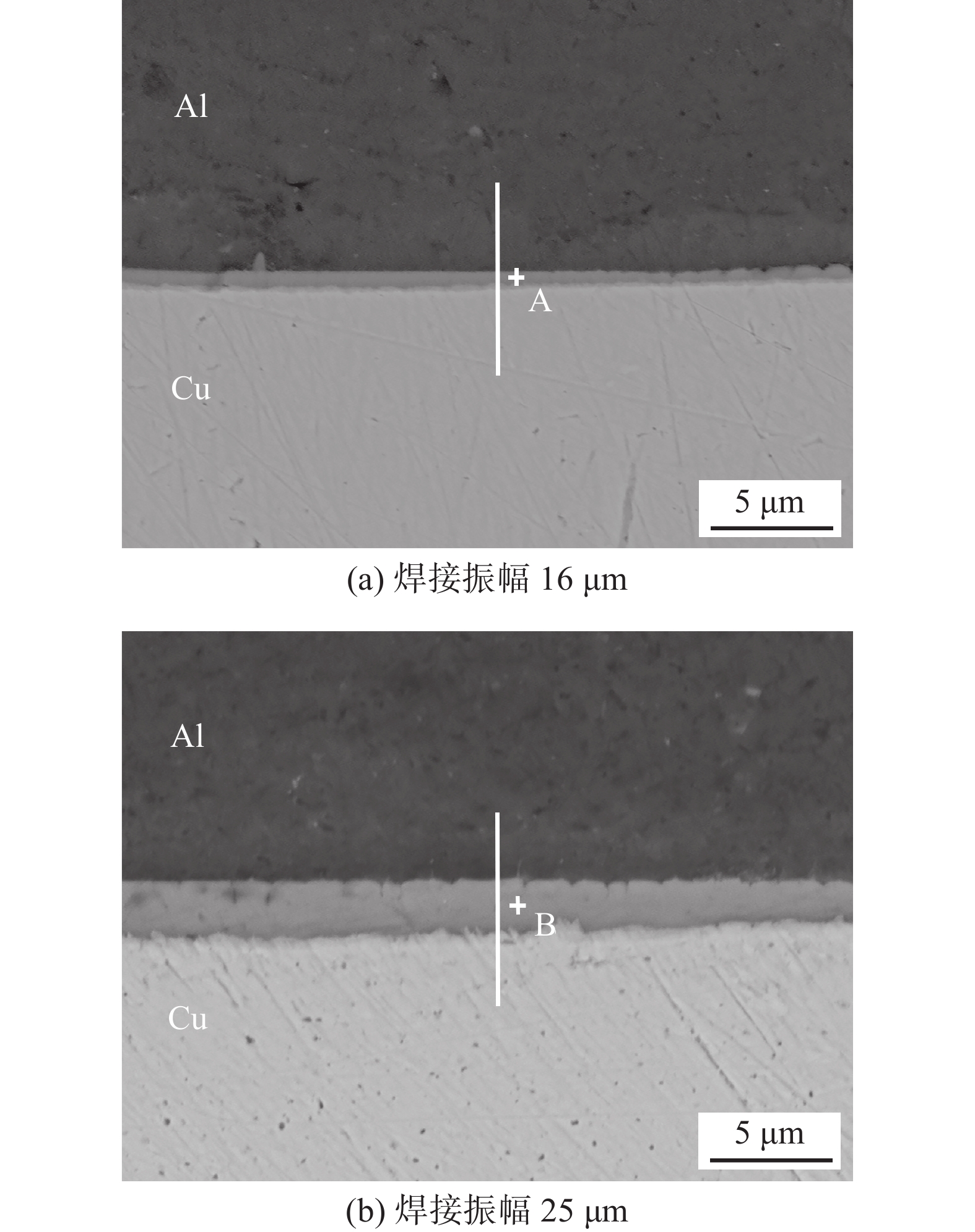
图13为焊接振幅16 μm和25 μm下焊接界面形貌. 在焊接振幅16 μm下焊接界面生成的IMC层厚度仅为0.7 μm,明显小于焊接振幅25 μm下生成的IMC层厚度2.1 μm,且后者的IMC分布相比更均匀. 这是因为焊接振幅提高,界面温度上升,塑性变形也随之提高,焊接区域的空位浓度增大,增加了铜、铝原子扩散的激活能,增强了铜、铝原子扩散[20],进而使IMC变厚.相比常规弧焊时,界面以晶界上的温度扩散为主,铜/铝超声波焊接的扩散主要为晶体内的扩散. 高的振幅使晶体内空位增多,因此冶金结合更紧密.
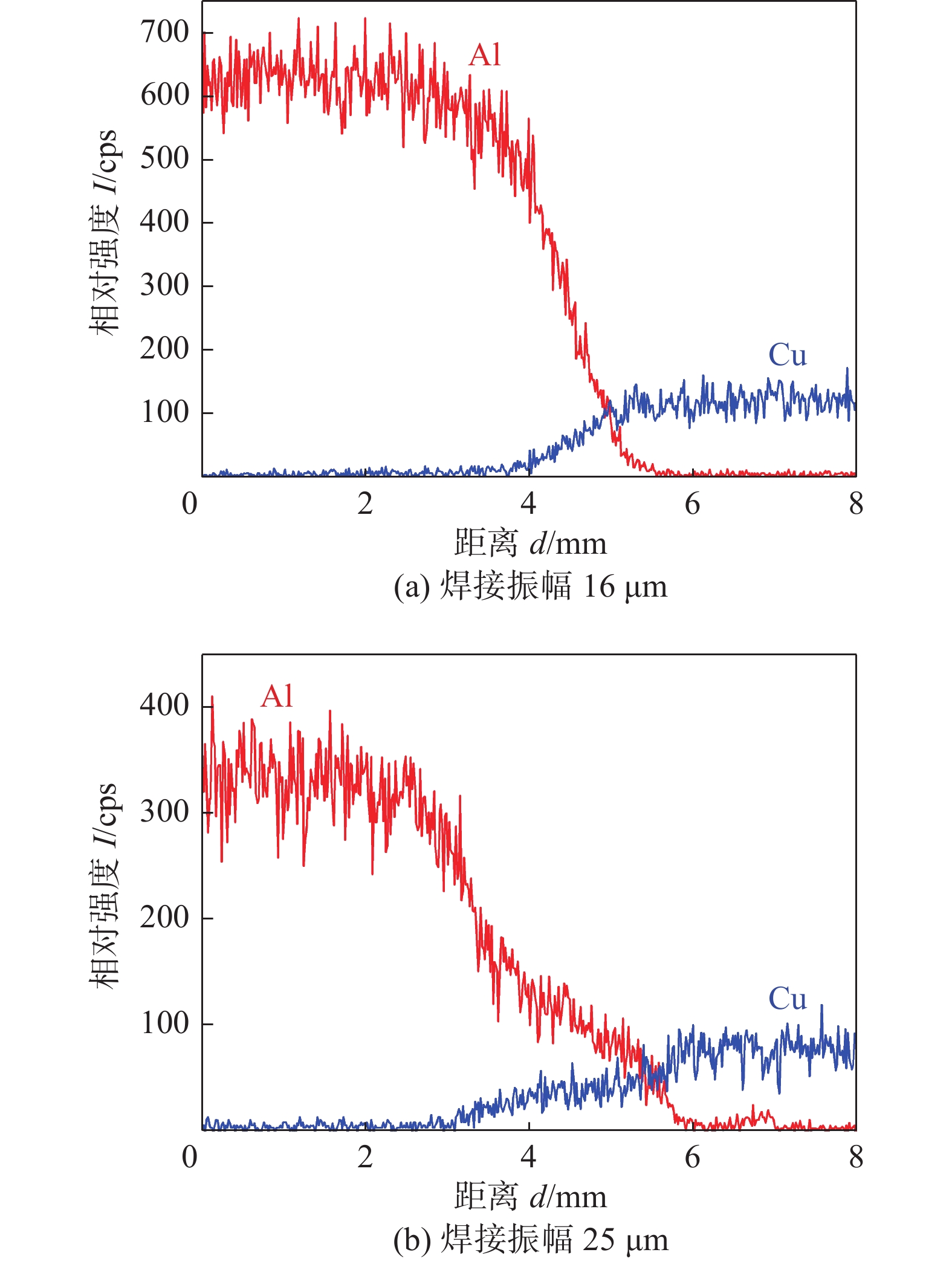
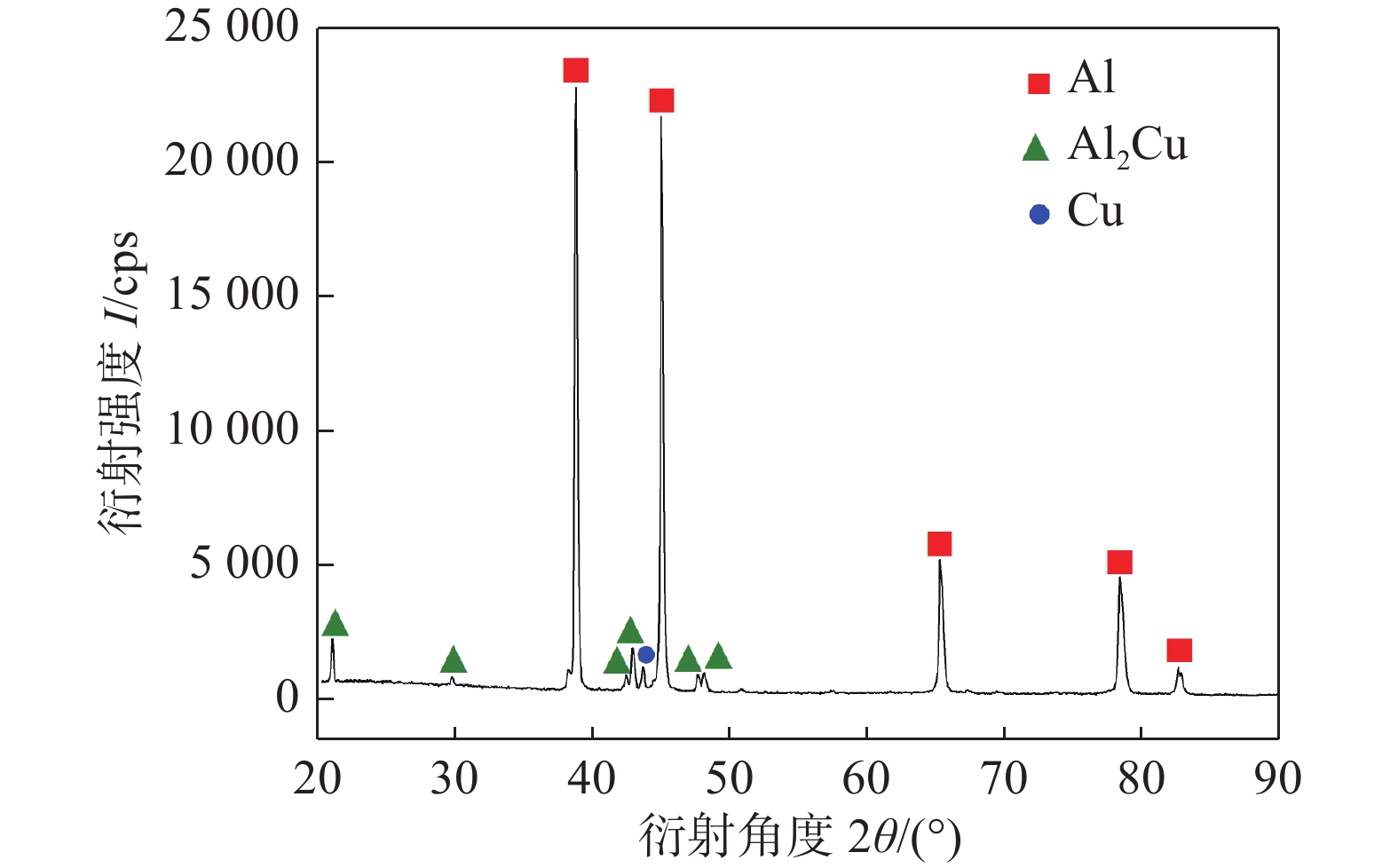
采用EDS获得了焊接界面的IMC的元素组成. 图14为焊接振幅16 μm和25 μm的线扫描结果,界面明显有IMC生成. 根据点扫描结果,点A,B(图13)对应的元素含量分别为60.96Al-39.04Cu和55.22Al-44.78Cu(质量分数),原子分数分别为78.62Al-21.38Cu和74.23Al-25.77Cu. 依据Cu-Al二元相图对比说明IMC为Al2Cu脆性相. 图15的Al侧界面断口的XRD分析进一步确定了界面中间相由Al2Cu相组成,该结果与谷晓燕等人[11]的研究一致.
3.5 焊接振幅对接头的力学性能影响
图16为铜/铝接头拉剪力与焊接振幅的关系. 当焊接振幅为25 μm时,接头拉剪力达到了3150 N(90 MPa),这比Satpathy等人[21]获得的1100铝纯铜超声波焊接接头强度要高.
较高的焊接振幅获得高的超声波焊接质量的原因是:在焊接初期,在高的振幅条件下,工件间相对运动速度提高(图6和图7),使氧化膜更早的破碎[22]、焊接界面处形成更多的微连接区域;随后初始金属连接面更早的形成,界面处发生原子间扩散. 高的振幅使界面处材料的塑性变形程度提高,晶体内空位浓度增高,更好地促进了界面的冶金结合(图13);在焊接后期,高的焊接振幅下界面温度更高(图9),界面处材料塑性变形越大,导致界面处以及界面附近的热影响区内微连接点增多;此外,界面处的剪切应力也越大,界面处形成强烈的机械互锁,最终形成更高质量铜/铝接头.
4. 结论
(1) 在焊接时间0.5 s、焊接压力1575 N下,焊头的振幅与振幅比例之间呈近似线性增加.随着焊接振幅的增大,上工件铜的振幅明显增大,而对于下工件振幅呈小幅度的增加.焊接振幅越高,工件之间的相对运动速度也越大.
(2) 随着焊接振幅越高,界面温度也越高,使焊头下压程度更深,促进了工件的塑性变形,增强了界面原子间扩散,使IMC层分布越均匀,这促进了铜/铝接头的形成.
(3) 铜/铝超声波焊接接头质量随焊接振幅的增加而增大. 在焊接压力1 575 N、焊接时间0.5 s、焊接振幅25 μm条件,获得最高拉剪力为3 150 N的铜/铝接头.
-
图 4 材料物理属性[15]
Figure 4. Material properties. (a) thermophysical properties; (b) mechanical properties
-
[1] Hu G F, Huang P F, Bai Z H, et al. Comprehensively analysis the failure evolution and safety evaluation of automotive lithium ion battery[J]. eTransportation, 2021, 10(11): 100140.
[2] Liu J, Cao B, Yang J W. Texture and intermetallic compounds of the Cu/Al dissimilar joints by high power ultrasonic welding[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 76(4): 34 − 45.
[3] 于江, 潘俊林, 苗惺林, 等. 铝/铜异种金属电阻热辅助超声波缝焊工艺特性[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(7): 76 − 81. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220124001 Yu Jiang, Pan Junlin, Miao Xinglin, et al. Process characteristics of the resistance heat-assisted ultrasonic seam welding of aluminum alloy and copper dissimilar metals[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(7): 76 − 81. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220124001
[4] Leon M D, Shin H S. Review of the advancements in aluminum and copper ultrasonic welding in electric vehicles and superconductor applications[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2022, 307(6): 117691.
[5] Yan S H, Shi Y. Influence of laser power on microstructure and mechanical property of laser-welded Al/Cu dissimilar lap joints[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 45(9): 312 − 321.
[6] Das A, Masters I, Williams D. Process robustness and strength analysis of multi-layered dissimilar joints using ultrasonic metal welding[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 101(1-4): 881 − 900. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2936-3
[7] Elkjaer A, Sorhaug J A, Ringen G, et al. Electrical and thermal stability of Al-Cu welds: Performance benchmarking of the hybrid metal extrusion and bonding process[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 79(7): 626 − 638.
[8] Feng M N, Yan X, Zhao C F, et al. Microstructure and mechanical performance of ultrasonic spot welded open-cell Cu foam/Al joint[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 33(6): 86 − 95.
[9] 柳健, 杨景卫, 曹彪, 等. 铜/铜超声波焊接的相对运动及断面微观演变[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(9): 41 − 44. Liu Jian, Yang Jingwei, Cao Biao, et al. Relative motion and its relation to microstructure evolution during high-power ultrasonic welding of copper sheets[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(9): 41 − 44.
[10] 李东, 赵杨洋, 张延松. 焊接能量对铝/铜超声波焊接接头显微组织的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2014, 35(2): 47 − 50. Li Dong, Zhao Yangyang, Zhang Yansong. Effect of welding energy on microstructures of the Al /Cu joints obtained by ultrasonic welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2014, 35(2): 47 − 50.
[11] 谷晓燕, 刘东锋, 刘婧, 等. 焊接能量对Cu/Al超声波焊接接头组织与性能的影响[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(5): 1600 − 1607. Gu Xiaoyan, Liu Dongfeng, Liu Jing, et al. Effect of welding energy on microstructure and mechanical properties of Cu/Al joints welded by ultrasonic welding[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(5): 1600 − 1607.
[12] Cheng X M, Yang K, Wang J, et al. Ultrasonic system and ultrasonic metal welding performance: A status review[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 84(12): 1196 − 1216.
[13] Kong C Y, Soar R C, Dickens P M. Characterisation of aluminium alloy 6061 for the ultrasonic consolidation process[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2003, 363(1-2): 99 − 106. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(03)00590-2
[14] Shin H S, De Leon M. Parametric study in similar ultrasonic spot welding of A5052-H32 alloy sheets[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 224(10): 222 − 232.
[15] Li H, Cao B, Liu J, et al. Modeling of high-power ultrasonic welding of Cu/Al joint[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 97(1-4): 833 − 844. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2002-1
[16] 李欢. 基于数值模拟的超声焊及电阻热辅助超声焊过程研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2018. Li Huan. Study of the ultrasonic welding and resistance heat assisted welding process based on simulation analysis[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2018.
[17] Wang Y X, Ao S S, Zhang W, et al. Numerical simulation of ultrasonic spot welding of superelastic NiTi alloys: Temperature distribution and deformation behavior[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering, 2022, 144(8): 081003. doi: 10.1115/1.4053523
[18] 李欢, 周亢, 曹彪, 等. 铝合金大功率超声波焊接界面及接头性能研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2021, 57(6): 87 − 95. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.06.087 Li Huan, Zhou Kang, Cao Biao, et al. Analysis of welding interface and joint properties of high power ultrasonic welding of aluminum alloy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 57(6): 87 − 95. doi: 10.3901/JME.2021.06.087
[19] Ni Z L, Yang J J, Gao Z T, et al. Joint formation in ultrasonic spot welding of aluminum to copper and the effect of particle interlayer[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 50(2): 57 − 67.
[20] Levine L. The ultrasonic wedge bonding mechanism: Two theories converge[C]//SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering. Proceedings of SPIE. Austin, United States, 1995: 242 − 246.
[21] Satpathy M P, Sahoo S K. Microstructural and mechanical performance of ultrasonic spot welded Al-Cu joints for various surface conditions[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2016, 22(4): 108 − 114.
[22] Ma Q C, Song C, Zhou J L, et al. Dynamic weld evolution during ultrasonic welding of Cu-Al joints[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2021, 823(8): 141724.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 袁明新,戴现令,刘超,孙宏伟,王磊. 基于空间位置和轮廓线距离的船舶焊缝特征参数提取. 焊接学报. 2023(01): 84-92+133-134 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 陈兵,贺晟,刘坚,陈圣峰,路恩会. 基于轻量化DeepLab v3+网络的焊缝结构光图像分割. 中国激光. 2023(08): 49-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张开放,刘蔓,陈欢群,柴绪彬. 基于电容式传感器的焊缝特征检测技术. 自动化与仪表. 2023(06): 81-84+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 祖海英,卢兴宇,宋玉杰,李大奇. 基于激光熔覆再制造PDC钻头的机器人仿真分析. 焊接学报. 2022(10): 71-76+117-118 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 夏卫生,方向瑶,杨帅,林富明,杨云珍. 基于频率调谐的焊缝红外图像显著性检测算法. 焊接. 2021(04): 8-12+62 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)



 下载:
下载: