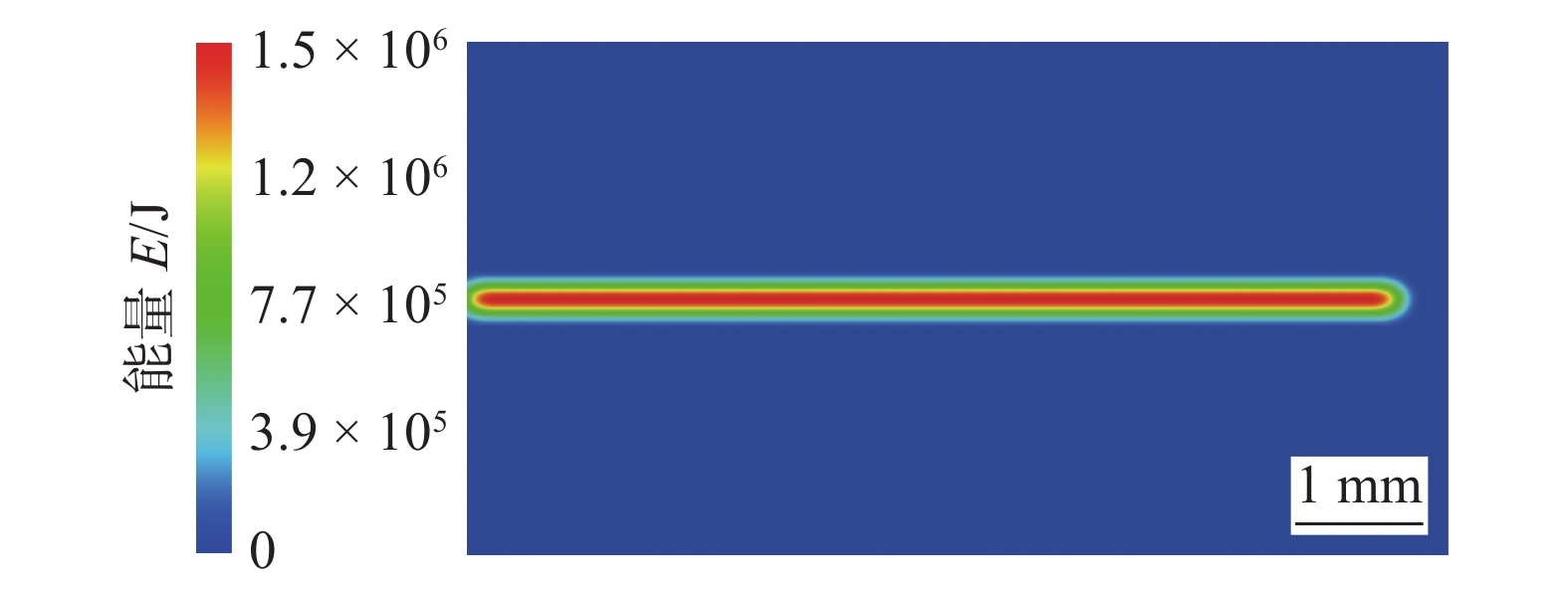
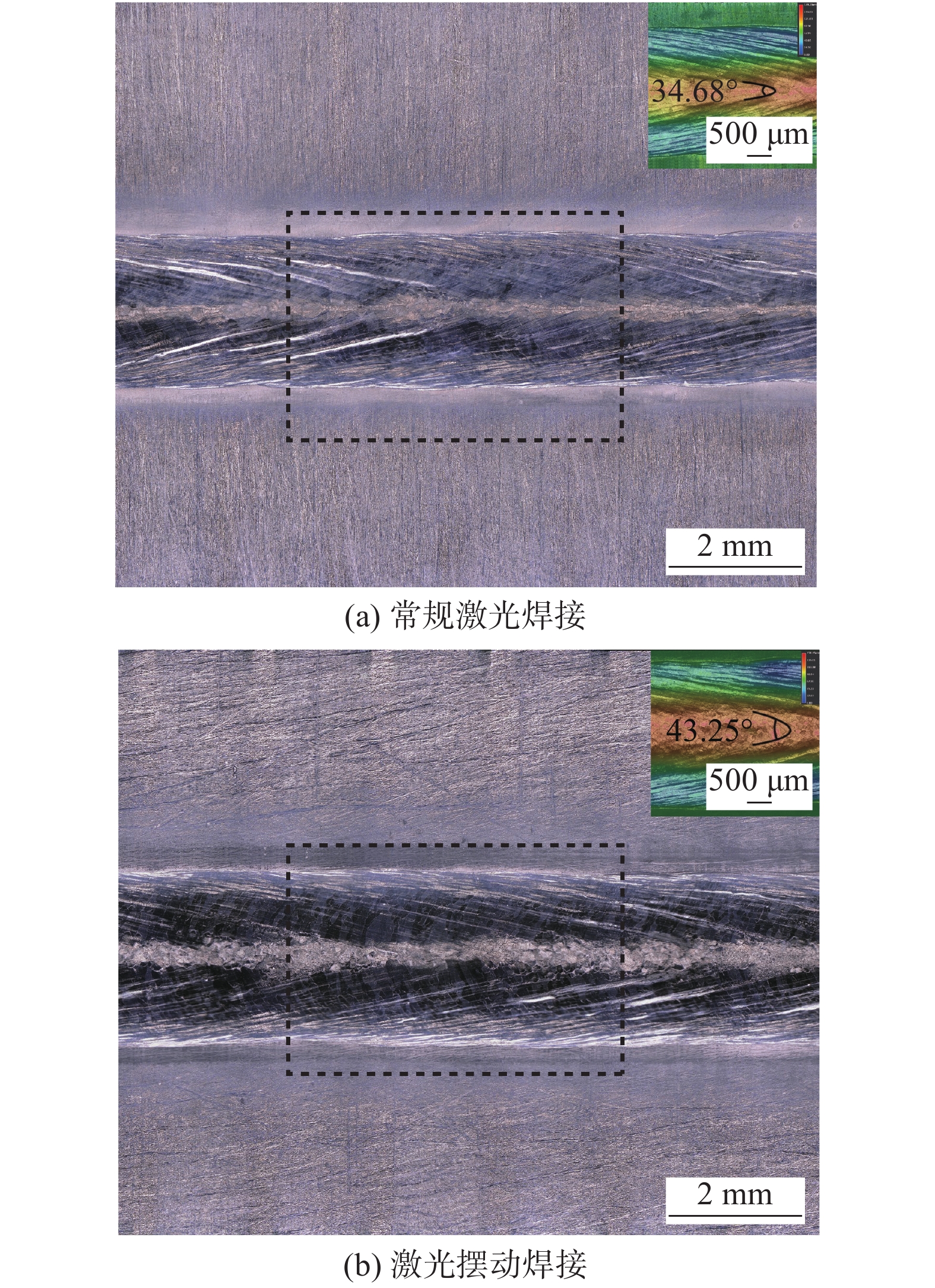
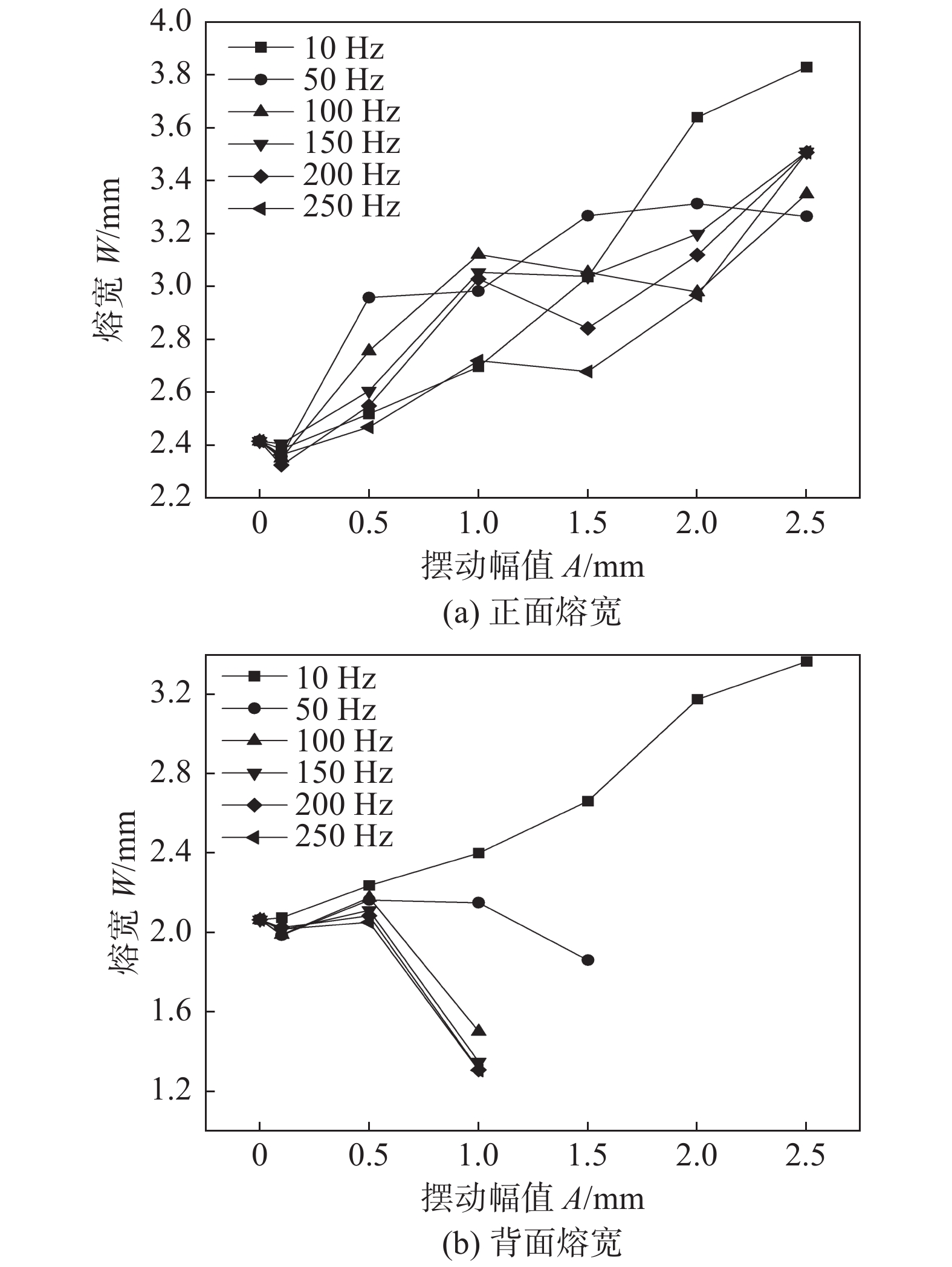
Effect of laser wobble on energy distribution and weld forming of Ti60 alloy laser welding
-
摘要: 对2.0 mm厚Ti60合金进行激光摆动焊接,研究光束圆形摆动时摆动频率和摆动幅值对焊缝成形及能量分布的影响. 结果表明:相较常规激光焊接,激光摆动焊接可以明显改善Ti60合金焊接接头焊缝成形;光束摆动参数对焊缝成形的影响与激光能量分布密切相关,可通过调整能量分布控制焊缝成形. 当摆动频率为100 ~ 150 Hz,摆动幅值为0.5 ~ 1.0 mm时,激光能量分布相对均匀,可获得焊缝成形良好的Ti60合金激光焊接接头. 与常规激光焊缝相比,摆动焊缝熔宽增加约30%,整体飞溅数量减少30%以上,为对接焊缝提供了更大的间隙适应性并有效改善了焊接质量. 在光束摆动参数中,摆动幅值对焊缝成形特征及能量分布的影响更明显.Abstract: Laser wobble welding is performed on a 2.0 mm-thick Ti60 sheet. The effects of wobble frequency and amplitude on weld forming and energy distribution are investigated when wobble track is circular. The result shows that, the weld forming of Ti60 welded joint can be significantly improved by using laser wobble welding. The effect of wobble parameters on weld forming is closely related to energy distribution, and the weld forming can be controlled by adjusting the energy distribution. When the wobble frequency and amplitude are in the range of 100 ~ 150 Hz and 0.5 ~ 1.0 mm, respectively, the laser energy distribution is relatively uniform, a uniform and a high-quality weld can be obtained. Comparing with the conventional laser welds, the weld width increases 30% and welding spatter decreases more than 30%, which offers a larger gap margin and an effect way of weld quality improvement. The wobble amplitude has a stronger influence on weld forming and energy distribution than the wobble frequency.
-
Keywords:
- Ti60 alloy /
- laser wobble welding /
- weld forming /
- energy distribution
-
0. 序言
在铝合金的焊接工艺中,由于MIG焊工艺的生产效率高、焊接质量好、易于填充金属等优点被广泛的应用于铝合金结构的制造工业中,适用于不同厚度的各种复杂焊接结构的连接[1-3]. 近年来,随着计算机技术与数值分析方法的高速发展,铝合金传统MIG焊数值模拟的研究也越来越多. 数值模拟中实现了诸多不同的焊接条件及影响,焊接计算结果不断的逼近于实际物理过程[4-10]. Baharnezhad等人[11]利用有限元分析技术选择双椭球体热源模拟了6xxx系铝合金MIG焊瞬态热过程和应力场,研究了铝合金MIG焊温度场,模拟并研究了电弧电压、焊接速度等焊接工艺参数对温度分布特性的影响规律. Azar等人[12]为了提高数值计算精度,开发了两个分割的双椭圆面热源模型,并利用高速摄像机捕捉和分析MIG焊熔池几何形貌,基于此试验结果给定了新型热源模型形状,通过有限元分析方式分析了MIG焊热过程. Mandal等人[13]基于双椭球体热源模型,加入电弧脉冲参数的影响因素,如基值电流及持续时间、峰值电流及持续时间、脉冲频率,数值模拟了铝合金脉冲熔化极气体保护焊热过程和焊缝几何形状,分析了焊接熔宽、熔深的变化行为. 秦国梁等人[14]根据搭接结构MIG焊热源非对称性,开发了基于搭接结构造成的电弧热源非对称分布的组合式热源模型,对薄铝合金和镀锌板MIG焊搭接温度场和应力场进行了有限元分析,模拟结果揭示了应力场的演变规律以及残余应力分布特点. 张晓鸿等人[15]对厚板高强铝MIG焊建立了由两个体热源构成组合热源模型,对比了建立的组合热源模型和单一传统热源模型的模拟结果. 结果表明,此热源模型能够合理地计算不同道次脉冲MIG焊熔池轮廓形状. 同时分析了铝合金脉冲MIG焊焊后残余应力分布规律和变形行为. 综上所述,在目前传统MIG焊数值计算与分析中,将MIG焊电弧和熔滴的能量一并看作经典的单一热源模型,或将其描述为组合式热源模型来完成MIG焊的相关数值分析,但忽略了MIG焊熔滴能量以及熔滴对焊接熔池的热效应和冲击效应. 因此,研究进一步优化和修正MIG焊热源模型,以便更加合理表达MIG焊的焊接过程,实现准确的数值计算过程.
基于焊接产热机理及热源特性的研究,以铝合金MIG焊工艺为研究对象,开发更完善、更符合实际情况的组合热源模型. 其中考虑了MIG焊过热熔滴对焊接熔池产生的热与力的影响. 通过开发的考虑熔滴动能和热能的组合热源模型,准确地描述MIG焊指状熔深特性,研究铝合金MIG焊热过程. 此项研究结果对传统MIG焊及其复合焊接数值模拟方面的相关研究及实际应用具有一定的指导意义.
1. 试验方法
试验采用7A52-T651铝合金作为母材,工件尺寸为250 mm × 100 mm × 11 mm. 焊接接头采用低强匹配的5系铝合金焊丝(ER5356焊丝)作为填充材料,焊丝的直径为1.6 mm. 母材7A52铝合金和ER5356焊丝的化学成分如表1所示.
表 1 7A52铝合金和ER5356焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of 7A52 aluminum alloy and ER5356 welding wire材料 Zr Zn Mg Fe Mn Si Cu Ti Al 7A52 0.05 ~ 0.15 4.00 ~ 4.80 2.00 ~ 2.80 0.30 0.20 ~ 0.50 0.25 0.05 ~ 0.20 0.05 ~ 0.18 余量 ER5356 — 0.06 ~ 0.20 4.50 ~ 5.60 0.40 0.08 0.20 0.05 ~ 0.20 0.08 余量 MIG焊焊接系统由Fronius TPS4000数字焊接电源和KUKA机械臂组成,整体焊接系统如图1所示. 熔滴过渡检测拍摄系统包括Baumer HX 13工业级高速CMOS摄像机、激光背景光源、减光镜窄带滤光器、808 nm ± 5 nm光学窄带滤波片和数据采集控制系统. MIG焊工艺参数如表2所示. 采用纯氩气(99.99%)作为MIG焊的保护气体. 焊接前采用15%HNO3和15%NaOH溶液清洗母材表面. 焊后采用1%HF + 1.5%HCl + 2.5%HNO3混合溶液(其余为去离子水) 对接头进行腐蚀抛光,然后采用Zeiss Stemi 2000 C型体式显微镜观察焊缝的宏观和微观组织形貌.
表 2 焊接工艺参数Table 2. Welding parameters焊接速度v0/(mm·min−1) 送丝速度vs /(m·min−1) 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 气体流量Q/(L·min−1) 400 13 290 22.6 20 2. MIG焊热源模型的建立
2.1 MIG焊热源特性
MIG焊的能量来自电弧热,部分电弧热熔化端部铝合金焊丝产生熔滴. 在保护气体吹力、电弧力和地心引力的作用下过热熔滴以较高的速度转移至MIG焊熔池. 熔滴转移过程包括能量和质量的传输. 其余电弧热量会作用于铝合金工件并对其进行加热. 熔滴转移至焊接熔池的过程中,因为熔滴受力和热的交互作用使其具有高频率和高速度的特点. 高速度和高频率的熔滴对MIG焊熔池会形成强烈的冲撞效应,导致MIG焊焊缝几何形貌似指状熔深. 通过焊接试验得到的铝合金MIG焊焊缝截面形貌如图2所示,MIG焊焊缝截面中间部位熔池具有显著下凹特点,产生了明显的指状熔深.
在铝合金MIG焊过程中,MIG焊电弧和过热熔滴既对焊缝熔深产生一定的作用,又对焊缝进行金属材料的填充.其中,MIG电弧总功率Q0为
$$ Q_0{\text{ = }}UI $$ (1) 式中:U为焊接电压;I为焊接电流. 作用于工件上的MIG电弧功率Q1为
$$ {Q}_{\text{1}}\text=\eta (UI-\frac{1}{4}{\text{π}} {d}^{2}\rho v_{\rm{s}}{H}_{\text{d}}) $$ (2) 式中:η为MIG焊电弧有效系数,此值选为0.8[16];ρ为填充金属ER5356铝合金密度;d为ER5356焊丝直径;vs为送丝速度;Hd为熔滴热焓.
以采样频率5 000帧/秒对熔滴过渡过程进行采集,随机采集获取一个周期内MIG焊熔滴过渡行为的投影照片如图3所示. 从图3可以看出,近似呈现球状形状的金属液滴向熔池快速转移与过渡. 采用高速摄像机计算分析模块,根据焊接熔滴背景图定义,获取了金属熔滴尺寸与速度. MIG焊熔滴到达焊接熔池中的速度为3.275 m/s,熔滴尺寸约为1.29 mm.
在MIG焊过程中,过热熔滴将携带大量热能和动能高速转移至焊接熔池,对MIG焊熔池产生显著的热作用与冲击作用. 熔滴过渡至MIG焊熔池时产生的热能可描述为[17]
$$ {Q_{{\text{d1}}}} = \frac{1}{4}{\text{π}} d_{}^2\rho v\left( {{H_{\text{d}}} - {H_{\text{v}}}} \right) $$ (3) 式中:Hv为MIG焊熔池热焓. MIG熔滴动能为[16]
$$ {Q_{{\text{d2}}}} = \frac{1}{2}mv_{}^2f $$ (4) 式中:m为熔滴质量;v为熔滴过渡速度;f为熔滴过渡频率. 建立热源模型时,基于热源产热机理、焊缝几何形貌分析和实现MIG焊电弧热量和熔滴热能与动能的考虑,合理地模拟MIG焊温度场分布.
2.2 MIG焊热源模型
根据以上进行的MIG焊热源产热及其特性分析可知,MIG焊热源有电弧和熔滴两种能量传递至母材. 因此,对MIG电弧和熔滴依次进行模型开发. 由于MIG焊热量主要来源电弧热,在电弧热作用下,铝合金工件会产生一定的焊接熔深. 因此,MIG焊电弧被描述表征为由Goldak等人[18]开发的经典双椭球体热源模型. 双椭球体热源模型前、后部分热流密度分布函数为
$$ {q_1} = \frac{{6\sqrt 3 {Q_1}{f_f}}}{{{a_f}bc{\text{π}} \sqrt {\text{π}} }}\exp \left( - \frac{{3{x^2}}}{{{a_f}^{\text{2}}}} - \frac{{3{y^2}}}{{b_{}^{\text{2}}}} - \frac{{3{{\textit{z}}^2}}}{{{c^{\text{2}}}}}\right), \; x\geqslant 0 $$ (5) $$ {q_2} = \frac{{6\sqrt 3 {Q_1}{f_r}}}{{{a_r}bc{\text{π}} \sqrt {\text{π}} }}\exp \left( - \frac{{3{x^2}}}{{a_r^2}} - \frac{{3{y^2}}}{{b_{}^2}} - \frac{{3{{\textit{z}}^2}}}{{c_{}^2}}\right), \; x< 0 $$ (6) 式中:ff,fr分别为双椭球体热源模型前、后半球能量份额;af,ar分别为前、后半球长轴尺寸;a为双椭球体短轴尺寸;c为球体高度.
MIG焊中的熔滴具有高速度、高频率的特性,在过渡至焊接熔池时会产生明显的加热作用与冲击作用,因此使MIG焊焊缝具有指状熔深特性. 此种焊缝形貌运用经典单一热源模型较难校核并计算出指状熔深的焊缝形貌. 为了合理表征MIG焊能量转递过程和指状熔深的焊缝特点,更合理计算MIG焊过程,基于焊接熔滴开发考虑熔滴热能和动能的组合体积热源模型. 由于过热熔滴形似于球体形状向焊接熔池转移,因此将熔滴能量分布类似表示成为具有热能与动能的均匀球体热源模型,其能量输入分布为
$$ {Q_2} = {Q_{{\text{d}} 1}} + {Q_{{\text{d2}}}} = \frac{1}{4}{\text{π}} d_{}^2\rho v\left( {{H_{\text{d}}} - {H_{\text{v}}}} \right){\text{ + }}\frac{{mv_{}^2f}}{2} $$ (7) $$ {q_3}\left( {x,y,{\textit{z}}} \right) = \frac{{3{Q_2}}}{{4{\text{π}} r_{}^3}} $$ (8) 式中:r为球体半径;
${\dfrac{1}{4}}{{\text{π}} {d}_{}^{2}{\rho }_{}{v}_{}({H}_{\text{d}}-{H}_{\text{v}})}$ 为熔滴热能;$\dfrac{{mv_{}^2f}}{2}$ 为熔滴动能.基于上述MIG焊电弧热源模型和熔滴热源模型的组合,最终开发的考虑熔滴热能与动能的MIG焊热源模型能量分布为
$$ {q_{\textit{z}}} = {q_1}{\text{ + }}{q_2}{\text{ + }}{q_3} $$ (9) 3. 有限元模型的建立
3.1 控制方程
为了简化计算模拟过程,达到高速模拟,重点考虑铝合金MIG焊温度场,执行焊接瞬态热传导计算.假设熔池液体金属没有流动. 沿焊接方向三维移动直角坐标系的热传导方程为
$$ \begin{split} & \rho {C_{\rm{P}}}\left[ {( - {v_0})\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial y}} + \frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial t}}} \right] = \frac{\partial }{{\partial x}}\left( {k\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial x}}} \right) + \frac{\partial }{{\partial y}}\left( {k\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial y}}} \right) +\\&\qquad\qquad \frac{\partial }{{\partial {\textit{z}}}}\left( {k\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}}} \right) + {q_{\textit{z}}} \end{split} $$ (10) 式中:ρ为材料密度;CP为材料等压比热容;k为材料热导率;v0为焊接速度;T为工件温度;qz热源能量密度. 数值计算中的边界条件为
$$ t=0, \;\; T(x,y,{\textit{z}},0)={T}_{0} $$ (11) 工件上、下表面边界条件为
$$ k\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}} = {q_{\rm{s}}} - \alpha \left( {T - {T_0}} \right) $$ (12) $$ - k\frac{{\partial T}}{{\partial {\textit{z}}}} = \alpha \left( {T - {T_0}} \right) $$ (13) 式中:qs为工件表面上热流;α为综合散热系数;T0为环境温度.
3.2 有限元几何模型和网格划分
有限元网格基于“生死单元”手段完成MIG焊焊缝金属充填.依据模拟要求,通过六面体八节点网格完成解析域离散化,网格采用不均匀方式,有效协调模拟耗时和准确度之间的冲突. 有限元网格模型为200 mm × 100 mm × 12 mm. 图4为12 mm厚铝合金MIG焊模拟所用的非均匀有限网格,网格共有90000余个单元. 其中焊缝及近缝区为精细的网格,保证计算精度. 远离焊缝区为稀疏网格缩短计算时间. 计算步长为0.633 s,计算总时间为2 800 s.
3.3 铝合金的热物理性能
在焊接热源加热的作用下,可热处理Al-Zn-Mg系合金(7xxx系铝合金)经历不同焊接热循环区域位置会产生脱溶与回归等过程. 在脱溶和回归中,此行为会使接头中第二相粒子发生溶解、析出以及重新分布. 这一过程会致使Al-Zn-Mg系合金的热物理性能发生转变,即热物理性能参数发生变化.
为了更准确数值计算铝合金MIG焊温度分布,测试了铝合金材料热物理性能参数(热扩散系数、热导率和连续比热容),如图5~图7所示. 图5为运用激光导热仪分析获取的不同温度下7A52铝合金热扩散系数. 图6为利用差示扫描量热法获取的室温至550 ℃范围内的连续等压比热容. 图7为7A52铝合金的热导率,随温度变化的热导率是基于热扩散系数、等压比热容以及密度计算获取的. 依据热物理性能参数测量分析结果,基于实测的热扩散系数、比热容以及热导率完成7A52铝合金热物理性能参数数据库的开发,更符合实际焊接过程的材料热物理参数数据库和MIG焊热过程的数值计算与分析.
4. 结果与分析
为了对比分析开发的MIG焊热源模型,分别通过传统经典双椭球体热源模型与建立的考虑熔滴热能和动能的组合体积MIG焊热源模型,数值模拟铝合金MIG焊热过程.图8为运用不同热源模型计算出的MIG焊焊缝截面温度场分布情况. 从图8可以看出,运用传统经典双椭球体热源模型和开发的热源模型模拟获取的焊缝截面熔合线形状具有一定差别. 前者模拟得到的焊缝形貌如似碗碟形状(图8a),焊缝截面熔合线形貌平缓且光滑. 采用后者考虑熔滴热能和动能组合体积热源模型,模拟获取的焊缝几何轮廓有明显下凹形迹,焊缝中间位置熔合线走势变化显著,焊缝整体轮廓近似指状熔深特性(图8b).
图9为运用开发的热源模型模拟获取的MIG焊缝截面轮廓和实际焊接结果对比. 从图9可以看出,模拟得到的MIG焊熔池几何形貌和实际得到熔池形貌吻合良好,两者的熔合线走势基本相同. 通过双椭球体热源模型模拟的MIG焊焊缝截面熔池几何形貌和实际获取的熔池形貌存在一定区别,这说明传统单一热源模型不能精准描述MIG焊热源特征,不能很好地考虑熔滴对MIG焊熔池热和冲击作用;而运用考虑熔滴热能和动能的热源模型能够更合理地描述MIG焊能量输入与作用模式. 对于MIG焊而言,此开发的热源模型具有良好的合理性和适用性.
图10为采用开发的热源模型计算获取的准稳态时铝合金试件上、下表面及纵向剖面MIG焊温度分布图. 从图10a可观察到,MIG焊熔池上表面呈现椭圆形,焊接熔池长度和宽度较大,且具有较大的金属熔化量. 从图10b观察到,铝合金工件并未熔透,焊接熔深到达了工件厚度的一半多,且其下表面等温曲线为椭圆形貌. MIG焊热源前端区域的温度梯度较大,后端区域的温度梯度较小,在整体焊接方向上焊接熔池具有显著的拖尾特征.
5. 结论
(1) MIG焊热量主要为电弧热,部分电弧热熔化焊丝形成熔滴,在热力耦合作用下熔滴转移至焊接熔池时进行热能和动能传输. 高频率、高速度的熔滴对焊接熔池产生一定的冲击作用,使MIG焊焊缝中间区域下凹,形成指状熔深.
(2) 基于MIG焊热源特性及焊缝截面形状,MIG焊电弧被表示为经典的双椭球体热源,熔滴能量被表示为均匀球体热源. 同时在开发的热源模型中考虑了熔滴所携带的动能,建立了考虑熔滴热能与动能的组合体积热源模型.
(3) 通过开发的考虑熔滴热能和动能的组合体积热源模型,数值模拟了7A52铝合金MIG焊热过程,模拟获取的焊缝轮廓形貌、尺寸和实际焊接结果吻合较佳. 这表明开发的热源模型能够合理表征MIG焊热源热输入形式和指状熔深特性.
-
表 1 Ti60合金的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of Ti60 titanium alloy
Al Sn Zr Mn Nb Ta Si Ti 5.2 ~ 6.2 3.0 ~ 4.5 2.5 ~ 4.0 0.2 ~ 1.0 0.2 ~ 0.7 0.2 ~ 1.5 0.2 ~ 0.6 余量 -
[1] 郭举乐, 田永武. 600 ℃高温钛合金的研究进展[J]. 铸造技术, 2020, 41(9): 894 − 896. Guo Jule, Tian Yongwu. Research and development of 600 ℃ high temperature titanium alloys[J]. Foundry Technology, 2020, 41(9): 894 − 896.
[2] 李毅, 赵永庆, 曾卫东, 等. 航空钛合金的应用及发展趋势[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(Z1): 280 − 282. Li Yi, Zhao Yongqing, Zeng Weidong, et al. Application and development of aerial titanium alloys[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(Z1): 280 − 282.
[3] 芦伟, 马旭颐, 段爱琴, 等. BTi6431S钛合金光纤激光焊接成形及稳定性分析[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2020, 57(13): 220 − 225. Lu Wei, Ma Xuyi, Duan Aiqin, et al. Weld formation and stability analysis of fiber laser beam welded BTi6431S titanium alloy[J]. Laser and Optoelectronics Progress, 2020, 57(13): 220 − 225.
[4] Li J, Liu Y, Zhen Z, et al. Analysis and improvement of laser wire filling welding process stability with beam wobble[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2021, 134: 106594.
[5] Hao K, Geng L, Ming G, et al. Weld formation mechanism of fiber laser oscillating welding of austenitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2015, 225: 77 − 83. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.05.021
[6] Hugger F, Hofmann K, Kohl S, et al. Spatter formation in laser beam welding using laser beam oscillation[J]. Welding in the World, 2015, 59(2): 165 − 172. doi: 10.1007/s40194-014-0189-9
[7] 包刚, 彭云, 陈武柱, 等. 超细晶粒钢光束摆动激光焊接的研究[J]. 应用激光, 2002, 22(2): 203 − 205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-372X.2002.02.032 Bao Gang, Peng Yun, Chen Wuzhu, et al. Study on laser welding of ultra-fine grained steel with weaving beam[J]. Applied Laser, 2002, 22(2): 203 − 205. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-372X.2002.02.032
[8] Li S, Mi G, Wang C, et al. A study on laser beam oscillating welding characteristics for the 5083 aluminum alloy: Morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2020, 53: 12 − 20. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2020.01.018
[9] 李军兆, 孙清洁, 张清华, 等. 空间多位置摆动激光填丝焊接熔池动态行为及焊缝成形[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(10): 35 − 39,61. Li Junzhao, Sun Qingjie, Zhang Qinghua, et al. Research on molten pool dynamic behavior and weld formation of transverse oscillating laser welding process for various positions in space[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(10): 35 − 39,61.
[10] 芦伟, 马旭颐, 巩玥, 等. 光束摆动对铝合金激光搭接焊缝成形及组织的影响[J]. 应用激光, 2022, 42(1): 9 − 14. doi: 10.14128/j.cnki.al.20224201.009 Lu Wei, Ma Xuyi, Gong Yue, et al. Effect of laser wobble on the weld formation and microstructure of aluminum alloy lap joint[J]. Applied Laser, 2022, 42(1): 9 − 14. doi: 10.14128/j.cnki.al.20224201.009
[11] 陈根余, 王彬, 钟沛新, 等. 2060铝锂合金扫描填丝焊接工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(4): 44 − 50. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20191016002 Chen Genyu, Wang Bin, Zhong Peixin, et al. Laser scanning welding of 2060 Al-Li alloy with filler wire[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(4): 44 − 50. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20191016002
[12] 雷正龙, 毕思源, 张新瑞, 等. 2195铝锂合金T型接头双侧激光摆动焊接组织与性能分析[J]. 中国激光, 2022, 49(8): 30 − 39. Lei Zhenglong, Bi Siyuan, Zhang Xinrui, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of double-sided laser swing welding of 2195 Al-Li alloy T-joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2022, 49(8): 30 − 39.
[13] Wang Z, Oliveira J P, Zeng Z, et al. Laser beam oscillating welding of 5A06 aluminum alloys: Microstructure, porosity and mechanical properties[J]. Optics & Laser Technology, 2018, 111: 58 − 65.
[14] Fetzer F, Sommer M, Weber R, et al. Reduction of pores by means of laser beam oscillation during remote welding of AlMgSi[J]. Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2018, 108: 68 − 77. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2018.04.012
[15] Wang L, Gao M, Zhang C, et al. Effect of beam oscillating pattern on weld characterization of laser welding of AA6061-T6 aluminum alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2016, 108: 707 − 717. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.07.053
[16] Thiel C, Hess A, Weber R, et al. Stabilization of laser welding processes by means of beam oscillation[C]//Laser Sources and Applications. SPIE, 2012, 8433: 225-234.
[17] 李坤, 王威, 单际国, 等. TC4 钛合金光纤激光摆动焊抑制小孔型气孔的原因分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2016, 37(11): 43 − 46. Li Kun, Wang Wei, Shan Jiguo, et al. Analysis of keyhole-type pore suppressing in fiber laser welded TC4 titanium alloy with beam weaving[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2016, 37(11): 43 − 46.
[18] Long J, Zhang L J, Zhuang M X, et al. Narrow-gap laser welding with beam wobbling and filler wire and microstructural performance of joints of thick TC4 titanium alloy plates[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2022, 152: 108089. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2022.108089
[19] Squillace A, Prisco U, Ciliberto S, et al. Effect of welding parameters on morphology and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V laser beam welded butt joints[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2012, 212(2): 427 − 436. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2011.10.005
[20] Mahrle A, Beyer E. Modeling and simulation of the energy deposition in laser beam welding with oscillatory beam deflection[C]//International Congress on Applications of Lasers and Electro-Optics. Laser Institute of America, 2007.
[21] Li J Z, Sun Q J, Kang K Q, et al. Process stability and parameters optimization of narrow-gap laser vertical welding with hot wire for thick stainless steel in nuclear power plant[J]. Optics and Laser Technology, 2020, 123: 105921. doi: 10.1016/j.optlastec.2019.105921
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李田,严佑锐凌,张明军,张跃敏. 基于8字形摆动的钢/铝激光焊接头组织和性能. 焊接学报. 2025(02): 112-119+135 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 王一丰,张忠明,马威龙,祁嘉伟,徐春杰,杨长林. 基于二次通用旋转组合设计的冷金属过渡电弧增材制造AZ31镁合金焊道截面尺寸研究. 热加工工艺. 2024(05): 18-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 弭光宝,孙若晨,吴明宇,谭勇,邱越海,李培杰,黄旭. 航空发动机钛合金分子动力学计算技术研究进展. 航空材料学报. 2024(02): 87-103 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张群兵,张阔,于佳恩,张勇进,陈旭飞,陈立明,张建勋. Ti60钛合金激光焊接接头微观组织与低周疲劳性能研究. 西安航空学院学报. 2024(05): 25-32+70 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)



 下载:
下载: