Effect of welding speed on material flow, microstructure and mechanical properties of BT-FSW 2219 aluminum alloy joints
-
摘要: 以4 mm厚2219-T87铝合金为研究对象,采用数值模拟和试验研究相结合的方法,研究了焊接速度对双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊接(BT-FSW)过程中金属流动行为、接头组织特征和力学性能的影响. 模拟结果表明,随着焊接速度增加,焊缝高温区逐渐变窄,轴肩附近的材料流动减弱,而搅拌针附近的材料流动增强. 试验结果表明,随着焊接速度增加,材料汇流区及S线缺陷均向前进侧(AS)靠近,焊接速度过大时AS附近的搅拌区(SZ)形成不连续组织. 接头SZ的硬度值随着焊接速度增加而增大,而拉伸强度先增大后稍降低. 当转速为300 r/min,焊接速度为150 mm/min时,接头获得最大的拉伸强度,为414 MPa ± 4MPa.Abstract: The influence of welding speed on material flow, microstructure and mechanical properties of bobbin-tool FSW (BT-FSW) joints was analyzed by numerical simulation and experimental method on 2219-T87 aluminum alloy with the thickness of 4 mm. The simulation results show that the high-temperature zone of the joint became narrower with the increase of welding speed. The material flow near the shoulder was weakened, while the material flow near the pin was enhanced. The experimental results show that with the increase of welding speed, the material confluence zone and S line defects were closer to the advancing side (AS). However, the stirring zone (SZ) on the AS formed a discontinuous structure when the welding speed was too high. The hardness of SZ increased with the increase of welding speed, while the tensile strength increased first and then decreased slightly. When the welding speed was 150 mm/min and the rotation speed was 300 rpm, the maximum tensile strength of the joint was 414 ± 4 MPa.
-
0. 序言
搅拌摩擦焊(FSW)作为一种先进的固相连接技术,因不涉及被焊金属的熔化,可有效解决铝合金的焊接性难题,已被广泛应用于航空航天、汽车、轨道交通等领域[1-3]. 但工件在常规FSW过程中所受轴向力较大,因此对工件背部固定要求较高,需要精密的工装夹具,极大地限制了FSW在中空薄壁等结构上的应用. 同时,由于搅拌头自身结构特点,其焊接空间适应性也受到一定限制,无法实现无支撑复杂空间曲面结构的搅拌摩擦焊. 而双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊(BT-FSW)作为常规FSW的一个变体,引入下轴肩来代替背部垫板,使FSW技术成功应用于中空及空间无支持薄壁结构的焊接[4-5]. 此外,由于上下轴肩的对称产热,焊接接头在厚度方向的温度分布更加均匀,接头组织也大大改善,从根本上消除了接头根部缺陷. 但BT-FSW也有其缺点,比如热输入增加,在焊缝中间出现了汇流区,容易导致组织缺陷,因此需要研究其形成规律与抑制措施.
目前,关于BT-FSW的研究主要集中在接头宏观成形、微观组织演变、力学性能、材料流动等方面,而关于焊接过程中材料流动行为的研究主要有试验和数值模拟两种方法. Chen等人[6]使用铜箔作为标记材料,试验研究了BT-FSW过程中的材料流动行为. 除常规的材料示踪技术之外,通过分析异质接头的宏/微观组织形貌也可以获得一定的接头内部材料流动信息. Tamadon等人[7]通过对多颜色橡皮泥层叠板进行BT-FSW,直观研究了BT-FSW过程中的材料流动特性,但结果的准确性并未得到充分验证. 尽管材料示踪技术已有效提升了人们对焊接过程中材料流动行为的认识,但试验方法仍存在诸多局限. 数值模拟方法作为现代材料加工过程研究的重要手段之一,在FSW过程材料流动行为研究中具有巨大潜力. 胡晓晴[8]使用Fluent软件研究了BT-FSW过程水平方向上的材料流动行为,得到了塑性材料流动二维模型迹线随时间变化规律. 目前,有关BT-FSW过程中塑性材料流动行为的模拟研究尚处于起步阶段[8-10],相关细节尚未被完全阐明. 课题组前期通过建立耦合欧拉−拉格朗日三维热力耦合计算模型,对BT-FSW的温度场和塑性应变场进行了初步研究,并在模型中预设示踪粒子,通过对粒子的运动轨迹追踪,阐明了材料的流动行为[11]. 而焊接工艺参数对BT-FSW过程中的温度场演变及材料流动起着至关重要的作用,工艺参数直接决定了焊接接头的质量.
文中以4 mm厚2219-T87铝合金为研究对象,通过固定上下轴肩间隙s为3.8 mm,搅拌头转速n为300 r/min,分析了不同焊接速度v下,BT-FSW过程中的材料流动行为、接头组织和力学性能特征.
1. 数值计算模型与试验方法
1.1 模型建立
选用ABAQUS有限元分析软件,基于耦合欧拉−拉格朗日法(CEL)建立了BT-FSW三维热力耦合模型. 如图1所示,该模型由焊板、搅拌头及欧拉空间三部分组成. 其中,欧拉空间尺寸为180 mm × 100 mm × 6.4 mm,焊板尺寸为150 mm × 100 mm × 4 mm,焊板位于欧拉空间中心,为观察前进侧/后退侧材料流动状态的差异,对左右焊板分别进行材料赋予(材料属性相同),如图1a所示. 欧拉空间采用梯度网格划分,近缝区网格尺寸为0.4 mm × 0.4 mm × 0.4 mm(图1b). 在实际焊接过程中,搅拌头轴肩通常采用凸面加涡旋槽设计. 为降低建模难度且较为准确地表达轴肩形貌在焊接过程中的作用,选择保留轴肩涡旋状特征,并将轴肩直径设定为13 mm,其余尺寸均与试验用焊接工具一致.
与课题组前期研究中的建模过程相同,采用Johnson-Cook材料模型,基于界面处的摩擦产热和材料塑性变形产热来计算焊接总产热. 忽略焊板与搅拌头之间的接触换热,设定焊板与夹具和空气之间的热交换系数分别为500 W/(m2·℃)和35 W/(m2·℃). 此外,采用对边界进行速度约束的方法模拟焊板表面位移边界,包括上下表面、左右侧面及前后侧面三部分.
为直观判断焊接过程中的材料流动情况,采用示踪粒子(Tracer particle)技术对焊接过程中的材料流动进行追踪. 如图2所示,在距焊接起始位置80 ~ 105 mm范围内根据研究目的不同,在三个位置分别放置示踪粒子,具体如下:(Ⅰ)判断焊接过程中材料流动的总体趋势,在距焊板上下表面0.4 mm及厚度中心分别放置一层示踪粒子,每层放置51个示踪粒子,间距为0.4 mm,呈线性分布;(Ⅱ)为判断焊接过程中塑性材料水平方向的流动行为,在距焊板上表面0.4 mm及厚度中心分别放置一层示踪粒子,每层放置870个示踪粒子,平铺于11.6 mm × 14.4 mm长方形范围内,间距为0.4 mm;(Ⅲ)为判断焊接过程中塑性材料板厚方向的流动行为,沿焊缝横截面布置示踪点,共设置11层示踪粒子,每层放置51个示踪粒子,间距为0.4 mm.
1.2 试验方法
文中选用的是4 mm厚2219-T87铝合金轧制板材. 2219是Al-Cu-Mn系铝合金,是一种典型的可热处理强化铝合金,具有比强度高、焊接性能好、力学性能优异等优点,目前已被广泛应用于航空航天领域,特别是在新一代航天火箭贮箱、燃料槽等部件有较好的应用前景[12].
采用北京赛福斯特技术有限公司生产的FSW-RL31-010型专用搅拌摩擦焊机进行BT-FSW试验,焊接设备及焊板装夹情况如图3所示. 搅拌工具的上下轴肩直径均为16 mm,表面带有涡旋状凹槽;搅拌针直径为6 mm,具有三平面特征. 为保证焊接过程中轴肩与焊板表面充分接触,将轴肩作凸面设计,两轴肩的搅拌针根部间距为3.8 mm,轴肩外边缘间距为4.2 mm. 搅拌头转速固定为300 r/min,焊接速度依次设置为50 mm/min,150 mm/min和250 mm/min.
焊接完成后,沿垂直焊接方向切取尺寸为50 mm × 10 mm × 4 mm的金相试样,并用砂纸对金相试样横截面进行磨制,随后对试样进行抛光和腐蚀,在OLYMPUS GX71型光学显微镜上观察试样截面组织特征. 此外,所有试样均沿横截面中心线进行显微硬度测试,试验载荷为1.96 N,保压时间为15 s. 拉伸试验在Instron 3382型电子万能试验机上进行,拉伸试样的标距为57 mm,拉伸速度为1 mm/min,拉伸性能以3个试样的平均值作为评价依据.
2. 材料流动行为分析
图4a为不同焊接速度下焊板上表面焊接温度场分布. 可以看到,随着焊接速度增加,焊缝横截面中心线最高温度变化不大,这是由于焊缝中心温度主要受搅拌头产热控制,而焊接速度变化对搅拌头与塑性材料之间的相对运动速度影响较小. 为定量分析焊接过程中搅拌头产热的影响,试验以高强铝合金常用热处理时效温度150 ℃为参考[13],定义焊缝高温区,如图4b所示. 虽然增加焊接速度对焊缝中心线最高温度影响较小,但焊缝高温区尺寸变化显著. 随着焊接速度由50 mm/min增加至250 mm/min,焊缝高温区逐渐减小,宽度逐渐增大,该区域高宽比(H/B)由0.89减小至0.70. 这是由于随着焊接速度的增加,焊接热输入降低,垂直于焊接方向的高温区向焊缝中心线收缩;同时,焊接速度增加加剧了搅拌头前后温差,使得前方温度梯度更大,后方温度梯度变小.
不同焊接速度下BT-FSW接头横截面中心线温度分布如图5所示. 可以看出,焊接速度的改变对焊缝内部温度影响较小,不同焊接速度下焊缝内部温度分布状态及大小均无明显差别. 但随着焊接速度增加,焊缝周围温度逐渐降低,这是由于在焊接过程中,整体焊接热输入与焊接速度成反比. 随着焊接速度增加,焊接热输入逐渐降低,焊接热影响区宽度逐渐减小.
不同焊接速度下BT-FSW接头横截面等效塑性应变如图6所示. 由图6可知,随着焊接速度增加,接头等效塑性应变值逐渐降低. 当焊接速度较高时,接头前进侧存在明显的低塑性应变区,这是材料填充不足所致;随着焊接速度降低,材料流动状态得到改善,该低塑性应变区逐渐向内收缩. 特别地,当焊接速度降至50 mm/min时,虽然上述区域已基本得到填充,但前进侧塑性变形区边缘仍存在少量未被消除的三角形低塑性应变区域(不充分搅拌区),且此时焊缝内部高塑性应变区中心出现反常降低,下面将结合焊后示踪粒子分布对该现象进行解释.
图7为不同焊接速度下轴肩和搅拌针附近水平方向示踪粒子焊后分布情况. 可以看到,随着焊接速度增加,搅拌头对材料的驱动范围整体上向内收缩. 对比不同初始位置示踪粒子的焊后分布状态可知,焊接速度变化时,轴肩附近材料与搅拌针附近材料的变化趋势截然相反. 随着焊接速度增加,轴肩附近前进侧材料的分布在焊后变化不大,而后退侧材料则明显向后退侧收缩. 在BT-FSW过程中,前进侧材料受搅拌针直接驱动,流动过程主要受接触状态影响,焊接速度的改变对接触状态影响较小,因此该部分材料流动过程变化不大. 而后退侧材料受搅拌针间接驱动,流动过程比较平缓,焊接速度的增加直接减少了对该部分材料的驱动时间,因此分布范围向后退侧收缩. 观察搅拌针附近示踪粒子的焊后分布状态可知,焊接速度的增加对后退侧材料的影响较小,而前进侧材料分布范围则向前进侧扩展. 不同于轴肩附近,搅拌针附近材料的运动完全由搅拌针和焊板界面的接触主导,运动过程比较平缓. 随着焊接速度增加,搅拌针前方接触压力提高,极大改善了搅拌针和焊板界面的接触状态. 同时,搅拌针外缘线速度较小,焊接速度增加导致的线速度叠加在该处已不可忽略. 在上述两方面的共同影响下,受搅拌针直接驱动的前进侧材料流动得到加强,因此焊后分布向前进侧偏移.
图8为不同焊接速度下轴肩与搅拌针附近板厚方向示踪粒子在焊后的分布情况. 由图8可知,随着焊接速度增加,板厚方向的材料流动减弱,焊缝区材料的混合状态也略有减弱. 当焊接速度较低时,轴肩附近的材料在前进侧搅拌头后方明显向厚度方向流动,并与搅拌针驱动的材料交汇,在此处形成典型的材料汇流区. 降低焊接速度在增强焊板表面材料流动的同时,也减弱了焊板中心的材料流动,因此不同厚度的材料混合并不充分,靠近板厚中心的材料仍保留部分层流特征.
对比图7与图8发现,上述低塑性应变区位于搅拌针驱动材料与次内层材料的交汇位置,流动较弱的三股材料在此处汇聚,从而形成了上述的低塑性应变区. 而此时前进侧搅拌针边缘发生外层材料的汇聚,形成高塑性应变区,但由于来自后退侧材料的挤压作用较弱,材料交汇形成的不充分搅拌区难以愈合.
3. 接头组织特征
3.1 典型BT-FSW接头组织特征
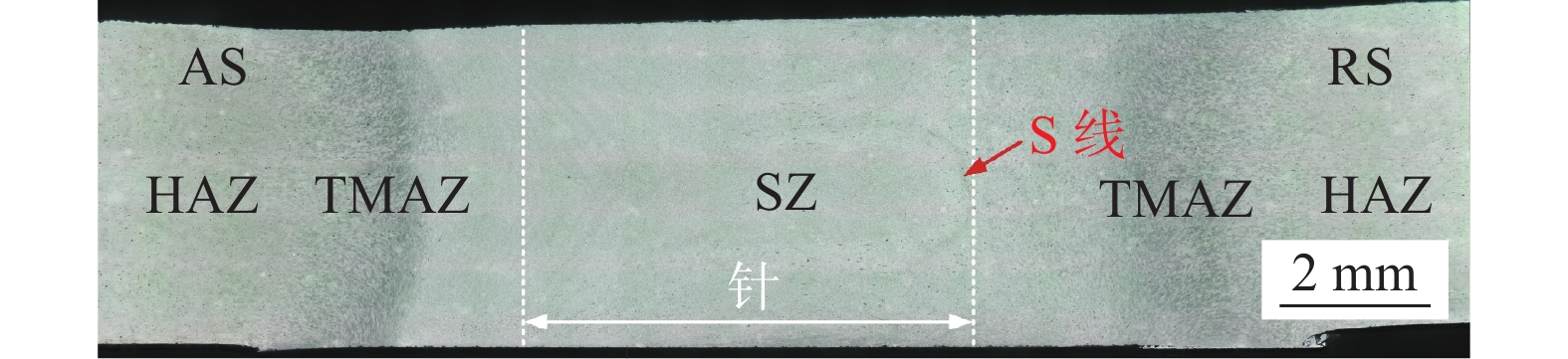
BT-FSW过程涉及复杂的产热与材料流动行为,接头内部组织形貌与焊缝成形过程中材料的流动行为密切相关. 图9为典型工艺参数下BT-FSW接头的横截面宏观组织形貌. 可以看到,接头不同区域组织存在明显差异. 与常规FSW接头相似,根据所经历的热循环和塑性变形程度的不同,BT-FSW接头可分为4个区域:焊核区(SZ)、热力影响区(TMAZ)、热影响区(HAZ)和母材(BM). 与常规FSW接头不同的是,由于上下轴肩的对称作用,BT-FSW接头横截面整体呈上下宽中间窄的哑铃形. 与此同时,下轴肩的引入增强了BT-FSW过程中的焊接热输入,焊缝整体温度略有升高,使得周围冷金属对热塑性金属的约束作用降低,SZ尺寸略有增加. 约束作用较弱,焊缝金属内部始终处于低压状态,因此对焊板原始对接面氧化物的破碎弥散作用不足,接头SZ内部清晰可见S线缺陷. 另外,与后退侧相比,接头前进侧TMAZ/SZ界面更为清晰,这是两侧材料流动状态的不同所致.
3.2 焊接速度对接头组织特征的影响
当转速为300 r/min时,不同焊接速度下焊缝内部材料流动也有所不同,图10为搅拌头转速n = 300 r/min时,不同焊接速度下接头的宏观组织形貌. 由图10可见,不同焊接速度下焊缝内部材料的流动模式并未发生变化,但随着焊接速度降低,同一迁移周期内受驱动材料的体积减少,不同材料层间距减小,前进侧汇流区的材料混合充分并向后退侧延伸. 可以发现减小焊接速度并不能大幅增强汇流区材料向后退侧的挤压作用,这是由于搅拌头对热塑性材料以剪切摩擦作用为主,焊接速度的减小仅提高了对材料的驱动时间,而没有从根本上增强搅拌头对材料的驱动作用. 如图10c所示,当焊接速度过大时(250 mm/min),接头前进侧SZ形成不连续组织.
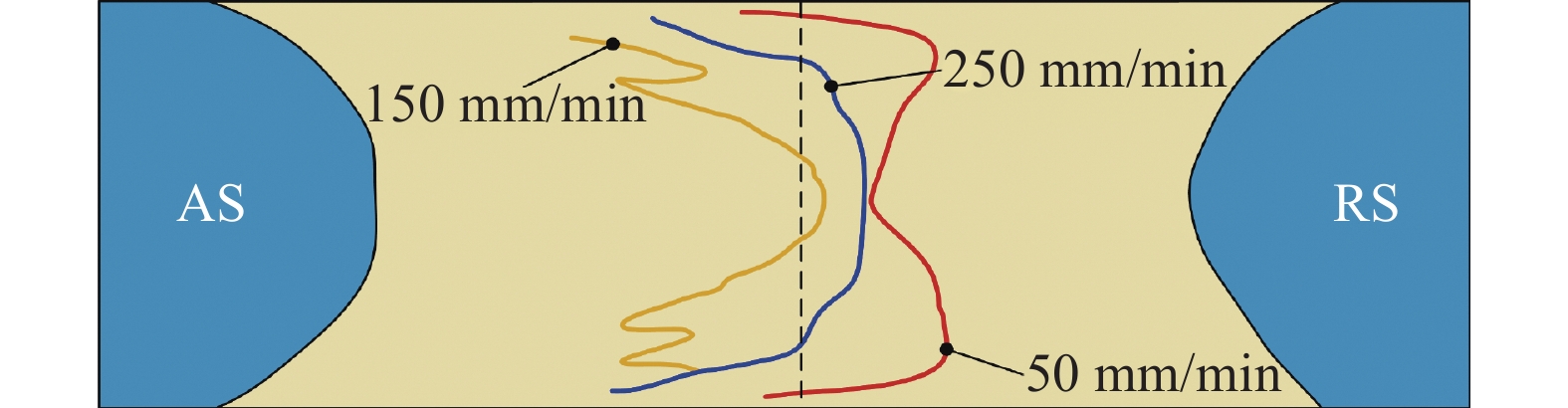
图11为不同焊接速度下接头S线形貌,由图可知,当焊接速度较高时,接头S线形貌受搅拌头直接驱动的材料主导,随着焊接速度的降低,S线向前进侧偏移且形状变得复杂;而当焊接速度较低时,接头S线形貌主要由汇流区的材料与搅拌头直接驱动材料之间的相互挤压作用决定,随着焊接速度降低,S线向后退侧偏移. 两者之间的差异在于改变焊接速度并不能直接影响搅拌头对材料的驱动作用,因此不同焊接速度下接头S线的变化范围较小.
4. 接头力学性能
4.1 显微硬度
不同焊接速度下接头的硬度分布曲线如图12所示.可以看出,接头硬度整体呈W形分布,硬度最低值均位于TMAZ附近. 随着焊接速度提高,接头硬度值整体呈上升趋势,这是由于焊接速度的提高降低了接头整体热输入,第二相回溶粗化现象减弱. 特别地,当焊接速度较高(250 mm/min)时,接头硬度最低点由后退侧转移至前进侧,造成该现象的原因主要是后退侧材料堆积程度不足. 后退侧材料堆积受焊接速度影响较大,焊接速度的提高导致该过程被削弱,热量累积作用减弱;而前进侧热量来源主要为搅拌头与焊板之间的摩擦产热,受焊速影响较小. 因此,随着焊接速度的提高,SZ外侧高温区由后退侧逐渐转移至前进侧,最终导致前进侧硬度低于后退侧.
4.2 拉伸性能
不同焊接速度下BT-FSW接头与母材抗拉强度及断后伸长率如图13所示. 可以看到,接头抗拉强度均低于母材. 当固定搅拌头转速为300 r/min时,随着焊接速度增加,接头力学性能先增大后稍有降低. 特别地,当焊接速度较低(50 mm/min)时,接头力学性能较差. 这是由于BT-FSW接头各区域组织差异较大,在拉伸过程中接头软化区往往会出现明显的应变局部化. 随着焊接速度降低,接头软化区硬度较低,因此接头强度随之减小.
5. 结论
(1) 当增加焊接速度时,焊缝中心温度变化不大,但整体焊接热输入降低. 焊缝高温区逐渐变窄,该区域高宽比(H/B)由0.89减小至0.70. 轴肩附近的材料流动减弱,搅拌针附近的材料流动增强,前进侧板厚中心材料混合状态略有减弱.
(2) BT-FSW接头可分为4个区域:焊核区(SZ)、热力影响区(TMAZ)、热影响区(HAZ)和母材(BM). 由于上下轴肩的对称作用,BT-FSW接头横截面整体呈上下宽中间窄的哑铃形. 当焊接速度增加时,材料汇流区及S线缺陷均向前进侧靠近,焊接速度过大时,前进侧SZ形成不连续组织.
(3) BT-FSW接头横截面显微硬度整体呈W形分布,硬度最低点位于后退侧TMAZ. 随着焊接速度增加,SZ硬度逐渐增高. 随着焊接速度增加,接头抗拉强度先增大后稍有降低. 当转速为300 r/min,焊接速度为150 mm/min时,接头的抗拉强度最大,为414 MPa ± 4 MPa.
-
-
[1] 董春林, 栾国红, 关桥. 搅拌摩擦焊在航空航天工业的应用发展现状与前景[J]. 焊接, 2008(11): 25 − 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2008.11.009 Dong Chunlin, Luan Guohong, Guan Qiao. Prospects of application and development of friction stir welding in aerospace and aviation industry[J]. Welding & Joining, 2008(11): 25 − 31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2008.11.009
[2] 宋建岭, 李超. 搅拌摩擦焊在运载火箭贮箱制造中的应用与发展[J]. 焊接, 2018(5): 21 − 27. Song Jianling, Li Chao. Application of FSW technology to tank manufacturing of launch vehicle and its development[J]. Welding & Joining, 2018(5): 21 − 27.
[3] 张华, 林三宝, 吴林, 等. 搅拌摩擦焊研究进展及前景展望[J]. 焊接学报, 2003, 24(3): 91 − 97. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2003.03.025 Zhang Hua, Lin Sanbao, Wu Lin, et al. Current progress and prospect of friction stir welding[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2003, 24(3): 91 − 97. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2003.03.025
[4] Thomas W M, Nicholas E D, Needham J C, et al. Improvements relating to friction welding[P]. UK: EP19940120385, 1995−07−05.
[5] 吴东, 李文亚, 温泉, 等. 双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊接头温度场和流场数值模拟分析[J]. 精密成形工程, 2019, 11(6): 114 − 118. Wu Dong, Li Wenya, Wen Quan, et al. Numerical simulation of temperature and fluid flow field during bobbin-tool FSW[J]. Journal of Net shape Forming Engineering, 2019, 11(6): 114 − 118.
[6] Chen S J, Lu A L, Yang D L, et al. Analysis on flow pattern of bobbin tool friction stir welding for 6082 aluminum[C]//Proceedings of 1st International Joint Symposium on Joining and Welding. 2013: 353-358.
[7] Tamadon A, Pons D J, Sued K, et al. Formation mechanisms for entry and exit defects in bobbin friction stir welding[J]. Metals, 2018, 8(1): 33 − 55.
[8] 胡晓晴. 基于示踪材料的双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊流场研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2015. Hu Xiaoqing. Research on the flow field of bobbin tool friction stir welding based on tracer material[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[9] 王非凡. Al-Li合金双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊成形机制及性能研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2016. Wang Feifan. Investigation on joint formation mechanism and mechanical properties of bobbin tool friction stir welding of Al-Li alloys[D]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2016.
[10] Wen Q, Li W Y, Gao Y J, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental investigation of band patterns in bobbin tool friction stir welding of aluminum alloy[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 100: 2679 − 2687. doi: 10.1007/s00170-018-2750-y
[11] 刘西畅, 李文亚, 高彦军, 等. 铝合金双轴肩搅拌摩擦焊过程材料流动行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(3): 48 − 56. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20201228002 Liu Xichang, Li Wenya, Gao Yanjun, et al. Material flow behavior during bobbin-tool friction stir welding of aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(3): 48 − 56. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20201228002
[12] Zhu H, Huang L, Li J J, et al. Strengthening mechanism in laser-welded 2219 aluminum alloy under the cooperative effects of aging treatment and pulsed electromagnetic loadings[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2018, 714: 124 − 139. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2017.12.081
[13] Hilgert J. Knowledge based process development of bobbin tool friction stir welding[D]. Geesthacht: Geesthacht Helmholtz-Zentrum Geesthacht, 2012.
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 孙浩东,吴晓晔,胡志伟,唐晓田,王志鹏. 窄边结构相变热控构件的搅拌摩擦焊工艺研究. 当代化工研究. 2025(04): 148-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张继元,毛育青,王金锴,黎宁,黄清. 旋转速度对铝合金锁底结构搅拌摩擦焊接头成形及力学性能的影响. 精密成形工程. 2024(08): 61-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 林森,党键,韩晓辉,李刚卿,张铁浩,赵存金. 基于焊接速度的6082铝合金FSW接头组织与力学性能调控研究. 电焊机. 2024(09): 30-37+54 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陶虎威,郝云飞,邵明皓,姜炳鑫,李志航,张华. 2219铝合金搅拌摩擦焊缝在弱腐蚀下的腐蚀行为. 有色金属工程. 2024(10): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 邓利芬,李超,丁艳霞,熊占兵,毕海娟. 大厚度2219铝合金搅拌摩擦焊组织和性能及工程因素分析. 焊接. 2023(06): 18-23 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: