Effect of copper vapor on arc characteristics under DC magnetic field
-
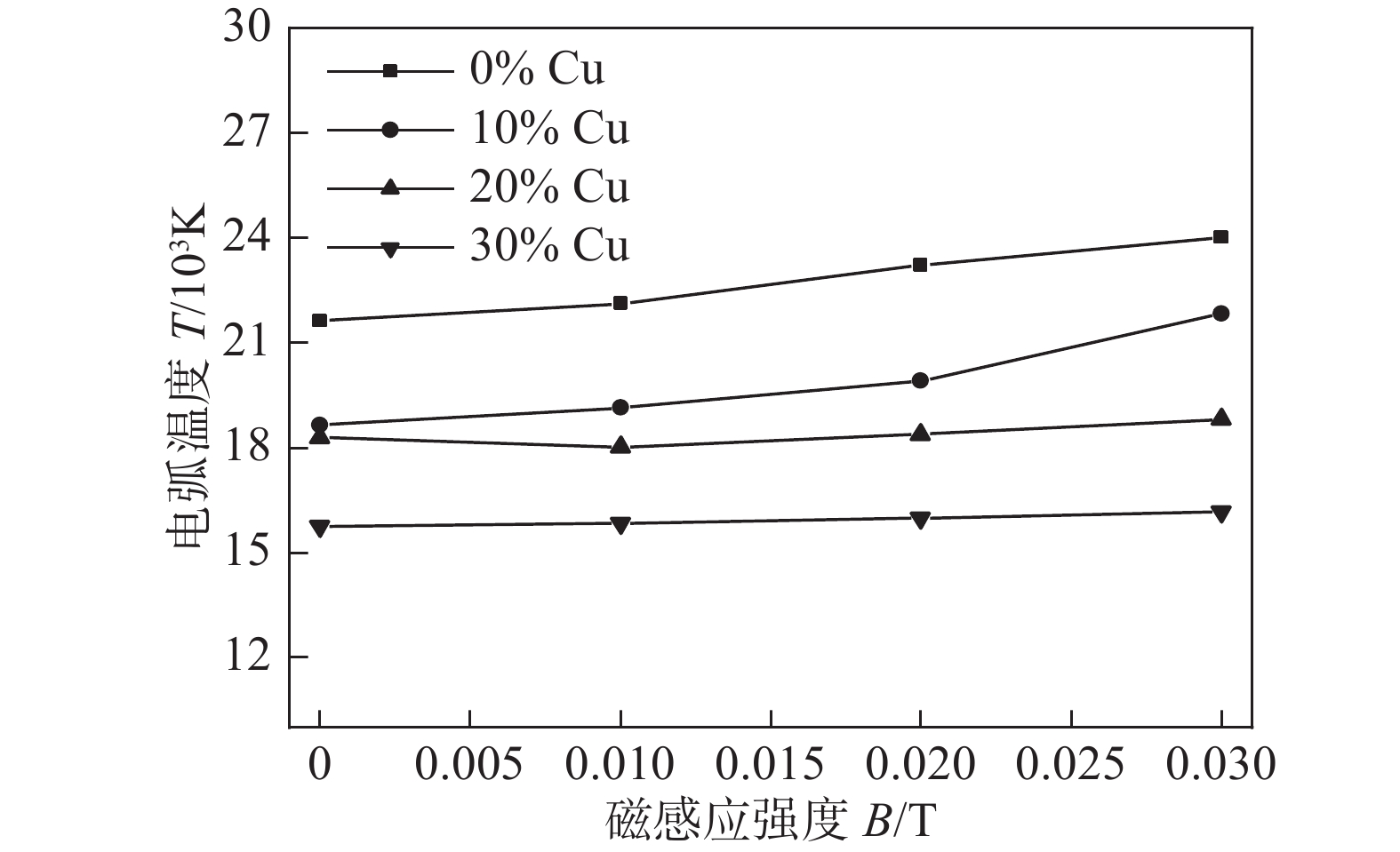
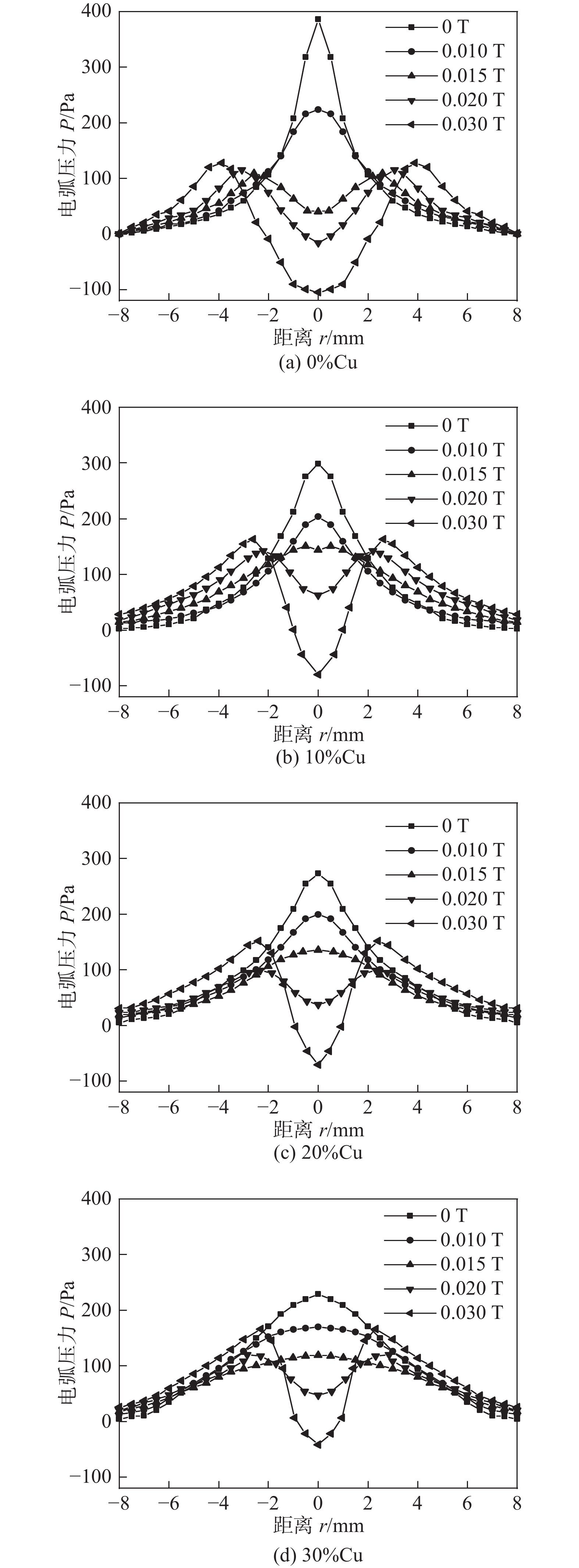
摘要: 为研究直流纵向磁场作用下金属蒸气对熔化极气体保护焊(gas metal arc welding,GMAW)电弧特性的影响,将钨铜复合材料制成特殊钨极代替熔化极产生铜蒸气,利用高速摄像法、光谱测温法以及小孔探测法对其进行了测试研究. 结果表明,铜蒸气进入电弧等离子体后,电弧出现分层,随铜蒸气含量的增加,弧芯外围区域半径随之增加,弧芯区的尺寸减小. 当铜含量为0%时,外加直流磁场后,电弧在阴极区收缩阳极区扩张,其轴向最高温度明显上升;电弧压力峰值偏离轴线,在外加磁场强度为0.015 T时呈现双峰分布,电流密度与电弧压力分布趋势相似;随着铜蒸气的介入,弧芯区电弧表现为阴极区收缩,阳极区扩张,弧芯周围的铜蒸气则明显收缩,电弧轴向最高温度上升的幅度明显降低. 随着铜含量的增加,电弧的导电面积增加,环向电磁力作用减弱,电弧中心压力下降幅度显著降低,阳极电流密度的分布趋势逐渐趋于扁平化.Abstract: In order to study the effect of metal vapor on the arc characteristics of gas metal arc welding (GMAW) under the action of DC longitudinal magnetic field, tungsten-copper composites were made into special tungsten electrode instead of molten electrode to produce copper vapor, which was tested and studied by high speed camera method, spectral temperature measurement method and keyhole detection method. The results show that when copper vapor enters the arc plasma, the arc appears delamination. With the increase of copper vapor content, the outer radius of arc core increases, and the size of the arc core area decreases. When the Cu content is 0%, after the DC magnetic field is applied, the arc shrinks in the cathode and expands in anode with an notable increase in the axial maximum temperature of the arc. The peak value of the arc pressure deviates from the axis, and when the magnetic field intensity B = 0.015 T , the arc pressure shows a bimodal distribution. The distribution of current density is similar to that of arc pressure. With the intervention of copper vapor, the arc in the arc core region shrinks in the cathode and expands in the anode region. While the copper vapor around the arc core shrinks obviously, and the rise of the maximum axial temperature of the arc decreases obviously. At the same time, the copper vapor expands the conductive area of the arc, weakens the circumferential electromagnetic force. The pressure at the arc center decreases, and the distribution of anode current density was flattened.
-
Keywords:
- gas metal arc welding /
- DC magnetic field /
- copper vapor /
- arc characteristics
-
0. 序言
Ti-6Al-4V钛合金具有比强度高、耐腐蚀性好、耐高温等优点,在航空航天、生物医疗和化学工程等领域得到了广泛的应用[1-2]. 对于传统的钛合金零件制造,大都采用锻造和铸造的方式,存在设备昂贵、小批量生产困难、难切削加工等缺点,极大地限制钛合金的广泛应用[3].随着增材制造技术地进一步发展,很好地解决了这些问题,该技术可以通过软件,根据零件的三维结构来对增材过程进行相应的路径规划,从而获得逐层堆积的几何实体[4].同时,在进行增材制造过程中不需要昂贵的设备,生产成本低,制造效率高,在新产品的设计上也具有更高的自由度[5].这些都使钛合金增材制造技术得到了广泛的应用.
利用等离子弧进行增材制造有比较广泛的研究,如徐俊强等人[6]利用等离子弧增材系统对异质异构的增材件进行制备,发现可以获得良好的沉积形貌.潘子钦等人[7]利用等离子弧对钛合金增材件的疲劳断裂行为进行研究,发现孔洞的存在使疲劳寿命产生较大的弥散性. 因此,Ti-6Al-4V钛合金增材制造过程中,电弧热作用将重熔前一道沉积层,使其温度升高,重复的加热冷却过程将会出现晶粒尺寸增加、残余应力等问题[8],会严重降低增材件的力学性能.因此,如何减小晶粒尺寸成为提高增材件性能的重要方法,国内外学者也对晶粒细化进行较为深入的研究,细化晶粒主要有化学冶金以及物理手段[9].化学冶金手段需要添加合金元素,易产生合金元素烧损、分布不均匀的问题.更多的学者选择用物理手段来进行细化晶粒和改善增材件性能.比如Zhang等人[10]通过在激光填丝试验过程中加入交流电,结果发现,交流电的加入使元素分布更加均匀,成形质量提高. 杨光等人[11]研究电磁搅拌对钛合金激光熔覆过程中熔池的影响,结果发现,电磁力会使熔池流速加快,降低熔池温度和凝固界面的温度梯度,使等轴晶数量增多. Sabzi等人[12]研究了脉冲电流对不锈钢焊接接头的影响情况,结果发现,增加峰值电流会使焊缝的柱状组织向更加精细的等轴组织转变,故在TIG增材制造工艺中加入辅助交流电的方式,可以显著改善增材件的微观组织以及性能.
文中提出外加交流电流辅助的方法,来降低晶粒尺寸,提高增材件的性能.外加在焊丝上的辅助交流会影响电弧的摆动以及熔池的流动,从而对微观结构产生影响,故对外加辅助交流的电弧形貌进行讨论,对增材件的微观组织及性能进行研究,从而揭示电弧增材过程中外加交流电流作用的内在机理,阐明外加交流电流对增材件的组织和性能的影响.为实现钛合金材料的性能强化提供新的技术与理论基础,为钛合金材料的增材制造提供可靠的技术解决方案.
1. 试验方法
试验过程中使用的基材与填充焊丝为同种材料,均为Ti-6Al-4V钛合金,化学成分如表1所示.其中,基板尺寸为100 mm × 100 mm × 3 mm,填充焊丝直径为1.2 mm. 试验前,先用砂纸去除基材表面的氧化膜,并用丙酮清洗表面.前期开展了大量的工艺研究并分析了影响堆垛层成形的主要因素,从而制定出最佳的试验参数,如表2所示.为了保证试验更具科学性,保证外加交流电流和主弧电流之和为90 A.
表 1 Ti-6Al-4V钛合金化学成分组成(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloyAl V Fe Si C O N H Ti 5.50 ~ 6.80 3.50 ~ 4.50 <0.30 <0.15 <0.15 <0.20 <0.05 < 0.0015 余量 表 2 试验参数Table 2. Test parameters序号 焊接速度
v/(mm·min−1)送丝速度
vs /(cm·min−1)电弧长度
L/mm气体流量Q/(L·min−1) 焊接电流
I/A外加交流电流
I0 /A氩气 氮气 1 110 160 5 8.8 1.2 90 0 2 110 160 5 8.8 1.2 80 10 3 110 160 5 8.8 1.2 70 20 4 110 160 5 8.8 1.2 60 30 试验所用的是DML-028D型等离子弧焊机,将辅助交流采用的是WSME-280i型交流焊机,并将填充焊丝和基板连接. 试验平台如图1所示. 采用同向堆垛的方式,使焊丝在熔池前端进行熔化,在堆垛完成一道后,进行空冷5 min,减少热积累对后一道焊道的影响,每次抬高2 mm,保证每道焊道的高度一致. 堆垛结束后,采用线切割机在增材件中切出金相试样以及压缩试样,试样位置如图1所示. 同时,利用高速摄像设备对增材过程中的电弧及熔池形态进行观察,利用蔡司 Axio Scope A1 型光学显微镜(OM)和场发射 FEG-450 型扫描电子显微镜(SEM)研究增材件的微观组织和元素分布,利用显微硬度测试仪和万能试验机对增材件的力学性能进行测试分析.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 增材件宏观形貌
利用高速摄像设备对电弧行为和熔滴过渡进行观察. 图2为一个周期20 ms下不同外加辅助交流钛合金增材过程中的高速摄像图. 交流电频率对电弧形态有很大影响,频率过大,会使电弧形态发生收缩、不稳定现象,经过多次试验发现,当频率为50 Hz时,最有利于试验的进行.图2a为未外加交流电流时,电弧为稳定的柱状,不存在周期性振荡的情况,电弧摆动幅度很小,熔滴主要为小滴搭桥过渡. 当外加交流电流为10 A时,电弧出现摆动,但是摆动的幅度较小,电弧的摆动和交流的频率相一致,熔滴形状较为明显,如图2b所示. 当外加交流电流为20 A时,电弧摆动幅度进一步变大,形成一定的偏转角,如图2c所示. 当外加交流电流为30 A时,焊丝端部的熔滴上面出现比较明显的交流电弧,并会周期性的熄灭和燃烧,如图2d所指出部分,同时电弧摆动幅度加剧,电弧偏转角显著变大.观察图2可以发现,同样时间内,当外加交流电流为30 A时,熔滴长大速度更快,并且电弧压力和电磁力引起的电弧摆动又会对熔池产生较为明显搅拌作用[13]. 随着外加交流电流的增大,电弧的摆动幅度加剧,熔滴的尺寸变大,熔滴的生长速度也会加快,从而会对熔池产生比较明显的振荡作用.
图3为不同外加交流电流下钛合金增材件的宏观形貌. 此试验采用单向堆垛方式,总堆垛10层,总高度约为20 mm. 从图3可以看出,在增材件的前端和末端都出现塌陷,中间部位焊接过程较为稳定,成形较为平整. 同时,从横截面也可以发现,当未加交流时,增材件的粗糙度较大,两侧出现明显的凹陷,层间分界比较明显.当外加交流电流为10,20 A时,制备的增材件的成形良好,堆垛层较为平直,没有明显表面缺陷.
为分析外加交流电流对钛合金增材件宏观形貌的影响,对增材件进行测量宽窄. 为了测量更加精确,采用多次测量以及选择图4中所示中间位置进行测量,从而评估增材件左右两侧的粗糙度. 从图4可以看出,未加交流的宽度相差较大,当外加交流电流为10 A和20 A时,宽度的变化不大,增材件侧壁表面的粗糙度较小,测量结果和图3一致.故外加交流电流可以显著提高钛合金增材件的成形质量.
2.2 组织与性能
当外加交流电流时,会形成耦合交流电弧,影响电弧中的电磁场分布,导致电弧产生周期性振荡,促进熔池的流动,转移固/液界面中的合金元素,降低成分过冷度,进而导致晶粒生长速度的降低,同时还很容易形成结构波动和温度波动,在熔池区域成核. 故外加交流电流会影响钛合金增材件的组织与性能.
2.2.1 微观组织
图5为不同外加交流电流下钛合金电弧增材件的微观组织. 钛合金增材件的显微组织主要由α相和β相组成,其中β晶粒会形成“束集”,α晶粒主要以片层状存在,与未加交流电流相比,加入交流电流后微观组织更加清晰,α相更加粗糙,同时β相的晶界也更加清晰,熔覆层中α相和β相的片层更加杂乱.
采用Image Pro-Plus软件对不同外加交流电流下钛合金增材件的晶粒尺寸进行统计,统计结果如图6所示. 当外加交流电流为0,10,20,30 A时,试样的晶粒尺寸分别为426.894,317.873,294.259 μm和241.798 μm. 从未加交流到外加交流电流30 A,晶粒尺寸减少了43.4%. 随着外加交流电流的增加,试样的晶粒尺寸逐渐变小,是因为外加交流电流所产生的电磁力使熔池内的传质以及传热更快,提高熔池液态金属的流速,电磁力的作用也对熔池产生一定的搅拌作用,使枝晶产生破碎,晶核的数量也进一步增多,从而细化了晶粒[14].
图7为不同外加交流电流试样的SEM面扫描元素分析. 由于试验过程中保护气体为氮气和氩气的混合气,采用含氮混合气可以使氮气和钛合金反应,从而生成氮化钛化合物,对堆垛层有较好的强化作用. 从图7可以看出,Ti,Al,V元素分布均匀,N元素主要集中在片层α相中,而对于β相中氮元素的分布较少,也能较为清晰的观察出钛合金α相和β相相间分布的片层组织.
2.2.2 力学性能
图8为不同外加交流电流下增材件的硬度,图8a显示了增材件上的显微硬度分布情况,可以发现增材件的上部第1~3层硬度普遍略低于中下部4~10层的硬度,中下部会有比较充分的后一焊道对前一焊道的热处理作用,即4~10层区域经过了反复的时效作用,从而会使αʹ等相产生分解,会对增材件硬度起到很好的强化作用[15]. 从图8b可以发现硬度值随着外加电流的增加也逐渐增加,外加电流为0,10,20,30 A的硬度值分别为406.45,423.39,446.59,454.15 HV.因为在较高的外加电流的作用下,一方面增材件产生更多的网篮组织[16],网篮组织相比于片层的α组织有着更高的硬度,并且网篮状的α和β界面相比片层状的α和β界面具有更高的界面能,能够更好地阻碍位错移动,从而提高硬度[17].另一方面,根据前面对晶粒尺寸的统计发现,随着外加辅助交流值的增加,晶粒尺寸明显减小,晶界相对面积增多,阻碍位错运动阻力增大,增材件的硬度也会增加.
图9为不同外加交流电流作用下钛合金增材件压缩试样的应力 —应变曲线,从图9可以发现,不同外加交流电流的增材件压缩应力变化不大,均在1 300 MPa左右,但是外加交流电流对塑性影响较大. 当未加交流电流时,压缩应变最低为0.110%,当外加交流电流为30 A时,试样的压缩应变最大为0.280%,相比未加交流电流增加2.5倍. 而外加交流电流分别为20 A和10 A时试样的压缩应变较为相近,分别为0.171%和0.186%.文献[14]中研究表明,外加辅助交流制造的钛合金增材件的力学性能取决于外加交流电流,当外加交流电流为30 A时, 增材件为等轴显微组织,塑性最好. 随着外加电流的引入,对增材件的抗压强度影响不大,但显著增加增材件的塑性.
3. 结论
(1)未加交流的钛合金增材件表面较为粗糙,存在明显凹陷.外加交流电流为10,20 A时,焊接过程稳定,增材件表面粗糙度小,成形较为平整.
(2)当外加交流电流为30 A时,电弧摆动幅度最大,产生耦合电弧. 微观组织中β相的晶界也更加清晰,而熔覆层中α相和β相的片层分布更加杂乱,晶粒尺寸也明显细化,相比未加交流的增材件晶粒尺寸减少了43.4%.
(3)钛合金电弧增材件的硬度随着外加交流电流的增加而增加,外加交流电流对增材件的压缩应力影响不大,均为
1300 MPa左右,但显著提升增材件的塑性,当外加交流电流为30 A时,应变相比未加交流提高2.5倍. -
表 1 焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Welding process parameters
焊接电流
I/A钨极直径
D/mm钨极角度
θ/(°)弧长
L/mm氩气流量
Q/(L·min−1)100 3.2 60 4 10 表 2 平均蒸发率
Table 2 Average evaporation rate
铜含量w(%) 蒸发率E/(mg·s−1) 0 0 10 0.173 5 20 0.566 7 30 1.315 3 -
[1] 闫飞, 周一凡, 唐本刊, 等. 基于磁控冶金的铝/钢异种金属焊接特性[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(5): 98 − 103. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220101004 Yan fei, Zhou Yifan, Tang Benkan, et al. Welding characteristics of Al/steel dissimilar metals based on magnetically controlled metallurgy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(5): 98 − 103. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20220101004
[2] 孙雅杰, 常云龙. 磁控电弧焊接过程及新技术研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2020, 34(21): 21155 − 21165. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19060200 Sun Yajie, Chang Yunlong. Development of magnetically controlled arc welding process and new technology[J]. Materials Reports, 2020, 34(21): 21155 − 21165. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19060200
[3] Wu Hong, Chang Yunlong, Lu Lin, et al. Review on magnetically controlled arc welding process[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2017, 91(9-12): 4263 − 4273. doi: 10.1007/s00170-017-0068-9
[4] Fan Ding, Yao Xinlong, Hou Yingjie, et al. The study of arc behavior with different content of copper vapor in GTAW[J]. China Welding, 2022, 31(2): 1 − 14.
[5] Tanaka K, Shigeta M, Tanaka M, et al. Investigation of transient metal vapour transport processes in helium arc welding by imaging spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Physics D:Applied Physics, 2020, 53(42): 1 − 8.
[6] Xiang J A, Chen F, Phb C, et al. Numerical study of the metal vapour transport in tungsten inert-gas welding in argon for stainless steel[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2020, 79: 713 − 728. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.11.001
[7] 肖磊, 樊丁, 黄健康, 等. 外加高频纵向磁场作用下的 TIG 焊电弧数值模拟[J]. 焊接学报, 2017, 38(2): 66 − 70. Xiao Lei, Fan Ding, Huang Jiankang, et al. Numerical simulation of TIG welding arc with extra high-frequency longitudinal magnetic field[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2017, 38(2): 66 − 70.
[8] Schupp J, Fischer W, Mecke H. Welding arc control with power electronics[C]//8th International Conference on Power Electronics and Variable Speed Drives. London, 2000: 443−450.
[9] Murphy A B. The effects of metal vapour in arc welding[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, 43(43): 434001.
[10] Tanaka M, Yamamoto K, Tashiro S, et al. Time-dependent calculations of molten pool formation and thermal plasma with metal vapour in gas tungsten arc welding[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 2010, 43(43): 434009.
[11] 斯红, 华学明, 张旺, 等. 基于Boltzmann光谱法的焊接电弧温度场测量计算[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 2012, 32(9): 2311 − 2313. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)09-2311-03 Si Hong, Hua Xueming, Zhang Wang, et al. Welding Arc temperature field measurements based on Boltzmann Spectrometry[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2012, 32(9): 2311 − 2313. doi: 10.3964/j.issn.1000-0593(2012)09-2311-03
[12] 黄勇, 瞿怀宇, 樊丁, 等. 耦合电弧AA-TIG焊电弧压力测量与分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(3): 33 − 36. Huang Yong, Zhai Huaiyu, Fan Ding, et al. Arc pressure measurement and analysis of coupling arc AA-TIG[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(3): 33 − 36.
[13] Murphy A B. A comparison of treatments of diffusion in thermal plasmas[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1996, 29(7): 1922 − 1932. doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/29/7/029
[14] Gleizes A, Gonzalez J J, Liani B, et al. Calculation of net emission coefficient of thermal plasmas in mixtures of gas with metallic vapour[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics, 1999, 26(11): 1921 − 1927.
[15] Xiao L, Fan D, Huang J. Tungsten cathode-arc plasma-weld pool interaction in the magnetically rotated or deflected gas tungsten arc welding configuration[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2018, 32: 127 − 137.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 卜华全,赵伟,臧晓飞,刘海定,任明皓,连轶博. 9%Ni钢用国产镍基焊丝的焊接试验研究. 压力容器. 2022(01): 19-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈国耀,徐彤,钟继如,章骁程,关凯书. 小冲杆和压入测试技术获取材料真应力-应变曲线的对比研究. 压力容器. 2022(09): 42-49+55 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 徐卫军. 锅炉异种金属焊接的缺陷思考. 化纤与纺织技术. 2022(08): 94-96 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载: