Application of variable layer thickness slicing algorithm in wire arc additive manufacturing
-
摘要: 在实际生产的过程中,应用电弧增材制造技术对失效模具进行修复时,会在边缘部位出现缺肉、凹陷、过堆积等成形不良的问题,从而导致熔覆层各处厚度不一、起伏较大,对实际的增材制造结果造成精度上的较大误差. 为了减少上述缺陷,提出了一种变层厚分层切片算法,主要包括模型前处理、焊接参数的确定、对模型实际切片厚度的修正,并完成最终的增材制造过程. 变层厚分层切片算法通过调节熔覆过程中的搭接率从而实现对成形件层厚变化的精准把握,提高成形精度的同时,还可以减少缺肉、凹陷、过堆积等缺陷. 通过选取不同的模型对其进行变层厚分层切片以及对应的路径规划,验证了算法的适用性. 最后,采用变层厚分层切片算法对棱台结构模型进行处理,并进行熔覆试验. 结果表明,理论计算得到的填充路径可以对当前分层面实现完全填充,实际的熔覆高度和平面尺寸与理论计算值相差较小,在热积累较小的时候,成形精度可以达到工业要求.Abstract: When applying wire arc additive manufacturing technology to repair damaged molds, poor forming problems such as gaps, dents and excessive accumulation may occur at the edges, which lead to the uneven thicknesses in the clading layer and impact the precision of the additive manufactured parts.In order to aovid these defects, a variable thickness layer slicing algorithm is proposed, which mainly consists of model pre-processing, determination of welding parameters, correction of slicing thickness, and completion of the additive manufacturing process. By adjusting the overlap rate during the cladding process, precise control of the thickness variation of the formed part can be achieved, which help to improve the forming precision and decrease the defects as mentioned above. Finally, this variable layer thickness slicing algorithm was used for pyramid structure models, and cladding experiments were conducted. The results showed that the calculated filling path could fully ensure the full filling of the specified layer, and there was little difference in height, length and width between the cladded part and the calculated one. Hence, the forming precision is satisfactory to the industrial requirements on condition that the heat accumulation is low.
-
-
图 12 各层路径规划及对应的熔覆结果
Figure 12. Path planning of each layer and corresponding cladding results. (a) path of second layer; (b) result of second layer cladding; (c) path of seventh layer; (d) result of seventh layer cladding; (e) overall path; (f) overall cladding result; (g) cross section of the fused forming prism
表 1 熔覆层几何尺寸与层高数据
Table 1 Geometric dimension and layer height data of cladding layer
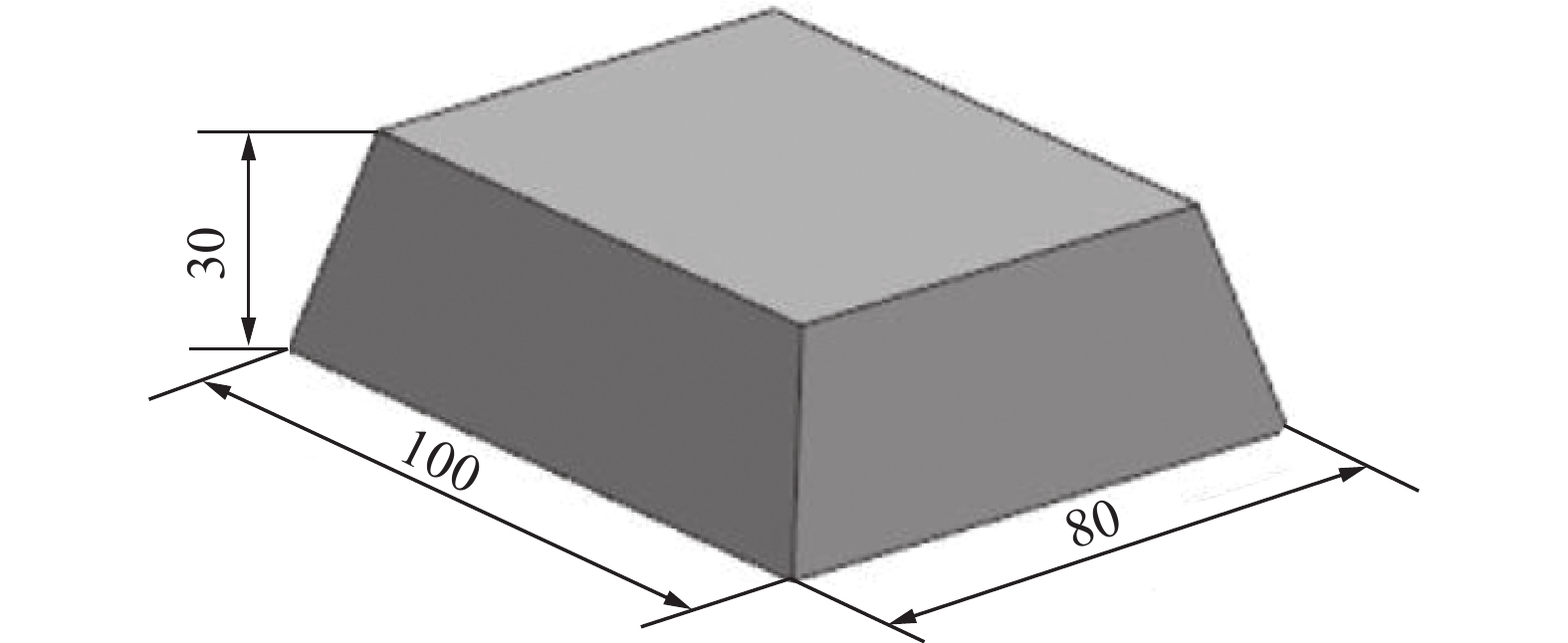
层数 搭接距离d/mm 模型尺寸/(mm × mm) 熔覆层尺寸/(mm × mm) 计算层高 hc /mm 熔覆层高 hf /mm 2 6.4 98.4 × 78.4 99.0 × 78.9 5.99 6.06 7 6.3 90.3 × 70.3 91.2 × 70.5 21.41 20.66 10 6.6 85.5 × 65.5 86.3 × 66.8 30.69 29.13 -
[1] 洪恩航, 刘美红, 黎振华. 基于开源切片路径规划的机器人电弧增材制造系统[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(11): 65 − 69. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20210312004 Hong Enhang, Liu Meihong, Li Zhenhua. Development of wire arc additive manufacturing robotic system based on open source slicing software for path planning[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(11): 65 − 69. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20210312004
[2] 夏玉峰, 滕海灏, 廖海龙, 等. 热锻模具电弧增材再制造技术研究进展[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2021, 42(8): 1 − 13. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2021-0150 Xia Yufeng, Teng Haihao, Liao Hailong, et al. Research progress of arc additive remanufacturing technology for hot forging die[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2021, 42(8): 1 − 13. doi: 10.13289/j.issn.1009-6264.2021-0150
[3] 刘文勇, 侯晓龙, 谭保森, 等. 基于曲面分层的三维空间定向打印路径规划及仿真分析[J]. 机械设计, 2018, 35(S1): 10 − 14. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2018.s1.003 Liu Wenyong, Hou Xiaolong, Tan Baosen, et al. Path planning and simulation of curved surface layering-based directional 3D printing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Design, 2018, 35(S1): 10 − 14. doi: 10.13841/j.cnki.jxsj.2018.s1.003
[4] Zhang Y M, Chen Y, Li P, et al. Weld deposition-based rapid prototyping: a preliminary study[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 135(2-3): 347 − 357. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(02)00867-1
[5] Sun S H, Lee H W, Lee M I. Adaptive direct slicing of a commercial CAD model for use in rapid prototyping[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2007, 34(7-8): 689 − 701. doi: 10.1007/s00170-006-0651-y
[6] 张李超, 张楠, 何森, 等. 一种自适应分层的增材制造方法: ZL 201710766233.6[P]. 2019-12-13. Zhang Lichao, Zhang Nan, He Sen, et al. An adaptive layered additive manufacturing method: ZL 201710766233.6[P]. 2019-12-13.
[7] Jiang J, Zhou J, Chen C, et al. Research on multi-objective optimization of GMAW welding of DH36 steel[J]. China Welding, 2021, 30(2): 25 − 34.
[8] 李冉. 电弧增材制造分层算法与路径规划方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2018. Li Ran. Research on slicing algorithm and path planning method of wire and arc additive manufacturing[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2018.
[9] Ding D, Pan Z, Cuiuri D, et al. A multi-bead overlapping model for robotic wire and arc additive manufacturing (WAAM)[J]. Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2005, 31: 101 − 110.
[10] Li Y, Sun Y, Han Q, et al. Enhanced beads overlapping model for wire and arc additive manufacturing of multi-layer multi-bead metallic parts[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 252: 838 − 848. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2017.10.017
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王祉冰,王剑,张硕. 基于FAD图法的铁路货车车体断裂评估. 轨道交通装备与技术. 2024(05): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载: