Control of the microstructure and mechanical properties of CMT arc wire additive manufactured Inconel 625 alloy by solution treatment
-
摘要: 对冷金属过渡(CMT)的电弧熔丝增材方法制备的Inconel 625合金试样进行不同温度的固溶处理. 研究了固溶处理对所制备的Inconel 625合金的微观组织和力学性能的影响规律. 结果表明,沉积态主要为沿沉积方向生长的柱状枝晶,基体组织主要为γ奥氏体相,在晶粒内和晶界上呈块状或链状分布着大量第二相Laves相以及微小MC颗粒. 固溶温度低于 1 000 ℃时,Laves相和碳化物溶解缓慢,此时固溶处理对合金组织性能的影响较小;当固溶处理温度增加至1 200 ℃时,第二相碳化物溶解,晶粒剧烈长大,并出现大量孪晶界,合金的硬度和抗拉强度有一定程度下降,屈服强度显著下降,断后伸长率显著提升.
-
关键词:
- CMT电弧熔丝 /
- 增材制造 /
- Inconel 625合金 /
- 固溶处理 /
- Laves相
Abstract: Inconel 625 alloy samples prepared by cold metal transfer arc additive manufacturing (CMT AA) were solution treated at different temperatures. The microstructure and mechanical properties of the solution treated Inconel 625 alloy were investigated. The results showed that the as-deposited sample primarily consisted of columnar dendrites growing along the deposition direction. The matrix structure was predominantly γ-Ni austenite phase with a large number of second phases, including Laves phase and tiny MC particles distributed inside the grains and on grain boundaries in the form of “blocks” or “chains”. When the solution temperature was below 1000 ℃, the solution treatment had little effect on the microstructure and properties of the alloy due to the slow dissolution of Laves phase and carbides. As the solution treatment temperature increased to 1200 ℃, the second phase carbides dissolved, and the grains grew sharply with many twins. The hardness and tensile strength of the alloy decreased to some extent. The yield strength decreased, and the elongation increased significantly. -
0. 序言
Inconel 625是一种镍基高温合金,其强度主要来自于镍铬基体中难熔金属铌和钼的固溶强化效应[1, 2] . 因其具有优异的高温强度、抗热腐蚀性能、疲劳性能、耐磨性能及焊接性能,被广泛应用于航空航天、石油化工、船舶和其它高温和腐蚀环境 [3-4]. 这些大型结构件体积庞大,形状复杂,采用传统的加工方法生产成本较高[5] .电弧增材制造(wire and arc additive manufacturing, WAAM)是一种以电弧为热源熔丝,逐层堆积的快速成形技术,由部件的三维数据驱动,通过材料的沉积完成,不需要任何工具和模具的帮助,是制造高质量金属零件的一种经济快速成形方法[6-9] .
电弧增材制造自身逐层堆积的特点决定了其需要经历循环加热和快速冷却,加上镍基合金中 Cr,Mo,Nb 等合金元素含量较高,致使合金在增材制造过程中会产生非平衡组织,伴随大量第二相析出、晶粒粗化等现象,样品综合性能下降[10-11] . 热处理作为一种常用的材料改性手段,可以有效调控合金强化相的数量、形态、尺寸以及分布,均匀组织成分,从而获得良好的综合性能[12-13] .研究人员采用了包括消除应力退火、固溶处理、热等静压(HIP)和固溶时效处理在内的多种后热处理手段对增材制造的镍基合金进行了改性处理. Dinda等人[14]研究了沉积态和热处理后的Inconel 625的显微组织演变和显微硬度.结果表明,沉积态的Inconel 625具有较高的热稳定性,在1 000 ℃时,树枝状亚结构较为稳定,在1 200 ℃左右发生完全再结晶,显微硬度随着退火温度的升高而降低. Miao等人[15]发现,在高温(1 140,1 160和1 180 ℃)下进行均匀化处理后,Inconel 718合金元素的微观偏析被消除. 同时,Laves相的体积分数降低,试样的力学性能得到明显改善. Li等人[16]研究了激光直接沉积Inconel 718高温合金在1 100 ℃高温均匀固溶处理后的组织和力学性能.经高温固溶双级时效处理后,显微组织更加均匀,沉积态组织由柱状晶向等轴晶转变.同时,缓解了枝晶间和枝晶核心的分离,完全消除了Laves相,提高了材料的综合力学性能.吕耀辉等人[17]采用等离子快速成形工艺制备了Inconel 625 合金块体,并研究了固溶温度对微观组织的影响. 结果表明,凝固后得到的微观组织第二相主要为 Laves相和δ相;在一定温度范围内随着固溶温度的升高,Laves相逐渐溶解,δ相发生部分回溶;固溶温度过高会导致γ基体晶粒粗化,得到的最佳固溶温度为980 ℃.
文中针对CMT电弧熔丝增材Inconel 625合金,开展热处理调控其组织与性能的研究. 结合典型Inconel 625合金平衡相图,设计了不同固溶处理工艺,研究其对合金γ基体组织和第二相变化的影响,探究其对微观组织、力学性能的影响规律.研究结果将为高效高质电弧增材方法制备镍基合金试样提供理论基础.
1. 试验材料及方法
1.1 CMT-WAAM过程
增材试验系统包括Fronius公司生产的CMT-5000i 焊机、ABB机器人、水冷却系统、计算机控制系统、送丝系统和保护气系统. 焊丝为直径1.2 mm的ERNiCrMo-3,其化学成分和力学性能分别见表1和表2. 采用316L不锈钢作为基体金属,尺寸为400 mm × 250 mm × 10 mm. 试验开始前,对基体表面进行打磨直至露出金属光泽,并用乙醇和丙酮进行表面清洗. 采用纯度为99.9%的氩气作为保护气体,气体流量为25 L/min,具体试验参数见表3.
表 1 焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of welding wireC Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo Nb + Ta 0.006 0.15 0.15 0.001 0.001 22.04 64.9 8.75 余量 表 2 Inconel 625焊丝的力学性能Table 2. Mechanical properties of Inconel 625抗拉强度
Rm /MPa屈服强度
ReL/MPa断后伸长率
A (%)750 350 30 表 3 试验参数Table 3. Experiment paraments扫描速度
v /(mm·s−1)送丝速度
vs/(m·min−1)焊丝伸出长度
L / mm气体流量
Q /(L·min−1)3.5 6.5 13 25 试验采用往复堆叠方式进行CMT-WAAM增材制造Inconel 625合金块体试样,采用优化后的焊接参数,选取50%的搭接率逐层沉积出尺寸为140 mm × 75 mm × 40 mm的块体,实物如图1所示. 制备好的试样根据后续的测试需要切割成合适的尺寸. 切割好的试样放入KSX-8-1100箱式炉进行不同温度的固溶处理,固溶温度分别选取900,1 000,1 100 和1 200 ℃,保温90 min后取出水淬.
1.2 组织和性能表征
试样研磨抛光后,用王水(HCl∶HNO3体积比为3∶1)蚀刻30 s观察金相. 随后,通过光学显微镜(HAL1000)、扫描电子显微镜(JSM-6480)、EDS对其宏观形貌和微观结构以及元素分布进行了表征. 采用 JEM-2100F型透射电镜观察材料的微观结构,确定析出的第二相元素组成及种类. 透射样品通过机械减薄和电解双喷获得. 利用Everonese MH5显微硬度计测试增材块体各部位的显微硬度. 焊接接头的拉伸试验按国家标准GB/T 228.1—2010标准设计和进行,不同方向拉伸件取样及拉伸试样尺寸如图2所示.
2. 试验结果与讨论
2.1 沉积态显微组织
图3为CMT-WAAM制备Inconel 625合金的微观组织. 从图3中可以看到,该结构在截面上表现出外延生长特征,外延生长的柱状晶粒内部的组织主要是柱状枝晶结构为主,枝晶生长方向与沉积方向之间存在一定的夹角,中部有明显的二次生长枝晶.
基体组织主要为γ奥氏体相,在晶粒内和晶界上呈块状或链状分布着大量第二相,以及零星分布的微小颗粒MC,如图3中的放大图. 为了研究合金元素在微观组织中的分布,对基体和块状物进行了EDS分析,如图4所示. 结果表明,合金元素分布不均匀,偏析严重. 枝晶核心富集Ni,Cr元素,枝晶间区Mo,Nb元素含量较高,可能是枝晶间区Mo,Nb元素的偏析导致了一些次生相的形成,次生相为大量Laves + MC颗粒. 据此可推断出,CMT-WAAM制备Inconel 625合金中,除γ-Ni基固溶体外,还形成了MC碳化物、Laves相等硬质相.
为进一步确定Inconel 625合金中第二相的组成和结构,采用TEM对块状颗粒进行分析. TEM成像(图5、图6)则进一步证实了枝晶间析出区存在Laves相和MC增强相. Laves相是一种脆性有害的金属间化合物. Nb和Mo元素在不平衡凝固过程中会产生偏析现象,使得枝晶间极易析出形成Laves 相,降低了γ-Ni固溶体中合金元素的含量[18]. 合金元素的减少会导致基体在高温时易软化,抗蠕变能力以及疲劳寿命降低[19].
除此之外,组织中析出的纳米级碳化物太小,扫描电镜无法检测到,需要通过透射电镜进一步观察,如图6所示,为在枝晶间或晶界处析出的 MC 颗粒. 这些MC 颗粒尺寸为200 ~ 700 nm,其存在有利于提高基体的强度性能,这主要是由于 MC 颗粒作为第二相质点,与基体保持良好的共格关系,对晶界的滑移起到抑制作用.
2.2 固溶处理对微观组织的影响
如前所述,CMT-WAAM熔池凝固过程中元素的偏析导致枝晶间区域形成大量的碳化物,Laves相和δ相. 为了获得均匀的组织,分别进行900,1 000,1 100和1 200 ℃下保温90 min的固溶处理,探讨固溶处理对合金组织和力学性能的影响.
通过光镜和扫描电镜观察不同固溶温度下的样品晶粒内部的微观结构,如图7所示. 固溶温度为 900 ℃ 时,一次枝晶臂未发生明显变化,约为 10 μm. 当固溶温度为1 000 ℃ 时,一次枝晶臂明显增大,平均尺寸约为12 μm. 当温度升高到1 100 ℃ 时,枝晶严重粗化,一次枝晶臂尺寸达到16 μm左右,作为第二相的碳化物提高了晶界扩散激活能,对晶界起到“钉扎”作用,使得晶粒不能过分长大[20 ]. 当温度达到1 200 ℃ 时,第二相碳化物溶解,对晶界的“钉扎”作用减弱,晶界发生迁移,晶粒合并长大为大尺寸晶粒,晶粒尺寸可达80 μm左右, 并出现大量孪晶界. 与沉积态相比,经过900 ℃固溶
处理后,链状Laves相开始断裂,Laves 相中Nb,Mo元素逐渐向基体中扩散,从而在 Laves 相附近析出大量纳米级针状相,经EDS分析可知其Ni + Cr的质量分数达到81.8%,Nb + Mo为18.2%,与δ-(Ni, Cr, Fe)3(Nb, Mo)相组成相似,因此可推断出针状析出相为δ相. 随着固溶温度的提高,Laves 相溶解量增加,大量Nb,Mo元素向基体中扩散,使得Laves相附近针状δ析出量发生回溶. 当固溶处理温度增加至1 200 ℃时,Laves相完全溶解,MC颗粒也大量溶解,仅剩少量呈细小的弥散状分布,δ相消失.
2.3 固溶处理对力学性能的影响
图8所示为经过不同温度固溶处理后的试样的显微硬度. 沉积态试样的显微硬度为274 HV,随着固溶温度的升高,试样显微硬度呈下降趋势,当固溶温度升高至1 200 ℃时,显微硬度为243 HV.
CMT-WAAM工艺制备的Inconel 625合金沉积态与热处理态试样的室温拉伸性能如图9所示. 从图9中可以看出,沉积态试样的抗拉强度为750 MPa,屈服强度为550 MPa,断后伸长率为34%. 固溶温度为900 ℃时,固溶处理后的试样屈服强度、抗拉强度和断后伸长率率都没有明显变化. 当固溶温度大于 1 000 ℃时,随着固溶温度的升高,屈服强度和抗拉强度都呈明显的下降趋势;当固溶温度为1 200 ℃时,合金的屈服强度下降到375 MPa,与沉积态试样的屈服强度相比下降了31.8%. 固溶处理合金的断后伸长率提高到45.2%,是沉积态试样断后伸长率的1.3倍. 对试样的断后伸长率影响较大,当固溶温度达到 1200 ℃时,CMT-WAAM工艺制备的Inconel 625合金的抗拉强度随着固溶温度的升高变化不大;当固溶温度为1 200 ℃时,抗拉强度为690 MPa.
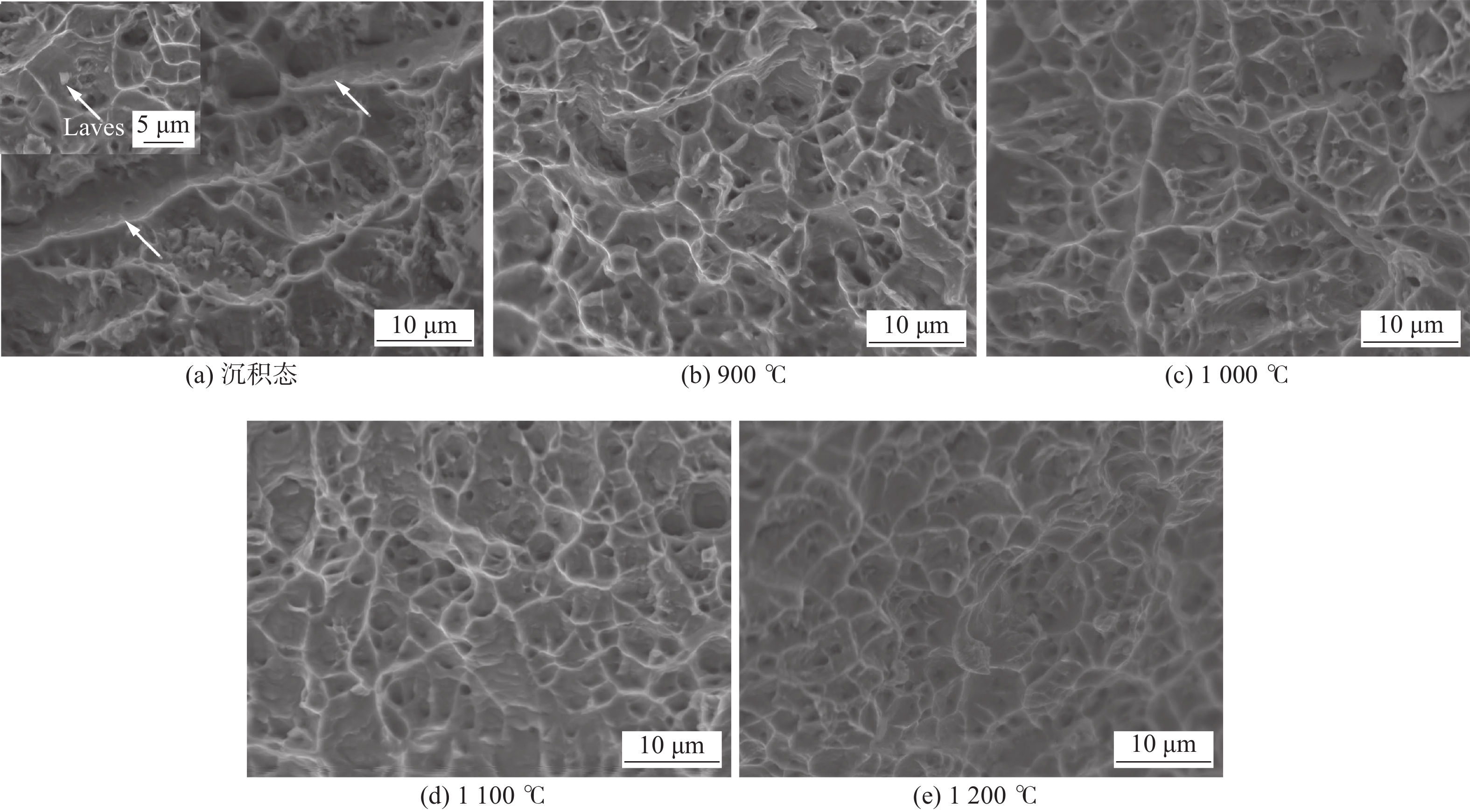
图10a ~ 图10e分别为沉积态、固溶温度为900,1 000,1 100和1 200 ℃拉伸断口扫描图像,均呈现大小相间的韧窝,为典型的韧性断裂. 断口形貌放大后显示,韧窝中有大量颗粒状物存在. 沉积态合金断口包含大量韧窝,在大尺寸韧窝底部发现粒状析出物,EDS 能谱确认这些颗粒为Laves相和少量MC. Laves相的存在不仅降低了Inconel 625合金的塑韧性、抗疲劳和蠕变断裂性能,同时 Laves相还占据了基体中部分合金元素,导致强化相的析出减少,为脆性裂纹的产生和扩展提供了便利条件. 除此之外,还有脆性断裂模式的迹象,如图10中白色箭头所示,究其原因可能是晶界碳化物,这将大幅度降低材料的断后伸长率. 经固溶处理后样品韧窝尺寸更小,更深,分布更均匀. 同时碳化物的溶解降低了晶界碳化物对晶界的弱化作用,大量的孪晶界弥补了晶界生长和晶界迁移的不利影响,降低了应力集中的概率,因此整体塑性增加[21].
3. 结论
(1)CMT-WAAM方法制备Inconel 625合金块体沉积态主要为沿沉积方向生长的柱状枝晶,基体组织主要为γ奥氏体相,在晶粒内和晶界上呈块状或链状分布着大量第二相Laves相以及微小MC颗粒. 合金有较高的硬度和抗拉强度,但塑性较差.
(2)经过900 ℃固溶处理后,链状Laves相断裂,Laves 相中Nb,Mo元素逐渐向基体中扩散,并析出大量纳米级针状δ相. 随着固溶温度的提高,Laves 相和碳化物发生回溶. 当固溶处理温度增加至1 200 ℃时,第二相碳化物溶解,对晶界的“钉扎”作用减弱,晶界发生迁移,晶粒剧烈长大,并出现大量孪晶界.
(3)在900 ~ 1 000 ℃ 固溶处理,热处理对合金力学性能影响较小,当固溶温度为1 200 ℃时,与沉积态试样相比,合金的屈服强度下降了31.8%,断后伸长率为沉积态试样的1.3倍,抗拉强度随着固溶温度的升高变化不大. 综合评价固溶处理后材料的硬度、抗拉强度和断后伸长率得出:固溶温度为1 000 ~ 1100 ℃时,材料的力学性能较好.
-
表 1 焊丝的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of welding wire
C Si Mn P S Cr Ni Mo Nb + Ta 0.006 0.15 0.15 0.001 0.001 22.04 64.9 8.75 余量 表 2 Inconel 625焊丝的力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of Inconel 625
抗拉强度
Rm /MPa屈服强度
ReL/MPa断后伸长率
A (%)750 350 30 表 3 试验参数
Table 3 Experiment paraments
扫描速度
v /(mm·s−1)送丝速度
vs/(m·min−1)焊丝伸出长度
L / mm气体流量
Q /(L·min−1)3.5 6.5 13 25 -
[1] 郭建亭. 高温合金材料学(上册)应用基础理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008. Guo Jianting. Materials science and engineering for superalloys (Volume one): Application of basic theory[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008
[2] 黄凤晓. 激光熔覆和熔覆成形镍基合金的组织与性能研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2011. Huang Fengxiao. An investigation on microstructure and properties of Ni-based alloy by laser cladding and laser cladding forming[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2011.
[3] Chen Y H, Xu M F, Zhang T M, et al. Grain refinement and mechanical properties improvement of Inconel 625 alloy fabricated by ultrasonic-assisted wire and arc additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2022, 910: 164957. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.164957
[4] Gamon A, Arrieta E, Gradld P R, et al. Microstructure and hardness comparison of as-built Inconel 625 alloy following various additive manufacturing processes[J]. Results in Materials, 2021, 12: 100239. doi: 10.1016/j.rinma.2021.100239
[5] Zhang F Y, Luo Y, Yang S Q, et al. Mechanical properties improvement of nickel-based alloy 625 fabricated by powder-fed laser additive manufacturing based on linear beam oscillation[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2022, 842: 143054. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.143054
[6] Wu B T, Qiu Z J, Dong B S, et al. Effects of synchronized magnetic arc oscillation on microstructure, texture, grain boundary and mechanical properties of wire arc additively manufactured Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2022, 54: 102723. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2022.102723
[7] Chen L, He Y, Yang Y, et al. The research status and development trend of additive manufacturing technology[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 89: 1 − 10.
[8] 陈国庆, 树西, 张秉刚, 等. 国内外电子束熔丝沉积增材制造技术发展现状[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(8): 123 − 128. Chen Guoqing, Shu Xi, Zhang Binggang, et al. State-of-arts of electron beam freeform fabrication technology[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(8): 123 − 128.
[9] Zhao P K, Fang K, Tang C, et al. Effect of interlayer cooling time on the temperature field of 5356-TIG wire arc additive manufacturing[J]. China Welding, 2021, 30(2): 17 − 24.
[10] Guo L L, Zheng H L, Liu S H, et al. Formation quality optimization and corrosion performance of Inconel 625 weld overlay using hot wire pulsed TIG[J]. Rare Metal Materials And Engineering, 2016, 45(9): 19 − 26.
[11] 蔡笑宇, 董博伦, 王俊哲, 等. 热处理对GTA增材制造TiAl合金组织与性能的调控[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(3): 7 − 12. Cai Xiaoyu, Dong Bolun, Wang Junzhe, et al. Control of the microstructure and mechanical properties of GTA-based wire arc additive manufactured TiAl alloys using post heat treatment[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(3): 7 − 12.
[12] Hu Y L, Lin X, Li Y L, et al. Influence of heat treatments on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 625 fabricated by directed energy deposition[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2021, 817: 141309.
[13] Marchese G, Lorusso M, Parizia S, et al. Influence of heat treatments on microstructure evolution and mechanical properties of Inconel 625 processed by laser powder bed fusion[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2018, 729: 64 − 75. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2018.05.044
[14] Dinda G P, Dasgupta A K, Mazumderb J. Laser aided direct metal deposition of Inconel 625 superalloy: Microstructures evolution and thermal stability[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2009, 509(1): 98 − 104.
[15] Miao Z J, Shan A D, Wu Y B, et al. Quantitative analysis of homogenization treatment of Inconel 718 superalloy[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2011, 21: 1009 − 1017. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60814-5
[16] Li S, Wei Q, Shi Y, Zhu Z, et al. Microstructure characteristics of Inconel 625 superalloy manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2015, 31: 946 − 952.
[17] 吕耀辉, 徐富家, 刘玉欣, 等. 固溶温度对等离子快速成形 Inconel625 合金组织的影响[J]. 材料科学与工艺, 2013, 21(2): 14 − 19. Lyu Yaohui, Xu Fujia, Liu Yuxin, et al. Effect of solution temperature on the microstructure of Inconel 625 alloy fabricated by PAW rapid prototyping[J]. Materials Science & Technology, 2013, 21(2): 14 − 19.
[18] Hu Y L, Lin X, Zhang S Y, et al. Effect of solution heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Inconel 625 superalloy fabricated by laser solid forming[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 767: 330 − 344.
[19] Eric A L, Mark R S, Michael B K, et al. Precipitation and dissolution of δ and γ″ during heat treatment of a laser powder-bed fusion produced Ni-based superalloy[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2018, 154: 83 − 86. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2018.05.025
[20] Pan J J, He X X, Zhao P C, et al. Numerical analysis of typical droplets transfer mode in wire and arc additive manufacture process[J]. China Welding, 2020, 29(3): 44 − 53.
[21] 胡显军, 孙丹丹, 张珂. 固溶温度对热轧 Inconel625 合金组织与力学性能的影响[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2019, 40(9): 64 − 69. Hu Xianjun, Sun Dandan, Zhang Ke, et al. Effect of solution temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of hot rolled Inconel625 alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat treatment, 2019, 40(9): 64 − 69.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 温淳杰,姚屏,范谨锐,曾祥坤,喻小燕,武威. 316L不锈钢和镍基合金梯度材料MIG焊电弧增材制造工艺研究. 精密成形工程. 2024(10): 208-216 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: