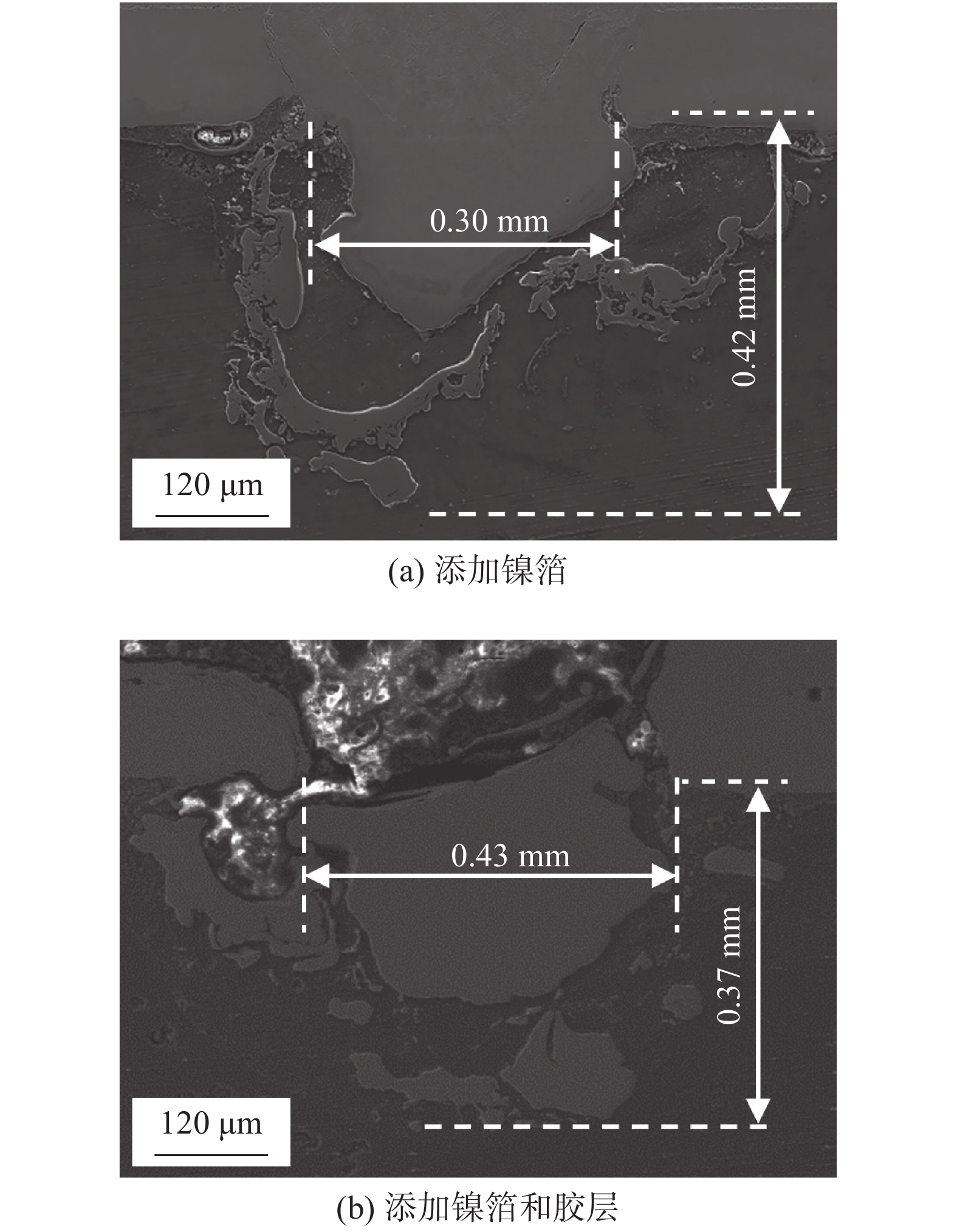
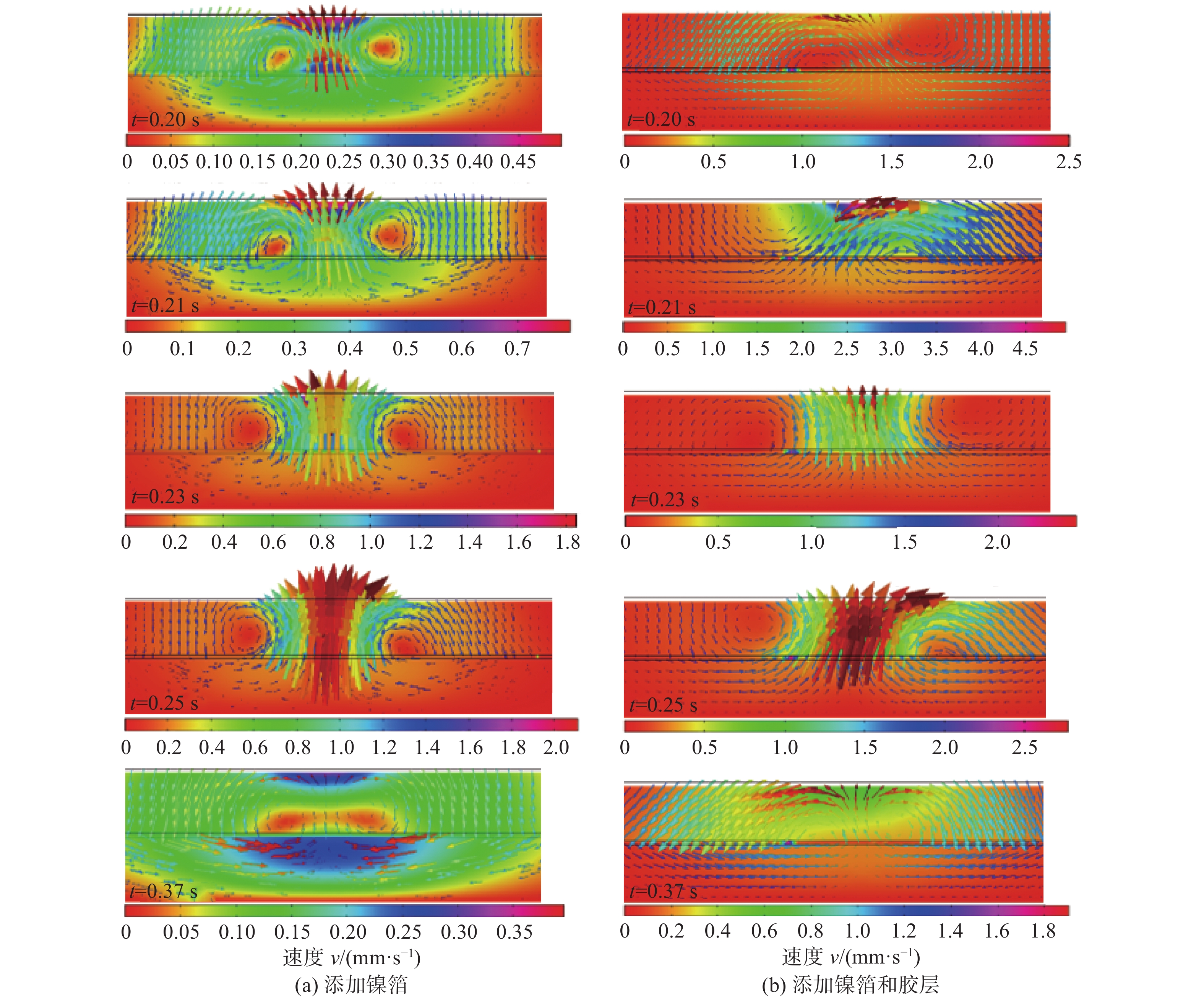
Microstructure and properties of steel/magnesium joint for adhesive layer-Ni foil assisted laser welding
-
摘要: 采用钢板在上、镁板在下且添加胶层-镍箔辅助的激光焊接技术,对厚度1.4 mm的DP590双相钢和厚度1.5 mm的AZ31B镁合金进行焊接, 基于热力学计算选择添加箔片元素,分析接头焊缝形貌、显微组织与力学性能,并对接头熔池温度场和流场进行数值模拟. 结果表明,激光功率1 800 W,焊接速度30 mm/s,离焦量为 + 2 mm,流量为15 L/min的氩气保护的工艺条件下,添加镍箔实现了镁/钢冶金连接,同时添加胶层和镍箔,与单一添加镍箔相比,接头平均抗剪强度提高1.73倍;添加胶层,焊缝连续光滑, 镁侧熔池的熔化宽度增大,钢/镁横向结合面积增加,熔池温度梯度降低,熔池流动速度提高,促进了界面元素相互扩散和冶金反应,因此钢/镁接头性能得到大幅提升.Abstract: DP590 dual-phase steel with thickness of 1.4 mm and AZ31B magnesium alloy with thickness of 1.5 mm were welded by adhesive layer-Ni foil assisted laser welding technology in an overlap steel-on-Mg configuration. Foil elements were selected based on thermodynamic calculation, weld morphology, microstructure and mechanical properties of the joint were analyzed, and the temperature field and flow field of molten pool were simulated. The results show that under the conditions of laser power of 1 800 W, welding speed of 30 mm/s, defocusing amount of + 2 mm and flow rate of 15 L/min, the metallurgical connection between magnesium and steel can be realized by adding Ni foil. While adding adhesive layer and Ni foil, the average shear strength of the joint is increased by 1.73 times compared with that of single Ni foil. The weld is continuous and smooth with the addition of adhesive layer, the melt width of magnesium side molten pool increases, the transverse bonding area of steel/magnesium increases, the transverse and longitudinal temperature gradient at interface decreases, the flow velocity of molten pool increases, and the element distribution uniformity is improved, which promotes the diffusion and metallurgical reaction of interfacial elements. Hence, the performance of the steel/magnesium joint is improved greatly.
-
Keywords:
- adhesive layer /
- laser welding /
- temperature field /
- velocity field /
- thermodynamics
-
0. 序言
近年来,随着飞行器技术的快速发展,低空经济逐渐成为战略性新兴产业,具有广阔的应用范围和经济前景[1]. 在飞行器制造行业中,采用高强度的轻质材料是至关重要的,这类材料不仅能够确保飞行器的整体结构强度,为人员、货物以及飞行器本身提供可靠的安全保障,还能显著减少因质量过大而带来的能耗成本,从而有效提升企业的经济效益. 铝合金、钛合金都具有密度小、强度高、耐腐蚀性好等优点,是飞行器制造行业中的常用轻质材料[2-3]. 钛合金成本较高、难加工,但其强度、耐高温性及耐磨性远高于铝合金,其更能应对一些极端特殊条件[4].若将钛合金和铝合金实现可靠的连接,形成复合材料零件,就可以降低制造成本,同时满足某些特殊工作条件,实现飞行器制造过程中结构性能和经济效益的平衡[5-7]. 实现钛合金与铝合金这两种异质金属的稳定可靠的连接,对于提升飞行器的整体性能、安全性和耐久性具有举足轻重的意义.
铝/钛异种金属连接研究热点主要集中在激光[8]、电弧[9]为热源的熔钎焊及搅拌摩擦焊[10]. 铝/钛接头强度由界面IMC决定,在铝/钛异种金属焊接过程中,焊缝界面处会形成硬脆的Ti-Al金属化合物(TiAl,TiAl2和TiAl3等),其厚度、成分及形貌会对接头的连接强度产生一定的影响[11-12]. 激光熔钎焊是一种实现铝/钛异种金属连接的有效可靠的方法,通过调整激光功率、焊接速度、填充物可以实现对Ti-Al金属间化合物层(IMC)控制[13]. Li等人[14]研究双点激光下激光功率对焊缝成形、界面IMC组织和接头抗拉强度的影响,发现随着激光功率的增加,IMC层的厚度也增加,IMC层的形貌由胞状转变为锯齿状,最后转变为棒状,界面IMC的组织成分以Ti(Al,Si)3为主,1 900 W接头抗拉强度最高为241 MPa;Zhang等人[15]提出在激光焊接TA2钛合金/AA5150铝合金接头处添加银网,制备含银合金的焊缝和连接界面,研究了有无银网的Ti/Al接头的显微组织和力学性能,试验结果显示,含Ag元素的铝晶粒比不含Ag元素的铝晶粒细小,MgAg新相的出现抑制了铝枝晶的生长,焊缝含有Ag元素合金可以降低了TiAl3 与Al之间的力学性能差异,提高接头的力学性能,接头的最佳平均抗剪强度从147.7 MPa增加到171.4 MPa;Tian等人[16]研究发现在极低和极高的热输入下,焊缝会产生不连续的IMC和较厚的Ti(Al,Si) + Ti(Al,Si)2 + Ti(Al,Si)3,降低接头强度.
使用不同Si元素含量填充焊丝对铝/钢进行激光熔钎焊,在界面扩散反应过程中Si元素更容易聚集在IMC处,Si元素的添加影响焊缝界面IMC的组织结构,提高了接头的抗拉强度[17-18]. 为了探究填充焊丝中Si元素含量的变化对TC4钛合金/6061-T6铝合金钎焊界面微观组织和力学性能产生影响,文中通过调整焊丝中Si元素含量研究Si元素的添加对铝/钛界面IMC成分、微观组织的影响. 在此基础上讨论了不同Si元素含量对接头的微观组织、力学性能和断裂行为的影响,为Ti/Al异种金属激光焊焊缝元素调控提供参考依据.
1. 试验方法
Ti/Al异种金属激光熔钎焊试验中母材为TC4钛合金和6061-T6铝合金,其尺寸均为100 mm × 50 mm × 2 mm,填充材料分别采用纯铝、AlSi5和AlSi12三种不同Si元素含量的焊丝,试验材料的主要化学成分见表1.
表 1 试验材料的主要化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical composition of the test materials材料 Si Fe Mg V Ti Al 6061Al 0.63 0.29 1 — 0.02 余量 TC4 — 0.135 — 3.93 余量 6.21 Al 0.05 0.1 — — — 余量 AlSi5 5 0.8 0.05 — 0.2 余量 AlSi12 12 0.8 0.05 — 0.2 余量 在焊接试验前,先使用丙酮对钛板和铝板表面进行擦洗,以去除表面残留油污和杂质,采用机械打磨的方法将焊接区域及其附近的氧化层去除,然后再将铝钎剂和丙酮混合液均匀涂抹在焊接区域,等待丙酮挥发干燥,最后将其固定在夹具上,采用平板对接的方式,钛板和铝板之间留1 mm间隙,不开坡口,为避免打磨部位再次氧化,涂抹完钎剂后尽快开始焊接试验. 试验系统由IPG公司的10 kW的YLS10000光纤激光器、KUKA KR70六轴机器人及Fronius的VR 7000 CMT送丝机组成,如图1所示.
选取最优的焊接工艺参数进行不同Si元素含量的焊接,参数选取为激光功率2 200 W、焊接速度0.36 m/min、送丝速度3.0 m/min、离焦量 + 20 mm、激光向铝侧偏移0.6 mm,保护气体为氩气、正面保护气体流量15 L/min、背面保护气体流量10 L/min,焊接时具体装配条件如图2所示.
在室温下,使用美特斯(MTS) E45.105型号电子万能试验机进行拉伸力学性能试验,拉伸速率为1 mm/min. 界面和断口微观结构使用赛默飞世尔科技公司(Thermo Scientific)生产的Helios 5 CX型号扫描电镜进行拍摄,IMC使用背散射电子(BSE)模式进行拍摄,断口微观结构则使用二次电子(SE)模式进行拍摄,利用扫描电镜自带的能谱仪分析选定区域的金属间化合物成分和元素分布规律.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 焊缝形貌
不同Si元素含量焊缝外观形貌及焊缝截面如图3所示. 三种不同Si元素含量焊丝的焊缝正面和背面均光滑且浸润良好,没有飞溅,无咬边缺陷,焊缝连续性较好. 通过观察焊缝截面可知,在铝钎剂的辅助下,纯铝、AlSi5和AlSi12都有效地浸润了钛合金板的正反两面,说明试验所采取的工艺参数合理.
2.2 焊接接头微观组织
用扫描电镜观察不同Si元素含量的焊接接头界面微观组织的3个不同区域(界面上部、界面中部及界面下部). 界面观察区域、界面IMC形貌和组织、界面元素分布如图4所示,选定区域的EDS点分析结果见表2.
表 2 图4中各点能谱分析结果(原子分数,%)Table 2. Contents of regions in IMC layer marked in Fig.4测试区域 Al Si Ti 1 80.4 0.6 19.0 2 72.7 1.1 26.2 3 75.9 0.4 23.7 4 72.5 6.9 20.6 5 75.1 5.0 19.9 6 69.9 6.3 23.8 7 71.9 11.7 16.4 8 70.1 9.1 20.8 铝/钛异种金属激光熔钎焊界面反应中生成IMC的厚度受界面热场影响较大,由于焊接过程中焊缝界面峰值温度由上而下递减,所以不同Si元素含量焊缝界面IMC也均呈现由上而下递减的趋势[19].
当焊丝为纯铝时,焊缝上部IMC较厚,呈现柱状,且分布不均匀,最大柱状IMC约为14.9 μm,最小柱状IMC约为2 μm,部分柱状IMC断裂熔入焊缝中,根据表2中EDS结果分析,IMC由19% Ti,80.4% Al和0.6% Si组成,因此柱状IMC由TiAl3构成;界面中部IMC和上部相比分布较为均匀,呈现层状,部分IMC有脱离层状熔入焊缝的趋势,最大厚度约为3.8 μm,层状IMC主要由TiAl3构成;界面底部IMC分布均匀,呈现薄层状,IMC由TiAl3构成,厚度约0.87 μm,Li等人[14]也观察到了类似的界面微观结构组成.
当焊丝为AlSi5时,上部IMC呈现柱状,与纯铝上部进行对比,其厚度减少,但依然存在较长的柱状IMC,最大IMC厚度约为9.2 μm;中部和底部IMC均为层状,中部和底部IMC厚度分别约为1.6 μm和0.9 μm.根据表2中EDS结果分析,IMC主要由Ti(Al,Si)3构成.
当焊丝为AlSi12时,上部较粗的柱状IMC生长在底部层状IMC之上,相较于纯铝、AlSi5的上部IMC,AlSi12上部更加均匀,没有非常突出的柱状IMC,根据表2中EDS结果分析,IMC由16.4% Ti,71.9% Al和11.7% Si组成,上部柱状IMC主要为Ti(Al,Si)3;中部IMC为锯齿状,厚度在2 μm左右,主要成分为Ti(Al,Si)3;底部只生成一层极薄的层状IMC,平均厚度约为0.36 μm.
不同Si元素含量下的IMC平均厚度如图5所示,IMC的平均厚度都出现由上部向下部递减的趋势,这与焊接过程的焊缝各个部位峰值温度及高温停留时间的差异有关,峰值温度由大到小依次为界面上部—中部—下部,因此界面IMC厚度从上到下依次减薄[20]. 此外,Si元素含量越高,相同位置的界面IMC越薄,这是由于Si元素的加入抑制了界面Ti和Al原子的反应速率,有效的降低铝/钛之间的冶金反应,大量减少了生成的硬脆的Al-Ti金属间化合物.
图6为不同Si元素含量IMC线扫描.图6(a)中纯铝IMC长度为4.1 μm,IMC处没有发现明显Si元素含量变化,随着距离钛合金界面越远,Ti元素含量快速下降,Al元素含量快速上升. 图6(b) 和图6(c)中AlSi5和AlSi12 IMC长度分别为2.5 μm和3.9 μm,在IMC处可以观察到明显Si元素聚集.
图7为不同Si元素含量IMC面扫描.可以明显观察到当焊丝中含有Si元素时,Si元素会呈现出在IMC处聚集趋势. 由于Si元素和Al元素具有相似的晶体结构和原子序号,在Si元素参与钛侧钎焊界面反应中,Si原子会替代部分Al原子形成Ti-Al-Si三元相,因此AlSi5和AlSi12的IMC主要由Ti(Al,Si)3构成[21]. 同时,在图6(b) AlSi5线扫描观察到IMC中出现明显Si元素含量的上升,在图7 (b)中AlSi5的IMC面扫描中观察到明亮的Si元素聚集. 据文献报道,铝/钛界面Si元素含量的陡然升高可能会导致新相Ti7Al5Si12的生成[22]. 由于Si元素的化学势能较低,在IMC处产生聚集效应,导致硅纳米团簇的产生形成位错,更多的Si原子被缺陷拖曳聚集,形成Ti7Al5Si12,此外,在Ti7Al5Si12形成过程中会消耗从钛侧扩散到焊缝中的Ti原子,减少了Ti原子与焊缝中Al原子反应的数量,抑制Ti(Al,Si)3相的生成,从而控制住IMC的厚度[16].
2.3 力学性能与断裂行为分析
不同Si元素含量接头拉伸测试结果如图8所示. AlSi12的抗拉强度是三者中最高,为197.69 MPa,纯铝抗拉强度最低,为175.09 MPa,AlSi12抗拉强度相比纯铝提高了13%. 铝/钛异种金属激光熔钎焊可以通过提高填充焊丝中Si元素含量提高接头的抗拉强度.
纯铝焊缝断裂形貌如图9所示,断裂路径如图9 (a)所示,断口界面EDS结果见表3. 纯铝断口上部呈现平滑的断裂面,为典型的脆性断裂,如图9 (b)所示.根据EDS结果分析,Ⅰ 处为TiAl3相,焊缝上部断裂位于在IMC上,断裂路径经过TiAl3构成的IMC层;中部断裂微观界面如图9 (c)所示,断裂截面出现微小台阶,为解理断裂,Ⅱ 处EDS分析,断裂层为TiAl3层;下部断裂微观界面如图9 (d)所示,存在大量韧窝,为典型的韧性断裂,根据 Ⅲ 处结果分析,其成分为Al,但断裂截面处的Ti元素含量略高于纯铝焊丝,因此断裂位置为焊缝靠近IMC处.
表 3 图9中能谱分析(原子分数,%)Table 3. EDS results of the marked points in Fig.9测试区域 Al Si Ti Ⅰ 79.1 0.9 20.0 Ⅱ 76.4 0.8 22.8 Ⅲ 97.9 0.3 1.8 AlSi5焊缝断裂形貌如图10所示,断裂路径如图10 (a)所示,断口界面EDS结果见表4. AlSi5上部断口微观界面如图10 (b)所示,断口界面平滑,为脆性断裂,Ⅰ处EDS结果显示,Al 元素含量为69.6%,Si 元素含量为5.0%,Ti 元素含量为25.4%,断裂界面成分为Ti(Al,Si)3;中部微观断裂界面如图10 (c)所示,界面呈现鱼骨状,为典型的解理断裂,根据 Ⅱ处EDS结果分析,Al 元素含量为86.6%,但存在少量的Ti元素(9.7%),因此在焊缝中部,裂纹沿着IMC层与焊缝连接界面扩展;下部断裂界面既存在微小阶梯状,也存在韧窝,因此下部断裂为脆性断裂和韧性断裂的混合断裂,如图10 (d)所示,根据EDS结果分析,脆性断裂 Ⅲ 处成分为Ti(Al,Si)3, 韧性断裂 Ⅳ 处为焊缝靠近IMC侧.
表 4 图10能谱分析(原子分数,%)Table 4. EDS results of the marked points in Fig.10测试区域 Al Si Ti Ⅰ 69.6 5.0 25.4 Ⅱ 86.6 3.7 9.7 Ⅲ 65.7 5.9 28.4 Ⅳ 82.0 2.4 15.6 AlSi12焊缝断裂形貌如图11所示,断裂路径如图11 (a)所示,断裂在铝母材处,断口存在大量韧窝,为韧性断裂,其断口EDS见表5. 由于Si元素的添加,减少铝/钛界面反应中硬脆金属间化合物的生成,降低了IMC的厚度,同时,中部IMC为2 μm左右的锯齿状,锯齿状IMC对裂纹扩展起到阻碍的作用.
表 5 图11中能谱分析(原子分数,%)Table 5. EDS results of the marked points in Fig.11测试区域 Al Si Ti Ⅰ 98.9 0.9 0.2 Li等人[23]提出由于焊缝界面残余应力较大,钎焊界面产生大量较厚的硬脆的IMC,会导致钎焊界面连接强度降低. 因此纯铝下裂纹最先出现在铝/钛钎焊界面上部,由上部IMC的TiAl3层向中部撕裂扩展,中部继续沿着TiAl3层撕裂,由于纯铝下部IMC较薄,平均厚度为1 μm,IMC没有发生断裂,裂纹沿着焊缝靠近IMC侧继续撕裂,直至焊缝完全断裂,如断裂路径示意图12 (a)所示.
AlSi5的断裂路径示意图12 (b)所示,AlSi5焊缝受到拉伸力作用时,裂纹出现上部较厚的Ti(Al,Si)3金属间化合物中,沿着Ti(Al,Si)3层扩展;焊缝中部,裂纹则沿着IMC层与焊缝连接界面扩展;下部则表现为混合断裂模式,其中包括Ti(Al,Si)3层的脆性断裂以及焊缝区域的韧性断裂.
AlSi12的断裂路径示意图如图12 (c)所示. 根据Tian等人[16]的研究,在Ti-Al-Si三元反应中,Si原子会替代部分Al原子生成Ti(Al,Si)3,Si 原子的取代释放Ti原子周围的电荷积累,软化了IMC. 异种金属在相同的金属间化合物连接下,IMC硬度越低,其抗断裂能力越强,焊接接头强度越高. 6061-T6铝合金是经过热处理强化后的铝合金,在焊接过程中热量形成热影响区会弱化热处理铝合金的强度和硬度,降低铝母材强度,更容易在铝母材热影响区处发生断裂.
3. 结论
(1) 铝/钛激光熔钎焊不同Si元素含量IMC界面层厚度均呈现由上而下的递减趋势. IMC层界面形貌主要分为柱状、锯齿状和薄层状,因为沿着焊缝厚度方向受峰值温度的影响,IMC上部生长较厚,主要为柱状,下部生长较薄,为薄层状. 随着Si元素含量的增加,IMC层厚度逐渐变薄.
(2) 纯铝IMC主要物相为TiAl3. 由于Si元素的添加,Si元素会聚集在IMC处,Si原子在Ti-Al二元反应中替代部分Al原子形成Ti-Al-Si三元相,AlSi5和AlSi12IMC层物相以Ti(Al,Si)3为主.
(3) 在AlSi5和AlSi12的界面IMC处出现Si元素异常聚集现象,由于Si元素的化学势能较低,促使Si原子在界面处富集,Si元素的聚集会降低界面Ti和Al原子的反应速度,从而降低界面IMC的厚度.
(4) 纯铝断裂路径上、中部为IMC层的脆性断裂,下部为沿着焊缝靠近IMC层处的韧性断裂,接头抗拉强度为175.09 MPa;AlSi5断裂路径为上部为IMC层的脆性断裂,中部为IMC与焊缝界面连接处的脆性断裂,下部为既有IMC层脆性断裂又焊缝韧性断裂的混合断裂,接头抗拉强度为188.05 MPa;AlSi12断裂路径为沿着6061-T6铝合金板热影响区的韧性断裂,接头抗拉强度最高,为197.69 MPa.
-
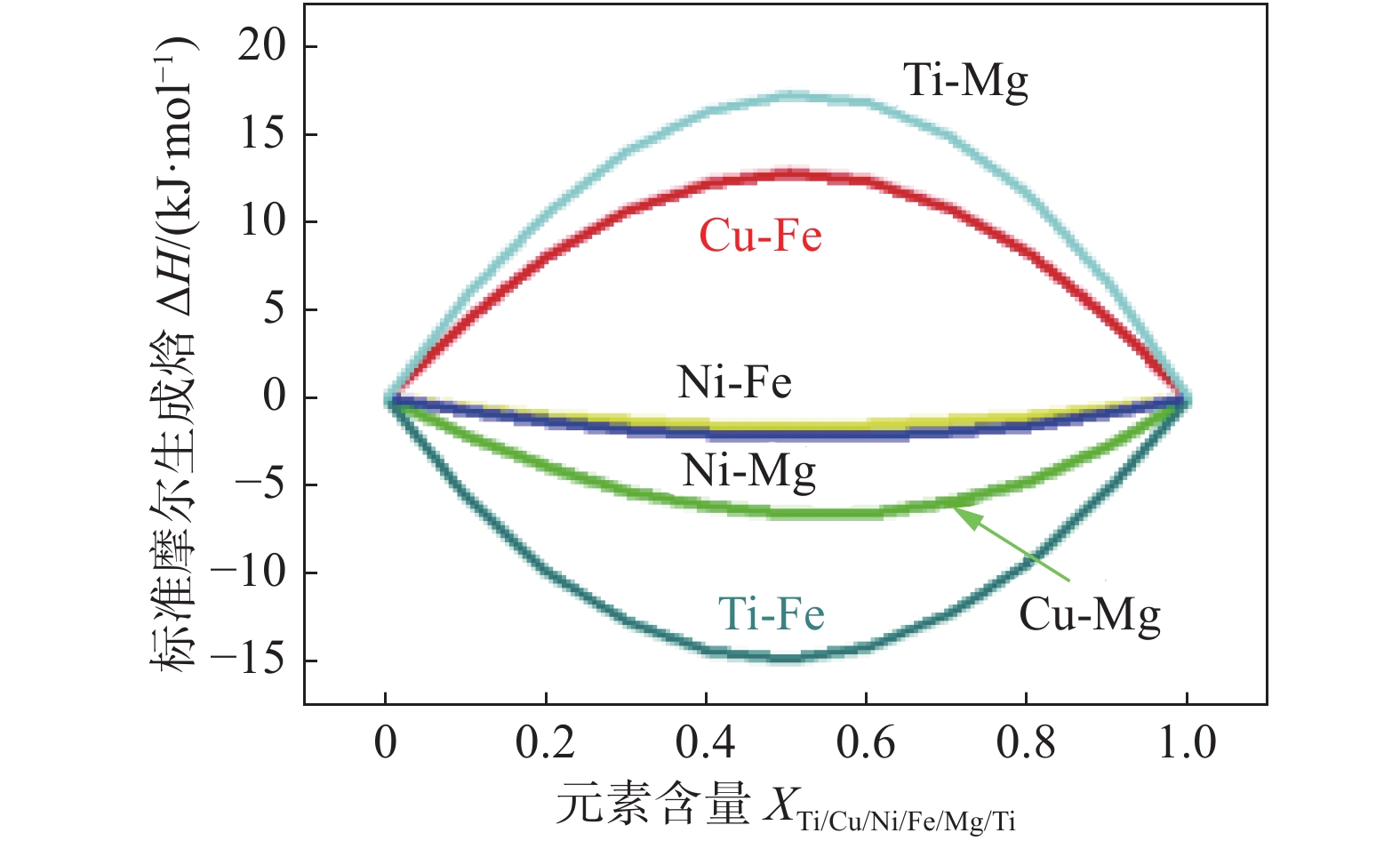
图 9 热力学计算结果
Figure 9. Thermodynamic calculation results. (a) standard molar generation enthalpy for binary systems; (b) chemical potentials of Fe-Ni-Mg-0.03Al system for Fe; (c) chemical potentials of Fe-Ni-Mg-0.03Al system for Mg ; (d) chemical potentials of Fe-Ni-Mg-0.03Al system for Al; (e) chemical potential of Fe-Ni-Al-0.03Mg system for Fe; (f) free energy of the Fe-Ni-Al-0.03Mg system
表 1 母材化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of base material
材料 Al Zn Mn Si C S P Fe Mg DP590 0.02 — 1.60 0.0446 0.068 0.015 0.011 余量 — AZ31B 3.12 0.95 0.15 0.10 — — — 0.03 余量 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding parameters
激光功率P/W 焊接离焦量L/mm 焊接速度v/(mm·s−1) 氩气流量Q/(L·min−1) 1 800 + 2 30 15 表 3 EDS点成分结果(原子分数,%)
Table 3 EDS point composition results
位置 Fe Ni Al Mg 可能相 P1 0.93 3.25 1.42 94.40 α-Mg P2 78.09 18.83 0.13 2.95 Fe + FeNi3 P3 0.45 0.08 1.41 98.06 α-Mg P4 0.44 6.50 1.65 91.41 α-Mg P5 2.19 9.37 1.88 86.56 α-Mg + Mg2Ni P6 0.94 4.33 1.26 91.71 α-Mg P7 0.74 4.09 1.21 92.59 α-Mg + Mg2Ni P8 56.42 11.31 2.49 25.91 Mg2Ni + FeNi3 -
[1] Mansoor B, Mukherjee S, Ghosh A. Microstructure and porosity in thixomolded Mg alloys and minimizing adverse effects on formability[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A-Structural Materials Properties Microstructure and Processing, 2009, 512(1-2): 10 − 18. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.01.070
[2] Tao T, Zhou D W, Liu J S, et al. Improvement of laser welded joint properties of AZ31B magnesium alloy to DP590 dual-phase steel produced by external magnetic field[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2022, 79: 270 − 283. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2022.04.069
[3] 李永兵, 马运五, 楼铭, 等. 轻量化多材料汽车车身连接技术进展[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(24): 1 − 23. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.24.001 Li Yongbing, Ma Yunwu, Lou Ming, et al. Advances in lightweight multi-material automotive body joining technology[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(24): 1 − 23. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.24.001
[4] Tan C W, Chen B, Song X G, et al. Influence of Al interlayer thickness on laser welding of Mg/steel[J]. Welding Journal, 2016, 95(10): 384 − 394.
[5] Wang H Y, Liu L M, Zhu M L, et al. Laser weld bonding of A6061Al alloy to AZ31B Mg alloy[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2007, 12(3): 261 − 265. doi: 10.1179/174329307X159784
[6] 任大鑫, 刘黎明. 镁合金激光胶接焊胶层作用分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2009, 45(8): 266 − 269. doi: 10.3901/JME.2009.08.266 Ren Daxin, Liu Liming. Analysis of the role of laser bonding welding adhesive layer for magnesium alloy[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 45(8): 266 − 269. doi: 10.3901/JME.2009.08.266
[7] 王红阳, 张兆栋, 曹贺. 基于镍合金中间层的镁/钢异质金属激光-电弧复合胶焊技术[J]. 焊接学报, 2014, 35(4): 83 − 86. Wang Hongyang, Zhang Zhaodong, Cao He. Laser-arc composite glue welding technology for magnesium/steel heterogeneous metals based on nickel alloy interlayer[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2014, 35(4): 83 − 86.
[8] Liu L M, Jiang J B. The effect of adhesive on arc behaviors of laser-TIG hybrid weld bonding process of Mg to Al alloy[J]. IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 2011, 39(12): 581 − 586.
[9] 周惦武, 李宁宁, 徐少华, 等. 双相钢/铝合金激光胶接焊胶层作用分析[J]. 机械工程学报, 2016, 52(14): 25 − 30. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.14.025 Zhou Dianwu, Li Ningning, Xu Shaohua, et al. Analysis of the role of laser glue layer for duplex/aluminum alloy welding[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(14): 25 − 30. doi: 10.3901/JME.2016.14.025
[10] 刘黎明, 王红阳, 王恒, 等. 镁合金激光胶接焊接头微观及力学性能[J]. 中国机械工程, 2007(3): 352 − 356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2007.03.025 Liu Liming, Wang Hongyang, Wang Heng, et al. Microscopic and mechanical properties of laser-glued welded joints of magnesium alloy[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2007(3): 352 − 356. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-132X.2007.03.025
[11] Miedema A R. The electronegativity parameter for transition metals: Heat of formation and charge transfer in alloys[J]. Journal of the Less Common Metals, 1973, 32(1): 117 − 136. doi: 10.1016/0022-5088(73)90078-7
[12] Luo Q, Li Q, Zhang J Y, et al. Comparison of muggianu model, toop model and general solution model for predicting the thermodynamic properties of Mg-Al-Zn system[J]. Calphad, 2015, 51: 366.
[13] Auwal S T, Ramesh S, Zhang Z Q, et al. Influence of electrodeposited Cu-Ni layer on interfacial reaction and mechanical properties of laser welded-brazed Mg/Ti lap joints[J]. Journal of Manufacturing Processes, 2019, 37: 251 − 265. doi: 10.1016/j.jmapro.2018.11.029
[14] 康悦, 赵艳秋, 李悦, 等. 驱动力对2219铝合金DLBSW焊接熔池行为的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2022, 43(2): 82 − 87. Kang Yue, Zhao Yanqiu, Li Yue, et al. Effect of driving force on the molten pool behavior of 2219 aluminum alloy DLBSW welds[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(2): 82 − 87.
[15] Qi J X, Miao G H, Ai J Y, et al. Study on numerical simulation of TA1-304 stainless steel explosive welding[J]. China Welding, 2021, 30(2): 11 − 16.



 下载:
下载: