Effect of welding time and temperature on properties of Sn35Bi0.3Ag/Cu welded joints
-
摘要: 分别在不同焊接时间和不同焊接温度下制备了Sn35Bi0.3Ag/Cu焊接接头,采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、万能拉伸试验机、超声波成像无损探伤检测仪等测试手段,研究了焊接时间(1 ~ 9 min)和焊接温度(210 ~ 290 ℃)对Sn35Bi0.3Ag/Cu焊接接头微观结构和力学性能的影响. 结果表明,在焊接过程中,Cu元素扩散到焊接界面处,形成了(Cu6Sn5, Cu3Sn)界面层,同时发现生成的Ag3Sn相能够抑制界面层的生长. 随着焊接时间的延长或焊接温度的升高,反应层变厚,抗剪强度先增大后减小. 对焊接接头断口形貌分析发现,焊接接头的断裂由Bi相颗粒及Cu6Sn5颗粒共同作用. 焊接接头的断裂发生在IMC/焊料一侧,Bi相颗粒及Cu6Sn5颗粒共同影响着接头的抗剪强度. 此外,当焊接时间为3 min、焊接温度为230 ℃时,接头的钎着率最大,为99.14%,抗剪强度达到最大值,为51.8 MPa.
-
关键词:
- 工艺参数 /
- Sn35Bi0.3Ag/Cu焊接接头 /
- 抗剪强度 /
- 钎着率
Abstract: Sn35Bi0.3Ag/Cu welded joints were prepared at different welding time and temperature. The effects of welding time (1 ~ 9 min) and welding temperature (210 ~ 290 ℃) on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Sn35Bi0.3Ag/Cu welded joints were studyed by means of scanning electron microscope (SEM), universal tensile testing machine and ultrasonic scan machine. The results show that the Cu element diffuses into the welding interface and forms the (Cu5Sn6, Cu3Sn) interface layer. The Ag3Sn phase can inhibit the growth of interfacial layer. With the increase of welding time or welding temperature, the reaction layer thickens and the shear strength increases first and then decreases. The analysis of the fracture morphology of the welded joint shows that the fracture of the welded joint is jointly affected by Bi phase particles and Cu6Sn5 particles.The fracture of the welded joint occurs on the IMC / solder side. Bi phase particles and Cu6Sn5 particles affect the shear strength of the joint.In addition, when the welding time is 3 min and the welding temperature is 230 ℃, the brazing rate is the highest (99.14%) and the shear strength reaches the maximum value (51.8 MPa). -
0. 序言
目前,国内开发的船用高强钢焊条及焊剂,其熔渣的设计通常采用CaO-SiO2-CaF2基础渣系或与其相近的渣系类型[1]. 在长期的工程应用中发现,当焊条或焊剂更换原材料批次时,其性能有时会产生较大波动,导致焊接材料的工艺性能或力学性能不能满足工程要求. 产生上述问题的根本原因是原材料批次改变,熔渣关键组元含量发生细微变化,熔化特性发生改变,进而直接影响焊接材料的工艺性能和焊接质量的好坏[2-4]. TiO2 和Al2O3为高强钢焊接材料渣系的关键组元,探明其对渣系黏度、熔化温度、表面张力等熔化特性的影响规律,对改善焊接材料性能、指导焊接材料配方设计等工作具有重要意义.
国内外关于渣系的研究主要集中在冶金领域,关于焊接渣系的研究较少. 在组元对熔渣熔化特性影响研究方面,Ju等人[5]研究了电渣重熔中TiO2对低氟CaF2-CaO-Al2O3-MgO-Li2O渣黏度和结构的影响,认为渣系黏度随着TiO2 的增加而降低,但达到一定温度后,TiO2 的加入对降低黏度影响较小. Tuset等人[6]也认为无论化学成分如何变化,当炉渣完全熔化后,黏度不再受温度升高影响. 张平等人[7]采用FactSage软件利用热力学模拟的方法同样证明了该结论的正确性. 在渣系熔化温度研究中,邓永春等人[8]以La2O3-SiO2-Al2O3为基础渣系,采用半球法对设定区域的熔化温度进行了研究,认为SiO2/Al2O3质量比为2时,渣系的熔化温度最低. 在渣系结构研究方面,李生平等人[9]采用XRD及激光拉曼光谱对高钛渣结构进行了初步表征,并对SiO2,CaO和MgO含量变化引起的熔渣结构变化原因进行了分析解释,对组元含量、物理性能及结构间影响关系研究具有一定的参考意义. 在焊接领域,李海新等人[10]重点研究了水下湿法焊接中TiO2 的加入量对焊接熔渣形貌及组织微观结构的影响,认为当药皮中TiO2加入量较大时,熔渣致密松脆,熔渣微观组织中存在粗大的灰白色条状相,有利于熔渣脱渣,能够改善焊接材料工艺性.
1. 试验方法
某690 MPa强度级别焊条渣化学成分见表1. 基于该渣成分进行四元焊接熔渣试样的制备,试剂均为分析纯,其纯度和熔点[1]见表2. 由XRF分析所得的试验前后四元渣的化学成分及变化见表3.
表 1 690 MPa强度级别焊条渣系主要化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Main chemical compositions of 690 MPa strength grade electrode slagCaO SiO2 CaF2 TiO2 Al2O3 MnO Na2O Fe2O3 MgO 46.53 25.72 11.27 5.14 3.52 2.52 3.07 1.63 0.60 表 2 试验所用化学试剂Table 2. Chemical reagent in present experiment试剂 纯度 (质量分数,%) 熔点T/℃ CaO 98.0 2 940 SiO2 99.8 1 713 CaF2 99.5 1 418 TiO2 99.0 1 825 Al2O3 99.0 2 050 表 3 试验前后焊接渣系的化学成分Table 3. Chemical compositions of welding slag before and after experiment试样序号 试验前成分 (质量分数,%) 试验后成分 (质量分数,%) CaO SiO2 CaF2 TiO2 Al2O3 CaO SiO2 CaF2 TiO2 Al2O3 1 54 28 18 0 — 58.24 26.23 15.53 0 — 2 53 27 18 2 — 57.19 25.04 15.87 1.90 — 3 52 26 18 4 — 56.88 24.14 15.36 3.62 — 4 51 25 18 6 — 55.70 22.90 15.95 5.45 — 5 50 24 18 8 — 54.99 22.38 15.22 7.41 — 6 53 27 20 — 0 57.98 23.94 18.08 — 0 7 52 26.5 20 — 1.5 57.34 23.22 17.80 — 1.64 8 51 26 20 — 3 56.76 22.78 17.69 — 2.77 9 50 25.5 20 — 4.5 55.22 22.36 17.91 — 4.51 10 49 25 20 — 6 54.87 21.94 17.46 — 5.73 试验中熔渣表面张力采用圆筒(柱)脱离法、黏度采用内圆柱体旋转法进行测量,熔化温度通过读取连续降温黏度曲线上拐点处对应温度值的方法获得,所用的测量设备均为RTW-2010型熔体物性综合测定仪,如图1所示. 该设备可以测量熔体黏度、表面张力、熔化温度、电导率、密度等物理性质,最高测量温度为1 700 ℃. 试验所用测头为钼制,坩埚为高纯石墨坩埚. 采用圆筒脱离法进行熔渣表面张力的测试,测试温度为1 600 ℃恒温,当炉温达到试验温度后保温30 min,使熔渣成分均匀、液面保持稳定,然后进行测定. 表面张力测试完成后,采用内旋转柱体法测量熔渣降温过程中的连续黏度,降温速率为8 ℃/min,试验转速为12 r/min. 并分别对每组高温熔渣淬冷样进行XRF,XRD和拉曼光谱分析.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 TiO2含量对CaO-SiO2-CaF2渣系熔化特性的影响
TiO2对CaO-SiO2-CaF2渣系黏度的影响如图2所示. 由图2可知,对于0 ~ 8%(质量分数)不同TiO2含量的熔渣,其黏度随温度变化趋势基本一致,即随着温度的下降,连续降温黏度曲线上会出现明显的拐点. 当高于拐点温度时,黏度随温度升高无明显变化,黏度值主要集中在0.06 ~ 0.2 Pa·s内. 当低于拐点温度时,黏度随温度下降急剧升高,结晶区间变窄,呈现明显的“短渣”现象(一般将黏度变化数值相同时,相应温度变化范围短的渣称为短渣).
由图3可知,TiO2含量与拐点温度存在相关性,随着TiO2含量的增加,拐点温度呈现下降趋势,当TiO2质量分数从0增加至6%时,拐点温度均匀下降,TiO2质量分数每增加2% ,温度下降8 ℃左右;当TiO2质量分数从6%增加到8%时,熔化温度下降显著,约为40 ℃,下降速度达到之前的5倍左右,熔化温度随TiO2含量变化十分敏感,因此,可认为6% ~ 8%的TiO2质量分数范围是熔化温度的“敏感区间”,在焊材配方设计时应予以考虑. 另外,熔化温度随TiO2含量的变化趋势也与氧势理论[1]相符,即TiO2作为酸性氧化物,加入碱性渣中,会使氧势增加,从而黏度下降,熔化温度也随之降低. 通常将熔渣在加热过程中,固体状态的熔渣全部转化为均匀的液体相,或指冷却的过程中,液体状态的熔渣开始析出固体时的温度,定义为熔化温度,因此,拐点温度可表示熔渣的熔化温度[11].
TiO2含量对渣系表面张力的影响如图4所示. 随着TiO2含量增加,表面张力呈连续下降趋势,总体位于230 ~ 370 mN/m的区间内, TiO2的质量分数每增加2%,表面张力相对初始渣系表面张力值分别下降了19.4,84.8,87.3和125 mN/m,下降明显,但下降速度有所不同,2% ~ 4%的TiO2质量分数范围是表面张力的“敏感区间”.
不同TiO2含量对应的熔渣物相的XRD衍射图谱如图5所示. 由图5可知,不同TiO2添加量的衍射峰基本类似,但物相含量及种类发生了一定变化. 当TiO2质量分数为0时,渣中主要物相为Ca4Si2O7F2(枪晶石),Ca2SiO2F2,含有少量CaSiO4和CaSiO3相;当TiO2的质量分数增加到2%及以上时,分别在32°,48°,58°出现了CaTiO3新相,并从衍射峰的强度可以看出,随着TiO2含量的增加,CaTiO3新相含量有增加的趋势,而熔渣主要物相中,Ca4Si2O7F2和Ca2SiO2F2两相含量明显降低,CaSiO4含量显著升高.
上述物相分析结果也解释了熔渣的黏度、熔化温度和表面张力三个熔化特性随TiO2添加量的不同而变化的规律. 在CaO-SiO2-CaF2基础焊接渣系中,SiO2的存在会使熔渣中形成硅酸盐网络结构,从而形成颗粒较大的高熔点稳定化合物,随着TiO2添加量的增加,高熔点的硅酸盐结构Ca4Si2O7F2被破坏,转变成了简单四面体结构的[SiO4] 4−,并生成了熔点较低的CaTiO3新相,从而使熔渣的黏度和熔化温度随之下降. 同样,加入的TiO2会与熔体中的O2−结合,形成静电势较小的复合阴离子氧化物[TiO3]2−,其与阳离子间的键能比O2−与阳离子之间形成的键能小的多,从而降低了熔渣表面张力.
2.2 Al2O3含量对CaO-SiO2-CaF2渣系熔化特性的影响
Al2O3含量对CaO-SiO2-CaF2渣系黏度的影响如图6所示. 由图6可知, Al2O3含量不同,渣系黏度曲线也会出现明显的拐点,但变化趋势有所不同. 高于拐点温度时,渣系黏度曲线变化趋势与TiO2影响一致,黏度随温度升高无明显变化,黏度值主要集中在0.1 ~ 0.2 Pa·s. 当低于拐点温度时,Al2O3的质量分数在4.5% ~ 6%,随着温度降低,黏度迅速增大,熔渣快速结晶,呈现明显的“短渣”现象;当Al2O3的质量分数在0 ~ 3%,渣系黏度从结晶开始,经过较宽的温度区间(约50 ℃)才升高到1 Pa·s以上,中间出现了一段“平台期”,说明增加Al2O3含量可缩短熔渣凝固温度区间.
Al2O3含量对渣系拐点温度的影响如图7所示.从图7可知,随着Al2O3含量的增加,拐点温度先略有升高后明显降低,Al2O3质量分数在0 ~ 1.5%时,拐点温度升高了13 ℃;Al2O3质量分数在1.5% ~ 6%时,每增加1.5%,拐点温度都会出现较大幅度下降,相对1.5% Al2O3含量渣系拐点温度值分别下降了27、98和135 ℃,说明在该范围内的Al2O3含量对拐点温度的影响较大,尤其在Al2O3的质量分数为3% ~ 4.5%的范围,是熔化温度的“敏感区间”.
Al2O3含量对渣系表面张力的影响如图8所示.与对拐点温度的影响类似,随着Al2O3含量的增加,表面张力先略有升高后明显降低,Al2O3质量分数为在0 ~ 1.5%时,表面张力增加了6.8 mN/m;Al2O3质量分数为1.5% ~ 6%时,随Al2O3含量升高,表面张力下降较快,Al2O3质量分数每增加1.5%,相对Al2O3的质量分数为1.5%时表面张力值分别下降了19.1,29.6和48.6 mN/m,从变化趋势来看,在Al2O3质量分数为1.5% ~ 3%和4.5% ~ 6%时,表面张力变化较为敏感.
不同Al2O3含量对应的熔渣物相的XRD衍射图谱如图9所示. 由图9可知,不同Al2O3添加量的衍射峰虽有类似之处,但物相含量及种类发生了一定变化. 当Al2O3质量分数为0时,熔渣主要物相为Ca4Si2O7F2,并含有少量CaSiO4和CaSiO3相;当Al2O3质量分数增加至1.5%时,熔渣主要物相基本不变,但产生了少量的Ca2Al(AlSiO7)新相;当Al2O3质量分数增加到3%及以上时,熔渣的衍射峰强度发生了较为明显的变化,熔渣主要物相Ca4Si2O7F2峰强度下降,含量降低,CaSiO4含量升高,并且除了生成的Ca2Al(AlSiO7)新相之外,还分别在28°和47°处出现了CaF2新相.
同样,上述物相测试结果也在一定程度上反映了熔渣熔化特性变化的深层次原因. 在Al2O3添加量为0时,基础渣系中存在大量的高熔点相Ca4Si2O7F2 ,故渣系整体黏度较大、熔化温度较高;当Al2O3质量分数增加至1.5%时,产生的Ca2Al(AlSiO7)新相同样结构复杂,并且从衍射峰强度上看,Ca4Si2O7F2相含量也略有增加,这也解释了当Al2O3质量分数为1.5%时,熔渣熔化温度出现了一定上升的原因;当Al2O3质量分数增加至3%及以上时,Ca4Si2O7F2相含量明显减少,转变成了简单四面体结构的[SiO4] 4−,并产生了低熔点的CaF2相,从而使熔渣熔化温度出现了显著降低.
Al2O3添加量对表面张力的影响,也可通过物相分析结果来解释. 当渣中加入少量Al2O3时,部分Si—O—Si键转变成了Si—O—Al键,后者键能较高,表面张力较大,故使熔渣表面张力上升;但随着Al2O3含量增加,产生了CaF2新相,由于液态CaF2的表面张力在1 470 ℃以上时仅为280 mN/m,可以显著降低熔渣的表面张力[11].
2.3 TiO2和Al2O3含量对CaO-SiO2-CaF2渣系结构的影响
采用激光拉曼光谱仪对不同TiO2和Al2O3添加量的熔渣进行全波长范围测试分析,并结合渣系XRD测试结果,共同完成渣系的物相和结构的分析及确定,熔渣拉曼光谱分别如图10,图11所示.
由图10 及表4可知,当质量分数为0 ~ 2%时,熔渣显示出3个Raman活性模式,分别为651.8,908.2和974.8 cm−1,其中,651.8 cm−1处峰是[SiO3]2−中的Si—O0弯曲振动所致,908.2 cm−1处峰是[Si2O7]6−中的Si—O−对称伸缩振动所致,974.8 cm−1处峰是[SiO3]2−中的Si—O−对称伸缩振动所致. 从上述结果可以看出,在不含或含少量TiO2的情况下,熔渣中以复杂的[Si2O7]6−网络结构为主,含有少量未形成网络的[SiO3]2−. 随着TiO2质量分数增加至4% ~ 8%时,熔渣显示出2个新的特征峰,分别位于840和855 cm−1左右,并且含量逐渐增加,根据文献分析,840 cm−1处峰是Ti—O—Ti伸缩振动所致,855 cm−1处峰是[SiO4]4−中的Si—O−对称伸缩振动所致,另外从图10中可看出,[Si2O7]6−中的Si—O−键含量逐渐减少. 原因可能是随着TiO2含量增加,生成了CaTiO3新物相,夺取了部分硅酸盐网络结构Ca4Si2O7F2中的Ca2 + ,使网络结构遭到破坏,生成了具有简单四面体结构的[SiO4] 4−.
表 4 CaO-SiO2-CaF2-TiO2四元渣系拉曼峰分析及其参考依据Table 4. Peak analysis of Raman in the quaternary CaO-SiO2-CaF2-TiO2 slag using established references拉曼位移ν/cm−1 振动模式 参考文献 ω(TiO2) = 0 ω(TiO2) = 2% ω(TiO2) = 4% ω(TiO2) = 6% ω(TiO2) = 8% 651.8 651.8 651.8 651.8 651.8 [SiO3]2−中Si—O0弯曲振动 [12],[13] — — 839.8 841.7 841.7 Ti—O—Ti 伸缩振动 [5] — — 854.3 854.3 855.2 [SiO4]4− 中Si—O−对称伸缩振动 [12],[13] 908.2 908.2 908.2 908.2 908.2 [Si2O7]6− 中Si—O−对称伸缩振动 [12],[13] 973.8 974.8 974.8 973.8 972.8 [SiO3]2−中Si—O−对称伸缩振动 [12],[13] 由图11及表5可知,当Al2O3质量分数为0 ~ 1.5%时,熔渣显示出3个Raman活性模式,分别位于651.8,908.2和974.8 cm−1,同样以复杂的[Si2O7]6−网络结构为主;当Al2O3质量分数为3% ~ 6%时,熔渣显示出2个新的特征峰,分别位于842.7和855 cm−1左右,根据文献分析,842.7 cm−1处峰是Si—O —Al伸缩振动所致,855 cm−1处峰是[SiO4]4−中的Si—O−对称伸缩振动所致. 分析结果可知,随着Al2O3含量不断增加,渣中含有较多的Al3 + ,容易置换出硅酸盐网络结构中的Si4 + ,生成少量含 Si—O—Al键的Ca2Al(AlSiO7)新相,导致网络结构被破坏,转变为结构简单的[SiO4]4−. 总体来看,TiO2 和Al2O3的加入均会促进复杂的硅酸盐网络结构解聚.
表 5 CaO-SiO2-CaF2-Al2O3四元渣系拉曼峰分析及其参考依据Table 5. Peak analysis of Raman in the quaternary CaO-SiO2-CaF2-Al2O3 slag using established references拉曼位移ν/cm−1 振动模式 参考文献 ω(Al2O3) = 0 ω(Al2O3) = 1.5% ω(Al2O3) = 3% ω(Al2O3) = 4.5% ω(Al2O3) = 6% 651.8 651.8 651.8 651.8 651.8 [SiO3]2−中Si—O0弯曲振动 [12],[13] — — 842.7 842.7 842.7 Si—O—Al 伸缩振动 [14],[15],[16] — — 855.2 855.2 855.2 [SiO4]4− 中Si—O−对称伸缩振动 [12],[13] 908.2 908.2 908.2 909.2 910.2 [Si2O7]6− 中Si—O−对称伸缩振动 [12],[13] 974.8 974.8 974.8 974.8 974.8 [SiO3]2−中Si—O−对称伸缩振动 [12],[13] 3. 结论
(1)焊接渣系黏度在降温过程中具有明显的拐点,高于拐点温度,黏度较低且基本保持不变,含TiO2 渣约为0.06 ~ 0.2 Pa·s,含Al2O3渣约为0.1 ~ 0.2 Pa·s. 在拐点附近,黏度随温度降低迅速增大,具有明显的短渣特性.
(2)随着TiO2含量上升,四元渣系的熔化温度和表面张力均随之下降;随着Al2O3含量上升,四元渣系的熔化温度和表面张力均随之先升高再降低. 并且发现了对熔渣熔化特性影响较大的TiO2和Al2O3含量敏感区间,对高强钢配套焊材配方设计具有一定的参考意义.
(3)经XRD和拉曼光谱分析可知,四元焊接熔渣中主要含具有硅酸盐网络结构的Ca4Si2O7F2高熔点化合物. TiO2的加入会夺取网络结构中的Ca2+,生成熔点较低的CaTiO3新相,并使复杂的硅酸盐网络结构转变成了简单四面体结构的[SiO4]4−;Al2O3的加入会置换出硅酸盐网络结构中的Si4+,同样使其解聚成简单的[SiO4]4−四面体结构,同时产生少量Ca2Al(AlSiO7)新相和低熔点的CaF2相.
-
表 1 Sn35Bi0.3Ag合金主要化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Compositions of Sn35Bi0.3Ag alloy soder
Sn Bi Ag 其他 64.0 ~ 65.0 35.0 ~ 35.5 0.3 ~ 0.4 0 ~ 0.2 表 2 材料的力学性能
Table 2 Properties of the materials
材料 熔点Tm/℃ 密度ρ1/(g·cm−3) 电阻率ρ2/(μΩ·cm) 硬度H/HV 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 断后伸长率δ(%) Sn35Bi0.3Ag 177.4 8.11 12 23.0 68.0 24.5 Cu 1 084.9 8.92 1.69 343 ~ 369 220 40 ~ 50 表 3 焊接时间参数的设置
Table 3 Setting of welding time parameters
预热温度T1/℃ 预热时间t1/min 焊接温度T/℃ 焊接时间t/min 120 1 210 1, 2, 3, 5, 7, 9 表 4 焊接温度参数的设置
Table 4 Setting of welding temperature parameters
预热温度T1/℃ 预热时间t1/min 焊接时间t/min 焊接温度T/℃ 120 1 3 210, 230, 250, 270, 290 表 5 不同焊接时间下钎着率与抗剪强度的关系
Table 5 Relationship between brazing rate and shear strength at different welding times
焊接温度t/min 钎着率K(%) 抗剪强度Rτ/MPa 1 97.4 30.0 2 97.5 42.2 3 98.9 50.4 5 94.5 46.0 7 93.7 41.6 9 92.7 26.3 表 6 不同焊接温度下钎着率与抗剪强度的关系
Table 6 Relationship between brazing rate and shear strength at different welding temperatures
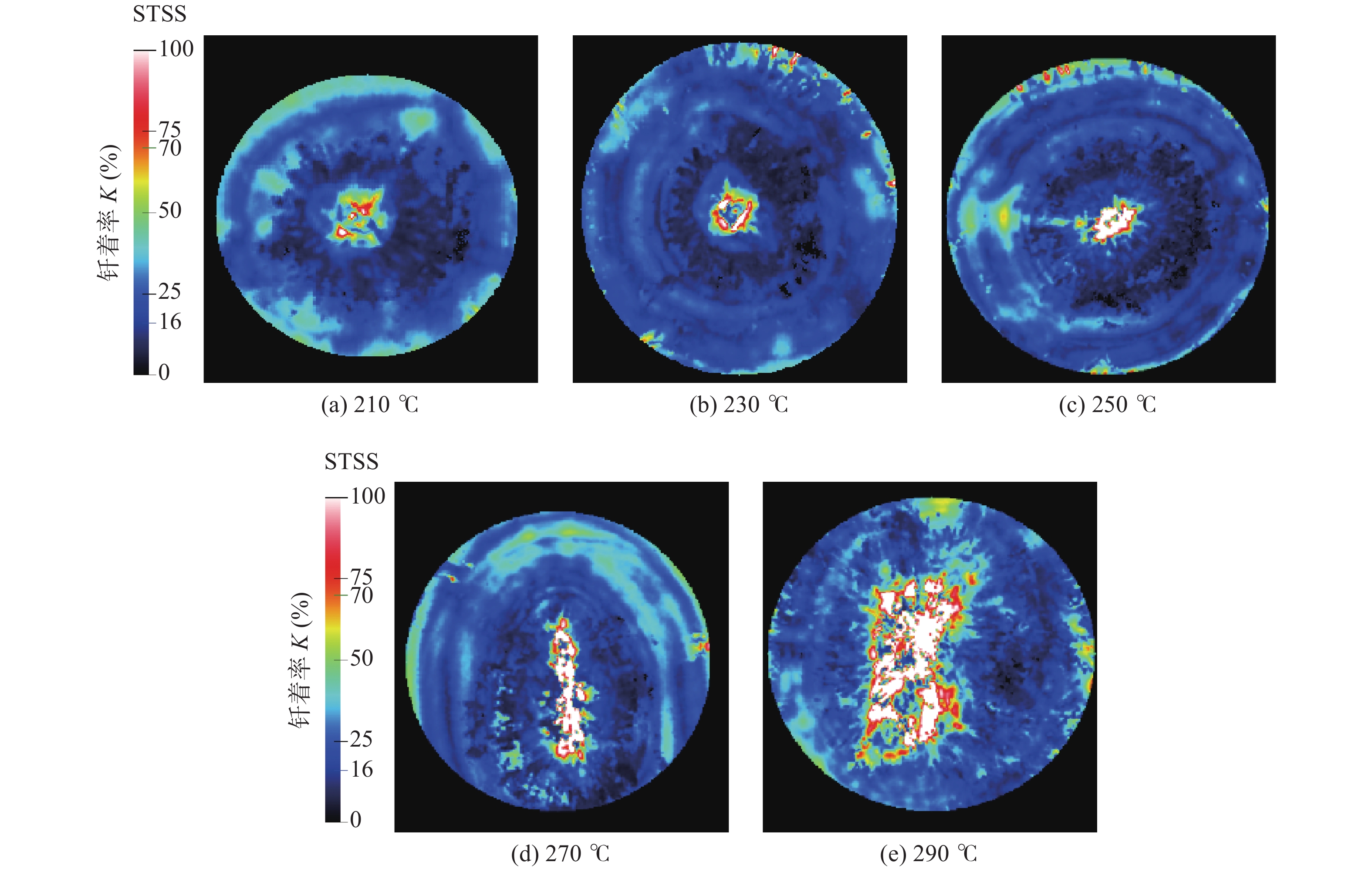
焊接温度T/℃ 钎着率K(%) 抗剪强度Rτ/MPa 210 98.92 50.4 230 99.14 51.8 250 98.49 45.8 270 96.58 35.0 290 90.36 29.7 -
[1] 邹阳, 郭波, 段学俊. 无铅焊点可靠性的研究进展[J]. 焊接, 2021(8): 41 − 48. Zou Yang, Guo Bo, Duan Xuejun. Research progress on reliabity of lead-free soldered joints[J]. Welding & Joining, 2021(8): 41 − 48.
[2] Peng F, Liu W, Ma Y, et al. Microstructure of Sn-20In-2.8Ag solder and mechanical properties of joint with Cu[J]. Soldering & Surface Mount Technology, 2019, 31(1): 1 − 5.
[3] Tong H M, Lai Y S, Wong C P. Advanced flip chip packaging[M]. Springer US, 2013.
[4] Xu K K, Zhang L, Gao L L, et al. Review of microstructure and properties of low temperature lead-free solder in electronic packaging[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2020, 21(1): 689 − 711. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2020.1824255
[5] 陈旭. Sn-Bi基焊料组织与性能研究[D]. 长沙: 东南大学, 2017. Chen Xu. Investigation on the microstructure and properties of Sn-Bi based solder alloys[D]. Changsha: Southeast University, 2017.
[6] 吴翠平. 稀土元素的添加对SnBi系焊料合金微观组织及界面反应的影响[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2011. Wu Cuiping. Influences of rare earth additions on the microstructure and interfacial reaction of SnBi solder alloys[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2011.
[7] Dong W, Shi Y, Xia Z, et al. Effects of trace amounts of rare earth additions on microstructure and properties of Sn-Bi-based solder alloy[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2008, 37(7): 982 − 991. doi: 10.1007/s11664-008-0458-8
[8] Kanlayasiri K, Ariga T. Physical properties of Sn58Bi-xNi lead-free solder and its interfacial reaction with copper substrate[J]. Materials & Design, 2015, 86: 371 − 378.
[9] Zhang L, Sun L, Guo Y H. Microstructures and properties of Sn58Bi, Sn35Bi0.3Ag, Sn35Bi1.0Ag solder and solder joints[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2015, 26(10): 1 − 6.
[10] 陆政, 舒慧, 蒋博. 浅谈回流焊炉温度设置及焊点的切片金相检测[J]. 科技创新导报, 2019, 16(29): 83 − 84. doi: 10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098X.2019.29.083 Lu Zheng, Shu Hui, Jiang Bo. Temperature setting of reflow soldering furnace and metallographic examination of solder joints[J]. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2019, 16(29): 83 − 84. doi: 10.16660/j.cnki.1674-098X.2019.29.083
[11] 曾宝, 周波, 张雪梅, 等. 无铅焊料锡须生长[J]. 印制电路信息, 2018, 26: 305 − 309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0096.2018.z1.042 Zeng Bao, Zhou Bo, Zhang Xuemei, et al. Lead-free solder whisker growth[J]. Printed Circuit Information, 2018, 26: 305 − 309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0096.2018.z1.042
[12] Laurila T, Vuorinen V, Kivilahti J K. Interfacial reactions between lead-free solders and common base materials[J]. Materials Science & Engineering, 2005, 49: 1 − 60.
[13] Cui B, Song L Y, Liu Z M, et al. Study of the morphology and properties of diamond joints brazed with carbide-reinforced Cu-Sn-Ti filler metal[J]. China Welding, 2022, 31(3): 53 − 60.
[14] Wan Y, Li S, Hu X, et al. Shear strength and fracture surface analysis of Sn58Bi/Cu solder joints under a wide range of strain rates[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2018, 86: 27 − 37. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2018.05.007
[15] 薛松柏, 胡永芳, 禹胜林. CBGA焊点热循环条件下的可靠性[J]. 焊接学报, 2005, 26(10): 81 − 83. Xue S B, Hu Y F, Yu S L. Reliability of CBGA soldered joint under thermal cycling[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2005, 26(10): 81 − 83.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 冯伟,于庭祥,徐锴,陈波,张庆素,周宝金. 1 000 MPa级高强钢埋弧焊熔敷金属组织及性能. 焊接. 2023(11): 6-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: