Effect of Ni content on microstructure and shearing property of 304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304 solder joints
-
摘要: 研究了Ni含量对Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi(x = 0, 0.5, 1和2,质量分数)钎料熔点和微观组织的影响,用Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi钎料对304不锈钢进行钎焊连接,分析了接头的界面组织与剪切性能. 结果表明,添加不同含量的Ni后,Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi均为近共晶钎料,其熔点约为245 ℃;Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎料组织由α相基体、Sb2Sn3 + Cu6Sn5 + Sn复合相和Cu6(Sn,Sb)5 相组成. 添加Ni元素后,钎料中块状Cu6(Sn,Sb)5转变为细小、均匀分布的 (Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5. 当Ni含量小于1%时,随Ni含量的增加,钎料中的复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相均增加;当Ni含量为2%时,钎料中的复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相均减少,但(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相中Ni含量增加至与Cu相当;Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎焊界面均形成了一层厚度约1.5 μm的扩散反应层,EDS分析显示,该层为FeSn2化合物. 钎缝中全部为Cu6Sn5型化合物,未见Sn-Sb 型化合物. Ni元素的添加,提高了304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎焊接头的抗剪强度,当Ni含量为0.5%时,接头抗剪强度最大,为67 MPa,与不含Ni钎料相比提高了60%. 所有接头的断裂位置均位于钎缝.
-
关键词:
- 304不锈钢 /
- Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎料 /
- 软钎焊 /
- 剪切性能
Abstract: Effect of Ni content on melting point and microstructure of Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi (x=0, 0.5, 1 and 2, mass fraction) solders were investigated. 304 stainless steel were joined by Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi solders, and interfacial microstructure and shearing property of the solder joints were analyzed. The results showed that all of the Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi with different Ni content are near eutectic solders, with a melting point of 245 ℃. The microstructure of Sn-8Sb-4Cu solder was consisted of α phase, Sb2Sn3 + Cu6Sn5+Sn composite phase and Cu6(Sn,Sb)5 phase. After the addition of Ni, the bulk Cu6(Sn,Sb)5 transformed into fine and uniformly distributed (Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5. When Ni content was less than 1%, the amount of composite phase and (Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5 phase increased with the increasing of Ni content. When Ni content increased to 2%, the amount of composite phase and (Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5 phase decreased with the increasing of Ni content, however, Ni content in the (Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5 phase increases to be comparable to Cu. A diffusion layer with a thickness of about 1.5 μm formed at the Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304 interface, which was identified to be Fe2Sn by EDS. Only Cu6Sn5 type intermetallic compounds formed in the solders of 304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304 joints. The addition of Ni element improved the shear strength of 304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304 brazed joints, and the maximum shear strength of 67 MPa was achieved when the Ni content was 0.5%, which was 60% higher compared to the Ni-free brazing material. The shear fracture locations of all joints were located in the soldering seam.-
Keywords:
- 304 stainless steel /
- Sn-8Sb-4Cu solder /
- soldering /
- shear property
-
0. 序言
不锈钢具有良好的成形性、耐腐蚀性和耐热性等性能,广泛应用于航空航天、轨道交通、核电、工业制冷、医疗、厨具等行业领域,是电子产品连接器的重要接脚材料[1]. 这些产品往往结构复杂,焊接位置较多,钎焊是非常高效的连接方法. 不锈钢硬钎焊常用的钎料有镍基、铜基和银基钎料[2-6],熔点较高,钎焊奥氏体不锈钢易发生敏化现象. 对于工作温度不高、强度要求较小,但要求密封性好,外观美观的场合,不锈钢软钎焊具有突出优势.
当前,不锈钢软钎焊的研究相对较少,这与缺乏满足要求的钎料和钎剂有关,管永星等人[7]研制了新型304不锈钢软钎焊用钎剂,结果发现,其铺展面积比磷酸和氯化锌-氯化铵钎剂提高2倍以上. 周许升等人[8]研究了不锈钢软钎焊的钎料和钎剂,结果发现,Sn-3.5Ag-0.7Cu钎料对不锈钢润湿性好、强度高、焊点明亮美观,然而银为贵金属,价格昂贵,限制了其应用.
Sn-Sb-Cu因其优异的摩擦磨损性能而被广泛应用于轴瓦材料,通过挂锡浇注、电弧喷涂、激光熔覆等方法在钢基体上制备Sn-Sb-Cu涂层,制成双金属轴瓦[9]. Yang等人[10]采用Sn-Sb-Cu-Ni钎料代替Sn-Ag-Cu和Sn-Pb钎料,以降低钎料成本和满足无铅化要求. 此外,Ni元素通过与锡基钎料反应形成针状金属间化合物,是改善锡基钎料力学性能的常用合金元素[11-12].
采用价格相对低廉的Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎料代替Sn-3.5Ag-0.7Cu钎料,并重点研究添加不同Ni含量对Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi钎料组织及Sn-Sb-Cu-xNi/304不锈钢钎焊接头剪切性能的影响,为不锈钢软钎焊钎料设计和工程应用提供理论基础和数据支撑.
1. 试验方法
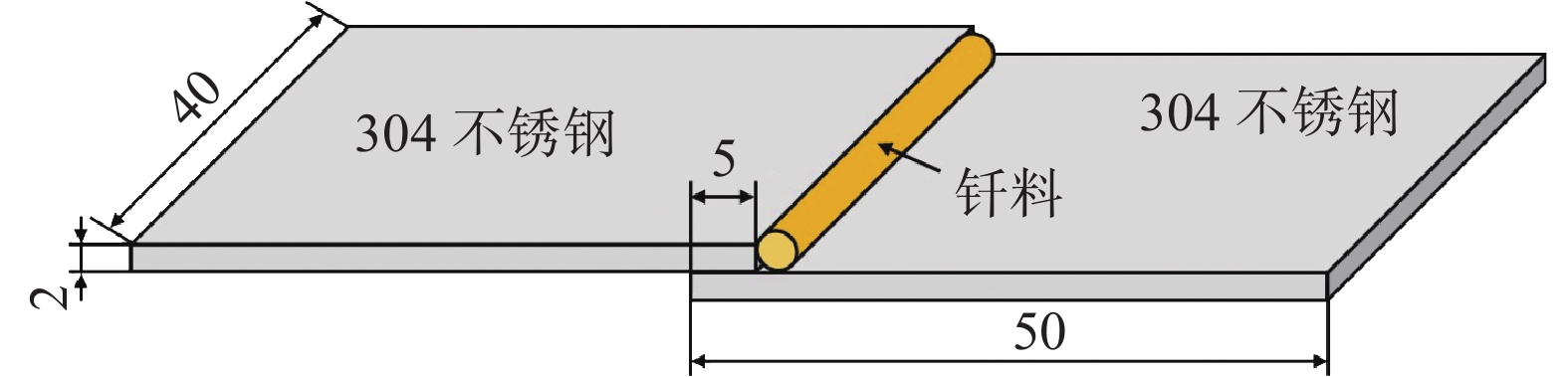
母材采用尺寸为50 mm × 40 mm × 2 mm 的304不锈钢板材,其化学成分如表1所示. 采用纯锡、纯铜、纯锑和纯镍为原料制备Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi(x = 0,0.5,1和2,质量分数). 钎料制备流程如下:首先制备Sn-5Ni(质量分数)中间合金,将称量好的纯锡和纯镍置于石墨坩埚内,并放入真空炉中加热,温度设置为650 ℃,保温3 h;其次,熔炼Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi钎料,按质量百分比称量好纯锡、纯铜、纯锑和Sn-5Ni,熔炼时先将纯锡置于石墨坩埚内,采用感应加热的方式加热到650 ℃,随后加入纯铜、纯锑和Sn-5Ni,并搅拌均匀,熔炼过程往液态钎料中加入ZnCl2和NH4Cl混合物,防止钎料氧化;最后,将熔融合金浇铸成棒状,并挤压成ϕ1.9 mm的丝材,供后续试验使用.
表 1 304不锈钢的化学成分(质量分数, %)Table 1. Chemical compositions of 304 stainless steelCr Ni C Mn P S Si Fe 18 ~ 20 8.0 ~ 10.5 0.08 2.00 0.035 0.015 0.75 余量 采用感应钎焊工艺制备304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎焊接头. 钎焊前,用酒精擦拭不锈钢母材待焊面,搭接长度为5 mm,间隙为0.02 mm,钎料预置方式如图1所示. 采用的钎剂为ZnCl2 + NH4Cl + HCl水溶液.
在高纯氮气保护下采用STA449 F3型同步热分析仪对钎料进行熔点测试,升温速率为10 ℃/min. 借助Zeiss Axio Vert, A1型光学显微镜(optical microscope, OM)、Zeiss EVO 10型扫描电子显微镜 (scanning electron microscope, SEM)及其自带的牛津Ultim Max型能谱仪 (energy dispersive spectrometer, EDS) 对不同成分的钎料及钎焊接头进行形貌观察和成分分析. 采用的腐蚀液为4%硝酸酒精溶液.
为得到不同钎料成分的钎焊接头的抗剪强度,采用线切割的方法将钎焊接头切割成95 mm × 5 mm的非标准剪切试样,采用MTS Exceed E44型电子万能试验机测试接头的剪切力,每种接头测试5个试样,取平均值为最终结果.
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 钎料DSC分析
图2为Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi(x = 0,0.5,1和2)钎料的差示扫描量热法(differential scanning calorimetry, DSC)分析结果. 所有钎料均只有一个吸热峰,峰值温度约为245 ℃. 添加质量分数2%以内的Ni含量对钎料熔点影响较小,制备的Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi均为近共晶钎料.
2.2 钎料微观组织
图3为Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi钎料的微观组织. 图3a显示Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎料的微观组织由3种相组成,基体成分为91.1% Sn,8.4% Sb,0.5% Cu(原子分数),为α相(Sb溶于Sn中形成的固溶体);白色颗粒化合物的成分为77.0% Sn,19.7% Sb,3.3% Cu(原子分数),可能为Sb2Sn3 + Cu6Sn5 + Sn复合相[13];灰色块状化合物的成分为53.9% Sn,44.4% Cu,1.7% Sb(原子分数),即固溶了少量Sb 的Cu6Sn5[14],由于Sn和Sb的原子半径相近,且大于Cu原子半径,因此Sb溶入Cu6Sn5后倾向于替代Sn原子,因此,将上述灰色物质记为Cu6(Sn,Sb)5[12].
添加0.5% Ni后,钎料由基体α相、数量较多的颗粒状黑色相和少量灰色相组成,相的分布更为均匀,如图3b所示. EDS分析显示,钎料中黑色相为固溶了少量Ni的Sb2Sn3 + Cu6Sn5 + Sn复合相;灰色相为固溶了少量Ni的Cu6(Sn,Sb)5,由于Ni和Cu的原子半径相近,Ni倾向于替换Cu,因此,钎料中黑色和灰色相分别为 Sb2Sn3 + (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Sn复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5. 添加1% Ni后,钎料的相组成未发生改变,基体成分为94.9% Sn,4.8% Sb,0.3% Ni(原子分数),α相中Sb含量降低. 钎料中Sb2Sn3 + (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Sn复合相分布更为细小均匀,(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相明显增加. Ni含量增加到2%后,基体成分为95.0% Sn,4.6% Sb,0.4% Cu(原子分数),α相中Sb含量略有降低. 钎料中Sb2Sn3 + (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Sn复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相均显著减少,EDS分析显示,此时(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相的成分为42.2% Sn,3.9% Sb,29.9% Cu,24.0% Ni(原子分数),(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相中Ni含量增加,接近于Cu的含量.
2.3 钎缝宏观形貌
图4为304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎缝宏观形貌.钎料填满整个缝隙,钎缝成形良好,正面、背面均呈内凹圆弧状,这是钎焊接头的典型形貌.
2.4 界面微观组织
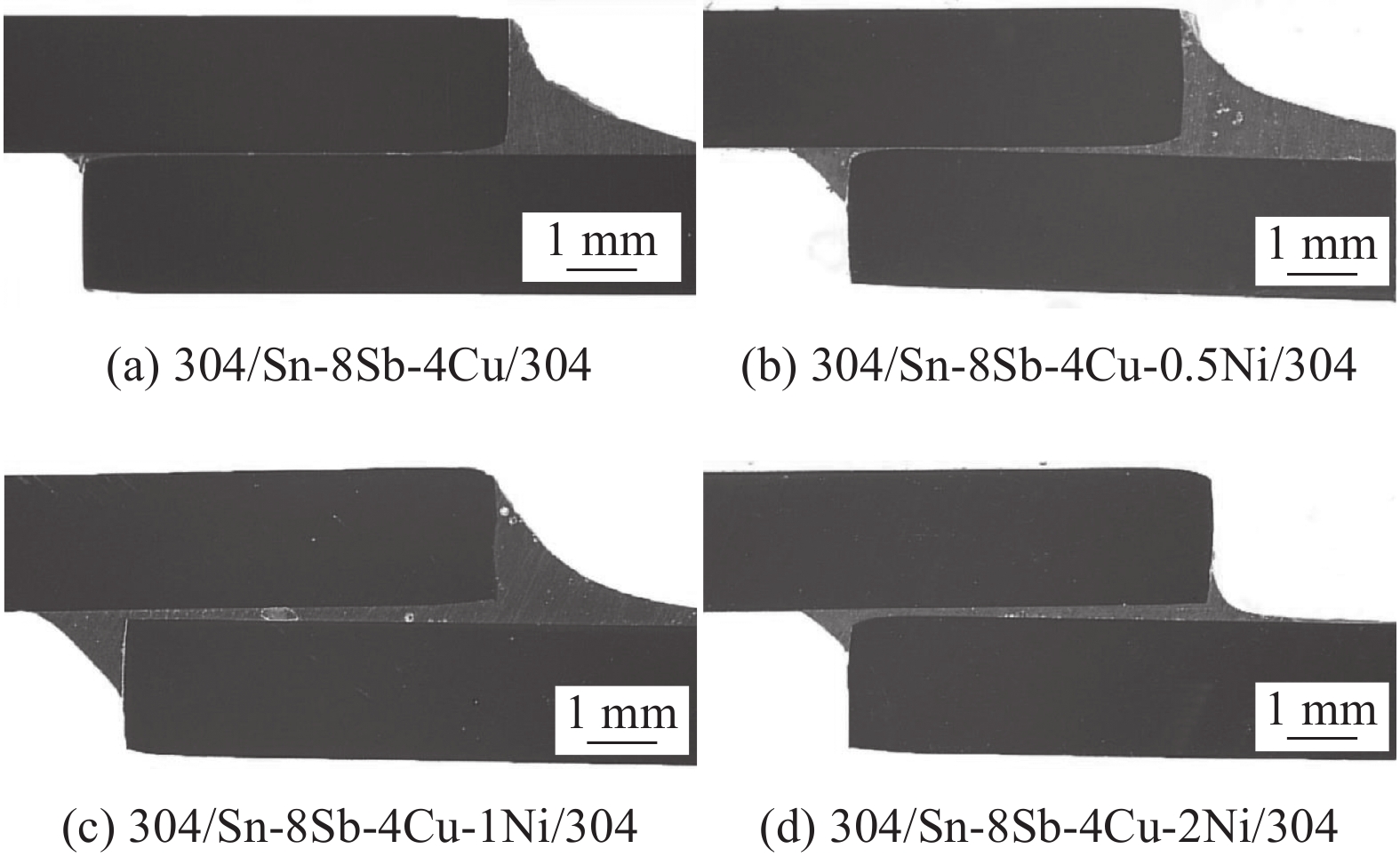
图5为304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎焊接头界面形貌,上侧为钎料,下侧为不锈钢母材. 图6为钎焊接头沿着图5箭头所示的线扫描结果. Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎焊界面形成了一层厚度约1.5 μm的扩散反应层,EDS分析结果如表2所示,界面扩散层的主要成分为Sn和Fe,A,B和D位置的Sn与Fe的原子分数近似于2∶1,该扩散反应层为FeSn2. C点的Sn含量偏高,这可能是由于界面层较薄,测试点向钎料一侧发生了偏移. 界面组织分析表明,钎料中Ni元素的添加并未显著影响Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304界面反应.
此外,钎料基体内部形成了大量金属间化合物(intermetallic compounds,IMCs),线扫描分析结果显示,未加Ni时,304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎缝IMCs为Cu6Sn5;当Ni含量为0.5%时,304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎缝IMCs为(Cu,Ni)6Sn5,且Ni含量很少.当Ni含量为1%和2%时,304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎缝中IMCs仍为(Cu,Ni)6Sn5,但其中Ni含量很高,与Cu接近. 钎焊后,钎缝中全部为Cu6Sn5型IMCs,而无Sn-Sb 型IMCs形成.
表 2 Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304界面化学成分(原子分数,%)Table 2. Chemical compositions of the Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304 interface位置 Sn Sb Cu Fe Cr Ni 扩散层化合物 A 58.6 1.5 1.6 31.8 5.4 1.1 FeSn2 B 56.4 2.8 2.2 28.7 7.9 2.0 FeSn2 C 75.5 2.5 1.2 15.0 4.2 1.6 FeSn2 + Sn D 54.1 3.0 3.5 28.9 8.3 2.2 FeSn2 2.5 钎缝抗剪强度
图7为不同成分钎料钎焊304不锈钢的钎焊接头抗剪强度. Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎焊后钎缝平均抗剪强度为42 MPa,添加Ni元素后,抗剪强度显著提高. 当Ni含量为0.5%时,钎焊接头抗剪强度最大,达到67 MPa,较不添加Ni时提高了60%. 从钎缝组织可以看出,Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎料中Cu6(Sn,Sb)5化合物呈大块状且分步不均匀,对基体产生割裂作用,抗剪强度较低. 添加0.5% Ni后,钎料中析出了更多细小、均匀的(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5化合物,因而抗剪强度显著提高;而当Ni含量大于1%时,析出了Ni含量更高的(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5,但(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相更少,抗剪强度有所降低. 图8为钎焊接头的断口形貌,两侧均有钎料残留,表明所有钎焊接头均断裂于钎缝.
3. 结论
(1) Sn-8Sb-4Cu钎料组织由α相、Sb2Sn3 + Cu6Sn5 + Sn复合相和Cu6Sn5相组成,添加不同含量Ni后,α相中Sb含量下降,且固溶了少量Ni或Cu;钎料中析出Sb2Sn3 + (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Sn复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相. 当Ni含量小于1%时,钎料中Sb2Sn3 + (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Sn复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相均增加,且分布更为均匀;当Ni含量为2%时,钎料中Sb2Sn3 + (Cu,Ni)6Sn5 + Sn复合相和(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相均减少,但(Cu,Ni)6(Sn,Sb)5相中的Ni含量明显增加,与Cu含量接近.
(2) Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi与304不锈钢钎焊的界面均形成了一层厚度约1.5 μm的扩散反应层,EDS分析显示,该反应层为FeSn2化合物. 钎缝中全部为Cu6Sn5型IMCs,而无Sn-Sb 型IMCs形成.
(3) Ni的添加不会改变Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi钎料的熔点,但提高了304/Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304钎焊接头的抗剪强度,当Ni含量为0.5%时,接头的抗剪强度达到最大值67 MPa,与不加Ni相比提高了60%. 所有接头均断裂于钎缝.
-
表 1 304不锈钢的化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 304 stainless steel
Cr Ni C Mn P S Si Fe 18 ~ 20 8.0 ~ 10.5 0.08 2.00 0.035 0.015 0.75 余量 表 2 Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304界面化学成分(原子分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical compositions of the Sn-8Sb-4Cu-xNi/304 interface
位置 Sn Sb Cu Fe Cr Ni 扩散层化合物 A 58.6 1.5 1.6 31.8 5.4 1.1 FeSn2 B 56.4 2.8 2.2 28.7 7.9 2.0 FeSn2 C 75.5 2.5 1.2 15.0 4.2 1.6 FeSn2 + Sn D 54.1 3.0 3.5 28.9 8.3 2.2 FeSn2 -
[1] 颜怡文, 刘为开. 封装中无铅焊锡与不锈钢及铁镍的界面反应[J]. 电子与封装, 2010, 10(6): 1 − 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1681-1070.2010.06.001 Yan Yiwen, Liu Weikai. Interfacial reactions in lead-free solders with Au/Ni/SUS 304 and alloy 42 in microelectronic packaging[J]. Electronics & Packaging, 2010, 10(6): 1 − 5. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1681-1070.2010.06.001
[2] 裴冲, 吴欣, 程耀永, 等. 采用BNi82CrSiB钎料钎焊1Cr12Ni3MoVN不锈钢的接头组织及性能[J]. 电焊机, 2020, 50(9): 268 − 272. doi: 10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2020.09.31 Pei Chong, Wu Xin, Cheng Yaoyong, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of brazing 1Cr12Ni3MoVN stainless steel joints with BNi82CrSiB filler metal[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2020, 50(9): 268 − 272. doi: 10.7512/j.issn.1001-2303.2020.09.31
[3] 范东宇, 汪一卉, 黄继华, 等. Cf/SiC复合材料与304不锈钢钎焊接头组织与性能 [J]. 焊接学报, 2014, 35(12): 31-34. Fan Dongyu, Wang Yihui, Huang Jihua, et al. Brazing Cf/SiC composite materials with 304 stainless steel using Ti-Zr-Be filler metal[J], Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2014, 35(12): 31-34.
[4] 张青科, 裴夤崟, 龙伟民. 奥氏体不锈钢钎焊界面裂纹形成机制研究[J]. 金属学报, 2013, 49(10): 1177 − 1184. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2013.00219 Zhang Qingke, Pei Yinyin, Long Weimin. Investigations on formation mechanisms of brazing cracks at the austenitic stainless steel/filler metal brazing joint interfaces[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2013, 49(10): 1177 − 1184. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2013.00219
[5] 王星星, 李帅, 彭进, 等. 基于镀锡银钎料钎焊304不锈钢接头的腐蚀行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(4): 63 − 66. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390097 Wang Xingxing, Li Shuai, Peng Jin, et al. Corrosion behaviors of 304 stainless steel joints brazed with Sn-electroplated Ag brazing alloys[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(4): 63 − 66. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2018390097
[6] Liu Xu, Huang Xiaomeng, Ma Huibin, et al. Microstructure and properties of the joints of ZrO2 ceramic/stainless steel brazed in vacuum with AgCuTi active filler metal[J]. China Welding, 2018, 27(2): 52 − 56.
[7] 管永星, 薛松柏, 韩若男, 等. 新型304不锈钢软钎焊用钎剂的研制[J]. 焊接学报, 2013, 34(2): 101 − 104. Guan Yongxing, Xue Songbai, Han Ruonan, et al. Development of flux for soldering of 304 stainless steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2013, 34(2): 101 − 104.
[8] 周许升, 龙伟民, 裴夤崟, 等. 不锈钢软钎焊用钎料和钎剂的研究[J]. 焊接, 2014(1): 26 − 29. Zhou Xusheng, Long Weimin, Pei Yinyin, et al. Study on solder and flux for soldering stainless steel[J]. Welding & Joining, 2014(1): 26 − 29.
[9] 郝云波, 赵凯, 杨萍, 等. 激光熔覆锡基巴氏合金微观组织和力学性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2018, 28(10): 2016 − 2023. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.10.08 Hao Yunbo, Zhao Kai, Yang Ping, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of tin-based babbitt alloy made by laser cladding deposition[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2018, 28(10): 2016 − 2023. doi: 10.19476/j.ysxb.1004.0609.2018.10.08
[10] Yang L, Jie X H, Guo L. Low-temperature property of new type lead-free solder Sn-X-Cu-Ni[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 154-155: 371 − 375.
[11] Ventura T, Terzi S, Rappaz M, et al. Effects of Ni additions, trace elements and solidification kinetics on microstructure formation in Sn-0.7 Cu solder[J]. Acta Materialia, 2011, 59(10): 4197 − 4206. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2011.03.044
[12] Tao Q B, Benabou L, Vivet L, et al. Effect of Ni and Sb additions and testing conditions on the mechanical properties and microstructures of lead-free solder joints[J]. Materials & Science Engineering: A, 2016, 669(4): 403 − 416.
[13] Lee C, Lin Y W, Yen Y W. The 260 ℃ phase equilibria of the Sn-Sb-Cu ternary system and interfacial reactions at the Sn-Sb/Cu joints[J]. Intermetallics, 2007, 15(8): 1027 − 1037. doi: 10.1016/j.intermet.2006.12.002
[14] 郭亚希, 谢敬佩, 王文焱, 等. 铸造方法对巴氏合金组织及性能的影响[J]. 河南科技大学学报, 2009, 30(4): 8 − 11,116. Guo Yaxi, Xie Jingpei, Wang Wenyan, et al. Effect of casting method on microstructure and property of babbitt alloy[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science & Technology (Nature Science), 2009, 30(4): 8 − 11,116.
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 刘勇,裴夤崟,梁赛,姜春鹏,李刚卿,韩晓辉. 高速列车铜合金管路密封连接绿色感应钎焊技术研究. 电焊机. 2024(09): 63-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: