Low-cycle fatigue properties of welded microzones based on the local strain approach
-
摘要: 针对忽略焊接力学不均匀性的名义应变法评价焊接接头低周疲劳性能不准确的问题,提出一种考虑焊接接头力学不均匀性、基于弹塑性有限元计算的局部应变法,对焊接接头的低周疲劳性能进行准确评价. 通过耐热钢电弧焊接头光滑试样和焊缝光滑试样的低周疲劳试验,以及焊接接头光滑试样在加载过程中的弹塑性有限元计算,采用名义应变法和局部应变法分别对耐热钢电弧焊接头光滑试样进行低周疲劳性能评价. 结果表明,耐热钢电弧焊接头在低周疲劳载荷下断裂于焊缝区域. 采用名义应变法评价该焊接接头时,结果偏保守. 由于局部应变法考虑了焊接接头的力学不均匀性,基于断裂微区的局部应变进行疲劳性能评价,发现采用局部应变法得到的焊接接头应变—寿命曲线与断裂微区焊缝的应变—寿命曲线一致.Abstract: Due to the inaccuracy of the nominal strain approach in evaluating the low-cycle fatigue (LCF) properties of welded joints, a local strain approach considering mechanical heterogeneity of welded joints and based on elastic-plastic finite element analysis was proposed to evaluate the LCF properties of welded joints accurately. The LCF tests of smooth specimens of the welded joint of heat-resistant steel and the weld metal were conducted. The elastic-plastic finite element analysis of the smooth specimens of the welded joints during loading was calculated. The LCF properties of the welded joint were evaluated using the nominal and local strain approach. The results showed that the smooth specimens of the welded joint fractured at the softened weld zone. The LCF properties evaluated by the nominal strain approach were conservative. Since the mechanical heterogeneity of the welded joint was considered by the local strain approach, the LCF properties were evaluated based on the local strain in the fractured microzone. Therefore, the strain−life curve of the welded joint obtained by the local strain approach was close to the strain−life curve of the material of the fractured microzone.
-
0. 序言
焊接接头的余高和表面凹陷等几何变化,焊缝到母材的材料梯度变化,以及宏微观焊接缺陷的存在等,导致焊接结构易从焊接接头处发生疲劳失效,因此焊接接头及其微区的疲劳研究对航空航天、轨道交通、海洋工程装备和化工机械等行业中焊接结构的长期安全运行起到了重要作用.
目前常用的焊接接头疲劳性能评价方法有名义应力法、热点应力法、结构应力法和临界距离法等. 其中名义应力法为全局法,操作简便,但不适用于标准中未涉及的焊接接头形式、载荷或新焊接方法. 热点应力法、结构应力法和临界距离法都属于局部法. 局部法认为疲劳破坏从应力/应变集中处开始,将集中区域的局部参量作为疲劳损伤的控制参量,与疲劳寿命通过S−N曲线建立联系. Zamzami等人[1]使用多种疲劳评价方法分析了铝合金焊接接头,认为有效缺口应力法和临界距离法的评价结果比名义应力法和热点应力法更准确,其中临界距离法的计算简便,更有利于工程应用. 杨鑫华等人[2]在钛合金焊接接头疲劳性能评价中分别采用了名义应力法和结构应力法,并认为采用结构应力法得到的数据更准确. 由于疲劳破坏的局部性,局部法比全局法的适用范围更广泛,但是需要根据经验公式、测量或计算得到局部应力和局部应变. 对于低周疲劳性能,由于峰值载荷较大,局部材料出现塑性损伤. 载荷较大时,应力变化幅度较小,采用应变能更好地反应材料的疲劳行为,因此低周疲劳试验通常采用应变控制和评价. Pei等人[3]提出了一种结构应变法,该结构应变法从结构应力法衍生而来,对有限元网格尺寸不敏感,既可用于低周疲劳性能评价,也可用于高周疲劳性能评价.
在低周疲劳过程中,通常会先产生应变集中,应变集中处易萌生疲劳裂纹[4]. 局部应变可采用应变计或数字图像相关法进行测量,也可通过Neuber法、能量法和有限元法等方法进行计算. 在低周疲劳过程中产生了塑性应变,需采用弹塑性有限元法进行计算,线弹性有限元法不再适用. Hanji等人[5]采用弹塑性有限元法计算了角焊缝焊根处的局部应力应变,建立了有效缺口应变与疲劳寿命的关系,采用有效缺口应变可忽略焊趾尺寸对疲劳行为的影响.
为了研究焊接力学不均匀性对疲劳曲线的影响,通过考虑焊接微区力学不均匀性的弹塑性有限元计算,采用一种新型局部应变法对耐热钢电弧焊接头光滑试样进行低周疲劳性能评价. 研究结果表明,采用不考虑焊接力学不均匀性的名义应变法得到的应变—寿命曲线偏保守,采用考虑焊接力学不均匀性的局部应变法更适合焊接接头及其微区的低周疲劳性能评价.
1. 试验方法
1.1 试验材料
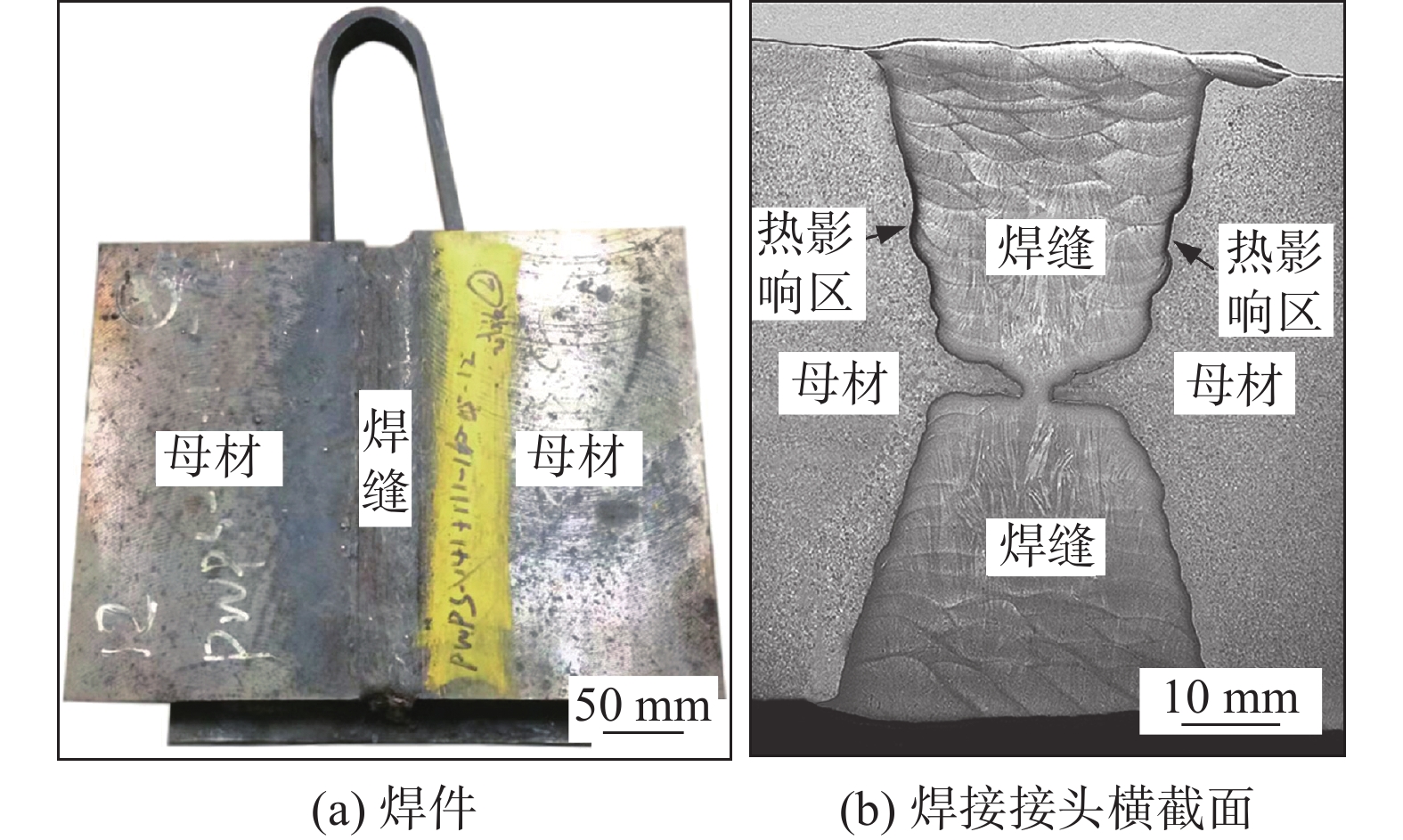
选用的母材为9% ~ 12%Cr马氏体耐热钢Co3W2,焊接材料为ENiCrFe-1镍基合金焊条. 研究对象为图1所示的耐热钢电弧焊接头,尺寸为400 mm × 280 mm × 70 mm. 母材和焊缝熔敷金属的化学成分如表1所示.母材的室温屈服强度为620 MPa,抗拉强度为890 MPa,断后伸长率为15.0%. 焊接接头的室温屈服强度为410 MPa,抗拉强度为680 MPa,断后伸长率为38.0%.
表 1 材料的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of materials材料 C Mn Cr Co W V Mo Ni Nb N Fe S P Si 母材 0.11 0.08 9.82 3.06 1.72 0.20 0.71 0.36 0.08 0.03 余量 — — — 熔敷金属 0.05 3.00 16.50 — — — 0.30 余量 2.60 — 6.50 0.01 0.01 0.40 1.2 焊接试验
该接头采用钨极氩弧焊打底,焊条电弧焊填充和盖面. 具体焊接工艺参数如表2所示. 耐热钢电弧焊热影响区可大致分为粗晶热影响区、细晶热影响区、临界热影响区和过回火热影响区,如图2所示.
表 2 焊接工艺参数Table 2. Welding process parameters焊接方法 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) 钨极氩弧焊 115 11 ~ 13 80 ~ 110 焊条电弧焊 150 28 ~ 31 250 ~ 280 1.3 显微硬度试验
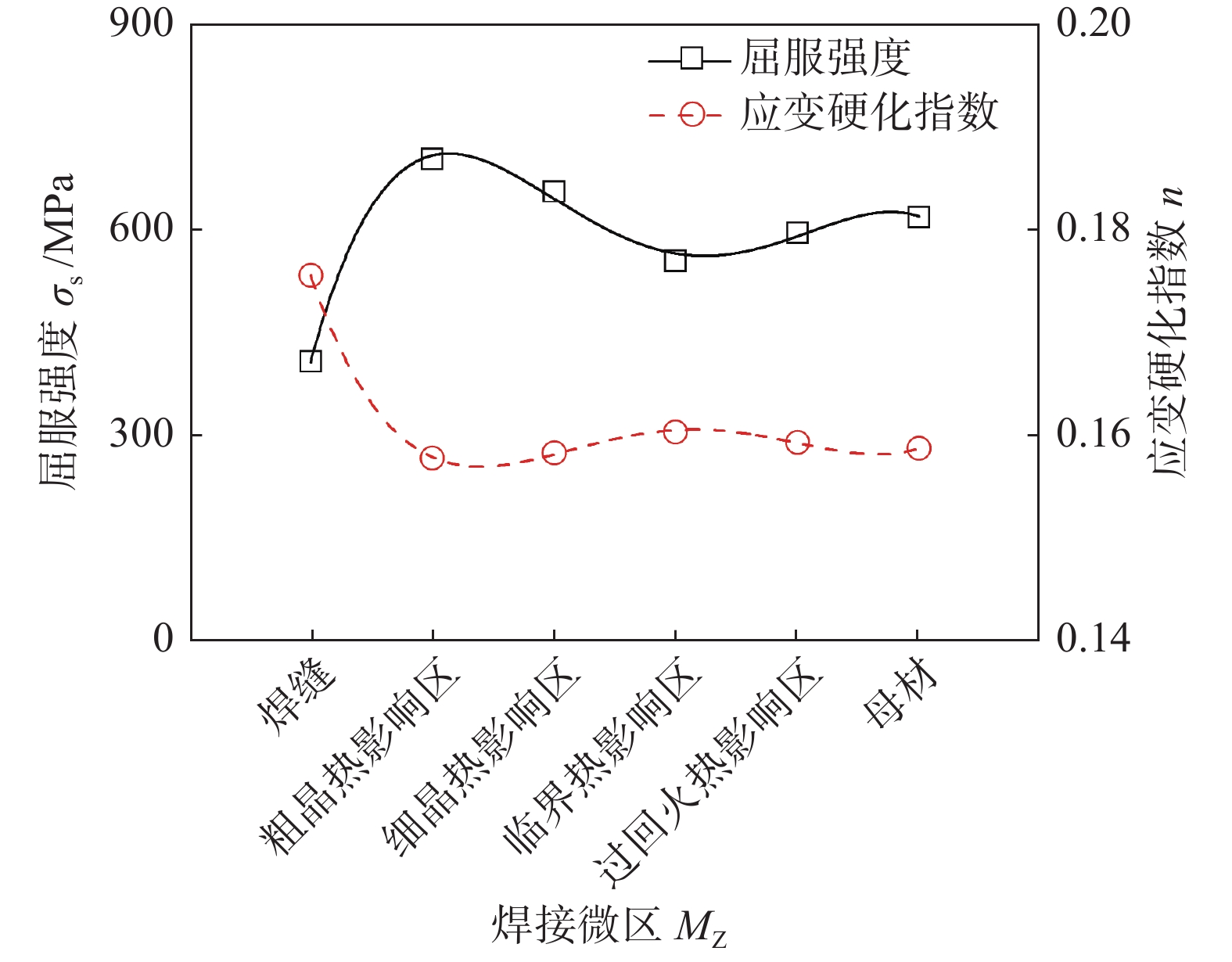
采用HXD-1000TMC/LCD显微维氏硬度计对焊接接头进行显微硬度试验,加载载荷为2.94 N,保载时间为10 s,其硬度分布如图3所示. 由于镍基合金的碳含量很低,镍基合金焊条的成分设计导致其硬度和强度远低于母材,焊缝的显微维氏硬度值在212 ~ 247 HV之间,母材的显微维氏硬度值在312 ~ 316 HV之间,说明焊缝的显微硬度远低于母材. 粗晶热影响区的显微硬度值在346 ~ 354 HV之间,细晶热影响区的显微硬度值在319 ~ 343 HV之间,粗晶和细晶热影响区的显微硬度均高于母材. 在热影响区中,临界热影响区的显微硬度最低.
1.4 低周疲劳试验
低周疲劳试验按照标准GB/T 26077—2010 《金属材料 疲劳试验 轴向应变控制方法》执行,使用PLS-100型电液压伺服试验机进行室温下拉—压疲劳试验,采用引伸计测量的名义应变进行控制,加载波形为三角波,应变比为−1,应变速率为0.004 s−1,应变幅为0.2% ~ 1.0%. 引伸计的标距为12.5 mm. 耐热钢电弧焊接头和焊缝的低周疲劳棒状光滑试样在填充焊缝处取样,如图4所示. 焊接接头疲劳试样的标距段包含了焊缝、热影响区和母材,且热影响区位于标距段的中间位置,如图4b所示. 焊缝试样的标距段只有焊缝.
1.5 局部应变法
局部应变法指采用疲劳损伤区内的局部应变来评价出现应变集中试样低周疲劳性能的一种方法,该方法通过弹塑性有限元分析计算低周疲劳试验过程中试样标距段内应变分布,适用于由于材料不均匀、几何不连续等产生应变集中的情况[6-7]. 定义局部应变为经过表面最大应变点的塑性区内危险截面与试样表面交线上所有节点的平均应变. 图5为局部应变法的实现过程. 首先,根据硬度试验和母材、焊缝的力学性能推算焊接微区力学性能. 进行不同名义应变控制下的低周疲劳试验,得到名义应变下的疲劳曲线. 然后对试样标距段建立有限元模型,将模型划分不同微区,赋予各自弹塑性力学性能. 对有限元模型施加与低周疲劳试验中名义应变对应的位移,计算不同名义应变下标距段内的应变分布. 根据应变分布计算不同名义应变下的“局部应变”,用弹塑性有限元计算得到的“局部应变”评估具有焊接力学不均匀性试样的低周疲劳性能.
2. 弹塑性有限元计算
2.1 有限元模型
对图4b所示的焊接接头试样标距段进行有限元建模,耐热钢电弧焊接头可划分为6个微区,按各微区尺寸和形貌对有限元模型进行划分,如图6所示. 对模型进行网格敏感性分析,当网格尺寸小于0.2 mm时,最大应变值的变化低于0.5%,因此选择0.2 mm的网格尺寸进行计算,此时网格数量为92 160个,如图6b和图6c所示. 边界条件为固定模型的一端,在另一端施加与名义应变对应的位移,实现加载时的应变控制,采用商业有限元软件ABAQUS进行计算.
2.2 材料参数
该局部应变法中的局部应变由弹塑性有限元计算得到,弹塑性有限元计算考虑了材料屈服后应力应变关系进入非线性状态的情况. 塑性计算中需要确定屈服准则、强化模型和应力应变关系. 屈服准则采用各向同性的von Mises屈服准则,该屈服准则综合考虑了第1、第2和第3主应力,常用于各向同性材料的疲劳破坏等评价. 强化模型采用双线性随动强化模型,随动强化模型考虑了包辛格效应,适用于循环加载的情况. 由于焊接微区较多,因此采用较简便的双线性随动强化模型. 对于大多数金属材料的应力应变关系,可分为弹性段和塑性段. 根据母材和焊缝的弹塑性材料参数,以及不同焊接微区的显微硬度推算热影响区的弹塑性材料参数,得到有限元模型中各焊接微区的材料参数.
弹性模量和泊松比受化学成分的影响较大,受热处理和微观组织影响较小,因此认为热影响区的弹性模量、泊松比与母材相同,焊缝的弹性模量和泊松比根据试验获得. 母材和热影响区的弹性模量为188 GPa,焊缝的弹性模量为157 GPa,泊松比均为0.3. 从文献[8]和相关标准可知,很多金属材料的强度和硬度间呈强相关关系. 根据母材和焊缝的屈服强度,以及焊接微区显微硬度分布,可以计算出各热影响区的屈服强度. 对于满足幂指数硬化规律的金属材料,Cahoon等人[9]提出了屈服强度、显微硬度和应变硬化指数的关系式,根据该公式可推导出应变硬化指数,即
$$ n=\dfrac{\lg \left(\dfrac{29.4 \sigma_{ {\rm{s}}}}{H}\right)}{\lg \left(\dfrac{12\;500 \sigma_{ {\rm{s}}}}{E}\right)} $$ (1) 式中:n为应变硬化指数;σs为屈服强度,MPa;H为显微维氏硬度,HV;E为弹性模量,GPa.
对各微区赋予各自的弹性和塑性力学性能,考虑焊接微区的力学不均匀性. 根据显微硬度与屈服强度和应度硬化指数的关系,得到耐热钢电弧焊接微区力学性能,如图7所示.
3. 试验和计算结果
3.1 低周疲劳试验结果
8个耐热钢电弧焊接头试样在低周疲劳载荷下全部断裂在焊缝区域,如图8所示,说明焊缝为该接头在低周疲劳载荷下的薄弱区域. 对于加载至最终断裂的试样,焊缝区域的试样表面存在明显塑性变形的痕迹,如图8b所示.
3.2 弹塑性有限元计算结果
不考虑焊接力学不均匀性时,即有限元模型中全部赋予母材的材料属性进行简化计算,计算结果如图9所示. 不考虑焊接力学不均匀性时,试样标距段内的应力和应变分布均匀. 加载的名义应变为0.003时,有限元计算得到的试样标距段内的应力为563 MPa,应变为0.003.
图10为考虑焊接力学不均匀性的有限元计算结果,即将焊接接头划分不同焊接微区,且对各微区赋予各自不同的材料属性. 图10中加载的名义应变也为0.003. 对比图3中显微硬度分布可知,轴向应力在显微硬度最高的粗晶热影响区内最高,轴向应变在显微硬度最低的焊缝内最高. 图10b中焊缝左端面的应变最大,经过试样表面最大应变点A的轴向路径AB上提取应变分布曲线,如图11所示.
图11为从焊缝到母材应变分布. 从图11可知,耐热钢电弧焊接头中焊缝处应变最高,母材处应变最低. 焊缝处应变远高于名义应变,母材和热影响区的应变远低于名义应变. 由于焊缝和粗晶热影响区的显微硬度相差较大,因此在焊缝和粗晶热影响区交界处应变的变化十分剧烈.
3.3 采用局部应变法修正焊接接头应变—寿命曲线
图12为采用局部应变法计算得到的耐热钢电弧焊接头在加载名义应变为0.003时的屈服情况,整个焊缝区域均发生了塑性变形,热影响区和母材仍为弹性变形. 根据弹塑性有限元计算得到的应变分布,首先确定试样表面最大应变点A,然后确定经过点A、垂直于载荷方向并在塑性区内的试样表面路径ACD,计算该路径上的应变平均值,即为用于该焊接接头低周疲劳性能评价的局部应变. 对于耐热钢电弧焊接头来说,表面应变最大值在左端面,且整个左端面均已屈服,因此该接头的局部应变即为左端面与圆柱面交线上节点的平均应变.
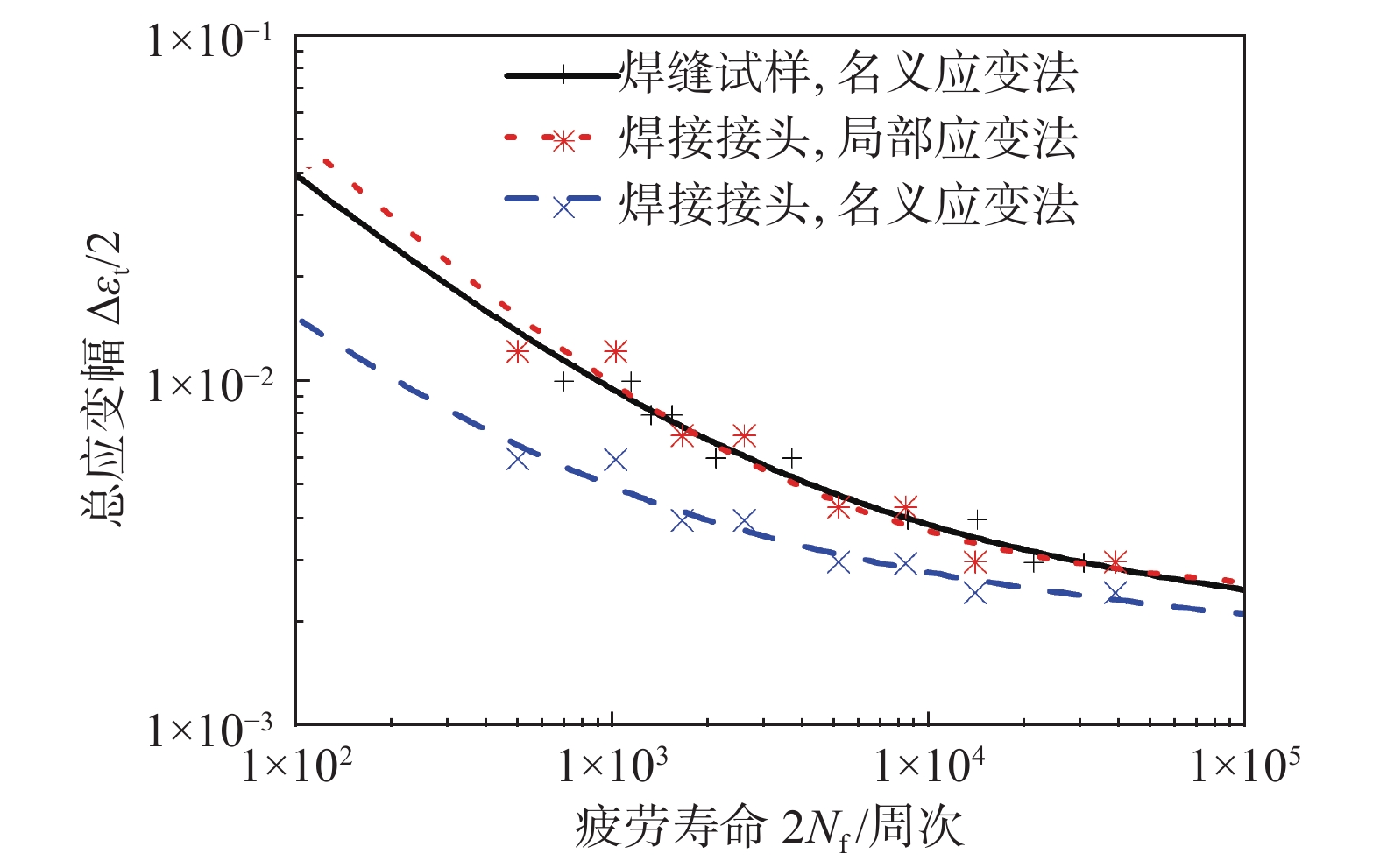
图13为使用局部应变法和名义应变法的耐热钢电弧焊接头试样与焊缝试样的低周疲劳性能对比. 焊缝试样标距段内全部为焊缝材料,因此焊缝试样低周疲劳试验测量的是焊缝材料的低周疲劳性能. 由于名义应变法未考虑焊接力学不均匀性引起的应变集中现象,导致采用名义应变法的耐热钢电弧焊接头试样的应变—寿命曲线与焊缝材料的应变—寿命曲线相比偏保守.
局部应变法考虑了焊接力学不均匀性引起的应变集中现象,用耐热钢电弧焊接头试样塑性区内的局部应变进行低周疲劳性能评价,此时的耐热钢电弧焊接头试样和焊缝材料的应变—寿命曲线十分接近. 这说明采用局部应变法可准确地评价焊接接头断裂微区的低周疲劳性能,而采用名义应变法评价焊接接头低周疲劳性能的误差较大. 此外,焊缝为耐热钢电弧焊接头的软化区,也是低周疲劳过程中疲劳损伤最严重的区域和最终断裂区域. 由于疲劳的局部性,采用焊接接头的光滑试样测试得到的应变—寿命曲线实际上是断裂微区材料的应变—寿命曲线. 经过局部应变法修正后,采用焊接接头的光滑试样即可得到焊接接头中断裂微区材料的应变—寿命曲线.
4. 结论
(1) 耐热钢电弧焊接头光滑试样在低周疲劳过程中断裂在软化区焊缝. 这是由于焊接力学不均匀性导致软化区出现应变集中和塑性变形,进一步导致了疲劳破坏.
(2) 对于焊接接头,采用名义应变法忽略了低周疲劳时焊接力学不均匀性引起的应变不均匀分布,导致评价结果偏保守.
(3) 提出了一种考虑焊接力学不均匀性、基于弹塑性有限元计算的局部应变法,根据焊接微区的显微硬度推测微区力学性能,采用塑性区内的局部应变进行疲劳性能评价,局部应变法得到的焊接接头应变—寿命曲线与断裂微区材料的应变—寿命曲线接近.
-
表 1 材料的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of materials
材料 C Mn Cr Co W V Mo Ni Nb N Fe S P Si 母材 0.11 0.08 9.82 3.06 1.72 0.20 0.71 0.36 0.08 0.03 余量 — — — 熔敷金属 0.05 3.00 16.50 — — — 0.30 余量 2.60 — 6.50 0.01 0.01 0.40 表 2 焊接工艺参数
Table 2 Welding process parameters
焊接方法 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 焊接速度v/(mm·min−1) 钨极氩弧焊 115 11 ~ 13 80 ~ 110 焊条电弧焊 150 28 ~ 31 250 ~ 280 -
[1] Zamzami A I, Susmel L. On the accuracy of nominal, structural, and local stress based approaches in designing aluminium welded joints against fatigue[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 101: 137 − 158. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2016.11.002
[2] 杨鑫华, 孙屹博, 邹丽. 网格不敏感结构应力的焊接疲劳数据分布[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(2): 11 − 14. Yang Xinhua. , Sun Yibo, Zou Li. Data distribution in welding fatigue analysis based on mesh-insensitive structural stress[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(2): 11 − 14.
[3] Pei X, Dong P. An analytically formulated structural strain method for fatigue evaluation of welded components incorporating nonlinear hardening effects[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2019, 42(1): 239 − 255.
[4] Littlewood P, Wilkinson A. Local deformation patterns in Ti-6Al-4V under tensile, fatigue and dwell fatigue loading[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2012, 43: 111 − 119. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.03.001
[5] Hanji T, Park J, Tateishi K. Low cycle fatigue assessments of corner welded joints based on local strain approach[J]. International Journal of Steel Structures, 2014, 14(3): 579 − 587. doi: 10.1007/s13296-014-3015-8
[6] Xu Z, Zhang J, Wang W, et al. Low-cycle fatigue properties of Ti6Al4V laser-welded joints based on a local strain approach[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2021, 30(4): 2772 − 2780. doi: 10.1007/s11665-021-05540-7
[7] 张建勋, 徐甄真, 白嘉瑜, 等. 一种焊接接头的低周疲劳性能评价方法: 中国, 202010042994.9[P]. 2021-01-19. Zhang Jianxun, Xu Zhenzhen, Bai Jiayu, et al. An evaluation method for the low cycle fatigue properties of welded joints: China, 202010042994.9[P]. 2021-01-19.
[8] Zhang P, Li S, Zhang Z. General relationship between strength and hardness[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2011, 529: 62 − 73. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2011.08.061
[9] Cahoon J, Broughton W, Kutzak A. The determination of yield strength from hardness measurements[J]. Metallurgical Transactions, 1971, 2(7): 1979 − 1983. doi: 10.1007/BF02913433
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 张旭,王汉生,李婷. 不同接头形式疲劳寿命数值模拟与试验验证. 焊接技术. 2024(07): 22-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载: