Effect of welding process on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo deposited metals
-
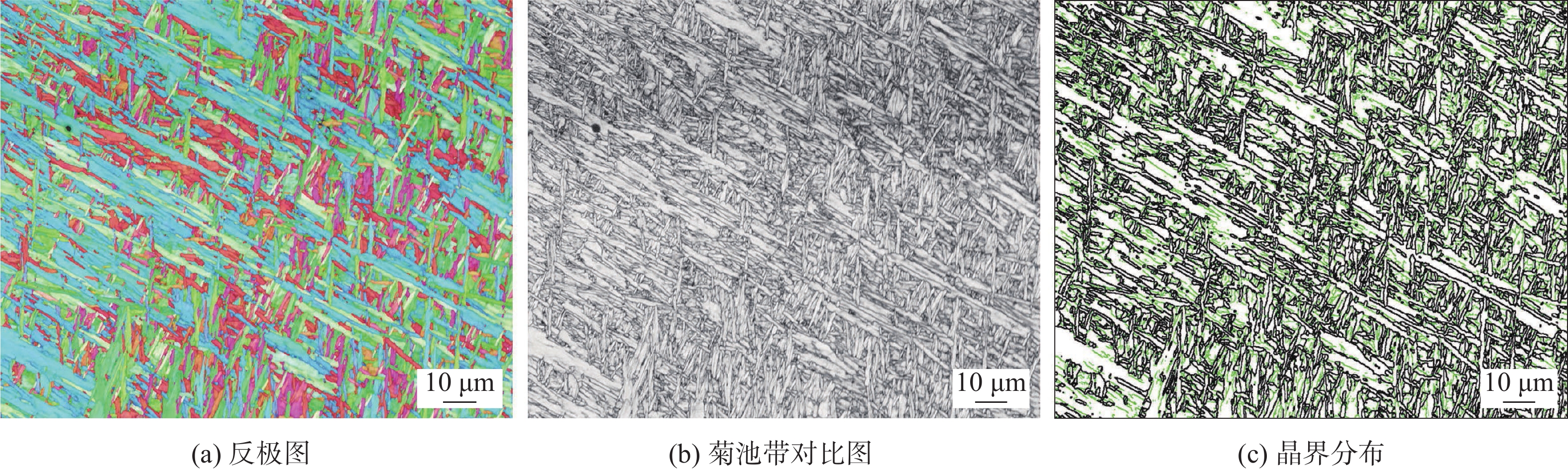
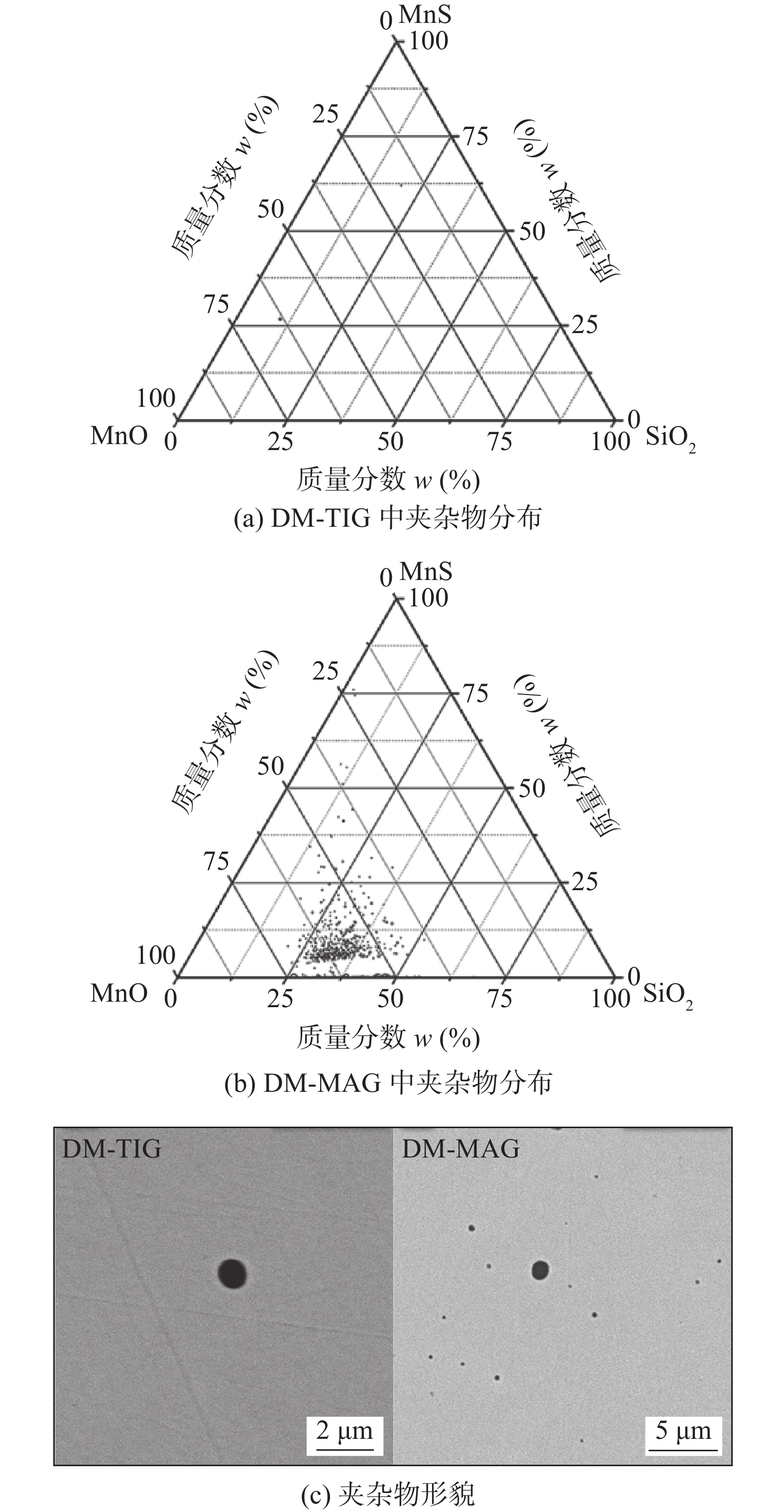
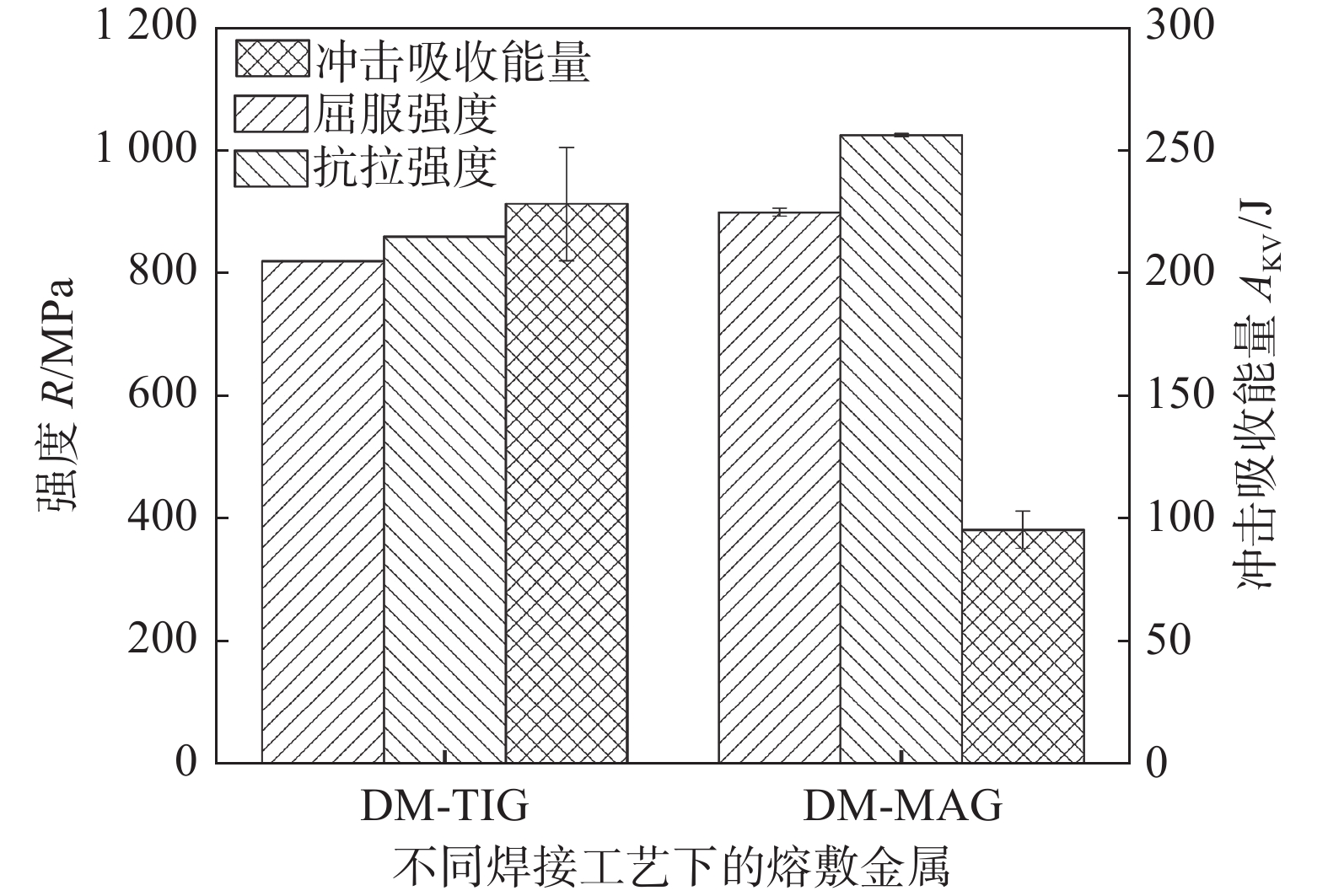
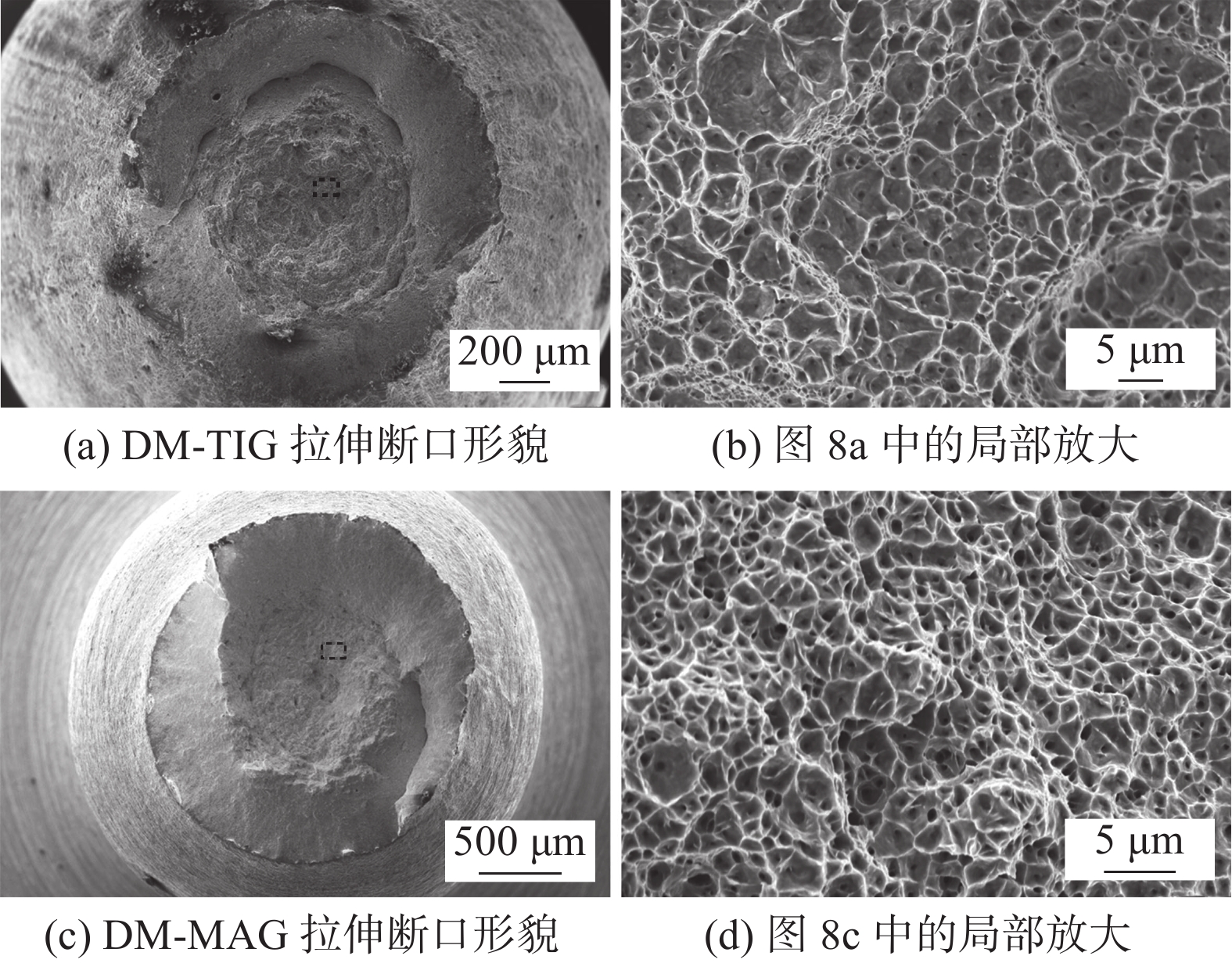
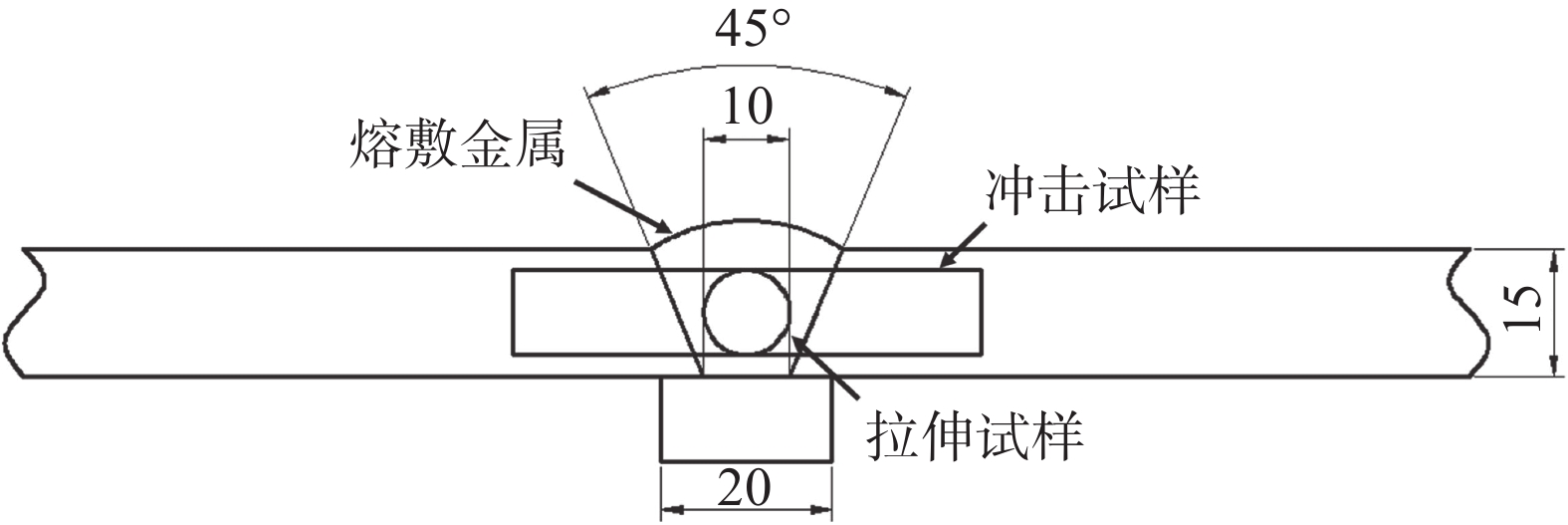
摘要: 分别采用钨极氩弧焊(TIG焊)和熔化极活性气体保护焊(MAG焊)方法制备了785 MPa级Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo系熔敷金属.利用扫描电子显微镜、透射电子显微镜和电子背散射衍射仪对熔敷金属的组织类型和晶体学特征进行了详细的表征分析,结果表明,采用不同焊接方法制备得到的熔敷金属组织均为贝氏体,但钨极氩弧焊熔敷金属(DM-TIG)中出现大量聚合贝氏体;由于焊接过程中使用的保护气体不同,熔化极活性气体保护焊熔敷金属(DM-MAG)中存在大量夹杂物. 经过电子背散射衍射分析结果表明,相比于DM-TIG,DM-MAG中由于存在大量自催化形核现象,晶体学取向非常复杂.力学性能测试结果表明,DM-MAG中大尺寸夹杂物在冲击过程中作为裂纹源,从而导致DM-MAG的韧性明显低于DM-TIG,实际工程应用中对于低温韧性要求较高的结构部件应合理选择焊接方法.Abstract: In this research, 785 MPa grade Fe-Cr-Ni-Mo deposited metals were prepared by tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding and metal active gas arc (MAG) welding processes, respectively. Scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and electron backscatter diffraction were adopted to characterize the microstructure and crystallographic characteristics of the deposited metals. The results showed that the microstructure prepared by different welding processes composed of lath bainite. However, a large amount of coalesced bainite appeared in the microstructure of the TIG deposited metal (DM-TIG). In addition, there were a large number of inclusions in the MAG deposited metal (DM-MAG) due to the active shielding gas. After electron backscatter diffraction analysis, results indicated that the crystallographic orientation of DM-MAG was complex compared to DM-TIG due to the large number of autocatalytic nucleation. The results of the mechanical properties of different deposited metals indicted that the toughness of DM-TIG was significantly better than that of DM-MAG. This was due to the large-sized inclusions in DM-MAG, which became the source of cracks during the fracture process. In practical engineering application, welding method should be selected reasonably for components with high requirement of low temperature toughness.
-
Keywords:
- coalesced bainite /
- autocatalytic nucleation /
- inclusion /
- mechanical properties
-
-
表 1 焊接工艺参数
Table 1 Welding parameters
焊接方法 保护气体 气体流量Q/(L·min−1) 焊接电流I/A 电弧电压U/V 热输入E/(kJ·mm−1) 层间温度T/℃ TIG焊 100% Ar 15 180 14 0.15 60 ~ 70 MAG焊 95% Ar + 5% CO2 20 240 29 1.39 80 ~ 110 表 2 母材、焊丝及熔敷金属的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 2 Chemical compositions of base metal, welding wires and deposited metals
材料 C Si Mn Cr + Ni + Mo V Fe A517GrQ 0.15 0.21 1.04 3.34 <0.01 余量 焊丝 0.036 0.38 1.08 6.41 <0.1 余量 DM-TIG 0.025 0.38 1.05 6.02 <0.1 余量 DM-MAG 0.061 0.32 0.93 6.74 <0.1 余量 表 3 夹杂物分析
Table 3 Analysis of inclusion
熔敷金属 扫描面积S/mm2 夹杂物数量n/个 平均直径d/μm 最大直径dmax /μm 面积分数wf (%) DM-TIG 26.68 9 1.36 2.58 0.003 DM-MAG 25.76 1 393 1.25 6.67 0.6 -
[1] 魏世同, 孙健, 刘景武, 等. V含量及回火工艺对高强钢TIG焊熔敷金属组织性能的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(11): 1 − 6. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200116001 Wei Shitong, Sun Jian, Liu Jingwu, et al. Effect of V content and tempering treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of the high strength steel TIG weld metal[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(11): 1 − 6. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200116001
[2] Barrick E J, DuPont J N. Microstructural characterization and toughness evaluation of 10 wt% Ni steel weld metal gas tungsten arc and gas metal arc weld fusion zones[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2020, 796: 140043.
[3] 李少峰, 马成勇, 宋志刚, 等. 800 MPa级高强钢焊接接头组织及力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(5): 91 − 96. Li Shaofeng, Ma Chengyong, Song Zhigang, et al. Study on the welding joint microstructure and mechanical properties of 800 MPa grade high stress steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(5): 91 − 96.
[4] 巴凌志, 王东坡, 张智, 等. 热输入对海工用钢不同合金系焊缝金属韧性的影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(6): 42 − 47. Ba Lingzhi, Wang Dongpo, Zhang Zhi, et al. Effect of welding heat input on toughness of different alloys weld metal in ocean engineering steel[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(6): 42 − 47.
[5] Mao G J, Cao R, Cayron C, et al. Microstructural evolution and mechanical property development with nickel addition in low-carbon weld butt joints[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2018, 262: 638 − 649. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2018.07.009
[6] Keehan E, Karlsson L, Andren H O, et al. Influence of carbon, manganese and nickel on microstructure and properties of strong steel weld metals: Part 1-effect of nickel content[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2006, 11(1): 9 − 18. doi: 10.1179/174329306X77830
[7] Pak J, Suh D W, Bhadeshia H, Promoting the coalescence of bainite platelets[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2012, 66(11): 951-953.
[8] Liu J, Sun J, Wei S, et al. Influence of chromium content on the bainite transformation nucleation mechanism and the properties of 800 MPa grade low carbon bainite weld deposited metal[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2022, 840: 142893.
[9] Nakanishi D, Kawabata T, Aihara S. Brittle crack propagation resistance inside grain and at high angle grain boundary in 3% Si-Fe alloy[J]. Acta Materialia, 2018, 144: 768 − 776.
[10] Fan S, Hao H, Meng L, et al. Effect of deep cryogenic treatment parameters on martensite multi-level microstructures and properties in a lath martensite/ferrite dual-phase steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering: A, 2021, 810: 141022.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 牛宗冉,莫文剑,袁志钟,易翠,王致远. 铜磷锡镍粉末钎料的钎焊性能和显微组织. 粉末冶金工业. 2025(01): 31-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 钟素娟,秦建,王蒙,崔大田,龙伟民. CuSn预合金粉芯复合银钎料的润湿铺展机理. 焊接学报. 2023(02): 16-21+129-130 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 郭亚东,陈明亮. 黄铜Type-C接口绿激光焊接工艺研究. 热加工工艺. 2022(09): 148-150 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 张冠星,钟素娟,董媛媛,刘晓芳,常云峰,薛行雁. 焊后钎剂残渣腐蚀行为分析. 焊接. 2022(11): 47-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王蒙,张冠星,钟素娟,沈元勋,龙伟民,董宏伟,刘晓芳. 低熔合金粉末对药芯银钎料钎焊过程的影响. 稀有金属材料与工程. 2021(08): 2859-2866 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 刘捷,黄建林,任刚,黄映杰. 黄铜-钢异种金属激光熔覆技术研究及应用. 江西科学. 2021(06): 1077-1079 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘晓芳,张冠星,常云峰,王蒙,钟素娟. 干燥过滤器焊后泄露原因. 焊接. 2021(10): 34-37+62-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李华晨,周广涛,陈梅峰,刘雪松,崔贺鹏,杨浩. 分步气体介质下低功率激光焊接薄板紫铜成形及组织和性能. 焊接学报. 2020(10): 65-72+101 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 王毅. 黄铜与铝合金纳秒激光焊接的工艺研究. 材料保护. 2020(12): 91-94+105 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张敏霞,潘光勇,鲍熠朗. 空调四通阀焊缝泄漏原因分析. 理化检验(物理分册). 2019(12): 859-863 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 于奇,潘建军,于新泉,纠永涛,鲍丽. 微量硅元素对铜磷锡粉状钎料性能的影响. 焊接. 2019(10): 17-20+66 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 刘文东,李红. 黄铜与不锈钢异种金属激光焊接工艺研究. 应用激光. 2019(06): 966-969 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)



 下载:
下载: