Preparation of Ag-Cu solid solution nanoparticles and the properties of low temperature sintered interconnect joint
-
摘要: 通过液相化学还原法制备Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒,采用低温热压烧结工艺制备“三明治”结构的互连接头.采用X射线衍射仪对所制备的Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒及烧结体进行物相表征;采用能谱仪对所制备的Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒的元素进行表征;采用纳米粒度仪对Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒粒径进行表征;通过扫描电子显微镜对互连接头的烧结组织和剪切断面形貌进行观察,分析颗粒烧结情况和互连接头断裂模式. 结果表明,通过液相化学还原的方法实现了室温下铜在银中的超饱和固溶,其中Ag原子分数为62.29%,Cu原子分数为37.71%,远超常温下常规块体材料的固溶度. 所制备的纳米颗粒在250 ℃以内保持相对稳定的固溶体相,260 ℃时发生相分离. 当烧结温度为300 ℃、烧结压力20 MPa时,所获得的互连接头具有优异的力学性能,平均抗剪强度达到105 MPa,且烧结组织呈现完整的脉络状,剪切断面全部为韧窝状,属于韧性断裂.Abstract: Ag-Cu solid solution nanoparticles were prepared by liquid phase chemical reduction, and sandwich joints were prepared by low temperature hot pressing sintering process. The phase characterization of Ag-Cu solid solution nanoparticles and sinter was detected by X-ray diffraction. The elements of Ag-Cu solid solution nanoparticles prepared were characterized by energy disperse spectroscopy. The particle size of Ag-Cu solid solution nanoparticles was characterized by nanometer. The sintering structure and shear section morphology of the interconnect joints were observed by scanning electron microscopy, and the particle sintering situation and fracture mode of the interconnect joints were analyzed. The results showed that the supersaturated solid solution of Cu in Ag at room temperature was realized by liquid phase chemical reduction, in which the percentage of Ag atoms and Cu atoms was 62.29% and 37.71%, far exceeding the solid solution of conventional block materials at room temperature. The solid solution phase remained relatively stable within 250 ℃, and phase separation occurred at 260 ℃.When the sintering temperature is 300 ℃ and the sintering pressure is 20 MPa, the interconnect joints obtained have excellent mechanical properties, the average shear strength reaches 105 MPa, the sintered structure shows a complete vein shape, and the shear sections are all dimpled, which belong to ductile fracture.
-
Keywords:
- Ag-Cu solid solution /
- nanoparticles /
- low temperature sintering /
- high strength
-
0. 序言
随着功率半导体行业的兴起,以碳化硅(SiC)和氮化镓(GaN)为代表的第三代宽禁带半导体材料具有击穿电压高、功率密度大、电子迁移率高、介电常数小等优点,在航空航天、新能源汽车的电源模块中具有广阔的应用前景[1-5]. 航空航天发动机附近的的传感器以及控制单元的工作温度要求在200 ~ 300 ℃[6];而新能源汽车中的传感器工作温度达到350 ℃以上[7]. 因此,对封装互连材料提出了高温服役、高导电导热和高抗电迁移等要求. 现有的半导体器件封装材料主要为锡基合金钎料,包括锡银共晶合金(Sn-Ag)、锡银铜共晶合金(Sn-Ag-Cu)和金锡共晶合金(Au-Sn)等. Sn-Ag共晶钎料和Sn-Ag-Cu共晶钎料的熔点过低,难以在高温下服役. 而Au-Sn共晶钎料的互连温度往往在320 ℃以上,易形成脆性的金属间化合物如Ag3Sn和AuSn4等,且金的价格非常昂贵,限制了其在第三代半导体中的应用. 纳米金属材料因尺寸效应,其熔点和烧结温度比常规块体低很多,可以在较低温度下实现烧结,理论上烧结之后可以达到对应块体材料的性能. 其中,银和铜凭借优异的电学、热学性能被广泛研究[8-9]. 然后,铜的抗氧化性能差,烧结工艺复杂,且极易在烧结过程中发生氧化,导致烧结接头的导电、导热和机械强度急剧下降,因此目前仍处于研发阶段[10]. 银具有很高的抗氧化性能,且在200 ~ 300 ℃下施加较小的压力甚至无压的工艺下即可获得高导电、高导热和高机械可靠性的焊点. 银属于极容易发生迁移的金属[11],作为高功率器件的互连材料,在服役过程中存在电迁移可靠性的风险. 因此,研发新型的低温烧结、高温服役和高抗电迁移的互连材料迫在眉睫.
通过液相化学还原法制备Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒,实现Cu原子在银晶格中的过饱和固溶. 采用热压烧结的方法制备“三明治”结构的互连接头,并研究烧结工艺对其烧结组织、抗剪强度和断口形貌的影响,为新一代封装材料及其烧结工艺的开发奠定基础.
1. 试验方法
通过液相化学还原法制备Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒,其中,硝酸银和硝酸铜作为前驱体,硼氢化钠作为还原剂,柠檬酸作为纳米颗粒的表面包覆剂,反应溶剂为去离子水. 首先,将前驱体按照Ag∶Cu原子比为3∶2溶于去离子水中,记为A溶液;包覆剂柠檬酸溶于去离子水中,记为B溶液,还原剂硼氢化钠溶于去离子水中,记为C溶液. 将A溶液和B溶液置于圆底烧瓶中,将C溶液逐滴滴加,反应过程伴随磁力以2 000 r/min的速度搅拌. 待反应结束,离心/清洗3遍,获得沉淀,即Ag-Cu固溶体纳米焊膏.
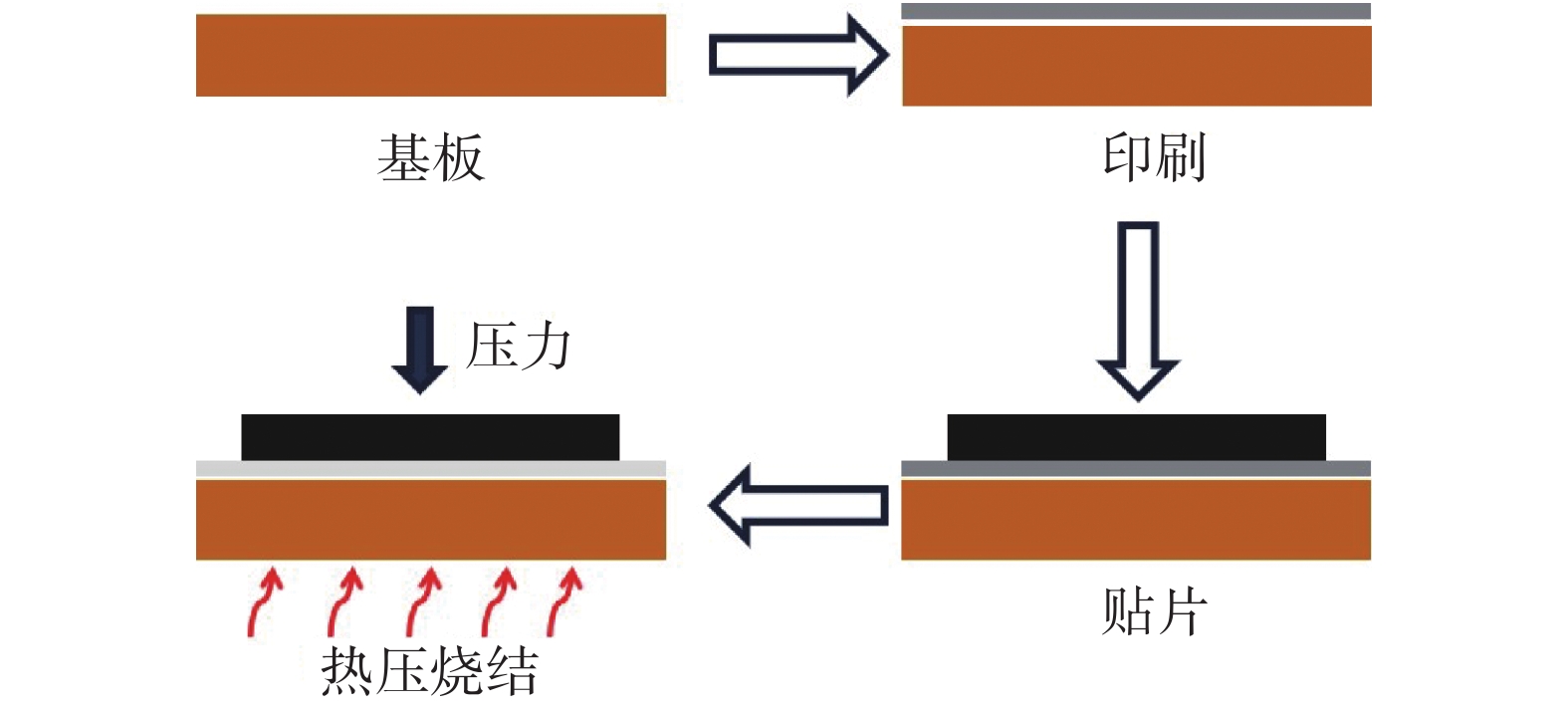
三明治结构的互连接头选用镀Ni/Ag的Cu基板,下基板的尺寸为5 mm × 5 mm × 1 mm,上基板的尺寸为3 mm × 3 mm × 1 mm. 互连接头烧结工艺流程如图1所示,首先用洗银水将基板进行清洗,以去除表面的氧化物,获得洁净的表面,通过钢网印刷的方法将Ag-Cu固溶体纳米焊膏印刷在下基板上,然后在80 ℃的烘箱中保温15 min,进行排胶,最后将上基板置于烘干的印刷图案上,进行热压烧结. 热压设备为深圳市先进连接科技有限公司生产的XL-TC200型快速热压机. 烧结温度为250 ~ 300 ℃,保温时间为20 min,烧结压力为10 ~ 20 MPa.
2. Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒的表征
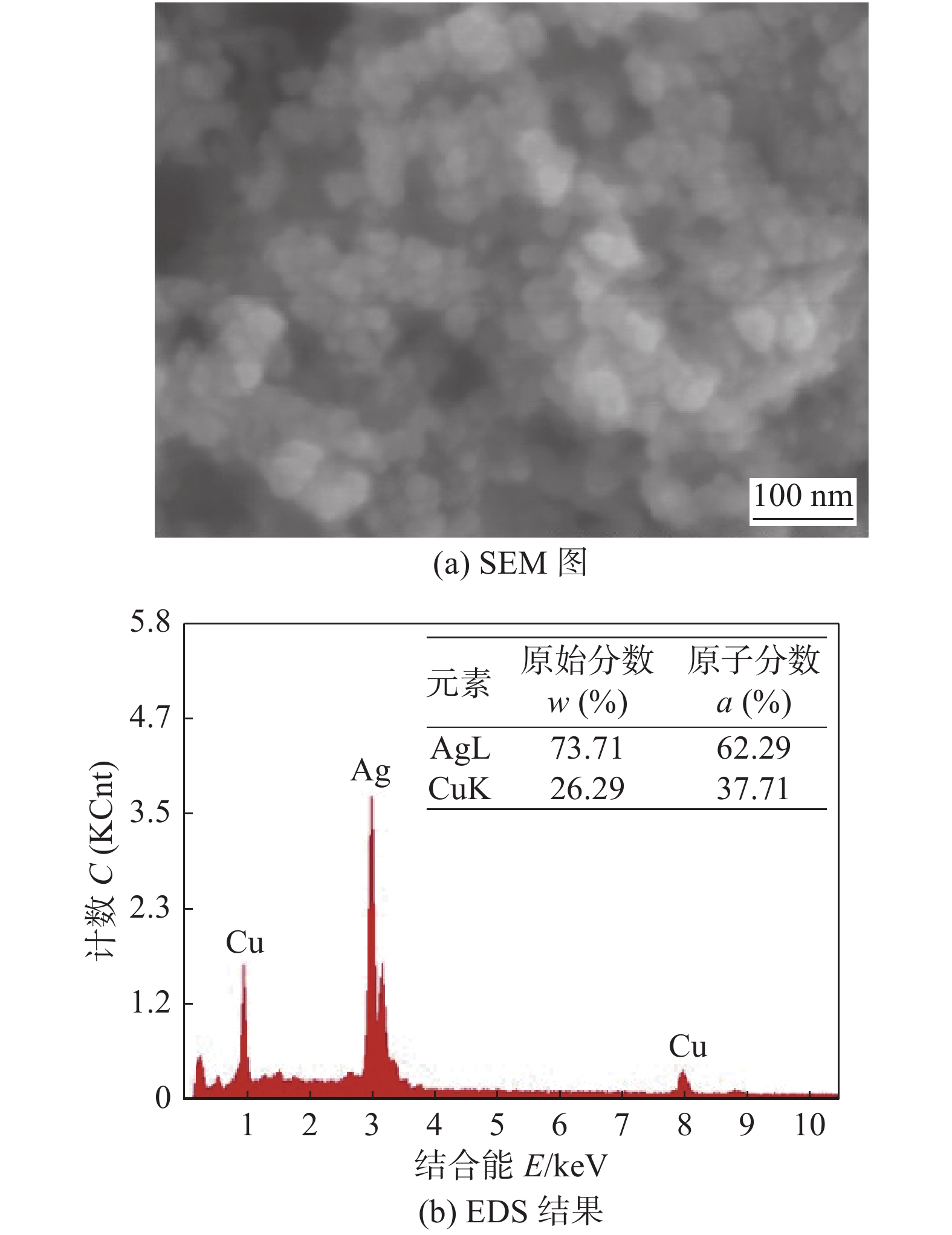
图2为通过液相化学还原法制备的Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒的扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscopy, SEM)和能谱仪(energy disperse spectroscopy, EDS)图. 从图2a可以看出,所制备的颗粒为纳米尺度的颗粒,形貌较为规则. 采用winner801型纳米粒度仪对其粒径进行测试,结果显示其粒径分布在30 ~ 60 nm,平均粒径为41.06 nm. 从图2b可见,Ag元素的原子分数为62.29%,Cu原子分数为37.71%,说明制备的Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒的成分比例与预先设计的成分比例相符.
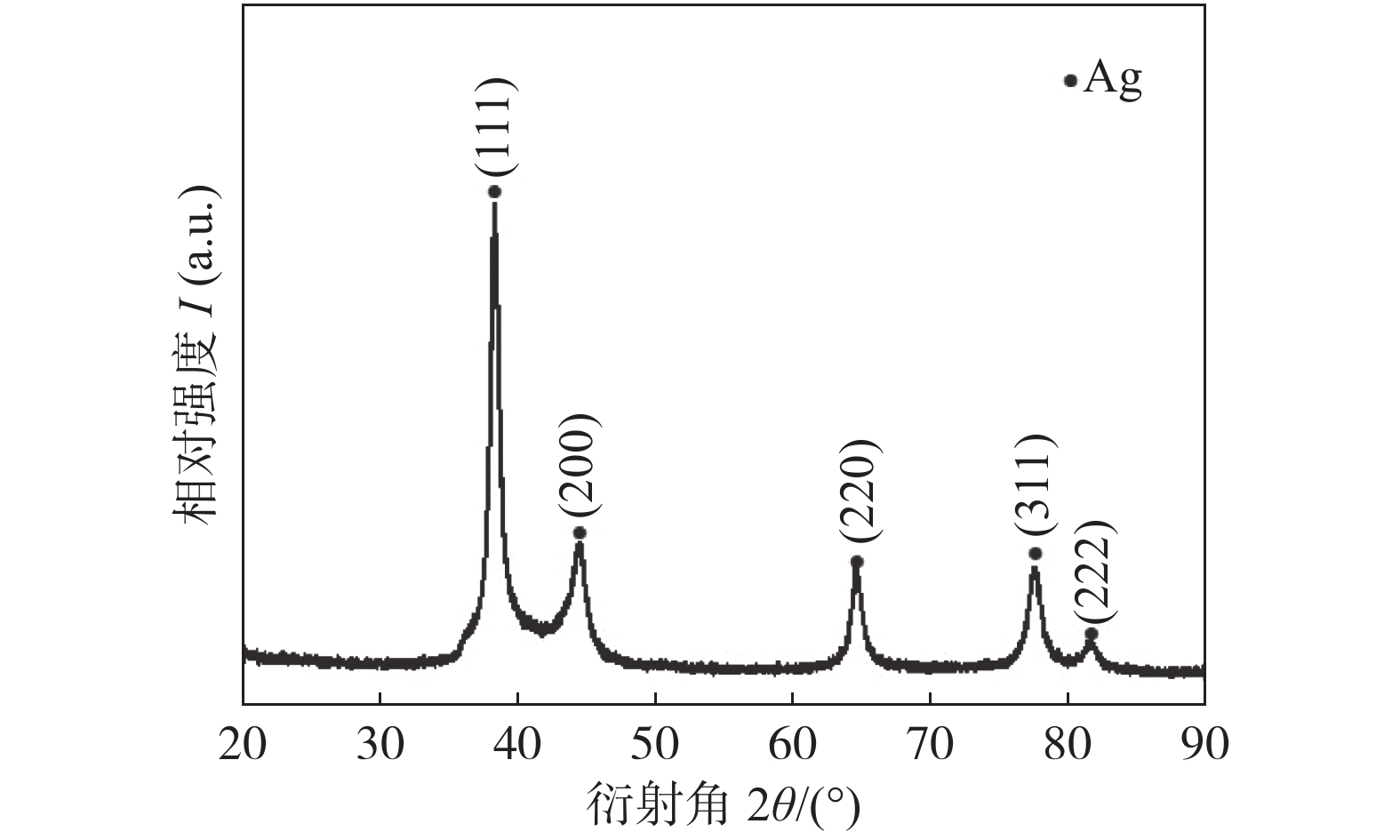
为了进一步说明Ag-Cu纳米颗粒的物相信息,对其进行X射线衍射仪(X-ray diffraction, XRD)表征. 图3为Ag-Cu纳米颗粒的XRD衍射图谱. 在衍射角37.9°,44.4°,64.4°,77.2°和 81.4°处出现 5 个尖锐的衍射峰,分别对应于面心立方银的(1 1 1),(2 0 0),(2 2 0),(3 1 1)和(2 2 2)晶面,与银的标准晶系卡片(PDF#0783)一致. 合成的纳米颗粒样品的 XRD 图谱中只出现了银的衍射特征峰,铜的衍射特征峰“消失”,表明所制备的纳米颗粒为单相结构,呈现银的晶体学特征,Cu元素以固溶的方式存在于银的晶格中,进而形成银基固溶体纳米颗粒. 由于所制备的固溶体颗粒晶粒细化导致银的衍射峰发生宽化.
然而,Ag与Cu原子尺寸的失配度达到 15%,导致铜与银的互溶度极低,即使在共晶温度779 ℃下,铜在银中的最大固溶度也只为 14.1%(原子分数),银在铜中的最大固溶度只有 4.9%(原子分数),而在室温下两者几乎不互溶(固溶度<1%)[12],且二者没有金属化合物的存在. 因此,通过液相化学还原法所制备的Ag-Cu固溶体远超常规块体材料的固溶度,属于高能量的不稳定相,因此对其热稳定性进行了研究.
将所制备的Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒置于Al2O3基板上,分别在220,230,240,250和260 ℃的烘箱中保温30 min,然后对其进行XRD分析. 图4为Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒热处理后的XRD图谱. 当热处理温度分别为220,230,240和250 ℃时,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒仍为单一Ag相,说明此温度下Cu原子未从银的晶格中析出,表现出较高的稳定性.
如图5所示,当温度升高至260 ℃时,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒的XRD图谱中出现了对应 Cu2O 的衍射峰. 随着温度的升高,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒的结构发生变化,原本固溶于银晶格中的 Cu 原子开始析出. 当在空气下发生析出时,铜极易与氧气发生反应,因此,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒在260 ℃处理后出现了Cu2O的衍射峰. 在形成互连接头时,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒在烧结的同时伴随Cu的析出,最终形成由富Ag相和富Cu相交替分布[13].
3. 互连接头的力学性能
互连接头优良的力学性能是保证器件服役时可靠性的关键因素. 因此,对不同烧结工艺所获得的互连接头进行剪切测试. 图6为烧结温度250 ℃时不同烧结压力下所获得的互连接头的抗剪强度. 随着烧结压力从10 MPa升高至20 MPa,互连接头的抗剪强度从19 MPa升高至44 MPa. 此温度下获得的互连接头的抗剪强度普遍较低,虽然当烧结压力为20 MPa时,抗剪强度满足了常规电子封装中对互连焊点的强度要求,但是不具有明显优势.
图7为烧结温度300 ℃时不同烧结压力下所获得的互连接头的抗剪强度. 随着烧结压力的升高,互连接头的抗剪强度有很大程度的提高. 当烧结压力为10 MPa,互连接头的平均抗剪强度为43 MPa. 随着烧结压力提高至15和20 MPa时,互连接头的抗剪强度分别为76 MPa 和105 MPa. 此抗剪强度比传统的软钎焊所获得的互连接头的抗剪强度(30 ~ 50 MPa)高很多.
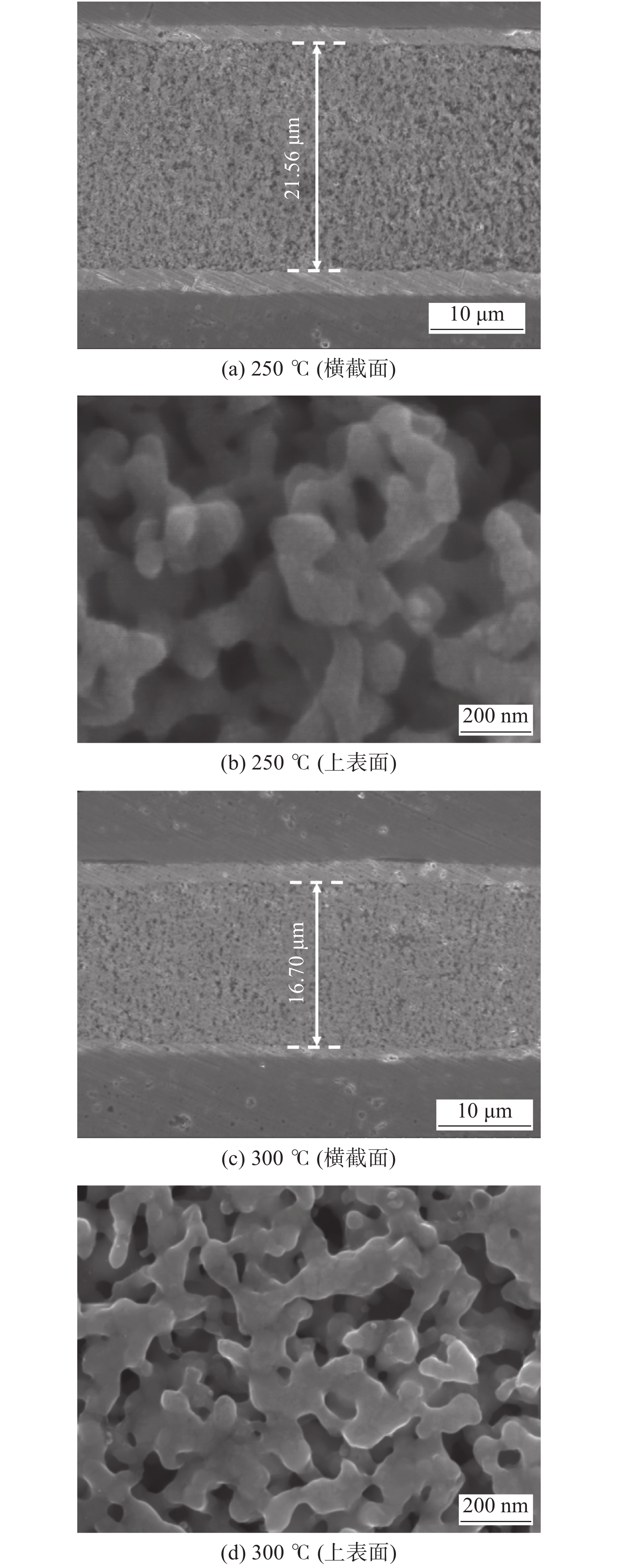
鉴于烧结压力为20 MPa、烧结温度为250和300 ℃可以取得满足要求的机械强度. 因此,对该烧结压力下所获得的互连接头进行组织分析,如图8所示. 从图8a和8c可以看出,在不同烧结温度下获得的互连接头的焊缝厚度有明显差异,根据标定,当烧结温度为250 ℃时,烧结后的焊缝厚度约为21.56 µm,而当烧结温度为300 ℃时,烧结后的焊缝厚度约为16.70 µm,比烧结温度250 ℃下获得的焊缝厚度减小约4.86 µm. 另外,在烧结温度250 ℃下获得的焊缝组织中存在的空隙具有细小而弥散的特点,而烧结温度300 ℃下获得的焊缝组织中孔洞变大,且数量有所减少. 从图8c和8d也可以看出,当烧结温度为250 ℃时,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒之间未发生充分的烧结,颗粒状明显,说明在此温度下颗粒之间难以发生充分的烧结. 而当烧结温度升高至300 ℃时,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒之间烧结成较完整的脉络状烧结体,几乎不存在颗粒状纳米颗粒. 也就是说,随着烧结温度的升高,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒发生了更充分的烧结,使得烧结组织更加致密,在烧结温度300 ℃下获得的焊缝厚度比烧结温度250 ℃下获得的焊缝厚度减小约5 µm.
为了进一步研究互连接头的断裂模式,对互连接头的剪切断口形貌进行分析,如图9所示. 从图9a可知,当烧结温度为250 ℃时,Ag-Cu固溶体纳米颗粒烧结后仍能观察到颗粒状纳米颗粒,且断裂发生在烧结不充分的位置,发生断裂时烧结组织未产生明显的塑性变形. 而当烧结温度为300 ℃时,颗粒状纳米颗粒全部消失,组织致密度明显提高,断口全部为韧窝状组织,表明互连接头的断裂方式为韧性断裂,并且这种断裂模式的互连接头拥有优异的力学性能,如图9b所示.
4. 结论
(1)通过液相还原法制备了Cu原子分数约为37.71%的超饱和Ag-Cu固溶体,在烧结温度250 ℃以内保持相对稳定性,在烧结温度260 ℃时发生两相分离.
(2)通过热压烧结的工艺制备互连焊点,当烧结温度为300 ℃、烧结压力为20 MPa时,互连接头的抗剪强度达到105 MPa,具有很高的机械可靠性.
-
-
[1] Sheng K, Yu L C, Zhang J, et al. High temperature characterization of SiC BJTs for power switching applications[J]. Solid-State Electronics, 2006, 50(6): 1073 − 1079. doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2006.05.004
[2] Matocha K. Challenges in SiC power MOSFET design[J]. Solid-State Electronics, 2008, 52(10): 1631 − 1635. doi: 10.1016/j.sse.2008.06.034
[3] She N. High-power robust semiconductor electronics technologies in the new millennium[J]. Microelectronics Journal, 2001, 32(5): 397 − 408.
[4] Lang F, Nakagawa H, Aoyagi M, et al. Impact of joint materials on the reliability of double-side packaged SiC power devices during high temperature aging[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Electronics, 2010, 21(9): 917 − 925. doi: 10.1007/s10854-009-0018-x
[5] Wright W, Carter J, Alexandrov P, et al. Comparison of Si and SiC diodes during operation in three-phase inverter driving ac induction motor[J]. Electronics Letters, 2001, 37(12): 787. doi: 10.1049/el:20010535
[6] Chen C M, Wang K J, Chen K C. Isothermal solid-state aging of Pb-5Sn solder bump on Ni/Cu/Ti under bump metallization[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2007, 432: 122 − 128. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.05.116
[7] Johnson R W, Evans J L, Jacobsen P. The changing automotive environment: high-temperature electronic[J]. IEEE Transactions on Electronics Packaging Manufacturing, 2004, 27(3): 164 − 176. doi: 10.1109/TEPM.2004.843109
[8] 吴炜祯, 杨帆, 胡博, 等. 用于大面积芯片互连的纳米银膏无压烧结行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(1): 83 − 90. Wu Weizhen, Yang Fan, Hu Bo, et al. Pressureless sintering behavior of nano-silver paste for large area chip interconnection[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(1): 83 − 90.
[9] Li M, Xiao Y, Zhang Z, et al. Bimodal sintered silver nanoparticle paste with ultrahigh thermal conductivity and shear strength for high temperature thermal interface material applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2015, 7(17): 9157 − 9168.
[10] Liu J, Chen H, Ji H, et al. Highly conductive Cu-Cu joint formation by low-temperature sintering of formic acid-treated Cu nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials and Interfaces, 2016, 8(48): 33289 − 33298.
[11] Riva R, Buttay C, Allard B, et al. Migration issues in sintered-silver die attaches operating at high temperature[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2013, 53(9-11): 1592 − 1596.
[12] Subramanian P R, Perepezko J H. The Ag-Cu (silver-copper) system[J]. Journal of Phase Equilibria, 1993, 14(1): 62 − 75.
[13] 刘晓剑. Ag-Cu超饱和固溶体纳米颗粒纳米冶金及抗电化学迁移机理[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2017. Liu Xiaojian. Nanoalloying and anti-electrochemical migration mechanisms of Ag-Cu supersaturated solid solution nanoparticles [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2017.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 黄玺,张亮,王曦,陈晨,卢晓. 电子封装用纳米级无铅钎料的研究进展. 材料导报. 2024(23): 136-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 汉晶,李腾,晋学轮,王乙舒,贾强. Research progress of molecular dynamics simulation for nanoparticles. China Welding. 2023(02): 16-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)



 下载:
下载: