On-line solution treatment process for welding production of 304 stainless steel thin-walled tube
-
摘要: 钢带经逐级卷板加工、焊接而制成钢管,因前期加工硬化导致钢管硬度增大,从而会显著影响管件的二次成形加工.文中通过在304不锈钢管生产线搭建在线固溶处理试验平台,研究了固溶温度、固溶冷却条件及固溶保护气种类对304不锈钢管焊缝和母材微观组织及性能的影响.结果表明,在试验温度范围内,提高固溶温度会使热影响区和母材晶粒度增大,促进碳化物固溶于奥氏体晶粒,明显降低热影响区和母材的硬度.焊缝区沿奥氏体晶界分布的铁素体部分溶解,晶粒尺寸增大程度较小,因此焊缝区的硬度略有降低;而调整冷却条件对焊缝及母材的硬度影响不大;在氩气作为固溶保护气时,调节固溶参数,管件母材平均硬度可降低至188.7 HV,与未固溶时相比降低了11.0%.在氢气作为保护气时,平均硬度可降低至182.7 HV,与未固溶时相比降低了13.8%.通过显微组织观察,硬度、扩口和压扁力学性能测试,在两种保护气条件下固溶处理的管件均满足国家标准.Abstract: The steel strip is made into steel tube by rolling and welding step by step. The hardness of the steel tube increases due to the early work hardening, which will significantly affect the secondary forming processing of the tube. In this paper, the effects of solution temperatures, solution cooling conditions and types of solution shielding gas on the microstructure and properties of 304 stainless steel thin-walled tube were studied by building an on-line solution treatment test platform in the 304 stainless steel tube production line. The results show that increasing the solution treatment temperature in the experimental temperature range will increase the grain size of the heat-affected zone and the base metal and promote the solid solution of carbides in and along the austenite grains, so as to significantly reduce the hardness of the heat-affected zone and the base metal. The ferrite distributed along the austenite grain boundary in the weld zone is partially dissolved, and the grain size increases to a small extent, so the hardness of the weld zone decreases slightly. However, adjusting the cooling conditions has little effect on the hardness of the weld and base metal. When argon is used as the solution treatment protective gas, the average hardness of the base metal of the tube can be reduced to 188.7 HV, which is 11.0% lower than that without solution treatment. When hydrogen is used as solution treatment protective gas, the average hardness can be reduced to 182.7 HV, which is 13.8% lower than that without solution treatment. Through microstructure observation, hardness test, flaring and flattening mechanical properties test, the solution-treated tubes under the two protective gas conditions all meet the national standards.
-
0. 序言
随着电子器件的可靠性要求越来越高,微小尺寸器件的气密性封装技术被越来越广泛的研究和应用[1-2]. 目前微小尺寸器件的封装形式主要采用芯片级尺寸封装(chip scale packaging, CSP)[3],在CSP器件的气密性封装结构中,使用高温共烧陶瓷作为载体或基板,而管帽则由金属材料制成,从而实现对内部芯片的有效保护[4]. Au-Sn共晶焊料由于具有优异的焊接性能和力学性能[5],成为CSP器件封装系统内实现金属管帽与陶瓷基板之间气密性可靠互连的首选材料[6].
Au80Sn20共晶钎料的熔点为278 ℃,钎焊温度达到了300 ~ 310 ℃,可以替代熔点在280 ~ 360 ℃内的高熔点铅基合金钎料,并且能够承受较高的处理温度,保证良好的耐腐蚀性和抗蠕变性. Au80Sn20共晶合金由两种金属间化合物ζ相和δ/AuSn相组成,具有较大脆性,用常规的方法难以加工成形[7]. 常用的制备技术有预成形片法[8]、丝网印刷法[9]、蒸发/溅射沉积法[10]和电镀沉积法[11-12]等.
预成形焊片法采用熔铸增韧工艺、叠层冷轧工艺或机械合金化工艺制备Au-Sn共晶焊料,但是合金成形困难,加工过程易氧化;丝网印刷法是将焊膏印刷在封装焊盘的金属化层上,通过回流熔融形成Au-Sn共晶合金,这种方法对印刷质量要求较高,回流时易形成空洞;蒸发/溅射沉积法通过分层沉积不同厚度的金层与锡层(或Au-Sn混合层),这种方法需要使用真空系统,存在设备昂贵、加工周期长、材料利用率低等问题,不适合大规模生产;电镀沉积法利用电化学方法将Au和Sn离子在基体表面实现沉积, 可以精确控制镀层的厚度及图形,具有设备简单、成本低廉、工艺成熟、易于大规模生产等优势.
采用电镀沉积法在陶瓷基板上制作了金锡镀层,并对镀层质量进行了表征分析,通过熔封曲线的调控实现了CSP器件的气密性封装,对金锡焊料的工程应用、工艺优化及封装结构可靠性具有重要意义.
1. 试验方法
与其它方法相比,金锡分层电镀沉积法可控性强,能够精确控制Au和Sn元素成分比例,因此采用电镀沉积方法在高温共烧陶瓷(HTCC)基板上制备了金属层,层结构如图1所示,其中W层作为陶瓷基板上的黏附层,Ni-Co则起到了扩散阻挡层和浸润层的作用. 通过分层电镀沉积不同厚度的金层与锡层,组成Au80Sn20(质量分数,%)共晶钎料,为了实现该比例,控制金层和锡层的厚度比为1.5∶1. 金/锡/金共晶焊料层总厚度设计为12 μm,另外Au元素和Ni元素之间无限互溶,进一步加强了镀层之间的浸润,表层的金则起到了抗氧化的作用.
为了评估金/锡/金镀层质量对互连界面的影响,分别选取两种镀层的基板进行金相表征和显微组织分析,显微组织分析采用FEI公司的环境扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscopy, SEM, Quanta 200),并利用其附带的EDAX能谱仪进行界面显微元素分析.
为了研究Au-Sn合金镀层质量对熔封效果的影响,将电镀后的高温共烧陶瓷基板置于320 ℃加热台回流30 s,对金/锡/金镀层的表面状态和横截面进行观察,确认Au-Sn镀层质量. 此处CSP器件封装管帽采用可伐合金材料冲压而成,其与基板的熔封在真空回流炉中实现,先抽真空,后充入高纯氮气,以使炉腔均匀快速升温,封装回流曲线如图2所示. 焊接工艺设置了预热阶段,预热至120 ℃并保持60 s,然后继续升温至310 ℃,保温90 s后空冷至室温.
回流完成后,对管帽与陶瓷基板的互连界面进行显微组织分析,同时对封装好的器件进行加压检漏和热循环试验,试验条件为−55 ~ 85 ℃. 采用SEM表征热循环之后互连界面的微观组织变化,进而评估金和锡镀层对管帽封装热循环可靠性影响.
2. 试验结果
2.1 陶瓷基板金属镀层的显微组织
图3为电镀完成后陶瓷基板表面的金属镀层显微形貌. 图3a为镀层质量差的陶瓷基板表面,由图可以看出,金/锡/金镀层质量差主要体现为①两侧金镀层厚度差距大,上侧金镀层较薄,仅有~ 2 μm,而下侧金镀层较厚,厚度为 ~ 6 μm;②下侧金层出现了孔洞,而且孔洞出现在金层和锡层之间,这说明金/锡/金镀层的层间结合力差. 与之相比,图3b显示的陶瓷基板上侧金/锡/金镀层的质量优良,两侧金镀层厚度差较小,上侧金镀层约为~ 3 μm,下侧金镀层厚度约为 ~ 4 μm,而且镀层的界面处未发现孔洞.
2.2 陶瓷基板金属镀层熔融后的显微组织
为了研究镀层质量对金/锡/金熔封过程的影响,进而阐明陶瓷基板上金属镀层的互连冶金过程,采用320 ℃加热台对陶瓷基板首先进行熔融处理. 图4为熔融完成后两种陶瓷基板表面的金相显微形貌,由图4a可知,金/锡/金镀层质量差的基板镀层熔融后,表面质量差,局部区域出现凹陷不平状,并伴有灰褐色斑块浮现. 与之相比,金/锡/金镀层质量优良的基板的镀层熔融后,表面光亮饱满,富有金属光泽,并未看到凹陷. 在局部区域甚至可以看到Au-Sn的共晶组织,如图4b所示,因此金/锡/金电镀层的质量对陶瓷基板熔融后的形貌与组织产生显著的影响.
为了深入分析金/锡/金电镀层的熔融过程,对熔融后陶瓷基板上侧的横截面组织进行了SEM表征,结果如图5所示. 可以看出,质量差的金/锡/金电镀层熔融之后,上侧的Au-Sn共晶层变得很薄,仅有 ~ 4 μm,这对应了图4a中陶瓷基板表面的凹陷部分. 与之相比,质量优良的金/锡/金电镀层熔融之后,形成了良好的Au-Sn共晶组织,如图5b所示,共晶层整体厚度均匀,与熔融前金/锡/金镀层厚度一致,约为11 μm(图3b).
考虑到金/锡/金电镀层熔融是一个连续升温的过程,而Au-Sn发生共晶反应的温度是278 ℃,因此在温度上升至320 ℃的过程中,中间的锡镀层会首先发生熔化,形成一个“熔池”;熔化的锡会溶解金层,形成Au-Sn化合物,但是当流动的锡熔体遇到镀层界面的孔洞时,没有金溶解,这就导致锡熔体流动到基板的其它地方,造成该处镀层变薄,凝固后出现凹陷.
以上分析进一步说明,与传统Au-Sn共晶焊不同,此处使用分层电镀方法制备的金/锡/金镀层并没有直接生成Au-Sn共晶组织,而是在升温过程中首先熔化的锡镀层溶解固态的金镀层,形成Au-Sn间化合物;当温度高于共晶温度278 ℃时,金/锡/金镀层才会迅速液化,发生共晶反应;随后冷却过程中,由液相中生成ζ相和δ相AuSn,ζ相和δ相以层片状排列,构成共晶组织,如图5b所示. 表1是图5b中共晶层的两相的能谱分析结果,由此可知,图5b中浅色的组织是ζ相,深色的组织是δ相(AuSn). 对比图5a和图5b可知,质量较差的金/锡/金镀层经历熔融和凝固之后,虽然生成了浅色的ζ相和深色的δ相,但其并没有形成层片状共晶组织,这说明金/锡/金镀层的质量直接影响熔封之后AuSn共晶组织的形态,进而影响陶瓷基板与金属管帽之间的互连结果与可靠性.
表 1 图5b中Au-Sn化合物的成分(原子分数,%)Table 1. Au-Sn intermetallic compounds in Fig. 5b位置 Au Sn Ni Co W 化合物 1 85. 64 14. 36 0 0 0 ζ 2 57. 88 42. 12 0 0 0 δ/AuSn 2.3 管帽与陶瓷基板封接后的界面组织分析
CSP封装结构的微腔保护了芯片的工作区域不受外界湿气和电磁的干扰 ,因此封装结构中管帽和陶瓷基板的互连可靠性关系到封装器件是否可以正常工作. 图6a是CSP器件封装结构的剖面图,冲压制作的可伐合金管帽与电镀后的HTCC基板上的Au-Sn焊料环熔封焊接,封装回流曲线如图2所示,采用缓慢升温的方式进行器件熔封,焊接峰值温度为310 ℃,保温90 s.图6b是管帽与陶瓷基板互连处的SEM表征与相应的界面各元素分布的能谱面扫描结果. 陶瓷基板上制备了质量优良的金/锡/金镀层(图3b),将可伐合金管帽与基板压在一起,然后升温实现连接. 表2是与图6b对应的界面Au-Sn共晶层的相组成分析结果. 根据界面的SEM形貌(图6b)和相分析(表2)可知,可伐管帽和HTCC基板之间形成了良好的连接,在Au-Sn共晶焊料层内生成了ζ相和δ/(Au,Ni)Sn相,其中(Au,Ni)Sn相主要分布在两侧,中间则是ζ相和富Sn相.
表 2 图6b中Au-Sn共晶层相成分(质量分数,%)Table 2. Au-Sn intermetallic compounds in Fig. 6b位置 Au Sn Ni Co Fe 化合物 1 48.1 40.9 9.2 0.8 1.9 (Au,Ni)Sn 2 60.6 33.4 4.6 0.9 0.5 富锡相 3 85.5 10.5 2.4 0.8 0.5 ζ 4 85.9 10.8 2.3 0.4 0.6 ζ 5 52.1 38.6 7.4 1.5 0.4 (Au,Ni)Sn 根据2. 2节的分析,当温度升高时,中间的锡镀层首先发生熔化,由中间向两侧溶解金层;温度升高至Au-Sn共晶点以上,Au-Sn之间发生共晶反应,金/锡/金镀层快速液化,进而溶解可伐合金镍层,形成ζ相和δ/AuSn相,其中由于金和镍是无限互溶的,镍会进入Au-Sn相的晶格内,形成(Au, Ni)Sn界面金属间化合物,实现可伐合金引脚与陶瓷基板的互连.
为探究不同封装回流曲线对Au-Sn共晶焊料封接效果的影响,将预热温度和峰值温度分别提高至220和330 ℃,同时提高了升温速率,但是将在峰值温度的保温时间缩短至30 s,改进后封装回流曲线如图7所示.
图8是采用图7所示的曲线获得的管帽-基板互连界面的微观组织形貌和面能谱分析. 改变封装回流曲线之后,可伐管帽与HTCC基板之间也获得了良好的互连;但采用图7所示的曲线,共晶焊料层的组织形态发生了变化,即共晶焊料层内出现了明显的分层,中间没有锡剩余. 结合表3所示的相成分分析,此时共晶焊料层由δ/(Au,Ni)Sn—ζ相—δ/(Au,Ni)Sn夹层结构组成.
表 3 图8中Au-Sn共晶层相成分(原子分数,%)Table 3. Au-Sn intermetallic compounds in Fig. 8b位置 Au Sn Ni Co Fe 化合物 1 48.0 40.2 10.0 0.6 1.1 (Au,Ni)Sn 2 87.6 10.6 1.3 0 0.5 ζ 3 84.5 12.8 1.9 0.5 0.3 ζ 4 87.3 10.6 1.3 0.5 0.3 ζ 5 49.1 38.9 8.5 3.2 0.3 (Au,Ni)Sn 6 49.9 38.7 7.9 3.1 0.4 (Au,Ni)Sn 对比两种曲线获得的互连界面组织,可以发现,当焊接峰值温度为310 ℃时(图2),金和锡之间反应并不完全,导致中间锡层仍有锡残余;当焊接峰值温度为330 ℃时(图7),虽然保温时间由90 s缩短至30 s,中间锡层已经全部转变成了Au-Sn化合物ζ相,说明此时金和锡之间反应完全. 根据前述管帽封接过程中金/锡/金镀层共晶冶金机理,Au-Sn共晶反应需要快速完成,避免升温过程中熔融锡过多消耗. 采用图2所示曲线时,由于升温速率慢,熔融的锡在溶解金形成富锡金属间化合物的同时,其熔池界面处的熔点也在升高,导致其溶解金能力下降,结果中间锡层没有反应完全,仍有大量的锡残留. 因此相对于保温时间,峰值温度对Au-Sn熔封的结果影响更大,采用快速升温方法达到更高的焊接温度所产生的熔封效果更好.
两种曲线获得的管帽-基板界面均出现了δ/(Au,Ni)Sn相偏聚在可伐管帽引脚一侧,这与图5b所示的陶瓷基板直接熔融之后形成的层片状共晶组织不同,其原因是管帽引脚镍层部分溶解进入δ/AuSn相所致,表明金锡共晶焊料与可伐管帽实现了有效焊接.
2.4 互连界面的热循环可靠性分析
对采用图7焊接曲线封装的管帽-基板进行检漏试验,试验条件如表4所示,检漏结果为合格.
表 4 密封检漏试验条件Table 4. Test conditions of leakage detection粗检漏 细检漏 按照GJB548B—2005方法1014. 2中C1规定进行试验,要求是器件粗检时应无同一位置出来的一串明显气泡或两个以上大气泡 按照GJB548B—2005方法1014. 2中A1规定进行试验,要求是器件细检漏率不大于5 × 10−3(Pa·cm3)/s 剪切力是衡量金锡焊料封接质量的另一项重要指标. 将器件固定在推力测试台上,平行于基板方向施加推力进行剪切力测试,测得管帽脱离推力分布在6 500 ~ 7 500 g,根据管帽封接环尺寸计算,其抗剪强度分布在41. 88 ~ 48. 32 MPa. 如图9所示,管帽推落端口焊缝规则完整,基板表面粘附层有拉扯脱落,表明金锡共晶封接质量较好.
对封装后的管帽-基板进行−55 ~ 85 ℃的热循环测试,试验按照GJB 548B—2005中方法1010. 1和下述规定进行,如表5所示. 在温度循环测试完成后,对封装的器件进行机械冲击测试,测试条件按照GJB 548B—2005中方法2002,即冲击力1 500 g,冲击方向为y1方向,冲击10次. 对经历温度循环和冲击测试后的器件,再次进行检漏,检漏结果器件合格,对其进行剪切力测试,抗剪强度保持在40 MPa以上,与试验前无明显改变. 图10是300次循环后界面的显微组织与元素分布.
表 5 温度循环试验条件Table 5. Test conditions of temperature cycle试验温度T/℃ 每步停留时间t1/min 冷热转换时间t2/min 循环次数N(次) −55 ~ 85 15 ≤1 100 表6是图10中Au-Sn互连层内的相分析结果. 由图10和表6可知,经历300次循环之后,互连界面的形态和组织并没有发生明显变化,Au-Sn互连层保持δ/(Au,Ni)Sn—ζ相—δ/(Au,Ni)Sn分层结构,在界面上并没有观察到疲劳裂纹,这表明采用金/锡/金电镀层,通过Au-Sn共晶反应实现CSP器件的金属管帽与陶瓷基板之间的封接是稳定可靠的.
表 6 图10中Au-Sn共晶层相成分(质量分数,%)Table 6. Au-Sn intermetallic compounds in Fig. 10位置 Au Sn Ni Co Fe 化合物 1 41.8 40.8 15.7 0.8 1.0 (Au,Ni)Sn 2 88.3 8.6 1.6 0.9 0.6 ζ 3 89.0 9.0 1.4 0.2 0.4 ζ 4 88.9 8.9 1.5 0.4 0.3 ζ 5 48.4 39.5 8.9 2.8 0.3 (Au,Ni)Sn 3. 结论
(1)分层电镀沉积法制备的金/锡/金镀层的质量,尤其是层厚度和层间的结合力,将会严重影响Au-Sn共晶焊料的封接质量.
(2)在焊接时,锡镀层首先熔化形成“熔池”,溶解上下两侧的金镀层,直至完成共晶反应生成δ/(Au,Ni)Sn—ζ相—δ/(Au,Ni)Sn分层组织结构.
(3)相比于保温时间,焊接温度对Au-Sn共晶焊料的封接结果影响更大,为了形成Au-Sn共晶组织,需要优化调整封装回流曲线.
(4)在HTCC基板上分层电镀金/锡/金,焊接温度在330 ℃,时间维持30 s时,Au-Sn共晶反应完全,实现可伐管帽与HTCC基板的可靠密封,该工艺稳定可靠,适合于批量化生产.
-
图 4 A1组别焊接接头金相组织与SEM图
Figure 4. Metallurgical structure and SEM diagram of welded joints in A1 group. (a) metallographic structure of welded zone; (b) metallographic structure of heat-affected zone; (c) metallographic structure of base metal; (d) SEM scanning diagram of welded zone; (e) SEM scanning diagram of heat-affected zone; (f) SEM scanning diagram of base metal
图 5 A4组别焊接接头金相与SEM图
Figure 5. Metallurgical structure and SEM diagram of welded joints in A4 group. (a) metallographic structure of welded zone; (b) metallographic structure of heat-affected zone; (c) metallographic structure of base metal; (d) SEM scanning diagram of welded zone; (e) SEM scanning diagram of heat-affected zone; (f) SEM scanning diagram of base metal
图 7 不同冷却条件时硬度分布曲线
Figure 7. Hardness distribution curve at different cooling conditions. (a) average hardness of base metal; (b) hardness distribution curve of welded joints at different initial cooling conditions; (c) hardness distribution curve of welded joints at different final cooling conditions
图 9 C4组别焊接接头金相与SEM图
Figure 9. Metallurgical structure and SEM diagram of welded joints in C4 group. (a) metallographic structure of welded zone; (b) metallographic structure of heat-affected zone; (c) metallographic structure of base metal; (d) SEM scanning diagram of welded zone; (e) SEM scanning diagram of heat-affected zone; (f) SEM scanning diagram of base metal
表 1 304不锈钢的化学成分(质量分数,%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of 304 stainless steel
C Mn Cr Ni Si Co Fe 0.054 0.956 18.18 10.21 0.325 0.236 余量 表 2 固溶处理工艺参数
Table 2 Solution treatment process parameters
序号 设备功率P/kW 固溶温度T/℃ A/C1 — — A2 505 890 A3 518 930 A4 528 970 A5 536 990 A6 540 1007 A7 557 1035 表 3 固溶处理工艺参数
Table 3 Solution treatment process parameters
序号 冷却条件 设备功率P/kW 固溶温度T/℃ B1 全开,不加水冷 505 890 B2 全开,加水冷 505 890 B3 接近关闭,不加水冷 505 890 B4 接近关闭,加水冷 505 890 表 4 固溶处理工艺参数
Table 4 Solution treatment process parameters
序号 设备功率P/kW 固溶温度T/℃ A/C1 — — C2 530 870 C3 567 980 C4 597 1035 C5 623 1050 C6 633 1083 C7 643 1120 表 5 扩口和压扁试验结果
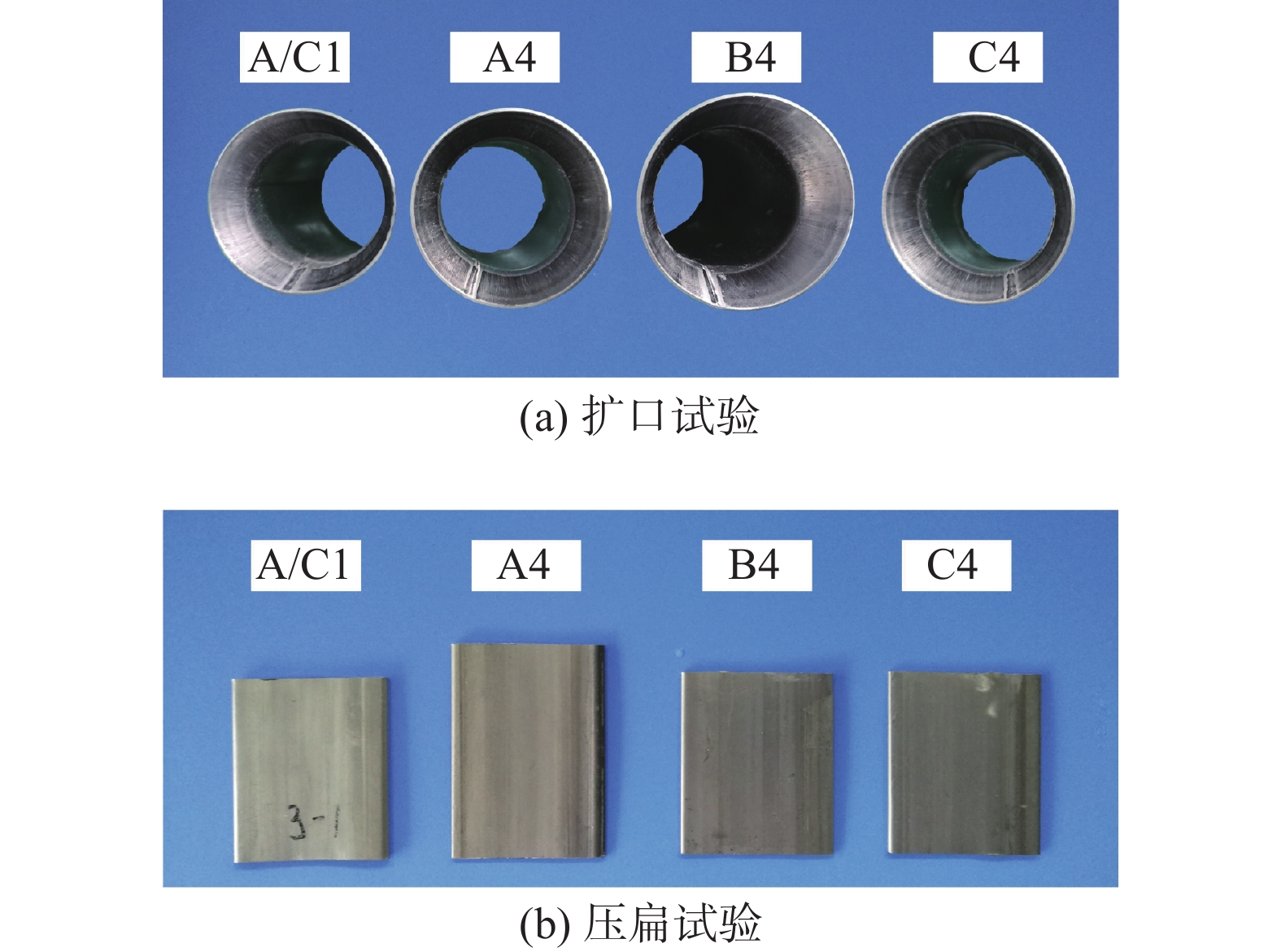
Table 5 Results of flaring and flattening test
组别 扩口率A(%) 扩口试验结果 压扁试验结果 A/C1 34.37 未出现裂纹 未出现裂纹 A4 37.50 未出现裂纹 未出现裂纹 B4 40.94 未出现裂纹 未出现裂纹 C4 37.50 未出现裂纹 未出现裂纹 -
[1] 王元清, 袁焕鑫, 石永久, 等. 不锈钢结构的应用和研究现状[J]. 钢结构, 2010, 25(2): 1 − 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2010.02.001 Wang Yuanqing, Yuan Huanxin, Shi Yongjiu, et al. Application and research status of stainless steel structure[J]. Steel Construction, 2010, 25(2): 1 − 12. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9963.2010.02.001
[2] 韩豫, 陈学东, 刘全坤, 等. 奥氏体不锈钢应变强化工艺及性能研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2012, 48(2): 6. Han Yu, Chen Xuedong, Liu Quankun, et al. Study of strain strengthening process and properties of austenitic stainless steel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(2): 6.
[3] 秦国梁, 马宏, 耿培皓, 等. 45钢/304不锈钢连续驱动摩擦焊接工艺[J]. 焊接学报, 2015, 36(8): 1 − 4. Qin Guoliang, Ma Hong, Geng Peihao, et al. 45 steel/304 stainless steel continuous drive friction welding process[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2015, 36(8): 1 − 4.
[4] 王延来, 刘世程, 刘德义, 等. 304奥氏体不锈钢固溶渗氮的研究[J]. 金属热处理, 2005, 30(5): 8 − 11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2005.05.003 Wang Yanlai, Liu Shicheng, Liu Deyi, et al. Study of solid solution nitriding of 304 austenitic stainless steel[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2005, 30(5): 8 − 11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-6051.2005.05.003
[5] Glage A, Weidner A, Biermann H. Cyclic deformation behaviour of three austenitic cast CrMnNi TRIP/TWIP steels with various ni content[J]. Steel Research International, 2011, 82(9): 1040 − 1047. doi: 10.1002/srin.201100080
[6] 刘巍. SA213-T P304奥氏体不锈钢固溶处理技术及应用[J]. 机械管理开发, 2014(4): 47 − 48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-773X.2014.04.016 Liu Wei. SA213-T P304 austenitic stainless steel solid solution treatment technology and applications[J]. Mechanical Management and Development, 2014(4): 47 − 48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-773X.2014.04.016
[7] 周慧, 李锡栋. 固溶处理对304不锈钢显微组织及力学性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2018, 47(24): 234 − 235. Zhou Hui, Li Xidong. Effect of solid solution treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 304 stainless steel[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2018, 47(24): 234 − 235.
[8] 史勤益, 颜余仁, 赵先锐, 等. 304奥氏体不锈钢的热处理工艺研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2011, 11(24): 5910 − 5913. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2011.24.039 Shi Qinyi, Yan Yuren, Zhao Xianrui, et al. Heat treatment process study of austenitic stainless steel[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2011, 11(24): 5910 − 5913. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2011.24.039
[9] 郭国林, 刘鹏, 杨莉, 等. 热处理对304不锈钢板激光焊接接头组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 热加工工艺, 2016, 45(21): 194 − 196. Guo Guolin, Liu Peng, Yang Li, et al. The effect of heat treatment on the organization and mechanical properties of laser welded joints of 304 stainless steel sheet[J]. Hot Working Technology, 2016, 45(21): 194 − 196.
[10] 唐峰. 热处理工艺对管用304不锈钢组织与性能的影响[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2016. Tang Feng. The effect of heat treatment process on the organization and properties of 304 stainless steel for pipes[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2016.
[11] 熊剑. 304不锈钢K-TIG焊电弧特性及接头性能研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2019. Xiong Jian. Study of K-TIG welding arc characteristics and joint performance of 304 stainless steel[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2019.
[12] Lippod J C, Savage W F. Solidification of austenitic stainless steel weldments: part 2 - the effect of alloy composition on ferrite morphology[J]. Welding Journal, 1980, 59(2): 48s − 58s.
[13] EI-Batahyg A M. Effect of laser welding parameters on fusion zone shape and solidification structure of austenitic stainless steels[J]. Materials Letters, 1997, 32(2-3): 155 − 163. doi: 10.1016/S0167-577X(97)00023-2
[14] Christensen R M, Lo K H. Solutions for effective shear properties in three phase sphere and cylinder models - ScienceDirect[J]. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 1979, 27(4): 315 − 330. doi: 10.1016/0022-5096(79)90032-2
[15] 王国强. 中厚板304不锈钢等离子弧焊接接头组织和性能的研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2019. Wang Guoqiang. Study on the organization and properties of plasma arc welded joints of 304 stainless steel in medium thickness plate[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2019.
[16] 孙伟, 王萍. 固溶处理对新型奥氏体不锈钢焊接接头性能的影响[J]. 电焊机, 2010(2): 128 − 131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2303.2010.02.031 Sun Wei, Wang Ping. Effect of solid solution treatment on the properties of new austenitic stainless steel welded joints[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2010(2): 128 − 131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2303.2010.02.031
[17] Ma H, Qin G, Geng P, et al. Effect of post-weld heat treatment on friction welded joint of carbon steel to stainless steel[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2016, 277: 24 − 33.
[18] 上海市热处理协会. 实用热处理手册[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2009. Shanghai Heat Treatment Association. Practical heat treatment handbook[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2009.
-
期刊类型引用(16)
1. 周金旭,祝哮,田春雨,叶树茂,恒俊楠. 6061铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头组织特征与力学性能研究. 铝加工. 2024(05): 65-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘杰,屈志军,遇境润. 装配间隙对铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头力学性能的影响. 焊接. 2023(05): 29-34+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘秀如,吴厦,陈大军,闫慧敏,张薇,付扬帆. 薄板铝合金搅拌摩擦焊的组织与力学性能. 兵器装备工程学报. 2023(11): 229-234 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 郁志凯,梁晨,毛孟颖,钮旭晶. 动车组连接板搅拌摩擦焊及熔化焊接头性能研究. 电焊机. 2022(10): 62-71 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 姜银松,叶卫林,靳少龙,邵真贵,高蒙,付静. 2A43高强度硬铝合金焊接性能研究. 电焊机. 2022(12): 91-95+102 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 秦丰,周军,侯振国,钮旭晶. 6082铝合金双面搅拌摩擦焊接头组织与性能. 焊接学报. 2021(02): 75-80+102 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 周平,戴启雷,张元杰. 根部缺陷对搅拌摩擦焊接头拉伸性能影响. 焊接. 2021(04): 52-56+64 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 宫文彪,朱芮,郄新哲,崔恒,宫明月. 6082铝合金超厚板搅拌摩擦焊接头组织与性能. 吉林大学学报(工学版). 2020(02): 512-519 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 史学海,吕赞,胡云瑞,王留芳. 冷-热源辅助对FSW残余应力影响的数值模拟. 精密成形工程. 2020(02): 55-60 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 尹欣. 工艺参数对铝合金FSW接头性能的影响. 机械工程与自动化. 2020(06): 114-115+118 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 张欣盟,何广忠,王贝贝,薛鹏,肖伯律,倪丁瑞,马宗义. 6082-T6铝合金填料搅拌摩擦焊工艺. 电焊机. 2020(12): 54-58+111 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 张欣盟,何广忠,王贝贝,杨超,薛鹏,倪丁瑞,马宗义. 氧化膜对6082铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头疲劳性能的影响. 材料研究学报. 2019(04): 299-305 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 郝云飞,毕煌圣,淡婷,郝志斌,王国庆. 搅拌针偏置对SR-FSW焊缝界面残留缺陷及接头力学性能的影响. 焊接学报. 2019(05): 30-35+162 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 邵帅,黄永德,陈玉华. 钛合金搅拌摩擦焊搅拌头研究现状. 精密成形工程. 2019(05): 115-122 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 孙大森,张志强,凌晨,何长树. 6082-T6铝合金FSW接头分层晶间腐蚀行为研究. 电焊机. 2019(11): 58-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 朱海,孙朝伟,孙金睿,张剑,于明玉. 2024铝合金搅拌摩擦焊工艺参数对焊接质量的影响研究. 热加工工艺. 2019(23): 159-162 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)




 下载:
下载: