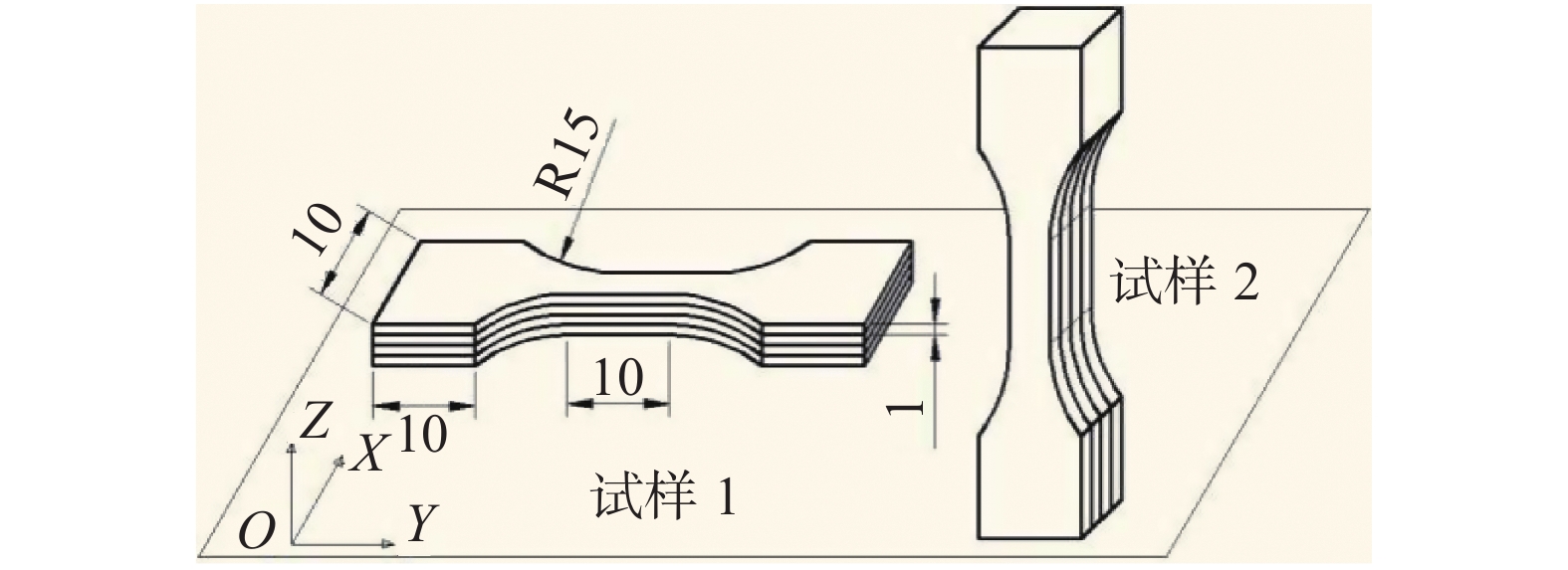
Study on special grain boundary distribution of Σ3n in micron selective laser melting of 316L stainless steel during tensile deformation
-
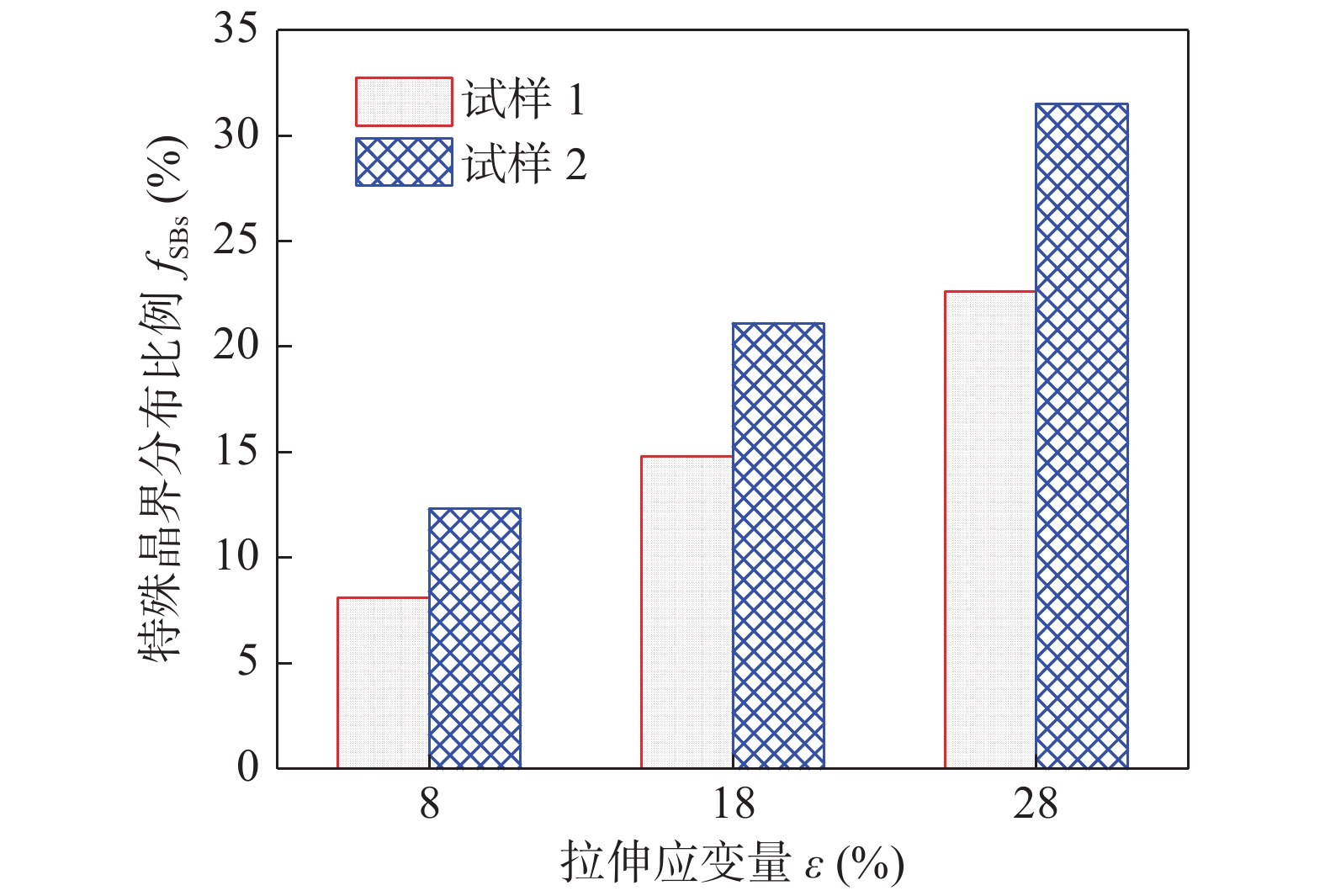
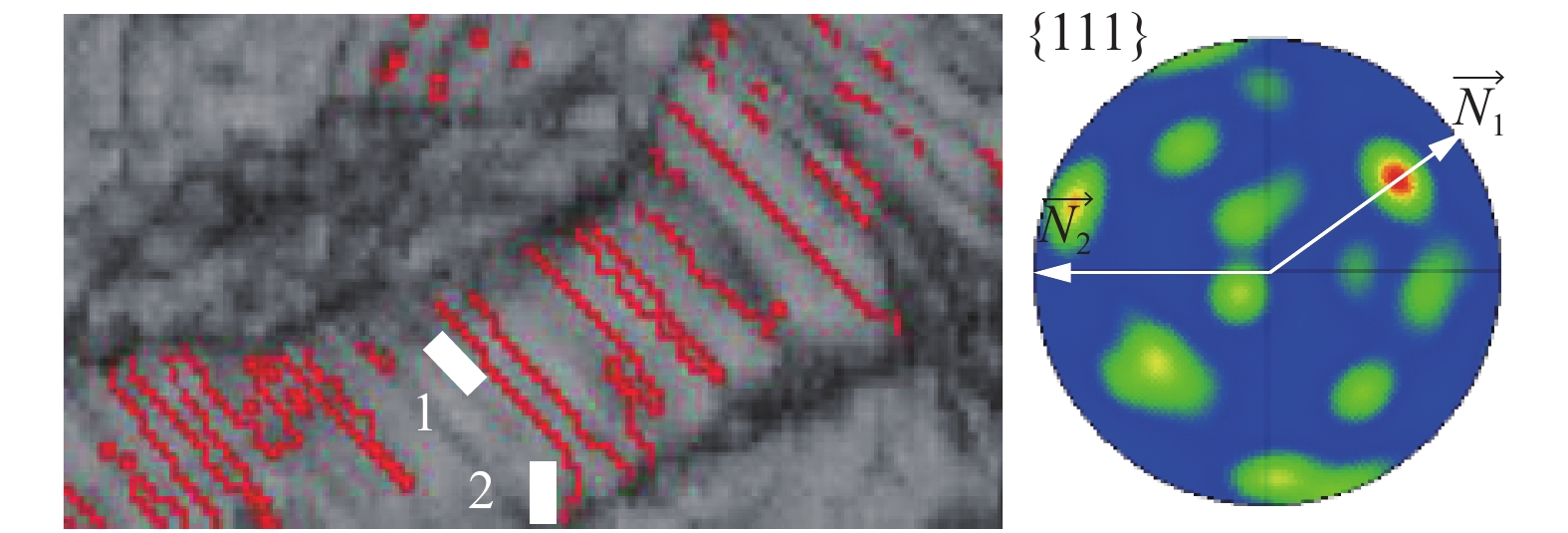
摘要: 利用电子背散射衍射(EBSD)技术研究了微米级选区激光熔化制备316L不锈钢横向拉伸试样和法向拉伸试样在8%、18%和28%拉伸应变下的晶界特征分布. 结果表明,随着拉伸应变的增加,横向试样和法向试样的Σ3晶界比例显著增加,Σ9 + Σ27晶界比例明显降低. Σ3晶界有效隔断了一般大角度晶界的贯通性. 通过微矩形截面法对Σ3特殊晶界的共格/非共格特征进行测定,其中,横向试样在18%拉伸应变下以Σ3IC为主,约占60%,而法向拉伸试样在同样条件下以Σ3C为主,约占73%. 进一步分析指出,非共格Σ3IC晶界的迁移并与Σ9晶界的汇合是促进拉伸应变过程中Σ3特殊晶界比例升高的原因.Abstract: In this paper, electron back scatter diffraction (EBSD) technique was used to study the grain boundary characteristic distribution of 316L stainless steel transverse tensile samples and normal tensile samples prepared by micron selective laser melting under 8%, 18% and 28% tensile strain. The results show that with the increase of tensile strain, the proportion of Σ3 grain boundaries of transverse and normal samples increased significantly, while the proportion of Σ9 and Σ27 grain boundaries decreased significantly. The connectivity of general high angle grain boundary network was effectively interrupted by Σ3 grain boundaries. The coherent/incoherent characteristics of special grain boundaries were measured by micro rectangular section method. When the transverse specimen was under 18% tensile strain, the special grain boundaries were mainly Σ3IC, accounting for about 60%. Under the same conditions, the special grain boundaries of normal tensile specimen were mostly Σ3C, accounting for about 73%. Further analysis pointed out that the migration of incoherent Σ3IC grain boundaries and the interaction with Σ9 grain boundaries were the reasons for the increase of the proportion of Σ3 special grain boundaries during the tensile strain.
-
Keywords:
- selective laser melting /
- 316L /
- plastic deformation /
- Σ3n grain boundary
-
0. 序言
在冶金、汽车、航空航天等工业领域中存在许多用于重载、高速、缺氧等环境下运行的摩擦运动副零部件,如柱塞泵缸体、气缸套、叶片等,在这样较为恶劣的工况下,摩擦运动副表面极易磨损,导致相关机构及零部件损毁失效,因此提高其表面耐磨减摩性具有重要意义[1-2].
金属基自润滑复合材料是以金属为主体,加入固体润滑材料以及一些附加成分,并经过适当的工艺所制备出来,综合了金属板材的力学性能和固体润滑材料优异的润滑性能,具有良好的摩擦学特性,可适应上述等特殊工况下的工作[3].几种常用的表面涂层技术,例如等离子喷涂、化学镀、激光熔覆均可以用来制备复合涂层,其中激光熔覆拥有能量密度高、热影响区小、基材与涂层良好的冶金结合等特点,具有明显的优势[4].目前金属基自润滑涂层以Ni基,Co基,Fe基等合金材料应用较为广泛,其中Ni基合金相较于Fe基合金有着更优的耐蚀性及抗氧化性,在高温性能方面不如Co基合金,但在Ni基中加入合适元素在高温下依然能维持良好抗氧化性能[5].Zhang等人[6]采用激光熔覆技术在45号钢表面制备了无裂纹的Ni60涂层,结果表明,涂层的显微硬度约为基体的2.6倍,且磨损率约为基体的磨损率的1/6.2,磨损性能得到了显著提升,但纯Ni基涂层的硬度及耐磨性往往还达不到实际工况的要求.为了提高表面的耐磨和耐腐蚀性能,涂层中通常会添加TiC,WC,SiC等作为增强相,而SiC具有硬度高、耐磨耐蚀、热膨胀系数小等一系列优点[7].二硫化钼MoS2与石墨和六方氮化硼一样为层状结构[8],其晶体由共价键合的薄片堆叠而成,片与片之间为弱范德华相互作用,因此具有较低的摩擦系数,特别是在缺氧及干燥环境下,可以长时间保持优异的自润滑性能.Zhai等人[9]采用激光熔覆技术在45号钢表面研究了不同MoS2添加量对熔覆层组织和耐磨减摩性能影响,结果表明,随MoS2含量增加,微观组织细化,摩擦系数先减小后增大,当MoS2含量为5%时,摩擦系数降幅最大,磨损量最小,耐磨性能比45号钢基体提高了79%.这里将SiC的耐磨特性与MoS2的自润滑特性相结合,对所制得的复合涂层的摩擦学性能会有重要影响.由于MoS2与金属的润湿性差且熔点低,在激光照射过程中容易烧损或以飞溅的形式流失,导致在涂层中沉积率降低,而软金属铜具有优异的润滑性能,可与MoS2进行组合润滑且Cu对激光的吸收率高[10],一定程度上可减小熔敷过程中的飞溅,二者可予以结合来缓解MoS2损失. Shin等人[11]通过磁控溅射在 Si 晶片和 AISI 304 基板上制备三元 Mo-Cu-N 涂层,发现随着Cu含量的增加,Mo-Cu-N 涂层的平均摩擦系数从 0.40 降低到 0.21.作为一种润滑剂,铜的添加可以在很宽温度范围内降低摩擦系数,同时铜在镍基合金中具有良好的润湿性[12],可以完全溶解在镍基中形成固溶体.将nano-Cu包覆于MoS2表面来提高与镍基合金的相容性,和MoS2粉末沉积率不失为一种有效方法.目前关于使用纳米铜包覆MoS2的激光熔覆复合涂层自润滑性能的数据很少,文中采用纳米Cu包覆MoS2,旨在提高MoS2与镍基合金的相容性,使涂层具有耐磨性质的同时亦能降低摩擦系数达到减摩效果,并讨论了不同润滑剂含量对复合涂层组织和摩擦磨损性能的影响.
1. 试验方法
基板材料为42CrMo钢板,试样尺寸为ϕ150 mm × 10 mm,试验前先用砂纸将基板表面打磨处理去除表面氧化膜,再用丙酮去除油渍、酒精清洗,熔覆材料选用目数均为300的Ni60,SiC和MoS2粉末,以及500 nm的高纯铜粉,Ni60自熔性合金粉末的化学成分见表1.
表 1 Ni60合金粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Chemical compositions of Ni60 alloy powderCr B C Si Fe Ni 16 3.3 0.9 4.5 ≤8.0 余量 将MoS2与nano-Cu按1∶2的体积比通过高能球磨方式进行球磨,球料比10∶1,持续1小时,以确保nano-Cu包覆的均匀性.图1为Ni60和nano-Cu/MoS2粉末的形貌,证明纳米铜颗粒包覆在MoS2颗粒的表面,其次,将不同质量百分比的Ni60,SiC和nano-Cu/MoS2粉末进行低速球磨混合,详细配比可见表2.
表 2 不同熔覆层合金粉末的化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 2. Chemical compositions of alloy powder for different cladding layers样品编号 Ni60 SiC Nano-Cu/MoS2 C1 90 10 — C2 85 10 5 C3 80 10 10 C4 75 10 15 采用预置粉末法,利用刮刀将混合粉末平铺在基板表面并放入干燥箱100 ℃下预热1 h,使用LWS-1000型Nd∶YAG激光器在气流量为11 L/min的氩气保护下进行激光熔覆,工艺参数为激光功率290 W、扫描速度6 mm/s、光斑直径1 mm,熔覆后将试样沿横截面切割,对切割后的试样打磨、抛光,再用50%的王水溶液腐蚀,腐蚀时间为15 s,采用Regulus8230型扫描电子显微镜及能谱(energy dispersive spectrometer,EDS)对熔覆样进行微观组织和成分分析,采用X'Pert PRO MPD型X射线衍射仪对熔覆层进行物相检测,使用VTD401数显显微维氏硬度计测量熔覆层的硬度分布,载荷为0.49 N,加载时间为10 s,采用推力垫圈试验机进行摩擦磨损试验,摩擦磨损试验前在熔覆层切取圆柱试样,尺寸为ϕ 10 mm × 10 mm,对磨副材料选用Cr12钢,硬度达到64 HRC,形状为ϕ 20 mm × 5 mm的圆片.试验在室温下进行,载荷为50 N,摩擦线速度为25 mm/s,磨损时间为20 min,磨损质量用精度为10−4 g电子称测量.
2. 试验结果与讨论
2.1 物相及显微组织分析
图2为4种不同含量nano-Cu/MoS2镍基合金熔覆层的XRD图谱,由图2结果可知,不加nano-Cu/MoS2时熔覆层中主要的物相为(Fe,Ni),碳铬化合物Cr7C3和CrB硼铬化合物并未显示出明显的SiC峰,这是由于激光熔覆产生的熔池温度高,使得SiC粉末在熔池对流中发生分解,形成C,Si,同时与镍基合金粉末中B,Cr,Fe形成新的具有高硬度的Cr7C3,CrB等硬质相.当加入nano-Cu/MoS2后,熔覆层产生了CrS,Cu和MoNi等新相,随着含量从5%、10%、15%增加相应的峰得到了明显的增强而未检测到明显的MoS2峰,可能高温下分解成了S和Mo. XRD表明润滑剂的加入会和镍基合金以及基体元素发生复杂的化学反应,润滑剂分解出的S和Mo分别和Cr,Ni等元素生成了CrS,MoNi等化合物,包覆的润滑剂加入对熔覆层物相新添了硫化物和软金属铜.
图3为不同含量nano-Cu/MoS2镍基合金熔覆层的微观组织形貌.熔覆层的区域可分为上部区域和接近熔合线的中下部区域,其上部区域主要由细密等轴晶组成,而中下部多由方向各异的条柱状晶构成,这是由于激光熔覆具有热输入大冷却速度快的优点,靠近熔合线的中下部温度梯度与冷却速度比值高促进了条柱状晶生成,反之顶部区域比值较低晶粒迅速形核后未来得及长大便已凝固形成了细小等轴晶粒.图3(a)为不含nano-Cu/MoS2熔覆层的中部区域组织,在条状晶间布满丰富的细晶以及部分枝晶,无裂纹无孔隙且组织致密.结合XRD的结果可知,SiC粉末在高温下分解形成的C,Si元素与镍基合金粉末中B,Cr,Fe元素形成了新的具有高硬度的Cr7C3,CrB等相对组织具有显著细化作用.采用EDS分析图3(a)~图3(f)中细晶粒块A化学成分见表3,该细晶组织富含Fe,Cr,Ni,可能由γ-Ni细晶和枝晶多元共晶组成且晶界处存在Cr,Ni偏聚.另外,图3中A ~ E区域细晶组织的Fe元素含量远高于预设,说明在激光熔覆的高温下,基体中的Fe元素扩散进熔池对覆层元素产生了明显的稀释,这与表3能谱结果相吻合.图3(b) ~ 图3(d)中nano-Cu/MoS2含量分别为5%、10%、15%熔覆层的显微组织发生了明显变化,排列紧密的一部分细晶逐渐转变为条带状组织,这是质软的润滑相加入影响了组织的生长分布.图3(g) ~ 图3(i)为nano-Cu/MoS2含量15%熔覆层,图3(d)中Cu,S,Mo分布状况,可知S,Mo分布区域基本一致,分析认为是留存的MoS2,由于基体Fe元素进入覆层较多导致稀释率较高,因此XRD图谱中未显示出明显的MoS2谱峰.图3(b)可以看出,除了平行分布的条带状组织和块状细晶组织在晶界处圈出区域还存在较少的黑色点状区域,初步猜测可能是熔覆过程中部分MoS2分解产生的SO2气体未及时溢出形成的气孔.随着润滑相含量增加,图3(c) ~ 图3(f)覆层组织中黑点增多如框选区域,但数量较少.采用EDS对图3(e)高倍下即图3(f)黑点区域分析其成分见表3中E所示,该区域富集S、Mo元素,根据元素分布规律及含量,应是未熔留存的MoS2.
![]() 图 3 不同含量nano-Cu/MoS2显微组织及区域EDS元素分布Figure 3. Microstructure and regional EDS element distribution of nano-Cu/MoS2 cladding layer with different content. (a) middle of C1; (b) middle of C2; (c) middle of C3; (d) middle region of C4; (e) top region of C4; (f) top region of C4 at high magnification; (g) Cu distribution in C4; (h) S distribution in C4; (i) Mo distribution in C4表 3 C1~C4不同区域的EDS分析结果(质量分数, %)Table 3. Results of EDS analysis for different regions of C1 ~ C4
图 3 不同含量nano-Cu/MoS2显微组织及区域EDS元素分布Figure 3. Microstructure and regional EDS element distribution of nano-Cu/MoS2 cladding layer with different content. (a) middle of C1; (b) middle of C2; (c) middle of C3; (d) middle region of C4; (e) top region of C4; (f) top region of C4 at high magnification; (g) Cu distribution in C4; (h) S distribution in C4; (i) Mo distribution in C4表 3 C1~C4不同区域的EDS分析结果(质量分数, %)Table 3. Results of EDS analysis for different regions of C1 ~ C4区域 B C Si S Fe Ni Cr Mo Cu A 4.29 9.04 1.49 — 76.12 6.32 2.73 — — B 2.54 9.8 1.47 — 77.40 6.35 2.43 — — C — 8.15 1.43 0.01 73.36 10.53 6.07 — 0.45 D — 6.31 1.38 0.03 81.65 6.93 2.76 0.13 0.82 E — 10.31 1.30 0.07 76.44 8.11 3.19 0.26 0.31 2.2 显微硬度分析
图4为不同nano-Cu/MoS2含量的镍基熔覆层显微硬度沿深度的变化.可以看到,在基板表面制备金属基镍基复合熔覆层可以显著提升其表面硬度,从涂层表面到基体界面硬度呈下降的趋势,符合涂层中相的分布. C1 ~ C4表面平均硬度分别486.52,377.42,369.92,342.46HV0.1,约为母材的1.45 ~ 2.06倍(母材约为236.62 HV0.1). 无nano-Cu/MoS2的熔覆层C1显微硬度与C2 ~ C4比明显要高,添加的SiC颗粒在熔池中会分解成C与Si,C与Cr,Fe形成高硬度的Cr7C3等新相弥散在熔覆层中起到第二相强化作用,提高了涂层的硬度.
此外,由覆层表面至熔合线附近硬度呈下降趋势,结合前面对显微组织的分析可知,沿深度方向硬度不同是由于激光熔覆具有快速结晶冷却的特点.在温度梯度与凝固速度比值的影响下覆层顶部主要为细密的等轴晶组成,中下部由方向各异的条状晶形成,由于细晶强化的作用导致顶部的硬度要高于熔覆层的底部.另一方面,由于稀释率的影响,基体大量Fe元素扩散进熔池的底部也会降低覆层中下部的显微硬度.而当引入润滑相nano-Cu/MoS2时,相比C1,C2 ~ C4熔覆层整体硬度值发生了显著下降,随着润滑相含量增加可见熔覆层硬度有所降低.这是因为覆层的显微硬度与其硬质相含量有着密切联系,质地较软的nano-Cu/MoS2 加入导致涂层的整体硬度下降,另外,高温下MoS2分解出的S元素同基体与Ni60中的Cr结合生成的铬的硫化物亦是一种对硬度不利的相.
2.3 摩擦磨损性能
对C1 ~ C4不同含量nano-Cu/MoS2的镍基合金熔覆层在室温下进行了摩擦磨损试验,表4为C1 ~ C4熔覆层的摩擦系数及磨损失重情况,对比表4中C1 ~ C4组的磨损失重和摩擦系数发现,随着nano-Cu/MoS2含量增加,其质量损失呈上升趋势,摩擦系数逐渐减小,耐磨性能有所降低并表现了一定的减摩性能.图5为试验后不同涂层表面SEM,其中C1涂层表面的磨痕窄而浅见图5(a),留下了一些深浅不一的犁沟,这是由涂层中硬质颗粒脱落磨削所造成的主要表现为磨粒磨损,此时磨损失重最小,为0.008 4 g,摩擦系数为0.517 5,具有良好耐磨性. 当加入nano-Cu/MoS2从5%、10%增加到15%时,质量损失分别为0.014 7、0.017 3和0.019 8,覆层失重增加而滑动摩擦系数逐渐减小,到C4的摩擦系数为0.443 0.一方面由Archard定律可知[13],材料硬度与其耐磨性能呈正相关,硬度较高时具有良好的抗塑性变形能力,质地较软的润滑剂加入降低了涂层的硬度,在载荷不变的情况下失重相对增加. 图5(b) ~ 图5(d)中C2 ~ C4磨损表面均黏着了一些摩擦产物,这是因为随着nano-Cu/MoS2含量增加,覆层里弥散的软金属铜和未熔化的MoS2以及新生成的硫化物变多,在摩擦时覆层接触面产生形变,弥散分布的Cu和MoS2脱落黏附在摩擦面与磨粒混合逐渐形成一层具减摩效果的润滑薄膜,阻止了与摩擦副间的直接接触的同时有一定润滑作用,降低了摩擦系数,表现为黏着磨损和磨粒磨损结合的复合磨损. 从C2到C4硬度逐渐降低而此时相对应的质量损失增加,可见覆层硬度对磨损失重有重要影响,硬度越高质量损失越低.上述探究表明,nano-Cu/MoS2镍基合金熔覆层确实具有明显耐磨、减摩效果,C4虽然摩擦系数最低但摩擦质量损失较多且力学性能相对较差,而C3具有一定减摩效果同时兼具较高的硬度,综合涂层的力学性能和摩擦系数及磨损质量损失情况,优选制备参数为10%nano-Cu/MoS2.
表 4 不同nano-Cu/MoS2含量熔覆层的摩擦系数及磨损量(质量损失)Table 4. Friction factor and wear loss of cladding layers with different nano-Cu/MoS2 contents式样
编号试验前重量
m1/g试验后质量
m2/g质量损失
Δm /g摩擦系数
µC1 5.455 7 5.447 3 0.008 4 0.517 5 C2 5.390 2 5.375 5 0.014 7 0.498 5 C3 4.301 9 4.284 6 0.017 3 0.479 3 C4 5.413 9 5.394 1 0.019 8 0.443 0 3. 结论
(1)采用激光熔覆技术制备了镍基合金复合涂层,熔覆层成型良好且组织致密,其中上部区域主要由细密等轴晶组成,中下部由方向各异的条柱状晶组成,与基体实现了冶金结合,加入质软的nano-Cu/MoS2后涂层组织发生明显变化,部分细晶转变为条带状,晶界附近分布一些细小黑色颗粒MoS2.
(2)激光熔覆过程中nano-Cu/MoS2粉末基本分解为相应的元素,仅有部分进入熔覆层,分解形成的Mo,S元素,与合金粉末产生新的化学反应,其中的S与Cr形成硫化物CrS并引入了新相软金属Cu,同时由于nano-Cu的包覆作用使得少量MoS2留存并弥散分布在晶界附近,而金属硫化物及残留MoS2和软金属铜的存在加上部分组织的粗化,使得覆层的硬度有一定的下降.
(3)随着润滑相nano-Cu/MoS2含量的增加,金属硫化物及残留MoS2和软金属铜的量增多,加上部分组织晶粒的粗化影响,使得熔覆层硬度相比未添加前有所降低,但与基体硬度相比约有1.45 ~ 2.06倍,仍然表现了较好的力学性能,而随着硬度降低相对应的摩擦质量损失也会增加,但同时覆层的减摩性能获得提升,摩擦系数逐渐降低.
(4) nano-Cu/MoS2镍基合金熔覆层确实具有明显耐磨、减摩效果,综合摩擦系数和摩擦质量损失考虑,激光熔覆层制备参数组合为10%nano-Cu/MoS2,激光功率290 W、扫描速度6 mm/s时其熔覆层力学及摩擦学性能为佳.
-
表 1 316L不锈钢粉末的化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 1 Chemical composition of 316L stainless steel powder
C Si Mn S P Cr Ni N O Fe 0.02 0.22 1.58 <0.006 <0.008 18.02 13.82 0.078 <0.015 余量 编号 角度公差θ(°) 晶界特征 编号 角度公差θ(°) 晶界特征 6b-1 + 2 C 6b-16 − 7 IC 6b-2 − 5 IC 6b-17 + 8 IC 6b-3 + 5 IC 6b-18 − 5 IC 6b-4 + 9 IC 6b-19 + 1 C 6b-5 + 1 C 6b-20 + 1 C 6b-6 − 2 C 6b-21 + 5 IC 6b-7 + 5 IC 6b-22 − 4 IC 6b-8 − 6 IC 6b-23 + 7 IC 6b-9 + 4 IC 6b-24 − 6 IC 6b-10 − 2 C 6b-25 − 4 IC 6b-11 0 C 6b-26 + 3 C 6b-12 + 2 C 6b-27 + 1 C 6b-13 − 8 IC 6b-28 − 4 IC 6b-14 + 5 IC 6b-29 0 C 6b-15 − 3 C 6b-30 − 5 IC 编号 角度公差θ(°) 晶界特征 编号 角度公差θ(°) 晶界特征 7b-1 + 2 C 7b-16 0 C 7b-2 − 3 C 7b-17 + 3 C 7b-3 + 1 C 7b-18 − 2 C 7b-4 − 5 IC 7b-19 + 4 IC 7b-5 + 3 C 7b-20 + 4 C 7b-6 − 2 C 7b-21 − 6 IC 7b-7 + 5 IC 7b-22 + 1 C 7b-8 − 3 C 7b-23 + 2 C 7b-9 + 1 C 7b-24 − 2 C 7b-10 + 7 IC 7b-25 − 3 C 7b-11 − 1 C 7b-26 + 1 C 7b-12 0 C 7b-27 + 5 IC 7b-13 + 2 C 7b-28 − 5 IC 7b-14 + 5 IC 7b-29 0 C 7b-15 − 3 C 7b-30 − 1 C -
[1] 兰红波, 李涤尘, 卢秉恒. 微纳尺度3D打印[J]. 中国科学:技术科学, 2015, 45(9): 919 − 940. doi: 10.1360/N092014-00397 Lan Hongbo, Li Dichen, Lu Bingheng. Micro-and nanoscale 3D printing[J]. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2015, 45(9): 919 − 940. doi: 10.1360/N092014-00397
[2] Liu G, Zhang X F, Chen X L, et al. Additive manufacturing of structural materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering:R:Reports, 2021, 145: 100596. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2020.100596
[3] Gunasekaran J, Sevvel P, Solomon I J. Metallic materials fabrication by selective laser melting: A review[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings, 2020, 37: 252 − 256.
[4] 金鑫源, 兰亮, 何博, 等. 选区激光熔化成形金属零件表面粗糙度研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(3): 3168 − 3175. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19100109 Jin Xinyuan, Lan Liang, He Bo, et al. A review on surface roughness of metals parts fabricated by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Reports, 2021, 35(3): 3168 − 3175. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19100109
[5] 张楠, 张海武, 王淼辉. 微米级选区激光熔化316L不锈钢的拉伸力学性能[J]. 金属学报, doi:10.11900/0412.1961.2022.00041 Zhang Nan, Zhang Haiwu, Wang Miaohui. Tensile mechanical properties of micron-selective laser melted 316L stainless steel [J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, doi:10.11900/0412.1961.2022.00041
[6] Fu Jin, Qu Shuo, Ding Junhao, et al. Comparison of the microstructure, mechanical properties and distortion of stainless steel 316 L fabricated by micro and conventional laser powder bed fusion[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2021, 44: 102067. doi: 10.1016/j.addma.2021.102067
[7] 余晨帆, 赵聪聪, 张哲峰, 等. 选区激光熔化316L不锈钢的拉伸性能[J]. 金属学报, 2020, 56(5): 683 − 691. Yu Chenfan, Zhao Congcong, Zhang Zhefeng, et al. Tensile properties of selective laser melted 316L stainless Steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2020, 56(5): 683 − 691.
[8] Salman O O, Gammer C, Chaubey A K, et al. Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and mechanical properties of 316L steel synthesized by selective laser melting[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2019, 748: 205 − 212.
[9] Liu L F, Ding Q Q, Zhong Y, et al. Dislocation network in additive manufactured steel breaks strength–ductility trade-off[J]. Materials Today, 2018, 21(4): 354 − 361. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2017.11.004
[10] Watanabe T. An approach to grain boundary design of strong and ductile polycrystals[J]. RES Mechanica, 1984, 11(1): 47 − 84.
[11] Shimada M, Kokawa H, Wang Z J, et al. Optimization of grain boundary character distribution for intergranular corrosion resistant 304 stainless steel by twin-induced grain boundary engineering[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(9): 2331 − 2341. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00064-2
[12] Brandon D G. The structure of high-angle grain boundaries[J]. Acta Metallurgica, 1966, 14(11): 1479 − 1484. doi: 10.1016/0001-6160(66)90168-4
[13] 张坤, 王卫国, 方晓英, 等. 不同温度轧制Pb-Ca-Sn-Al合金高温退火后的晶界特征分布[J]. 金属学报, 2008, 44(6): 652 − 658. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2008.06.003 Zhang Kun, Wang Weiguo, Fang Xiaoying, et al. Grain Boundary character at elevated temperature after rolled at different temperatures[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica[J], 2008, 44(6): 652 − 658. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2008.06.003
[14] 王卫国, 周邦新, 冯柳, 等. 冷轧变形Pb-Ca-Sn-Al合金在回复和再结晶过程中的晶界特征分布[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(7): 715 − 721. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2006.07.008 Wang Weiguo, Zhou Bangxin, Feng Liu, et al. Grain boundary character distributions (GBCD) of cold-rolled Pb-Ca-Sn-Al alloy[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(7): 715 − 721. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0412-1961.2006.07.008
[15] Reed B W, Kumar M. Mathematical methods for analyzing highly-twinned grain boundary networks[J]. Scripta Materialia, 2006, 54(06): 1029 − 1033. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.11.045
[16] Kumar M, Schwartz A J, King W E. Microstructural evolution during grain boundary engineering of low to medium stacking fault energy FCC materials[J]. Acta Materialia, 2002, 50(10): 2599 − 2612. doi: 10.1016/S1359-6454(02)00090-3
[17] Randle V, Hu Y. The role of vicinal Σ3 boundaries and Σ9 boundaries in grain boundary engineering[J]. Journal of Materials Science, 2005, 40: 3243 − 3246. doi: 10.1007/s10853-005-2692-2
[18] 方晓英, 王卫国, 郭红, 等. 304不锈钢冷轧退火∑3 n特殊晶界分布研究[J]. 金属学报, 2007, 43(12): 1239 − 1244. Fang Xiaoying, Wang Weiguo, Guo Hong, et al. ∑3n special boundary distributions of the cold-rolled and annealed 304 stainless steel[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2007, 43(12): 1239 − 1244.
[19] 祁斌, 刘玉德, 石文天, 等. 脉冲式激光选区熔化成形搭接率的研究[J]. 激光技术, 2018, 42(3): 311 − 317. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.03.005 Qi Bin, Liu Yude, Shi Wentian, et al. Study on overlap ratio of pulse laser selective melting forming[J]. Laser Technology, 2018, 42(3): 311 − 317. doi: 10.7510/jgjs.issn.1001-3806.2018.03.005
[20] 马英怡, 刘玉德, 石文天, 等. 扫描速度对选区激光熔化316L不锈钢粉末成形缺陷及性能的影响[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(10): 210 − 219. Ma Yingyi, Liu Yude, Shi Wentian, et al. Effect of scanning speed on forming defects and Properties of Selective Laser Melted 316L Stainless Steel Powder[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(10): 210 − 219.
[21] 石文天, 王朋, 刘玉德, 等. 选区激光熔化成形316L表面质量及工艺试验研究[J]. 表面技术, 2019, 48(3): 257 − 267. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2019.03.035 Shi Wentian, Wang Peng, Liu Yude, et al. Experimental Study on Surface Quality and Process of Selective Laser Melting Forming 316L[J]. Surface Technology, 2019, 48(3): 257 − 267. doi: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2019.03.035
[22] Afkhami S, Dabiri M, Piili H, et al. Effects of manufacturing parameters and mechanical post-processing on stainless steel 316L processed by laser powder bed fusion[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2021, 802: 140660.
[23] Kumar P, Jayaraj R, Suryawanshi J, et al. Fatigue strength of additively manufactured 316L austenitic stainless steel[J]. Acta Materialia, 2020, 199: 225 − 239. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2020.08.033



 下载:
下载: