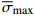Microstructure and mechanical properties of T-type friction stir welded SiCp/2009Al composite matrix material
-
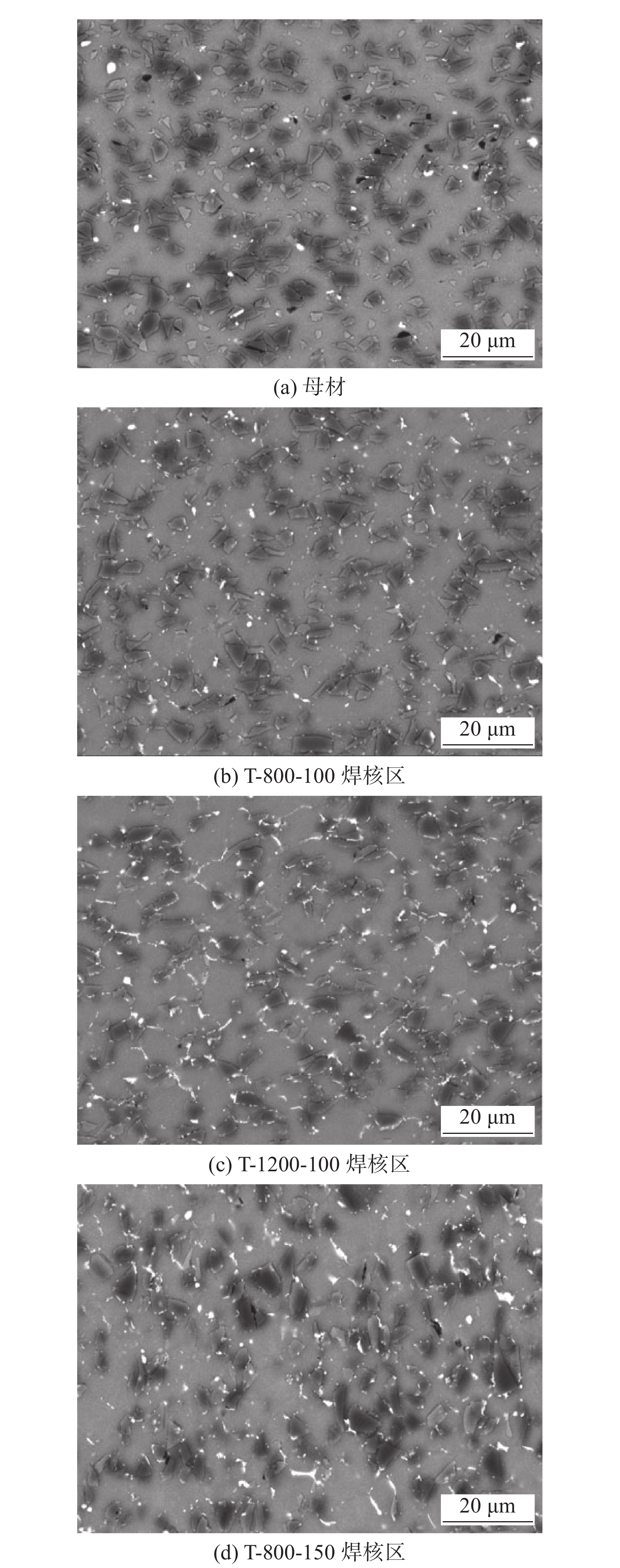
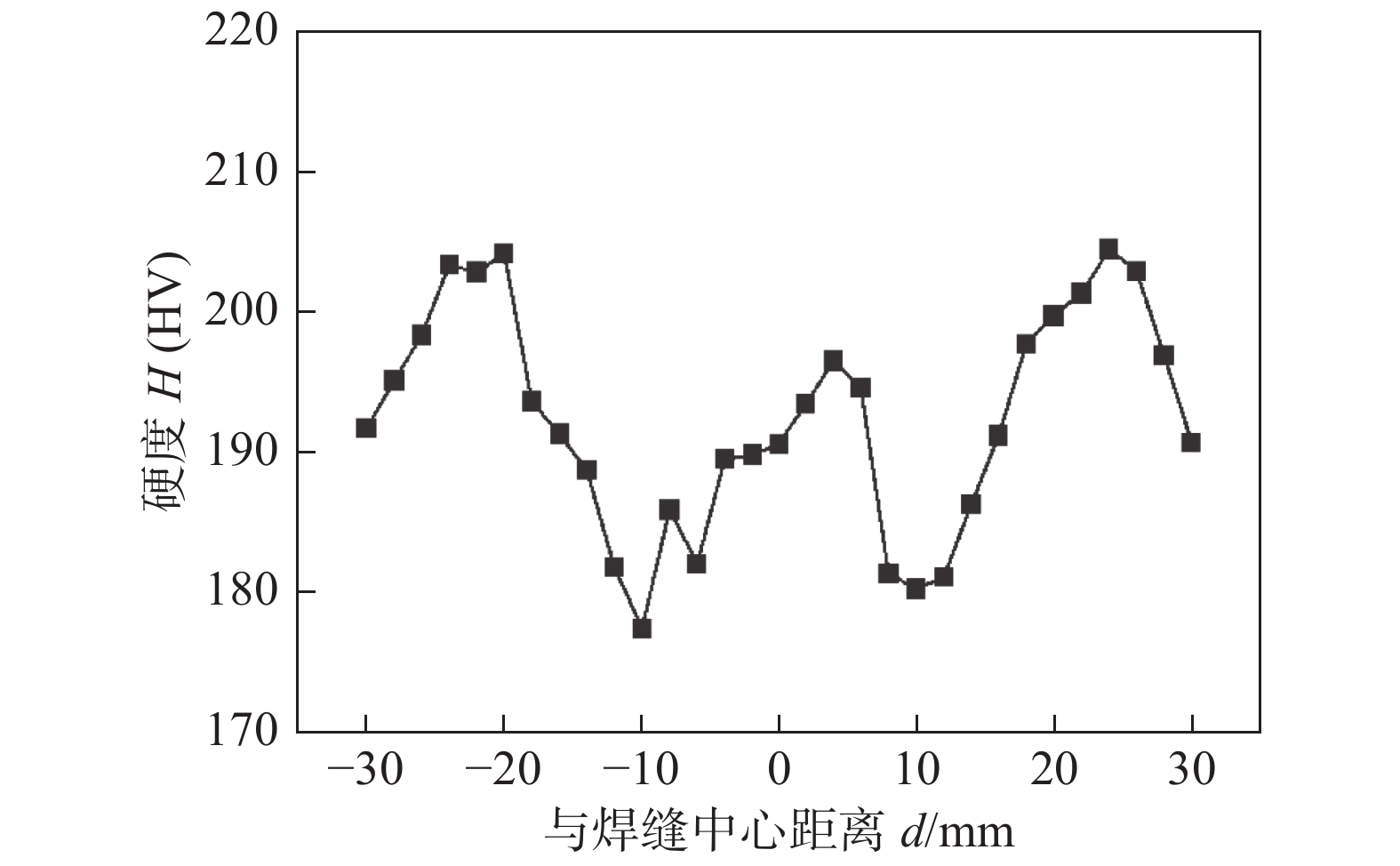
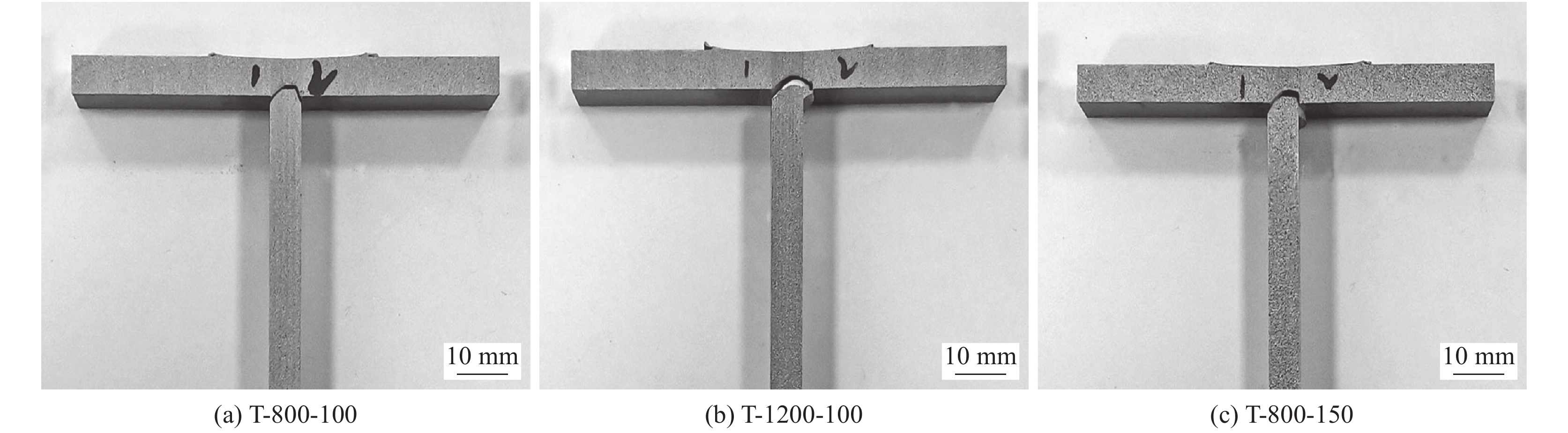
摘要: 在工具转速800 ~ 1200 r/min、焊接速度100 ~ 150 mm/min的工艺参数下,对6 mm厚的硬态(自然时效态)体积分数为15% SiCp/2009Al复合材料轧制板材进行T形搅拌摩擦焊(friction stir welding, FSW),均获得了致密无缺陷的接头. 结果表明,FSW过程中,剧烈塑性变形使焊核区部分SiC颗粒发生一定程度的破碎,破碎程度随转速的增加而增加,随焊接速度的增加而减弱;焊核区中的微米级强化相发生破碎、溶解,并沿焊核区细晶界面析出. T形接头横板两侧各存在2个低硬度区,靠近焊核区的低硬度区的硬度比远离焊核区的低硬度区的硬度低;固定焊接速度为100 mm/min时,转速从800 r/min增加到1200 r/min时,接头的抗拉强度不变;固定转速为800 r/min时,将焊接速度从100 mm/min增加到150 mm/min时,接头的抗拉强度轻微降低. 接头拉伸过程中在横板与竖板交界处受应力最大,所有接头均在此区域断裂.Abstract: 6 mm thick 15vol.% SiCp/2009Al matrix composite rolled plates were subjected to T-type friction stir welding (FSW) under the rotation rates of 800−1 200 r/min and welding speeds of 100−150 mm/min. The results show that, defect-free joints were obtained and the SiC particles were broken up during FSW; The crushing degree of SiC particles increased with enhancing the welding speed and decreased with the increase of the welding speed. The micron-level precipitates in the nugget zone (NZ) were broken up and dissolved, and then reprecipitated along the fine grain interface of NZ. There are two low hardness zones (LHZ) at both advancing and retreating sides of the horizontal plate of T-type joint, and the hardness of the LHZ close to the NZ is lower than that of the LHZ far away from the NZ. Under the constant welding speed of 100 mm/min, the tensile strength of the T-type joint was unchanged when increasing the rotation rate from 800 r/min to 1 200 r/min. Under the constant rotation rate of 800 r/min, the tensile strength of the joint increased as increasing the welding speed from 100 mm/min to 150 mm/min. The T-type joints fractured at the junction of horizontal and vertical pates during tension test.
-
0. 序言
铝合金因其比强度高和切削性好等特点被广泛应用于高速列车、核电、船舶、石油化工等领域[1]. 国内外研究学者分别从铝合金焊接工艺和焊接材料等方面开展相关研究. 焊接工艺方面,激光-电弧复合焊兼具激光焊接的高效和电弧的高工况适应性[2]. 激光与电弧复合后,激光与焊丝端部建立辅助导电通道,提高了电弧的稳定性和焊接速度. 电弧的引入降低铝合金焊接对激光反射率和装配精度. 韩晓辉等人[3]研究了高速列车用铝合金型材激光-电弧复合焊工艺,在优化的焊接工艺参数下,激光-MIG复合焊成形良好,无明显气孔、裂纹等缺陷,且焊接接头间隙适应性明显提高. 雷振等人[4]在激光-MIG复合焊的基础上外加一根焊丝,解决了激光-MIG复合焊熔敷效率与高速焊接的矛盾问题. 焊接材料方面,铝合金多股绞合焊丝由于其结构的特殊性,使其焊接具有独特的电弧特性、能量分布特性和工艺特性,也为铝合金焊接提供了相应的解决方案. 董晓晶等人[5]研究了铝合金多股绞合焊丝MIG焊焊接接头组织与性能,结果表明多股绞合焊丝能细化晶粒减少合金元素烧损,控制接头软化.
目前,国内外对铝合金实心焊丝激光-电弧复合焊和铝合金多股绞合焊丝MIG焊的研究较多[6-9];而对铝合金激光-多股绞合焊丝MIG焊的研究还未见详细报道. 文中选用1 × 3结构直径1.6 mm的ER5356铝合金多股绞合焊丝,结合激光-MIG复合焊焊接优势. 对5A06铝合金板材的激光-多股绞合焊丝MIG复合焊平板对接焊接接头的力学性能进行研究. 结合金相、扫描电镜等方法,分析了5A06铝合金激光-多股绞合焊丝MIG复合焊焊接接头微区的组织与性能之间的关系.
1. 试验方法
试验材料为20 mm厚5A06铝合金,抗拉强度为346 MPa,母材选用尺寸为300 mm × 150 mm × 20 mm的平板,加工60°的Y形坡口(单边30°),钝边尺寸为4 mm,无间隙. 焊丝选用1 × 3结构直径为1.6 mm的ER5356多股绞合焊丝. 多股绞合焊丝如图1所示,母材及焊丝的主要化学成分如表1所示. 焊接过程示意图和焊接接头坡口示意图如图2和图3所示. 基于前期工艺试验,进行对接接头工艺验证,选取的焊接工艺参数如表2所示[10]. 焊缝由1道打底焊和8道填充焊组成,焊缝间隔时间为10 ~ 15 min. 焊接接头截面图及EBSD取样位置如图4所示.
表 1 母材及焊丝的主要化学成分(质量分数,%)Table 1. Main chemical compositions of base metal and filler material材料 Mg Fe Si Zn Ti Mn Cu Al 5A06 5.82 0.35 0.072 0.011 0.022 0.69 0.026 余量 ER5356 5.12 0.15 0.052 0.001 0.082 0.148 0.011 余量 表 2 焊接试验参数Table 2. Welding technology parameters焊层 激光功率
P/kW焊接电流
I/A光丝间距
D/mm离焦量
f/mm焊接速度
v/( m·min−1)打底层 5.5 ~ 6.0 160 ~ 180 4 + 5 0.8 填充层 4.0 ~ 4.5 160 ~ 180 4 + 20 0.8 焊接接头性能测试依据国家标准GB/T2651—2008《焊接接头拉伸试验方法》,进行室温拉伸试验,拉伸速率为3 mm/min;采用维氏硬度计测试接头的显微硬度,加载载荷为1 N/kg,加载时间10 s,截取金相试样,经打磨、抛光、腐蚀后使用金相显微镜进行微观组织观察及EBSD分析.
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 微观组织分析
2.1.1 析出相成分
对焊缝区、热影响区和母材第二相粒子进行成分分析,焊接接头和母材的EDS分析结果如图5所示. 焊接区组织中的第二相主要为Al3Mg2相,其弥散分布在焊缝中;热影响区和母材存在三种第二相分别为黑色粗大的Mg2Si相、块状浅白色Al6(FeMn)相和细小的Al3Mg2相. 其中Al3Mg2相弥散分布,阻碍位错运动进一步提高强度,Mg2Si相为典型的杂质相,会降低材料的塑性,Al6(FeMn)相是一种难熔的第二相,熔点高,难以溶解于基体中,大部分Al6(FeMn)相以块状出现,主要是经过重熔又析出的过程产生,由于冷却速度快,焊缝处的相来不及聚集长大,便以很快的速度冷却析出,最后凝固为小尺寸块状的白色相,但其成分并未发生改变仍为Al6(FeMn)相.
2.1.2 金相组织
打底焊的焊缝区和热影响区放大500倍下的金相组织,熔合区100倍、200倍下的金相组织如图6所示. 焊缝区Al3Mg2相以较为细小均匀的分布在焊缝中,随着液态金属的快速冷却,首先析出α(Al),随着温度的继续降低,先析出相α(Al)枝晶间的液态金属发生共晶反应,生成α(Al)和Al3Mg2相. 热影响区存在三种第二相分别为较为粗大的Mg2Si相、块状Al6(FeMn)相和细小的Al3Mg2相. 熔合区为组织过渡区,表现为焊缝区中细小的Al3Mg2强化相向热影响区块状强化相过渡,且熔合区在焊接热循环的作用下Al3Mg2相重熔进入基体,导致熔合区细小的Al3Mg2相减少.
填充焊的焊缝区和热影响区放大500倍下的金相组织,熔合区100倍、200倍下的金相组织如图7所示. 与打底焊相比Al3Mg2相更加细小均匀的分布在α(Al)基体上. 热影响区存在三种第二相分别是粗大的Mg2Si相、块状Al6(FeMn)相和细小的Al3Mg2相. 与打底焊相比,填充焊热影响区的Mg2Si相和Al6(FeMn)相减少. 与打底焊相比,熔合区处细小的强化相Al3Mg2相更加致密.
2.1.3 EBSD分析
母材的晶粒形貌进行EBSD检测,母材晶粒形貌如图8所示. 母材为轧制的纤维状组织特征,晶粒呈现出一定的方向性.
打底焊和填充焊焊缝及热影响区的晶粒形貌如图9所示. 打底焊和填充焊的焊缝区以等轴晶为主,打底焊的焊缝区晶粒平均尺寸略大于填充焊的平均晶粒尺寸. 打底焊和填充焊的热影响区晶粒失去轧制生长的方向性,晶粒细小,存在回复再结晶.打底焊的热影响区晶粒平均尺寸与填充焊的平均晶粒尺寸相差不大. 对打底焊和填充焊的焊缝区和热影响区EBSD晶粒尺寸统计分析结果如表3所示. 可以看出,打底焊和填充焊在焊缝区晶粒的平均尺寸为37.31 μm和32.36 μm,其中打底焊选区中晶粒尺寸最大值为101.03 μm最小值为4.64 μm,其中填充焊选区中晶粒尺寸最大值为98.13 μm最小值为4.53 μm. 打底焊和填充焊在热影响区晶粒的平均尺寸为10.14 μm和10.28 μm,其中打底焊选区中晶粒尺寸最大值为63.29 μm最小值为4.64 μm,其中填充焊选区中晶粒尺寸最大值为65.24 μm最小值为10.28 μm.
表 3 焊接接头的晶粒尺寸Table 3. Grain size of welded joints方法 焊缝区晶粒尺寸d1/μm 热影响区晶粒尺寸d2/μm 最大值 最小值 平均值 最大值 最小值 平均值 打底焊 101.03 4.64 37.31 63.29 4.64 10.14 填充焊 98.13 4.53 32.36 65.24 4.53 10.28 基于EBSD单个晶粒内部平均取向差(IAM)获得再结晶区域图(RF). 5A06铝合金经历焊接热循环作用后,会导致热影响区软化导致性能降低.打底焊和填充焊热影响区的变形晶粒、亚晶粒和再结晶晶粒在扫面区域分布特征如图10所示. 打底焊热影响区再结晶晶粒、亚晶粒和变形晶粒占比分别为2.9%、67.7%和29.4%;填充焊热影响区再结晶晶粒、亚晶粒和变形晶粒占比分别为1.9%、50.9%和47.2%. 打底焊热影响区比填充焊热影响区再结晶晶粒占比提高约1%,打底焊和填充焊热影响区均以亚晶粒为主;打底焊热影响区比填充焊热影响区亚晶粒占比提高约16.8%;打底焊热影响区比填充焊热影响区变形晶粒占比降低约13.3%. 与填充焊热影响区相比打底焊热影响区焊接热输入大,导致打底焊热影响区所受到热输入也相对增加促进位错运动. 同一滑移面上同号位错在晶界聚集缠结发展成胞状组织,逐渐发展为亚结构,亚结构胞璧由位错相互缠绕形成,内部位错密度很低;同一滑移面上异号位错相互消耗而消失,非同一滑移面的异号韧性位错通过空位凝聚或逃逸导致半原子面消失,降低位错密度,导致材料软化性能降低.由于打底焊热影响区比填充焊热影响区热输入大,亚晶粒占比增加变形晶粒占比减少,提高了热影响区的软化程度.
通过不同颜色代表晶界取向差分布,铝合金晶粒取向差>15°的大角度晶界用黑色粗线代表,晶粒取向差<15°的小角度晶界用红色粗线代表. 小角度晶界对位错运动起到阻碍作用,进而提高材料的强度与硬度. 焊接接头晶界角度差分布如图11所示. 打底焊和填充焊的热影响区发生再结晶,导致变形晶粒发生合并长大几乎消失,造成小角度晶界转变为大角度晶界;打底焊和填充焊的热影响区小角度晶界占比分别为60.9%和68.3%. 结合图10亚结构分布图分析可知,打底焊的热输入大于填充焊热输入,打底焊热影响区亚结构占比增加,亚晶界为<2°的小角度晶界,因此小角度晶界增多. 但是亚结构增多晶粒内部位错密度减少,导致软化,打底焊和填充焊表现为小角晶界增加但硬度下降的现象.
平均取向差(KAM)表示同一晶粒给定点与其最近相邻点的平均错向,描述变形引起的晶粒内部的局部方向梯度,用来评价塑性应变的情况. 焊接接头热影响区局部平均取向差分布如图12所示. 打底焊和填充焊热影响区变形较为均匀,打底焊和填充焊热影响区组织均受到回复再结晶的影响导致内部组织的变形程度降低,在很大程度上减少局部取向偏差. 与打底焊热影响区相比填充焊位错取向峰向右移动,说明填充焊热影响区发生较为明显的塑性变形,填充焊热影响区取向差大说明热影响区处引入大量的塑性变形,主要是由于5A06铝合金母材为轧制态,同时填充焊的热输入低,所以在填充焊处位错密度多,导致填充焊热影响区发生塑性变形大于打底焊的热影响区.
2.2 力学性能分析
2.2.1 显微硬度
20 mm厚5A06铝合金焊接接头显微硬度分布如图13所示. 打底焊和填充焊从焊缝区向母材显微硬度先降低后升高,母材位置硬度平均值88.3 HV,打底焊和填充焊焊接接头各个区域硬度值和平均硬度值有明显差异. 打底焊和填充焊在焊缝区的平均硬度分别为77.3 HV和79.3 HV,平均硬度分别达到母材的87.5%和89.8%;打底焊和填充焊在熔合区的平均硬度分别为77.4 HV和74.7 HV,平均硬度分别达到母材的87.7%和84.6%. 打底焊在焊缝区、熔合区和热影响区显微硬度略高于填充焊,且打底焊和填充焊均在熔合区硬度最低.结合打底焊和填充焊金相组织,上述结果可能是因为填充焊与打底焊相比,填充焊中Al3Mg2相分布更加细小均匀;熔合区硬度值最低,熔合区硬度值最低主要是因为熔合区处Al3Mg2强化相重熔进入α(Al)基体中,导致强度降低,填充焊与打底焊相比熔合区处Al3Mg2相更致密;热影响区填充焊与打底焊相比Mg2Si相和Al6(FeMn)相减少,同时填充焊热输入低Al3Mg2相重熔进入基体量更少. 综上所述,打底焊和填充焊焊接接Al3Mg2相含量的差异是导致显微硬度差异的原因.
2.2.2 拉伸性能
20 mm厚5A06铝合金焊接接头拉伸性能测试如表4所示. 如表4所示,焊接接头平均抗拉强度为291.66 MPa,焊接接头强度系数为0.842,断裂位置在熔合线附近. 上述结果可能是因为,熔合线处容易出现缺陷和应力集中,焊缝存在软化现象,显微硬度值在焊接接头熔合区最低,此位置为由焊缝低强度向母材高强度过渡的薄弱区,在受到拉应力的作用下更容易发生断裂.
表 4 焊接接头的力学性能Table 4. Mechanical properties of welded joints拉伸测试 编号 抗拉强度Rm/MPa 断裂位置 强度系数平均值 数值 均值 母材 1-1 354 347 — 1.0 1-2 339 — 焊接接头 2-1 309 292 熔合线 0.84 2-2 271 熔合线 2-3 295 熔合线 2.2.3 拉伸断口形貌
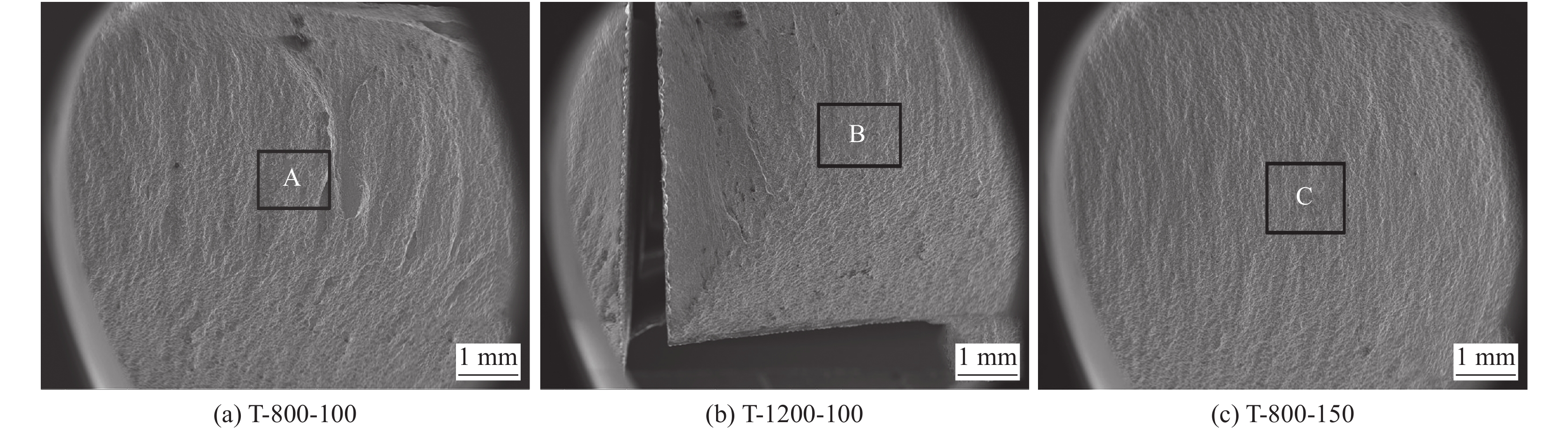
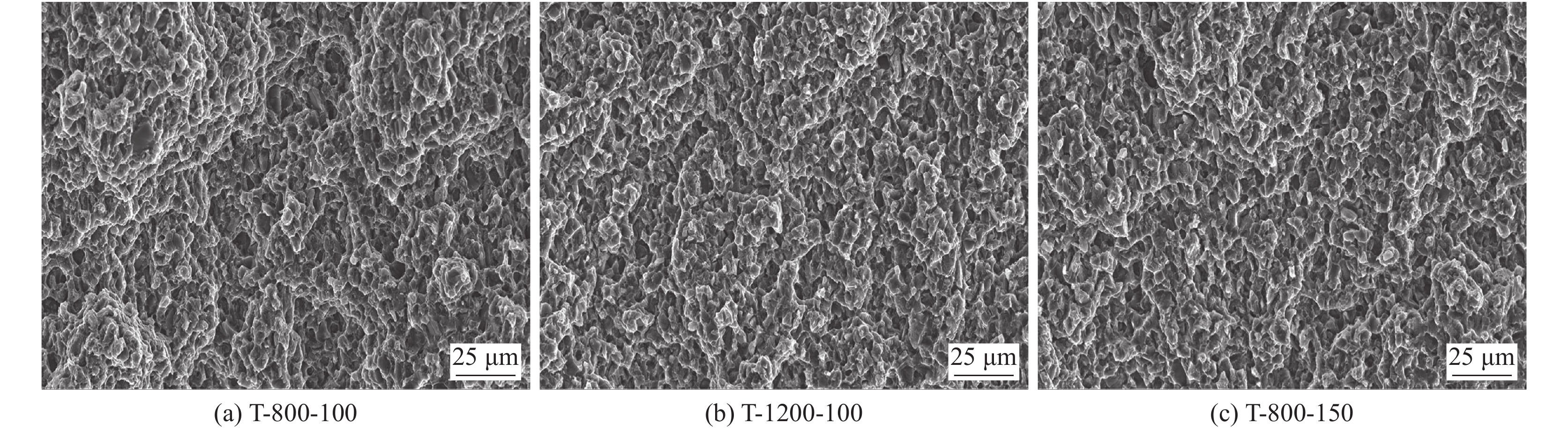
拉伸试样的断口形貌如图14所示. 焊接接头的断口形貌表现为断口由大量小尺寸韧窝和撕裂脊,韧窝断裂是金属韧性断裂的最典型的断口形态,在外力的作用下,随着塑性变形的产生便形成显微空穴,微空穴易在基体界面和第二相中萌生,第二相粒子的增多使得显微空穴更容易形核、长大,形成微裂纹,使断裂过程变得更容易.
3. 结论
(1) 激光-多股绞合焊丝MIG复合焊接接头焊缝区主要由α(Al)基体和弥散分布细小的Al3Mg2第二相组成,熔合区和热影响区主要由粗大的Mg2Si相、块状Al6(FeMn)相和细小的Al3Mg2相组成.
(2) 激光-多股绞合焊丝MIG复合焊接接头焊缝区以等轴晶为主,晶粒的平均尺寸为34.83 μm;热影响区晶粒失去轧制生长的方向性,晶粒细小,存在回复再结晶,晶粒的平均尺寸为10.21 μm. 打底焊热影响区热输入大于填充焊影响区,导致亚晶粒占比增加变形晶粒占比减少,位错密度降低,提高了热影响区的软化程度.
(3) 激光-多股绞合焊丝MIG复合焊接接头存在一定的软化现象,熔合区较薄弱硬度值为74.7 HV,达到母材硬度值的84.6%.焊接接头的平均抗拉强度为292 MPa,达到母材抗拉强度的84.2%;拉伸断口断裂位置为熔合区附近,呈韧性断裂.
-
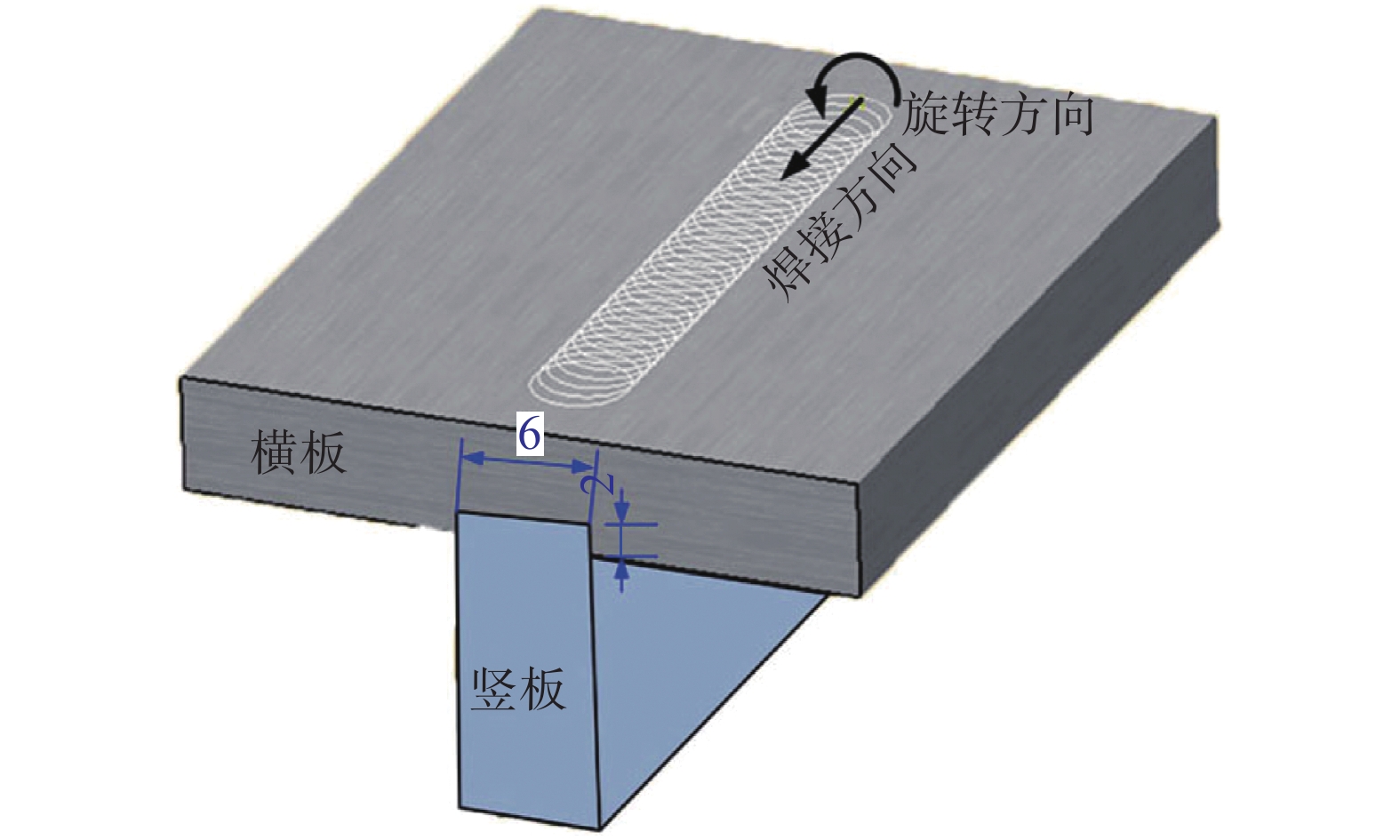
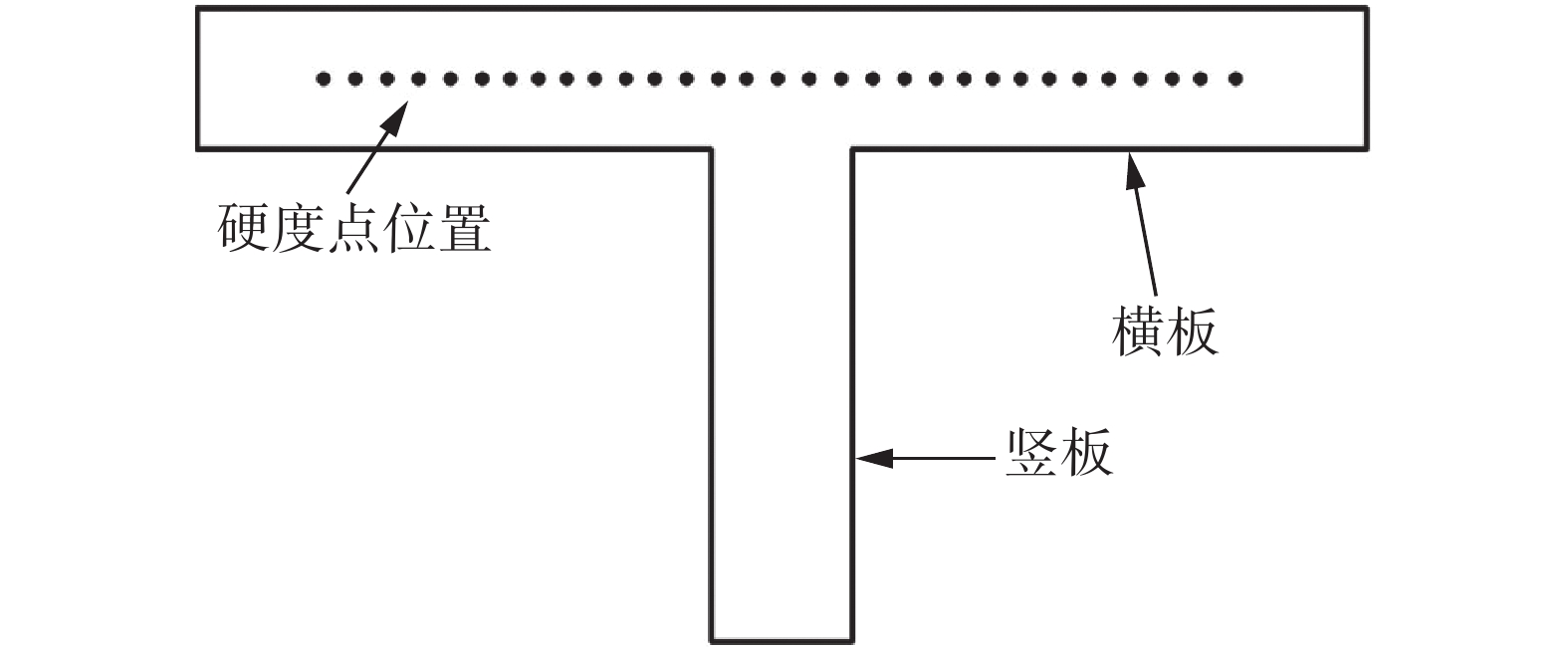
表 1 SiCp/2009Al复合材料T形接头FSW工艺参数
Table 1 FSW welding parameters of SiCp/2009Al T-type joints
序号 转速n/(r·min−1) 焊接速度v/(mm min−1) 简称 1 800 100 T-800-100 2 1200 100 T-1200-100 3 800 150 T-800-150 表 2 SiCp/2009Al T形接头拉伸性能
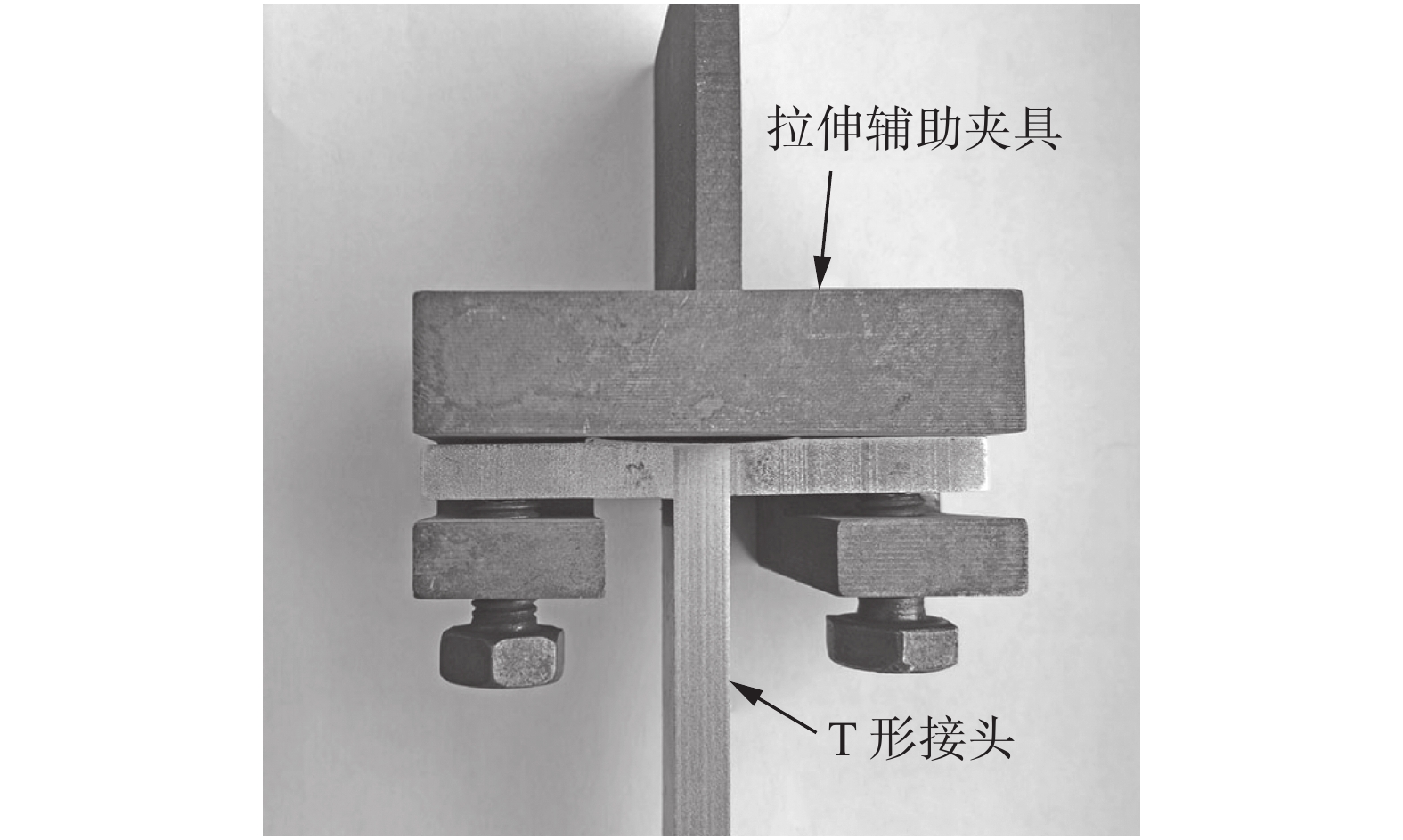
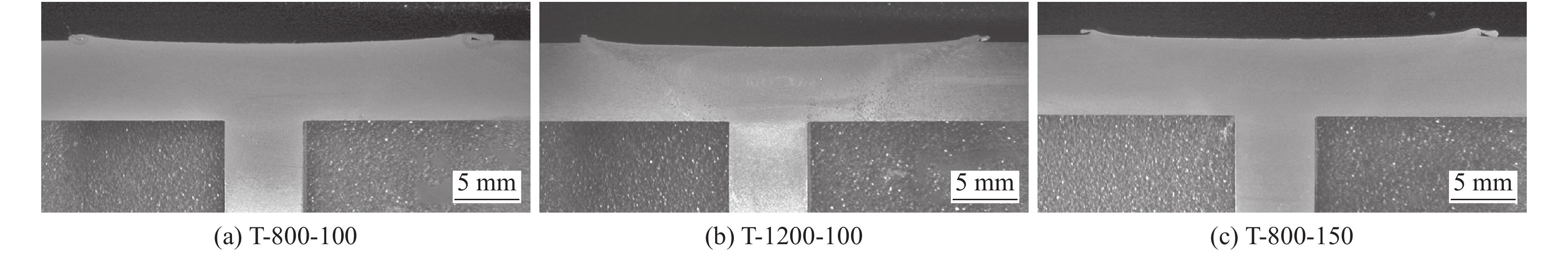
Table 2 Tensile properties of SiCp/2009Al T-type joints
序号 样品编号 横板厚度δ0/mm 竖板厚度δ/mm 样品宽度a/mm 最大应力 $\sigma_{ {\rm{max} } } $ /kN平均最大应力 $\overline \sigma_{{\rm{max}}}$ /kN1 T-800-100 5.76 5.83 11.91 16.64 16.4±0.3 2 5.77 5.81 11.96 16.05 3 5.7 5.88 11.93 16.50 4 T-1200-100 5.64 5.72 11.90 15.89 16.3±0.6 5 5.65 5.79 12.15 16.99 6 5.64 5.8 12.11 16.14 7 T-800-150 5.64 5.96 11.92 15.83 15.8±0.4 8 5.76 5.98 12.07 15.32 9 5.675 5.99 11.99 16.16 -
[1] 王东, 王全兆, 肖伯律, 等. 焊前热处理状态对SiCp/Al-Cu-Mg复合材料搅拌摩擦焊接头微观组织和力学性能的影响[J]. 金属学报, 2014, 50(4): 489 − 497. Wang Dong, Wang Quanzhao, Xiao Bolv, et al. Effect of heat treatment before welding on microstructure and mechanical properties of Friction Stir Welded SiCp/Al-Cu-Mg composite joints[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2014, 50(4): 489 − 497.
[2] 马凯, 张星星, 王东, 等. SiCp/2009Al复合材料的变形加工参数的优化仿真研究[J]. 金属学报, 2019, 55(10): 1329 − 1337. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00020 Ma Kai, Zhang Xingxing, Wang Dong, et al. Optimization and simulation of deformation parameters of SiCp/2009Al Composites[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019, 55(10): 1329 − 1337. doi: 10.11900/0412.1961.2019.00020
[3] 许世娇, 肖伯律, 刘振宇, 等. 高能球磨法制备的碳纳米管增强铝基复合材料的微观组织和力学性能[J]. 金属学报, 2012, 48(7): 882 − 888. Xu Shijiao, Xiao Bolv, Liu Zhenyu, et al. Microstructures and mechanical properties of CNT/Al composites fabricated by high energy ball-milling method[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(7): 882 − 888.
[4] Wang Xihe, Niu Jitai, Guan Shaokang, et al. Investigation on TIG welding of SiCp-reinforced aluminum-matrix composite using mixed shielding gas and Al-Si filler[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 499(1-2): 106 − 110. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2008.07.037
[5] 牛济泰, 程东锋, 高增, 等. SiC颗粒增强铝基复合材料的连接现状[J]. 焊接学报, 2019, 40(3): 155 − 160. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400090 Niu Jitai, Cheng Dongfeng, Gao zeng, et al. Current status of SiC particle reinforced aluminum-based composites[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2019, 40(3): 155 − 160. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.2019400090
[6] 马宗义, 肖伯律, 王东, 等. 铝基复合材料焊接的研究现状与展望[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010, 29(4): 8 − 16. Ma Zongyi, Xiao Bolü, Wang Dong, et al. Progress and outlook in welding of aluminum matrix composites[J]. Matrials China, 2010, 29(4): 8 − 16.
[7] Uttam Acharya, Barnik Saha Roy, Subash Chandra Saha. A study of tool wear and its effect on the mechanical properties of friction stir welded AA6092/17.5 SiCp composite material joint[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2018, 5: 20371 − 20379. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2018.06.412
[8] Mishra Rajiv, Ma Zongyi. Friction stir welding and processing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: R: Reports, 2005, 50(1-2): 1 − 78. doi: 10.1016/j.mser.2005.07.001
[9] 曹立超, 华鹏, 李先芬, 等. 颗粒增强铝基复合材料搅拌摩擦加工的研究现状及展望[J]. 焊接, 2016(6): 15 − 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2016.08.003 Cao Lichao, Hua Peng, Li Xianfen, et al. Research status and prospect of particle-reinforced aluminum-based composite processing[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016(6): 15 − 19. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1382.2016.08.003
[10] 王东. SiCp/2009铝基复合材料的搅拌摩擦焊接[D]. 沈阳: 中国科学院金属研究所, 2013. Wang Dong. Friction stir welding of SiCp/2009Al composites[D]. Shenyang: Institute of Metal Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2013.
[11] Qiao Qi, SuYishi, Ouyan Qiubao, et al. Microstructural characterization and mechanical properties of 120 mm ultra-thick SiCp/Al composite plates joined by double-sided friction stir welding[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2019, 50: 3589 − 3602. doi: 10.1007/s11661-019-05270-5
[12] 冯涛. SiCp/2024Al铝基复合材料的焊接[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2007. Feng Tao. Research on welding of the SiCp/2024Al aluminum metal matrix composite[D]. ShangHai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2007.
[13] Wang Dong, Xiao Bolv, Wang Quanzhao, et al. Friction stir welding of SiCp/2009Al composite plate[J]. Material Design, 2013, 47: 243 − 247. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2012.11.052
[14] Ni Dingrui, Chen Daolun, Wang Dong, et al. Tensile properties and strain-hardening behaviour of friction stir welded SiCp/AA2009 composite joints[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014, 608: 1 − 10.
[15] Zhang Zhen, Xiao Bolv, Ma Zongyi. Hardness recovery mechanism in the heat-affected zone during long-term natural aging and its influence on the mechanical properties and fracture behavior of friction stir welded 2024Al-T351 joints[J]. Acta Materialia, 2014, 73: 227 − 239. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2014.04.021
[16] 刘德佳, 丁江灏, 涂文兵, 等. T型接头搅拌摩擦焊接的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(12): 68 − 73. Liu Dejia, Ding Jianghao, Tu Wenbing. et al. Friction stir welding with T joint: A review[J]. Material Reports, 2016, 30(12): 68 − 73.




 下载:
下载: