Effect of stepped reverse-threaded pin on mechanical properties of friction stir lap welded 2A12-T4 aluminum alloy
-
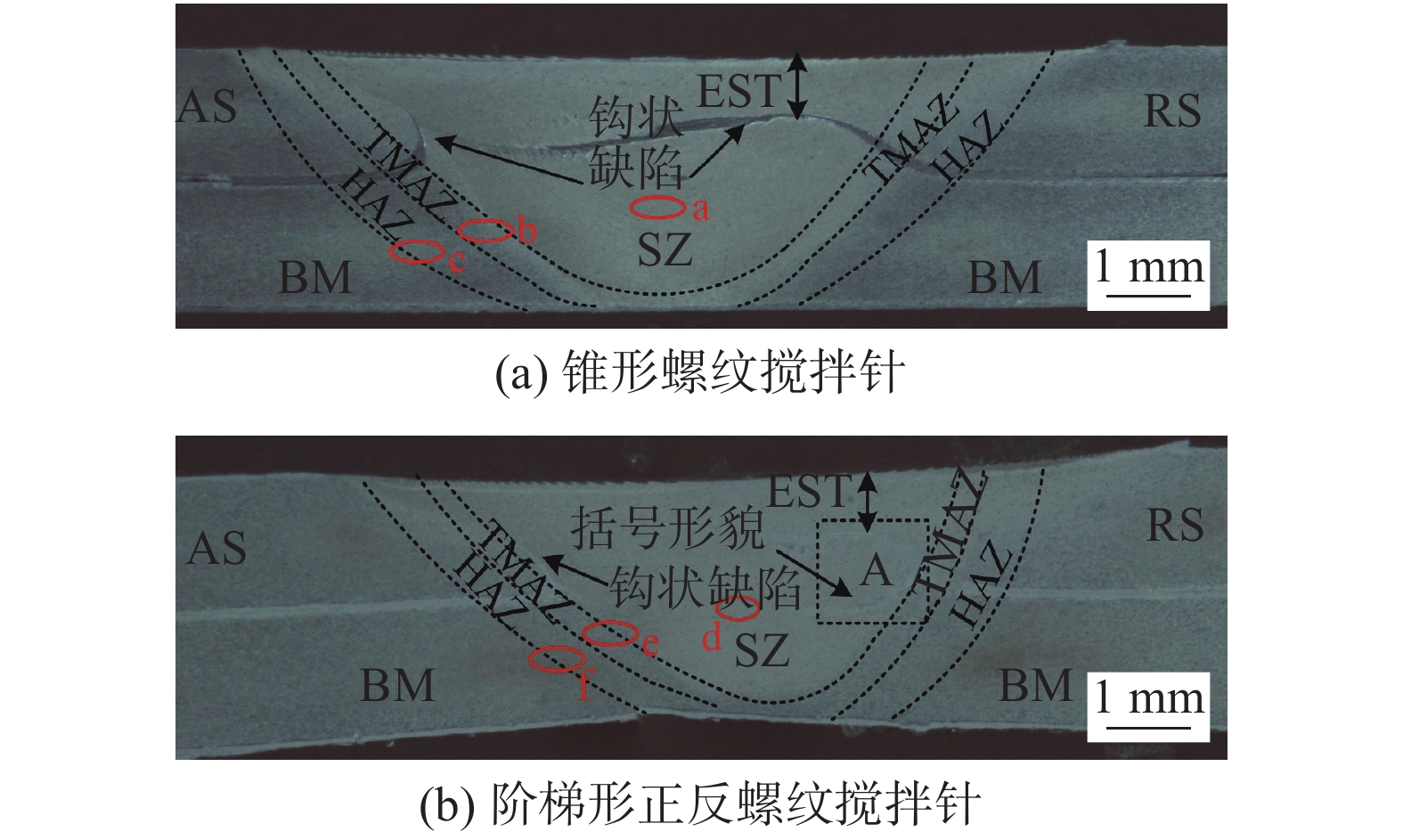
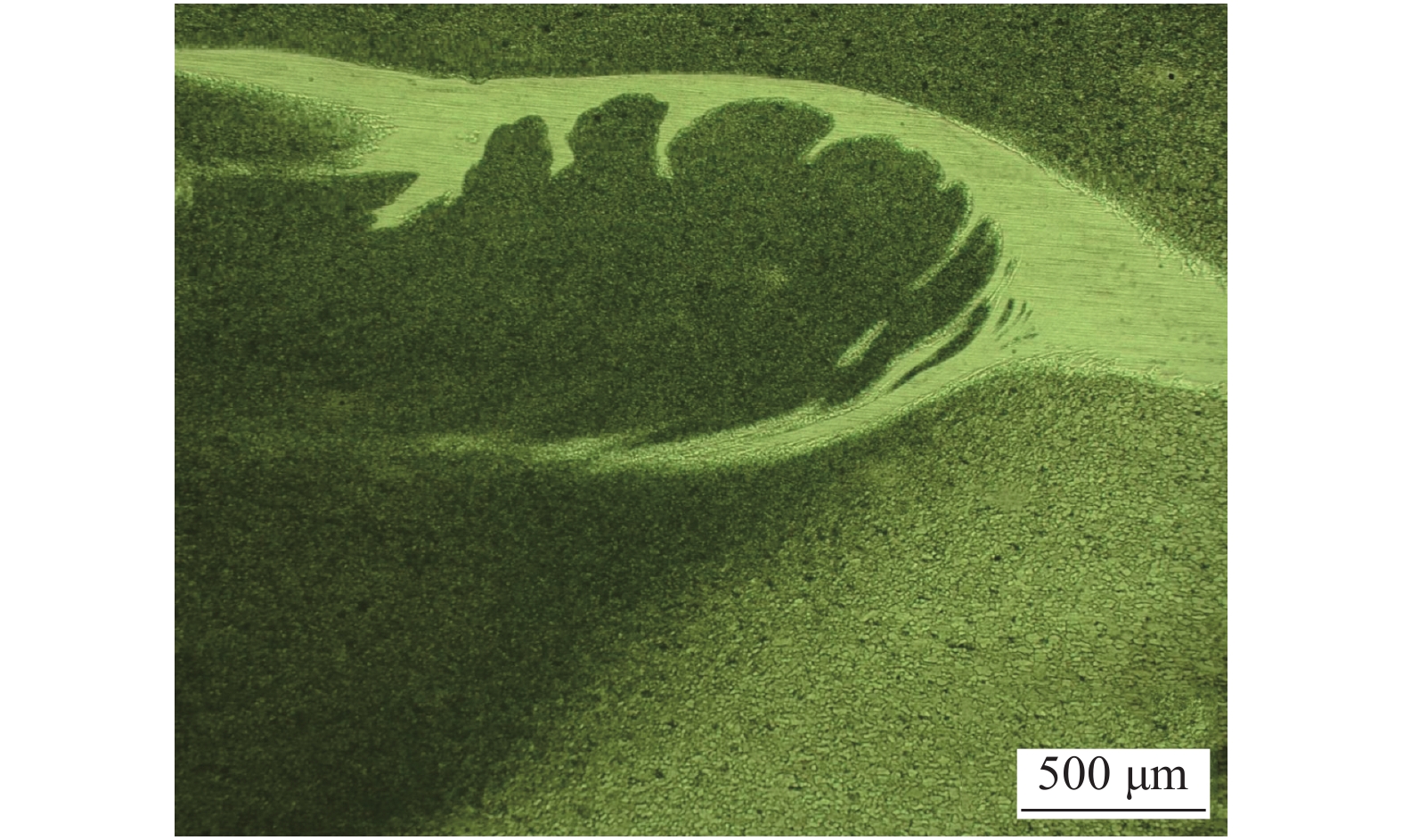
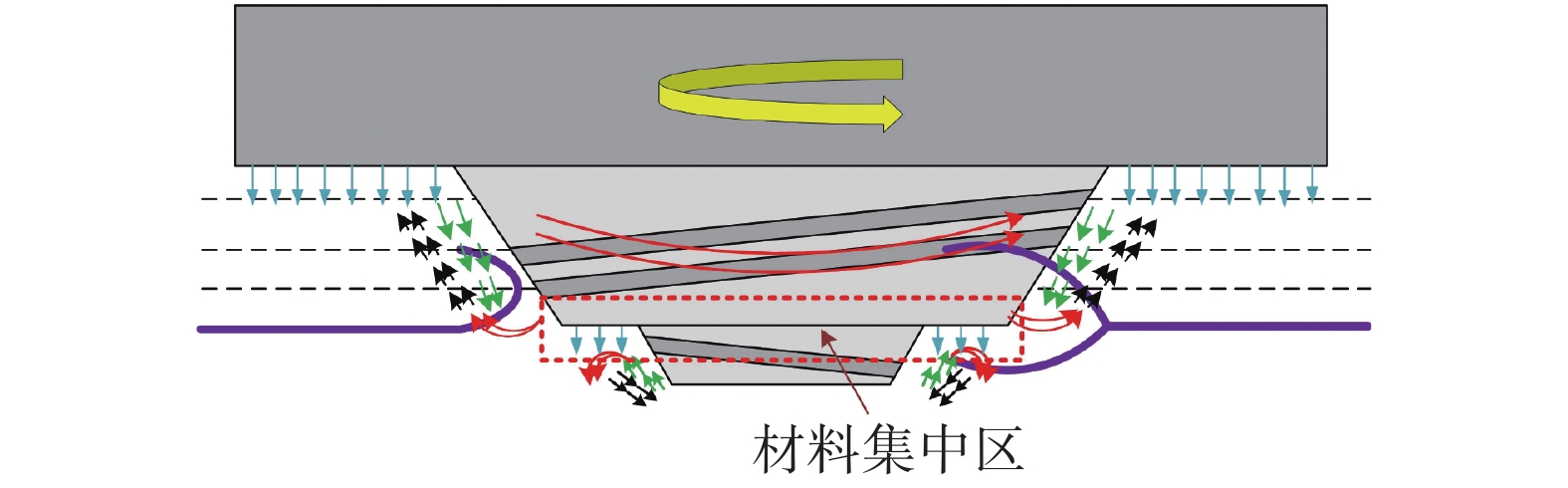
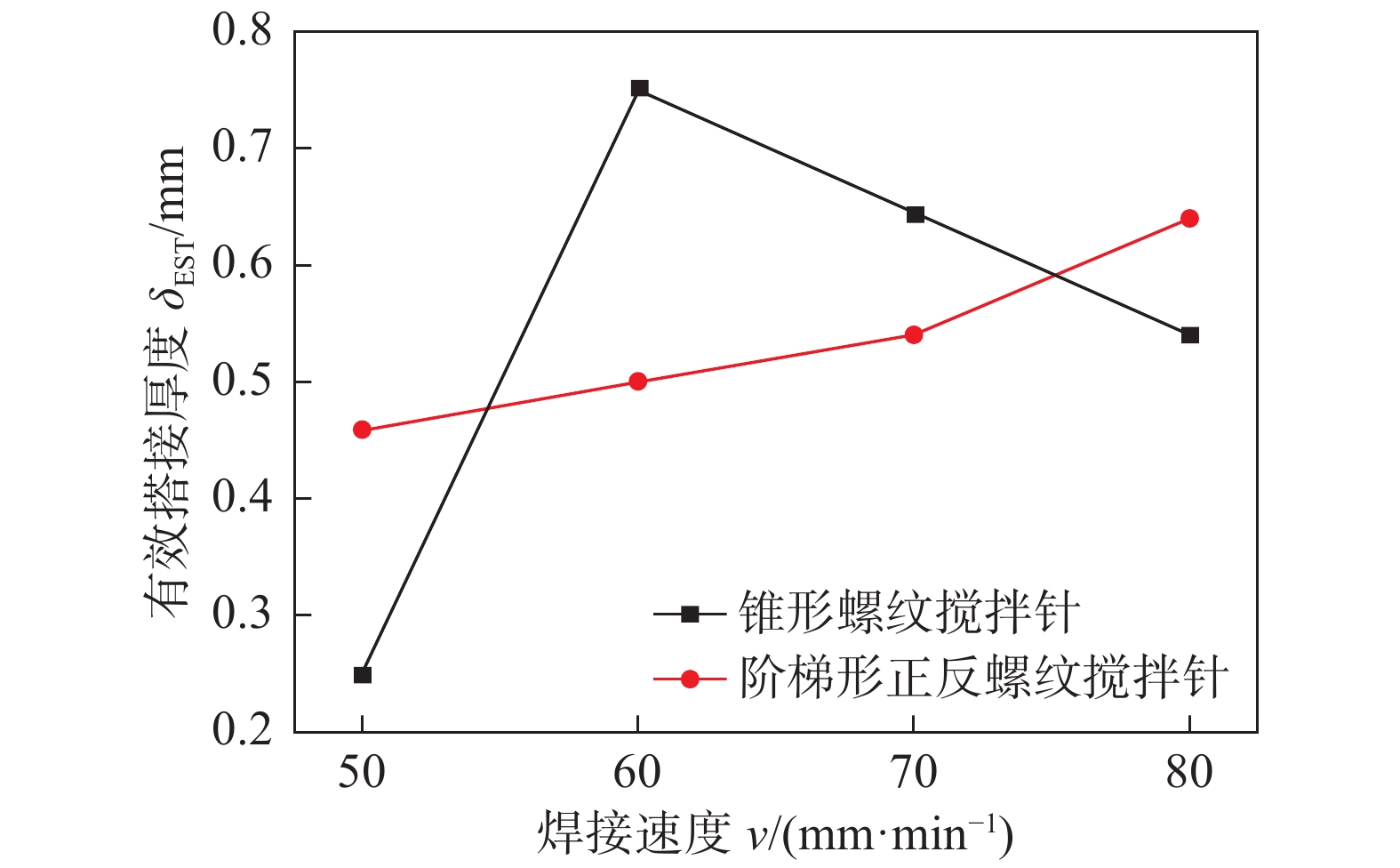
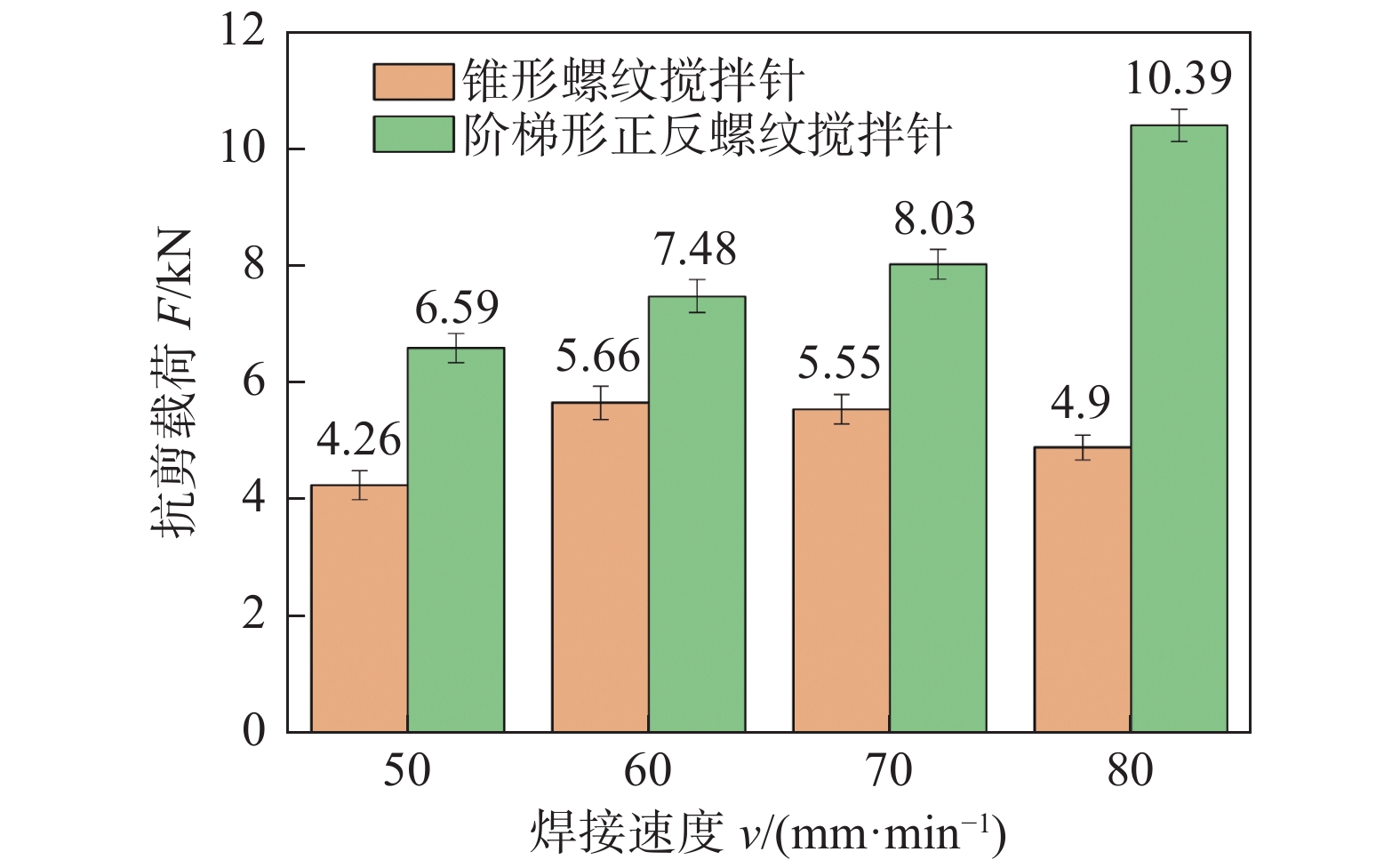
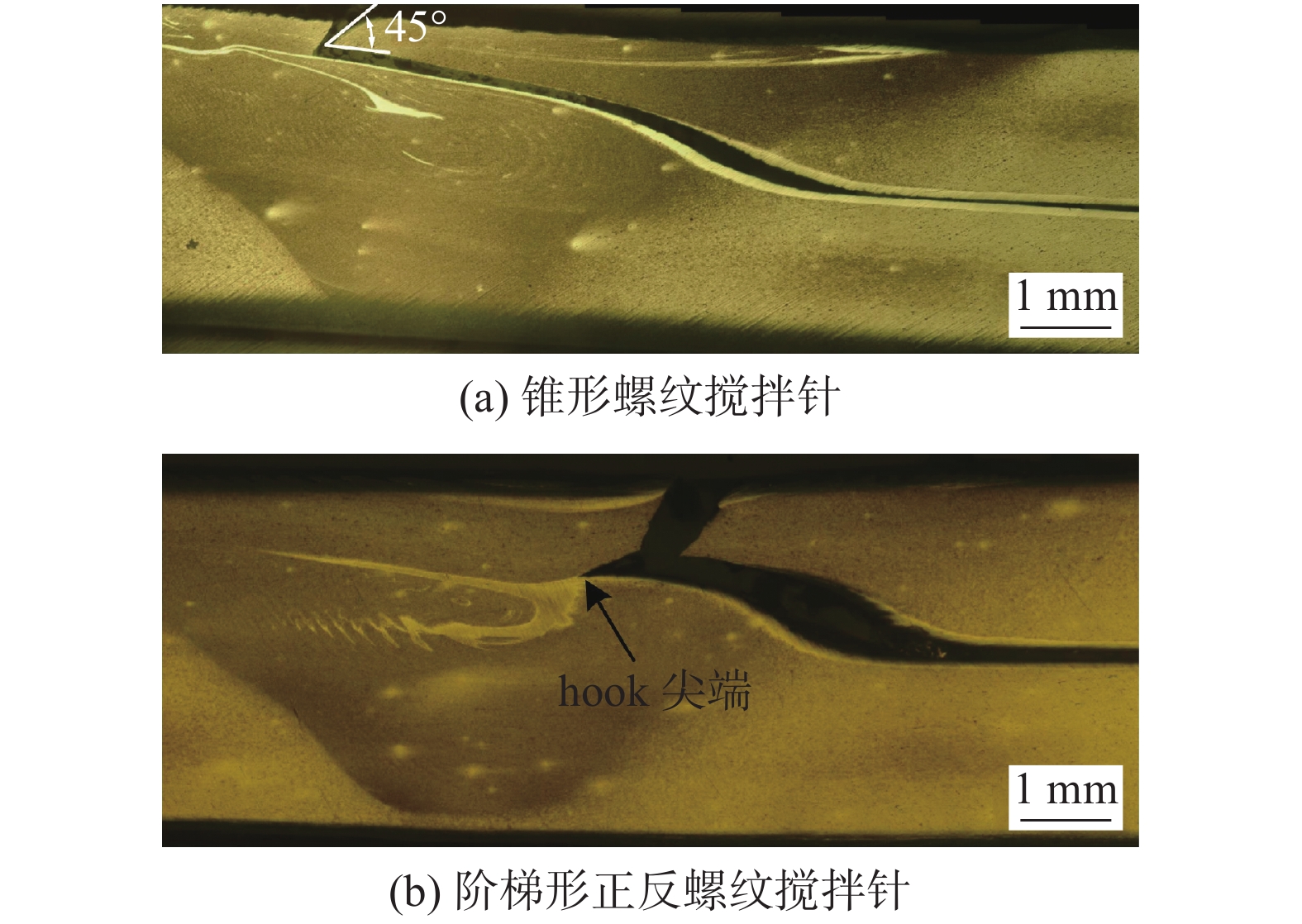
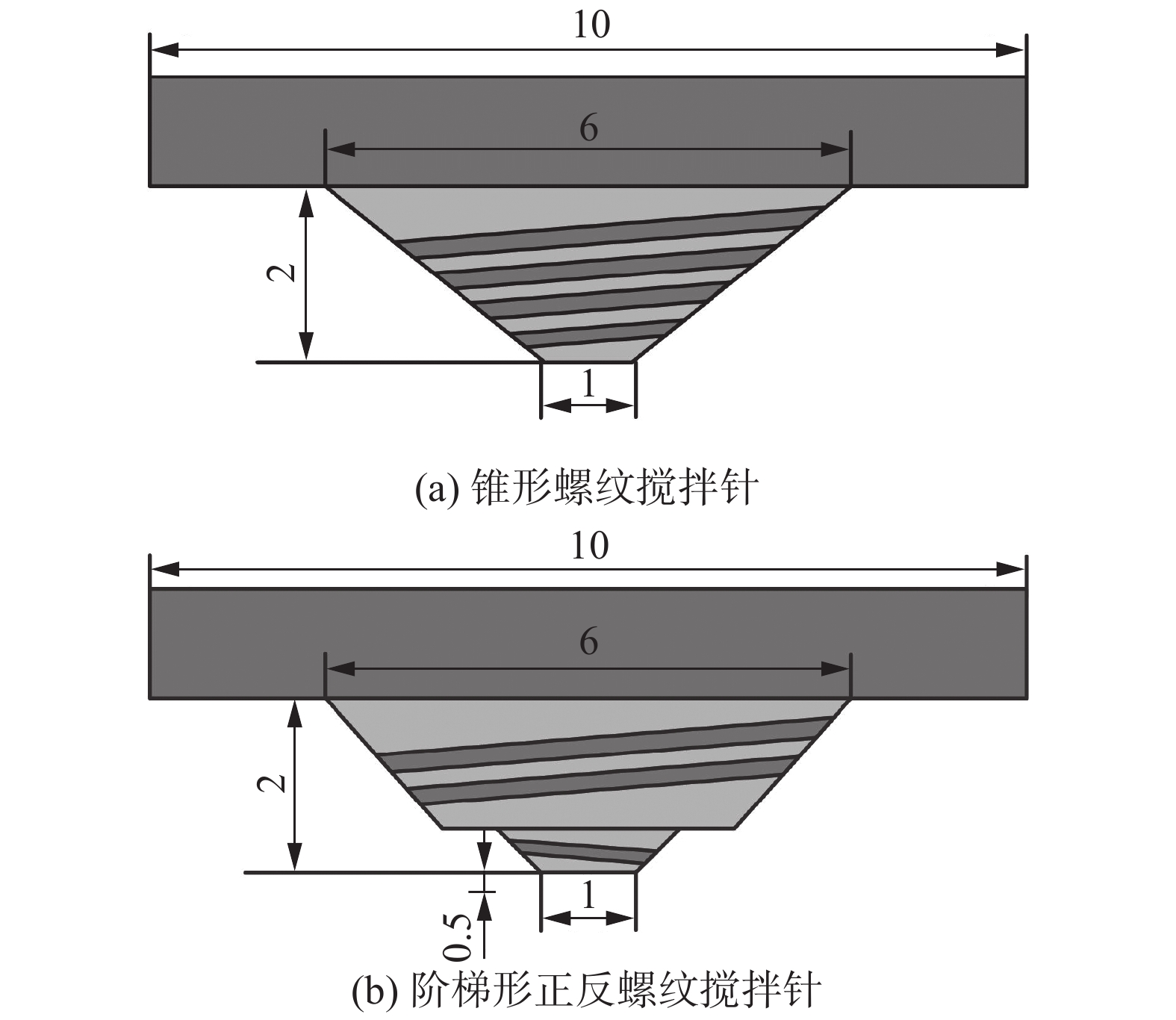
摘要: 搅拌针上螺纹分布情况会对搅拌摩擦焊接头内部材料流动行为产生重要影响,进而影响接头成形及力学性能. 采用锥形螺纹搅拌针和阶梯形正反螺纹搅拌针进行2A12-T4铝合金搅拌摩擦搭接焊试验,对比分析了两种搅拌针下搅拌摩擦搭接焊接头横截面形貌、显微组织、拉剪性能及接头断裂位置. 结果表明,两种搅拌针下接头横截面形貌均呈现“碗状”. 然而,在阶梯形正反螺纹搅拌针焊接下搭接界面后退侧出现特有的“括号”形貌. 相对于锥形螺纹搅拌针,阶梯形正反螺纹搅拌针下的接头热力影响区与热影响区晶粒分布相差不大,但焊核区晶粒细化程度更加明显;接头在焊接速度80 mm/min下可获得最大拉剪性能,其值为10.39 kN. 阶梯形正反螺纹搅拌针下接头界面后退侧出现的“括号”形貌阻碍了裂纹向焊核区进一步扩展,断裂模式表现为拉伸断裂.
-
关键词:
- 搅拌摩擦搭接焊 /
- 阶梯形正反螺纹搅拌针 /
- 横截面形貌 /
- 拉剪性能
Abstract: The distribution of the thread on the pin has an important effect on the material flow behavior in the friction stir welded joint, and then affects the joint formation and mechanical properties. In order to investigate cross-section morphology, microstructure, shear failure performances and fracture position of FSLW joints, the taper-threaded pin and the stepped reverse-threaded pin were used to weld 2A12-T4 aluminum alloy. The results showed that the morphologies of joints in cross section under the two types of pins presented “bowl-shaped”. However, the unique “parenthesis” morphology appears at the retreating side of joints using the stepped reverse-threaded pin. Compared with the taper-threaded pin, the grain distribution in the thermo-mechanically affected zone and heat affected zone of the joint welded by the stepped reverse-threaded pin was not different, but the grain refinement degree of stir zone was more obvious. Meanwhile, the maximum shear failure performance was 10.39 kN at the welding speed of 80 mm/min. The “parenthesis” shape on the retreating side of the joint welded by the stepped reverse-threaded pin prevented the crack from spreading to the stir zone, and the fracture mode was tensile fracture. -
-
表 1 2A12-T4铝合金的化学成分(质量分数, %)
Table 1 Chemical compositions of 2A12-T4 Al alloy
Cu Mn Mg Zn Ti Al 3.8 ~ 4.9 0.3 ~ 0.9 1.2 ~ 1.8 0.3 0.15 余量 -
[1] 栾国红, 郭德伦, 关桥, 等. 飞机制造工业中的搅拌摩擦焊研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2002(10): 43 − 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2002.10.017 Luan Guohong, Guo Delun, Guan Qiao, et al. Research on friction stir welding in aircraft manufacturing industry[J]. Aviation Manufacturing Technology, 2002(10): 43 − 46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2002.10.017
[2] 王磊, 付强, 安金岚, 等. 2A12-T4铝合金搅拌摩擦焊多区域疲劳裂纹扩展行为[J]. 焊接学报, 2021, 42(2): 24 − 29. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200724001 Wang Lei, Fu Qiang, An Jinlan, et al. Multi-zone fatigue crack growth behavior of friction stir welding of 2A12-T4 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2021, 42(2): 24 − 29. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200724001
[3] Thomas W M, Nicholas E D. Friction stir welding for the transportation industries[J]. Materials & Design, 1997, 18(4): 269 − 273.
[4] Ji S D, Shi Q Y, Zhang L G, et al. Numerical simulation of material flow behavior of friction stir welding influenced by rotational tool geometry[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2012, 63: 218 − 226.
[5] 李兵, 谢里阳, 张君一, 等. 2A12铝合金搅拌摩擦焊工艺与焊缝组织特征分析[J]. 制造技术与机床, 2008(1): 69 − 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2402.2008.01.024 Li Bing, Xie Liyang, Zhang Junyi, et al. Research on the welding process and microstructure characteristic of the friction stir welding line[J]. Manufacturing technology & Machine tool, 2008(1): 69 − 72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2402.2008.01.024
[6] 罗贤道, 李文亚, 余敏, 等. 搅拌头及工艺参数对厚板7050铝合金搅拌摩擦焊成形的影响[J]. 电焊机, 2011, 41(5): 72 − 74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2303.2011.05.017 Luo Xiandao, Li Wenya, Yu Min, et al. Effects of pin tool and processing parameters of friction stir welding of 7050 aluminum alloy[J]. Electric Welding Machine, 2011, 41(5): 72 − 74. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2303.2011.05.017
[7] Babu S, Ram G, Venkitakrishnan P V, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of friction stir lap welded aluminum alloy AA2014[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2012, 28(5): 414 − 416.
[8] Salari E, Jahazi M, Khodabandeh A, et al. Influence of tool geometry and rotational speed on mechanical properties and defect formation in friction stir lap welded 5456 aluminum alloy sheets[J]. Materials & Design, 2014, 58(jun.): 381 − 389.
[9] Cantin G M D, David S A, Thomas W M, et al. Friction skew-stir welding of lap joints in 5083–0 aluminium[J]. Science and Technology of Welding and Joining, 2005, 10(3): 268 − 280.
[10] Xu R Z, Cui S L, Li H, et al. Improving hook characterization of friction stir lap welded Al alloy joint using a two-section stepped friction pin[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2019, 102(9): 3739 − 3746.
[11] 傅志红, 贺地求, 周鹏展, 等. 7A52铝合金搅拌摩擦焊焊缝的组织分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2006, 27(5): 65 − 68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2006.05.016 Fu Zhihong, He Diqiu, Zhou Pengzhan, et al. Structure investigation of friction stir welding of 7A52 aluminum alloy[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2006, 27(5): 65 − 68. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-360X.2006.05.016
[12] 王春炎, 曲文卿, 姚君山, 等. 2219-T87铝合金搅拌摩擦焊接头组织与力学性能[J]. 焊接学报, 2010, 31(10): 77 − 81. Wang Chunyan, Qu Wenqing, Yao Junshan, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 2219-T87 aluminum alloy friction stir welded joints[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2010, 31(10): 77 − 81.
[13] Sem A, He A, Se A, et al. Relationship between microstructure, residual stress and thermal aspect in friction stir welding of aluminum AA1050 –science direct[J]. Procedia Manufacturing, 2019, 32: 889 − 894. doi: 10.1016/j.promfg.2019.02.299
[14] 刘建, 刘雪松, 邢艳双. 针长对异种铝合金FSLW接头成形及力学性能影响[J]. 焊接学报, 2018, 39(6): 91 − 95. Li Jian, Liu Xuesong, Xing Yanshuang. Influence of pin length on formation and shear failure load of dissimilar Al alloys FSLW joint[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2018, 39(6): 91 − 95.
[15] 马青娜、邵飞、白林越, 等. 7075铝合金FSW接头腐蚀疲劳性能及断裂特征[J]. 焊接学报, 2020, 41(6): 72 − 77. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200320001 Ma Qingna, Shao Fei, Bai Linyue, et al. Study on corrosion fatigue properties and fracture characteristics of 7075 aluminum alloy FSW joint[J]. Transactions of the China Welding Institution, 2020, 41(6): 72 − 77. doi: 10.12073/j.hjxb.20200320001



 下载:
下载: